MP Board Class 11th Special Hindi शुद्ध वाक्य रचना सम्बन्धी नियम
वाक्य रचना की सामान्य अशुद्धियाँ
वाक्य रचना में होने वाली सामान्य अशुद्धियाँ प्रायः इस प्रकार हैं
1. वचन सम्बन्धी अशुद्धियाँ-आदि, अनेक अथवा बहुवचन संज्ञा की क्रियाओं में प्रायः वचन सम्बन्धी त्रुटियाँ हो हैं। जैसे-
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) मैंने आज फूल आदि खरीदा। – (1) मैंने आज फूल आदि खरीदे।
(2)मैंने अनेकों स्थान देखे। – (2) मैंने अनेक स्थान देखे।
(3) बार-बार एक ही बात सुनते-सुनते मेरा कान पक गया। – (3) बार-बार एक ही बात सुनते-सुनते मेरे कान पक गये।
2. लिंग सम्बन्धी अशुद्धियाँ-विशेषण और विशेष्य का लिंग एक जैसा हो, समस्त पदों के सर्वनाम का लिंग एवं क्रिया का लिंग अन्तिम पद के अनुसार होना चाहिए। उदाहरण
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) सीता एक विद्वान् छात्रा है। – (1) सीता एक विदुषी छात्रा है।
(2) मैं अपनी देवी-देवताओं को मानता हूँ। – (2) मैं अपने देवी-देवताओं को मानता हैं।
(3) रीता ने आज मिष्ठान्न और नमकीन खरीदी। – (3) रीता ने आज मिष्ठान्न और नमकीन खरीदे।
3. अर्थ सम्बन्धी अशुद्धियाँ
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) आपकी सौजन्यता से मुझे कार्य मिला। – (1) आपके सौजन्य से मुझे कार्य मिला। [2009]
(2) निरपराधी को दण्ड देना अनुचित है। – (2) निरपराध को दण्ड देना अनुचित है। [2009]
(3) तुम अपने लड़के को मेरे यहाँ भेजो। – (3) तुम अपने पुत्र को मेरे यहाँ भेजो।
(4) शोक है कि तुम अनुत्तीर्ण हो गए। – (4) खेद है कि तुम अनुत्तीर्ण हो गए।
4. काल सम्बन्धी अशुद्धियाँ
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) मैंने कल पुस्तकें खरीदूंगा। – (1) मैं कल पुस्तकें खरीदूंगा।
(2) वह अगले साल दिल्ली गया था। – (2) वह पिछले साल दिल्ली गया था।
(3) मैं अगले सप्ताह विदेश जाता हूँ। – (3) मैं अगले सप्ताह विदेश जाऊँगा।
5. पुनरुक्ति सम्बन्धी अशुद्धियाँ
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) वह सदैव हमेशा सच बोलता है। – (1) वह सदैव सच बोलता है।
(2) वे सज्जन पुरुष आए हैं। – (2) वे सज्जन आए हैं।
(3) पूरे संसार जगत् में ईश्वर व्याप्त है। – (3) पूरे संसार में ईश्वर व्याप्त है।
6. मात्रा सम्बन्धी अशुद्धियाँ
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) राना सांगा एक ऐतिहासिक पुरुष थे। – (1) राणा सांगा एक ऐतिहासिक पुरुष थे।
(2) सौन्दर्यता सबको मोह लेती है। [2009] – (2) सुन्दरता सबको मोह लेती है।
(3) उसे रास्ते में सात पुरुष मिलें। – (3) उसे रास्ते में सात पुरुष मिले।
7. अन्य अशुद्धियाँ
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) घर में चीनी केवल नाममात्र को है। – (1) घर में चीनी नाममात्र को है।
(2) राम अथवा श्याम गए हैं। – (2) राम अथवा श्याम गया है।
(3) वह एक फूलों की माला लाया। – (3) वह फूलों की एक माला लाया।
(4) राम ने कहा कि राम का भाई आया हैं। – (4) राम ने कहा कि उसका भाई आया है।
(5) आज मोहन मीरा के साथ आया है। – (5) मोहन आज मीरा के साथ आया है।
शब्द-बोध
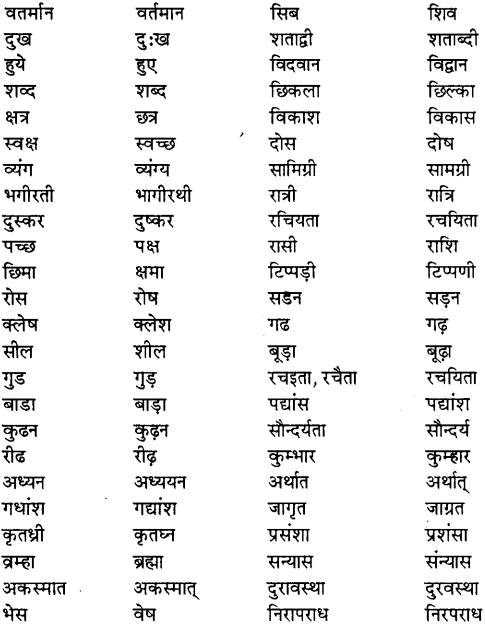
1. वर्तनी की दृष्टि से शुद्ध शब्दों का प्रयोग
वर्तनी (Spelling) का तात्पर्य अक्षर-विन्यास से है। पहले इसके लिए ‘हिज्जे’ या ‘अक्षरी’ नाम प्रचलित थे। उच्चारण की शुद्धता के अनुसार एवं व्याकरण की दृष्टि के अनुरूप शब्दों को लिखना ही, वर्तनी की दृष्टि से शुद्ध शब्दों का प्रयोग कहलाता है। – इन अशुद्धियों के कारण होते हैं-अज्ञान, भ्रान्ति, असावधानी, बनकर बोलने की दुष्प्रवृत्ति और विदेशी प्रभाव।
शुद्ध लेखन के लिए शुद्ध वर्तनी अपेक्षित होती है। वर्तनी ही भाषा की प्रभाव-क्षमता बढ़ाती है। अत: वर्तनी के सुधार या शब्द-शुद्धिकरण के लिए नीचे कुछ अशुद्ध शब्दों के शुद्ध रूप दिये हैं-

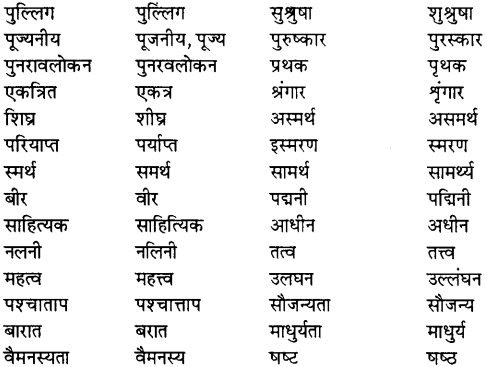
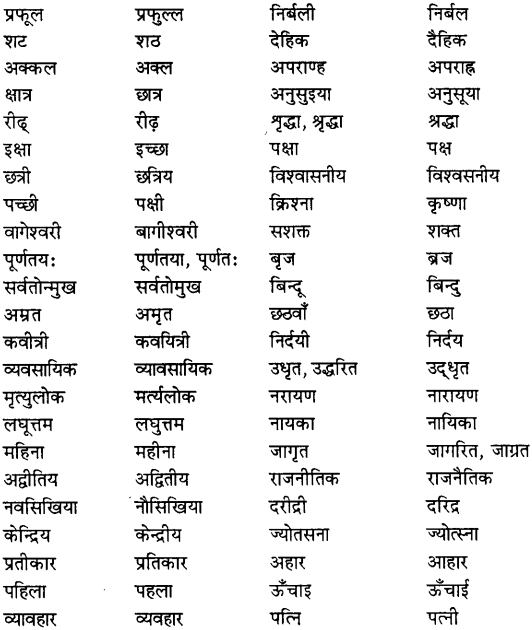
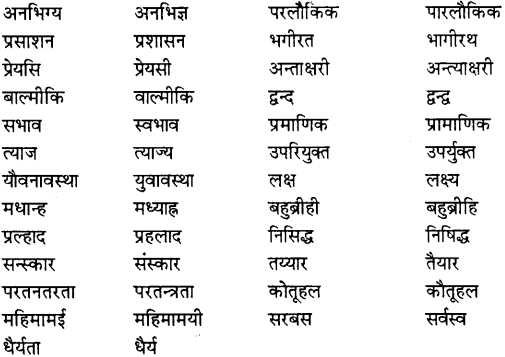
2. अर्थ की दृष्टि से सही शब्दों का चयन
हिन्दी में कतिपय ऐसे शब्द हैं जिन्हें ऊपर से देखने पर कोई अर्थ-भेद नहीं दिखाई देता है, पर सूक्ष्मतः उनमें अन्तर होता है। ऐसे शब्दों का ज्ञान आवश्यक है।
कुछ शब्दों का अर्थ तो एक ही रहता है, पर प्रयोग में उनमें कुछ अन्तर रहता है। कभी-कभी सम्बद्ध शब्दों के प्रयोग से भी वाक्य अशुद्ध हो जाता है। जैसे
अशुद्ध वाक्य – शुद्ध वाक्य
(1) उसे व्यापार में हानि होने की आशा है। – (1) उसे व्यापार में हानि होने की आशंका है।
(2) विनय को परीक्षा में उत्तीर्ण होने की आशा है। – (2) विनय को परीक्षा में उत्तीर्ण होने की आशंका है।
(3) राम बुरी तरह प्रसिद्ध है। – (3) राम बुरी तरह बदनाम है।
(4) शोक है कि आपने मेरे पत्रों का उत्तर नहीं दिया है। – (4) खेद है कि आपने मेरे पत्रों का उत्तर नहीं दिया।
(5) मैंने एक वर्ष तक उसकी प्रतीक्षा देखी। – (5) मैंने एक वर्ष तक उसकी प्रतीक्षा की।
(6) रमा एक मोतियों का हार गले में पहने है। – (6) रमा मोतियों का एक हार गले में [2009] पहने है।
(7) मीना चाचाजी के ऊपर विश्वास करती है। – (7) मीना चाचाजी पर विश्वास करती है।
(8) शब्द केवल संकेत मात्र होते हैं। – (8) शब्द संकेत मात्र होते हैं।
(9) आपके एक-एक शब्द तुले हुए होते हैं। – (9) आपका एक-एक शब्द तुला हुआ होता है।
(10) उसे अनेकों व्यक्तियों ने आशीवाद दिया। – (10) उसे अनेक व्यक्तियों ने आशीर्वाद दिया।
(11) विंध्याचल पर्वत के दक्खिन में नर्मदा स्थित है। – (11) विंध्याचल के दक्षिण में नर्मदा स्थित है।
(12) मैं अपनी बात का स्पष्टीकरण करने के लिए तैयार हूँ। [2009]- (12) मैं अपनी बात का स्पष्टीकरण देने के लिए तैयार हूँ।
(13) मैं अपने गुरु के ऊपर बहुत श्रद्धा करता है। – (13) मैं अपने गुरु पर बहुत श्रद्धा रखता हूँ।
(14) सौन्दर्यता सबको मोह लेती है। [2009] – (14) सुन्दरता सबको मोह लेती है।
(15) हवा, चल रही है। – (15) हवा बह रही है।
(16) महादेवी वर्मा विद्वान महिला थी। – (16) महादेवी वर्मा एक विदुषी महिला थी।
(17) श्रीकृष्ण के अनेकों नाम हैं। [2009] – (17) श्रीकृष्ण के अनेक नाम हैं।
(18) यह घी की शुद्ध दुकान है। – (18) यह शुद्ध घी की दुकान है।
(19) मोहन आटा पिसाकर लाया। – (19) मोहन अनाज पिसाकर लाया।
(20) वे सज्जन पुरुष कौन हैं? – (20) वे सज्जन कौन हैं?
(21) प्रत्येक वृक्ष फल देते हैं।। – (21) प्रत्येक वृक्ष फल देता है।
अर्थ की दृष्टि से सही शब्दों का चयन करने के लिए सूक्ष्म अन्तर वाले शब्दों को कान लेना चाहिए जिससे सही अर्थ का ज्ञान हो तो हम सभी जगह उसका उपयोग कर सकें। जैसे
(1) अनुराग = स्त्री-पुरुष के बीच होने वाला स्नेह। प्रेम = स्नेह सम्बन्ध मात्र। वात्सल्य = छोटों के प्रति बड़ों का स्नेह। भक्ति = बड़ों के प्रति छोटों का श्रद्धायुक्त स्नेह।
(2) अस्त्र = जो फेंक कर मारा जाय, जैसे-तीर, भाला, बम। शस्त्र = जिससे काटा जाय; जैसे-तलवार, छुरा। आयुध = लड़ाई के सभी साधन, आयुध कहलाते हैं। इसमें अस्त्र-शस्त्र के अतिरिक्त लाठी, गदा, छड़ आदि को भी ले सकते हैं। हथियार = हाथ से चलाये जाने वाले आयुध।
(3) अशुद्धि = अपवित्रता, मिलावट, लिखने अथवा बोलने में कमी, इन सभी को अशुद्धि कहते हैं। भूल = विस्मृति, जिसमें कर्ता की असावधानी प्रकट होती है। त्रुटि = वस्तु में किसी कमी का होना।
(4) अमूल्य = वस्तु जो मूल्य देकर प्राप्त न की जा सके, जैसे-विद्या, ज्ञान, प्रेम, सफलता, सुख, विश्वास। बहुमूल्य = जिसका अधिक मूल्य देना पड़े, जो वस्तु साधारण मूल्य की न हो। जैसे-सोना, प्लेटिनम, हीरा। महँगा = जिस वस्तु को बदलते बाजार भाव के कारण अधिक मूल्य देकर पाया जाये।
(5) अलभ्य = जिसे किसी उपाय से न पाया जाय। दुर्लभ = जिसे अधिक कष्ट उठाकर पाया जाय।
(6) अलौकिक = जो संसार में इन्द्रियों के द्वारा सुलभ न हो। असाधारण = जो सांसारिक होकर भी अधिकता से न मिलता हो। अस्वाभाविक = अप्राकृतिक, जो प्रकृति के नियमों से बाहर का प्रतीत हो।
(7) अर्पण = शरणगति का भाव लिए अर्पण। प्रदान = धार्मिक भावना के साथ दूसरे का स्वत्व स्थापित करना, जैसे-जलदान, दीपदान, विद्यादान, गोदान, अन्नदान। प्रदान = सामान्य रूप से बड़ों के द्वारा छोटों को देना। वितरण = समाज में उत्पादित वस्तुओं के विभाजन की प्रणाली।
(8) अनुग्रह बड़े की ओर से छोटों के अभीष्ट सम्पादन की स्नेहपूर्ण क्रिया अनुग्रह है। अनुकम्पा = दुःख दूर करने की चेष्टा से युक्त कृपा। दया = दुःख देखकर द्रवित होना। कृपा = दुःख-निवारण के सामर्थ्य से युक्त दया। सहानुभूति = दूसरे के दुःख में समभागी होने का भाव। करुणा = दुःख निवारण की व्याकुलता लिए हुए द्रवित होना। ममता = माता के समान किसी पर वत्सल भाव।
(9) अंग = (अवयव) भौतिक समष्टि का भाग, जैसे-शरीर का अंग, वृक्ष का अंग, शाखा आदि। देह = शरीर। आकृति = रेखाओं से बनी कोई समष्टि, चाहे वह सजीव हो या निर्जीव।
(10) अमर्ष = द्वेष या दु:ख जो तिरस्कार करने वाले के कारण होता है। क्रोध = प्रतिकूल आचरण के बदले में प्रतिकूल आचरण की प्रवृत्ति। कलह = क्रोध को जब सक्रिय रूप दिया जाता है तो उससे होने वाला वाचिक या शारीरिक आचरण।
(11) असुर = दैत्य या दानव-एक जाति विशेष, जो देवों के समकक्ष थी। राक्षस = यह अनुचित आचरण के कारण मनुष्य जाति के लिए आता है।
(12) अनुपम = बेजोड़-जिसकी तुलना न हो सके। अपूर्व = जिसे पहले भनुभव न किया गया हो। अद्भुत = जो विस्मयजनक हो।
(13) आयु = जीवन के सम्पूर्ण समय को आयु कहते हैं। वयस् = जीवन के शरीर विकास सूचक भाग को वयस् कहा जाता है, जैसे-शैशव। अवस्था = दशा-जीवन के प्रसंग में बीते हुए जीवन का भाग। वयस् के अर्थ में भी चलता है, जैसे-युवावस्था, वृद्धावस्था।
(14) अबला = स्त्री की संज्ञा है जिससे उसकी कोमलता एवं निर्बलता का संकेत मिलता है। नारी = केवल नर जाति की स्त्री या मानवी। कान्ता = प्रिया, किसी पुरुष के स्नेह-सम्बन्ध से दिया हुआ स्त्री का नाम-जो चमक को भी प्रकट करता है। भार्या = वह स्त्री जो किसी पुरुष से अपने भरण-पोषण की प्राप्ति का अधिकार रखती हो। पत्नी = पति से सम्बद्ध धार्मिक कार्यों में पति का साथ देने वाली, जिसका धार्मिक रीति से विवाह सम्पन्न हुआ हो। वधू = विवाह के बाद नारी की संज्ञा। अंगना = अंगों की कोमलता तथा सुन्दरता की सूचक स्त्री की संज्ञा।
(15) आनन्द = समस्त मन, प्राण, शरीर, आत्मा के सम्मिलित सुखानुभूति को आनन्द कहते हैं, हर्षित, प्रसन्न। सुख = मन के अनुकूल किसी भी प्रतीति को सुख कहते हैं। हर्ष = सुख या आनन्द के कारण शरीर की रोमांचमयी अवस्था हर्ष है। उल्लास-उमंग = मन में सुख की वेगयुक्त अल्पकालिक क्रिया।
(16) भिज्ञ = विषय के ज्ञान से सम्पन्न। विज्ञ = विषय का विशेष ज्ञान रखने वाला। बहुज्ञ = अनेक विषयों का ज्ञाता।।
(17) अंश = मूर्त, अमूर्त तत्त्व का भाग। खण्ड = मूर्त पदार्थ का विभाजन।
(18) अन्न = मुख्य भोजन का धान्य विशेष। दाना = किसी भी वस्तु का गोलाई लिए छोटी इकाई का नाम, जैसे-माला का दाना, मोती का दाना, अनाज का दाना। शस्य = फसल; जो खेत में काटने हेतु लगी हो। खाद्य = सभी प्रकार का भोजन योग्य पदार्थ। पकवान = पका हुआ भोजन।
(19) आज्ञा = बड़ों द्वारा छोटों के प्रति काम की प्रेरणा। अनुज्ञा = श्रोता की इच्छा के समर्थन में स्वीकृतिसूचक कथन। अनुमति = बड़ों द्वारा सहमति अथवा किसी काम करने की इच्छा का समर्थन। आदेश = प्रायः कार्याधिकारी द्वारा दी गई आज्ञा।
(20) अनुनय = किसी बात पर सहमत होने की प्रार्थना। विनय = निवेदन, शिष्टता, अनुशासन। प्रार्थना = किसी कार्यसिद्धि या वस्तु प्राप्ति के लिए विनययुक्त कथन। निवेदन = अपनी बात विनयपूर्वक रखना। आवेदन = अपनी योग्यता आदि के कथन द्वारा किसी पद या कार्य हेतु प्रस्तुत होना।
(21) आमन्त्रण = किसी अवसर पर सम्मिलित होने का बुलावा। निमन्त्रण = उत्सव के अवसर पर बुलाना। आह्वान = ललकारना, संघर्ष के लिए बुलाना।
(22) इच्छा = किसी वस्तु के प्रति मन का राग। आशा = इच्छा के साथ प्राप्ति की सम्भावना का सुख। उत्कण्ठा = जिज्ञासा। स्पृहा = उत्कृष्ट इच्छा। मनोरथ = अभिलाषा।
(23) उत्साह = बड़े कार्यों के प्रति प्रेरित करने वाला आनन्ददायक भाव। साहस = सहने की शक्ति को साहस कहते हैं।
(24) तेज = बाहरी प्रकाश। कान्ति = चमक। प्रकाश = किरण समूह।
(25) ईर्ष्या = दूसरे की उन्नति न सह पाना। स्पर्धा = दूसरे को उन्नत देखकर स्वयं उन्नति की होड़। असूया = दूसरे के गुणों में दोष ढूँढ़ना। द्वे ष- दूसरे की बुराई की कामना। बैर = बहुत दिनों का संचित क्रोध का रूप।
(26) खेद = अनिष्ट सूचना। अवसाद= मन-शरीर की निश्चेष्टता। क्लेश = मन-शरीर दोनों का पीड़ित होना। कष्ट = दुःखजनक स्थिति। व्यथा = पीड़ा। वेदना = पीड़ा का मानसिक अनुभव। यातना = दुःख भोगने की मनोदशा। यन्त्रणा = दुःख की दीर्घकालिक जकड़न।
(27) ऋतु = छः ऋतुएँ होती हैं। मौसम = पारिस्थितिक भेद।