MP Board Class 11th Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 1 Accounting
Accounting Important Questions
Accounting Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The art of recording all business transactions in a systematic manner in a set of books is called –
(a) Accounting
(b) Book – keeping
(c) Ledger
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Book – keeping
Question 2.
The process of recording, classifying and summarizing all business transactions in order to know the financial result is called –
(a) Book – keeping
(b)Accounting
(c) Journalizing
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b)Accounting
Question 3.
Cash, goods or assets invested by the proprietor in the business for earning profit is called –
(a) Profit
(b) Capital
(c) Fixed assets
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Capital
![]()
Question 4.
The person, firm or institution who does not pay the price in cash for the goods purchased or the services received is called –
(a) Creditor
(b) Proprietor
(c) Debtor
(d)None of these.
Answer:
(c) Debtor
Question 5.
Book – keeping is –
(a) An art
(b) A science
(c) An art and science both
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) An art and science both
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The document certifying the purchase or sale of goods or any monetary transaction is called …………….
- The thing which is purchased and sold in the business is called …………….
- The things or properties which helps in smooth functioning of the business and which are owned by the business are called ……………. of the business.
- The unsold goods left at the end of the year is called ……………..
- ……………. represents the excess of assets over liabilities.
Answer:
- Voucher
- Goods
- Assets
- Closing stock
- Capital
Question 3.

Answer:
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (e).
Question 4.
Answer in one word/sentence:
- Any legal activity performed for earning profit is called.
- The head under which transactions pertaining to a person, institution, firm, expenses, assets etc. is recorded is called.
- The system in which only one aspect of the transaction is recorded is called.
- The concession given on cash transactions is called.
Answer:
- Business
- Account
- Single entry system
- Cash discount.
![]()
Question 5.
State True or False:
- Trade discount is given on credit transactions only.
- Furniture purchased by a Trader dealing in Furniture will be treated as ‘purchases’ for him.
- Cash is a Fixed Asset of a Business.
- The goods invested at the commencement of the business is called closing stock.
Answer:
- False
- True
- False
- False.
Accounting Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain any five advantages of accounting towards Traders?
Answer:
1. Important information – With the help of it, the trader can attain many important informations regarding the business easily.
2. Helps in purchase and sale – If the businessman wants to sale or purchase the business, he can collect the informations from the books of accounts.
3. Comparative study – It enables the trader to formulate policies for the future, for more profit by comparing with old books of accounts.
4. Helps in taking loans – On the basis of systematic books of accounts prepared the trader can take loans easily.
Control of an employee:
By checking the books of accounts prepared by the employee, errors and frauds can be detected and easily corrected.
Question 2.
Explain any two objects of accounting?
Answer:
The following are the objects of accounting:
1. Knowledge of assets and liabilities – By book keeping and accountancy, the knowledge of assets and liabilities can be ascertained.
2. Knowledge of profit and loss – The knowledge of profit and loss of a business can be known from the books of accounts.
3. To know the financial position of the business – Accounting provides valuable information about business assets and liabilities. The name of these information known is balance sheet.
4. Meeting statutory requirement – Under companies act 1956, and for registered partnership, maintenance of accounts are compulsory as per law.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the following terms?
- Capital
- Drawings
- Entry
- Bad debt
- Assets
- Insolvent
- Voucher
- Commission
- Debtors
- Creditors
- Closing stock.
Or
Describe the following:
(a) Bad debts
(b) Insolvent.
Answer:
1. Capital:
Capital represents that amount which is invested by the proprietor in the business. It may be in the form of cash, goods or assets. It is excess of assets over liabilities at a given time. Capital – assets – liabilities.
2. Drawings:
The withdrawal of goods or cash from the business by the proprietor for his personal use or domestic use is called drawings. It reduces the capital of the business.
3. Entry:
Recording of business transactions in the books of accounts is called entry. It is recorded as journal entry in journal book.
4. Bad debts:
The debts which can’t be recovered from the debtors are called bad debt. It arises when a debtor becomes insolvent or bankrupt.
5. Assets:
The properties which are vital for running the business are called assets, e.g., Buildings, furniture, machinery, etc. These are things of value owned by the firm.
6. Insolvent:
A person who is unable to pay his debt to his creditors, he is said to be insolvent by the court. He is also known as ‘Bankrupt’. The liabilities of such persons are more than the value of assets he possesses.
7. Voucher:
A written document. Certificate or paper verifying the business trans¬actions is called voucher, e.g.; invoice, money receipt, cash memo etc.
8. Commission:
The remuneration or allowance either paid or received for buying or selling of goods or for any other services for the business is called commission. It may be in the form of a fixed amount or percentage.
9. Debtor:
A debtor is a person who owe money Or money’s worth to the business. A person becomes a debtor when he purchases goods from the business on credit, i.e., to the business, the person who buys the goods becomes a debtor.
10. Creditor:
The person from whom goods are purchased on credit is known as creditor. Creditor arises when there is credit purchase of goods.
11. Closing stock:
The unsold goods remaining on a particular date or during a particular period is called stock in hand. It is estimated at the end of the accounting year for the purpose of calculating profit of the business, is called closing stock. At the beginning of the next accounting year it becomes opening stock of the business.
Question 4.
Mention the various characteristics of accountancy?
Answer:
The various characteristics of accountancy are:
- It is both an art and a science.
- In accoutancy, only business transactions are recorded.
- The transactions are entered in a systematic manner on the basis of certain definite principles in the book of accounts.
- It is prepared for a particular accounting period.
- In accountancy only specific accounts are opened.
Question 5.
Is book – keeping a ‘science’ or an ‘art’? Explain.
Answer:
Book – keeping is an ‘art’:
The business transactions are recorded in a systematic manner in separate books. On the basis of some accepted theories, principles and rules the business transactions are entered in achieving a desired object. Thus, it is an ‘art’.
Book – keeping is a ‘science’:
It is an organized and systematic body of knowledge which is based on certain basic principles. The summarizing and classifying of transactions are done on fixed basic principles. They are universally accepted. Hence, we can say that book – keeping is both an ‘art’ and a ‘science’.
![]()
Question 6.
Differentiate between cash discount and trade discount (any five)?
Answer:
Difference between trade discount and cash discount:
Trade Discount:
- It is allowed on the time of sale.
- The object of trade discount is to promote sales.
- It is shown in invoice.
- T.D. is allowed to every customer according to the terms and conditions of the business.
- T.D. is calculated on the list price of goods.
Cash Discount:
- It is allowed on the payment of cash within or fixed period.
- The object of cash discount is encourage the customer to make payment promptly.
- It is not shown in invoice.
- C.D. is not allowed to all customers.
- C.D. depends on the amount to be paid.
Accounting Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the various systems of book – keeping?
Or
Describe the different systems of accounting?
Answer:
The various systems of book – keeping are:
1. Indian accounting system:
This system is also known as Mahajani System. It is written in any Indian languages, according to the customs and rules prevailing in a particular area.
2. English system of accounting:
This system is originated in England. It is of two types. They are as follows:
(i) Double entry system:
According to this system, each transaction has two aspects: debit and credit. On this base transactions are entered. This system is popular all over the world. It is the only one scientific system which we can relie.
(ii) Cash system:
Under this system, only a cash – book is maintained in the business to enter the cash transactions. Generally, this system is following by non – trading concerns.
(iii) Single entry system:
Under this system, along with cash-book, some other accounts are also maintained. It includes the personal accounts of debtors and creditors. It is also known as incomplete system of accounting.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the importance / advantages of accountancy?
Or
What are the advantages of accounting to businessmen/traders?
Answer:
Accountancy not only reveals correct profits and loss and financial position of business but also benefits Govt., society and other sections of society. This can be explained as under:
I. Advantages to traders:
- Important information – With the help of it, the trader can attain many important informations regarding the business easily.
- Helps in purchase and sale – If the businessman wants to sale or purchase the business, he can collect the informations from the books of accounts.
- Comparative study – It enables the trader to formulate policies for the future, for more profit by comparing with old books of accounts.
- Helps in taking loans – On the basis of systematic books of accounts prepared the trader can take loans easily.
- Control of an employee – By checking the books of accounts prepared by the employee, errors and frauds can be detected and easily corrected.
II. Advantages to government:
- On the basis of the progress of the business, the government can collect the informations regarding the development of commercial and industrial sector of the nation.
- Determination of taxes: The tax authorities can determine different taxes like income tax, sales tax, etc. easily on the basis of accounts kept in the business.
- The government can know which business or industrial unit is sick and steps can be taken to remove it, on the basis of accounts kept in the business.
- For issuing the various licences by the government, it makes use of accounts.
- If any business or industry needs financial assistance, the government can provide it on the basis of accounts.
III. Advantages to Investors:
Accounting reveals the actual financial position of the business which helps a lot to the investors for investing their money at right place.
IV. Advantages to consumers:
If appropriate cost accounting procedure is adapted, then per unit cost of production can be ascertained which helps for fixing the selling price of f the commodity. Thus it saves the consumers from being exploited.
Question 3.
Differentiate between Book – keeping and Accounting.
Answer:
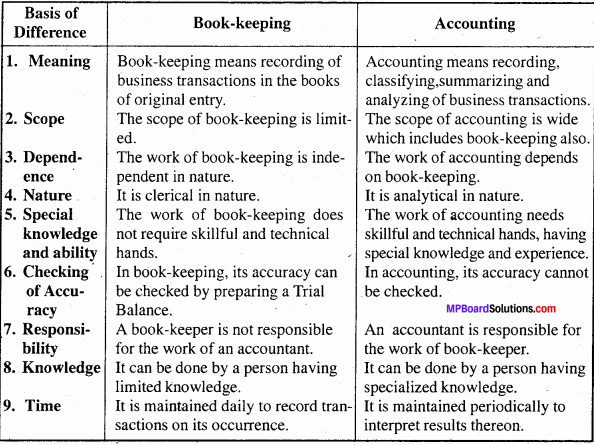
Question 4.
Explain some properties of Accounting Informations?
Answer:
Accounting Information:
As we all know, accounting information relating to business is very benefecial for all parties related to the business. Hence, the preparation and presentation of accounting information should be scientific and clear. For it, the following characteristics must be present in the accounting information.
1. Reliability:
It is essential for accounting information to be reliable. The information must be prepared in such a way that its reliability can be checked and proved. The information can be trustworthy. If it is based on various source documents used in the business like cash memo, invoice Agreement, letters, etc. The information can be checked and tested anytime with the help of these source documents.
2. Relevance:
The accounting information given in the financial documents must be in accordance with the objectives laid down by the organization. Relevant informations refers to the informations that helps the various parties connected with the business in taking decisions. The information contained in financial documents is beneficial to all parties of business if the accountants had collected the information keeping in mind the requirements of various parties.
The same information displayed in financial documents may be general to some and special or important to others the information is general or special depends on the objects of various parties/users of information.
3. Understandibility:
The presentation of accounting information must be so simple and logical that’any party having interest in the business can understand the information easily. There are of course, various information which could be comprehended by people having knowledge of accounting, terms but such information can be accompanied by explanation wherever needed so that a common man may also understand the meaning inherent in the disclosed information.
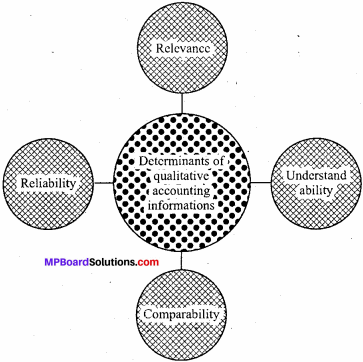
4. Comparability:
While preparing financial documents it must be borne in mind that accounting information relating to current year can be presented in a comparative manner with previous year’s information, facts and figures if presented in this way helps in the formation of business policies for future. A comparative study can be conducted and reasons can be sorted out for any unfavorable information and according remedial measures can be taken in the interest of the business.