MP Board Solutions for 12th English Chapter 8 The Beggar Questions and Answers aids you to prepare all the topics in it effectively. You need not worry about the accuracy of the Madhya Pradesh Board Solutions for 12th English as they are given adhering to the latest exam pattern and syllabus guidelines.
You Can Download MP Board Class 12th English Solutions Questions and Answers Notes, Summary, Lessons: Pronunciation, Translation, Word Meanings, Textual Exercises. Enhance your subject knowledge by preparing from the Chapterwise MP Board Solutions for 12th English and clarify your doubts on the corresponding topics.
MP Board Class 12th English A Voyage Solutions Chapter 8 The Beggar (Anton Chekhov)
Kick start your preparation by using our online resource MP Board Solutions for 12th English Chapter 8 The Beggar Questions and Answers. You can even download the Madhya Pradesh Board Class 12th English Solutions Questions and Answers for free of cost through the direct links available on our page. Clear your queries and understand the concept behind them in a simple manner. Simply tap on the concept you wish to prepare in the chapter and go through it.
The Beggar Textbook Exercises
Word Power
A. Refer to a dictionary and find out the meanings of the words given below and use them in sentences of your own:
expelled, scrutinized, indebted, pampered, desperately, assault, disgust, wrath.
Answer:
- Expfelled-dismissed-Mr Chaudhary was expelled from the party for his indisciplined behaviour.
- Scrutinized-examined-The case was scurtinized by an expert committee.
- Indebted-to be in debt, obliged-I feel indebted to him for his prompt help, otherwise I was ruined.
- Pampered-protected-Your child is over pampered which is not good.
- Desperately-out of frustration-He killed himself desperately.
- Assault-insult-I can’t bear the assault on women’s character.
- Disgust-bore-I was disgusted with his arrogant behaviour.
- Wrath-anger-He was full of wrath at his friend’s irresponsible act.
B. Complete each of the following sentences given below with a word from the story which is equivalent to the word given in brackets:
1. Ravi was …….. to work in severe cold. (forced)
2. The woodcutter …….. up the heavy log very quickly. (cut)
3. The principal …….. the students for misbehaving in the class. (called)
4. The boy opened the …….. and looked outside. (casement)
5. The juniors …….. the proposal. (opposed)
Answer:
- compelled
- chopped
- summoned
- window
- protested.
C. Complete the network with words with similar connotation. Add as many bubbles as you can.
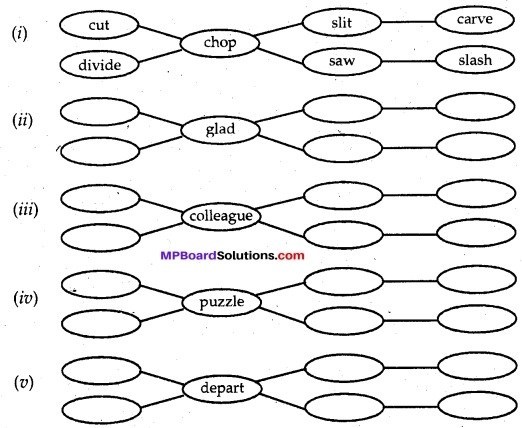
Answer:
(ii) glad—happy, joyful, cheerful, delighted, ecstatic, pleased.
(iii) colleague—mate, friend, ally, aid, helper, partner.
(iv) puzzle—confuse, confound, bewilder, perplex, doubt.
(v) depart—set out, embark, leave, go away, retire, quit.
D. Find words from the text that have the opposite meanings of the following words:
departed, prove, protest, refuse, pleasure, abuse, backward, disinclined, forget.
Answer:
Words – Opposite words from the text
- departed – appeared
- prove – disproved
- protest – defend
- refuse – consent
- pleasure – sorrow
- abuse – prize
- backward – forward
- disinclined – inclined
- forget – remember
Comprehension
A. Choose the correct alternatives and complete the following sentences:
The Beggar Class 12 Question 1.
The beggar actually was a
(a) a lawyer
(b) a schoolmaster
(c) a student
(d) a singer
Answer:
(d) a singer
The Beggar Summary Class 12 Mp Board Question 2.
The beggar confessed to Skvortsov that he begged because-
(a) he was turned out of the Russian Choir
(b) he was scolded by the lawyer
(c) he was caught by the police
(d) he was ashamed of himself.
Answer:
(a) he was turned out of the Russian Choir
The Beggar Class 12 Questions And Answers Question 3.
The beggar agreed to work as-
(a) a factory hand
(b) a billiard marker
(c) a house porter
(d) a wood chopper
Answer:
(d) a wood chopper
The Beggar Actually Was A Class 12 Question 4.
Which adjective does Skvortsov use to describe his cook?
(a) gentle
(b) cross
(c) cool
(d) hot.
Answer:
(b) cross
Question 5.
Who brought about a change in the beggar?
(a) Skvortsov’s colleague
(b) the cook
(c) Skvortsov
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(b) the cook
B. Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
Why did Skvortsov look askance at the beggar?
Answer:
Skvortsov looked askance at the beggar because he had doubts about him.
Question 2.
What reasons did the beggar give for begging? (in the beginning of the story)
Answer:
The beggar said that he was very hungry for he had not tasted food for three days. So, he needed some money. Neither he has enough money for night lodgings.
Question 3.
Why did the beggar confess that he lied?
Answer:
The beggar confessed that he lied because the narrator threatened him to hand him over to the police.
Question 4.
Why was Skvortsov was angry with the beggar?
Answer:
Skvortsov was angry with the beggar because the beggar was begging in the name of a schoolmaster to earn more sympathy from people.
Question 5.
According to Skvortsov, the beggar couldn’t be a house porter or a factory hand. What reason did he give to support his statement?
Answer:
He gave the reason that the beggar was too gentle for that sort of work.
Question 6.
The beggar says, “It’s rather late for him to be a shopman.” What reason did he give to support his statement?
Answer:
In his view one has to begin from a boy in a trade, so he was not a right choice to be a shopman.
Question 7.
What was the reason that made Skvortsov feel ashamed and sore?
Answer:
Skvortsov felt ashamed and sore at the thought that he had made a pampered, drunken and sick man to do hard rough work in cold.
Question 8.
What made the men with the vans laugh at the beggar?
Answer:
The men with the vans laughed at the beggar for his idleness, feebleness and ragged coat.
Question 9.
What made Skvortsov so happy when he met the beggar at the theatre?
(M.P. Board 2015)
Answer:
The beggar was in a much better position with a considerable income. It made Skvortsov happy.
Question 10.
Why did Olga shed tears over the beggar?
Answer:
Olga shed tears over the beggar because she wanted to bring about a change in the beggar’s soul.
C. Answer the following questions in about 60 to 75 words each:
Question 1.
Why was Lushkov, the beggar compelled to beg?
Answer:
Lushkov was a beggar. When he approached Skvortsov for help, he was caught in an unexpected situation. He told Skvortsov that he was hungry. He had not tasted food for three days. He do not have five-kopeck piece for a night’s lodging. He added that, he was once a schoolmaster in a village and had lost his post because of a conspiracy. He wanted to convince the writer with his plea that he was a victim of false witness. He said that he was out of place for a year and now he had been offered a post in the Kaluga province. However, he had no means for the journey. Hence, he was begging for help.
Question 2.
Why did the beggar get a merciless scolding? (M.P. Board 2012)
Answer:
The beggar while begging approached Skvortsov, the narrator. He began to explain his helplessness and tried to convince him for help. However, the narrator recollected his memory and remembered that was the man who just a day back was begging in the name of an expelled student. This time he was begging in the name of a schoolmaster. He was using the name of a schoolmaster and a student in order to attract more sympathy from people. He was trying to blackmail people emotionally. It made the narrator angry and he scolded him mercilessly and also threatened to hand him over the police.
Question 3.
“I cannot get on without lying,” said the beggar. Why did he say so?
Answer:
The narrator was very angry with the beggar for he was using the name of a student and a village schoolmaster in order to exploit the sentiments of the public. When he scolded him and threatened to call the police, the beggar was scared. He immediately confessed that he was lying. But he said, he had no option other than lying. Whenever he told the truth, no one would believe it. The reality was that he was neither a student nor a schoolmaster but was in a Russian choir and was turned out of it for drunkenness. Truth couldn’t give him food. He was dying of hunger and freezing in cold. So, he was compelled to lying.
Question 4.
How did the beggar defend his act of begging?
Answer:
In the course of his begging, when Lushkov asked Skvortsov for help, he was caught in a wrong box this time. Skvortsov was angry for his begging in the name of a student and a schoolmaster. He scolded him and threatened to send him to jail. Lushkov tried to convince him with his plea but Skvortsov did not agree. Finally, when Skvortsov asked him, why did he not find a job or do labour, Lushkov defended himself by saying that begging was the best option for him.
He said that he couldn’t get manual work. He was too old for being a shopman for trade was to be learnt from the very beginning. He couldn’t get a job of house porter for he was not of that class. He also could not get any job in factory, for doing any work, one must be skilled but he knew nothing. So, he very suitably chose begging.
Question 5.
As soon as the beggar was offered a job, he refused it and made excuses. What were the excuses?
Answer:
Lushkov wanted to convince Skvortsov with his plea that begging was the best and suitable job for him. He said that he was not to get any job. Skvortsov, however offered him a job. As Lushkov was not willing to do labour, he refused it by giving excuses. He said that he won’t get manual work. He couldn’t do shopman’s job or a trade’s job. As he was not of a class of house porter, he won’t get this job. He was not a skilled person, so he can’t do any work. Finally, when Skvortsov gave him the job of wood chopping, he said that it was not a regular one. When Skvortsov asked him to accept it, he had no other way and joined the work.
Question 6.
The author says that the beggar had been taken at his words. Do you agree? Support your answer.
Answer:
There was a long discussion between Skvortsov and Lushkov. Skvortsov was not convinced with the begging of Lushkov. Lushkov had all justifications for his work. Finally, when Lushkov said that no one would give him any job, Skvortsov offered him a job of wood chopping. Lushkov first wanted to refuse it, giving the plea that wood chopping was not regular.
Skvortsov asked him first to accept it, then he may get more and then Lushkov had no option other than accepting this offer. Skvortsov gave him the job. When the day’s work was done, he asked his maid Olga to give Lushkov half a rouble and asked him to come the next day, if he wished. So, the next day, Lushkov came and did the ” job under the supervision of Olga.
Question 7.
In the beginning of the story, Skvortsov was ready to handover the beggar to the police; but in the later part of the story, the author says, “Skvortsov’s wrath had passed off”. What does this indicate about Skvortsov’s character?
Answer:
Skvortsov is a central character in the story The Beggar. He is an advocate by profession in Peterburg. He is a man of ideal character. He believes in reality and prefers work. First, when Lushkov comes to him, Skvortsov looks at him keenly. Very soon, he recognizes that he had seen the man before. He had seen him begging in the name of a student and now he was begging in the name of a schoolmaster. He becomes angry and he scolds him for using such names to exploit public sentiment because one can easily be carried away with such names.
So, he threatens him to send him to jail if he doesn’t tell the truth. Here, he appears to be a rude man but reality is that he has high regards for students , and schoolmasters. He dislikes the act of begging. When Lushkov reveals his reality, Skvortsov offers him job. With his effort, one day, Lushkov comes to a very good position. Skvortsov feels pleasure with Lushkov’s betterment. It shows that Skvortsov is a man of good character.
Question 8.
Olga behaved with the beggar very badly. Was her behaviour real? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Olga is the maid servant of Skvortsov, the advocate. When Skvortsov offers the job of wood chopping to Lushkov, he deputes Olga to observe the work. Olga, as Skvortsov says, is a cross creature. She feels irritated with Lushkov as he is a drunkard. He is always not in proper state of mind. Olga abuses him and talks to him in a rude manner, saying that he is an unlucky fellow with no gladness in life. These words are very hurting, however, she also chops the wood herself and tells Skvortsov that Lushkov had done it. It shows that her rudeness is just to hurt Lushkov, so that he can change himself. Finally, it happened, Lushkov becomes a better person.
Question 9.
Did Skvortsov really succeed in reforming the beggar? Give reasons to support your answer.
Answer:
Skvortsov was a man of perfection. He scolded Lushkov for his begging. He didn’t like Lushkov’s lies in the name of student and schoolmaster for begging. He wanted to reform that man. So, he offered him job with a promise that he would give him regular work. Lushkov, however, came to do wood chopping regularly. It impressed Skvortsov and he sent him to one of his friends for some official work. It changed Lushkov’s life completely. He came to a very good position. Had Skvortsov not helped Lushkov, he would have . been still begging. So, Skvortsov succeeded in reforming the life of a beggar, as at the end of the chapter we come across Lushkov who himself acknowledges the good deeds bestowed on him by Skvortsor and also thanks Olga for changing his inner soul.
Question 10.
“It was the attitude, not the words that brought about a change in the beggar.” Explain.
Answer:
In the course Of assigning a job to Lushkov, Skvortsov gave him the work of wood chopping and he deputed his maid servant, Olga, to supervise the work. Olga was a lady of cross nature. She used to get irritated very soon. When she saw a man, Lushkov, who was not in his proper mental condition, she was irritated. Lushkov was in a drunken state. He was feeble and weak. He was not Working properly. So, Olga began crossing him. She called him unlucky fellow and poor drunkard and said that he was a sorrowful creature and that he would go to hell. Olga’s selfless deeds towards Lushkov, her act of cutting ‘ woods for him gradually brought a change in him. Thus it was Olga’s attitude not Skvortsov’s words which brought a change in beggar.
Question 11.
What moral do you draw from the story?
Answer:
Anton Chekhov’s story The Beggar, presents a fine specimen of a life, which was caught in a wrong trap. It usually happens with a man in real life that he follows an easy going method. Sometimes, he adopts the wrong way of life, being depressed from the world. In this story Lushkov who was once in a Russian choir adopts begging as a means of livelihood. He was expelled from his job for his drunkenness or due to fabrication. However, when Skvortsov offered him a job, he did it.
Later, the words of Olga also put impact on him and Lushkov changed his life. Now, he was in a good position. So, the moral of this story is that one must not give up hopes. One should have a wish to do good. One should make efforts for betterment through right ways. Also, if a person wants to change, society must help him not only through words but by actions too.
Question 12.
Imagine yourself a lawyer and write what you would do if you come across such a person like the beggar.
Answer:
Had I been a lawyer and had got a chance to meet a person like Lushkov, a beggar, I would have done a little different. First, I would have asked him politely, who he was, why he was begging. I would not have scolded him or threatened him to put behind bars. Scolding or threatening might lead him not to tell the truth. So, a sympathetic treatment might expose him. Such a person can be treated compassionately. If compassion doesn’t work, then use any other form of behaviour. I would also have given him work to do.
Grammar:
A. Read the following sentences that are in passive voice:
- ………… that the wood had been chopped.
- ………….. an old pair of trousers was sent out to him.
The above sentences in passive voice are used without the agent ‘by’ Whenever it is evident who the agent is, it is unnecessary to mention him/her “. in the passive form. It may also not be used when the agent is unknown or when we do not care to name the agent, as ‘The ship was wrecked’.
Now change the following sentences into Passive form, without mentioning the agent:
1. The audience loudly cheered at the Mayor’s speech
2. Somebody cleans the room every day.
3. People don’t use this road very often.
4. They have cancelled the flight because of fog.
5. They are building a new ring road round the city.
Answer:
- The Mayor’s speech was cheered loudly.
- The room is cleaned every day.
- This road is not used very often.
- The flight has been cancelled because of fog.
- A new ring road is being built round the city.
B. Look at the phrases in bold in the following sentences:
- Skvortsov looked at his goloshes of which one was shallow like a shoe.
- While the other came high up the leg like a boot.
- You reek of vodka like a pothouse!
Notice that in the above sentences a word or phrase has been compared with something else to show that the two things have the same qualities and to make the description more powerful. This is called a simile. Simile is easy to understand. If you see the phrase in example, you will notice that one of the goloshes was shallow like a shoe. It seemed like a shoe while the other seemed like a boot i.e. a long shoe.
Now form smiles by filling the gap with the appropriate words.
1. He walks fast like a
2. Her skin is white like a
3. The bed was hard like an
4. The boy is slow like a
5. He is strong like an
6. It is hard like a
7. The boy is brave like a
8. The dog is hungry like a
9. The night-guards are watchful like a
10. The child is playful like a
Answer:
- rabbit
- duck
- armour
- snail
- ox
- rod
- soldier
- wolf
- dog
- squirrel
Speaking Activity
A. ‘Kindness touches the very core of one’s heart’. Discuss the statement with your classmates.
B. Divide the class into groups and arrange a debate on the above topic.
Answer:
A. Do yourself at class level. Some points are given here:
- Kindness is a bliss of God.
- It touches one’s core of the heart.
- It moulds a man and also an animal.
- It shows one’s depth and gravity.
- There are various examples of kindness shown.
B. Do at class level.
Writing Activity
Write a short essay on ‘Begging in India’ touching the following points:
- Causes
- Effects
- Remedies.
Answer:
Begging in India is a great curse for us. Everywhere, we come across beggars at footpaths, around religious places, platforms, stations, tourist places, etc. It is a blot for our nation. The cause of begging is the scarcity of proper food and living for the poor people and above all the rising unemployment. Natural disasters lead to poverty. Uncertainty of monsoon cripples our crops. Illiteracy also leads one to adopt this way of living for it is the easiest way, though illegal as the rule provides.
Its effect is very bad. It damages our prestige in the global arena. It leads to the growth of depression. It also leads to growth of crimes in our society. The beggar uses all the possible ways for earning, though all illegal.
The remedies for removing this worst blot have to be firm. A consciousness among people needs to be promoted. One should discourage it. Firm and strict laws should be made and implemented. Beggars should be rehabilitated. They should be engaged in other works. Literacy will help a lot in this direction.
Think It Over
A. Do you think it right to beg in order to gain something?
Think over it.
Answer:
You can extract answer from the above answer.
Things to Do
A. Borrow books from the library and read other stories written by Chekhov.
Answer:
Do yourself.
The Beggar by Anton Chekhov Introduction
The Beggar is a story about a man who was turned out of the Russianchoir for drunkenness. He took to tying and begging but suddenly the man changed his life completely.
The Beggar Summary in English
The story begins with the narrator’s exposition about how he met a strange beggar. One day a beggar approached him and asked for help. The beggar said that he was a schoolmaster and needed some help as he had no money for his journey. He said that he was out of service for a year and now he had been offered a post in the Kaluga province, but he had no fare to travel.
The narrator, Skvortsov, a lawyer by profession at Peterburg was filled with doubt because he had seen that man somewhere before. So, he scolded him for begging in the name of a schoolmaster and threatened him to hand him over to the police. Then the beggar exposed himself and said that once he was a musician in the Russian choir but he was turned out for drunkenness. Now he was workless.
The narrator offered him help if he agreed to work. The beggar agreed. The narrator assigned him the job of wood-chopping. He asked his maid Olga to take work from him. Olga was a lady of cross behaviour. She offered an axe to the beggar. As the beggar was not behaving properly because of his drunken stage, Olga was irritated. She got annoyed with the man and abused him but extended her hand and the wood was chopped. After an hour she said to the lawyer that the work was finished. The lawyer asked her to give him half a rouble and also asked her to ask him to come the next day if he wished for wood-chopping. The beggar came next day and again did the same thing and got half a rouble for it. Olga was deputed to watch over his work.
Later, Skvortsov was impressed with his sober behaviour. He liked him for his inclination to work. He offered him one rouble. Then he sent him to one of his friends for some good official job. Lushkov, as his name was, then went away. Two years passed. One day, Skvortsov saw a man at a ticket office of a theatre paying for his ticket. He recognised him. It was Lushkov. He was happy to know that Lushkov was now in a good position in a Notary’s office and earned thirty-five roubles.
Skvortsov was delighted that it was his effort that turned a beggar to such a good position. But Lushkov said that it was all due to Olga who did that. He said that Olga never let him chop wood. She did it herself but everyday all the time, she used to muse for him. She used to say to him, “You unlucky fellow! you have no gladness in this world, and in the next you will burn in hell, poor drunkard! You poor sorrowful creature!” This all changed Lushkov’s Life and he was so affected that he left drinking and changed himself. He was highly obliged to her because whatever she did, it was all for his better future. Then, Lushkov went away as the bell had rung.
The Beggar Summary in Hindi
The Beggar एक ऐसे व्यक्ति की कहानी है जिसे एक रूसी संगीत मंडली से उसके नशे की लत क कारण निकाल दिया गया था। उसने झूठ बोलना और भीख माँगने का पेशा अपना लिया था लेकिन अचानक उसे एक ऐसा आदमी मिला जिसने उसके जीवन को पूरी तरह बदल दिया। कहानी की शुरुआत होती है कहानीकार के उस खुलासे से जब वह बताता है कि कैसे उसकी मुलाकात एक अजीब भिखारी से हुई। एक दिन एक भिखारी उसके पास आया और उससे मदद माँगी। भिखारी ने कहा कि वह एक स्कूली शिक्षक था और उसे कुछ मदद की ज़रूरत थी क्योंकि उसकी यात्रा के लिए उसके पास पैसे नहीं थे।
उसने कहा कि एक साल से वह नौकरी से बाहर था और अब उसे Kaluga प्रान्त में जगह दी गई है। लेकिन उसके पास वहाँ जाने के लिए किराये का पैसा नहीं था। कथाकार Skvortsov, जो Perterburg में पेशे से वकील था, को संदेह हुआ क्योंकि उसने पहले कहीं उसे देखा था। इसलिए उसने एक स्कूली शिक्षक के नाम पर भीख माँगने के लिए उसे डाँटा और पुलिस के हवाले करने की धमकी दी। तब उस भिखारी ने अपनी असलियत बताई और कहा कि पहले कभी वह एक रूसी संगीत मंडली में गायक था लेकिन उसके नशेबाजी के कारण उसे निकाल दिया गया था। अब वह बेकार था।
कथाकार ने उसे काम देने के लिए कहा अगर वह तैयार हो तो। भिखारी तैयार हो गया। कथाकार ने उसे लकड़ी काटने का काम दिया और अपनी नौकरानी Olga को उससे काम लेने को कहा। Olga एक चिड़चिड़े स्वभाव की महिला थी। उसने भिखारी को कुल्हाड़ी दी। भिखारी नशे के कारण ठीक से व्यवहार नहीं कर रहा था। Olga चिढ़ गई। वह गुस्से में थी और उसने उसे गालियाँ दी। फिर भी उसने लकड़ी काटने में उसका हाथ बटाया। एक घंटे बाद उसने वकील से कहा कि काम समाप्त हो गया। वकील ने उससे उसे आधा रूबल दे देने को कहा और यह भी कहा उसे अगले दिन भी आने को कह दे यदि वह चाहे तो। भिखारी अगले दिन भी आया और वही किया और इसके लिए उसे आधा रूयल मिला। Olga को उसके काम की देखरेख के लिए कहा गया था।
बाद में Skvortsov उसके मृदु व्यवहार से प्रभावित हुआ। उसने उसके काम के प्रति लगाव को पसंद किया। उसने उसे एक रूबल दिया। फिर उसने उसे अपने एक दोस्त के पास कुछ अच्छे ऑफिशियल काम के लिए भेजा। Lushkov जैसा उसका नाम था तब चला गया। दो वर्ष बीत गये। एक दिन Skvortsov ने एक थियेटर की टिकट खिड़की पर एक व्यक्ति को टिकट खरीदते देखा। उसने उसे पहचान लिया। वह Lushkov था। वह बहुत खुश हुआ कि Lushkov अब एक नोटरी के कार्यालय में अच्छी स्थिति में था और पैंतीस रूबल कमाता था। Skvortsov आनन्दित हो रहा था कि उसके प्रभाव से एक भिखारी इतनी अच्छी स्थिति में पहुँच गया। लेकिन Lushkov ने उसे बताया कि यह सब Olga के कारण हुआ जिसने यह सब किया।
उसने बताया कि Olga ने कभी उसे लकड़ी काटने नहीं दिया। उसने खुद यह सब किया। लेकिन प्रतिदिन हर समय उसे कोसती रहती थी। वह कहा करती थी, “कसे अभागे हो तुम! इस संसार में तुम्हारे लिए कोई खुशी नहीं है और तुम नरक में जाओगे भिखारी, नशेबाज, बेचारा इंसान।” इस सभी ने Lushkov के जीवन को बदल दिया और वह इतना प्रभावित हुआ कि उसने नशा करना छोड़ दिया और पूरी तरह अपने को बदल लिया। वह उसके प्रति काफ़ी आभारी था क्योकि उसने जो कुछ भी किया, उसके बेहतर जीवन के लिए किया। फिर Lushkov चला गया क्योंकि घंटी बज चुकी थी।
The Beggar Word Meanings

The Beggar Important Pronunciations

The Beggar Passages for Comprehension
Read the passages given below and answer the questions that follow:
1. “Kind Sir, be so good as to notice a poor, hungry man?; I have not tasted food for three days. I have not a five-kopeck piece for a night’s lodging. I swear by God! For five years, I was a village schoolmaster and lost my post through the intrigues of the Zemstvo. I was the victim of false witness. I have been out of place for a year now.” Skvortsov, a Peterburg lawyer, looked at the speaker’s tattered dark blue overcoat, at his muddy, drunken eyes, at the red patches on his cheeks, and it seemed to him that he had seen the man before. (Page 58)
Questions:
(i) Who is addressed to as “Sir” in the first line?
(ii) What was the profession of the beggar? Why did he lose his job?
(iii) Make noun of the word ‘drunken
(iv) Find a word from the passage which means same as ‘old and torn’.
Answers:
(i) Mr. Skvortsov is addressed to as “Sir” in the first line.
(ii) The beggar was a village schoolmaster. He lost his job through the intrigues of his colleague and false witness.
(iii) ‘Drunkard’ is the noun for the word ‘drunken’.
(iv) ‘Tattered’ means same as ‘old and torn’.
2. Skvortsov flew into a rage and gave the beggar a merciless scolding. The ragged fellow’s insolent lying aroused his disgust and aversion, was an offence against what he, Skvortsov, loved and prized in himself: kindliness, a feeling heart, sympathy for the unhappy. By his lying, by his treacherous assault upon compassion, the individual had, as it were, defiled the charity which he liked to give to the poof with no misgivings in his heart. The beggar at first defended himself, protested with oaths, then he sank into silence and hung his head, overcome with shame. (Page 59)
Questions:
(i) How did Skvortsov behave with the beggar?
(if) Find a word from the above passage which is opposite in meaning to ‘kind’.
(iii) Give a word similar in meaning to ‘hate’.
(iv) Make adjective of ‘charity’.
Answers:
(i) Skvortsov flew into a rage and gave the beggar a merciless scolding.
(it) ‘Merciless’ is opposite in meaning to ‘kind’.
(iii) ‘Aversion’ has similar meaning to ‘hate’.
(iv) ‘Charitable’ is adjective of ‘charity’.
3. Then he saw the pseudo-schoolmaster and pseudo-student seat himself on a block of wood, and, leaning his red cheeks upon his fists, sink into thought. The cook flung an axe at his feet, spat angrily on the ground, and, judging by the expression of her lips, began abusing him. The beggar drew a log of wood towards him irresolutely, set it up between his feet, and diffidently drew the axe cross it. The log toppled and fell over. The beggar drew it towards him, breathed on his frozen hands, and again drew the axe along it as cautiously as though he were afraid of its hitting his golosh or chopping off his fingers. The log fell over again. (Page 60)
Questions:
(i) Why is he is referred to as ‘pseudo-schoolmaster’ and ‘pseudo-student’?
(if) Give noun form of the word ‘angrily’.
(iii) Find a word from the above passage which is similar in meaning to ‘cutting’.
(iv) Find a word from the passage which means opposite to ‘carelessly’.
Answers:
(i) He is referred to as ‘pseudo-schoolmaster’ and ‘pseudo-student’ because he was begging using the name of schoolmaster and student. He was neither of them.
(ii) ‘Anger’ is the noun form of the word ‘angrily’.
(iii) ‘Chopping’ has similar meaning to ‘cutting’.
(iv) ‘Cautiously’ means opposite to ‘carelessly’.
4.”Why, it was like this. I used to come to you to chop wood and she would begin: ‘Ah, you drunkard! You God-forsaken man! And yet death does not take you!’ and then she would sit opposite me, lamenting, looking into my face and wailing: ‘You unlucky fellow! You have no gladness in this world, and in the next you will burn in hell, poor drunkard! You poor sorrowful creature!’ and she always went on in that style, you know.
How often she upset herself and how many tears she shed over me, I can’t tell you. But what affected me most she chopped the wood for me! Do you know, sir, I never chopped a single log for you—she did it all! How it was she saved me, how it was I changed, looking at her, and gave up drinking. I can’t explain. I only know that what she said and the noble way she behaved brought about a change in my soul, and I shall never forget it. It’s time to go up, though, they are just going to ring the bell.” (Page 61)
Questions:
(i) How did the maid servant behave with the beggar? Why?
(ii) Give the noun form of ‘explain’.
(iii) Give a word which has the opposite meaning to ‘unlucky’.
(iv) Find a word from the passage which means the same as ‘crying with pain’.
Answers:
(i) The maid showed dual expressions. On his arrival, she used to abuse and curse him and then she used to lament on his poor conditions. She also made efforts to prick his consciousness by chopping the woods herself. This brought a change in beggar.
(ii) ‘Explanation is the noun form of ‘explain’.
(iii) ‘Fortunate’ is opposite in meaning to ‘unlucky’.
(iv) Wailing in the word having same in meaning to ‘crying with pain’.
We believe the information shared regarding MP Board Solutions for 12th English Chapter 8 The Beggar Questions and Answers as far as our knowledge is concerned is true and reliable. In case of any queries or suggestions do leave us your feedback and our team will guide you at the soonest possibility. Bookmark our site to avail latest updates on several state board Solutions at your fingertips.