MP Board Class 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NCERT Intext Exercises
Question 1.
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols :
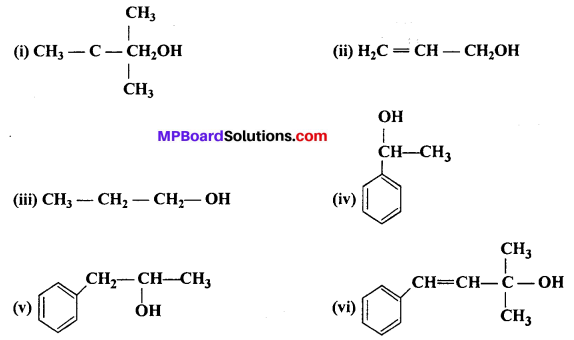
Answer:
(i) 1°, (ii) 1°, (iii) 1°, (iv) 2°, (v) 2°, (vi) 3°.
Question 2.
Identify allylic alcohols in the above examples.
Answer:
Allylic alcohols are (ii) and (vi).
Question 3.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system :
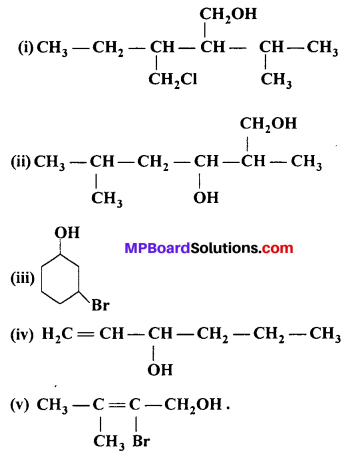
Answer:
(i) 3-chloromethyl-2-isopropyl pentan-1-ol.
(ii) 2,5-Dimethyl hexane-1,3-diol.
(iii) 3-Bromocyclohexan-l-ol.
(iv) Hex-l-en-3-ol.
(v) 2-Bromo-3 -methyl but-2-en- l-ol.
Question 4.
Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal ?

Answer:
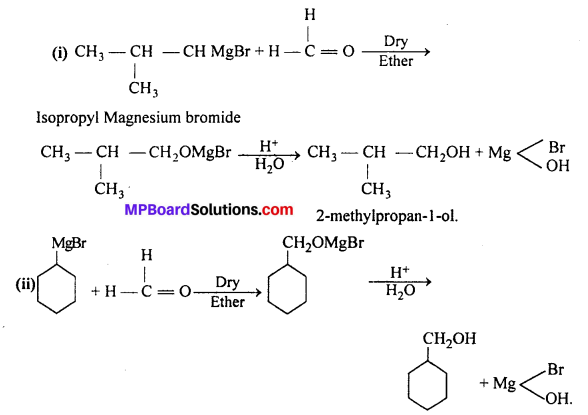
Question 5.
Write structures of the products of the following reactions:
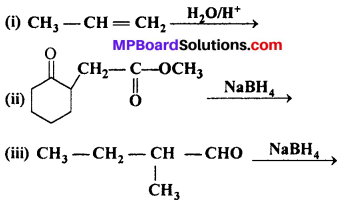
Answer:
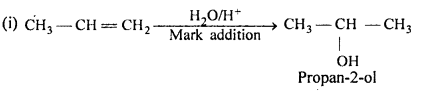
(ii) NaBH4 is weak reducing agent, it reduces aldehyde/ketones and not the esters.
Thus,
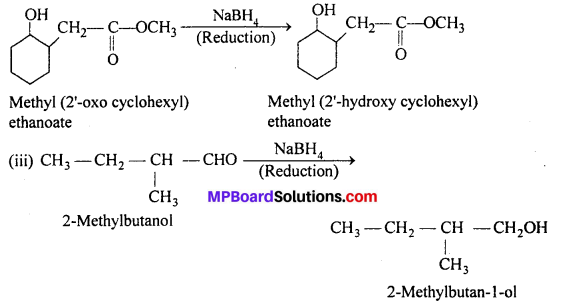
Question 6.
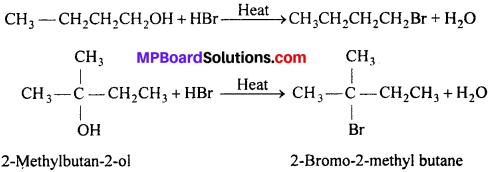
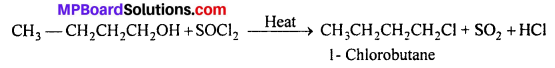
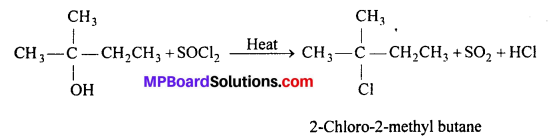
Give structures of the products you would expect when each of the following alcohol reacts with (a) HCl -ZnCl2, (b) HBr and (c) SOCl2 : (i) Butan-l-ol , (ii) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol.
Answer:
(a) With ZnCl2-HCl (Lucas reagent) : Butan-l-ol (1° alcohol) does not react with Lucas reagent at room temperature. However, turbidity appears only after heating but- 2-methyl butan-2-ol (3° alcohol) reacts with Lucas reagent at room temperature immediately gives turbidity
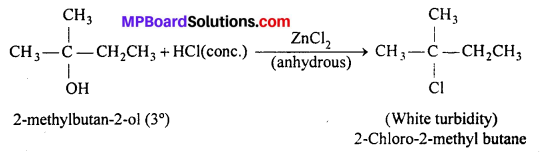
(b) With HBr : Both the alcohols react with HBr to give corresponding alkyl bromides.
(c) With SOCl2 : Both the alcohols react with SOCl2 to give corresponding alkyl chlorides.
![]()
Question 7.
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of:
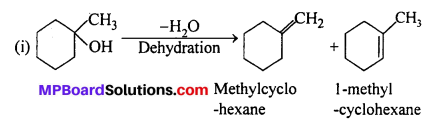
(i) 1-methylcyclohexanol and (ii) butan-l-ol.
Answer:
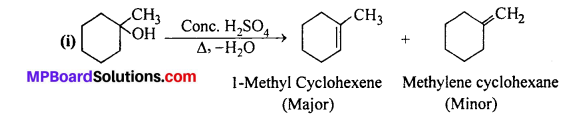
According to Saytzeff rule, the highly substituted product is the major product.
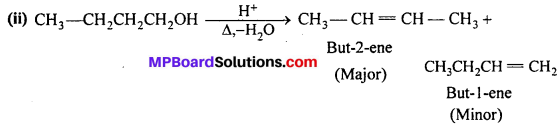
Question 8.
ortho and para nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol. Draw the resonance structures of the corresponding phenoxide ions.
Answer:
(i) Phenoxide ion:
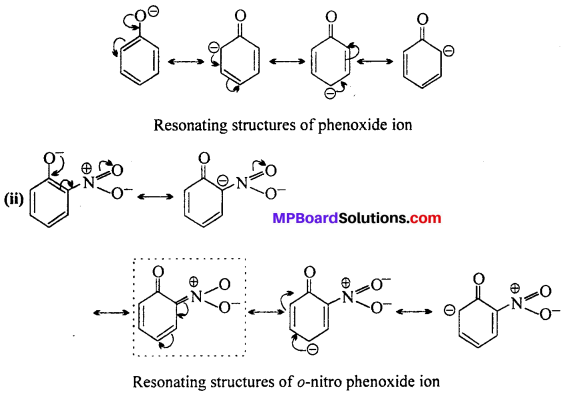
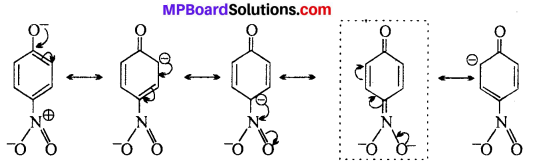
Resonating structures of p-nitro phenoxide ion. In substituted phenols, the presence of electron withdrawing group (-R effect) such as -NO2 group, increases the acidic strength of phenol, ortho and para nitrophenoxide ions are more stable (because of additional resonance structures show in boxes) than phenoxide ion due to effective delocalisation of negative charge in phenoxide ion. As a result o-and p- nitrophenols are more acidic than phenols.
Question 9.
Write the equations involved in the following reactions :
(i) Reimer – Tiemann reaction
(ii) Kolbe’s reaction.
Answer:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction : When phenol is treated with chloroform in presence of aqueous sodium hydroxide at 60°C, o-Hydroxy benzaldehyde (Salicylaldehyde) and p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde are formed. The ortho-isomer is the major product. This reaction is called Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
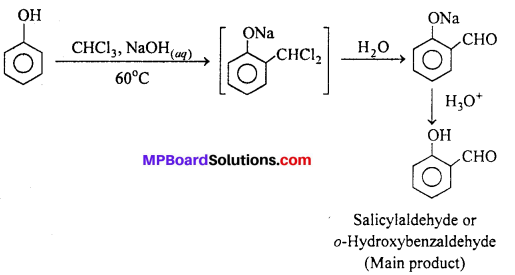
If carbon tetrachloride is used in place of chloroform, salicylic acid is obtained as the main product.
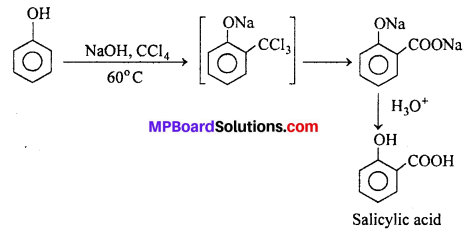
(ii) Kolbe- Schmidt reaction : When sodium salt of a phenol is heated with CO2 at 130°C. (403K) and 4-7 atm pressure, sodium salicylate is formed. This on acidification gives salicylic acid.
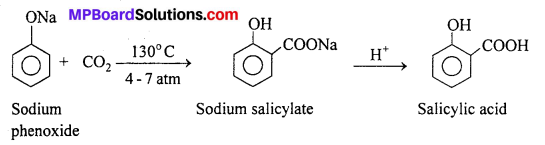
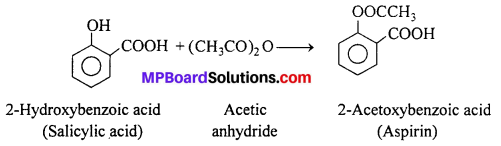
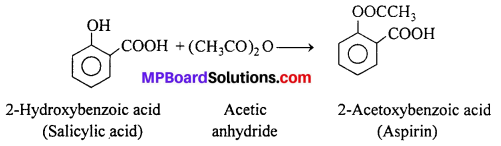
Salicylic acid is the starting material for the manufacture of aspirin which is an important analgesic.
Question 10.
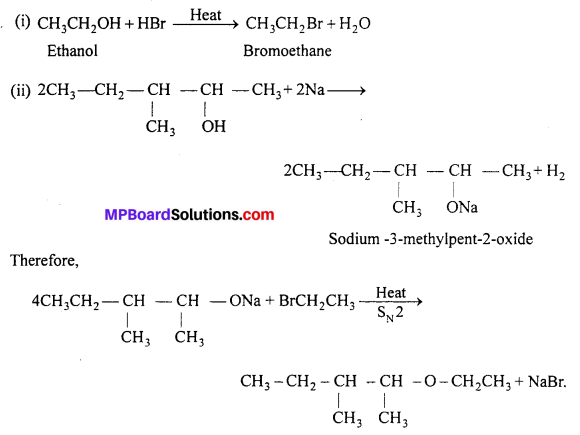
Write the reactions of Williamson synthesis of 2-ethoxy-3-methylpentane starting from ethanol and 3-methylpentan-2-oI.
Answer:
Williamson’s synthesis is reaction of alkyl halide (1°) with sodium alkoxide to give ether by SN2 mechanism. Thus, alkyl halide should be derivde from ethanol and alkoxide ion from 3-methyl pentan-2-ol. The complete reaction is as follows :
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following is an appropriate set of reactants for the preparation of l-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene and why ?
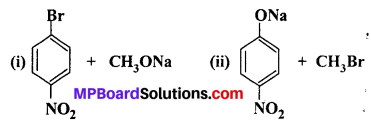
Answer:
Chemically both sets are equally probable. In set (A) the Br group is activated by the electron withdrawing effect of —NO2 group. Therefore, nucleophilic attack of CH3ONa followed by elimination of NaBr gives the desired ether.
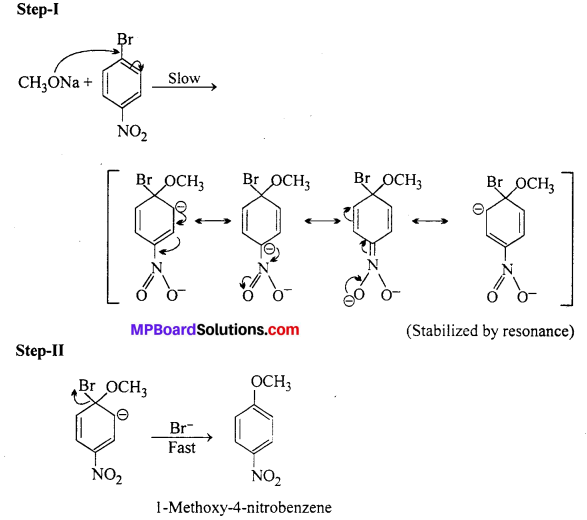
In set (B) nucleophilic attack of 4-nitrophenoxide ion on methylbromide gives the desired product.
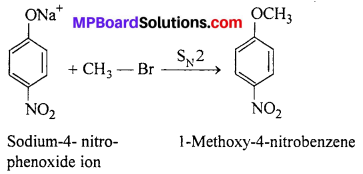
Question 12.
Predict the products of the following reactions:
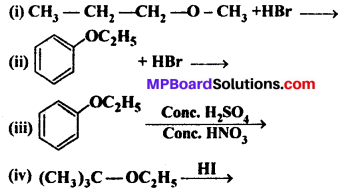
Answer:
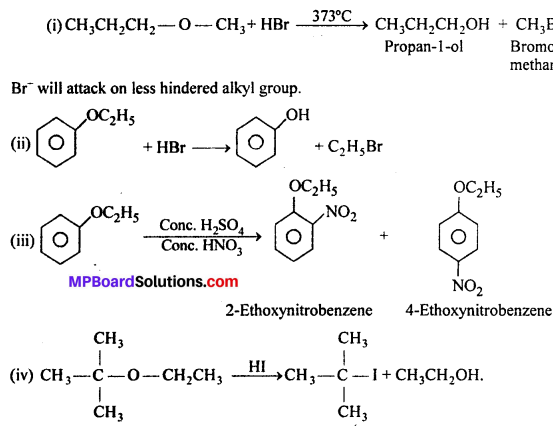
When one of the groups in unsymmetrical ether is tertiary, then the halide formed is tertiary halide.
![]()
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds :
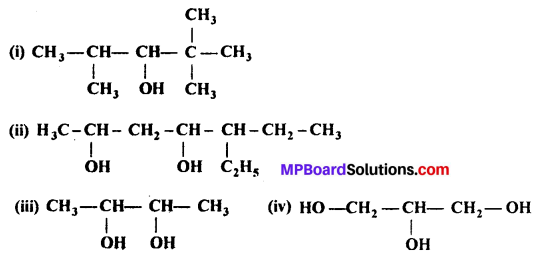
Answer:
(i) 2,2,4-Trimethyl pentan-3-ol
(ii) 5-Ethylheptane-2,4-diol
(iii) Butan-2,3-diol
(iv) Propane-1,2,3-triol
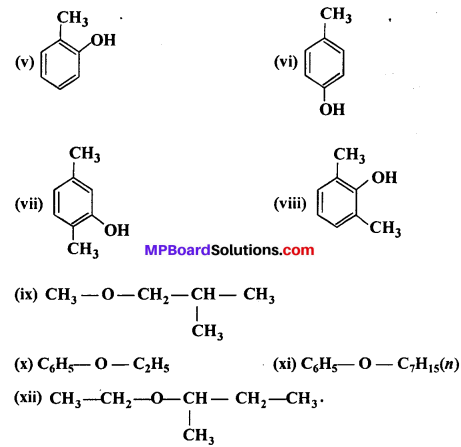
(v) 2-Methylphenol
(vi) 4-Methylphenol
(vii) 2,5-Dimethylphenol
(viii) 2,6-Dimethylphenol
(ix) l-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
(x) Ethoxybenzene
(xi) 1-Phenoxyheptane
(xii) 2-Ethoxybutane.
Question 2.
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows :
(i) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
(ii) l-Phenylpropan-2-ol
(iii) 3,5-Dimethylhexane -1, 3, 5-triol
(iv) 2,3 – Diethylphenol
(v) 1 – Ethoxypropane
(vi) 2-Ethoxy-3-methylpentane
(vii) Cyclohexylmethanol
(viii) 3-CycIohexylpentan-3-ol
(ix) Cyclopent-3-en-l-
(x) 4-Chloro-3-ethylbutan-l-ol.
Answer:
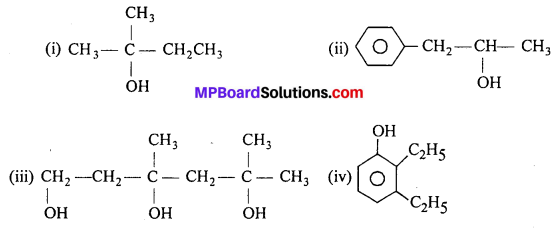
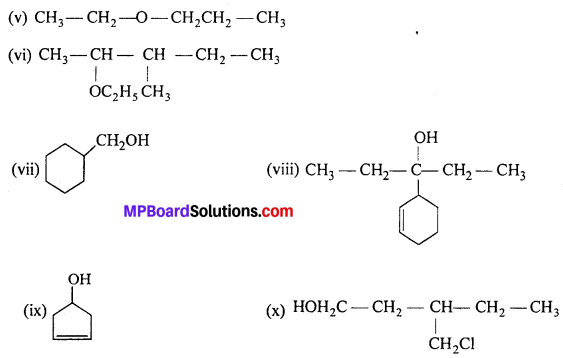
Question 3.
(i) Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C5H12O and give their IUPAC names.
(ii) Classify the isomers of alcohols in question (i) as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Answer:
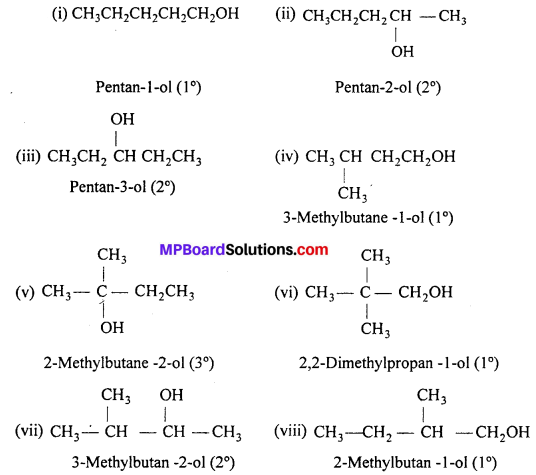
Isomers (ii), (vii) and (viii) contain chiral centres can exhibit enantiomerism.
Question 4.
Explain, why propanol has higher boiling point than that of the hydrocarbon, butane ?
Answer:
The molecules of butane are held together by weak van der Waals’ force of attraction while those of propanol are held together by stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
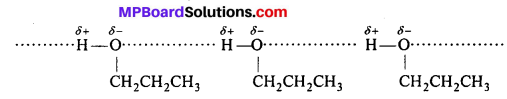
Therefore, the b.p. of propanol is much higher than that of butane.
Question 5.
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact.
Answer:
Alcohols can form hydrogen bonds with water and break the H—bond exist between water molecules. Hence, they are soluble in water.
On the other hand, hydrocarbons cannot form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and hence are insoluble in water.
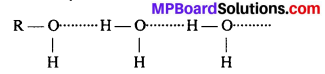
Question 6.
What is meant by hydroboration-oxidation reaction ? Illustrate it with an example.
Answer:
The addition of diborane to alkene to form trialkyl boranes followed by their oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxide to form alcohol is called hydroboration-oxidation. For example:
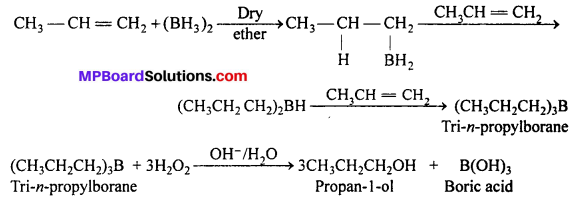
The alcohols obtained by this process appear to have been formed by direct addition of water to the alkene against MarkownikofFs rule.
Question 7.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula, C7H8O.
Answer:
Three isomers are :
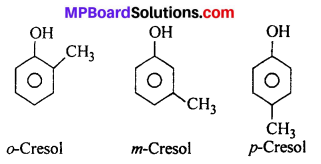
![]()
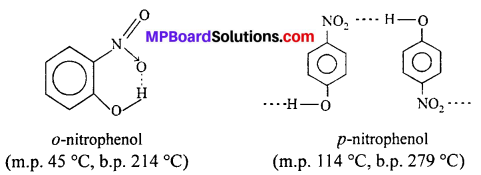
Question 8.
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenois by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reason.
Answer:
Orthonitrophenol is steam volatile while para-nitrophenol is not. This is on ac¬count of chelation (intramolecular H—bonding) in the molecule of o-nitrophenol. As a result its boiling point is less than that of p-nitrophenol, which is not steam volatile and its molecules are linked by intermolecular H—bonding.
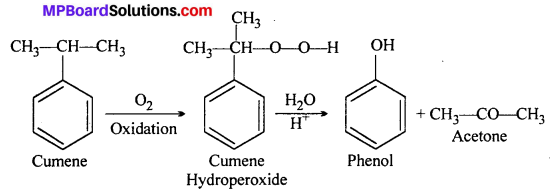
Question 9.
Give the equations of reactions for the preparation of phenol from cumene.
Answer:
Question 10.
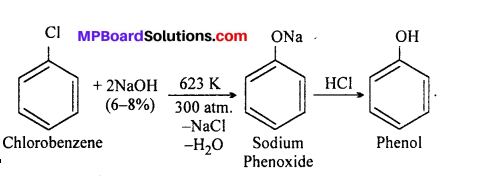
Write chemical reaction for the preparation of phenol from chloroben zene.
Answer:
Question 11.
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
Answer:
Direct addition of water to ethene in presence of an acid does not occur. Indirectly, ethene is first passed through cone. H2SO4 at room temperature to form ethylhydrogen- sulphate, which is decomposed by water on heating to form alcohol.
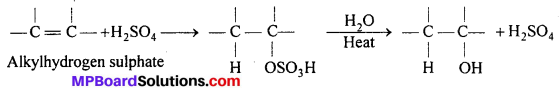
Mechanism : H2SO4 → H+ + OΘ SO2OH
Step-I: Protonation of alkene to form carbo-cation by electrophilic attack of hydronium ion (H3O+).
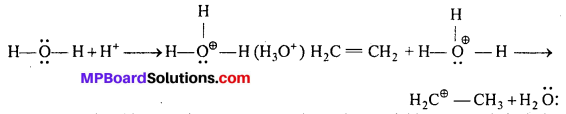
Step-II: Nucleophilic attack by water on carbo-cation to yield protonated alcohol.
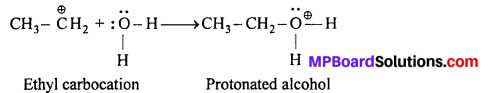
Step-III: Deprotonation (loss of proton) to form an alcohol:
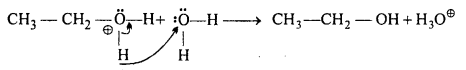
Question 12.
You are given benzene, cone. H2SO4 and NaOH. Write the equations for the preparation of phenol using these reagents.
Answer:
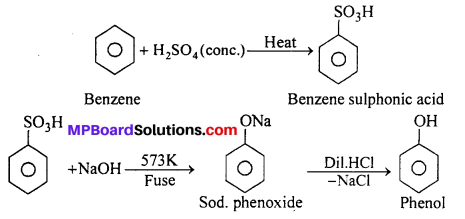
Question 13.
Show how will you synthesis :
(i) 1-Phenylethanol from a suitable alkene ?
(ii) Cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by an SN2 reaction ?
(iii) Pentan-l-ol using a suitable alkyl halide ?
Answer:
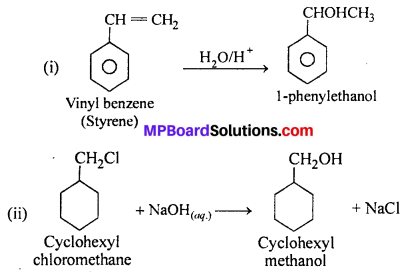
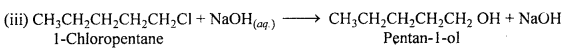
Question 14.
Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol. Compare acidity of phenol with that of ethanol.
Answer:
The reactions showing acidic character of phenols are :
(i) Reaction with sodium : Phenol reacts with Na to give H2 gas.
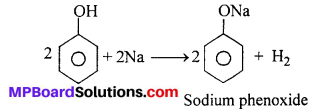
(ii) Reaction with NaOH : Phenol dissolves in NaOH to give sodium phenoxide and OH
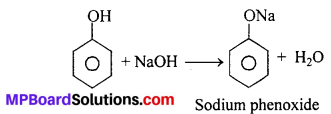
Phenol is more acidic than ethanol. This is due to the reason that phenoxide ion left after the loss of a proton from phenol is stabilized by resonance (for structure refer text acidic nature of phenol) while ethoxide ion (left after loss of a proton from ethanol) is not.
Question 15.
Explain, why ortho nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol ?
Answer:
Due to strong -R and -I effect of -NO2 group, electron density in O-H bond decreases and hence the loss of proton becomes easy.
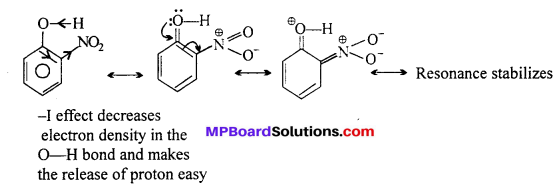
-R effect results in +ve charge on O-atom and hence facilitates the release of proton. Moreover, o-nitrophenoxide formed after the loss of a proton is stabilized by resonance.
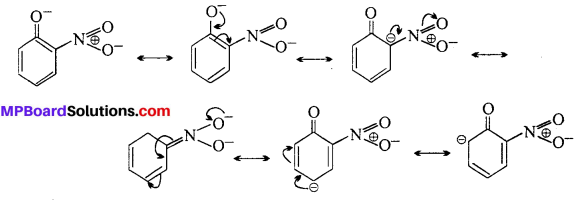
o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilized by resonance and hence o-nitrophenol is a stronger acid. On the other hand, due to +R effect of the —OCH3 group,the electron density in the O—H bond increases and this makes the loss of proton difficult.
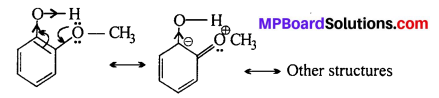
Further more after the loss of proton o-methoxy- phenoxide ion left is destabilized by resonance.
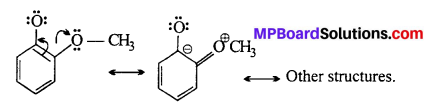
The two -ve charge repel each other and therefore destabilize the o-methoxyphenoxide ion. Thus, it is less acidic than o-nitrophenol.
Question 16.
Explain, how does the -OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activate it towards electrophilic substitution ?
Answer:
The -OH group exerts +R effect on the benzene ring under the effect of attacking electrophile. As a result, there is an increase in the electron density in the ring particularly at ortho and para positions, therefore electorphilic substitution occurs mainly at o-and p-positions. (For resonance hybrid structures of phenol refer to NCERT text-book.)
Question 17.
Give equations of the following reactions:
(i) Oxidation of propan-l-ol with alkaline KMnO4 solution.
(ii) Bromine in CS2 with phenol.
(iii) Dilute HNO3 with phenol.
(iv) Treating phenol with chloroform in presence of aqueous NaOH.
Answer:
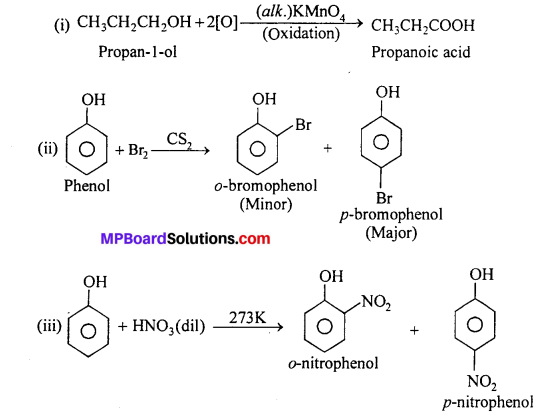
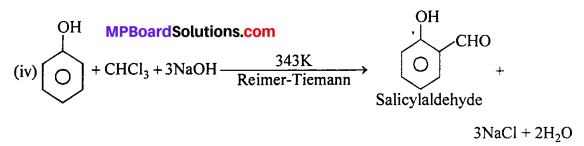
Question 18.
Explain the following with an example :
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(ii) Kolbe’s reaction
(iii) Williamson-ether synthesis
(iv) Unsymmetrical ether.
Answer:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction : When phenol is treated with chloroform in presence of aqueous sodium hydroxide at 60°C, o-Hydroxy benzaldehyde (Salicylaldehyde) and p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde are formed. The ortho-isomer is the major product. This reaction is called Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
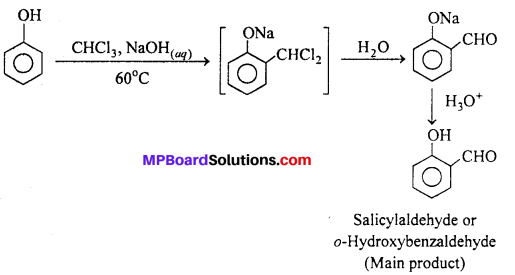
If carbon tetrachloride is used in place of chloroform, salicylic acid is obtained as the main product.
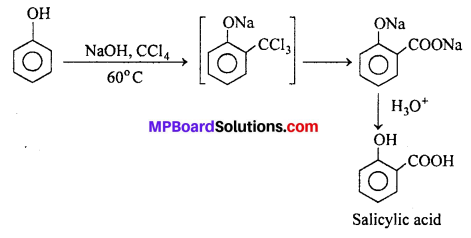
(ii) Kolbe- Schmidt reaction : When sodium salt of a phenol is heated with CO2 at 130°C. (403K) and 4-7 atm pressure, sodium salicylate is formed. This on acidification gives salicylic acid.
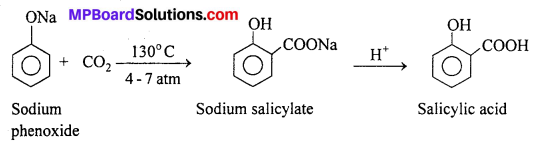
Salicylic acid is the starting material for the manufacture of aspirin which is an important analgesic.
(iii) Williamson-1 ether synthesis : This is the best method for preparation of ethers because both symmetrical and unsymmetrical (Aliphatic as well as aromatic) ethers can be prepared. When haloalkane is treated with sodium alkoxide then ether is formed. It is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction in which halide ion (X-–) of haloalkane is replaced by alkoxy or aroxy group.
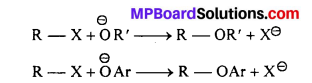
Example : Reaction of ethyl bromide with sodium ethoxide gives diethyl ether
C2H5Br + C2H5ONa → C2H5OC2H5 + NaBr
(iv) Unsymmetrical ether : An unsymmetrical ether is an ether where two groups on the two sides of an oxygen atom differ (i.e., have and unequal number of carbon atoms.
For example; ethyl methyl ether (CH3—O—CH2CH3)
Question 19.
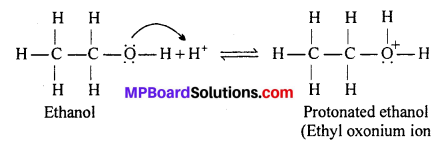
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Answer:
The mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yeild ethene involes the following three steps:
Step 1 : Protonation of ethanol to form ethyl oxonium ion :
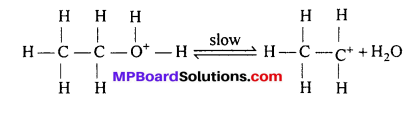
Step 2 : Formation of carbocation (rate determinning step):
Step 3 : Elimination of a proton to form ethene:
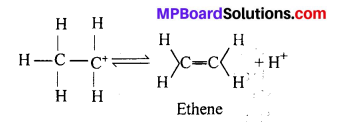
The acid consumed in step I is released in Step 3. After the formation of ethene, it is removed to shift the equilibrium in a forward direction.
![]()
Question 20.
How are the following conversions carried out:
(i) Propene → Propan-2-ol.
(ii) Benzyl chloride → Benzyl alcohol.
(iii) Ethyl magnesium chloride → Propan-1-ol.
(iv) Methyl magnesium bromide → 2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
Answer:
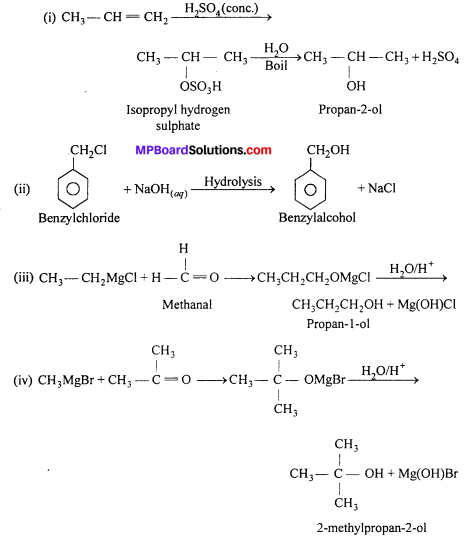
Question 21.
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
- Oxidation of a primary alcohol to carboxylic acid.
- Oxidation of a primary alcohol to aldehyde.
- Bromination of phenol to 2,4,6-tribromo-phenol.
- Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid.
- Dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene.
- Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol.
Answer:
- Acidified K2Cr2O7 or neutral acidic or alkaline KMnO4.
- Pyridinium chlorochromate (pec) in CH2Cl2 or Cu at 573 K.
- Bromine water (Br2/H2O)
- Acidified or alkaline KMnO4
- Cone. H2SO4 at 443K or 85% phosphoric acid at 443K.
- Ni/H2 or NaBH4 or LiAlH4.
Question 22.
Give reason for the higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to methoxymethane.
Answer:
The boiling point of ethanol is higher than methoxymethane because of the presence of strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding between ethanol molecule. As a result ethanol exist as associates molecules.
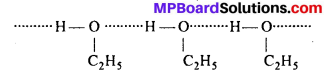
However no such H-bonding is present in methoxy methane.
Question 23.
Give IUPAC names of the following ethers:
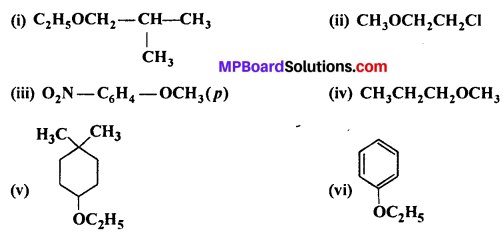
Answer:
(i) 1-Ethoxy-2-methylpropane
(ii) 2-Chloro-1-methoxyethane
(iii) 4-Nitro anisole
(iv) 1-Methoxypropane
(v) 1 -Ethoxy-4,4-dimethylcyclohexane
(vi) Ethoxybenzene.
Question 24.
Write the names of reagents and equations for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis:
(i) 1-Propoxypropane
(ii) Ethoxybenzene
(iii) 2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
(iv) 1-Methoxyethane
Answer:
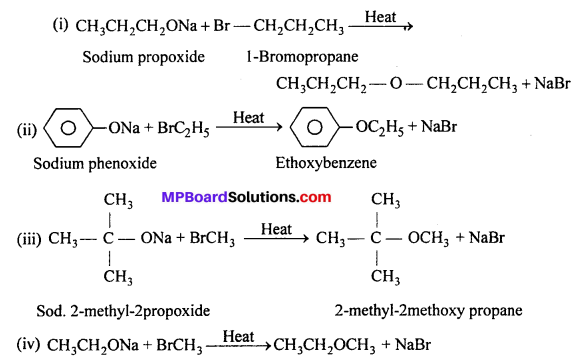
Question 25.
Illustrate with examples the limitations of Williamson synthesis for the preparation of certain types of ethers.
Answer:
Limitations of Williamson synthesis : (i) Better results are obtained, if the alkyl halide is primary. In case of secondary and tertiary alkyl halides, elimination completes over substitution. If a tertiary alkyl halide is used, an alkene is the only reaction product and no ether is formed. For example, the reaction of CH3ONa with (CH3)3C—Br gives exclusively 2-methylpropene.
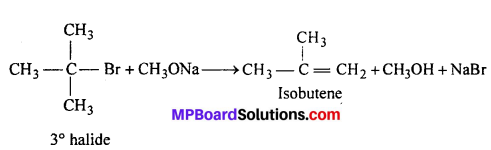
It is because alkoxides are not only nucleophile but strong bases as well. They react with alkyl halide leading to elimination reaction. Thus, in order to prepare methyl tertiary butyl ether, we must use methyl halide (primary) and sodium tertiary butoxide.
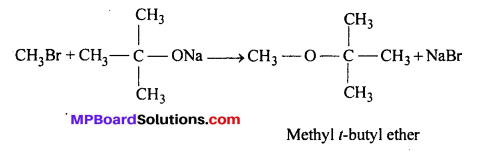
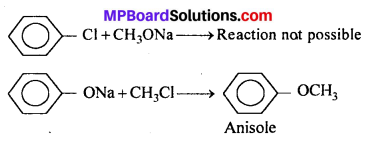
(ii) Aryl halides and vinyl halides cannot be used as substrate for the preparation of aromatic aliphatic ether because aryl halide and vinyl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Question 26.
How is 1-propoxypropane synthesized from propan-l-ol ? Write mechanism of this reaction.
Answer:
(a) It can be prepared by Williamson’s synthesis.
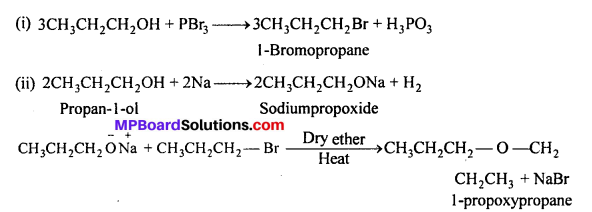
(b) It can also be prepared by dehydration of propan-l-ol
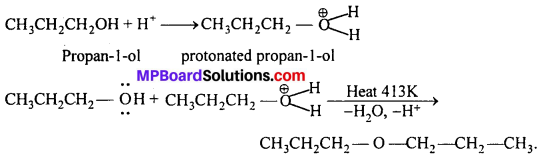
![]()
Question 27.
Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohol is not a suitable method. Give reason.
Answer:
The 1° alcohol gets protonated. Now it is attacked by another alcohol molecule. The mechanism is SN2 (Nucleophilic attack)
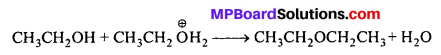
The 2° and 3° alcohols also get protonated. But another molecule of alcohol cannot attack it due to steric hindrance. The protonated alcohol loses a molecule of H2O to form a stable 2° or 3° carbo-cation. The carbocation prefers to lose a proton to form alkene.
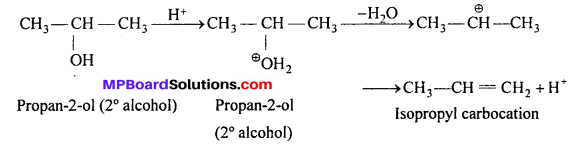
Similarly, the 3° alcohol (CH3)3COH forms isobutane.
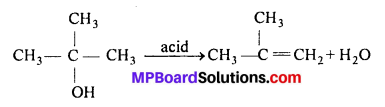
Question 28.
Write the equation of the reaction with hydrogen iodide :
(i) 1-Propoxypropane
(ii) Methoxybenzene and
(iii) Benzyiethylether.
Answer:
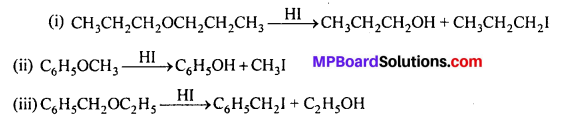
Question 29.
Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers :
(i) The aikoxy group activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution and
(ii) It directs the incoming substituents to ortho and para positions in benzene ring.
Answer:

In aryl alkyl ethers, due to the +R effect of the aikoxy group, the electron density in the benzene ring increases as shown in the following resonance structure.
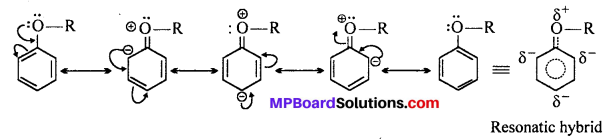
Thus, benzene is activated towards electrophilic substitution by the aikoxy group.
(ii) It can also be observed from the resonance structure that the electron density increases more at the ortho para positions than at the meta position. As a result, the incoming substituents are directed to the ortho and para positions in the benzene ring.
Question 30.
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Answer:
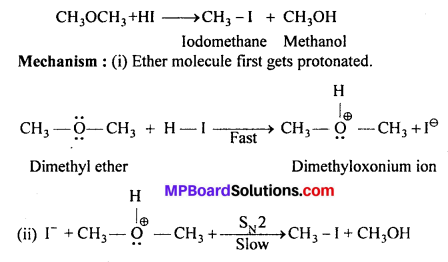
Protonated ether undergoes SN2 attack by 1- ion and gives a mixture of methyl iodide and methyl alcohol. However, if HI is taken in excess, the methyl’alcohol formed in (ii) is also converted into methyliodide by the following mechanism.
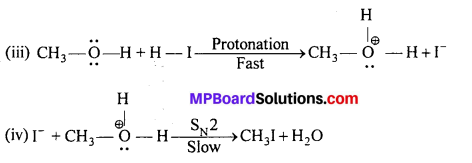
Question 31.
Write equations of the following reactions:
(i) Friedel-Craft’s reaction – alkylation of anisole.
(ii) Nitration of anisole.
(iii) Bromination of anisole in ethanoic acid medium.
(iv) Friedel-Craft’s acetylation of anisole.
Answer:
(i) Friedel-Crafts reaction – alkylation of anisole : Anisole undergoes Friedel- Crafts reaction i.e., the alkyl and aryl group is introduced at ortho and para-positions by reaction with alkyl halide and aryl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride (Lewis acid) as catalyst.
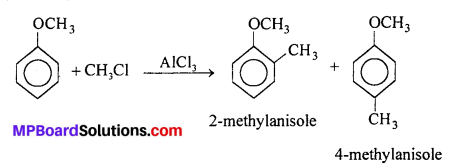
(ii) Nitration of anisole : Anisole reacts a mixture of concentrated sulphuric and nitric acids to yield a mixture of ortho and para nitroanisole.
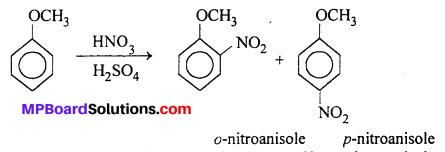
(iii) Bromination of anisole in ethanoic acid medium : Phenetole or anisole undergoes bromination with bromine in ethanoic acid even in absence of iron (III) bromide catalyst. It is due to the activation of benzene ring by the ethoxy group, para-isomer is obtained in 90% yield.
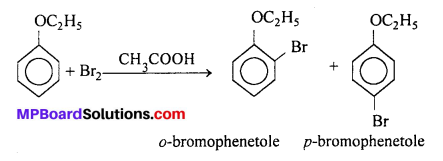
(iv) Friedel-Craft’s acetylation of anisole :
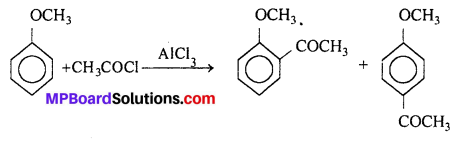
Question 32.
Show how would you synthesize the following alcohols from appropriate alkenes ?

Answer:
(i) Alcohols on dehydration give alkene. Dehydrate the given alcohol. The alkene formed will give the desired alcohol on adding a molecule of H2O. The addition of H2O molecule takes place according to MarkownikofFs rule. In case dehydration of the given alcohol gives two alkenes, then see which alkene will give the desired alcohol.
Both the alkene give the desired alcohol on adding a molecule of H2O.
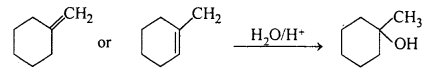
(ii) Two alkenes are formed. They will give the desired alcohol on adding a H2O molecule.
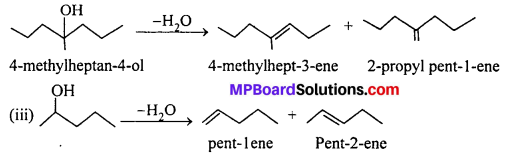
Addition of H2O molecule to pent-1-ene gives the desired alcohol. Remember that -OH group comes to that carbon atom of the double bond which contains less number of H-atoms. In case of pent-2-one, both the carbon atoms of double bond have one H-atom. Therefore, -OH group may come to either of the carbon atom. This alkene will give pentan-2-ol as well as pentan-3-ol.
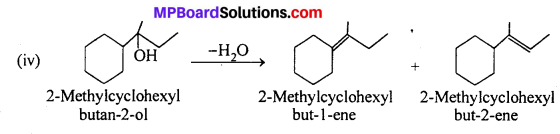
Addition of H2O molecule to 2-methylcy-clohexyl but-2-ene will give the desired alcohol -OH group comes to that carbon atom of double bond which contains less number of H- atom.
Question 33.
When 3-methylbutan-2-ol is treated with HBr, the following reaction takes place:
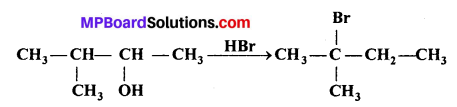
Give a mechanism for this reaction.
(Hint : The secondary carbocation formed in step-II rearranges to a more stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride ion shift from 3rd carbon atom.)
Answer:
Alcohol gets protonated and then a H2O molecule is given out to give a carbocation.
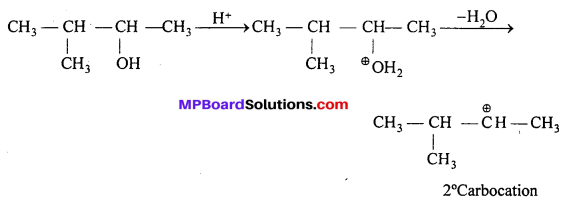
Now, the 2° carbocation rearrange to form more stable 3° carbocation, one H—atom migrates from the adjacent carbon atom to C+. It is called 1,2-shift. Then addition of Br– takes place.
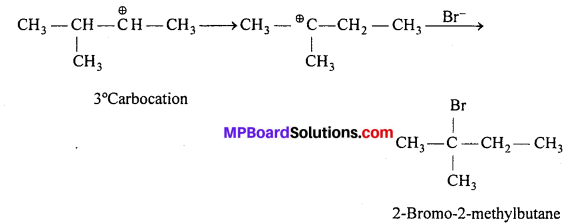
![]()
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Other Important Questions and Answers
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Sodium dissolves easily in alcohol because :
(a) Alcohol has higher density than water
(b) Alcohol is lighter than water
(c) Alcohol is neutral
(d) Alcohol is amphoteric.
Answer:
(d) Alcohol is amphoteric.
Question 2.
Most acidic among the four compound is :
(a) Phenol
(b) o-nitrophenol
(c) m – nitrophenol
(d) p – nitrophenol.
Answer:
(c) m – nitrophenol
Question 3.
Reaction for the formation of salicylaldehyde from phenol is :
(a) Rosenmund reaction
(b) Friedel Crafts reaction
(c) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(d) Wurtz’s reaction.
Answer:
(c) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Question 4.
Most effective reagent which converts propanol-2 to propanone :
(a) LiAlH4
(b) Cu/300°C
(c) CO2
(d) K2Cr2O7.
Answer:
(b) Cu/300°C
Question 5.
Carbolic acid is :
(a) Phenol
(b) Phenyl benzoate
(c) Phenyl acetate
(d) Methyl salicylate.
Answer:
(a) Phenol
Question 6.
Which compound is known as oil of winter green :
(a) Phenyl benzoate
(b) Phenyl salicylate
(c) Phenyl acetate
(d) Salol.
Answer:
(d) Salol.
Question 7.
Reaction of Lucas reagent is fastest with :
(a) (CH3)3 C-OH
(b) (CH3)2 CHOH
(c) CH3-(CH2)2 OH
(d) CH3CH2OH.
Answer:
(a) (CH3)3 C-OH
Question 8.
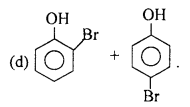
At low temperature phenol reacts with Br2 in CS2 to give
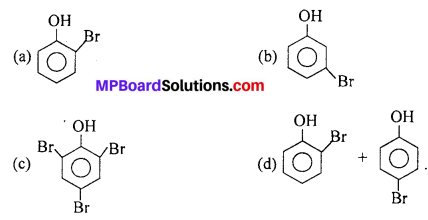
Answer:
Question 9.
Which compound is obtained on passing vapours of ethanol on hot Al2O3:
(a) Ethyl ether
(b) Acetone
(c) Acetaldehyde
(d) Ethane.
Answer:
(a) Ethyl ether
Question 10.
Which of the compound is Aspirin :
(a) Acetyl salicylic acid
(b) Salicylic acid
(c) Acetamide
(d) Salicyl amide.
Answer:
(a) Acetyl salicylic acid
Question 11.
The following compound reacts with phthalic acid to give acid-base indicator :
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Phenol
(c) Alcohol
(d) Ether.
Answer:
(b) Phenol
Question 12.
Bakelite is formed when phenol is condensed with :
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3CHO
(c) C6H5CHO
(d) CH3COCH3.
Answer:
(a) HCHO
Question 13.
Used as an anaesthetic :
(a) CH3OH
(b) C2H5OH
(c) CH3—CHO
(d) (C2H5)2 O.
Answer:
(d) (C2H5)2 O.
Question 14.
Lucas reagent is :
(a) Cone. HCl
(b) Cone. H2SO4
(c) Anhydrous ZnCl2
(d) Cone. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2.
Answer:
(d) Cone. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2.
Question 15.
Ether and alcohol can be distinguished by the following :
(a) Reaction with Na
(b) Reaction with PCl5
(c) Reaction with 2,4 dinitrophenyl hydrazine
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Reaction with Na
Question 16.
Which is used for poisoning the alcohol:
(a) Methyl alcohol
(b) Ethyl alcohol
(c) Glycerine
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(a) Methyl alcohol
Question 17.
Gives Libermann’s nitroso test:
(a) C6H5OH
(b) CH3-OH
(c) C2H5—OH
(d) CH3-O-CH3
Answer:
(a) C6H5OH
Question 18.
Which is identified by Lucas reagent:
(a) Phenol
(b) Ether
(c) Aldehyde
(d) Alcohol.
Answer:
(d) Alcohol.
Question 19.
Alcohols are soluble in water. Its main reason is :
(a) O—H bond
(b) Hydrogen bond
(c) Covalent bond
(d) Electrovalent bond.
Answer:
(b) Hydrogen bond
Question 20.
Which is formed on heating ethyl alcohol with bleaching powder :
(a) Diethyl ether
(b) Phenol
(c) Chlorobenzene
(d) Chloroform.
Answer:
(d) Chloroform.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
- General formula of ether is ……………….
- Main product of Kolbe-Schmidt reaction of phenol is ……………….
- By the hydrogenation of phenol ………………. is formed.
- Alcohol reacts with I2 and a base to give a yellow precipitate of ……………….
- Phenol on being heated with Zn powder forms ……………….
- On heating formaldehyde with ………………. bakelite is formed.
- Diethyl ether is used as an ……………….
- On heating RX with NaOR, ROR is formed. Name of this reaction is ……………….
- Alcohol is ………………. whereas phenol is of ………………. nature.
- On heating alcohol with cone. H2SO4 for 160 – 170°C ………………. is formed.
- By the dehydration of ethyl alcohol ………………. and ………………. are obtained.
- Rectified spirit is a mixture of ………………. % alcohol and ………………. water.
Answer:
- CnH2n+1OCnH2n+1
- Salicylic acid
- Cyclohexanol
- Iodoform (CHI3),
- Benzene
- Phenol
- Anaesthetic
- Williamson synthesis
- Neutral, acidic
- Alkene
- Ethylene, diethyl ether
- 95-5%, 4-5%.
Question 3.
Match the following :

Answer:
- (f)
- (d)
- (e)
- (g)
- (b)
- (a)
- (j)
- (c)
- (h)
- (i).
Question 4.
Answer in one word/sentence :
- Diethyl ether does not reacts with Na. Why ?
- Fire caused due to ether cannot be extinguished by water. Why ?
- Which is formed on burning ether ?
- Write name of the enzyme which converts maltose to glucose.
- Sulphuric ether is known as.
- Reaction of ether with HI is used for the detection of what ?
- Phenol reacts with Br2 in presence of CS2 to form.
- In Victor Meyer method, 1° alcohol gives which colour with base.
- Phenol reacts with phthalic anhydride in presence of H2SO4 to form.
- Which gas is obtained during fermentation ?
- Name the primary alcohol which gives iodoform test.
- Name the reaction in which phenol reacts with chloroform and sodium hydroxide to form salicylaldehyde.
Answer:
- Absence of acidic H-atom
- Lighter than water and insoluble
- CO2 and H2O
- Maltase
- Diethyl ether
- Alkoxy (Ziesel)
- o-and p-bromophenol,
- Red
- Phenolphthalein
- CO2
- C2H5—OH
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
![]()
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why ether is less soluble in saturated solution of NaCl ? Explained.
Answer:
Ether is a weak polar compound and saturated solution of NaCl decrease the polarity ofthe ether. Na+ and Cl– ions attract H2O molecules more strongly than ether molecules, thus the solubility of ether decreases in saturated solution of NaCl.
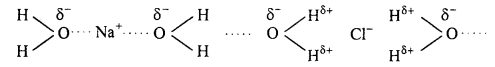
Question 2.
What is absolute alcohol ? How is it prepared ?
Answer:
100% ethanol is known as Absolute alcohol. Benzene is mixed in absolute spirit and fractionally distilled. Azeotropic mixture of 74% water, 18 5% alcohol and 74% ben¬zene is distilled on 64-8% alcohol. After the removal of water at 68-2°C binary mixture of alcohol (32-4%) and benzene (67-6%) is distilled. When entire benzene is removed then at 78-l°C impure alcohol is distilled. It contains 100% alcohol.
Question 3.
Give equations for the preparation of ethyl alcohol by starch and write name of enzymes.
Answer:
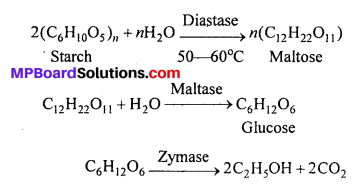
Enzymes : (1) Diastase, (2) Maltase, (3) Zymase.
Question 4.
What is Lucas reagent ? How are primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol identified by it ? Explain.
Answer:
Mixture of anhydrous ZnCl2 and cone. HCl is known as Lucas reagent.
- Tertiary Alcohol : On adding Lucas reagent in alcohol at normal temperature, immediately white oily precipitate of Alkyl chlorides is formed, then it is tertiary alcohol.
- Secondary Alcohol: If on adding Lucas reagent in alcohol, at normal temperature, a white oily precipitate of alkyl chloride is obtained after 5 minutes, then it is secondary alcohol.
- Primary Alcohol: Primary alcohol does not show any reaction with Lucas reagent at normal temperature.
Question 5.
Why the b.p. of alcohol are higher than ethers and alkene ?
Or,
C2H5OH and CH3OCH3 both have same molecular formula (C2H6O) but the b.p. of alcohol is 78.4°C and b.p. of ether is -240°C. Explain the reason.
Answer:
In case of C2H5OH there is strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the molecules of alcohol. So alcohols (C2H5OH) required much energy to evaporate than ether molecules. In other words, we can say that the C2H5OH molecules are in associated form due to H-bonding so the b.p. of C2H5OH is very higher than ether and alkene.
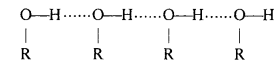
Question 6.
What do you understand by Methylated spirit or denaturing alcohol ?
Answer:
Methylated Spirit : Ordinary rectified spirit is known as industrial alcohol.
Methylated spirit is 90% ethanol to which nauseating materials like methyl alcohol, pyridine or mineral naphtha have been added. These materials are added so that the ethanol will not be used for beverage purposes. This process is called denaturing. It is of two types :
It is used for the preparation of spirit, varnish etc. By it misuse of ethanol as a beverage is controlled.
Question 7.
Explain the manufacture of CH3OH by water gas.
Answer:
From water gas : Steam is passed over red hot coke when water gas is formed.
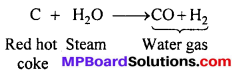
Water gas is mixed with half its volume of hydrogen, compressed to about 200 atm and passed over a catalyst which is a mixture of oxides of copper, zinc and chromium at 300°C.
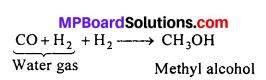
Question 8.
Give chemical equation of the following conversion :
(i) Diethyl ether from ethanol
(ii) Ethanol from diethyl ether
(iii) Ethyl acetate from ethanol
(iv) Ethanol from glucose.
Answer:
(i) Diethyl ether from Ethanol:
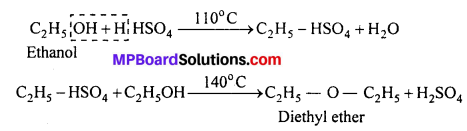
(ii) Ethanol from Diethyl ether :
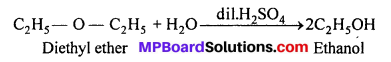
(iii) Ethyl acetate from Ethanol :

(iv) Ethanol from Glucose :

Question 9.
Differentiate between Phenol and Alcohol and write Libermann’s reaction related to phenol.
Answer:
Differences between Phenol and Alcohol:
Phenol:
- Physical properties : Characteristic phenolic odour, sparingly soluble in water.
- It is acidic and dissolve in bases to form salt.
- On oxidation, hybrid coloured product is formed.
- Produce characteristic colour with Ferric chloride.
- It does not react with halogen acid.
- With PCl5, mainly form triaryl phosphate.
Alcohol:
- Pleasant odour, fairly soluble in water.
- It is neutral and do not reacts with bases.
- It can easily oxidize to Aldehydes and ketones.
- It does not reacts with ferric chloride.
- Forms Alkyl halide.
- Alkyl chloride are formed.
Libermann’s Reaction : On adding few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid and little sodium nitrite in phenol first dark blue colour is produced on adding water colour becomes red and on adding an alkali red colour again changes to blue colour.
Question 10.
Pure phenol is a colourless solid but why it is converted into pink after some time ?
Or,
What change in colour is observed in phenol in presence of oxygen ? Explain with reaction.
Answer:
In the presence of air pure phenol oxidises into quinone.
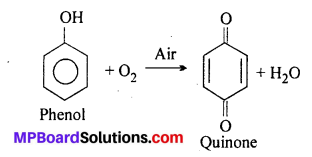
This quinone again combines with two molecules of phenol by H-bond and gives pink phenoquinone.
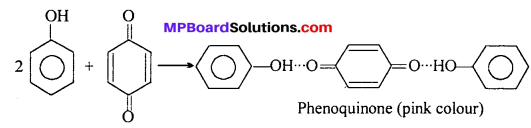
Question 11.
Write reaction of phenol with ferric chloride.
Answer:
Phenol reacts with FeCl3 to form water soluble coloured complex. The colour varies from violet to red including green and blue.
6C6H5OH + FeCl3 → (C6H5O)6 Fe + 3HCl + 3H+
Question 12.
Boiling point of higher than corresponding alkane. Why ?
Answer:
Boiling point of alcohols is much higher than hydrocarbons of nearly similar molecular mass due to inter molecular hydrogen bond. Alcohols molecules associate kilo calories mole-1. Thus, extra energy is required for the separation of these molecules, which lead to increase in boiling point. Hydrocarbons do not form hydrogen bond, thus their boiling point is comparatively less.
Question 13.
Ethyl alcohol and phenol both contain — OH group. What is the reason that phenol is acidic and alcohol has alkaline effect ?
Or,
Ethyl alcohol and phenol both contain — OH group. What is the reason that phenol is acidic and alcohol is neutral in nature ?
Answer:
Explanation of acidic nature of phenol: One possible explanation why phenols are stronger acids as compared to alcohols is that phenols exist as a resonance hybrid.
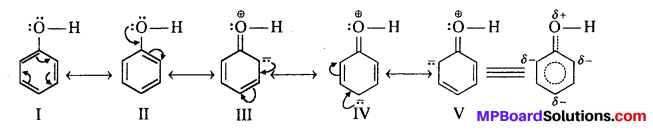
Due to resonance, the oxygen atom gets a positive charge and attracts the electron pair of the O—H bond and thus facilitates the release of a proton. The phenoxide ion formed after the release of a proton is also stabilized by resonance.
![]()
In alcohols, no resonance is possible hence the hydrogen atom is more firmly linked to the oxygen.
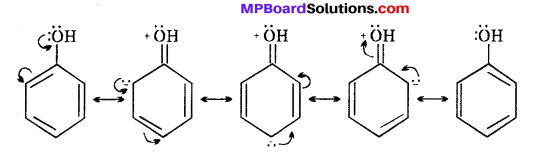
![]()
Question 14.
Write Victor Meyer method to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Answer:
Victor Meyer’s method : (i) The given alcohol is converted into an iodide by concentrated HI or red phosphorus and iodine.
(ii) The iodide is treated with silver nitrite to form nitroalkane.
(iii) Nitroalkane is finally treated with nitrous acid (NaNO2 + H2SO4) and made alkaline with KOH.
If a blood red colour is obtained, the original alcohol is primary.
If a blue colour is obtained, the alcohol is secondary.
If no colour is produced, the alcohol is tertiary.
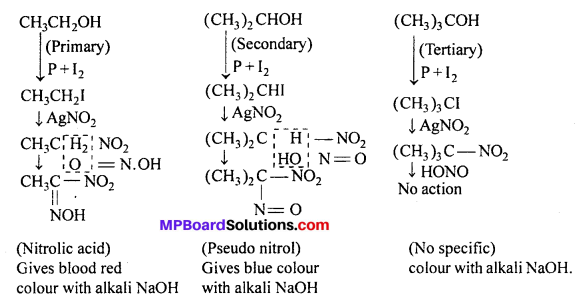
Question 15.
What is Williamson continuous etherification process ? Is it a continuous process ? Explain. Give labelled diagram.
Or,
Describe the laboratory method of preparation of diethyl ether. How ether thus obtained is purified ?
Answer:
Laboratory Method for the Preparation of Diethyl Ether (Sulphuric Ether):
Diethyl ether is prepared in the laboratory and industry by the Williamson continuous etherification process, i.e., by heating ethanol (in excess) with concentrated sulphuric acid.

Sulphuric acid is regenerated in the reaction hence, it appears as if only a small amount of acid may convert an excess of alcohol into ether. So, this method is called Williamson continuous etherification process but actually we cannot get ether continuously.
This is due to the following two reasons :
- Water formed in the reaction dilutes the acid and its reactivity decreases.
- A part of sulphuric acid is reduced by alcohol into sulphur dioxide.
Method : Ethanol and H2SO4 (2:1) are taken in a flask and heated on sand bath at ‘ 140°C. Ethanol is added at the same rate at which ether distilled over and is collected in a receiver cooled in ice-cold water.
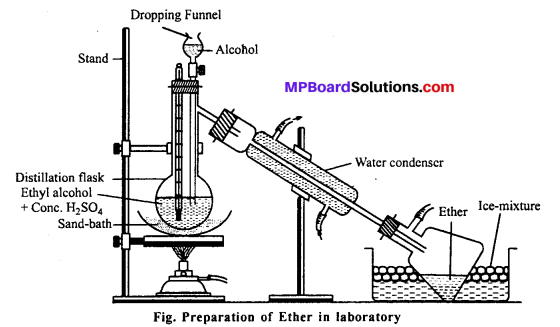
Purification: Ether contain ethanol, water and sulphuric acid as impurities. It is washed with NaOH to remove sulphuric acid and then agitated with 50% solution of calcium chloride to remove alcohol. It is then washed with water, dried over anhydrous calcium chloride and redistilled.
Question 16.
Write a notes on fermentation.
Answer:
Fermentation : In this method, molasses or starch are used as raw materials. This is the old method and is used at present also. Fermentation (Latin-fermentare means to boil) proceeds with fast evolution of CO2 producing much foam giving appearance as if the solution is boiling. “It is a process of decomposition of complex large molecules into simple and small molecules slowly and by enzyme.” Enzymes are of many kinds and are present in yeast which is a living and complex substance containing several types of bacteria which are called enzymes. It is a good ferment. The enzymes present in yeast are zymase, mal- tase, invertase, etc.
When yeast is mixed in glucose solution and kept at proper conditions, ethyl alcohol is formed as a result of fermentation.
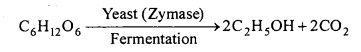
Favourable conditions for Fermentation:
- Favourable temperature: It is between 25-35°C.
- Other substances : Some inorganic salts like ammonium sulphate or ammonium nitrate function as food for fermentation.
- Concentration : Solution should be dilute (Concentration 8-10%).
- Air : The process occur in presence of air.
Question 17.
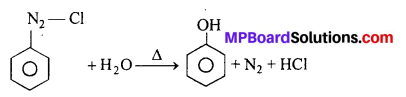
(i) How can we obtain phenol from benzene diazonium chloride ?
(ii) What is the reaction of diethyl ether with HI acid ?
Answer:
(i) Phenols are prepared by hydrolysis of diazonium salts by water, dil. acids etc.
(ii) The reaction of diethyl ether with cone. HI acid, on heating gives one molecule of ethyl iodide and one molecule of ethyl alcohol.
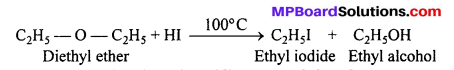
Question 18.
Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol.
Answer:
(a) The reactions showing acidic character of phenol are:
(i) Reaction with sodium : Phenol reacts with sodium to give H2 gas.
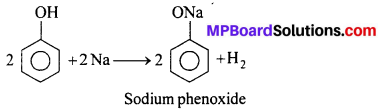
(ii) Reaction with NaOH: Phenol dissolve in NaOH to give sodium phenoxide.
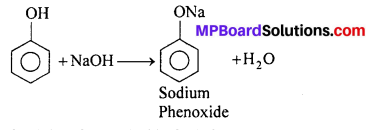
(b) Comparison of Acidity of Phenol with alcohol.
C2H5OH + NaOH → No reaction
But phenol reacts with NaOH and exhibits its strong acidic nature.
Ionization of Ethanol and Phenol is as follows :
On the other hand ethoxide ion and ethanol do not represent resonance thus negative charge is on oxygen of ethoxide ion whereas charge displacement occur in phenoxide ion.
pKa value of ethanol is 15.9 where of phenol is 10.0. Thus, phenol is many more times’ more acidic than ethanol.
![]()
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the mechanism of dehydration of alcohol.
Answer:
Dehydration of alcohol:
(i) When ethyl alcohol is heated in excess of cone. H2SO4 molecule of water is eliminated and alkene is formed.
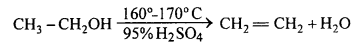
Mechanism : (i) Protonation of alcohol by H2SO4
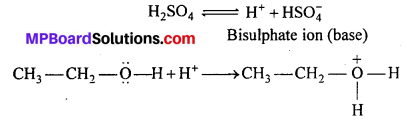
(ii) Removal of water
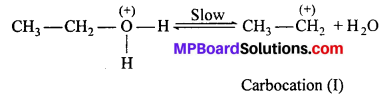
(iii) Elimination of β-hydrogen in the form of proton by base (bisulphate ion)
![]()
Stability of the carbocation (I) determines the case of dehydration and order of stability of carbocation is :
CH3 < C2H5 < Isopropyl < Tertiary butyl
Question 2.
How is ethyl alcohol obtained by molasses ? Explain in brief.
Or,
What are molasses ? How is alcohol obtained by fermentation ? Explain. Tell favourable conditions of fermentation. Draw labelled diagram of coffee still.
Answer:
From molasses : Molasses is the syrupy solution of sugar left after the separa¬tion of cane sugar or beet sugar crystals from the concentrated juice.
The different steps of the manufacture processes are :
(a) Dilution : The molasses is diluted with water so that a concentration of 8-10 percent sugar is obtained in solution. This is acidified with dilute sulphuric acid to retard other bacterial growth. A solution of ammonium salts is also added which acts as food for the ferment.
(b) Alcoholic fermentation : The dilute solution obtained above [From step (a)] is taken in big fermentation tanks and some yeast is added. The mixture is kept for a few days and the temperature is maintained at about 30°C. The fermentation reaction starts and the enzyme Invertase (From Yeast) converts sucrose into glucose and fructose which are then converted into ethanol by Zymase (From Yeast).
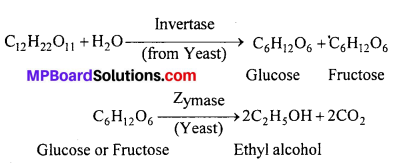
The fermentation is completed in about 3 days. The carbon dioxide is collected as a by product.
(c) Distillation : The fermented liquor is technically called wash or wort which contains about 9-10 percent ethanol. It is then distilled in a continuous still called Coffey’s still. It consists of two tall fractionating columns which are called analyser and the rectifier. It works on the counter current principle and the steam and wash travel in opposite directions through the still.
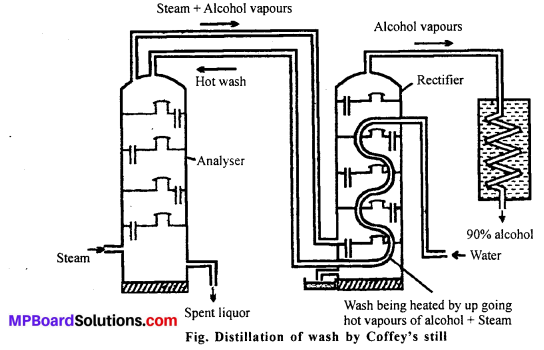
The steam goes upwards in the analyser and takes away the alcohol vapours from the down coming dilute alcohol. The mixture leaves the analyser from the top and enters the rectifier at the base. Here it heats the wash flowing through the pipes on its way to the analyser. Most of the steam condenses and the alcohol vapours condenses in the condenser. The distillate contain 90% alcohol.
(d) Rectification : Wash is rectified by fractional distillation.
Question 3.
How can you change the following : (i) Methanol to ethanol, (ii) Ethanol to methanol.
Answer:
(i) Methanol to ethanol:
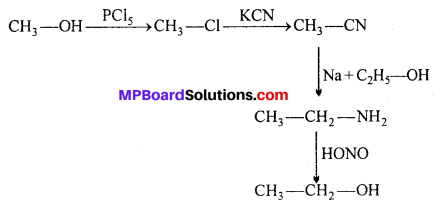
(ii) Ethanol to methanol:
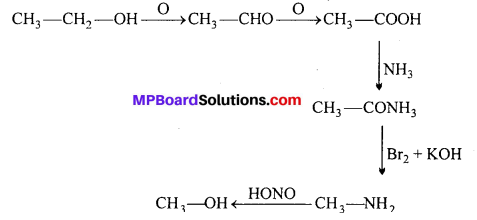
Question 4.
Differentiate primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol by oxidation and dehydrogenations method.
Answer:
1. Oxidation : The oxidizing agents generally used for oxidation of alcohols are acid dichromate, acid or alkaline KMnO4 and dilute HNO3.
(i) A primary alcohol is easily oxidized to an aldehyde and then to an acid both containing the same number of carbon atoms as the original alcohol.
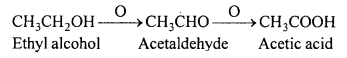
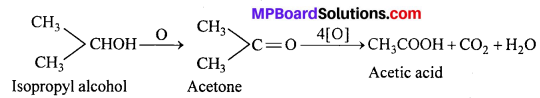
(ii) A secondary alcohol on oxidation gives a ketone with the same number of carbon atoms as the original alcohol, ketones are oxidized with difficulty but prolonged action of oxidizing agents produce carboxylic acids containing fewer number of carbon atoms than the original alcohol.
(iii) A tertiary alcohol is resistant to oxidation in neutral or alkaline solutions but is readily oxidized by an acid oxidizing agent giving a mixture of ketone and acid each having lesser number of carbon atoms than the original alcohol.
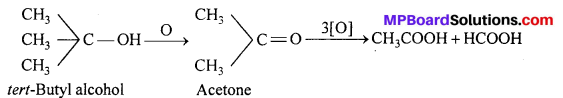
2. Dehydrogenation (Action of hot reduced copper at 300°C): Different types of alcohols give different products when their vapours are passed over Cu gauze at 300°C.
Primary alcohols lose hydrogen and yield an aldehyde.
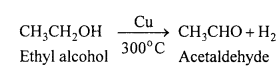
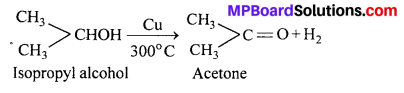
Secondary alcohols lose hydrogen and yield a ketone.
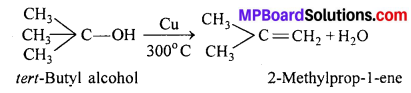
Tertiary alcohols are not dehydrogenated but lose a water molecule to give alkenes.
Question 5.
How can you obtained following compounds from phenol :
(i) 2, 4, 6-Tribromophenol
(ii) Picric acid
(iii) Aniline
(iv) Benzene
(v) Phenolp- hthalene
(vi) p-cresol, o-cresol.
Answer:
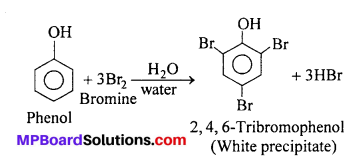
(i) Phenol to Tribromophenol : Phenols readily react with halogens to give polyhalogen substituted compounds. Phenol gives white precipitate of 2, 4, 6-tribromo- phenol with bromine water.
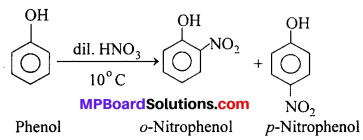
(ii) Phenol to Picric acid : Nitration : On nitration, phenols give a variety of products depending upon the conditions.
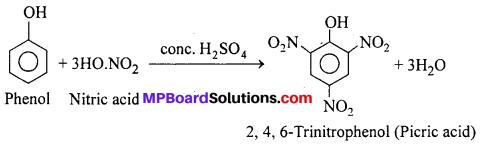
Nitration of phenol with conc. HNO3 in presence of conc. H2SO4 gives, 2,4,6-Trinitro-phenol (Picric acid).
(iii) Phenol to Aniline:

(iv) Phenol to Benzene:
![]()
(v) Phenol to Phenolphthalene : Phenol condenses with phthalic anhydride in pres¬ence of cone. H2SO4 to give phenolphthalein which is an indicator for acid-base titrations and is used as a laxative in medicine.
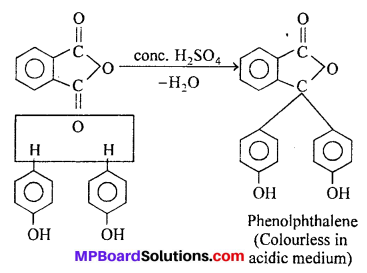
(vi) Phenol to ortho and para cresol:
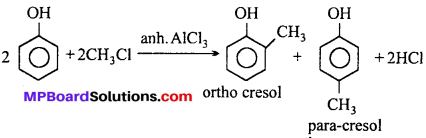
Question 6.
Give chemical equation of the following conversion:
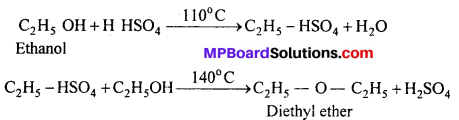
(i) Diethyl ether from ethanol
(ii) Ethanol from diethyl ether
(iii) Ethyl acetate from ethanol
(iv) Ethanol from glucose.
Answer:
(i) Diethyl ether from Ethanol:
(ii) Ethanol from Diethyl ether:
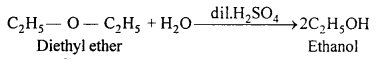
(iii) Ethyl acetate from Ethanol:
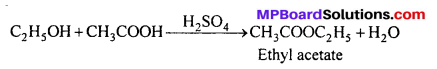
(iv) Ethanol from Glucose :

Question 7.
Describe the manufacture method of methanol by the destructive distillation of wood.
Answer:
Manufacture of methanol: By the destructive distillation of wood: Dried wood is heated (350°C) in closed retorts for about 3 hours. Different products obtained are given ahead:
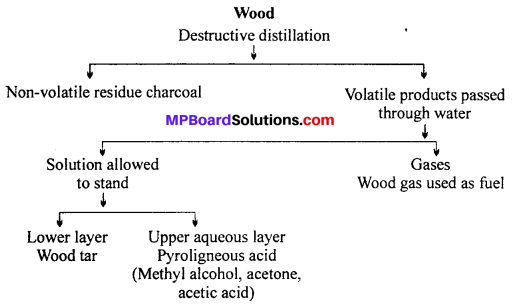
Recovery of methyl alcohol from pyroligneous acid : Pyroligneous acid contains methyl alcohol (2-4%), acetone (0-5 to 1%), acetic acid (about 10%) and water.
The pyroligneous acid is taken in a copper vessel and distilled. The vapours are passed through hot milk of lime which retains acetic acid as non-volatile calcium acetate. Methyl alcohol and acetone vapours pass over and are condensed. This mixture is subjected to fractional distillation to separate methyl alcohol (b.p. 65°C) and acetone (b.p. 56°C). Methyl alcohol obtained by fractional distillation is about 95% pure. To purify further methyl alcohol is treated with anhydrous calcium chloride when it forms solid derivative CaCl2.4CH3OH. This solid derivative is separated and methyl alcohol is recovered by distillation.
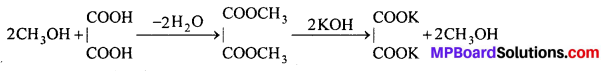
Question 8.
Give equations for three methods of preparation of phenol.
Answer:
Methods of preparation of phenol:
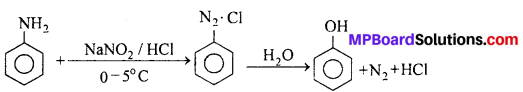
(i) By the hydrolysis of Benzene diazonium salts: Benzene diazonium salt is formed by aromatic primary amine (aniline) with nitrous acid at 0-5°C. On boiling aqueous solution of this salt phenol is formed.
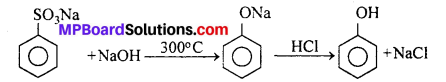
(ii) By alkaline fusion of sodium benzene sulphonate : On fusing sodium benzene sulphonate with NaOH, sodium phenoxide is formed which on acidification forms phenol.
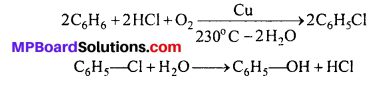
(iii) Rasching method : On heating benzene with mixture of HCl and air to 230°C in the presence of Cu catalyst chlorobenzene is formed which on hydrolysis form phenol.