MP Board Class 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chemistry in Everyday Life Important Questions
Chemistry in Everyday Life Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why should not medicines be taken without consulting doctors? (NCERT)
Answer:
The drugs or medicines have side effects also. These side effects arise because the drug may bind to more than one type of receptor. Further their wrong choice and over – dose can cause havoc and even may cause death. Therefore, it is must that the medicines should not be given without consulting doctors.
Question 2.
Explain the term, target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal chemistry. (NCERT)
Answer:
Drugs taken by a patient interact with macromolecules such as proteins, carbo-hydrates, lipids and nucleic acids and these are called drug targets. These macromolecules or drug targets are known to perform several role in the body. The drugs are designed to interact with specific targets so that these have least chances of effecting the other targets. This minimises the side effects and localises the action of the drug.
Question 3.
While antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with the function of histamines, why do these not interfere with the function of each other? (NCERT)
Answer:
They do not interfere with the functioning of each other because they work on different receptors in the body. Secretion of histamine causes allergy and acidity while ant-acid removes only acidity.
![]()
Question 4.
Low level of noradrenaline is the cause of depression. What type of drugs are needed to cure this problem? Name two drugs. (NCERT)
Answer:
Noradrenaline induces a feeling of well being and helps in changing the mood. If the level of noradrenaline is low, then the signal sending activity of the hormone becomes low and the person suffers from depression. In such cases, the patient needs anti – depressant drugs which inhibit the enzymes which catalyses the degradation of noradrenaline. The common drugs used as anti – depressant are iproniazid and phenelzine.
Question 5.
Sleeping pills are recommended by doctors to the patients suffering from sleeplessness but it is not advisable to take its doses without consultation with the doctor. Why? (NCERT)
Answer:
Sleeping pills contain drugs that may be tranquilizers or anti – depressant. They affect the nervous system, relieve anxiety, stress, irritability or excitement. But they should strictly be used under the supervision of a doctor. If not, the uncontrolled and overdose can cause harm to the body and mind because in higher doses, these drugs act as poisons.
Question 6.
With reference to which classification has the statement, “ranitidine is an antacid” been, given? (NCERT)
Answer:
This statement refers to the classification of drugs according to pharmacological effects of the drugs because any drug which is used to neutralise the excess acid present in the stomach will be called an antacid and ranitidine prevents the interaction of histamine with the receptors present in the stomach wall. Histamine stimulates the secretion of pepsin and HCl in the stomach.
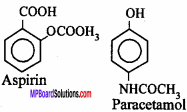
Question 7.
What are germicides?
Answer:
Germicides are substances which possess the power Aspirin to destroy germs. Sulphur compounds, mercury compounds (mercuric iodide) and phenolic compounds are used as germicides. Sulphur compounds in soap protect the skin from pimples, dandruff and skin infection. Phenolic compounds are mostly used as germicides. Cresyclic acid which is a mixture of m – cresol and p – cresol is mixed in soap as a germicide.
Question 8.
How are synthetic detergents better than soaps? (NCERT)
Answer:
- Soaps cannot be used in hard water but detergents can be used.
- Soaps cannot be used in acidic water but detergents can be used.
Question 9.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples: (NCERT)
- Cationic detergents
- Anionic detergents and
- Non – ionic detergents.
Answer:
1. Cationic detergents are those which have cationic hydrophilic group. These are mostly acetates, chlorides or bromides of quaternary ammonium salts. For example, cetyltrimethyl ammonium chloride.
[CH3(CH2)15N(CH3)3]++Cl–
2. Anionic detergents are those which have anionic hydrophilic group. These are of two types:
- Sodium alkyl sulphate example sodium lauiyl sulphate CH3(CH2)10CH3OSO3– Na+
- Sodium alkyl benzene sulphonate example sodium 4 – (1 – dodecyl) benzene sulphonate (SDS)

3. Non – ionic or neutral detergents are esters of high molecular mass alcohols as in fatty acids. For example, polyethylene glycol stearate
CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH
Polyethylene glycol stearate.
Question 10.
What are bio – degradable and non – biodegradable detergents? Give one example of each. (NCERT)
Answer:
1. Bio – degradable detergents are degraded by bacteria. In them, hydrocarbon chain is unbranched. They do not cause water pollution and are bitter.
Example : Sodium lauryl sulphate.
2. Non – biodegradable detergents possess highly branched hydrocarbon chain so bacteria cannot degrade them easily. They cause water pollution.
Example : Sodium 4 – (1, 3, 5, 7 – tetramethyl – actyl) benzene sulphonate.
![]()
Question 11.
Why do soaps not work in hard water? (NCERT)
Answer:
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium salts. Therefore, in hard water, soaps get precipitated as insoluble calcium and magnesium soaps which being insoluble stick to the cloth as gummy mass and blocks the ability of soap to move oil or grease from the cloth.
Question 12.
Explain each with an example.
- Antibiotics
- Analgesic (Pain Killer).
Answer:
1. Antibiotics:
Chemical substance which are produced by micro – organism and used to destroy micro – organism are called antibiotics.
These are of two types :
- Broad spectrum Antibiotic : Example : Tetracycline, chloramphenicol, Penicillin
- Narrow Spectrum Antibiotic : Example : Niastatin, Penicillin antibiotic medicines are used for the treatment of typhoid, whooping cough, Pneumonia.
2. Analgesic:
Drugs which give relief from pain or reduced pain are called analgesics.
Types and Examples :
- Narcotics : Morphine, Codeine.
- Non – Narcotics : Aspirin, Analgin, Paracetamol.
Question 13.
What is preservative? Give the name and formula of any two preservatives.
Answer:
A preservative is defined as “A substance added to food, capable of retarding the growth of micro – organism which deteriorate the food within no time.
The preservative may be natural compounds such as sugars, salt, acids, etc. as well as they may be synthetic i.e. Sodium benzoate.
Example:
- Vinegar or acetic acid : CH3 – COOH
- Sodium benzoate : C6H5COONa.
Question 14.
What are the main differences between soap and detergents?
Answer:
Differences between Soap and Detergents :
Soap:
- Soaps are sodium salts of higher fatty acids.
- These cannot be used with hard water.
- Their aqueous solution is alkaline in nature.
- These contain oil and are not good cleansing agent.
- These cannot be used for soft and delicate cloth.
Detergents:
- Detergents are sodium salt of alkyl benzene sulphonate.
- These can be used with hard water.
- Their aqueous solution is neutral in nature.
- These do not contain oil and are better cleansing agent.
- These can be used for soft and delicate cloth.
Question 15.
What do you understand by antipyretics?
Answer:
These are used to lower down the body temperature in high fever. These drugs are used both as antipyretic and as analgesic, example aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), paracetamol (4 – acetamido phenol), phenacetin (4 – ethoxy acetanilide), analgin, etc.

Question 16.
What are Antibiotics? Write name of any two antibiotics. (MP 2018)
Answer:
Antibiotics:
are chemical substances which are produced by micro – organisms like bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes and destroy some other micro – organisms are like, virus, ricketsia or obstruct their growth.
Example : Penicillin, Streptomycin etc.
Question 17.
What is Immune system? How does it develop?
Answer:
For the destruction of bacteria or antigen in our body, lymphocytes are developed which are known as Immune. These are a specific type of white blood cells. These prepare and release a special type of protein called globulin to destroy the poison. These proteins destroy the attacking virus, bacteria and poisonous substances. Lymphocyte bind the antigen and themselves divide fast by which immunization increase and effect of antigen is destroyed.
Question 18.
What are antiseptics?
Answer:
Antiseptics:
An antiseptic kills the bacteria or prevents the multiplication of bacteria. These also prevent pus formation. Antiseptics do not harm living tissues. Tincture iodine, phenol (0 – 2%), dettol, chloroxylenol, etc. are applied on skin and bactrim, septran, etc. are taken orally as pills. Bad odour coming out of the wounds due to bacterial decomposition on the body or in the mouth are also reduced by the use of antiseptics. For such purposes, antiseptics are usually incorporated in face powder, breath purifiers, deodorants, etc. to reduce the intensity of bad odour.
Neem soaps containing the extract of neem seeds are also used as antiseptic soaps. Dettol is a mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol in a suitable solvent is commonly used antiseptic. Bithionol antiseptic is added to soap to provide antiseptic properties to it. Tincture iodine is 2 – 3% solution of iodine in alcohol and water.
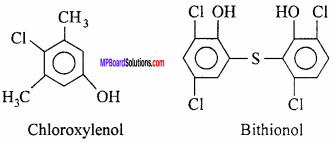
Question 19.
What do you mean by Antibiotics? Name the first antibiotic.
Answer:
Chemical substances which are produced by mirco – organism and are used to destroy other micro-organism, are called antibiotics. These chemicals checks the life cycle of bacteria and stop reproduction resulting in release from disease. Antibiotics are almost specific for kinds of illness.
The first antibiotic penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. He was awarded Nobel prize in 1945 for this important discovery. General formula of penicillin is C9H11N2O4S – R. It is a narrow spectrum drug and used in bronchitis, pneumonia, sore throat and abcesses. Before administration, tolerance has to be tested.
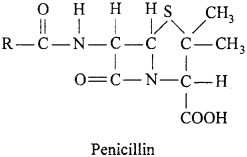
By changing the group R, different penicillin are prepared.
![]()
Question 20.
What are artificial sweetening agents? Give two examples. (MP2018)
Answer:
Artificial sweetening agents are the substances produced wholly or partially by chemical synthesis, which are added to food to impart sweet taste.
Example:
- Sucrose
- Saccharin.
Question 21.
Give definition of antihistamine drug with name and uses.
Answer:
These are amines which controls the allergy effect produced by histamines. Histamine is found in all body tissue and is also released in allergic conditions due to which allergic responses such as tissue inflammation, asthma, itching etc. are introduced in the body. Drugs which prevent the production of histamine and fight against the allergy effects are called antihistamines.
Example:
1. Entergon : It is used in strong allergic conditions.
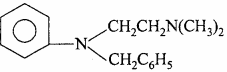
2. Benadryl:
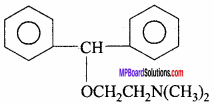
Chemistry in Everyday Life Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write short notes on:
- Antifertility drugs (MP 2108),
- Detergents
- Antacids (MP 2018)
- Sedatives
- Sulpha drugs.
Answer:
1. Antifertility drugs:
Drugs which are used to check pregnancy in women are called antifertility drugs. Actually, these drugs control the female menstrual cycle and ovu-lation. The antifertility agent in these drugs are steroids and these drugs are used in the form of oral pills. A mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone derivative are used as birth control pill. These are more effective than the natural hormone. Ethynylestradiol and nore- thindrone are the content of common contraceptive pills.
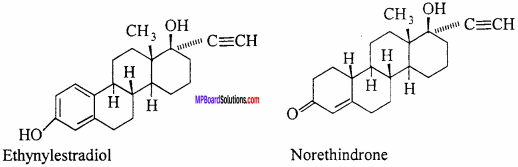
2. Detergents:
Unsaturated hydrocarbon of ethylene type containing 10 to 18 carbon atoms on treatment with sulphuric acid forms organic acid. Sodium salt of organic acid have moisture absorbing and purification property. This compound is called synthetic detergent. Example : Sodium n – dodecyl benzene sulphonate, Sodium n – dodecyl sulphate.
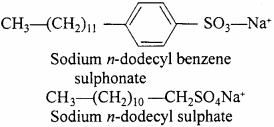
Synthetic detergents have two parts :
- A long chain of hydrocarbon which is hydrophobic (Water repellent).
- Small ionic chain is hydrophilic (Water attracting). Ionic chain is generally of sul- phonate (SO3Na) or sodium sulphate (SO4Na).
Detergents are surface active compounds which decreases surface tension of water. When these compounds are dissolved in water they scatter dirt particles leaving the surface clean.
Properties of detergents : Detergents are superior to soap.
- Detergents can be used in hard as well as soft water because they do not form insoluble salt with calcium and magnesium ions of hard water while soap cannot be used in hard water.
- Aqueous solution of detergent is neutral. Therefore, detergents can clean soft fibres without damaging them. Soap solution is alkaline due to hydrolysis and is harmful for washing soft fibres.
Uses of detergents:
Detergensts act as cleansing agent. Like soap it can be used for cleaning cotton, woollen, silky and synthetic fibre cloth and for cleaning other domestic items.
3. Antacids:
Substance which remove the excess acid in the stomach and raise the pH to appropriate level are called antacid Calcium carbonate, Sodium bicarbonate, Magnesium hydroxide or Aluminium hydroxide is used in the form of aqueous suspension or tablets to treats hyperacidity. These substances react with excess hydrochloride acid and neutralizes it partially. Nowadays Omeparazole and Lansoparazole are prescribed as antacids.
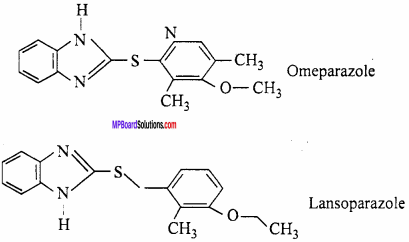
4. Sedatives:
These are given to those patients who are violent and mentally agitated.
Example:
- Equanil
- Barbituric acid.
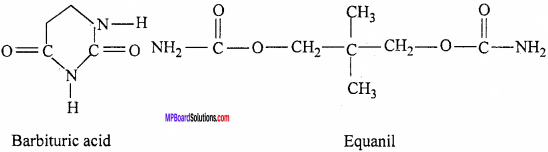
5. Sulpha drugs:
Like antibiotics, sulpha drugs are used to kill micro – organism. These are prepared in laboratory. Sulphadiazine, sulphanilamide, sulphathiazole, sulpha guanidine, etc. are important sulpha drugs.
![]()
Question 2.
Write notes on the following:
- Tranquillizers and Hypnotics (MP2018)
- Antidepressant
Answer:
1. Tranquillizers:
Tranquillizers are the chemical substances which affect higher centres of central nervous systems and reduce anxiety and tension. Tranquillizers are also called psychotherapeutic drugs. These drugs make the patient passive temporarily so that emotional distress or depression is reduced. The patient restores confidence. These drugs if taken for long – time make the person habitual. Luminal, Barbituric acid, seconal, equanil, etc. are the drugs of this class. These are components of sleeping pills.
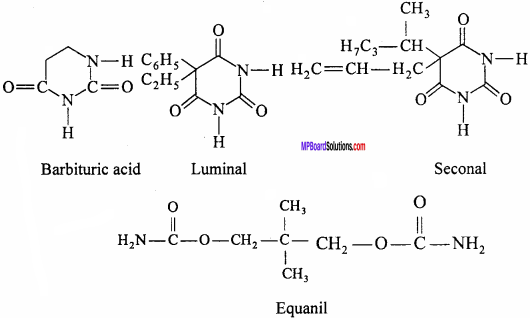
2. Antidepression:
These are given to patient for boosting their morals in the stage of acute depressions. Some mood elevator drugs are vitellin, methadone, cocaine, etc. These act on the central nervous system. Person becomes healthy by its use and de-velop confidence. These should be taken by the advice of doctor. Tophrenil is one such medicine. The amphetemin group of medicine help to upraise the mental level. Its common example is benzedine.
Question 3.
Write example of the following chemicals :
- Two Analgesics
- Two Antiseptic
- Two Antiseptic chemical
- Two Antibiotic
- Two Anaesthetic
- Two Sulpha drug
- Two Rocket propellant
- Two uses of chloramphenicol antibiotic.
Answer:
- Two Analgesic : (i) Morphine, (ii) Aspirin.
- Two Antiseptic : (i) Dettol, (ii) Bithional.
- Two Antiseptic Chemical: (i) Boric acid, (ii) Gention violet.
- Two Antibiotic : (i) Terramycin, (ii) Streptomycin.
- Two Anaesthetic : (i) Cyclopropane, (ii) Pelledyne.
- Two sulpha drug : (i) Sulphonide, (ii) Sulphadyne.
- Two Rocket Propellant: (i) Polyurethane, (ii) Ammonium perchlorate.
- Two use of Chloramphenicol Antibiotic : (i) In Typhoid, (ii) High fever and diarrhoea.
Question 4.
Write two differences between Dyes and Pigments.
Answer:
Differences between Dyes and Pigments :
Dyes:
- These are organic substance.
- They colour fibres and food materials also.
Pigments:
- These are inorganic substance.
- Mixed with safeda (white lead) it is used to colour metals and wood.
Question 5.
Give one example of Acidic dye and Basic dye.
Answer:
Acidic dye:
In these, acidic group like phenolic, sulphonic (S03H) are in the form of sodium salts. These colour animal fibre like wool, silk etc. Example : Orange – I and II.
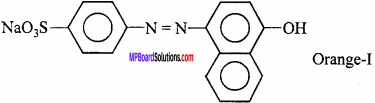
- Acidic dye : Methyl orange , Methyl red.
- Basic dye : Malachite green, Aniline yellow.
![]()
Question 6.
What is meant by the term ‘broad spectrum antibiotics’? Explain. (NCERT)
Answer:
The range of bacterias or other micro – organisms that are affected by a certain antibiotic is expressed as its spectrum of action. The term broad spectrum antibiotics means an antibiotic which kills or inhibits a wide range of Gram negative and Gram -positive bacteria.