MP Board Class 9th Sanskrit Solutions Durva Chapter 1 जयतु मे माता (गीतम्)
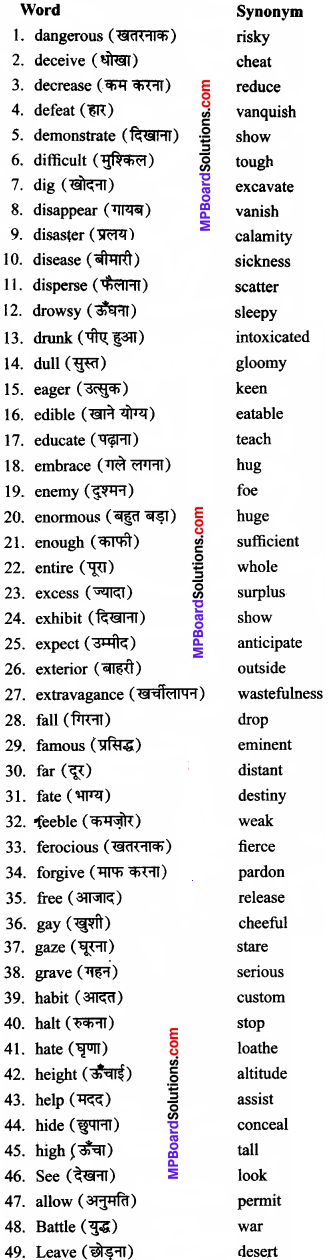
MP Board Class 9th Sanskrit Chapter 1 पाठ्य पुस्तक के प्रश्न
Class 9 Sanskrit Chapter 1 Mp Board प्रश्न 1.
एकपदेन उत्तरं लिखत-(एक शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए)।
(क) गीतायाः गाता क? (गीता का गाने वाला कौन है?)
उत्तर:
गीतायाः गाता कृष्णः। (गीता का गान करने वाला कृष्ण है।)
(ख) सीमान्तरक्षकः कः अस्ति? (सीमा का रक्षक कौन है?)
उत्तर:
सीमान्तरक्षकः सैनिकः अस्ति। (सीमा का रक्षक सैनिक है।)
(ग) वेदोपनिषज्जनयित्री का? (वेद और उपनिषद् की माता कौन है?)
उत्तर:
वेदोपनिषज्जनयित्री भारतभूमिः। (वेद और उपनिषद् की माता भारतभूमि है)
(घ) निष्कारणविद्वेषकरः कुत्र याति? (बिना कारण के बैर करने वाला कहां जाता है?)
उत्तर:
निष्कारणविद्वेषकर कालमुखिः याति। (बिना कारण के बैर करने वाला काल के मुख अर्थात् मृत्यु के मुख में जाता है)
(ङ) मातुः कष्टकर दुर्दैवं कः शमयतु? (माता के दुखों या कष्टों को कौन दूर करता है)
उत्तर:
मातुः कष्टकरं दुर्दैवं विधाता शमयतु। (माता के दुखों व कष्टों को विधाता दूर करता है।)
You can download MP Board 10th sanskrit solution to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Mp Board Class 9 Sanskrit Chapter 1 प्रश्न 2.
एकवाक्येन उत्तरं लिखत्-(एक वाक्य में उत्तर लिखें)।
(क) मातर्यशशांगाता कः? (माता की यश महिमा का गान करने वाला कौन है?)
उत्तर:
चतुर्दिगन्तवहः पवनः। (चारों दिशाओं में बहने वाली हवा।)
(ख) भारतमाता कैः वंदिता?। (भारत माता किसके द्वारा वंदित की गई है।)
उत्तर:
हर्ष-भोज-शिवराज वंदिता। (हर्ष-भोज और शिवराज के द्वारा पूजी गई।)
(ग) भारतमाता कैः नंदिता? (भारत माता किसके द्वारा प्रसन्न की गई है?)
उत्तर:
मौर्य-शुङ्ग गुप्ताभिनन्दिता। (मौर्य-शुङ्ग और गुप्त के द्वारा प्रसन्न की गई है।)
(घ) अहिंसाव्रती किमर्थं वाणसंधान करोति? (अहिंसा का व्रत धारण करने वाले वाणों का संधान किसलिए करते हैं?)
उत्तर:
निजरक्षार्थमहिंसाव्रती। (अपनी रक्षा के लिए अहिंसाव्रत धारी भी वाण संधान करता है।)
(ङ) आदौ ज्ञानभानुः कुत्र उदितः? (पहले ज्ञान का सूर्य कहां उदित होता है?)
उत्तर:
ज्ञान भानुरादौ त्वय्युदितः।। (ज्ञान का सूर्य तुम ही से उदित होता है।)
संस्कृत कक्षा 9 पाठ 1 Question Answer MP Board प्रश्न 3.
रिक्त स्थानानिपूरयत-(रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो)
(क) येन न दस्यति कोऽपि तक्षकः।
(ख) भारत रामायण कवयित्री।
(ग) मौर्य शुंङ्ग गुप्ताभिनन्दिता।
(घ) कच्छ शम रूपान्त वासिनी।
(ङ) निष्कारणविद्वेषकरस्तव कालमुखं प्रतियाता।
Mp Board Class 9 Sanskrit Solution प्रश्न 4.
संधिविच्छेदं कृत्वा सन्धेः नाम लिखत् (संधि विच्छेद कर संधि नाम लिखो)।
(क) त्वय्युदित
उत्तर:
त्वयि + उदिता = यण स्वर संधि।
(ख) शूरस्ते
उत्तर:
शूरः + ते = विसर्ग संधि।
(ग) गणोऽयम्
उत्तर:
गणः + अयम् = पूर्वरूप स्वर संधि।
(घ) कोऽपि
उत्तर:
कः + अपि = पूर्वरूप स्वर संधि।
(ङ) विद्वेषकरस्तव
उत्तर:
विद्वेषकरः + तव = विसर्ग संधि।
कक्षा 9 संस्कृत अध्याय 1 सवाल जवाब MP Board प्रश्न 5.
यथायोग्यं योजयत (सही जोड़ी बनाओ)

कक्षा 9वी संस्कृत के प्रश्न उत्तर MP Board प्रश्न 6.
शुद्धवाक्यानां समक्षम् “आम्” अशुद्धवाक्यानां समक्षं “न” इति लिखत् उदाहरणम्
यथा- पवनः चतुदिर्गन्तवहः अस्ति। – आम्
अस्याः तनः हिंसार्थम् बाण संधाता। – न
(क) गोपालः गीतायाः गाता।
(ख) भारत माता मौर्य शुङ्ग-गुप्ताभिवन्दिता अस्ति।
(ग) सकल लोकगणः सीमां त्राता अस्ति।
(घ) अस्यां आदौ ज्ञानभानु न उदितः।
उत्तर:
(क) आम्
(ख) आम्
(ग) आम्
(घ) न
संस्कृत कक्षा 9 पाठ 1 सवाल जवाब MP Board प्रश्न 7.
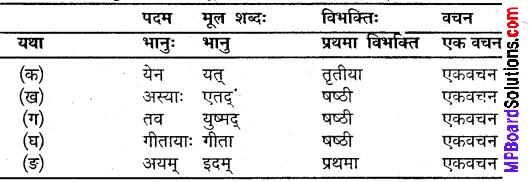
उदाहरणानुसारं पदानां मूल शब्द विभन्ति च लिखत
जयतु मे माता पाठ संदर्भ/प्रतिपाद्य
आधुनिक काल में भी संस्कृत में गद्य-पद्य लेखन की बहुलता है। इस भाषा के मूर्धन्य विद्वान, कवि और लेखकों के बीच आचार्य डॉ. प्रभुदयाल अग्निहोत्री का विशेष स्थान है। इनकी संस्कृत साहित्य में दर्शन, इतिहास, मनोविज्ञान, कथा, काव्य, नाटक आदि विधाओं में अनेक पुस्तकें प्रकाशित हुई हैं। ‘त्रिपथगा’ कविता संग्रह 2005 में प्रकाशित हुई। प्रस्तुत गीत भी ‘त्रिपथगा’ नामक कृति से ही लिया गया है। इस गीत में स्वतंत्रता सेनानी एवं संस्कृत के मूर्धन्य विद्वान अग्निहोत्री दारा सुंदर, मधुर एवं भावपूर्ण शब्दों में भारत माता की वंदना की गई है।
जयतु मे माता पाठ का हिन्दी अर्थ
1. जयतु जयतु मे माता,
अस्याः कष्टकरं दुर्दैवं शमयतु सदा विधाता।।
शब्दार्थ :
जयतु-जय हो-Vicrory; अस्याः -इसकी-Her/Him; कष्टकरंदुखी-Sorrow; दुर्दैवं-दुर्भाग्य को या बाधाओं को-Misfortune/Unfortunately; शमयतु-शांत कराये/ दूर करवाये; विधाता-ब्रह्मा-God Almighty; सदा-हमेशा-Always.
हिन्दी-अर्ध :
मेरी माता (मातृभूमि) की जय हो, जय हो। हे विधाता! तुम इसके कष्टों एवं आपदाओं को सदैव के लिए शान्त करें।
2. त्वं वेदोपनिषज्जनयित्री,
भारत-रामायण कवयित्री
अजनिष्ठाः कृष्णं गोपालं यो गीतायाः गाता॥
शब्दार्थ :
त्वं–तुम्हारा-Your; वेदोपनिषद्-वेद और उपनिषद्-Ved and Upnishad; जनयित्री-पैदा करने वाली-Mother, Originatee; गाता-गान करने वाले-Singer.
हिन्दी अर्थ :
हे भारत भूमि-तुम ही वेद और उपनिषदों की जननी हो। हे माँ! तुम ही महाभारत, रामायण की रचयित्री हो। हे माँ! तुम ही गीता का गान करने वाले मुरली-मनोहर कन्हैया की जननी हो।
3. ज्ञान-भानुरादौ त्वरयुदितः,
शूरस्ते तनयः सम्मुदितः,
केवल-निजरक्षार्थमहिंसाव्रती वाण-सन्धाता।
शब्दार्थ :
ज्ञान-ज्ञान-Knowledge; भानु-सूर्य-Sun; तनयः-पुत्र-Son; शूर-वीर-Brave; निज-स्वयं के-Myself; वाण-सन्धाता-वाण से लक्ष्य भेद करने पाला-Arjun or Bowman.
सरलार्थ :
हे भारत माँ! तुममें ही ज्ञान का सूर्य सर्व प्रथम उदित हुआ (अर्थात् भारतभूमि पर सर्व प्रथम ज्ञान रूपी सूर्य उदित हुआ।)। वीर पुत्र की जननी तुम्ही हो (अर्थात् वीरों का जन्म भारतभूमि पर ही हुआ)। केवल अपनी रक्षा के लिए अहिंसा का व्रत धारण करने वाला भी वाण संधान करता है अर्थात् वाणों से लक्ष्य साधता है।
4. मौर्य-शुङ्ग-गुप्ताभिनन्दिता,
हर्ष-भोज-शिवराज-वंदिता,
संप्रति लोकगणोऽयं सकल स्तव सीम्नां त्राता॥
शब्दार्थ :
नंदिता-प्रसन्न की गई-Toglad; वंदिता-पूजित-Worshipper; सम्प्रति-इस समय-This time; अयमं-इस-It; सकल-सभी-All, every; सीमनां-सीमाओं के-Limit; त्राता-रक्षक-Guard.
सरलार्थ :
हे भारत माँ! तुम मौर्य, शुंग, गुप्त वंशों द्वारा पूजित हो और (राजा) हर्ष, (राजा) भोज एवं शिवाजी द्वारा वंदित हुई हो। हे माँ! (इस पावन भूमि पर पैदा हुए) सभी जन तुम्हारी रक्षा करने वाले हैं।
5. कालिदास-कविता-रस-मग्ना,
सांख्ययोग-साधन-संलग्ना,
नालन्दाजन्ता मातस्ते श्रद्धाञ्जलि-प्रदाता॥
शब्दार्थ :
मग्ना-मग्न-Meditate; सांख्ययोग-सांख्ययोग-Sankhyoga; संलग्ना-संलग्न-Enclouse; नालन्दाजन्ता-नालन्दा और अजंता-Nalanda & Ajanta; प्रदाता-प्रदान करने वाले-Giver, Doner.
सरलार्थ :
हे मातृभूमि! कविता (की मधुर रागिनी) रस में मग्न कालिदास (सदृश कवि), सांख्य (दर्शन) योग में निमग्न अजंता एवं नालंदा के विद्वान जन तुम्हारी चरण वंदना करते हैं।
6. कच्छे-कामरूपान्त-वासिनी,
गङ्गा-कावेरी-सुहासिनी,
चतुर्दिगन्तवहः पवनस्ते मातर्यशसां गाता॥
शब्दार्थ :
वासिनी-निवास करने वाली-Inhahitant; चतुर्दिगन्तवहः-चारों दिशाओं में बहने वाला-Omni; पवनः-पवन-Air; ते-तुम्हारे-Your.
सरलार्थ :
हे भारत माते! तुम कच्छ से कामरूप तक निवास करने वाली (के अंक में) को गंगा-कावेरी (आदि नदियाँ) शोभायमान करती हैं तथा चारों दिशाओं में प्रवाहित होने वाला वायु तुम्हारी महिमा गान करता है।
7. सावहितः सीमान्त-रक्षकः
येन न दंशति कोऽपि तक्षकः
निष्कारण-विद्वेषकरस्तव कालमुखं प्रतियाता॥
जयतु जयतु मे माता। जयतु जयतु मे माता॥
शब्दार्थ :
सावहितः-सावधान-Attention; दंशति-दशता है-Sting; येन-जो-Who, what, which; तक्षकः-लुटेरा-Robber; कोपि-कोई भी-Any one; निष्कारण-बिना कारण के-Without reason; विद्वेष-द्वेष के कारण-Reason of jealous; प्रतिभाता-समाहित होता है-To meet.
सरलार्थ :
हे भारत माता की सीमा को रक्षित करने वाले रखवालो (जवानों)! सावधान रहो जिससे कोई बाहरी दस्यु भारत का नुकसान न कर सके। हे माँ! जो तुमसे (अर्थात् इस भूमि से) वैर भाव रखता है. वह काल रूपी गाल में समा जाता है। हे भारत माता! तुम्हारी जय हो, तुम्हारी जय हो, जय-जय हो माँ।