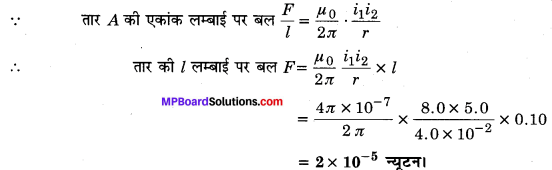
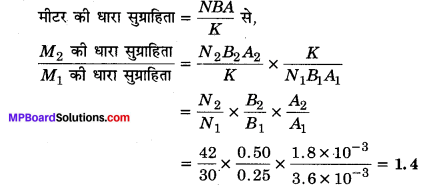
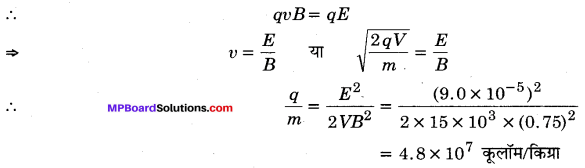
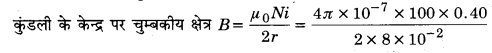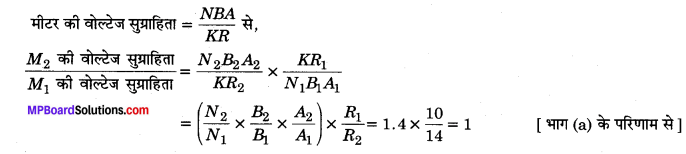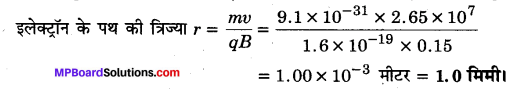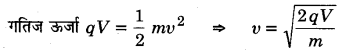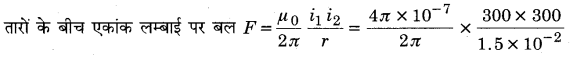Guys who are planning to learn the fundamentals of English can avail the handy study material using MP Board Solutions for Class 8 General English Solutions Chapter 6 Measure for Measure Questions and Answers. You Can Download MP Board Class 8 English Solutions Questions and Answers, Notes, Summary, Guide, Pdf. Refer to the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for English PDF available and score better grades. Simply click on the quick links available for MP Board Solutions for Class 8 General English Solutions Chapter 6 Measure for Measure Questions and Answers and prepare all the concepts in it effectively. Take your preparation to the next level by availing the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for Class 8 English prepared by subject experts.
MP Board Class 8th General English Solutions Chapter 6 Measure for Measure
Do you feel the concept of English is difficult to understand? Not anymore with our MP Board Solutions for Class 8 General English Solutions Chapter 6 Measure for Measure Questions and Answers. All the Solutions are given to you with detailed explanation and you can enhance your subject knowledge. Use the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for Class 8 English PDF for free of cost and prepare whenever you want.
Measure for Measure Textual Exercise
Read and Learn
(पढ़ो और याद करो):
Answer:
Do Yourself.
Word Power
(शब्द सामर्थ्य):
Replace the underlined words / phrases with correct ones from the text:
(रेखांकित शब्दों / शब्द समूहों को उद्धरण में दिए सही शब्दों से बदलें।)
Answer:
- When they put the first morsel of food in their mouth, the people began to pant and rasp asking water again and again.
- We dined in sumptuous surroundings.
- Raja Varma drew images of prominent characters of men and women from the Purana’s.
- He played a majestic part in the campaign.
- I phoned him up on the spur of the moment.
- Patronage of the art comes mostly from business and private individuals.
- The king was pleased with the artist when his portrait was ready.
Comprehension
(बोध प्रश्न):
Answer the following questions:
(निम्न प्रश्नों के उत्तर दें:)
Measure For Measure Class 8 MP Board Question 1.
Who was invited to the court to draw the portrait of the King ?
(हू वॉज़ इनवाइटिड टु द कोर्ट टु ड्रौ द पोरट्रेट ऑफ द किंग ?)
राजसभा में राजा का चित्र बनाने के लिए किसे आमन्त्रित किया गया ?
Answer:
Raja Varma, a fine artist was invited to the court to draw the portrait of the King.
(राजा वर्मा, अ फाइन आर्टिस्ट वॉज़ इनवाइटिड टू द कोर्ट टू ड्रॉ द पोरट्रेट ऑफ द किंग।)
एक कलाकार जिसका नाम राजा वर्मा था, को राजा का चित्र बनाने के लिए राजसभा में बुलाया गया।
Class 8 English Chapter 6 Measure For Measure MP Board Question 2.
Why did Raja Varma become – close and dear to the King?
(व्हाय डिड राजा वर्मा बिकम क्लोज़ एण्ड डीयर टू द किंग ?)
राजा वर्मा राजा के निकट और प्रिय क्यों हो गया ?
Answer:
Raja Varma made very live portraits of the King and prominent characters from the Puranas. So he became close and dear to the King.
(राजा वर्मा मेड व्हेरी लाइव पोरट्रेट्स ऑफ द किंग एण्ड प्रॉमिनेन्ट कैरेक्टर्स फ्रॉम द पुरानाज़। सो ही बिकेम क्लोज़ एण्ड डिअर टू द किंग।)
राजा वर्मा ने राजा और पुरानों के महत्वपूर्ण पात्रों के सजीव चित्र बनाए। इसलिए वह राजा के इतने नजदीक और प्रिय बन गया।
Measure For Measure Class 8 Questions And Answers Question 3.
Why were the people unhappy with the administration of the chief minister ?
(व्हाय वर द पीपल अनहैप्पी विद द एडमिनिस्ट्रेशन ऑफ द चीफ मिनिस्टर ?)
लोग मुख्यमंत्री के प्रबन्धों से नाखुश क्यों थे ?
Answer:
Everything in the state was thrown into disorder and chaos because of Raja Varma’s hasty decisions and bad-management. So the people were unhappy.
(एवरीथिंग इन द स्टेट वॉज़ थ्रोन इनटू डिसऑर्डर एण्ड केऔस बिकॉज़ ऑफ राजा वर्मास हैस्टी डिसीज़न्स एण्ड बैड मैनेजमेन्ट। सो द पीपल वर अनहैप्पी।)
राज्य में राजा वर्मा के जल्दी निर्णय व गलत तरीकों से सब अस्त-व्यस्त हो गया। इसलिए लोग नाराज थे।
Mp Board Class 8 English Chapter 6 Question 4.
Who wanted Tenali Raman’s help?
(हू वॉन्टेड तेनाली रामन्स हैल्प ?)
तेनाली रामन की मदद कौन चाहता था ?
Answer:
The elders of the town wanted the help of Tenali Raman.
(द एलडर्स ऑफ द टाउन वॉन्टेड द हेल्प ऑफ तेनाली रामन।)
शहर के बुजुर्ग तेनाली रामन की मदद चाहते थे।
Class 8 English Chapter 6 Mp Board Question 5.
Who was given the job of preparing the food in Tenali raman’s house?
(हू वॉज़ गिवन द जॉब ऑफ प्रिपेयरिंग द फूड इन तेनाली समस?)
सिवानी रोमनके घर में खाना बनाने का काम निको दिया गया ?
Answer:
A Very good carpenter given the job of preparing the food in Tenali raman’s house.
(अ व्हेरी गुड कारपेन्टर वॉज़ गिवन द जॉब ऑफ प्रिपेयरिंग द फूड इन तेनाली रामन्स हाउस।)
एक बहुत अच्छे बढ़ई को तेनाली रामन के घर खाना बनाने का काम दिया गया।
Mp Board Class 8 English Book Solution Question 6.
Did the cook prepare very tasty food ? If not, why?
(डिड द कुक प्रिपेयर व्हेरी टेस्टी फूड ? इफ नॉट व्हाय?)
क्या रसोईदार ने बहुत स्वादिष्ट भोजन बनाया ? यदि नहीं, क्यों?
Answer:
No, the cook did not prepare very tasty food because it is not a carpenter’s job to cook.
(नो द कुक डिड नॉट प्रिपेअर व्हेरी टेस्टी फूड बिकॉज़ इट इज नॉट अ कारपेन्टर्स जॉब टू कुक।)
नहीं, रसोईदार ने खाना ज्यादा स्वादिष्ट नहीं बनाया क्योंकि बढ़ई का काम खाना बनाना नहीं होता।
Question 7.
Why did Tenali Raman invite the king, queen and some courtiers to his house ?
(व्हॉय डिड तेनाली रामन इनवाइट द किंग, क्वीन एण्ड सम कोर्टियर्स टू हिज़ हाउस ?)
तेनाली रामन ने राजा, रानी और कुछ दरबारियों को अपने घर क्यों बुलाया ?
Answer:
Tenali Raman invited the king, the queen and some courtiers to his house for lunch as: he wanted to execute the plan which he had thought to make the King realise that the artist is not eligible to be a Chief Minister.
(तेनाली रामन इनवाइटिड द किंग, द क्वीन ऐण्ड सम कोर्टियर्स टू हिज़ हाउस फॉर लंच ऐज़ ही वॉन्टिड टू ऐक्सिक्यूट द प्लान विच ही हैड थॉट, टु मेक, द किंग रीयलाइज दैट द आर्टिस्ट इज नॉट इलिजिबल टु बी अ चीफ मिनिस्टर।)
तेनाली रामन ने राजा, रानी और दरबारियों को अपने घर खाने पर बुलाया। क्योंकि वह अपनी योजना के अनुसार राजा को अहसास दिलाना चाहता था कि कलाकार मुख्यमंत्री बनने लायक नहीं है।
Question 8.
How did the King realize his mistake ?
(हाउ डिड द किंग रियलाइज़ हिज़ मिस्टेक ?)
राजा को अपनी गलती का अहसास कैसे हुआ ?
Answer:
When Tenali Raman put a good carpenter to prepare food for the king, then the king realized his mistake.
(व्हेन तेनाली रामन पुट अ गुड कारपेन्टर टू प्रिपेअर फूड फॉर द किंग, देन द किंग रियलाइज्ड हिज मिस्टेक।)
जब तेनाली रामन ने एक बढ़ई को राजा के लिए खाना बनाने का काम दिया तो राजा को अपनी गलती का अहसास हुआ।
Question 9.
When did Raja Varma resign from his post ?
(व्हेन डिड राजा वर्मा रिजाइन फ्रॉम हिज पोस्ट ?)
राजा वर्मा ने अपने पद से कब त्यागपत्र दिया ?
Answer:
When Raja Varma came to know about the awkward incident at Raman’s house, he immediately resigned from his post. (व्हेन राजा वर्मा केम टु नो अबाउट द ऑकवर्ड इन्सीडेन्ट ऐट रामन्स हाउस, ही इमीडिएटली रिज़ाइन्ड फ्रॉम हिज , पोस्ट।)
जब राजा वर्मा को रामन के घर में हुए भद्दे किस्से के बारे में पता चला तो राजा वर्मा ने तुरन्त त्यागपत्र दे दिया।
Question 10.
Was Raja Varma happy when he was the Chief Minister of the state ? If not, why ?
(वॉज राजा वर्मा हैप्पी व्हेन ही वॉज द चीफ मिनिस्टर ऑफ द स्टेट ? इफ नॉट, व्हाय ?)
क्या राजा वर्मा खुश था.जब वह राज्य का मुख्यमंत्री था? यदि नहीं. क्यों ?
Answer:
No, Raja Varma was not happy when he was the Chief Minister of the state because he told Tenali in the end that he was happy to remain an artist.
(नो, राजा वर्मा वॉज़ नॉट हैप्पी व्हेन ही वॉज द चीफ मिनिस्टर ऑफ द स्टेट बिकॉज़ ही टोल्ड तेनाली इन द एण्ड दैट ही वॉज हैप्पी टू रिमेन एन आर्टिस्ट।)
राजा वर्मा मुख्यमंत्री के पद पर खुश नहीं था क्योंकि उसने तेनाली को अन्त में कहा कि वह कलाकार रहकर ही खुश था।
Question 11.
Select the appropriate words and fill in the blanks:
(a) The King invited ………… to the court and asked him to draw his portrait.
(i) Tenali Raman
(ii) One of the courtiers
(iii) Raja Varma
(iv) One of his Ministers.
(b) Tenali Raman did not invite ………..
(i) The king
(ii) The queen
(iii) The courtiers
(iv) Raja Varma.
Let’s Learn
(आओ याद करें):
(A) Frame Yes/No questions for the following situations:
(निम्नलिखित स्थितियों के लिए yes/no प्रश्न बनाइए:)
Answer:
- Sunita, has Raju ever been to Bhopal ?
- Sunita and Raju, are you going to Mahesh war ?
- Suresh, does Mohan play tennis ?
- Did you enjoy your holiday ?
- Rakesh shall we both go for a walk ?
- Ashok, will you be at the zoo today?
- Is the train on time?
- Sunita, can I borrow your pen ?
- Vijay, do you have a motor bike ?
(B) What would you say in these situations:
(इन स्थितियों में आप क्या कहौंगो:)
You are talking to a boy at a party. Ask him:
(1) Name of his school.
Answer:
What is the name of your school ?
(2) His residence.
Answer:
Where do you live?
(3) His age.
Answer:
How old are you?
(4) When the course finishes.
Answer:
When will your course finish?
(5) What the date is today.
Answer:
What is the date today?
(C) Complete the conversation, put in the negative forms of the following words:
(नीचे दिये नकारात्मक शब्दों से वार्तालाप पूरा करें:)
Answer:
- → doesn’t
- → didn’t
- → weren’t
- → wasn’t
- → isn’t
- → don’t
- → haven’t.
(D) Change the following sentences into Negative and Interrogative sentence:
(निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को नकारात्मक एवं प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में बदलें:).
(1) There is a park in-front of my house.
(2) All birds fly in the sky.
(3) They will help her.
(4) We should keep our promises.
(5) The postman was delivering the letters.
(6) Ashok has written this letter.
(7) Meera is cooking the dinner.
(8) Lightning had struck the house.
(9) He has bought a new car.
(10) The farmer has sown the seeds.
Answer:
(1) Negative – There is not a park in front of my house.
Interrogative – Is there a park in front of my house?
(2) Negative – All birds do not fly in the sky.
Interrogative – Do all birds fly in the sky ?
(3) Negative – They will not help her.
Interrogative – Will they help her ?
(4) Negative – We should not keep our promises.
Interrogative – Should we keep our promises?
(5) Negative – The postman was delivering the letters.
Interrogative – Was the postman delivering the letters ?
(6) Negative – Ashok has not written this letter.
Interrogative – Has Ashok written this letter ?
(7) Negative – Meera is not cooking the dinner.
Interrogative – Is Meera cooking the dinner ?
(8) Negative – Lightning had not struck the house.
Interrogative – Had lightning struck the house?
(9) Negative – “He has not bought a new car.
Interrogative – Has he bought a new car?
(10) Negative.- The farmer has not sown the seeds.
Interrogative – Has the farmer sown the seeds ?
Let’s Talk
(आओ बात करें):
Answer:
Do Yourself.
Let’s Read
(आओ पढ़ें):
(A) Read the flow chart and answer the questions given below:
Question 1.
What do you do if there is a fault in the valve ?
Answer:
If there is a fault in the valve, we replace it.
Question 2.
What do you do after removing the wheel ?
Answer:
After removing the wheel, we remove the tube from the type.
Question 3.
How do you check the tube for leakage ?
Answer:
We pump air from the pressure machine and put the tube in water to check the leakage.
Question 4.
What do you do after you have found the leakage.
Answer:
We mark the place of leakage and take it out.
Question 5.
How do you repair the puncture ?
Answer:
We repair the tube with puncture solution and a piece of rubber.
(B) Read the passage given in the text book and answer the questions given below:
Question 1.
Who is the father of the Green Revolution of India ?
Answer:
Dr. M. S. Swaminathan.
Question 2.
How did Dr. Swaminathan bring the Green Revolution ?
Answer:
He developed seeds of high yielding varieties and brought a revolution in farming 1966.
Question 3.
What is the result of the Green Revolution ?
Answer:
Due to this, our country is now self – sufficient in food grain production especially cereals i.e., wheat, rice and maize.
Question 4.
What two things give us food grain safety ?
Answer:
We have better food grain collection and distribution network that gives us food grain safety.
Question 5.
How do we help other countries fight famine ?
Answer:
We are exporting surplus food grains to other countries and meet and their food needs.
Let’s Write
(आओ लिखो):
Use the clues in the correct form and complete the description.
(संकेतों का सही रूप में प्रयोग कर वर्णन को पूरा करें।)
Answer:
A train is coming, now. Don’t worry. This isn’t our train. The engine is making a thunderous noise. People are running here and there. The driver is peeping out. The guard is waving a red flag. The train has stopped now. All the passengers are rushing towards the compartments. They are trying to get on, while those inside the compartment are trying to get off. Some of them are shouting “Coolie ! Coolie”! Some are buying fruits. There’s so much confusion.
Let’s do it
(आओ इसे करें):
Answer:
Do Yourself.
Measure for Measure Word Meanings
Patronage (पेट्रोनेज) – संरक्षण; Portrait (पोरट्रेट) – चित्र; Majestic (मेजस्टिंक) – तेजस्वी, आकर्षक; Overwhelm (ओवरद्वैल्म) – ओत – प्रोत होना; Impulse (इमपल्स) – मनोवेग Sumptuous (सम्पच्युअस) – शानदार, वैभवशाली, भव्यः Morsel (मॉर्सल) – ग्रास, कौर, निवाला; Courteously (कर्टिअसली) – विनम्रतापूर्वक
Embarrassment ( एमबैरेसमेन्ट) – उलझन; Livid (लिविड) – क्रोधित; Pant (पैन्ट) – हाँफना; Rasp ( रैस्प) – हाँफते हुए आवाज निकालना; Inept (इनैप्ट) – अयोग्य; Error (ऐरर) – गलती; Awkward (ऑकवर्ड) – भद्दा, अकुशल। Spur (स्पर) – उसी क्षण; Chaos (केऑस) – उपद्रव; Courtiers (कोटियस) – दरबारी।
Measure for Measure Summary, Pronunciation & Translation
1. King Krishna Devaraya was known for his patronage of poets and scholars and he was equally fond of fine arts. Once he came to know about a brilliant artist named Raja Varma. He invited Raja Varma to the court and asked him to draw his portrait.
(किंग कृष्ण देवराय वॉज़ नोन फॉर हिज़ पेट्रोनेज़ ऑफ पोइट्स एण्ड स्कॉलर्स एण्ड ही वॉज़ ईक्वली फॉण्ड ऑफ फाइन आर्ट्स. वन्स ही केम टु नो अबाउट अ ब्रिलिएण्ट आर्टिस्ट नेम्ड राजा वर्मा. ही इनवाइटिड राजा वर्मा टु द कोर्ट एण्ड आस्क्ड हिम टु ड्रॉ हिज़ पोरट्रेट.)
अनुवाद:
राजा कृष्ण देवराय कवियों और विद्वानों के संरक्षक के रूप में जाने जाते थे और वह ललित कलाओं के भी बराबर प्रशंसक थे। एक बार उन्हें राजा वर्मा नामक प्रतिभाशाली चित्रकार के बारे में ज्ञात हुआ। उन्होंने राजा वर्मा को दरबार में आमन्त्रित किया और उसे अपना एक चित्र बनाने को कहा।
The king was very pleased with the artist when his portrait was ready. In the portrait the majestic and handsome king seemed to have come alive within the frame.
(द किंग वॉज़ वैरी प्लीज्ड विद द आर्टिस्ट व्हैन हिज पोरट्रेट वाज रैडी. इन द पोरट्रेट द मेजस्टिक एण्ड हैण्डसम किंग सीम्ड टु हैव कम अलाइव विदिन द फ्रेम.)
अनुवाद:
राजा कलाकार से बहुत प्रसन्न हुआ जब उसका चित्र तैयार हुआ। चित्र में प्रतापी तथा सुन्दर राजा फ्रेम में सजीव दिखाई पड़ता था।
2. This portrait apart, Raja Varma drew images of prominent characters of men and women, from the ‘Puranas’, and so on. He became well-known for his genius, and close and dear to the king. Overwhelmed with joy, Krishna Devaraya called the artist and asked him what he wanted. When Raja Varma did not reply, the king, on the spur of generous impulse, rewarded him with the chief ministership.
(दिस पोरट्रेट अपार्ट, राजा वर्मा ड्रयू इमेजेज ऑफ प्रॉमिनेंट कैरेक्टर्स ऑफ मैन एण्ड वुमैन फ्रॉम द ‘पुरानाज’ एण्ड सो ऑन. ही बिकेम वैल-नोन फॉर हिज जीनियस, एण्ड क्लोज। एण्ड डीयर टु द किंग. ओवरव्हेल्म्ड विद जॉय, कृष्ण देवराय कॉल्ड द आर्टिस्ट एण्ड आस्क्ड हिम व्हॉट ही वान्टेड. व्हेन राजा वर्मा डिड नॉट रिप्लाइ, द किंग, ऑन द स्पर ऑफ जनरस इम्पल्स, रिवार्डेड हिम विद द चीफ मिनिस्टरशिप.)
अनुवाद:
इस चित्र के अलावा राजा वर्मा ने और भी पुराणों के प्रमुख स्त्री एवं पुरुष पात्रों के चित्र बनाए। वह अपनी प्रतिभा के कारण राजा का प्रिय व नजदीकी बन गया। अत्यधिक प्रसन्नता के साथ कृष्ण देवराय ने कलाकार को बुलाया और उससे पूछा कि वह क्या चाहता है। जब राजा वर्मा ने उत्तर नहीं दिया तो राजा ने तुरन्त उदारतावश उसे मुख्यमंत्री के पद से पुरस्कृत किया।
3. Though Raja Varma was a good man and a brilliant artist, he had no experience whatsoever of administration. Soon everything was thrown into disorder and chaos because of his hasty decisions and bad management of the state affairs. Though people were unhappy with his administration, they did not dare complain to the king because the king was very fond of him. The elders of the town finally approached and sought Tenali Raman’s help in getting rid of the new and inept Chief Minister. Tenali Raman assured them, “I shall soon find a harmless way to remove the artist from the Chief ministership.”
(दो राजा वर्मा वॉज़ अ गुड मैन एण्ड अ ब्रिलिएण्ट आर्टिस्ट, ही हैड नो एक्सपीरिएन्स व्हाटसोएवर ऑफ एडमिनिस्ट्रेशन. सून ऐवरीथिंग वॉज थ्रोन इनटु डिसआर्डर एण्ड केओज बिकॉज ऑफ हिज़ हेस्टी डिसीज़न्स एण्ड बैड मैनेजमेंट ऑफ द स्टेट अफेयर्स दो पीपुल वर अनहैपी विद हिज़ एडमिनिस्ट्रेशन, दे डिड नॉट डेअर कम्पलेन टु द किंग बिकॉज़ द किंग वाज़ वैरी फॉण्ड ऑफ हिम. द ऐल्डर्स ऑफ द टाउन फाइनली अप्रोच्ड एण्ड सॉट तेनाली रामन्स हैल्प इन गैटिंग रिड ऑफ द न्यू एण्ड इनेप्ट चीफ मिनिस्टर. तेनाली रामन एश्योर्ड दैम, “आइशैल सून फाइण्ड अ हार्मलैस वे टु रिमूव द आर्टिस्ट फ्रॉम द चीफ मिनिस्टरशिप.”)
अनुवाद:
यद्यपि राजा वर्मा एक अच्छा व्यक्ति और कुशल कलाकार था, उसको प्रशासन का कोई अनुभव नहीं था। जल्दी ही, उसके जल्दबाजी में लिए गये निर्णयों और राज-काज के गलत प्रशासन के कारण सब कुछ अस्त-व्यस्त हो गया। यद्यपि लोग उसके प्रशासन से अप्रसन्न थे, वे राजा से शिकायत करने का साहस नहीं जुटा सके क्योंकि राजा उससे अधिक प्यार करता था। अन्त में शहर के बुजुर्ग तेनाली रामन के पास गये और नये व अयोग्य मुख्यमन्त्री से छुटकारा पाने में उसकी सहायता माँगी। 1 तेनाली रामन ने उन्हें आश्वासन दिया, “मैं मुख्यमंत्री पद से कलाकार को हटाने का एक हानिरहित तरीका जल्दी ही निकाल लूँगा।”.
4. After a few weeks Tenali Raman invited the king, the queen and some courtiers to his house for lunch. Meanwhile, he found a very good carpenter and put him on the job of preparing a sumptuous feast for the king. · The king and others sat for lunch and at Tenali Raman’s order, the carpenter began serving them. As soon as they put the first morsel of food in their mouths, the people began to pant and rasp, asking for water again and again.
(आफ्टर अ फ्यू वीक्स तेनाली रामन इनवाइटिड द किंग, द क्वीन एण्ड सम कोर्टियर्स टु हिज हाउस फॉर लंच. मीनव्हाइल, ही फाउण्ड अ वैरी गुड कारपेन्टर एण्ड पुट हिम ऑन द जॉब ऑफ प्रिपेयरिंग अ सम्पटस फीस्ट फॉर द किंग. द किंग एण्ड अदर्स सैट फॉर लंच एण्ड ऐट तेनाली रामन्स ऑर्डर, द कारपेन्टर बिगेन सर्विंग दैम. ऐज़ सून ऐज़ दे पुट द फर्स्ट मॉर्सल ऑफ फूड इन देअर माउथ्स, द पीपुल बिगेन टु पैंट एण्ड रैस्प, आस्किंग फॉर वाटर अगेन एण्ड अगेन.)
अनुवाद:
कुछ सप्ताह बाद तेनाली रामन ने राजा, रानी और कुछ दरबारियों को भोजन के लिए अपने घर पर आमन्त्रित किया। इस अवधि में उसने एक बहुत अच्छा बढ़ई ढूँढ़ा और राजा के लिये एक शानदार भोज की तैयारी का काम उसे सौंप दिया। राजा और अन्य लोग भोजन के लिए बैठ गए और तेनाली रामन के आदेश पर बढ़ई उन्हें खाना परोसने लगा। जैसे ही उन्होंने भोजन का पहला कौर अपने मुँह में डाला लोग बार-बार पानी माँगते हुए हाँफने और अजीब सी आवाजें निकालने लगे।
5. Soon after tasting the food, the king realized that the food was badly cooked and was unbearably hot. He was livid.
(सून आफ्टर टेस्टिंग द फूड, द किंग रियलाइज्ड दैट द फूड वॉज़ बैडली कुक्ड एण्ड वॉज़ अनबीयरेब्ली हॉट. ही वॉज़ लिविड.)
अनुवाद:
जल्दी ही भोजन का स्वाद लेने के बाद राजा को एहसास हुआ कि खाना बेहद खराब था और उसमें अत्यधिक मिर्च थी। वह अत्यधिक नाराज हो गया।
6. “Raman, who has cooked this food ? Do you want us all to suffer and die by eating this horrible food ?” In his usual humble way Tenali Raman said, “I I beg your Majesty’s forgiveness.” Then he showed the In carpenter to the king. “I have never come across such at excellent carpenter and I have put him on the job of cooking the lunch for today’s feast.”
(रामन, हू हैज कुक्ड दिस फूड ? डू यू वॉन्ट अस ऑल टु सफर एण्ड डाइ बाइ ईटिंग दिस हॉरिबल फूड ?” इन हिज़ यूजुअल हम्बल वे तेनाली रामन सैड, “आइ बैग योर मैजस्टीज़ फॉरगिवनैस.” दैन ही शोड द कारपेन्टर टु द किंग. “आइ हैव नैवर कम अक्रॉस सच एन एक्सीलेंट कारपेन्टर एण्ड आइ हैव पुट हिम ऑन द जॉब ऑफ कुकिंग द लन्च फॉर टुडेज़ फीस्ट.”)
अनुवाद:
“रामन, किसने यह भोजन पकाया है ?” क्या तुम हम सभी को इस भयंकर खराब भोजन को खिलाकर बीमार करना या मारना चाहते हो ?”
सदैव की तरह नम्रता के साथ तेनाली रामन ने कहा, “मैं हुजूर से क्षमा चाहता हूँ”. तब उसने राजा को बढ़ई को दिखाया। “मैंने इससे अच्छा बढ़ई आज तक नहीं देखा है और आज के भोज के लिए खाना पकाने का काम मैंने इसे ही सौंपा था।”
7. The king began laughing loudly. “Have you lost all sense, Raman ? A good carpenter should be employed to work on wood but not on food. How did you get this funny idea ?” Tenali Raman asked the king courteously, “Lord! If an artist can become a chief minister, can’t a carpenter become a cook ?” The king at once understood that Tenali Raman got a carpenter to make him realize his error in making Raja Varma the chief minister.
(द किंग बिगैन लाफिंग लाउडली. हैव यू लॉस्ट ऑल सैन्स, रामन ? अ गुड कारपेन्टर शुड बी एम्पलॉयड टु वर्क ऑन वुड बट नॉट ऑन फूड. हाउ डिड यू गैट दिस फनी आइडिया ?” तेनाली रामन आस्क्ड द किंग कर्टियसली, “लॉर्ड ! इफ एन आर्टिस्ट कैन बिकम अ चीफ मिनिस्टर, कॉन्ट अ कारपेन्टर बिकम अ कुक ?” द किंग ऐट वन्स अन्डरस्टुड दैट तेनाली रामन गॉट अ कार्पेन्टर टु मेक हिम रियलाइज़ हिज एरर इन मेकिंग राजा वर्मा द चीफ मिनिस्टर.)
अनुवाद:
राजा जोर से हँसने लगा। “रामन, क्या तुम्हारा विवेक चला गया है ? एक अच्छे बढ़ई को लकड़ी का काम करने के लिए रखना चाहिए न कि भोजन के लिए। तुम्हें यह हास्यास्पद विचार कैसे सूझा ?” तेनाली रामन ने राजा से विनम्रता से पूछा, “महाराज, यदि एक कलाकार मुख्यमंत्री बन सकता है तो एक बढ़ई रसोइया क्यों नहीं बन सकता है ?” राजा तुरन्त समझ गया कि तेनाली रामन राजा वर्मा को मुख्यमंत्री बनाने की उसकी गल्ती का एहसास कराने के लिए ही एक बढ़ई को लायें।
8. The king was saved the embarrassment of removing Raja Varma from the post, because, when Raja Varma came to know about the awkward incident at Raman’s house, he immediately resigned from his post. Later Raja Varma told Tenali Raman that he was happy to remain an artist.
(द किंग वॉज़ सेव्ड द एम्बैरेसमेंट ऑफ रिमूविंग राजा वर्मा। फ्रॉम द पोस्ट, बिकॉज, व्हेन राजा वर्मा केम टु नो अबाउट द ऑकवर्ड इन्सीडेंट ऐट रामन्स हाउस, ही इमीडिएटली रिज़ाइन्ड फ्रॉम हिज पोस्ट. लेटर राजा वर्मा टोल्ड तेनाली रामन दैट ही वॉज हैपी टु रिमेन एन आर्टिस्ट.)
अनुवाद:
राजा वर्मा को पद से हटाने की परेशानी से राजा। कृष्ण देव राय बच गये क्योंकि जब राजा वर्मा को रामन के घर में घटित अप्रिय घटना के बारे में मालूम हुआ तो उसने तुरन्त अपने पद से त्याग-पत्र दे दिया। बाद में राजा वर्मा ने तेनाली रामन से कहा कि वह कलाकार बने रहने में ही प्रसन्न है।
We wish the knowledge shared regarding MP Board Solutions for Class 8 General English Solutions Chapter 6 Measure for Measure Questions and Answers has been helpful to you. If you need any further help feel free to ask us and we will get back to you with the possible solution. Bookmark our site to avail the latest updates on different state boards solutions in split seconds.