MP Board Class 12th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 10 Finance Market
Finance market Important Questions
Finance market Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Primary and Secondary market:
(a) Compete with each other
(b) Complement to each other
(c) Functions independently
(d) Control each other
Answer:
(b) Complement to each other
Question 2.
The number of stock exchange in India was :
(a) 20
(b) 21
(c) 24
(d) 23
Answer:
(c) 24
Question 3.
REPO is:
(a) Repurchase agreement
(b) Reliance petroleum
(c) Read and process
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Repurchase agreement
Question 4.
NSEI commenced future trading in the year:
(a) 1999
(b) 2000
(c) 2001
(d) 2002
Answer:
(b) 2000
Question 5.
The settlement cycle in NSEI is :
(a) T + 5
(b) T + 3
(c) T + 2
(d) T + 1
Answer:
(c) T + 2
Question 6.
Liquidity is formed by :
(a) Organised market
(b) unorganized market
(c) Primary market
(d) Secondary market
Answer:
(c) Primary market
Question 7.
The headquarter of SEBI is :
(a) Delhi
(b) Mumbai
(c) kolkata
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(b) Mumbai
Question 8.
The foremost stock exchange was established in :
(a) Delhi
(b) London
(c) Tokyo
(d) New york
Answer:
(b) London
Question 9.
In India the main organ of unorganised market is :
(a) Desi banker
(b) Mahajan and Sahukar
(c) Both ‘(a)’ and ‘(b)’
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Both ‘(a)’ and ‘(b)’
Question 10.
The axis of central bank is :
(a) Reserve bank
(b) Commercial bank
(c) Co-operative bank
(d) Desi bank.
Answer:
(a) Reserve bank
Question 11.
NSEI was established in :
(a) 1900
(b) 1991
(c) 1992
(d) 1994.
Answer:
(c) 1992
Question 12.
These are not securities of capital market:
(a) Equity share
(b) Preferential shares
(c) Debentures
(d) Commercial bill.
Answer:
(d) Commercial bill.
Question 13.
The first stock exchange of India was established in the year:
(a) 1857
(b) 1877
(c) 1887
(d) 1987.
Answer:
(c) 1887
Question 14.
Treasury bills are :
(a) Instrument of short term borrowings ‘
(b) Long term borrowings
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Instrument of short term borrowings
Question 15.
For stock exchange the servies of SEBI is :
(a) Volantary
(b) Essential
(c) Not essential
(d) Compulsory.
Answer:
(d) Compulsory.
Question 16.
In 2004 the number of stock exchange in India was :
(a) 25
(b) 21
(c) 23
(d) 24
Answer:
(d) 24
Question 17.
Only buying security takes place in :
(a) Stock exchange
(b) Primary market
(c) Capital market
(d) Money market.
Answer:
(b) Primary market
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The paid up capital of NSEI is ……………..
- OTCEI maintains the liquidity in the securities of…………….. companies.
- OTCEI was established in ……………..
- NSEI was established in ……………..
- Stock exchange which provides nation wide investor base to small companies is ……………..
Answer:
- Rs. 3 crores
- Small
- 1990
- 1992
- OTCEI.
Question 3.
Write the answer in one word/sentence :
- Which market deals with long-term funds ?
- Where is the purchase and sale of securities take place ?
- In which market dealings of short-term funds take place ?
- Which organization is formed to protect and safeguard the interest of investors ?
- Write the name of one all India level stock exchange.
- Which instrument is issue at discount ?
- Which market is regulated and developed by SEBI ?
- Which capital market is related with new issues ?
- Which Stock Exchange is the greatest stock Exchange of the country ?
- What are the two parts of capital market ?
Answer:
- Capital market
- Stock exchange
- Money market
- SEBI
- NSEI
- Treasury bill
- Stock exchange
- Primary market
- Bombay Stock Exchange
- Primary, Secondary.
Question 4.
Write true or false :
- Sebi is established to protect and safeguard the interest of investors.
- In India there are 24 stock exchanges.
- Headquarter of SEBI is in Mumbai.
- Full form of SEBI is securities and exchange board of India.
- In stock exchange transaction of new securities take place.
- There is no control of SEBI on Mutual fund.
- Money market deals long-term funds.
- Money market is controlled by SEBI.
- For industrial development healthy capital market is must.
- There is difference between the primary market and secondary market.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
Question 5.
Match the columns :

Answer:
1. (d)
2. (e)
3. (b)
4. (a)
5. (c)
6. (g)
7. (f)
8. (i)
9. (h)
Finance Market Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define capital market.
Answer:
“An individual or private firm receiving deposits and dealing in hundies or lending money. Those who do not accept deposits were to be treated as money lenders.”
![]()
Question 2.
Write the names of two parts capital market ?
Answer:
There are two parts of capital market:
- Capital market.
- Money market.
Question 3.
What do you mean by stock exchange ?
Answer:
A stock exchange is a place for the purchase and sale of its industrial and financial curities Shares, debentures, funds etc.) take place.
Question 4.
What is the full form of SEBI ?
Answer:
Full form of SEBI is : Securities and Exchange board of India.
Question 5.
Mfiatdo you mean by money market ?
Answer:
Money market refers to that market where transaction of lending and borrowing of short term funds take place.
Question 6.
What do you mean by Treasery bill ?
Answer:
A treasury bill is basically an instrument of short-term borrowing by the government of India maturing in less than one year.
Question 7.
Write the elements of money market.
Answer:
- Central bank.
- Commercial banks.
- Co-operative banks.
- Saving bank.
- Acceptance house.
Question 8.
Write two characteristics of Debentures.
Answer:
The characteristics of Debentures are :
(1) Debenture holder has the right to get interest.
(2) Debenture is merely a written instrument signed by the company under its common seal acknowledging the debt due by it to its holders.
Question 9.
Write three characteristics of capital market.
Answer:
The characteristics of capital market are :
- SEBI controls the capital market.
- In it, transactions in long-term funds take place.
- Capital market arranges capital in large scale.
Question 10.
What do you mean by secondary market ?
Answer:
Under secondary market capital is formed or received, from various sources. Generally it is called Stocks Exchange.
Question 11.
Whatis SEBI.
Answer:
SEBI was constituted by government of India in April 1988 as administrative body. It was aseparate body for orderly functioning of capital market.
![]()
Question 12.
What do you mean by RAPO rate ?
Answer:
The rate at which reserve bank of India. Repurchase the government securities is RAPO rate.
Question 13.
Write the name of index of NSE ?
Answer:
The name of index is called NIFTY.
Question 14.
“Blue Chip” shares are of which company ?
Answer:
Shares of a big prosperous company is called “Blue chip”.
Question 15.
In India how many stock exchanges are there ? Which is the oldest one ?
Answer:
There are total 24 stock exchanges in India. Mumbai stock exchange is the oldest one.
Question 16.
When preference shareholders can vote ?
Answer:
Preference shareholders generally don’t have the voting rights but the preference shareholders can use voting rights only in matters pertaining to their interest and not other matters.
Question 17.
What is debenture ?
Answer:
Money received as a loan is called ‘Borrowed capital’. The documents issued to the lender for money borrowed from him by the company is called debenture.
Debenture is merely a written instrument signed by the company under its common seal acknowledging in debt due by it to its holders.
![]()
Question 18.
What do you mean by commercial bill ?
Answer:
Commercial bill is a bill of exchange used to finance the working capital requirements of business firms. It is a short term negotiable self liquidating instrument. Which is used to finance the credit sales of firms.
Question 19.
How is value determined in securities in share bazar ?
Answer:
Share market provides a platform for securities here forces of demand and supply work together. Thus value is fixed by securities.
Question 20.
What do you mean by Boli price ?
Answer:
The price which a customer is willing to play for securities is called Boli price.
Question 21.
Write the elements of capital market.
Answer:
- Development bank.
- Commercial banks
- Stock exchange.
Question 22.
Write the objectives of SEBI.
Answer:
The objectives of the establishment of SEBI are as follows :
- The main objective of SEBI is to provide security to the investors.
- To attract the savings of the people to the capital market.
- To keep an eye on activities of the brokers in order to control the capital market.
- To promote development of securities market.
- To provide efficient services to all the parties operating in the capital market.
Question 23.
What do you mean by Financial assets ?
Answer:
Debentures, Shares, Bills etc. are included into Financial assets.
Finance Market Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the importance of money market.
Answer:
Money market provides important functions and’ services which increases the importance of money market. The importance of money market are as follows :
1. Provides funds: Money market helps financial institutions, business enterprises to meet their short term funds requirement. This ensures smooth operations and functioning of business enterprises.
2. Use of surplus funds: If the capital of any enterprise remains unused that it will lead to business losses. Thus, through capital market the surplus funds are utilised time to time.
3. Helps in financial mobility : By sending the securities from one area to another and by investing money market helps in financial mobility. For the industrial and economical development of a nation financial mobility is essential.
4. Equilibrium between demand and supply : Necessary steps and initiatives are taken by money market time to time for maintaining equilibrium between demand and supply.
5. Economy in the use of cash : The use of cash is properly performed through money market. The procedure of this market is not complex that’s why unnecessary expenses are not incurred for the use of cash funds.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the types of capital market.
Answer:
Capital market is two types :
1. Organized capital market: In organised capital market there remain banks and different financial institutions in Indian capital market, Reserve Bank of India, State Bank of India, different nationalized banks, financial institutions, post office, savings bank, stock exchange etc. are included.
2. Unorganized capital market: In an unorganized capital market, indigenous bankers, merchants, personal investment, institutions as chit funds etc. are included.
Question 3.
What do you mean by Treasury bill ?
Answer:
Treasury Bill: A Treasury bill is basically an instrument on mg by the Government of India maturing in less than one year. They are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds issued by the Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short-term requirement of funds. Treasury bills are issued in the form of a promissory note. They are highly liquid and have assured yield and negligible risk of default. They are issued at a price which is lower than their face value and repaid at par.
The difference between the price at which the treasury bills are issued and their redemption value is the interest receivable on them and is called discount. Treasury bills are available for a minimum amount of Rs 25,000 and in multiples therefore. Example: Suppose an investor purchases a 91 days Treasury bill with a face value of Rs. 1,00,000 for Rs. 96,000. By holding the bill until the maturity date, the investor receives Rs. 1,00,000. The difference of Rs. 4,000 between the proceeds received at maturity and the amount paid to purchase the bill represents the interest received by him.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you mean by RAPO and Reverse RAPO Rate.
Answer:
RAPO Rate : RAPO rate is that rate at which RBI gives loans to bank for a particular period of time. A bank repurchase go securities and is exchange receives wealth. Due to discount in RAPO rate the bank gets money at low rate whereas due to increase in RAPO rate the loan from RBI becomes expensive. If it makes loan cheper to bank it reduces the RAPO rate.
Reverse RAPO rate : It is a rate of transaction of short term loan, at which Reserve Bank of India takes loan from commercial bank within our country.
Question 5.
What do you mean by CD ? or certificate of deposit ?
Answer:
Certificate of deposit: Certificates of deposit (CD) are unsecured, negotiable, short-term instruments in bearer form, issued by commercial banks and development financial institutions. They can be issued to individuals, corporations and companies during periods of tight liquidity when the deposit growth of banks is slow but the demand for credit is high. They help to mobilize a large amount of money for short periods.
Question 6.
Differentiate between NSEI and OTCEI.
Answer:
Differences between NSEI and OTCEI:
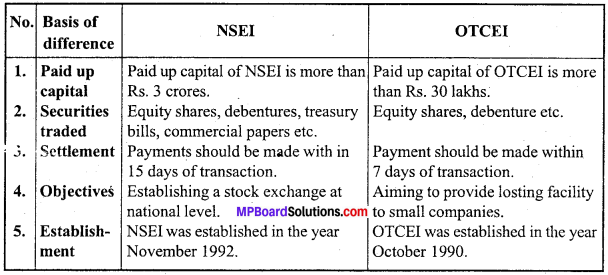
Question 7.
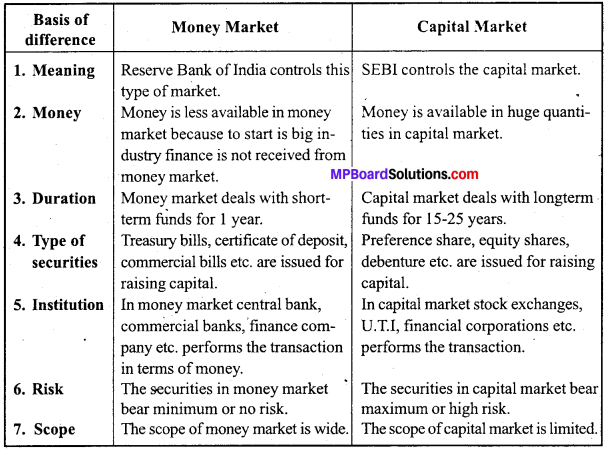
What is the difference between Primary and Secondary Market.
Answer:
Differences between Primary and Secondary Market:
Question 8.
How many stock exchanges are there in India ?
Answer:
Recognized Stock Exchange in India :
- The Stock Exchange—Bombay (Mumbai)
- The Stock Exchange—Ahmedabad
- Madras Exchange Ltd.—Madras (Chennai)
- The Calcutta Stock Exchange Association Ltd.—Calcutta (Kolkata)
- The Delhi Stock Exchange Association Ltd.—New Delhi
- The Madhya Pradesh Stock Exchange—Indore
- The Hyderabad Stock Exchange Ltd.—Hyderabad
- Bangalore Stock Exchange Ltd.—Bangalore
- U.P. Stock Exchange Association—Kanpur
- Cochin Stock Exchange Ltd.—Cochin
- Pune Stock Exchange Ltd.—Pune
- The Ludhiana Stock Exchange Ltd.—Ludhiana
- Mangalore Stock Exchange Ltd.—Mangalore
- The Magadh Stock Exchange Ltd.—Patna (Bihar)
- Jaipur Stock Exchange Ltd.—Jaipur (Rajasthan)
- The Gohati Stock Exchange Ltd.—Gohati
- The Vadodara Stock Exchange Ltd.—Vadodara
- Saurashtra Stock Exchange—Rajkot (Gujarat)
- Bhubane ishwar Stock Exchange Association Ltd.—Bhubaneshwar
- Thiruva nanthapuram Stock Exchange Ltd.—Kerala.
![]()
Question 9.
What do you mean by NSEI ? What are its objectives ?
Answer:
The I National Stock Exchange of India (N.S.E.I.) was established in the form of a public limit’ »d company in 30th November 1992 with a paid up capital of Rs. 25 crore. On its recognition as a stock exchange under the securities contracts act 1956 in April 1993 NSEI comment Jed operations in the wholesale debt market segment in June 1994. The capital market segrpent commenced operations in November 1994 and operations in derivatives segment commenced in June 2000.
It is an e exchange where business is carried on in the securities of the medium and large sized compar lies and the government securities. On the basis of the transactions of securities done on NSJ 31, it can be divided into two parts :
(i)Whole sale debt market
(ii) Capital market segment.
NSE i has removed the short comings of traditional share markets. It has attempted to provide be facilities to investors.
Objectives of NSEI: NSEI is established for the following objectives :
- To reduce the transaction costs.
- To promote trading facilities for equities and debt instrument throughout the nation
- To reform Indian securities market in terms of market practices.
- To establish a stock exchange of international level.
- It aims at the settlement of securities, deals within short period through easy and quick process.
- To set up the agenda for useful and effective change in the securities market.
Question 10.
Write the importance of capital market ?
Answer:
The various characteristics of market
- Here transactions in long-term funds take place.
- In capital market, shares, debentures and securities are bought and sold.
- Capital market is emerging and well-organized.
- Capital market consists of different institutions having their own interest and limits dons.
- It is a Barometer of national growth and dynamic economy.
Question 11.
Write the importance of capital market ?
Answer:
Following are the importance of capital market:
- Capital market assist in national capital formation and development.
- Capital market plays important role in capital investors and money savers.
- Capital market provides liquidity to investors to invest securities.
- A number of financial intermediaries work in capital market such as banks, merchants exchanges etc.
- Capital market helps to generate savings in the country channelizing the same into small investments in different fields.
- It helps in the mobilization of capital.
- The goods- are found in market in the same way long term, medium term and short term loans can be found in capital market.
- It creates saving tendency among the public.
- The head of capital market is the Reserve Bank of India which is the Banker’s bank, it helps in controlling the credit.
- Capital market helps in the agricultural, industrial and commercial development of the nation.
- In various areas of business organisation capital is needed and it is fulfilled through capital market.
- Interest rates remain same due to organised capital market.
- Directors and managers of company also give loans when need
- Capital market fulfills the need of capital.
![]()
Question 12.
Discuss some characteristics of primary market.
Answer:
The features/characteristics are :
- New securities : It deals with new securities only.
- Direct issue: Securities can be issued directly by issues on through intermediaries.
- Direct promotion of capital market: It promotes capital formatic m by use this funds is investment in plants machinery etc.
- Price determination : Prices of securities, generally, are determined by the management of the respective company.
- Place : There is no fixed place for primary market.
Question 13.
Explain the functions of Share Market or Stock Exchange.
Answer:
The functions of stock exchange are as follows :
1. Establishing fixed market: Stock exchange establishes a fixed place or market for securities because for the purchase and sale of securities a fixed market is necessary which is provided by stock exchanges.
2. Liquidity of capital : Stock exchange is completely a capital market. Different types of securities are purchased and sold here. That’s why an owner of securities can re convert this investment into cash. In this way stock exchange enhances the liquidity of cap
3. Evaluation: Stock exchange is totally a market of shares. Here there are experts to evaluate the shares and other securities. Correct evaluation of all the secretes are do by the experts is possible through stock exchanges. Thus investors can safely invest with the help of stock exchanges.
4. Helps in capital formation for new companies : All the new companies need capital, which is difficult for these new companies to form. Thus, through stock exchange it becomes easy to form capital for such type of new firms.
5. Provides business information : Stock exchanges provide necessary information on about securities and capital market to all its members. These information are very useful ft or the member in knowing the general business trends.
6. Contribution to economic growth: Stock exchange encourage the people to their money is securities. This money is invested in industries which helps in the economic development of the nation. Stock exchange acts as a barometer of nation’s economic development and progress.
7. Protection of securities: Various types of securities are transacted in stock exchange. Every transaction takes place under securities contracts (Regulation) Act 1956. The interests of the investors are fully protected. The members of the stock exchange must follows the rules and regulation of stock exchange.
8. Publication : Stock exchange publishes different types of information useful in business. It publishes information in magazines, daily news papers, directories etc. related with stock exchange to common people.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain the concepts of primary and secondary markets.
Answer:
1. Primary market : The place from where the public directly receives the capital first time as called primary market. Though this system the company issues new shares and debentures to public and forms capital. The ownership is transferred from company to the buyer. There is no fixed location of primary market. During the establishment of company the shares are issued and capital.is formed which is called primary capital. The capital which is received first time from the public through any medium is called primary capital
2. Secondary market: Under secondary market capital is formed or received from various sources and again it is invested this process is called secondary market. Generally it is known as stocks exchange where shares, securities etc. are bought and sold. Secondary market is located at a specified place. The secondary market creates a cluster of shares and stock brokers, underwriters and other well versed in financial matters.
![]()
Question 15.
What services are provided by SEBI investors ?
Answer:
The following services are provided by SEBI to its investors :
1. Liquidity of Investment: A stock exchange ensures liquidity of investment by ready marketability of securities. Investors can avail of services of expert professionals who operate on the stock exchange.
2. Collateral Security : As the securities dealt in stock exchanges are negotiable they can be pledged as ‘collateral security’ for raising loans.
3. Safe and Fair Dealings : A stock exchange ensures safe and fair dealings in securities. It makes scrutiny before listing.
4. Educate the Public : Wide publicity of working of a stock exchange helps to educate the public. Investors are able to find out the market value of their investment. They can make a rational choice among various securities. Some stock exchanges publish data and reports. They serve as clearing house of business information and provide advice and guidance to investors.
5. Quick Disposal: Facility for quick disposal of securities at the stock exchanges helps to minimize the risk of investment in securities. It becomes possibility to diversify investments and risks.
Question 16.
What are its trading process of NSEI ?
Answer:
1. Placing the order : In this the seller or purchaser gives information about securities like name of company, price, number, time etc.
2. Conveying the message to computer : The terminal operator after receiving the order feeds it in the computer. NSEI established in all parts of our country continuous feeds the orders in computer.
3. Starting of matching process : As soon as the computer receives messages or orders, it starts the matching process. While matching orders, the best matching order is sought to be found.
4. Accepting orders : After selecting the best matching of buying and selling orders, its list is obtained on computer screen immediately. It tells us at what rate, time and to whom order has been transacted.
5. Delivery and Payment: The delivery and payment are made according to the rules of NSEI after the transaction has been settled.
![]()
Question 17
What do you mean by OTCEI ? What are its objectives ?
Answer:
The OTCEI was established under section 25 of the companies act 1956 in October 1990. Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI), Unit Trust of India (UTI), Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC), Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), SBI capital market limited and Canbank financial services limited are the promoters of OTCEI, The need of OTCEI was felt due to the existance of large number of new and small companies which remain unnoticed and consequently their shares remain largely untraded. The OTCEI is a completely computerised in which buying and selling of securities is absolutely transparent.
Control: The functions and activities of OTCEI is under the supervision of government of India and SEBI.
Objectives : The objects of the establishment of the OTCEI are as follows :
- To maintain the liquidity in the securities of small companies.
- To provide speedy solution to the problems of investors.
- To maintain the transparency of transactions.
- To bring the stock exchange within the reach of an ordinary man.
- To provide facilities for listing of small companies.
Question 18.
Write the special features of secondary market.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of secondary market:
1. It creates liquidity: It creates liquidity in securities. By liquidity we mean changing of securities in cash very soon. This work is done by secondary market.
2. It comes after primary market: Under secondary market public do not get the capital first time, under secondary market capital is formed or received from various sources and again it is invested this securities are first sold in primary market and then in secondary market.
3. It has a particular place : Secondary market is located at a particular place which is called an exchanges. It is not compulsory that selling and buying of shares should be done through exchange also. Two persons can do it directly.
4. It encourages new investments : In share market the rates of shares goes on changing. To take advantage of this situation new investors enters this market which encourages industrial sectors.
![]()
Question 19.
What is meant by money market ? Discuss its characteristics.
Answer:
Money market refers to that market where transaction of lending and borrowing of short term funds take place. It is divided into two sectors i.e., organised market and unorganised market. Organised market consists of Reserve Bank of India on the other hand unorganised market consist of indigenous bankers and money lender.
The characteristics of money market:
- Dealing in short term fund: Money market provides short term funds for use. By short term use means four period up to one year.
- Meeting short term financial needs : Money market focuses on meeting the short term financial requirement.
- Safety : The securities of money market and normally safe. They have minimum risk of default due to shorter term and financial soundness of the issuers.
- High liquidity: These are highly liquid because they can be changed into cash very easily.
- Types of Securities : Treasury bills, certificates of deposits, commercial bills etc. are issued for raising capitals.
- Control: Reserve Bank of India controls this type of market.
Question 20.
Write the characteristics of Treasury Bill.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of Treasury Bill :
(1) Treasury bill is basically an instrument of short term borrowing by the government of India maturing in less than one year.
(2) They are also known as zero coupon bonds issued by Reserve Bank of India. On behalf of the central government to meet its short-term requirement of funds.
(3) Treasury bills are issued in the form of promissory note. They are highly liquid and have assured yield and negligible risk of default.
(4) They are issued at a price which is lower than their face value and rapid at par. The difference between the price at which the treasury bills are issued and their redemption value is the interest receivable on them and is called discount.
Question 21.
Write the features of call money.
Answer:
Following are the features of call money :
(1) Call money is short term finance repayable on demand, with a maturity period of
one day to fifteen days, used for inter-bank transactions. .
(2) Commercial banks have to maintain a minimum cash balance known as cash reserve ratio.
(3) The Reserve Bank of India changes the cash reserves ratio from time to time which in turn affects the amount of funds available to be given as loans by commercial bank.
(4) Call money is a method by which banks borrow from each other to maintain the cash reserve ratio. The interest rate paid on call money loans is known as the call rate. It is a highly volatile rate that varies from day to day and sometimes even hour to hour.
(5) There is an inverse relationship between call rates and other short term money market instruments such as certificates of deposits and other commercial papers.
Question 22.
Describe the function of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Answer:
The functions of SEBI are as follows :
- To protect the interests of investors in the security market and to properly develops the security market.
- 10 regulate the business being done in the security market. .
- To check the function of stock brokers, share transfer agents, trustees, sub-brokers etc. and register them.
- To register and regulate investment schemes like mutual food.
- To carry on research work related with security market.
- To restrict and prohibit unfair and fraudster of trade practices related with security market.
- To promote and control self regulatory organization.
- To provide education to the investors related with securities.
- To check insiders trading in securities.
Finance Market Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the importance of financial management.
Or
“Finance is the life-blood of business.” Explain in any five points.
Answer:
1. Basis of success of enterprise : Irrespective of the size of organization, financial management paves the way for success of any enterprise, as proper management of funds is assured
2. Increases efficiency: Financial management ensures smooth running of enterprise, as it is essential in every stage of business. Finance is not only essential for promotion but marketing and winding-up.
3. Essential for determination of capital sources : Financial management helps identify proper sources of capital and raise appropriate funds required. Hence, it is very essential.
4. Determination of capital structure: Capital structure refers to the combination of various sources, or the ‘mixes’ of various sources of capital. It is the composition of various sources. Financial management helps in deciding the appropriate capital structure.
5. Best utilization of available funds: Financial management ensures best utilization of existing funds. Financial management consists of estimation of capital, raising of capital and use of it in a judicious way. Hence, the available funds are used in the best possible way.
6. Importance to the Shareholders and Investors : Shareholders and other investors always expect the safety of their money. They invest their small savings in shares and other investment channels and they should be informed of the rate of return they will get on their investments. This is possible through financial management only. In the absence proper knowledge about the return on their investments, the investors may suffer loss at the hands of brokers or middlemen.
7. Importance to the Financial Institutes : The fundamental function of financial institutes is finance only. Therefore, these institutes should possess the required knowledge about financial management so that there is a proper balance between the safety of their money (capital) and its liquidity.
8. Importance to the Employees : Finance management leads to growth of an enterprise and it earns more profit. With growth in profit of the enterprise, the employees will be benefited. Therefore, financial management has both direct and indirect importance for the employees.
9. National Importance : Every developed or developing nation must possess the knowledge of proper financial management. This is the reason why a person having financial expertise is chosen as the finance ministry of the country. The importance of financial management becomes even more important in countries like India which have shortage of finance.
10. Importance to other Persons : Knowledge of financial management is also important for other persons like economists, mercantile experts, brokers, middlemen, politicians because every person in a society has to deal with finance. A person may hurt his financial planning in the absence of knowledge of financial management. Therefore, knowledge of financial management is necessary for every member of the society.
![]()
Questions 2.
Write the importance of personnel management.
Answer:
The importance of personnel management can be stated as follows :
1. To achieve targets: Targets of an enterprise can be achieved only if the personnel working in any enterprise are fully satisfied. This is possible if there exists a department to look after the requirements and pacify the grievances of personnel.
2. To face competition : In today’s cut throat competition, it is very hard to be ‘the best’. Mentally satisfied and physically strong personnel ensures that the targets are achieved on time and this work is done by personnel management.
3. Overall personality development: Under the guidance of personnel management, the employees live together and work with full cooperation and under proper discipline. It results in the overall development of the employees.
4. Universal need: For proper development of an enterprise and its success, a personnel management is essential. It is also essential for industries, profession, etc.
5. Increase in efficiency of employees: Proper training, good working environment, appraisals, rewards, etc. done by personnel management increases the efficiency of employees which ultimately helps the organization to achieve its predetermined objects.
Question 3.
Discuss the factors determine working capital requirements of a business enterprises.
Answer:
The capital invested in current assets such as stock of material and finished goods, bills receivable, short-term securities and cash at hand and cash at bank. The two senses of working capital are “Gross Working Capital” and “Net Working Capital”.
The factors which govern the amounts of working capital in a business are :
1. Nature of Business : Public utilities and service organizations require little working capital as sales are on cash basis. There is little time gap between production and sales and these enterprises do not maintain large stock of goods. In trading and manufacturing concerns, on the other hand large amount of working capital is needed to maintain stocks.
2. Size of the Business : The volume of business has a direct influence on working capital requirements. Large firms require greater working capital for investment in current assets and to pay current liabilities.
3. Production Cycle : The length or duration or production process also affects working capital requirement. Where production takes longer time, More working capital is required because more funds are needed for raw material, labour and other expenses. On the other hand, smaller production cycle need less working capital.
4. Turnover of Working Capital: Turnover implies the speed with which the working capital circulates in business. The rate of turnover of working capital is measured by the ratio of sales to current assets. More rapid is the flow of working capital, lesser is the need for working capital.
Question 4.
What is the meaning of financial management ? Give one definition of it. Write the main objectives of it.
Answer:
Meaning : Financial management is a functional activity of business management and it is a part of management. Financial management is responsible for the financial activities of a business. This is a group which deals with the finance, decision-making and formulating policies for the finance related activities of an enterprise. Financial management represents the wider interests of an enterprise and in this sense it is a watchdog of the enterprise. Financial management maintains coordination between sources of finance and their uses so that optimum utilization of the available finance could be made. Financial management includes cash flow, budget, credit, profit and loss, income etc.
Definitions : Different experts have defined financial management as under:
1. E.F.L. Breach says, “Financial management is that aspect of management which makes optimum and effective utilization of financial resources.”
According to a narrow view, the immediate objectives of financial management are to arrange for a suitable system for the organization’s liquidity, and profitability. But in a wider perspective, the objectives of financial management are to arrange for maximum financial facilities for the enterprise so that owners of the enterprise get the maximum benefit. Thus, main objectives of financial management have been proposed as under :
I. Profit Maximization : Traditionally, business is considered to be a profit-earning entity and profit has been considered to be the basis of measuring the efficiency and standard of an enterprise. Therefore, the primary objective every business is to earn the maximum profit. No limit has been demarcated as to what is ‘maximum profit’. Therefore, the following points should be kept in mind :
- Profit should be rational and justified;
- Social welfare should be kept in mind while earning profit;
- There should be a standard or decisive policy for earning profit;
- The profit earned should be used for social welfare also;
- Higher profit is a motivating factor for better business.
II. Maximization of wealth : It is a novel concept that value of wealth be maximized instead of maximizing profit. This will ensure growth of the business thereby benefiting the shareholders, managers, employees etc. With the increase in the value of the wealth of an enterprise, it will enjoy goodwill and will be stronger. Therefore, the objective of financial management should be to maximize the value of wealth.
III. Mobilizing adequate finance at minimum cost: The main objective of financial management is to arrange finance at minimum cost for the business because if cost increases than profit margin will reduce in business.
IV. Maximum rate of return : The objective of financial management is to get maxi¬mum returns on the invested capital so that shareholders can get maximum dividend and more interest can be given on debentures and apart from that various allowances can be given to employees.
Question 5.
What are the steps involves in trading procedure ?
Answer:
The Trading procedure involves the following steps :
1. Selection of a broker : The buying and selling of securities can only be done through SEBI registered brokers who are members of the Stock Exchange. The broker can be an individual, partnership firms or corporate bodies. So the first step is to select a broker who will buy/sell securities on behalf of the investor or speculator.
2. Opening D’mat Account with Depository : D’ mat (Dermaterialized) account refer to an account which an Indian citizen must open with the depository participant (banks or stock brokers) to trade in listed securities in electronic form. Second step in trading procedure is to open a D’mat account.
The securities are held in the electronic form by a depository. Depository is an institution or an organization which holds securities (e.g., Shares, Debentures, Bonds, Mutual Funds etc.). At present in India there are two depositories : NSDL (National securities Depository Ltd.) and CDSL (Central Depository Services Ltd.). There is no direct contact between depository and investor. Depository interacts with investors through depository participants only.
Depository participant will maintain securities account balances of investor and intimate investor about the status of their holdings from time to time.
3. Placing the Order : After opening the D’mat Account, the investor can place the order. The order can be placed to the broker either (DP) personally or through phone, email, etc. Investor must place the order very clearly specifying the range of price at which securities can be bought or sold, e.g., “Buy 100 equity shares of Reliance for not more than Rs 500 per share.
4. Executing the Order : As per the Instructions of the investor, the broker executes the order, i.e., he buys or sells the securities. Broker prepares a contract note for the order executed. The contract note contains the name and the price of securities, name of parties and brokerage (commission) charged by him. Contract note is signed by the broker.
5. Settlement: This means actual transfer of securities. This is the last stage in the trading of securities done by the broker on behalf of their clients. There can be two types of settlement.
(a) On the spot settlement : It means settlement is done immediately and on spot settlement follows. T + 2 rolling settlement’ This means any trade taking place on Monday gets settled by Wednesday :
(b) Forward settlement: It means settlement will take place on some future date. It can be T 5 or T + 7 etc. All trading in stock exchanges takes place between 9-55 am. and 3-30 pm. Monday to Friday.
Question 6.
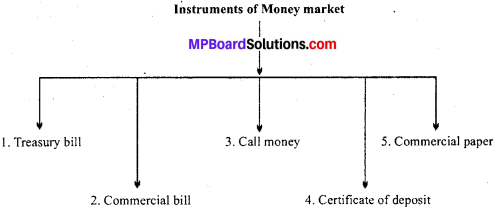
Explain the various documents or instruments of money market.

1. Treasury BUI: Treasury Bill: A Treasury bill is basically an instrument on mg by the Government of India maturing in less than one year. They are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds issued by the Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short-term requirement of funds. Treasury bills are issued in the form of a promissory note. They are highly liquid and have assured yield and negligible risk of default. They are issued at a price which is lower than their face value and repaid at par. The difference between the price at which the treasury bills are issued and their redemption value is the interest receivable on them and is called discount.
Treasury bills are available for a minimum amount of Rs 25,000 and in multiples therefore. Example: Suppose an investor purchases a 91 days Treasury bill with a face value of Rs. 1,00,000 for Rs. 96,000. By holding the bill until the maturity date, the investor receives Rs. 1,00,000. The difference of Rs. 4,000 between the proceeds received at maturity and the amount paid to purchase the bill represents the interest received by him. ,
2. Commercial paper: Commercial paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a fixed maturity period. It is issued by large and creditworthy companies to raise short-term funds at lower rates of interest than market rates. It usually has a maturity period of 15 days to one year. The issuance of commercial paper is an alternative to bank borrowing for large companies that are generally considered to be financially strong. It is sold at a discount and redeemed at par. The original purpose of commercial paper was to provide short-terms funds for seasonal and working capital needs.
For example, companies use this instrument for purposes such as bridge financing. Example : Suppose a company needs long-term finance to buy some machinery. In order to raise the long term funds in the capital market the company will have to incur flotation costs (costs associated with floating of an issue are brokerage, commission, printing of applications and advertising etc.). Funds raised through commercial paper are used to meet the flotation costs. This is known as Bridge Financing.
3. Call money : Call money is short term finance repayable on demand, with a maturity period of one day to fifteen days, used for inter-bank transactions. Commercial banks have to maintain a minimum cash balance known as cash reserve ratio. The Reserve Bank of India changes the cash reserve ratio from time to time which in turn affects the amount of funds available to be given as loans by commercial banks. Call money is a method by which banks borrow from each other to be able to maintain the cash reserve ratio. The interest rate paid on call money loans is known as the call rate. It is a highly volatile rate that varies from day-to-day and sometimes even from hour-to-hour.
There is an inverse relationship between call rates and other short-term money market instruments such as certificates of deposit and commercial paper. A rise in call money rates makes other sources of finance such as commercial paper and certificates of deposit cheaper in comparison for banks raise funds from these sources.
4. Certificate of deposit:Certificate of deposit: Certificates of deposit (CD) are unsecured, negotiable, short-term instruments in bearer form, issued by commercial banks and development financial institutions. They can be issued to individuals, corporations and companies during periods of tight liquidity when the deposit growth of banks is slow but the demand for credit is high. They help to mobilize a large amount of money for short periods.
5. Commercial bill : A commercial bill is a bill of exchange used to finance the working capital requirements of business firms. It is a short-term, negotiable, self-liquidating instrument-which is used to finance the credit sales of firms. When goods are sold on credit, the buyer becomes liable to make payment on a specific date in future. The seller could wait till the specified date or make use of a bill of exchange. The seller (drawer) of the goods draws the bill and the buyer (drawer) accepts it.
On being accepted, the bill becomes a marketable instrument and is called a trade bill. These bills can be discounted with a bank if the seller needs funds before the bill matures. When a trade bill is accepted by a commercial bank, it is known as a commercial bill.
![]()
Question 7.
Write the objectives and functions of SEBI.
Answer:
Objectives : The objectives of the establishment of SEBI are as follows:
- The main objective of SEBI is to provide security to the investors.
- To attract the savings of the people to the capital market.
- To keep an eye on activities of the brokers in order to control the capital market.
- To promote development of securities market.
- To provide efficient services to all the parties operating in the capital market.
Functions of SEBI: The functions of SEBI are as follows :
- To protect the interests of investors in the security market and to properly develops the security market.
- To regulate the business being done in the security market.
- To check the function of stock brokers, share transfer agents, trustees, sub-brokers etc. and register them.
- To register and regulate investment schemes like mutual food.
- To carry on research work related with security market.
- To restrict and prohibit unfair and fraudster of trade practises related with security market.
- To promote and control self regulatory organization.
- To provide education to the investors related with securities.
- To check insiders trading in securities.
Question 8.
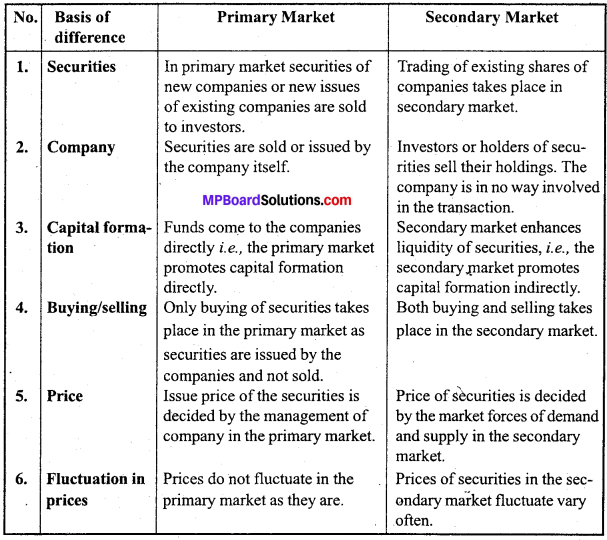
Differentiate between money market and capital market.
Answer;
Differences between Money Market and Capital Market:
Question 9.
What are the factors affecting fixed capital ?
Answer:
The various factors affecting fixed capital are :
1. Nature of industry : Fixed capital requirement largely depends on the nature of industry. When there is a need of land, building, machinery etc. in industry, the need of capital increases.
2. Nature of production : The requirement of fixed capital also depends on the nature of production, whether it is capital based or labour based.
3. Scope of business : If business is only a buyer or only a seller the capital requirement is less and if it is both the capital needed is comparatively more.
4. Expansion of business : If business is to be expanded in future then fixed capital is required in great sum. Due to modem machines and management the expenses increases. So capital requirement increases.
5. Preliminary expenses : The need of fixed capital will increase if the promoters at the time of establishment of company speed more on salary of promoters, establishment expenses, purchase of patent etc.
6. Attitude of management: If the manger wants to enter in the market as a major producer from. The very beginning than more fixed capital will be needed.
Question 10.
Describe the establishment, objects and advantages of Unit Trust of
India (UTI)
Answer:
Unit Trust of India (UTI):
The basic idea underlying the creation of the unit trust, as with similar trusts in other [ countries is to afford the small savers, a means of acquiring a share in the widening prosperity
based on steady industrial growth of the country through providing facilities for investment j which combines the benefit of wide diversification, a reasonable return and expert services I of management talent. The trust commenced its operations with affect from July, 1964.
Objectives of UTI
(i) It mobilizes savings of the community and channelizes them into productive investment. By promising savers triple benefits of safety, liquidity and profitability of investments, the trust encourages individual savings.
(ii) It gives everyone a chance to indirectly own shares and debentures in a large number of select companies and thus enables the investor to share in the widening prosperity of industrial growth.
Management
The trust is managed by a board of trustees consisting of 11 persons including some of the distinguished men in finance and business. The chairman of the board is appointed by the central Govt, in consultation with IDBI. The executive trustee and four other members : are appointed by IDBI. The remaining members are appointed by Reserve bank of India,Life Insurance Corporation and Commercial Banks.
Performance of Unit Trust in the Field of Investment of Funds
Investment of funds constitutes another aspect of operations of UTI. During the past 33 years of its life, the trust has been able to build up sizeable funds. As on 30th June, 1984 aggregating Rs. 1261-33 crores is collected. During the year 1983-84, the investable funds recorded funds recorded a marked rise of Rs. 391 -09 crore.
The cardinal feature of the trust’s investment activity has been to build a balanced flexible investment portfolio composed of corporate securities, Govt, securities and other investments representing fixed deposits with companies, advance deposits for shares and debentures, bridging finance, application money and money at call and short notice so as to ensure reasonable return with safety of capital and capital appreciation.
Units are gaining popularity because they are highly liquid in the sense that an investor can sell them whenever he wants.
Uses of resource : The fund of UTI has been invested in so many ways.
The percentage of investment is as follows :
- On shares and debentures of companies 55%
- On fixed deposits and other deposits in the bank 45%
![]()
Question 11
What is the functions of finance management ?
Answer:
Finance is required in every field like business, industry, commerce, professional service etc. All persons working in these fields need knowledge of financial management. In each field, the person who manages and plans the financial resources is called the finance manager. A finance manager performs the following functions :
(A) Administrative Functions : All these functions relate to decision-making and the finance manager has to perform all these functions as the general functions. These are :
- To make prior financial estimates;
- To make financial planning;
- To organize the financial activities;
- To maintain coordination between different departments.
(B) Executive Functions: “The finance manager performs certain executive functions which are as under:
1. Arrange/Organize Finance: A finance manager has to find and arrange the various sources of finance required for the enterprise sd that, on the basis of the finance available, the operations of the enterprise may be carried on.
2. Allotment of Available Funds : The funds available with the finance manager are meant for requirements of the entire enterprise. Therefore, it is the responsibility of the finance manager to allot funds as and where needed in the enterprise.
3. Management of Assets : Under these are covered activities like purchase of current and fixed assets, arrangements for their safety, maintenance etc. Which are carried on under the instructions of the finance manager. The finance manager has also to consider, before allotting funds, the use and justification for the funds in different departments.
4. To Organize Expenditure : The finance manager should prepare budget estimates for expenditure required in the entire enterprise and invest the same in a planned manner. For this, the finance manager has to consider the expenditure on pay, interest, taxes, development activities etc.
5. Profit Planning : The finance manager makes proper planning for increasing the profits. He takes necessary steps to increase the profitability e.g., to fix proper prices, to control the costs, to control the expenditure, to exercise control on unproductive expenditure.
6. To Submit Reports: The finance managers submits various a few important reports from time to time which include report on availability of funds, monthly income and expenditure statement, position of balance of cash, a note indicating the financial position of the enterprise etc.
7. To Maintain Records : The finance manage has to prepare records of the various documents relating to finance and preserve them so that they may be used for future planning.