MP Board Class 12th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Management
Financial Management Important Questions
Financial Management Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
The main function of Financial Management is :
(a)Financial planning
(b) To receive fund .
(c) Distribution of net profit
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(d) All the above.
Question 2.
The cheapest source of finance is :
(a) Debenture
(b) Equity share capital
(c) Preference share
(d) Retained earning.
Answer:
(d) Retained earning.
Question 3.
Fixed assets should be financed through :
(a) A long-term liability
(b) A short-term liability
(c) A mix of long and short-term liabilities
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(c) A mix of long and short-term liabilities
Question 4.
Current assets of a business firm should be financed through :
(a) Current liability only
(b) Long-term liability only
(c) Partly from both types i.e., long and short-term libilities
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(c) Partly from both types i.e., long and short-term libilities
Question 5.
Other things remaining the same, an increase in the tax rate on corporate profit will:
(a) Make debt relatively cheaper
(d) Make debt relatively less cheap home
(c) No impact on cost of debt
(d) We can’t say
Answer:
(a) Make debt relatively cheaper
Question 6.
On equity share the rate of dividend is …………..
(a) Not fixed
(b) Fixed
(c) Both (a) and
(b) (d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Not fixed
Question 7.
Capital structure refers to the composition of …………..
(a) Long-term funds
(b) Short-term funds
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Long-term funds
Question 8.
It is a source of working capital …………..
(a) Preference shares
(b) Periodic loan
(c) Public deposit
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(d) All the above.
Question 9.
Determinants of working capital are…………..
(a) Size of organization
(b) Period of construction
(c) Availability of raw material
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(d) All the above.
Question 10.
For joint stock company to pay dividend is ………….
(a) Voluntary
(b) Compulsory
(c) Necessary
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Voluntary
Question 11.
Bonus decision is the determinants of …………..
(a) Quantity of profit
(b) Liquidity of fund
(c) Age of the company
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(d) All the above.
Question 12.
Out of it which is the element of capital structure…………..
(a) Cash flow situation
(b) Interest ratio
(c) Age of the firm
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(d) All the above.
Question 13.
Current assets are those assets which are converted into cash…………..
(a) Within 6 months
(b) Within 1 year
(c) Within a month and 3 years
(d) Within 3 years to 5 years.
Answer:
(d) Within 3 years to 5 years.
Question 14.
Debenture holder of a company is called as …………..
(a) Debtor
(b) Creditor
(c) Owner
(d) Servant.
Answer:
(b) Creditor
![]()
Question 15.
Higher dividends per share is associated with :
(a) High earning, high cash flows, unusable earning and higher growth opportunities.
(b) Low earning, high cash flows, stable earning and lower growth opportunities
(c) High earning, high cash flows, stable earning and lower growth opportunities
(d) High earning, low cash flows, stable earning and lower growth opportunities.
Answer:
(c) High earning, high cash flows, stable earning and lower growth opportunities
Question 16.
A decision to acquire a new and modern plan to upgrade an old
(a) Financing decision
(b) Working capital decision
(c) Investment decision
(d) Dividend decision.
Answer:
(c) Investment decision
Question 17.
Companies with higher growth paternal are likely to :
(a) Pay lower dividends
(b) Pay higher dividends
(c) Dividends are not affected by growth consideration
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Pay lower dividends
Question 18.
Which is not the cause of over capitalization :
(a) High promotion expenses
(b) Over capital issue
(c) Formation of company in inflation period
(d) Underestimate of earings.
Answer:
(d) Underestimate of earings.
Question 19.
Which is not the cause of under capitalization :
(a) Formation of business during deflation
(b) Under estimate of capital requirement
(c) Liberal dividend policy
(d) High standard of efficiency.
Answer:
(c) Liberal dividend policy
Question 20.
What is not included in fixed capital:
(a) Machines
(b) Building
(c) Furniture
(d) Stock.
Answer:
(d) Stock.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
- In business the form of mixture of capital is called
- refers to the act of deciding in advance the quantum of fund requirements of a firm.
- If the actual value of assets of a company is less than the book value, it is called
- When rate of dividend of equity shares is distributed at a higher rate, such type of situations is called
- capital is utilized to maintain day to day activities.
Answer:
- Capital structure
- Capitalization
- Over capitalization
- Under-capitalization,
- Working capital,
Question 3.
Write the answer in one word/sentence :
- Which ensures availability and profitable utilization of acquired funds in less cost ?
- What is the result by promotion expenses ?
- What is the situation faced by a company when capital is estimated less ?
- In which situation more wages are demanded by workers ?
- What is the mutual and proportional relation of various sources of long-term in an enterprise called ?
- Which is the life blood of business ?
- When is the issue of debentures profitable ?
- Which is called the heart of financial planning ?
- When is asset value more in an organization ?
- Which is undesirabile or capitalization or under capitalization ?
- What is the financial planning for five years or more than five years called ?
- What is the tendency to get more profit on preferential share called ?
- Who respresants the quantity of capital ?
- Which capital is used to purchase raw material ?
- What is the difference between the current asset and current liability known ?
- Who makes investment decision ?
- What is the period of long-term ferm finance ?
- What is the main objective of financial management ?
- How finance should be used in financial planning ?
- By what control is done on financial work ?
Answer:
- Financial management
- Over capitalization
- Under capitalization
- Under capitalization
- Capital structure
- Finance
- In depression
- Financial accountancy
- When market value of shares are more
- Both
- Long-term financial objectives
- Preferential shares
- Capitalization
- Working capital
- Working capital
- Financial Manager
- Not more than 12 Months
- Profit maximization
- Long-term finance
- Financial Management.
Question 4.
Write true or false :
- Nature of goods affect the requirement of fixed capital.
- Financial planning is the main function of financial management.
- Financial management is a part of business management.
- Need of study of financial management is not for shareholders.
- Term “capitalization” is used at all levels of capitalization.
- Working capital is required for long-term period.
- Fixed assets are arranged through long-term funds.
- Equity shareholders enjoy voting rights.
- In capital structure working capital is included.
- By structure of capital we mean fixed capital.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True.
Question 5.
Match the columns :
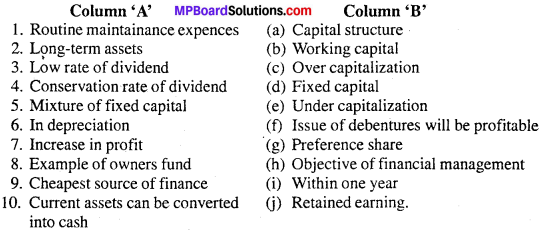
Answer:
1. (b)
2. (d)
3. (c)
4. (e)
5. (a)
6. (f)
7. (h)
8. (g)
9. (j)
10. (i)
Financial Management Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the cheapest source of finance ?
Answer:
Loan.
Question 2.
What do you mean by business finance ?
Answer:
Financial management is the part of general management. It is concerned with the managing finance of the business for smooth functioning and successful accomplishment of the enterprise objectives.
Question 3.
Why is finance needed ?
Answer:
Finance is needed for establishing business to run it and for its modernization.
Question 4.
What do you mean by financial risk ?
Answer:
The risk of default of payment is called financial risk.
Question 5.
What do you mean by working capital ?
Answer:
Working capital is aggregate of current assets.
Question 6.
Which is the most expensive capital for a company ?
Answer:
For any company the most expensive capital is equity share capital whereas devident on it is not fixed.
Question 7.
What do you mean by over capitalization ?
Answer:
An enterprise is said to be over capitalized when its long-term funds are more than the amount of proper capitalization as justified by its requirements.
Question 8.
What do you mean by equity trade or trading on equity ?
Answer:
Trading on equity means borrowing funds at reasonable rate with the help of share capital. Trading on equity also affects the capital structure of an enterprise.
Question 9.
What do you mean by capitalization ?
Answer:
Capitalization is an important constituent of Financial plan. Capitalization refers to the act of deciding in advance the quantum of fund requiremets of a firm.
Question 10.
What do you mean by fixed capital ?
Answer:
Fixed capital refers to the amount invested to acquire fixed assets. Fixed capital provides the basic foundation on which the structure of business is laid.
Question 11.
What do you mean by watered capital ?
Answer:
When any assets is purchased more than its actual price then it is called watered capital.
Question 12.
What do you mean by financing decision ?
Answer:
Financing decision is about the quantum of finance to be raised from various long term sources.
Question 13.
Write the names of two factors which affect financial decision.
Answer:
1. Cost
2. Risk
Question 14.
Write the name of two factors which affect the investment decision.
Answer:
(a) Cash flows on project
(b) The rate of return.
Question 15.
What are public deposits ?
Answer:
Public deposit is an important source of business finance. As bank accepts the savings of public so also company does. The company receives funds in the form of public deposits to run their business.
Question 16.
What do you mean by gross working capital and net working capital ?
Answer:
Gross working capital deals with the problems of managing individual current assets in day today operations. The net working capital represents excess of current assets over current liabilites.
Question 17.
Write two needs of working capital.
Answer:
The need of working capital arises for :
- For purchasing raw material
- For payment of salaries and wages.
Question 18.
“Working capital affect both liquidity and profitability of business” how ?
Answer:
Working capital are more liquid but they contribute less in profitability. Thus with more working capital liquidity increases but profitability decreases.
![]()
Question 19.
What do you mean by financial planning ?
Answer:
Financial planing is the process of determine the objective policies, procedures, programmed and budgets to deal with financial activities of enterprise. It is an intellectual process which decides in advance the capital structure and capitalization of enterprise.
Question 20.
When do shareholders get profit ?
Answer:
Shareholders get profit when market value of their shares increases.
Question 21.
What do you means by cash flow ?
Answer:
Cash flows means series of cash receipts and payments over a specific period of time.
Question 22.
What is dividend ?
Answer:
Dividend is that portion of profit which is distributed to the shareholders.
Question 23.
What do you mean by production cycle ?
Answer:
Production cycle means the time gap between receiving the raw material and turning them into finished products.
Question 24.
What do you mean by equity shares ?
Answer:
Equity shares are regarded as comer store of the financial structure of a company without which a company can’t be founded. Management procures debt and preference shares capital against the strength of these shares. Equity shares represent the owner’s equity.
Question 25.
“The main aim of Financial Management is to minimise risk”. Explain.
Answer:
There is always a risk in carrying business activities. These risks may be due to various unforeseen natural economic and physical causes. Future is always uncertain, so element of risk will always remain there in business. Efforts are made so that these risk may be minimised.
Question 26.
What do you mean by capital budgeting ?
Answer:
Capital budgeting is long financial decision making of the firm. It requires decision regarding the purchase of new assets taking into consideration the utility of various other uses of assets.
Question 27.
What do you mean by trading on equity ?
Answer:
Trading on equity means borrowing funds at reasonable rates with the help of share capital. Trading on equity also affects the capital structure of an enterprise. It should be adopted by the enterprise which have regular income and have good will.
![]()
Question 28.
What do you mean by divident decision ?
Answer:
Dividend decision is to take decision by the manager how much profit earned by the company (after paying tax) is to be distributed to the share holders and how much of it should be retained in the business.
Question 29.
On what overall financial risk depends ?
Answer:
The overall financial risk depends upon the proportion of debt in the total capital.
Question 30.
What do you mean by floation cost ?
Answer:
The fund raising exercise also costs something which is called floation cost.
Question 31.
Write the meaning of Financial planning ?
Answer:
Financial planning is the process of determining the objectives, policies, procedures, programmes and budgets to deal with financial activities of enterprise.
Question 32.
What do you mean by cash budget ?
Answer:
By cash budget we mean expected incoming and outgoing of cash in a particular time.
Question 33.
Write the meaning of over capitalization.
Answer:
When the earnings of enterprise are not large enough to yield a fair return then it is said to be over capitalization.
Question 34.
What are the main source of funds for a shareholders ?
Answer:
The main sourcess of funds for a firm are shareholders fund and borrowed funds.
Question 35.
What do you mean by borrowed funds ?
Answer:
Borrowed funds refer to finance raised as debentures or other forms of debt. Interest on borrowed funds have to be repaid at a fixed time.
Financial Management Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Capital structure.
Answer:
The term ‘Capital Structure’ refers to the composition or make-up of the amount of long-term financing. According to Gerstanberg, “Capital structure means the type of securities to be issued and the proportionate amounts that make up the capitalization.” It includes all long-term capital resources viz., loans, reserves, shares and bonds. Symbolically,Capital structure = Owner’s capital + Debt capital.Owner’s capital consists of long-term funds provided by the company’s owners. Debt capital includes any type of long-term funds obtained through borrowings. The ratio between owner’s capital (equity) and debt capital is decided under capital structure.
Question 2.
Discuss the two objectives of Financial Planning.
Answer:
Financial Planning strives to achieve the following two objectives :
1. To ensure ‘Availability of Funds’ whenever these are required: This includes a proper estimation of the funds required for different purposes such as for the purchase of long term assets or to meet day-to-day expenses of business etc.
2. To see that the Firm does not raise resources unnecessarily : Excess funding is almost as bad as Inadequate funding. Efficient financial planning ensures that funds are not raised unnecessarily in order to avoid unnecessary addition of cost.
Question 3.
What is ‘Financial risk’ ? Why does it arise ?
Answer:
It refers to the risk of company not being able to cover its fixed financial costs The higher level of risks are attached to higher degrees of financial leverage with the increase in fixed financial costs, the company its also required to raise its operating profit (EBIT) to meet financial charges. If the company cannot cover these financial charges, it can be forced into liquidation.
![]()
Question 4.
Define a ‘Current assets’ and give four examples.
Answer:
Current assets are those assets of the business which can be converted into cash within a period of one year. Cash in hand or at bank, bills receivable, debtors, finished goods inventory are some of the examples of current assets.
Question 5.
Financial management is based on three broad financial decisions. What are these ?
Answer:
Financial management is concerned with the solution of three major issues relating to the financial operations of a firm corresponding to the three questions of investment, financing and dividend decision. In a financial context, it means the selection of best financing alternative or best investment alternative. The finance function therefore, is concerned with three broad decision which are as follows :
1. Decision : The investment decision relates to how the firm’s funds are invested in different assets.
2. Financing Decision : This decision is about the quantum of finance to be raised from various long term sources and short term sources. It involves identification of various available sources of finance.
3. Dividend Decision : This decision relates to distribution of dividend. Dividend is that portion of profit which is distributed to shareholders, the decision involved here is how much of the profit earned by company is to be distributed to the shareholders and how much of it should be retained in the business for meeting investment requirements.
Question 6.
What is the main objective of financial management ? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Primary aim of financial management is to maximise shareholder’s wealth, which is referred to as the wealth maximisation concept. The wealth of owners is reflected in the market value of shares, wealth maximisation means the maximisation of market price of shares.
According to the wealth maximisation objective, financial management must select those decisions which result in value addition, that is to say the benefits from a decision exceed the cost involved. Such value addition increase the market value of the company’s share and hence result in maximisation of the shareholder’s wealth.
Question 7.
Discuss about working capital affecting both the liquidity as well as profitability of a business.
Answer:
The working capital should neither be more nor less than required. Both these situations are harmful. If the amount of working capital is more than required, it will no doubt increase liquidity but decrease profitability. For instance, if large amount of cash is kept as working capital, then this excessive cash will remain idle arid cause the profitability to fall.
On the contrary, if the amount of cash and other current assets are very little, then lot of difficulties will have to be faced in meeting daily expenses and making payment to the creditors. Thus, optimum amount of both current assets and current liabilities should be determined so that profitability of the business remains intact and there is no fall in liquidity.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the functions of Financial Management ?
Answer:
Functions of financial management:
- Forecasting financial needs.
- Capital budgeting.
- Working capital management.
- Making finance decision.
- Making dividend policy decision.
- Appraisal of finance performance.
- Communication of finance performance. In addition to the above functions following advisory functions are performed :
- Management of assets
- Management of funds.
According to Ernest Dale, the financial management performs the following functions:
- Safe custody of funds and investment
- General accounting work
- Maintenance of books of accounts
- Preparation of financial statement and reports
- Auditing of books of accounts
- Cash management
- Cash disbursement system
- Calculation of accounting rations
- Preparation of cash flow and funds flow statement
- Cost accounting
- Payroll accounting and disbursement.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the importance of financial planning.
Answer:
The importance of financial planning are as follows :
1. Successful! promotion of business : Before starting any business, it is essential to make a perfect financial plan for achieving success. A financial plan should be made keeping in mind the size and expected expansions of business before the starting of business. Other plans remain incomplete without this plan.
2. Efficient management of business : For each and every activity of business finance is required, without sufficient finance any enterprise cannot be managed properly. Finance is required for establishment of business, purchase of asset raw materials, distribution of salary, etc.
3. Development and expansion of business: To earn more and more profit in business different types of policies related to development are made. To achieve this objective business is expanded. Proper financial plans are helpful in facing the financial problems.
4. Business liquidity : Due to successful financial plan sufficient amount of liquid fund can be kept in business. The important requirement of financial plan is easy liquidity of assets to meet the routine capital needs.
5. For future development of business : A good financial plan is essential for the smooth woking of an enterprise. To attract new industrial units perfect capital planning is compulsory.
6. Proper coordination among capital sources : Through efficient financial planning proper coordination among various sources of capital can be established. This reduces business risk and doesn’t affect goodwill in negative manner.
7. Safety of capital: Effective financial helps in providing safety to capital. It proves very helpful in facing the risks like incirease or decrease in demands, fashion, ups and downs of future, etc.
![]()
Question 10.
Discuss the aims/object:s of financial management.
Or
Discuss some functions of financial management.
Answer:
1. Increase in profit: A :firm should always increase its revenues in order to maximize its value. It is a normal practice for a firm to formulate and implement all possible plans of expansion and take every opportunity to maximize profit.
2. Reduction in cost: Capital and equity funds are factor inputs in production. A firm has to take every effort to reduce cos t of capital and to launch economy drive in all of its operations.
3. Risk minimization : There Ls always a risk in carrying business activities. Element of risk will always remain in the business. Efforts are made so that these risks may be minimized.
4. Effective utilization of fund s : In financial management efforts are made to utilize the funds properly and to control the misuse of wastage of funds.
Question 11.
Discuss the factors determine working capital requirements of a business enterprises
Answer:
The factors which govern the amounts of working capital in a business are :
1. Nature of Business: Public: utilities and service organizations require little working capital as sales are on cash basis,. There is little time gap between production and sales and these enterprises do not maintain large stock of goods. In trading and manufacturing concerns, on the other hand large amount of working capital is needed to maintain stocks.
2. Size of the Business : The volume of business has a direct influence on working capital requirements. Large firms require greater working capital for investment in current assets and to pay current liabilities.
3. Production Cycle: The length or duration or production process also affects working capital requirement. Where production takes longer time, More working capital is
required because more funds are needed for raw material, labour and other expenses. On the other hand, smaller production cycle need less working capital.
4. Turnover of Working Capital: Turnover implies the speed with which the working capital circulates in business. The rate of turnover of working capital is measured by the ratio of sales to current assets. More rapid is the flow of working capital, lesser is the need for working capital.
5. Terms of Trade : The terms of business also have lot of bearing on working capital requirement. If raw material can be had on credit and finished goods are sold for cash then less working capital is needed. On the other hand., if purchases have to be made cash and sales are on credit, then business will need more working capital. This happens in most of the wholesale trading business where margins are less and to take benefit of cash discount, wholesalers purchase for cash but have to sell on credit to have more sales.
6. Cyclical and Seasonal Fluctuations : Business firms which are subject to business cycles and seasonal demand may need greater working capital. During depression, investment in stock and debtors may be high while in a boom sales tend to be quick and stocks are smaller.
Question 12.
Write any four characteristics of an ideal financial plan.
Answer:
Following should be the characteristics of an ideal financial plan :
- Simplicity : Financial plans should be made with the idea of simplicity. This simplicity must not effect working capacity.
- Complete: The financial plans must possess quality of compactness and complete.
- Cheaper : While making plans for acquiring capital it must be kept in mind that they should be cheap.
- Flexibility : For the success of any organization it must be kept in mind that all the plans are flexible in nature.
Question 13.
Write any four executive functions of financial management.
Answer:
Executive Functions : The finance manager performs certain executive functions which are as under.
1. Arrange/Organize Finance : A finance manager has to find and arrange the various sources of finance required for the enterprise so that, on the basis of the finance available, the operations of the enterprise may be carried on.
2. Allotment of Available Funds : The funds. available with the finance manager are meant for requirements of the entire enterprise. Therefore, it is the responsibility of the finance manager to allot funds as and where needed l in the enterprise.
3. Management of Assets : Under these are covered activities like purchase of cur-rent and fixed assets arrangements for their safety’, maintenance etc. which are carried on under the instructions of the finance manager. The finance manager has also to consider, before allotting funds, the use and justification for the funds in different departments.
4. To Organize Expenditure : The finance manager should prepare budget estimates for expenditure required in the entire enterprise and invest the same in a planned manner. For this, the finance manager has to consider the expenditure on pay, interest, taxes, development activities etc.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain factors affecting the dividend decision.
Answer:
Dividend decision relates to distribution of profit to the shareholders and its retention in the business for meeting the future investment requirements.
How much of the profits earned by a company will be distributed as profit and how much will be retained in the business is affected by many factors. Some of the important factors are discussed as follows :
1. Earnings : Dividends are paid out of current and past year earnings. Therefore, earnings is a major determinant of the decision about dividend.
2. Stability: Of earnings other things remaining the same, a company having stable earning is in a position to declare higher dividends as against this, a company having unstable earnings is likely to pay. smaller dividend.
3. Growth Opportunities : Companies having good growth opportunities retain more money out of their earnings so as to finance the required investment. The dividend in growth companies is therefore, smaller than that in non-growth companies.
Question 15.
What qualities should be there in an ideal planning ?
Answer:
The success or failure of.any business enterprise depends upon effective financial planning. Following are the characteristics of best financial planning :
1. Simplicity : The financial plan should be such that it should be simple to manage the capital and easier to estimate the formation of capital. In future difficulties may arise in those financial plans where the formation of capital is a complex procedure. Thus financial plans should be understandable to all the persons concerned.
2. Flexibility : The financial plans of an enterprise should not be rigid. According to needs of enterprise and future uncertainties, financial plans should be such that necessary changes can be made.
3. Farsightedness : Financial plans should be made in such a manner that it should run for a long time. Capitalization should be such that fixed and current expenses of enterprise can be properly managed.
4. Liquidity : Financial planning should be such that it should maintain the balance between inflow and outflow of funds. It should make the liquid funds available throughout the year. Financial plan must ensure the maximum utilization of funds.
5. Utility : Whatever capital is invested in business must be properly utilized so that shareholders can receive proper dividend and investors will be attracted towards the enterprise. This will encourage them to invest more in the enterprise. All these provisions are made in the financial planning.
6. Wholeness : It is one of the important characteristic of financial planning that it should have the quality of wholeness. Wholeness means it should pay attention in every area of enterprise. If any area is left than it will cause loss in future.
Question 16.
What is Under Capitalisation ? Write its two causes.
Answer:
Under Capitalisation refers to the situation in which the company’s rate of profit is exceptionally have in relation to the return enjoyed by similar companies. The two causes are as :
- The enterprises has made excess provision for depreciation on its assets thereby creating secret reserves.
- It may have acquired assets at low prices due to depreciation. “
Question 17.
Capital structure decision is essentially optimization of risk-return relationship. Comment.
Answer:
Capital structure refers to the mix between owners and borrowed funds. It can be calculated as Debt/Equity.
Debt and equity differ significantly in their cost and riskiness for the firm. Cost of debt is lower than cost of equity for a firm because lender’s risk is lower than equity shareholder’s risk, since lenders earn on assured return and repayment of capital and therefore they should require a lower rate of return. Debt is cheaper but it is more risky for a business because payment of interest and the return of principal is obligatory for the business. Any default in meeting these commitments may force the business to go into liquidation. There is no such compulsion in case of equity, which is therefore, considered risk less for the business. Higher use of debt increases the fixed financial charges of a business, as a result increased. Use of debt increases the financial risk of a business.
Capital structure of a business thus, affects both the profitability and the financial risk. A capital structure will be said to be optimal when the proportion of debt and equity is such that it results in an increase in the value of the equity share.
![]()
Question 18.
A capital budgeting decision is capable of changing the financial fortune of a business. Do you agree ? Why or why not ?
Answer:
Investment decision can be long term or short term. A long term Investment decision is also called a capital budgeting decision. It involves committing the finance on a long term basis, e.g., making investment in a new machine to replace an existing one or acquiring a new fixed assets or opening a new branch etc. These decisions are very crucial for any business. They affect its earning capacity over the long-term, assets of a firm, profitability and competitiveness, are all affected by the capital budgeting decisions, Moreover, these decisions normally involve huge amounts of investment and are irreversible except at a huge cost.
Therefore, once made, it is almost impossible for a business to wriggle out of such decisions. Therefore, they need to be taken with utmost career decisions must be taken by those who understand them comprehensively. A bad capital budgeting decision normally has the capacity to severely damage the financial fortune of a business.
Question 19.
Discuss the merits of equity shares. Write its characteristics.
Answer:
1. Fixed capital : These shares constitute a good source of fixed capital for a company as the company is not bound to return it during its life.
2. Flexible dividend policy: The rate of dividend on equity shares is not always fixed and definite. The company may skip dividend. A flexible dividend policy can be adopted in the case of equity shares.
3. Safety of the company : Equity share capital is safety wall for the company on the basis of which it can face any financial crisis easily.
4. Arrange additional capital: The company can raise long term loan on the,security of these shares and thus it can arrange additional capital.
Characteristics :
- On such shares rate of dividend is not fixed.
- Equity shareholders enjoy voting rights over the others.
- Equity shares are redeemed only at the time of liquidation.
- At the event of liquidation the equity capital is refunded only after the preference shares are paid back.
- Dividend of such shares are paid only after the preference dividend is paid.
Question 20.
What do you mean by capital budgeting ?
Answer:
Meaning : Capital budgeting is long financial decision making of the firm. It requires decision regarding the purchase of new assets taking into consideration the utility of various other uses of assets.
Characteristics :
- Its nature is to have heavy investment
- It increases long term profitability
- In its decision the risk factor is more
- It becomes difficult to change its decisions. ‘
Question 21.
Distinguish between Fixed capital and Working capital
Answer:
Differences between Fixed capital and Working capital:
Fixed capital
- Fixed capital is that capital which more or less remains permanently invested in business.
- It is known as long term capital. For example : Land, machine etc.
- There is very less liquidity in this capital because these are not easily meant for resale.
- Requirement of fixed capital depend on size of the enterprise.
Working capital
- This is the capital required to meet day to day expenses of the business.
- It is also known as short term capital.Like purchase of raw material, payment of salaries or wages.
- It is a liquid capital because flow of this capital does not slop suddenly.
- It is invested in production of goods.
Question 22.
What are the factors affecting fixed capital ?
Answer:
The various factors affecting fixed capital are :
- Nature of industry : Fixed capital requirement largely depends on the nature of industry. When there is a need of land, building, machinery etc. in industry, the need of capital increases.
- Nature of production : The requirement of fixed capital also depends on the nature of production, whether it is capital based or labour based.
- Scope of business : If business is only a buyer or only a seller the capital requirement is less and if it is both the capital needed is comparatively more.
- Expansion of business : If business is to be expanded in future then fixed capital is required in great sum. Due to modem machines and management the expenses increases. So capital requirement increases.
- Preliminary expenses: The need of fixed capital will increase if the promoters at the time of establishment of company speed more on salary of promoters, establishment expenses, purchase of patent etc.
- Attitude of management: If the manager wants to enter in the market as a major producer from. The very beginning than more fixed capital will be needed.
![]()
Financial Management Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between Over capitalization and Under capitalization.
Answer:
Differences between Over capitalization and Under capitalization :
Question 2.
What are the sources of long term working capital ?
Answer:
Sources of Long-Term Working Capital (These are also the Sources of Fixed Capital).
Some part of working capital is permanently required in the organisation and its sources have also to be such which can provide capital for a long time. Following are the sources of long-term or permanent working capital:
1. Issue of shares : For procurement of permanent working capital both equity and preference shares can be issued but equity shares prove better because, unlike on preference shares, no dividend at fixed rate has to be paid.
2. Issue of debentures : Issue of debentures is also a preferred source of long-term working capital. Debentures are issued when it is felt that after sometime there will be lesser need of working capital. Money can be refunded by redeeming redeemable debentures. Equity share capital cannot be returned back during the life time of the company (except by buy back of shares). It proves better to raise permanent working capital partly by issue of equity shares and partly through issue of debentures so that money raised from issue of debentures can be returned back when not required.
3. Publishing back of profits : Reinvestment of profit, called ploughing back of profits, is an important source of raising permanent working capital. It is a free of charge method which does not create a burden on future profits of the business. As the company expands, the need for permanent working capital also increases. This need can be met by reinvesting profits in business; but to do so the management has to adopt a tight or conservative dividend policy and the shareholders have to make a sacrifice. This method can be adopted by profit making companies only.
4. Public deposits : Under this method companies accept deposits from public for medium period at attractive rates of interest. The defect of this method is that public will place deposits only in financially sound companies and there will be rush for withdrawals in cash of financial difficulties.
5. Loans from financial institutions : Various state governments and the central government have set-up specialised financial institutions which provide medium and long term loans to industries. These institutions have become major sources of finance of medium and large scale industries. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), State Financial Corporations (SFCs), Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI), Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) and Unit Trust of India (UTI) are examples of such financial institutions.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the causes of over capitalization ?
Answer:
Following are the causes of over capitalization :
1. More promotion expenditure : When in a company formation, over time is taken and over expences is done on un appropriate promotion then it gives rise to over capitalization promotion expenditure should be in accordance with the trading of company. When amount of capital is fixed more than acquired capital then over capitalization takes place.
2. Issue of over capital: When in a company more than required capital is issued then in a company more than requirement. When it is not used properly the problem of over capitalization.
3. Formation of company during inflation : When any company is formed during the period of inflation. During inflation it is expensive to purchase assets and they are not profitable to purchase in future. Whenever period of inflation is over the problem of over capitalization starts.
4. More income than expected at the time of promotion : When more income is expected at the time of promotion then over capitalization takes place.
Question 4.
Explain the types of working capital.
Answer:
There are two types of working capital:
1. Fixed or regular working capital: Some type of working capital is that which is required for the whole year. Arrangement of such type of capital is done permanantly through long term capital. Regular or working capital is required to maintain minimum stock, to keep minimum amount of cash in banks, wear and tear of business electricity, wages, salary etc. For general working of the business it is essential. By this capital business can make progress.
2. Seasonal or Variable working’capital: It is such type of capital which is used in a specific season in a year. This expenditure is goes on changing. Due to this reason, it is called seasonal or variable working capital.
For example, capital required to purchase woollen clothes in winter season, rainy materials before rainy season. The year in which more rainfall is there or more cold is there such products are sold on large scale. Thus proportion of capital increases.
Question 5.
What is the importance of working capital ?
Answer:
1. Prompt payment to suppliers and others : A business enterprise with sufficient working capital can make prompt payments to its suppliers and meet other liabilities promptly. It increases credit standing or reputation of the enterprise.
2. Can avail benefits of cash discounts : A business with sufficient working capital can avail cash discounts by making prompt payments to its creditors.
3. Garbing business opportunities : Adequate working capital enables Finns to take advantage of any favourable business opportunity like purchasing and storing raw material at low prices or executing special orders.
4. Increase in credit worthiness and goodwill : Availability of sufficient working capital is considered as sign of good financial position by creditors and banks and there is no difficulty in borrowing funds in case of need.
5. Distribution of dividend : If there are sufficient liquid assets with an organisation, it can afford to declare and distribute good dividends. A firm starved of working capital can not do so, it has to plough back its profits in business.
6. Facing emergencies : A company having sufficient working capital can overcome short-term financial difficulties and meet other emergencies.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the disadvantages of equity shares ?
Answer:
Disadvantages of Equity Shares are :
1. Disruption in working : By exercising their rights in company meetings equity shareholders may cause disruption in smooth working of the company for their own gains.
2. Loosing benefit of trading on equity : By raising whole the capital through equity shares the company cannot take benefit of trading on equity. .
3. Danger of over capitalization : Excessive issue of equity shares may lead to over capitalization which is harmful for the company.
4. Loss of control on management: With the sale of equity shares, there is transfer of voting right also. If any group is able to acquire a large number of shares in the company, it may gain control over its affairs and the present management may be ousted.
5. Payment of high dividends : To attract investors in equity shares the management has to maintain high rate of divident. Dividend paid is not deductible as a business expense. All this makes equity shares method of raising finance a costly affair.
6. Difficulty in increasing share capital: If the authorised capital of the company has to be increased or some shares with special rights have to be issued, the consent of existing equity shareholders has to be obtained which is not an easy task always.
7. Uncertainty of income : From the viewpoint of investors, equity shares do not guarantee a regular income, the rate of dividend may vary each year and there may be non in some years.
8. Fall in value of shares : Due to speculation and other economic and political factors there may be fall in the value of equity shares which may cause financial loss to investors.
Question 7.
Write the advantages of preferential shares ?
Advantages of Preference Shares :
- Trading on equity is possible : As preference shareholders get dividend at fixed rate, trading on equity are available to equity shareholders.
- No burden on company : Though rate of dividend is fixed on preference shares but if profits in any year are insufficient, their payment can be postponed.
- Retaining control on management: As preference shareholders have limited voting rights, the management can get capital without granting any voting rights and, thus retain control over the company.
- No charge over assets of the company : Issue of preference shares creates no charge over assets of the company (as is the case when secured debentures are issued). The company can, therefore, utilize its assets for borrowing later.
- Flexibility : To get funds for medium term the company can issue redeemable preference shares adding flexibility to its capital structure.
- Cautious investors are attracted : By issuing preference shares, which offer special security, the company can raise capital from cautious investors, not willing to undertake risks.
![]()
Question 8.
What is the bad effects of over capitalization on company ?
Answer:
Effects or demerits of over capitalization : The effects or demerits of over capitalization are as follows :
- Loss of goodwill
- Difficulty in obtaining capital
- Difficulty in obtaining loans
- It creates artificial high dividend rate
- Demand for winding up can be raised
- It is difficult to face competition
- Shareholders receive dividend at low rate
- The face value of shares reduces due to over capitalization
- Welfare facilities of employees is reduced
- It also affects the society as the prices of products increases
- Low quality of goods are provided to consumers
- It creates unemployment
- Frustration in economic system develops due to over capitalization.
Question 9.
What are the internal factors affecting the capital structure ?
Answer:
Internal Factors : The following internal factors affect capital structure :
1. Nature of business : The nature of business of an enterprise effects the business
most. Enterprises indulged in the process of manufacturing requires more fixed capital compared to working capital. While other business enterprises require more working capital than fixed capital. The enterprises which require more capital can form it through long term loans or shares while working capital can be formed through other sources.
2. Regularity and certainty of income : The regularity and certainty of income also affects the capital structure. Thus, according to estimated incomes capital structure should be formed. If enterprise has certainty of income then capital should be formed by issuing debentures, bonds and preference shares but when there is uncertain income, capital should be formed by issue of equity shares.
3. Future plans : In the capital structure of an enterprise the current needs as well as the future development plans should be also kept in mind, so that in future the required capital can be formed. First of all equity shares are issued and later on according to needs preference shares and debentures are issued. Thus, future plans affects capital structure.
4. Trading on equity : Trading on equity means borrowing funds at reasonable rates with the help of share capital. Trading on equity also affects the capital structure of an enterprise. It should be adopted by the enterprise which have regular income and have goodwill.
5. Structure of commercial assets : The enterprises in which the structure of commercial assets include more fixed capital, in its capital structure consists more share of long term loans and debentures while less share of share capital. But the structure of commercial which includes more current assets, in its capital structure consists of less long term loans.
6. Desire to control the business : Desire to control business also affects the capital structure. If funds are raised by issuing equity shares then the number of owners controlling the company increases. It will not be acceptable to existing shareholders. But when funds are raised through debt capital there is no effect on the control of company because debenture holders have no control over the affairs of enterprise.
7. Age of firm: The goodwill of a new enterprise is very less in the market and extent of risk is more. Thus, it is difficult for these type of firms to raise the capital. So these firms try to raise capital at their own risk. Later on when these enterprise increases the goodwill then it becomes easier to raise the funds.
Question 10.
What are the external factors of affecting capital structure ?
Answer:
External factors: The following external factors also affect the capital structure:
1. Conditions of capital market: The conditions of capital market also affects capital structure up to a certain extent. At the time of depression when rate of interest is low and chances of profit is uncertain then in place of shares, debentures are more popular.
2. Psychological condition of investors : The capital structure of an enterprise is affected by the nature and types of investors. The psychological conditions and risk facing ability of investors affects the capital structure. According to these conditions the various types of securities are issued.
3. Legal Provision : Capital structure is also influenced by the legal provisions or government regulations. The public issue of shares and debentures have to be made under SEBI guidelines.
4. Tax provisions : The tax rules and regulations of any country affects the capital structure.
Question 11.
Write the types of Financial planning.
Answer:
Following are the types of financial planning :
(1) Short term financial planning: Generally in a business planning is made for one year is called short term financial planning. In short term financial planning mainly working capital is used. Short term planning is the part of long term and mid term planning.
(2) Mid term financial planning: Mid term planning is that planning which is made for more than one year and less than five years. This type of planning is made for maintenance of business and for developmental work.
(3) Long term financial planning : Planning which is made for five years or more than five years is called Long-term financial planning. This type of planning is based on broad type of outlook. This type of planning is done for long term problems.
Question 12.
What do you mean by investment decisions ? Write the factors affecting investment decisions.
Answer:
It means the selection of best financing alternative or best investment alternative. Financial decision-making is concerned with three broad decisions. A firm’s resources are
scarce in comparison to the uses to which they can be put. A firm, therefore, has to choose where to invest these resources, so that they are able to earn the highest possible return for their investors.
The investment decision, therefore, relates to how the firm’s funds are invested in different assets. Factors which affect capital budgeting decisions :
(a) Cash flows of the project : When a company takes an investment decision involving huge amount it expects to generate some cash flows over a period. These cash flows are in the form of a series of cash receipts and payments over the life of an investment. The amount of these cash flows should be carefully analysed before considering a capital budgeting decision.
(b) The rate of return : The most important criterion is the rate of return of the project. These calculations are based on the expected returns from each proposal and the assessment of risk involved. Suppose, there are two projects A and B (with the same risk involved) with a rate of return of 10 percent and 12 percent, respectively, then under normal circumstance, project B will be selected.
(c) The investment criteria involved : The decision to invest in a particular project involves a number of calculations regarding the amount of investment, interest rate, cash flows and rate of return. There are different techniques to evaluate investment proposals which are known as capital budgeting techniques.These techniques are applied to each proposal before selecting a particular project.
![]()
Question 13.
What is meant by working capital ? How is it calculated ? Discuss five important determinants of working capital requirements.
Answer:
Working capital is that part of total capital which is required to meet day-to-day expenses. To buy raw materials, to pay wages and other expensess of routine nature in the production process or we can say it refers to excess of current assets over current liabilities.
Working Capital = Current Assets-Current Liabilities
Factors affecting working capital requirement are :
(i) Nature of Business : The basic nature of a business influences the amount of working capital required. A trading organisation usually needs a lower amount of working capital compared to a manufacturing organisation. This is because in trading. There is no processing required. In a manufacturing business, however raw materials need to be converted into finished goods. Which increases the expenditure on raw material, labour and other expenses.
(ii) Scale of Operation : The firms which are operating on a higher scale of operations, the quantum of inventory, debtors required is generally high. Such organisations there fore, require large amount of working capital as compared to the organisations which operate on a lower scale.
(iii) Production Cycle : Production cycle is the time span between the receipts of raw materials and their conversion into finished goods. Some businesses have a longer production cycle while some have a shorter one. Working capital requirement is higher in terms with longer processing cycle and lower in firms with shorter processing cycle.
(iv) Credit Allowed : Different firms allow different credit terms to their customers. A liberal credit policy results in higher amount of debtors, increasing the requirements of working capital.
(v) Credit Availed : Just as a firm allows credit to its customers, it also may get credit from its suppliers. The more credit, a firm avails company may be profitable but short on cash. Availability of enough cash in the company is necessary for declaration of dividend by it.