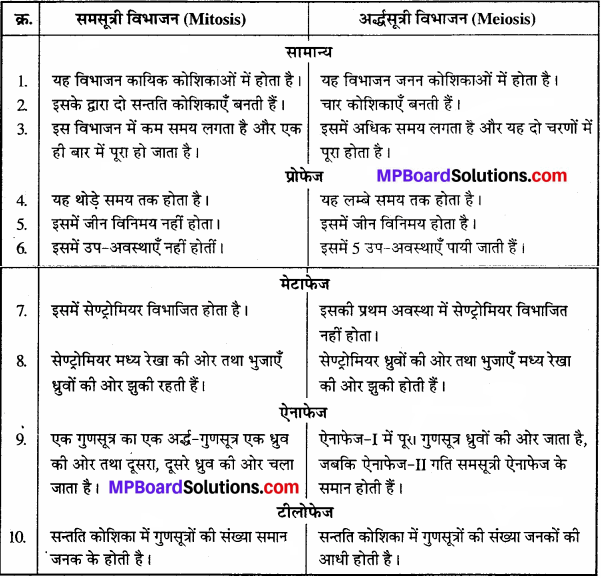
MP Board Class 7th Sanskrit Solutions Surbhi Chapter 21 सूक्तयः
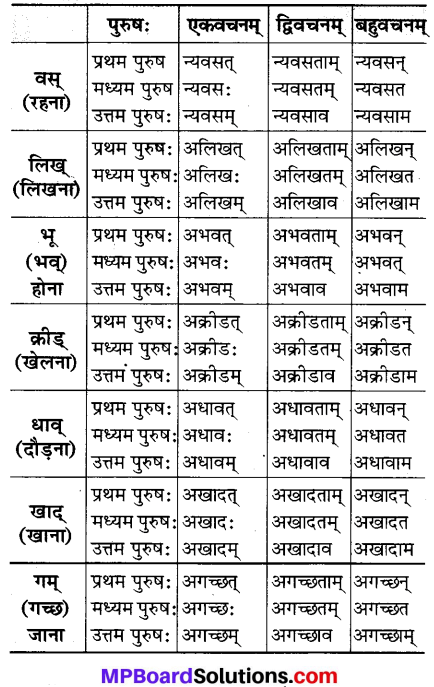
MP Board Class 7th Sanskrit Chapter 21 अभ्यासः
सूक्तयः Class 7 MP Board प्रश्न 1.
एक शब्द में उत्तर लिखो
(क) कः परमो धर्म:? [परम धर्म कौन-सा है?]
उत्तर:
आचारः
(ख) विपरीत बुद्धिः कदा भवति? [बुद्धि किस समय विपरीत हो जाती है?]
उत्तर:
विनाशकाले
(ग) कूपखननं कदा न युक्तम्? [कुएँ का खोदना कब उचित नहीं है?]
उत्तर:
प्रदीप्तेवह्निकागृहे
(घ) केन कार्याणि सिद्धयन्ति? [कार्य किससे सिद्ध हो जाते हैं?]
उत्तर:
उद्यमेन
(ङ) किं सर्वत्र वर्जयेत्? [सभी स्थानों पर क्या वर्जनीय है?]
उत्तर:
अति।
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 21 MP Board प्रश्न 2.
एक वाक्य में उत्तर लिखो-
(क) कानि परेषां न समाचरेत्? [कौन-से कार्य दूसरों के लिए नहीं करने चाहिए?]
उत्तर:
आत्मनः प्रतिकूलानि परेषां न समाचरेत्। [जो काम अपने लिए विपरीत हों, उन्हें दूसरों के लिए नहीं करना चाहिए।]
(ख) संसर्गजाः के भवन्ति? [संगति से क्या हो जाते हैं?]
उत्तर:
संसर्गजा दोषगुणाः भवन्ति। [संगति से दोष भी गुण हो जाते हैं।]
(ग) सर्वोत्तम भूषणं किम् अस्ति? [सबसे अच्छा आभूषण क्या है?]
उत्तर:
वाग्भूषणं सर्वोत्तमं भूषणं अस्ति। [वाणी का आभूषण ही सबसे अच्छा आभूषण है।]
Sanskrit Sukti Class 7 MP Board प्रश्न 3.
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो
(क) ……… वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम्।
(ख) हितं मनोहारि च ………. वचः।
(ग) आत्मनः ……….. परेषां न समाचरेत्।
(घ) न ……… युक्तं प्रदीप्ते वह्निकागृहे।
(ङ) विनाशकाले ……….
उत्तर:
(क) उदारचरितानां तु
(ख) दुर्लभम्
(ग) प्रतिकूलानि
(घ) कूपखननं
(ङ) विपरीतबुद्धिः।
Pratikulani Ka Vilom Shabd MP Board प्रश्न 4.
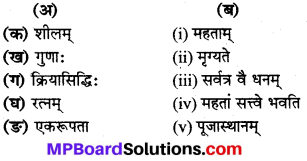
उचित शब्दों का मेल करो

उत्तर:
(क) → (3)
(ख) → (4)
(ग) → (1)
(घ) → (5)
(ङ) → (2)
Class 7 Sanskrit Vilom Shabd MP Board प्रश्न 5.
समानार्थक शब्द लिखो
(1) वह्निना
(2) युक्तम्
(3) उद्यमेन
(4) वसुधा।
उत्तर:
(1) अग्निना
(2) सहितम्
(3) परिश्रमेन
(4) पृथिवी।
प्रश्न 6.
अधोलिखित शब्दों के विलोम शब्द पाठ से चुनकर लिखो
(क) अनुदारचरितानाम्
(ख) अनुकूलानि
(ग) सुलभम्
(घ) आलस्येन
(ङ) समृद्धिकाले।
उत्तर:
(क) उदारचरितानाम्
(ख) प्रतिकूलानि
(ग) दुर्लभम्
(घ) उद्यमेन
(ङ) विनाशकाले।
प्रश्न 7.
शुद्ध वाक्यों के समक्ष ‘आम्’ तथा अशुद्ध वाक्यों के समक्ष ‘न’ लिखो
(क) संसर्गजा दोषगुणाः न भवन्ति।
(ख) आत्मनः प्रतिकूलानि परेषां समाचरेत्।
(ग) वाग्भूषणं भूषणं न अस्ति।
(घ) अति सर्वत्र न वर्जयेत्।
(ङ) कार्याणि मनोरथैः सिध्यन्ति।
उत्तर:
(क) न
(ख) न
(ग) न
(घ) न
(ङ) न
प्रश्न 8.
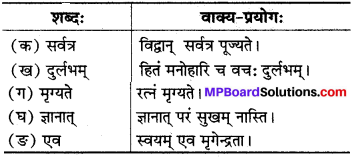
संस्कृत वाक्यों में प्रयोग करो
(क) खलु
(ख) सततं
(ग) गृहे
(घ) बृद्धिः
उत्तर:
(क) सः खलुः अत्र आगच्छेत्.
(ख) सततम् श्रम करणेन साफल्यं भवति।
(ग) गृहे सति कः मित्रम् भवति।
(घ) विपत्तिकाले बद्धिः विपरीतम् भवति।
प्रश्न 9.
रेखांकित शब्दों के आधार पर प्रश्न बनाओ
(क) अति सर्वत्र वर्जयेत्।
(ख) आचारः परमो धर्मः।
(ग) उद्यमेन हि सिध्यन्ति कार्याणि।
(घ) उदारचरितानां तु वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम्।
उत्तर:
(क) का सर्वत्र वर्जयेत्?
(ख) कः परमो धर्मः?
(ग) केन हि सिध्यन्ति कार्याणि?
(घ) केषाम् तु वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम्?
सूक्तयः हिन्दी अनुवाद
- आचारः परमोधर्मः।
- संसर्गजाः दोषगुणाः भवन्ति।
- उदारचरितानां तु वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम्।
- हितं मनोहारि च दुर्लभं वचः।।
- उद्यमेन हि सिध्यन्ति कार्याणि न मनोरथैः।
- अति सर्वत्र वर्जयेत्।
- विनाशकाले विपरीतबुद्धिः।
- न कूपखननं युक्तं प्रदीप्ते वह्निना गृहे।
- आत्मनः प्रतिकूलानि परेषां न समाचरेत्।
- क्षीयन्ते खलु भूषणानि सततं वाग्भूषणं भूषणम्।
अनुवाद :
- आचरण सबसे बड़ा धर्म है।
- संगति से दोष भी गुण हो जाया करते हैं।
- उदार चरित्र वाले लोगों के लिए तो सारी पृथ्वी ही कुटुम्ब के समान होती है।
- हितकारी और मनोहारी वचन दुर्लभ होते हैं।
- परिश्रम करने से ही कार्य हुआ करते हैं, इच्छाओं से नहीं।
- किसी काम की अति सभी जगह रोक लेनी चाहिए।
- जब विनाशकाल आता है, तो बुद्धि भी उल्टी हो जाती है अर्थात् मनुष्य का आचरण भी विपरीत होने लगता है।
- घर में आग लगने पर कुएँ का खोदना उचित नहीं होता है।
- जो काम अपने लिए विपरीत हो, वह दूसरों के लिए नहीं करना चाहिए।
- आभूषण तो नष्ट हो जाते हैं परन्तु वाणी का आभूषण सदा आभूषण रूप में बना रहता है।
सूक्तयः शब्दार्थाः
उद्यमेन = मेहनत से। संसर्गजाः = साथ रहने से। प्रदीप्ते = जलने पर। कूपखननं = कुआँ खोदना। आत्मनः = अपने। क्षीयन्ते = नष्ट हो जाते हैं। भूषणानि = गहने।