MP Board Class 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
Structure of Atom Important Questions
Structure of Atom Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which orbit is more close to nucleus:
(a) M
(b) N
(c) K
(d) L
Answer:
(c) K
Question 2.
Radius of atomic nucleus is approximately:
(a) 10-10cm
(b) 10-13cm
(c) 10 -15cm
(d) 10-8cm
Answer:
(b) 10-13cm
Question 3.
Magnetic quantum number is related to:
(a) Size
(b) Shape
(c) Orientation
(d) Spin
Answer:
(c) Orientation
![]()
Question 4.
The de – Broglie’s relationship is:
(a) λ = \(\frac { h }{ mp } \)
(b) \(\frac { h }{ mc } \) = p
(c) λ = \(\frac { h }{ mv } \)
(d) mv = \(\frac { nh }{ 2\pi } \)
Answer:
(c) λ = \(\frac { h }{ mv } \)
Question 5.
Neutron is discovered by:
(a) Rutherford
(b) Newton
(c) Goldstein
(d) Chadwick
Answer:
(d) Chadwick
Question 6.
There are three unpaired electrons in the electronic configuration of nitrogen:
(a) According to Hund’s rule
(b) According to Aufbau’s principle
(c) According to Pauli’s exclusion
(d) According to Heisenberg’s principle
Answer:
(a) According to Hund’s rule
Question 7.
Electrons are filled according to increasing order of energy of different orbitals, this is the statement of:
(a) Aufbau’s principle
(b) Pauli’s exclusion principle
(c) Hund’s rule
(d) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
Answer:
(a) Aufbau’s principle
![]()
Question 8.
The value of \(\frac { e }{ m } \) for electron is given by:
(a) J.J. Thomson
(b) M. Faraday
(c) R.A. Mulliken
(d) Rutherford
Answer:
(a) J.J. Thomson
Question 9.
In Isotope of element atom have:
(a) Same atomic mass and different atomic number
(b) Same atomic number and different atomic mass
(c) Different atomic number and atomic mass
(d) Different electronic configuration
Answer:
(b) Same atomic number and different atomic mass
Question 10.
Which rays used by Rutherford in their experiment:
(a) β – rays
(b) γ – rays
(c) Helium atom
(d) α – particle
Answer:
(d) α – particle
Question 11.
For a given value of quantum number / the number of allowed values of m is given by:
(a) 2l
(b) nl
(c) (2l + 1)
(d) (n – l)
Answer:
(c) (2l + 1)
![]()
Question 12.
Outer electronic configuration of Cr is:
(a) 4s13d5
(b) 4s23d4
(c) 4s13d4
(d) 4s23d5
Answer:
(a) 4s13d5
Question 13.
de – Broglie’s equation is applicable to:
(a) Proton
(b) Electron
(c) Neutron
(d) All substance
Answer:
(d) All substance
Question 14.
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle:
(a) ∆x ∆p ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
(b) ∆x ∆v ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
(c) ∆x \(\frac { c }{ \lambda } \) ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
(d) ∆x ∆m ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
Answer:
(a) ∆x ∆p ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
Question 15.
In Nodal plan probability of finding an electron is:
(a) Zero
(b) One
(c) Maximum
(d) None of the these
Answer:
(a) Zero
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- Energy packets of light radiation are called ……………………..
- Wave function of electron in atom and molecule is called ……………………….
- 2px, 2py and 2pz are identical in shape but different in ………………………
- Orbitals of equal energy are called ……………………..
- Transition of electron from fourth energy level to first in hydrogen spectrum forms lines in ……………………. series.
- Magnetic quantum number for last electron of sodium is ……………………….
- The increasing order of e/m for electron, proton and neutron and α – particle is ………………………..
- Electromagnetic radiation having maximum wavelength is …………………………..
- Einstein was awarded Nobel prize for the discovery of …………………………….
- Electronic configuration 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p4 represents element, where atomic number is ………………………..
- The total mass of an atom is concentrated in the ……………………..
- Neutron carries ………………………. charge.
- In negatively charged ion the number of electron present is ……………………………. than the normal atom.
- In a normal atom the number of ……………………… is equal to the number of ………………………..
- If atomic mass of an element is 35 and its atomic number is 17, then the number of neutrons present in its nucleus are ……………………….
- In isotopes of an element number of ……………………. are different.
Answer:
- Photon
- Orbital
- Three dimensional orientation
- Degenerate
- Lyman
- Zero
- n, a, p, e
- Radiowave
- Photochemical effect
- Sulphur
- Nucleus
- No
- More
- Proton, electron
- 18
- Neutrons
Question 3.
Answer in one word/sentence:
- What is the mass of electron?
- What is de – Broglie equation?
- Azimuthal quantum number is represented by?
- Formula of Heisenberg uncertainty principle is?
- What is the reason of filling of electron is 4s orbital before 3d orbital?
- Electronic configuration 6C12 will be:
- The short form of scanning tunneling microscope is:
- Who discover neutron?
- Maximum number of electrons in first and second shell is:
Answer:
- 9.1 × 1028gm
- λ = \(\frac { h }{ mv } \) = \(\frac { h }{ p } \)
- l
- ∆x × ∆p ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
- Aufbau’s (n + l) rule
- 1s2, 2s2, 2p2
- STM
- Chadwick
- 48
Question 4.
Match the following:
[I]

Answer:
- (e)
- (c)
- (a)
- (c)
- (b)
- (f)
[II]

Answer:
- (e)
- (d)
- (a)
- (c)
- (b)
- (f)
[III]

Answer:
- (e)
- (d)
- (a)
- (c)
- (b)
- (f)
Structure of Atom Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Isotope have same number of?
Answer:
Proton.
Question 2.
Number of orbital in f – subshell is?
Answer:
7.
Question 3.
Magnetic quantum number is related to?
Answer:
Orientation of orbitals.
Question 4.
What is the total number of orbitals for principal quantum number?
Answer:
n2
![]()
Question 5.
Which is the highest wavelength radiation?
Answer:
Radio wave.
Question 6.
What is the shape of orbital if the value of azimuthal quantum number is (1)?
Answer:
Dumbel.
Question 7.
The place surrounding the nucleus where the probability of finding of electron is maximum is?
Answer:
Orbital.
Question 8.
Who discovered electron?
Answer:
J.J. Thomson.
Question 9.
Who discovered neutron?
Answer:
Chadwick.
Question 10.
What is de – Broglie’s equation?
Answer:
λ = \(\frac{h}{p}\) = \(\frac{h}{mv}\)
Question 11.
Helium nucleus is known as which particle?
Answer:
α – particle (alpha).
Question 12.
Formula of Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle is?
Answer:
∆x∆p ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
Question 13.
Azimuthal quantum number is represented by?
Answer:
l.
![]()
Question 14.
Who discovered nucleus?
Answer:
Rutherford.
Question 15.
What is Threshold frequency?
Answer:
The minimum value of specific frequency energy after that the photoelectric effect can be occur.
Question 16.
What is the charge of an electron?
Answer:
1.60 × 10-19 coulombs.
Question 17.
Why Aufbau’s principle is known as (n + 1) rule?
Answer:
Because the measurement can be done by the sum of energy level of principal quantum number (n) and azimuthal quantum number (l).
Question 18.
Number of electrons in CN ion is:
Answer:
14.
Question 19.
In hydrogen spectrum, spectral lines of Balmer series are present in region of:
Answer:
Visible region.
Question 20.
Number of unpaired electrons in Ni+2 ion is.
Answer:
2.
Structure of Atom Short Answer Type Questions – I
Question 1.
Differentiate between Atomic number and Mass number?
Answer:
Differences between Atomic number and Mass number:
Atomic number:
- Atomic number is equal to the number of proton present in the nucleus of an atom.
- It is represented by Z.
Mass number:
- Mass number is equal to the sum of number of proton and neutron present in the nucleus of an atom.
- It is represented by A.
Question 2.
Write the characteristics of electrons?
Answer:
Characteristics of Electrons:
- Electrons are present in all gases and they are produced in the discharge tube at 10-2 atmospheric pressure and high voltage from the cathode.
- Electrons is the necessary particle with a charge of 1 .6 × 10-19 coulombs. Charge of electron is supposed to be of unit charge.
- Atomic mass of an electron is \(\frac { 1 }{ 1837 } \) times that of hydrogen atom (Mass of electron = 9.1 × 10-31kg).
- Nature of electron does not depend on the gas taken in the discharge tube or the material of the cathode which proves that electron is the fundamental particle of every substance.
- Electron is represented as -1°e.
Question 3.
How was neutron discovered? Write its main properties?
Answer:
Chadwick in 1932 bombarded a thin sheet of beryllium element with α – particles and observed highly penetrating rays of neutral particles. He called these neutral particles as neutrons. The mass of a neutron is approximately same as the mass of a proton but there is no charge on neutron.
![]()
Thus, a neutron may be defined as, “A fundamental particle present in an atom having a mass of l.67 × 10-24 gm and no charge.” It is represented by 0‘n.
Question 4.
Write the two characteristics of cathode rays?
Answer:
- When a solid object is placed in the path of cathode rays, its shadow is produced at the end opposite to cathode. This shows that cathode rays travel in straight line.
- Cathode rays produce X – rays when they strike against hard metals like tungsten, copper etc.
Question 5.
How was anode rays discovered? Write its main properties?
Answer:
In 1836, E. Goldstein observed a new type of luminous rays passing through the holes or perforation of the cathode and moving in a direction opposite to the cathode rays. Thus these rays consisted of positively charged particle moving away from the anode and were named as positive rays or anode rays.
Characteristics of anode rays:
- Anode rays travel in a straight line.
- The anode rays can rotate a light paddle wheel placed in their path. This shows that they consist of material particles.
- The anode rays are deflected by electric and magnetic field. The direction of deflection is opposite to that of cathode rays. This shows that anode rays consist of positively charged particle.
- The charge to mass ratio for anode rays is considerably smaller than electron.
![]()
Question 6.
To determine exact position and velocity simultaneous of fast moving electron is not possible. Why? Explain?
Answer:
Electron is a micro particle which can be seen by X – rays or y rays at low wave – length. To see it is essential that photon of light colloids with electron and returns for vision. But due to collision, momentum (Velocity) of electron changes. Therefore to locate the exact position of electron its momentum (Velocity) changes.
Question 7.
What is the maximum number of emission lines when the excited electron of a H atom in n = 6 drops to the ground state? (NCERT)
Answer:
The number of lines may be calculated from simple formula,
Number of lines = \(\frac { n(n-l) }{ 2 } \)
= \(\frac { 6(6-1) }{ 2 } \)
= \(\frac { 6\times 5 }{ 2 } \) = 15
Question 8.
What is Zeeman effect?
Answer:
Zeeman in 1896, observed that when a magnetic field is applied on a source producing spectral line, the spectral lines get split into several fine lines. This phenomenon is called Zeeman effect.
Question 9.
What is a particles?
Answer:
Each a particle carry two unit of positive charge (+2) and four unit mass. Hence it is called Helium nucleus and represented as 2He4.
Question 10.
Write the characteristics of protons?
Answer:
Characteristics of protons:
1. Proton is the fundamental particle of proton by passing an electric discharge through a gas in a discharge tube H+ ions obtained are called protons or bombarding electron on H atom electrons is released and H+ is obtained.
H + e → H+ + 2e–
By taking different gases in the discharge tube positive particles of different masses are obtained. Positive particle (proton) obtained from hydrogen is the least. Thus, proton is the fundamental particle of an atom.
![]()
Question 11.
Why electronic configuration of Cr is 4s13d5 in place of 4s23d4?
Answer:
If Cr contains four electron in 3d subshell, 3d subshell is in complete filled orbital and represented unstable state. If one electron of 4s subshell existed into vacant 5d orbital, both 4s and 3d orbitals are half filled and represents stable state. That is why electronic configuration of Cr is 4s13d5 in place of 4s23d4.
Question 12.
Why is emission spectrum called line spectrum?
Answer:
On passing current in a discharge tube containing hydrogen gas at high voltage, radiations are emitted. When these radiations pass through prism, split into different sharp lines. On viewing by spectroscope, it is clear that here are many series of coloured lines. Each line has definite wavelength. Due to presence of lines of different wavelength in emmission spectrum, it is called line spectrum.
Question 13.
What is Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle? Write its mathematical form?
Answer:
Heisenberg in 1927, put forward a principle known as Heisenbeig’s uncertainty principle. It states that: “It is not possible to measure simultaneously both the position and momentum of a microscopic particle with absolute accuracy”. Mathematically, this law may be expressed as ∆x∆p ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \) Or ∆x × m∆v ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \)
Where, ∆x = uncertainty in position
∆p = uncertainty in momemtum
∆v = uncertainty in velocity
m = mass of the particle
h = Planck constant
The sign ≥ means that product of Ax and Ap can be either greater or equal to \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \) It can never be less than \(\frac { h }{ 4\pi } \) Therefore, the sign of equality refers to minimum uncertainty associated since the minimum product of ∆x and ∆p is constant.
Question 14.
In A1 and Si, there are unpaired electrons in 3p orbitals. Which electron will feel more effective nuclear charge from nucleus?
Answer:
13Al = 1s2, 2s22p6,3s23p1
14Si = 1s2, 2s22p6,3s23p2
In both the elements the number of orbitals are same. Due to more nuclear charge on Si (+4) than A1 (+3), it will feel more effective nuclear charge.
Question 15.
Which of the following are isoeiectronic species Le. those having the same number of electron:
Na+,K+,Mg+2,Ca+2,S-2,Ar.
Answer:
- Number of electron in 11Na+ = 10 [11 – 1 = 10]
- Number of electron in 19K+ = 18 [19 – 1 = 18]
- Number of electron in 12Mg+2 = 10 [12 – 2 = 10]
- Number of electron in 20Ca+2 = 18 [20 – 2 = 18]
- Number of electron in 16S-2 = 18 [16 + 2 = 18]
- Number of electron in 1gAr = 18 [16 + 2 = 18]
Hence, (i) Na+, Mg+2 are isoeiectronic (10 electron each), (ii) Ca+2, K+, S-2, Ar are isoelectronic (18 electron each).
![]()
Question 16.
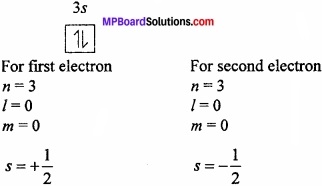
Write the value of all four quantum number for last and unpaired electron of chlorine?
Answer:
17Cl = 1s2, 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p5 image 4
For last electron n = 3, l = 1, m = 0, s = \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
For unpaired electron n = 3, l = 1, m = +1, s= + \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 17.
What is quantum?
Answer:
According to quantum theory of radiation, emmission or absorption of energy is not continuous but energy is transformed in the form of small energy packet or quanta which are always in integer number e.g. 1, 2, 3 …. Unit of energy is called quantum.
Structure of Atom Short Answer Type Questions – II
Question 1.
What is Pauli’s exclusion principle?
Answer:
Pauli’s exclusion principle: “No two electrons in an atom can have the same value of all four quantum number”. It means even if two electron have the same values for n, 7 and m they must have different values of s.
Example: The value of four quantum number for 2 electrons present in 3s orbital.
The three quantum numbers are same for these two electrons but one quantum number is different in spin quantum number which proves the Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Importance: Using this principle, the number of electrons in a shell or main energy level can be known because the number of electrons in an orbit is equal to the number of groups of four quantum numbers in different combinations.
Question 2.
Write the characteristics of cathode rays?
Answer:
- These rays travel in a straight line and have velocity equal to that of light.
- These rays exert mechanical pressure. If a paddle wheel is placed in the path of these rays.
- Cathode rays get deflected towards positive plate when an electric field is applied to it. This showed that cathode rays themselves are negatively charged.
- These rays ionize gases and affect photographic plate.
- Cathode rays produce X – rays when they strike on a very hard metals like copper.
Question 3.
What is (n + l) rule?
Answer:
According to this rule, the new electron will occupy that orbital which have minimum (n + l) value, where n and l represent principle quantum number and azimuthal quantum number respectively. If two or more orbitals have same (n + l) value, the new electron will enter in the orbital having lowest n value (principle quantum number).
Example: 2s and 2p orbital value 2, 3 respectively. So electron will occupy first 2s orbital. 4s and 3p orbital have same (n + l) value 4 but n value is lower in 3p, so firstly 3p orbital will be filled.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the symbols of orbitals of p, d and f subshell?
Answer:
In p subshell, total 3 orbitals Px, Py, Pz.
In d subshell, total 5 orbitals , dxy, dyz, dxz, d\(x^{ 2 }-y^{ 2 }\), dz2
In f subshell, total 7 orbitals f3x,f3y, f3z, fx(\(z^{ 2 }-y^{ 2 }\)) , fy(\(x^{ 2 }-z^{ 2 }\)), fz(\(y^{ 2 }-x^{ 2 }\), fxyz.
Question 5.
Write the main characteristics of Summerfield atomic model?
Answer:
The main characteristics of Summerfield atomic model is as follows:
- Electrons revolves in orbitals as well as in shells where they is two radius.
- Shells are made up of sub-shells.
- The number of sub-shells in a shell is equal to quantum number ‘n’.
Question 6.
Write the Bohr – Bury arrangement for filling of shells by electrons?
Answer:
The sequential arrangement of filling of shells in atom is given by scientist Bohr – Bury:
- In any n shell the maximum number of electrons will be 2n2.
- In last shell 8 electrons and a shell second to last shell should not be contained more than 18 electrons.
- In last shell 2 electrons and in penultimate shell the electrons number will be 9 only when all the inner shells are full-filled.
- Next shell is filled when the last shell contains 8 electrons.
- It is not necessary that the electrons cannot go in the next shell, when the inner orbitals are filled with 2n2 rule.
Question 7.
What are isoelectronic ions? Give examples?
Answer:
The ions of different elements who have different charges, but have same number of electrons in ionic state are called isoelectronic ions.
Example 1:
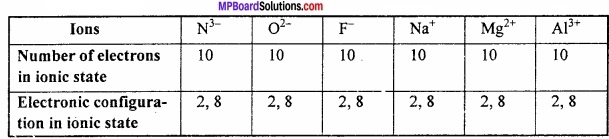
Example 2:
K+ and Ca+ are isoelectronic ion.
Number of electron in K+ = 18
Number of electron in Ca+2 = 18
Electronic configuration = 2,8,8
Electronic configuration = 2,8,8
Question 8.
What is difference between atom and ion?
Answer:
Differences between atom and ion:
Atom:
- They are fully neutral.
- The number of proton and neutron is same.
- Atom is unstable and takes part in chemical reaction.
Ion:
- It is positively or negatively charged.
- The number of proton and neutron is not same.
- Ions are stable in solutions.
Question 9.
Write Aufbau principle?
Answer:
Aufbau is a German word which means building up. According to this principle electron one filled in different energy subshells according to the increasing order of their energies. Thus subshell of minimum energy are filled first.
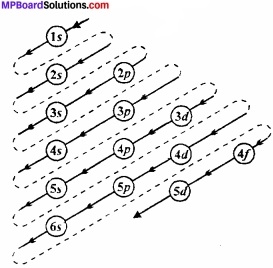
The increasing order energies of various orbital is:
1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d < 6p < 7s < 5f < 6d < 7p.
Question 10.
(a) How many sub – shells are present in n = 4?
(b) How many electrons are present in the sub – shell which have ms = \(\frac{-1}{2}\) and n = 4?
Solution: (a) For n = 4, Imax = (n – 1)
= 4 – 1
= 3
l = 0,1,2,3
∴four sub – shells 4s, 4p, 4d and 4f.
(b) Number of shells in n = 4, n2 – 42 = 16
Maximum electrons in any orbital = 2
In each orbital number of electrons having ms = \(\frac{-1}{2}\), spin = 16.
Question 11.
Show that the circumference of the Bohr orbit for the hydrogen atom is an integral multiple of the de – Broglie wavelength associated with electron revolving around the orbit?
Answer:
According to Bohr theory,
mvr = \(\frac { nh }{ 2\pi } \)
2πr = \(\frac{nh}{mv}\) or mv = \(\qquad \frac { nh }{ 2\pi r } \) …… (i)
According to de – Broglie equation
λ = \(\frac{h}{mv}\) or mv = \(\frac{h}{λ}\)
Compairing eqn. (i) and eqn. (ii)
\(\frac { nh }{ 2\pi r } \) = \(\frac{h}{λ}\) or 2πr = nλ
Thus, the circumference 2 nr of the Bohr orbit for hydrogen atom is an into the de Broglie wavelength.
![]()
Question 12.
What is Planck’s quantum theory?
Answer:
1. Energy is neither emitted nor absorbed continuously in the form of small energy packet or quanta which are always in integer number (1, 2, 3 …).
2. Unit of energy absorbed or emitted is quantum.
3. The amount of energy associated with a quantum of radiation is proportional to the frequency of light.
E ∝ v
E = hυ
Where h is constant called Planck’s constant.
4. The total amount of energy emitted or absorbed by a body will lie some whole number multiple of quantum, i.e. E = nhυ Where n = 1, 2, 3 ….
Question 13.
What is the number of photons of light with wavelength 4000 pm which provide 1J of energy?
Solution:
λ = 4000 pm = 4 × 10-9m, h = 6.626 × 10-34 Js, c = 3 × 108 m/s
E = nhυ = \(\frac { nhc }{ \lambda } \)
or n = \(\frac { E\lambda }{ hc } \) = \(\frac { 1\times 4\times 10^{ -9 } }{ 6.26\times 10^{ -34 }\times 3\times 10^{ 8 } } \) = 2.01 × 1016 photons.
Question 14.
Write the differences between Anode and Cathode rays. Ans. Differences between Anode and Cathode rays:
Answer:
Anode rays:
- These are made by positively charged particles.
- The nature of Anode rays are depends upon the gas taken in discharging tube.
- The mass of particles present in Anode rays are equal to the mass of gas taken in discharge tube.
Cathode Rays:
- These are made by negatively charged particles.
- The nature of Cathode rays are not depends on the nature of gas taken in discharge tube.
- The mass of particles present in Cathode rays are negligible.
Question 15.
Write the observation and conclusion of Rutherford’s scattering experiment?
Answer:
Observation and Conclusions of Rutherfords experiment:
1. Most of the α – particles passed through the gold foil undeflected which concludes that there is a lot of empty space in an atom.
2. Few α – particles were deflected through small angles. Thus the central part of an atom consist of positive charge which is called nucleus.
3. Out of the 20,000 particles bombarding only one particle gets deflected and returns back. Thus the volume of nucleus is a minute part of the atom. Rutherford determined that the radius of the atom is 10-8 cm (1Å) and radius of nucleus is 10-13cm.
4. Electrons revolve in great speed around the nucleus. Due to this speed the centrifugal force produced balanced the electrostatic force of attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the electrons. Due to this balance electron do not fall into the nucleus.
Question 16.
Write the defects of Rutherford Model?
Answer:
Defects of Rutherford’s Model: In 1913 Neel Bohr pointed out the following defects in Rutherfords model:
1. According to the electromagnetic theory of Maxwell, a charged particle when accelerated emits energy in the form of electromagnetic radiations. Since electrons are charged particles, therefore, electrons revolving in an orbit should continuously emit radiations.
As a result of this, it would slow down and would no longer withstand the attractive forces of the nucleus. Hence, it would move closer and closer to the nucleus and would finally fall in the nucleus following a spiral path. This means that atom should collapse. But we all know that atom is quite stable in nature. Thus, Rutherford’s model failed to explain stability of atoms.
2. Rutherford’s model also failed to explain the existence of definite lines in the hydrogen spectrum. If the electrons were to lose energy continuously, the atomic spectrum of hydrogen should have been continuous. But it was found to be discontinuous in the form of lines of definite wavelength.
3. This model does not determine the number of electrons in each orbit. Thus, the Rutherford’s model could not explain the stability of an atom and line spectra of atoms.
![]()
Question 17.
What are the main defects of Bohr’s model?
Answer:
- The theory could not explain the atomic spectra of the atoms containing more than one electron or multielectron atoms.
- Shell of electrons are spherical according the Bohr’s theory but these shells are long eliptical.
- It is not explained Heisenberg’s theory.
- It is not explained the dual nature of light.
Question 18.
Explain Hund’s rule with an example?
Answer:
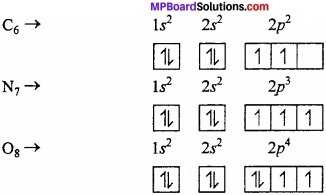
Hund’s rule:
This rule deals with degenerate orbitals (orbitals having similar energy). It states as, “Pairing of electron in the orbitals of a particular subshell (p, d, f) does not take place until all the orbitals of the subshell are singly occupied.”
Question 19.
Caluculate the wavelength, frequency and wavelength of light wave whose period 2.0 × 10-10s.
Solution:
Frequency (υ) =
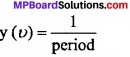
1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2.0\times 10^{ -10 }s } \)
Wavelength (λ) = \(\frac{c}{υ}\) = \(\frac { 3\times 10^{ 8 }ms^{ -1 } }{ 5\times 10^{ 9 }s^{ -1 } } \) = 6.0 × 10-2m
Wave number (\(\bar { \upsilon } \)) = \(\frac{1}{λ}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6\times 10^{ -2 }m } \) = 16.66 m-1
Question 20.
What is the maximum number of emission lines when the excited electron of a atom in n = 6 drops to the ground state?
Solution:
The posible transitions are:

The maximum number of emission lines,
= \(\frac { n(n-1) }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 6(6-1) }{ 2 } \) = 15.
Question 21.
Caluculate the wavelenth of the emission transition if is from the orbit have radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm. Name the series to which this transition being and the region of the spectrum?
Solution:
Radius of the orbit of H – like species \(\frac { 0.529n^{ 2 } }{ Z } \) pm.
r1 = 1.3225 nm = 1322.5 pm = \(\frac { 0.529n_{ 1 }^{ 2 } }{ Z } \)
r2 = 211.6 pm = \(\frac { 0.529n_{ 2 }^{ 2 } }{ Z } \)
\(\frac { r_{ 1 } }{ r_{ 2 } } \) = \(\frac{1322.5}{211.6}\) = \(\frac { n_{ 1 }^{ 2 } }{ n_{ 2 }^{ 2 } } \)
\(\frac { n_{ 1 }^{ 2 } }{ n_{ 2 }^{ 2 } } \) = 6.25 or \(\frac { n_{ 1 } }{ n_{ 2 } } \) = (6.25)1/2 = 2.5
If n1 = 2, n2 = 5, this transition corresponds to transition from 5th orbit to 2nd orbit. This means the transition belongs to Balmer series.
\({ \bar { \upsilon } }\) = R \(\frac { 1 }{ n_{ 1 }^{ 2 } } -\frac { 1 }{ n_{ 2 }^{ 2 } } \)
= 1.097 × 107 \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } -\frac { 1 }{ 25 } \) m-1 = 1.097 × 21 × 105m-1
λ = \(\frac { 1 }{ \bar { \upsilon } } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 1.097\times 21\times 10^{ 5 } } \) = 434 × 10-9m = 434 nm.
If n1 = 2, n2 = 5, this transition corresponds to transition from 5th orbit to 2 nd orbit. This means the transition belongs to Balmer series.

It lies the visible region of light.
Question 22.
Atomic spectrum is called linear spectrum. Why?
Answer:
This type of spectrum is given by the atoms of all elements. It contains continuous thin coloured, sparkled lines, separated by black lines. Every element gives spectral type of line spectrum and these spectrums are their specific identity.
For example: In the spectrum of sodium, their obtained two clear yellow lines on 5890 A and 5896 A. If in a discharge tube, a hydrogen gas is filled at low pressure and electricity is passed, then a red coloured light can be seen. In this way the analysis of this emitted light can be done by spectroscope and a discontinuous spectrum is obtained in which four main lines are obtained which are called Hα, Hβ, Hγ and Hg. The spectrum in which only lines are obtained is called linear spectrum.
Question 23.
What do you mean by dual nature of a tiny particle like electron?
Or, A moving electron shows particle as well as wave nature. Give reason?
Answer:
Electron is a tiny particle, and it have a specific momentum due to particle nature and behave like a wave due to mobility, due to their refraction pattern appears and electron shows both the effects simultaneously. Other particles proton, neutron as well as atoms show dual nature when move with high velocity. The wavelength of wave produced by a moving particle is shown by de – Broglie equation. According to this the wavelength is inversely proportional to momentum.
λ = \(\frac { h }{ mv } \)
or λ = \(\frac { h }{ p } \) or λ ∝\(\frac { 1 }{ p } \)
Where, λ = wavelength of tiny particle like electron, m = mass of particle, v = velocity of particle, p = momentum of particle, h = Planck’s constant.
![]()
Question 24.
Quantum number of electron is given below. Arrange them in the increasing order of energy. Is the energy of any of them is same?
- n = 4, l = 2, ml = -2, ms = \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
- n = 3, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = \(\frac{+1}{2}\)
- n = 3, l = 1, ml = -1, ms = \(\frac{+1}{2}\)
- n = 3, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
- n = 3, l = 1, ml = -1, ms = \(\frac{+1}{2}\)
- n = 4, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = \(\frac{+1}{2}\)
Solution:
The energy of multi electron atom depends upon the total of (n + l)
Sub – shells for (a) set 4d = (n + l) = 4 + 2 = 6
Sub – shells for (b) set 3d = (n + l) = 3 + 2 = 5
Sub – shells for (c) set 4p = (n + l) = 4 + 1 = 5
Sub – shells for (d) set 3d = (n + l) = 3 + 2 = 5
Sub – shells for (e) set 3p = (n +l) = 3 + 1 = 4
Sub – shells for (f) set 4p = (n + l) = 4 + 1 = 5
3p < 3d = 3d < 4p < 4p < 4d (Increasing of energy).
Question 25.
Find the mass of 1 mole electron?
Solution:
Mass of electron = 9.1 × 10-28 gm
1 mole electron = 6.023 × 1023 electron
Mass of 1 mole electron = 9.1 × 10-28 × 6.023 × 1023 = 5.48 × 10-4 gm.
Question 26.
Find the charge on 1 mole electron?
Solution:
Charge on electron = 1.6 × 10-19 coulomb
1 mole electron = 6.023 × 1023 electron
Charge on 1 mole electron = 1.6 × 10-19 × 6.023 × 1023
= 9.63 × 104 coulomb.
Structure of Atom Long Answer Type Questions – I
Question 1.
Write difference between Isotopes and Isobar?
Answer:
Differences between Isotope and Isobar:
Isotopes:
- Different atoms of same elements having same atomic number but different mass number are called isotopes.
- Number of protons present in nucleus is same but number of neutrons is different.
- Similarity in chemical properties.
- Number of electrons present in outermost orbit is same.
Isobars:
- Different atoms of different elements whose mass number is same but atomic number is different are known as isobars.
- Number of protons and neutrons present in nucleus is different.
- Dissimilarity in chemical properties.
- Number of electrons present in outer – most orbit is different.
Question 2.
Write the observation and conclusion of Rutherford’s scattering experiment?
Answer:
Observation and Conclusions of Rutherfords experiment:
1. Most of the α – particles passed through the gold foil undeflected which concludes that there is a lot of empty space in an atom.
2. Few α – particles were deflected through small angles. Thus the central part of an atom consist of positive charge which is called nucleus.
3. Out of the 20,000 particles bombarding only one particle gets deflected and returns back. Thus the volume of nucleus is a minute part of the atom. Rutherford determined that the radius of the atom is 10-8 cm (1Å) and radius of nucleus is 10-13cm.
4. Electrons revolve in great speed around the nucleus. Due to this speed the centrifugal force produced balanced the electrostatic force of attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the electrons. Due to this balance electron do not fall into the nucleus.
Question 3.
The emission transition of Paschen series starts from n shell and ends at n = 3 shell. So, determine the value of it and give the area of spectrum?
Solution:
Frequency,
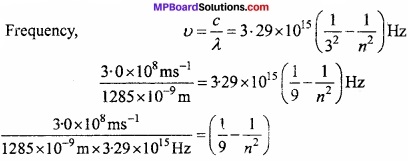
0.0709 = 0.1111 – \(\frac { 1 }{ n^{ 2 } } \)
\(\frac { 1 }{ n^{ 2 } } \) = 0.1111 – 0.0709 = 0.0402 = 0.04 ~ 0.04 = \(\frac{1}{25}\)
or n2 = 25 or n = 5
∴Electron jumps from n = 5 to n= 3, so transistion takes place in Paschen series and present in IR range.
Structure of Atom Long Answer Type Questions – II
Question 1.
Write the main postulates of Bohr’s atomic model?
Answer:
The main postulates of Bohr’s atomic model: Niels Bohr followed quantum theory and describe model of atom as:
1. Electron moves around the nucleus in closed circular orbit. These orbits are called energy levels, its energy is fixed.
2. When an electron moves in an orbit it neither absorbs nor liberates energy. During revolution in orbit electron neither absorbs nor emits energy,
3. An electron undergoes a process of emission or absorption of energy when it goes from one energy level to other i.e., E2 – E1 = hυ
4. Various energy levels are shown by simple no. 1,2,3, ……………. etc. or K, L, M, ………………………. etc. and these are called principle quantum no. The angular momentum of orbits are integral multiple of h/2π i.e., mvr = nh/2π
![]()
Question 2.
What are quantum numbers? How many types of quantum number are there? Explain the informations obtained from them?
Answer:
Calculation of laws of quantum mechanics gives certain numbers which can be used to trace out possible states of electrons such as location and energy of electrons are known as Quantum numbers.There are four types of quantum numbers characteristics of these are given below:
1. Principal quantum number (n):
This shows the principal orbit of electron. Its value is any number 1, 2, 3, …………….. from this quantum number, i.e., ‘n’ we know about the average distance of electron from nucleus and energy state.
The energy states corresponding to different principal quantum numbers are designated by letters K, L, M, N, etc. These are called energy shells.

2. Azimuthal quantum number (l):
From this, we know about angular momentum and shape of orbital. For each value of principal quantum number, l has values from 0 to (n – 1) which shows the suborbital obtained. Different values of l corresponding to n are:
When n = 1, n = 2, n = 3, n = 4
Then l = 0, l = 0,1, l = 0, 1, 2 l = 0, 1, 2, 3
The orbitals are designated by letters s, p, d, f for the corresponding value of 4. Thus,

3. Magnetic quantum number (m):
This explains effect of spectrum of atom when kept in magnetic field known as Zeeman effect. For each value of azimuthal quantum number l, m has values -l to 0 to +l, i.e., total (2l + 1) values. Thus,

It tells us about the orientation of the orbitals in space. s – orbital has 1 orientation, p – orbital has 3, d – orbital has 5 and f – orbital has 7 orientations.
4. Spin quantum number (s):
The electron moving around the nucleus spin on its axis in left (↓) and right side (↑) For each value of m, s has two values +1/2, -1/2.
Use of quantum numbers:
- It helps in writing the electronic configuration in a systematized way.
- Each electron of an element can be recognized separately because any two electrons cannot have the same value of all the four quantum numbers.
Question 3.
Write differences between Orbit and Orbital?
Answer:
Differences between Orbit and Orbital:
Orbit:
- It is a well defined circular path around the nucleus in which the electron revolves.
- Orbit is circular or elliptical in shape.
- It represents the movement of an electron in one plane.
- The maximum number of electrons in an orbit is according to 2n<sup>2</sup>, where n is number of orbit.
- It represents that position as well as momentum of an electron can be known.
Orbital:
- It is a region in three-dimensional space around the nucleus where the probability of finding the electron is maximum.
- Orbitals may be spherical, dumb-bell or double dumb – bell in shape.
- It represents the movement of an electron in the three – dimensional space.
- The maximum number of electrons in an orbital is 2.
- It represents that position as well as momentum of an electron cannot be known.
Question 4.
Write the de – Broglie’s hypothesis?
Answer:
de – Broglie explains the wave nature of the electron. According to this,“Every tiny particle shows the properties of a wave”. According to the Planck’s quantum theory,
E = hυ …….. (i)
According to Einsteins’s mass – energy realation,
E = mc2 …………. (ii)
From eqn. (1) and (2)
mc2 = hυ
⇒ mc2 = h \(\frac { c }{ \lambda } \) [υ = \(\frac { c }{ \lambda } \)]
⇒ mc = \(\frac { h }{ \lambda } \)
⇒ λ = \(\frac{h}{mc}\)
The nature of particle is wave like, so c is substituted with v. If a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v, then
λ = \(\frac{h}{mv}\) …… (3)
So, λ = \(\frac{h}{p}\) [mv = p] ………….. (4)
So, it is clear from eqn. (4) that the wavelength of any moving particle depends upon its momentum.
![]()
Question 5.
Calculate the Bohr radius?
Answer:
When the single electron of hydrogen revolves around the nucleus, then two forces act on it.
- Attraction force by nucleus = \(\frac { Ze^{ 2 } }{ r^{ 2 } } \)
- Centrifugal force acting outside = \(\frac { mv^{ 2 } }{ r } \qquad \)
Where, Z = atomic number, m = mass of electron, v = velocity of electron, e = charge, r = atomic radius.
The centripetal and centrifugal forces of a moving electron works in opposite direction and if their value is same than they balance each other and the electron rotate at its position.
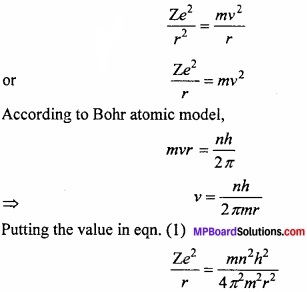
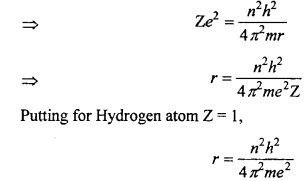
This equation is known as Bohr’s radius.
Question 6.
What is Balmer formula? How it explains the line spectrum of hydrogen?
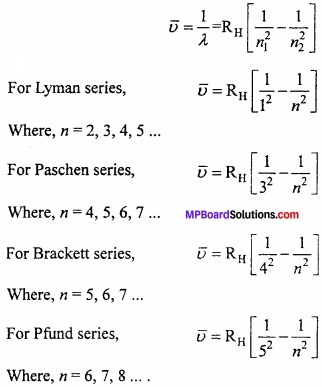
Answer:
According to J.J. Balmer, the frequency of spectrum in visible range of hydrogen atom can be shown by following formula:
\(\bar { \upsilon } \) = RH = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2^{ 2 } } -\frac { 1 }{ n^{ 2 } } \)
Where, RH = Rydberg’s constant and n = 3, 4, 5, 6, ……..
These line series falls in visible range and known as Balmer series. After this four more series were discovered. Lyman series in ultraviolet region, Paschen series, Brackett series and Pfund series in IR region. To explain these series Balmer formula is converted into following formula: