MP Board Class 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Important Questions
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
The process of transfer of enetic information from DNA to RNA is :
(a) Transversion
(b) Transcription
(c) Translation
(d) Translocation.
Answer:
(b) Transcription
Question 2.
Transcription involves :
(a) Synthesis of RNA over DNA
(b) Joining of amino acids over polypeptides
(c) Synthesis of RNA over ribosomes
(d) Synthesis of DNA.
Answer:
(a) Synthesis of RNA over DNA
Question 3.
In operon model, RNA polymerase binds to :
(a) Structural gene
(b) Promotor gene
(c) Operator gene
(d) Regulator gene.
Answer:
(b) Promotor gene
Question 4.
The process of translation is :
(a) Ribosome synthesis
(b) Protein synthesis
(c) DNA synthesis
(d) RNA synthesis.
Answer:
(b) Protein synthesis
![]()
Question 5.
Operon model of gene expression is prokaryotes was proposed by :
(a) Meselson and stahl
(b) Wilkins and Franklin
(c) Beadle and Tatum
(d) Jacob and Monod.
Answer:
(d) Jacob and Monod.
Question 6.
Reverse transcription was discovered by :
(a) Beadle and Tatum
(b) Temin and Baltimore
(c) Watson and Crick
(d) Khorana.
Answer:
(b) Temin and Baltimore
Question 7.
Nitrogen base present in a codon are :
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1.
Answer:
(a) 4
Question 8.
A non – sense/termination codon is :
(a) UUU
(b) GCG
(c) UAA
(d) CCC.
Answer:
(a) UUU
Question 9.
A unit of lac – operon which in the absence of lactose, suppresses the activity of operator gene is :
(a) Structural gene
(b) Regulator gene
(c) Repressor gene
(d) Promoter gene.
Answer:
(d) Promoter gene.
Question 10.
Sequence of nitrogenous bases on t RNA is known as :
(a) Anti codon.
(b) Terminating coon
(c) Repressor codon
(d) Initiate codon.
Answer:
(a) Anti codon.
Question 11.
Which is found in nucleosome :
(a) Histone molecule
(b) Luxary genes
(c) Nucleoplasmine
(d) House keeping genes
Answer:
(a) Histone molecule
Question 12.
Functional gene is :
(a) Gene battery
(b) Luxary genes
(c) Mylud gene
(d) House keeping genes.
Answer:
(d) House keeping genes.
Question 13.
Which RNA has very short life span :
(a) m RNA
(b) t RNA
(c) r RNA
(d) Sn RNA.
Answer:
(a) m RNA
Question 14.
Who terminate the transcription :
(a) Co – protein
(b) Sigma factor
(c) Raw Protein
(d) Omega factor.
Answer:
(c) Raw Protein
Question 15.
A Person which has a trisomy on 21 st chromosome is called :
(a) Klinefelter syndrome
(b) Down’s syndrome
(c) Turner syndrome
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Down’s syndrome
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- ……………… is found in RNA, in the place of DNA’s thymine.
- Formation of ……………… from DN A is called transcription.
- In ……………… ribosomes are of 70s type.
- ……………… is an exogenous gene that has been introduced into the genome of other organism.
- The joining of DNA strands together by ………………
- ……………… is the vector of genes.
- ……………… enzyme is necessary for transcription.
- ……………… discovered polytene chromosome.
- Intron is known as ………………
- ……………… nitrogenous protein which bind the DNA molecule with chromosome.
- Highly condensed chromatin which is not available for transcription is called ………………
- ……………… vims infects the bacteria.
- ……………… is the outer covering of viruses.
- ……………… type of RNA is found in ribosome.
- ……………… is made by joining of peptide bond.
Answer:
- Uracil
- mRNA
- Prokaryotes
- Transgenic
- Ligase
- Plasmid
- RNA Polymerase
- Balbiani
- Junk DNA
- Histone
- Hetero chromatin
- Bacteriophage
- Capsid
- Ribosomal RNA
- Polypeptide.
Question 3.
Match the followings :
I.

Answer:
- (c)
- (a)
- (d)
- (b)
II.

Answer:
(b)
(a)
(d)
(c)
III.

Answer:
- (c)
- (d)
- (a)
- (b)
Question 4.
Write the answer in one word/sentences:
- Who discovered nucleic acid for the first time?
- How many codons are coded to 20 types of amino acid?
- Which codon is known as the starting of codon?
- Name the RNA which function as enzyme.
- Who proposed the operon model of gene regulation?
- Name the organism which contain single stranded DNA.
- Name the process in which to make R&IA from DNA.
- Which bond is produce when sugar and phosphoric acid combine in DNA?
- Name the enzyme which help in transcription.
- How many nucleotides are found in a gene?
- Name any one termination codon.
- Genes which are not expressed their characters.
- Who developed the DNA finger printing technique?
- Name the gene which is control the activity of other gene?
- Write the name of amino acid which starts the protein synthesis.
Answer:
- Friedrich Meischer
- 64
- AUG
- Ribozyme
- Jacob and Monod
- ϕ x 174
- Transcription
- Phosphodiester
- RNApolymerase
- 1000
- UAA
- Silent gene
- Alec Jaffreys
- Regulator gene
- Methionine.
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Structure formed by regulation + structural + operator + promoter gene.
Answer:
Operon.
Question 2.
What are the animals that have a foreign gene deliberately inserted into their genome?
Answer:
Transgenic animals.
Question 3.
What are the group of cells or organisms which have same hereditary characters?
Answer:
Clone.
Question 4.
By which the instructions of our DNA are converted into a functional product?
Answer:
Gene expression.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the name of sugar found in RNA.
Answer:
Ribose sugar.
Question 6.
Which codon is AUG?
Answer:
Anticodon.
Question 7.
Name the enzyme which takes part in transcription.
Answer:
RNA Polymerase.
Question 8.
Who tell that DNA is a heredity material?
Answer:
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase.
Question 9.
Which bond is made in DNA when join the sugar and phosphoric acid?
Answer:
Phosphodiester bond.
Question 10.
Name the segment in which any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is removed by RNA splicing during maturation of the final RNA products.
Answer:
Intron.
Question 11.
Who gave the operon model?
Answer:
Jacob and Monod.
Question 12.
What do you mean by commaless genetic code?
Answer:
Between two codon has no internal punctuation.
Question 13.
Write the full name of Sn RNP.
Answer:
Small nuclear Ribonucleo Proteins.
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides :
Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine.
Answer:
Adenine, Guanosine, Thymine, Uracil and Cytosine are nitrogenous bases. (Adenine and Guanosine → Purine, Thymine, Uracil and Cytosine → Pyrimidine) Cytidine is a nucleoside.
Question 2.
If a double stranded DNA has 20 % of cytosine, calculate the percent of adenine in the DNA.
Answer:
According to Chargaff’s rule, the DNA molecule should has an equal ratio; Cytosine = 20 % therefore, Guanine = 20%
A + T = 100 – (G – C)
A + T = 100 – 40 since, both Adenine and Thymine are in equal amounts.
Thymine = Adenine = \(\frac { 60 }{ 2 }\) = 30%
So, quantity of Adenine is 30% in DNA helix.
Question 3.
What are oncogenes?
Answer:
Genes which are responsible for production of cancer in host by uncontrolled mitotic cell division are called as oncogenes.
Question 4.
What are Okazaki fragments and leadings strands?
Answer:
Okazaki fragments:
On second parental DNA template new complementary DNA strands are formed in smaller fragments starting from RNA primer. These short fragments are called Okazaki fragments.
Leading strands:
Second strand is formed on 5’ → 3’ strand of parental DNA in a continuous stretch in reverse direction 3’ → 5’ and is called as leading strand.
![]()
Question 5.
DNA nucleotides are formed by which molecule?
Answer:
Components of DNA Nucleotides:
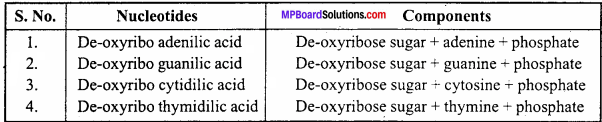
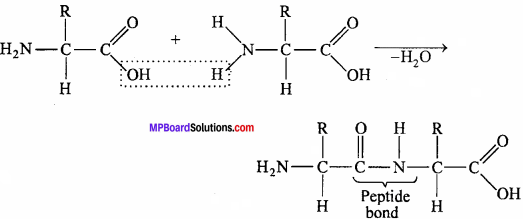
Question 6.
What is peptide bond?
Answer:
The bond formed between the carboxylic group (- COOH) of one amino acid and amino group (- NH2) of another amino acid is called as peptide bond. A molecule of water is released during the formation of peptide bond.
Question 7.
Write five characters of gene hypothesis.
Answer:
Sutton, Bridges, Muller and Morgan suggest these theory. The characters of gene of this theory are as follows:
- Genes are situated on the chromosome.
- They make the physiological character of organisms.
- These are called functional unit of specific characters.
- Genes have the capacity of self-transcription.
- They perform mutation.
- Characters go to one generation to other by parents.
Question 8.
What is gene expression? Explain by different methods of gene expression in animals.
Answer:
The mechanism at molecular level by which a gene is able to express itself in the phenotype of an organism is called gene expression.
Different methods of gene expression in animals are:
1. Transduction:
It is the process in which bacteriophages pick up pieces of DNA from one bacterial cell and transfer the same to another on infection.
2. Transformation:
It is the process by which DNA isolated from one type of cell when introduced into another, is able to bestow some of the properties of the former to the later.
Question 9.
What is proof reading and repair of DNA?
Answer:
Variety of environmental factors such as radiations, chemicals etc. may cause damage in DNA of a cell. The bacterial DNA polymerase III can do proof reading, in the sense that it can go back and remove the wrong base before it proceeds to add new bases in the 5′ → 3′ direction. It is called proof reading. Obviously, the survival of the cell depends on its availability of damages:
1. Monoadduct:
Which involve alterations in a single nitrogenous base.
2. Diadducts :
They are the alterations involving more than one nitrogenous base. Number of nucleases have been found to be involved in repair replication such as Exonucleases (defined as phosphodiesterases which require a terminus for hydrolysis and cut’off terminal nucleotides), Endonucleases (which are also phosphodiesterases which do not require a terminus for hydrolysis and break internal bonds). The endonucleases which act on the damaged DNA and cause repair or correction of this molecule are referred to as correctional nucleases. The following steps are said to be involved in the repair replication i.e., Incision, Excision, Reinsertion and joining of newly formed strands.
Question 10.
Write any four differences between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
Differences between DNA and RNA:
DNA:
- It contains deoxyribose sugar.
- It has adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine as nitrogenous bases.
- It consists of two polynucleotide chains coiled into a double helix.
- It is main constituent of chromosome which is found in nucleus.
RNA:
- It contains ribose sugar.
- It has adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine as nitrogenous bases.
- It consists of single polynucleotide chains which may get folded on it self to form double helix.
- It is main constituent of ribosome and generally found in cytoplasm.
Question 11.
Write the names of enzymes used in DNA replication.
Answer:
The names of enzymes used in DNA replication are as follows:
- DNA helicase : For unwinding of two strands.
- DNA gyrase : For relieving tension.
- Primase : For formation of primer.
- DNA polymerase : For DNA synthesis.
- RNA primer : For initiation of the synthesis of DNA segments.
- DNA ligase : For joining of DNA Okazaki segments.
Question 12.
What is transcription? Name the enzyme catalysing it.
Answer:
Transcription:
Formation of wRNA from DNA in the presence of enzyme is called transcription. It is the first stage of protein synthesis which is catalysed by RNA polymerase enzyme. The process of transcription involves in the following steps:
1. Exposing of the bases of DNA:
The two strands of DNA are separated due to presence of an unwinding protein and thus, their bases are exposed. The exposed chain of DNA functions as template for the synthesis of oiRNA in the presence of RNA polymerase enzyme.
2. Base pairing:
The ribonucleotides are jointed in a definite fashion on the exposed strand of DNA. G is bonded with ‘C’ ‘C’ bonded with ‘G’, ‘T’ bonded with ‘A’ and ‘A’ bonded with ‘T’ respectively.
3. Synthesis of RNA chain:
The new ribonucleotide bonded on DNA template are jointed with the help of RNA polymerase and thus, forming a new chain of RNA. Then this mRNA is separated from DNA and reaches the cytoplasm where it combines with ribosomes and thus, initiating the synthesis of protein.
![]()
Question 13.
What is translation? Explain it.
Answer:
Translation:
The translation step of protein synthesis involves translation of the language of nucleic acids (available in the form of mRNA) into language of protein. The sequence of bases in wRNA, decides the sequence of amino acids in proteins. Each amino acid is programmed by a triplet code. It consists of a sequence of three bases in the DNA and the complementary bases in /wRNA. The synthesis of protein occurs in three steps, initiation, elongation and termination. After the final step i.e., termination, the proteins are transported out of the cell or translocated within the cell. Thus, the transformation of nucleotides chain of RNA into polypeptide chain of protein is called as translation.
It is completed in following steps:
- Activation of amino acids.
- Binding of activated amino acids with?RNA.
- Binding of mRNA with smaller unit of ribosome.
- Initiation of polypeptide chain.
- Elongation of polypeptide chain.
- Termination of polypeptide chain.
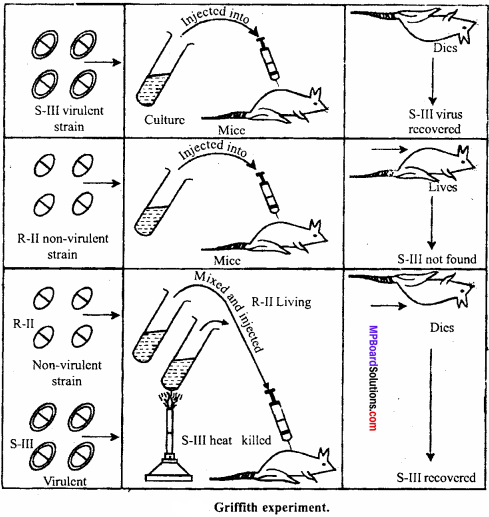
Question 14.
Describe the evidence given by Griffith in support of DNA as genetic material. Explain it along with suitable diagram.
Answer:
Griffith had done transformation experiments in mice to prove that DNA is the genetic material. He took virulent strain of Diplococcus pneumonae (S – III) which causes pneumonia in mice and injected it into mice which resulted in the production of pneumonia in mice. He also injected a non – virulent strain of that bacteria in the body of mice and found that all the mice were unaffected. In third experiment he injected heat killed (S – III) strain and non-virulent strain R – II strain together in the body of mice and found that all the mice suffered from pneumonia and became dead.
After analysis it was found that these mice contained both the strains of Diplococcus pneumonae. Thus, this experiment proved that any substance of S – III strain is transferred into R – II strain due to which R – II strain become virulent. Later, McLeod, Avery and McCarty observed that DNA molecules are transferred from S – III to R – II strain and make virulent; Thus, it is proved that DNA is the genetic material.
Question 15.
Explain the semi-conservative method of replication of DNA.
Or
Explain the method of DNA duplication.
Answer:
Synthesis of new DNA strands:
The DNA polymerase plays an important role in adding the building blocks to the primer in a sequence as influenced by the template. Replication of DNA is not continuous. It takes place by semi – conservative method. The parent DNA unwinds sequentially in local areas. A nick in one strand of the helix provides two free ends in one strand and a swivel in the other to absorb the twist that occur in the unwinding process.
When the double stranded DNA gets unwound up to a point it will represent a Y – shaped replication fork. This unwinding exposes the internal bases for replication.The enzyme DNA polymerase (discovered by Kornberg in 1957) now starts adding the nucleotides complementary to the DNA templates in the direction 5′ → 3′. Since, the two strands run in anti – parallel manner, the synthesis of new strands will be in opposite direction. As the synthesis of new strand progresses the point of divergence of the fork will be seen moving further due to unwinding of the strands of parental DNA.
Second strand is formed on 5′ → 3′ strand of parental DNA in a continuous stretch in reverse direction 3′ 5′ and is called the leading strand. However, on the second parental DNA template, the new complementary DNA strands are formed in smaller fragments starting from the RNA primer.
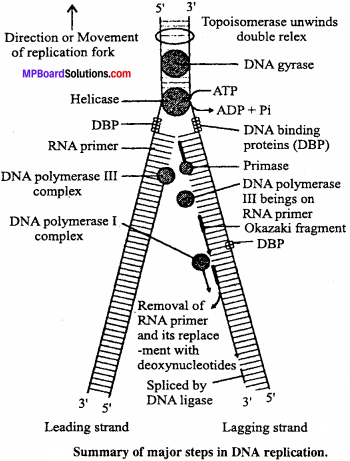
These short fragments are called Okazaki fragments after the name of scientist who discovered them. Since these fragments are joined later to form the complete strand it is called the lagging strand. The enzyme which joins the Okazaki fragments with the help of the RNA primer to form the lagging strand is called polynucleotide ligase or the joining enzyme.
Question 16.
Give the functions of nucleotides.
Answer:
Functions of Nucleotides:
- It works as a activated precursors of DNA and RNA.
- They are perform the storage and conduction of energy to the form of ATR
- It required for activation of intermediates in many biosynthetic pathway.
- It works as Carrier of methyl group in the form of SAM.
- It components of co – enzyme : NAD, FAD and Co A.
- Some functions are as a vitamin.
- They are control and coordinates different activities in our body.
Question 17.
Write four features of genetic code.
Answer:
According to Nirenberg, Khorana and Holley, genetic code is that sequence of nitrogenous bases of DNA in which genetic informations for the synthesis of protein are coded.
Characteristic features of genetic code:
1. The code is triplet:
The codon is a specific sequence of three nitrogenous bases of mRNA.
2. The code is commaless:
The sequence of bases read in blocks of three at a time form a particular position. There is no gap between two subsequent codons.
3. Code is degenerating:
Presence of more than one codon for one amino acid is called as degeneracy of codons, example Serine having three codons UCU, UCA, AGU.
4. Codes are universal:
Codons are similar in all organisms, example serine is coded by UCU codon in all the living beings.
5. Codes are non – ambiguous:
The position of genetic code in cellular medium is nonambiguous because a codon always codes only one amino acid. Sometimes a codor codes more than one amino acid, example in E. coli. UUV codon generally code phenylalanine, after treatment of their ribosome with streptomycin. It can also code isoleucine, leucine and serine.
6. Initiation and termination codon:
Codons responsible for the initiation of polypeptide chain are called as initiation codon, example AUG. Likewise codons responsible for the termination of polypeptide chain are called as chain termination codon, example UAA, U AG, UGA.
![]()
Question 18.
Define Codon and Anticodon.
Answer:
Codon:
A specific sequence of three consecutive nucleotides that is a part of the genetic code and that specifies a paticular amino acid in a protein or starts or stops protein synthesis example AUG codon which is situated on the wRNA, code methionine amino acid.
Anticodon:
A sequence of three adjacent nucleotides located on one end of transfer RNA. It bounds to the complementary coding triplet of nucleotides in wRNA during translation phase of protein synthesis. For example, the anticodon for Glycine is ccc that binds to the codon (which is GGE) ofwRNA.
Question 19.
Explain DNA duplication in short.
Answer:
Watson and Crick after giving the double helix model of DNA, also postulated the mechanism of DNA duplication, also known as replication. According to them, during duplication, the weak hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base of the nucleotides get separated, so that two polynucleotide chains of DNA also separate and uncoil. The chains thus, separated are complementary to one another. These strands act as template and because of the specificity of base pairing each nucleotide of separated chain attracts its complementary nucleotide from the cell cytoplasm.
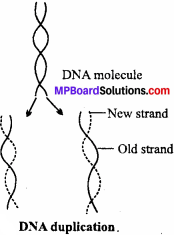
Once the nucleotides are attached by their hydrogen bonds their sugar radicals write through their phosphate components completing the formation of a new polynucleotide chain. This results in the formation of two double helixes of DNA where each molecule has one old strand contributed by parent DNA and one synthesized new. This method of DNA duplication is known as semi-conservative method.
Question 20.
Describe the functions of nucleic acids.
Or
Explain the utility of nucleic acids.
Answer:
Utility of Nucleic acids:
- Nucleic acids are the hereditary materials of organisms which involve in the transfer of hereditary characters from one generation to the next.
- DNA controls the synthesis of enzymes which control the various activities of the body.
- Nucleic acids also control protein synthesis.
- Nucleic acids form maximum portion of chromatin network.
- It causes mutation in living beings.
- They form enzymes.
Question 21.
Explain the structure of RNA.
Answer:
RNA molecules are single stranded nucleic acids composed of nucleotides. Four types of bases are present in RNA. These nitrogenous bases joint in different manner and form the ribonucleoside. Ribonucleoside joins together and make a polyribonucleotide chain.
All four types of nucleoside and nucleotide are as follows:
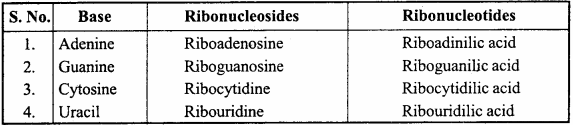
Question 22.
Depending upon the chemical nature of the template (DNA or RNA) and the nature of nucleic acid synthesized from it (DNA or RNA) list the types of nucleic acid polymerases.
Answer:
These are two different types of nucleic acid polymerases:
- DNA – dependent DNA polymerases
- DNA – dependent RNA polymerases
The DNA dependent DNA polymerases use a DNA template for synthesizing a new strand of DNA, whereas DNA dependent RNA polymerases use a DNA template strand for synthesizing RNA.
Question 23.
List two essential roles of ribosome during translation.
Answer:
Two essential roles of ribosome during translation are:
- One of the RNA acts as a peptidyl transferase ribozyme for formation of peptide bonds.
- Ribosome provides sites for attachment of TMRNA and charged fRNA for polypetide synthesis.
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How did Hershey and Chase differentiate between DNA and protein in their experiment while proving that DNA is the genetic material?
Answer:
Hershey and Chase experiment:
1. They grew some bacteriophages on a medium that contained radioactive phosphorus and some in another medium that contained radioactive sulphur.
2. Viruses grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive DNA but not radioactive protein as phosphorus is present only in DNA.
3. Viruses grown on radioactive sulphur contained radioactive protein but not radioactive DNA because DNA does not contain sulphur.
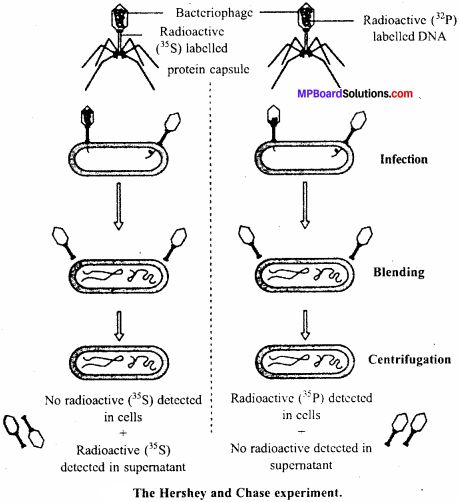
4. It was found that bacteria which were infected with bacteriophages that had radioactive DNA were radioactive, indicating that DNA was the material that passed from the virus to the bacteria.
5. Bacteria that were infected with viruses that had radioactive proteins were not radioactive. This indicated that proteins did not enter the bacteria from the viruses.
6. This was a clear cut proof that DNA is the genetic material that is passed from virus to bacteria.
![]()
Question 2.
Differentiate between the followings:
- Repetitive DNA and Satellite DNA.
- OTRNA and IRNA.
- Template strand and Coding strand.
Answer:
1. Differences between Repetitive DNA and Satellite DNA :
Repetitive DNA :
- DNA in which certain base sequences are repeated many times are called repetitive DNA.
- Repetitive DNA sequences are transcribed.
Satellite DNA:
- DNA in which large protein of the gene is randomly repeated is called satellite DNA.
- Satellite DNA sequences are not transcribed.
2. Differences between mRNA and tRNA:
mRNA:
- It is linear.
- It carries coded information.
- mRNA undergoes additional processing, i.e., capping and tailing splicing
- Nitrogen bases are unmodified.
tRNA:
- It is clover – leaf shaped.
- It carries information for association with an amino acid and a anticodon for its in corporation in a polypeptide.
- It does not require any processing.
- Nitrogen bases may be modified.
3. Differences between Template strand and Coding strand:
- Template strand:
- It is the strand of DNA which takes part in transcription.
- The polarity is 3 ’ → 5′
- Nucleotide sequence is complementary to the one present in mRNA.
Coding strand:
- It is the stand that does not take part in transcription.
- The polarity is 5’ → 3’.
- The nucleotide sequence is same as the one present in mRNA except for presence of Thymine instead of Uracil.
Question 3.
Explain (in one or two lines) the function of the followings:
- Promoter
- tRNA
- Exons.
Answer:
1. Promoter is an essential component of the transcription unit. It is located at the beginning of 5’-end. It provides a site for the attachment of transcription factors and RNA polymerase.
2. tRNA is a small sized RNA molecule that takes part in transcription. It physically picks up activated amino acids from the cytoplasm and carries (transfers) them to ribosomes, where they join together through peptide bonds and leave the /RNA to fetch more amino acids.
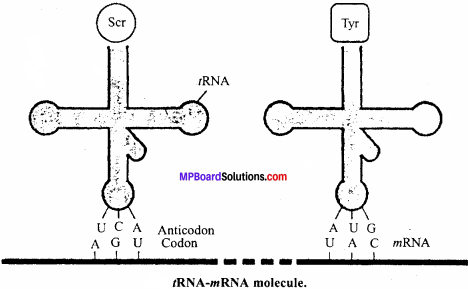
3. Exons are the coding sequences of DNA that are transcribed and translated.
Question 4.
Why is the human genome project called a mega project?
Answer:
Human genome project is called a mega project because:
- Its aim was to determine the nucleotide sequence of complete human genome which was a task of enormous magnitude.
- A total of 3 x 109 base pairs were to be sequenced and the cost was about 9 billion US dollars.
- It requires bioinformatics data base techniques and other contemporary devices for the analysis, storage and retrieval of information.
- Many countries worked jointly to complete this timed project.
![]()
Question 5.
What is DNA Fingerprinting? Mention its application.
Answer:
DNA Fingerprinting:
Every human individual is characterised by unique print at the fingertips. The study of fingers, palm and sole print is called ‘dermatoglyphics’. Like prints of the fingertips, each individual has unique DNA fingerprint. Unlike the prints of finger, the DNA fingerprints can not be altered by surgery. The later is exactly similar in all the cells and tissues of an individual. It can not be changed by medical treatment.
The distinction of individuals on the basis of DNA fingerprint is due to sequence of nucleotides in whole genomic DNA. The technique to identify a person on the basis of his/her DNA specificity is called DNA fingerprinting. This was invented by Sir Alec Jeffreys in 1984 at Leicester University, U.K. In India, Dr. V. K. Kashyap and Dr. Lalji Singh started this technique at CCMB, Hyderabad.
DNA fingerprinting involves following steps:
- The DNA of the organism to be tested is isolated, it is called host DNA
- Host DNA is cleaved with the help of specific restriction enzymes into several fragments.
- Double stranded DNA fragments are denatured to produce single stranded DNA by alkali treatment.
- DNA segments are separated by electrophoresis.
Question 6.
Briefly describe the following:
- Transcription
- Polymorphism
- Translation
- Bioinformatics.
Answer:
1. Transcription:
It is the formation of RNA over the template of DNA. It forms single-stranded RNA which has a coded information similar to the sense or coding strand of DNA with the exception that thymine is replaced by uracil. One strand of DNA is used as template strand for the synthesis of a complementary strand of RNA called mRNA.
2. Polymorphism:
Genetic polymorphism means occurrence of genetic material in more than one form. It is of three major types, i.e., Allelic, SNP and RFLP.
(a) Allelic polymorphism:
Allelic polymorphism occurs due to multiple alleles of a gene. Allele possess different mutations which alter the structure and function of a protein formed by them as a result, change in phenotype may occur.
(b) SNP or Single Nucleotide Polymorphism:
Over 1 – 4 million single base DNA differences have been observed in human beings. According to SNP, every human being is unique. SNP is very useful for locating alleles, identifying disease associated sequence and tracing human history.
3. Translation:
The translation step of protein synthesis involves translation of the language of nucleic acids (available in the form of mRNA) into language of protein. The sequence of bases in mRNA, decides the sequence of amino acids in proteins. Each amino acid is programmed by a triplet code. It consists of a sequence of three bases in the DNA and the complementary bases in mRNA. The synthesis of protein occurs in three steps, initiation, elongation and termination. After the final step i.e., termination, the proteins are transported out of the cell or translocated within the cell. Thus, the transformation of nucleotides chain of RNA into polypeptide chain of protein is called as translation.
It is completed in following steps:
- Activation of amino acids.
- Binding of activated amino acids with tRNA.
- Binding of mRNA with smaller unit of ribosome.
- Initiation of polypeptide chain.
- Elongation of polypeptide chain.
- Termination of polypeptide chain.
4. Bioinformatics:
The science which deals with handling storing of huge information of genomics as databases, analysing, modelling and providing various aspects of biological information, especially the molecules connected with genomics and proteomics is called bioinformatics.
![]()
Question 7.
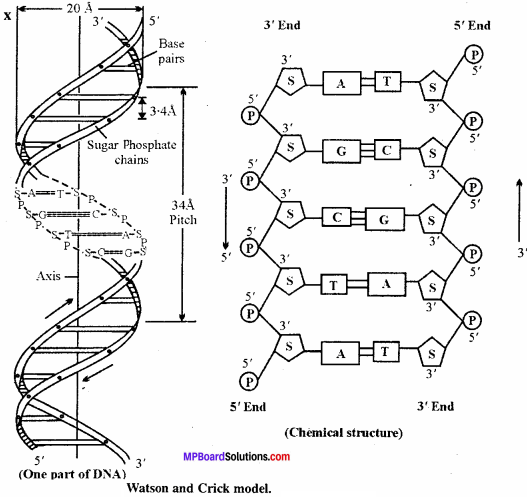
Explain the Watson and Crick model of DNA.
Answer:
The structure of DNA was proposed by Watson and Crick. It is twisted ladder like structure. It has got two coiled polynucleotides which are joined together by nitrogen bases with hydrogen bond in the centre. The longitudinal strands of DNA are made of sugars and phosphates of nucleotides. The horizontally placed nitrogen bases are of two types, purine and pyrimidine. Purines are adenine and guanine whereas pyrimidines are cytosine and thymine.