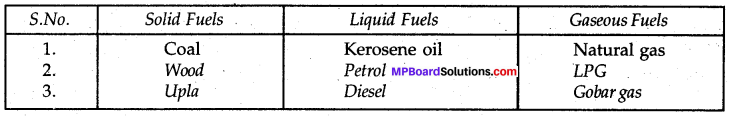
MP Board Class 8th Science Solutions Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
MP Board Class 8th Science Coal and Petroleum NCERT Textbook Exercises
Mp Board Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Question 1.
What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Answer:
The advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels are:
- CNG and LPG are a non-polluting fuel vehicles.
- CNG is used for power generation.
- LPG can be used directly for burning in homes and factories.
- CNG and LPG fuels are easy to store.
Mp Board Class 8 Science Solution Chapter 5 Question 2.
Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Answer:
These days bitumen is used for surfacing of roads in place of coal-tar.
Mp Board Class 8 Social Science Solution Chapter 5 Question 3.
Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called?
Answer:
About 300 million years ago, the earth had dense forests in low lying wetland areas. Due to natural processes like flooding, these forests got buried under the soil. As more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. The temperature also rose as they sank deeper and deeper. Under high pressure and high temperature, dead plants got slowly converted to coal. As coal contains mainly carbon, the slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called carbonisation. Since it was formed from the remains of vegetation, coal is also called a fossil fuel.
Mp Board Class 8th Science Chapter 5 Question 4.
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Fossil fuels are and
(b) Process of separation of different- constituents from petroleum is called
(c) Least polluting fuel for vehicle is
Answer:
(a) coal, petroleum, natural gas.
(b) refining
(c) CNG.
Mp Board Class 8 Social Science Chapter 5 Question 5.
Tick TruelFalse against the following statements:
(a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory. (T/F)
(b) CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol. (T/F)
(c) Coke is almost pure form of carbon. (T/F)
(d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances. (T/F)
(e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel. (T/F)
Answer:
(a) False, (b) False, (c) True, (d) True, (e) True.
Mp Board Solution Class 8 Science Question 6.
Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Answer:
Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels. The amount of these resources is limited in nature and is used by human activities. This is why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Mp Board Question 7.
Describe characteristics and uses of coke.
Answer:
Coke is obtained as a solid residue by heating coal in a closed tube in the absence of air. Coke is a tough porous black substance. It is almost pure form of carbon. Uses of Coke:
- It is used in the manufacture of steel.
- It is used in the extraction of many metals.
Mp Board Class 8 Science Solution Chapter 4 Question 8.
Explain the process of formation of petroleum.
Answer:
Petroleum was formed from organisms living in the sea. As these organisms died, their bodies settled at the bottom of the sea and got covered with layers of sand and clay. Over millions of years, absence of air, high temperature and high pressure transformed the dead organisms into petroleum and natural gas.
Mp Board 8th Class Science Solutions Question 9.
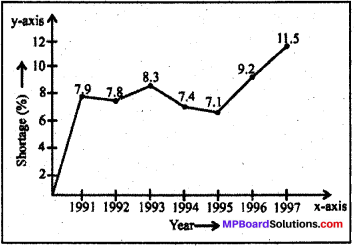
The following table shows the total power shortage in India from 1991-1997. Show the data in the form of a graph. Plot shortage percentage for the years on the Y-axis and the year on the X-axis.
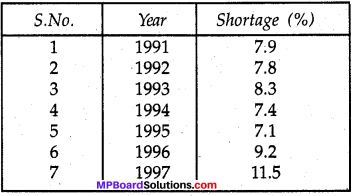
(Source: CME, D&B researchcea.nic.in)
Answer:
MP Board Class 8th Science Coal and Petroleum NCERT Intext Activities and Projects
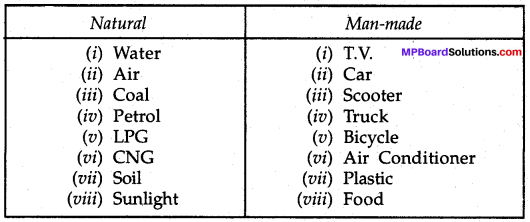
Mp Board Class 8th Science Solution Activity 5.1
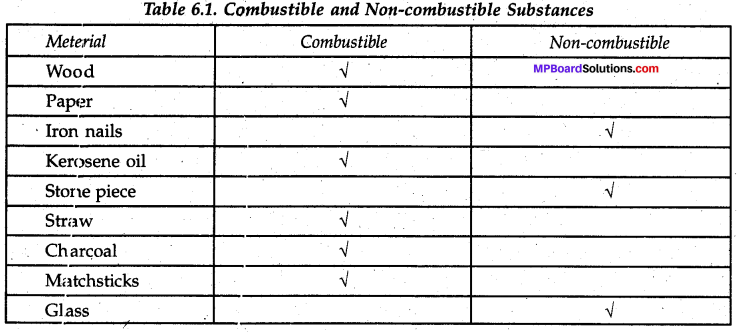
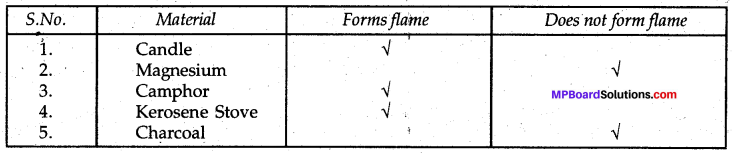
Make a list of various materials used by us in daily life and classify them as natural and man-made.
MP Board Class 8th Science Coal and Petroleum NCERT Additional Important Questions
A. Short Answer Type Questions
Mp Board Solution Science Class 8 Question 1.
Define inexhaustible natural resources with examples.
Answer:
These resources are present in unlimited, quantity in nature and are not likely to be exhausted by human activities. Examples are sunlight, air.
Class 8 Science Mp Board Solution Question 2.
Define exhaustible natural resources with examples.
Answer:
The amount of these resources in nature is limited. They can be exhausted by human activities. Examples of these resources are forests, wildlife, minerals, coal, petroleum, natural gas etc.
Mp Board Class 8 Science Solution Question 3.
Why charcoal is better fuel than wood?
Answer:
Charcoal is a clean fuel and gives very less smoke which is equivalent to negligible. But wood is not a clean fuel and gives a lot of smoke on burning.
Mp Board Class 8 English Chapter 5 Question 4.
Why should we conserve energy?
Answer:
We should conserve energy:
- to overcome the problem of energy crisis.
- to save non-renewable sources of energy.
- to make the sources last long.
Class 8 Coal And Petroleum Question Answer Question 5.
Why are we using coal and petroleum
even though a large amount of sun’s energy is falling on the earth?
Answer:
Even though a large amount of the sun’s energy is falling on earth, it is very much diffused. In order to use sun’s energy we have to collect and concentrate it.
B. Long Answer Type Questions
Mp Board Solution Class 8 Subject Science Question 6.
What are the uses of LPG?
Answer:
At high pressure, LPG is stored in liquid form. Therefore, it can be filled at high pressure in small cylinders which can be sent for household and industrial uses. When regulator fitted on the cylinder is turned on, pressure inside the cylinder reduces and LPG converts in gaseous form and passes through a pipe to the burner where it is used as fuel.
Question 7.
Write a short note on Compressed Nature Gas.
Answer:
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): Natural gas is mainly composed of methane (CH4) with ethane C2H6 and propane C3H8 gases in lesser amount. Methane is the major component (95%) of the natural gas. Usually petroleum gases are obtained at the top level of petroleum oil in petroleum wells. CNG is natural gas compressed at high pressure. CNG is used as a fuel in houses and in automobiles. It is more pollution free than other fuels.
Question 8.
Define the term fossil fuel. Name three fossil fuels.
Answer:
The period between 200 to 300 million years ago is known as carboniferous age. During this period large trees covered many areas of the earth. The generations of trees died and were gradually buried. These trees were converted very slowly into peat, then lignite and finally coal. It is called fossil fuels. Examples of fossils fuels are coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Question 9.
What is PCRA? What does it advise?
Answer:
PCRA stands for Petroleum Conservation Research Association. It advises people how to save petrol/diesel while driving. Their tips are:
- drive at a constant and moderate speed as far as possible.
- switch off the engine at traffic lights or at a place where one has to wait.
- ensure correct tire pressure.