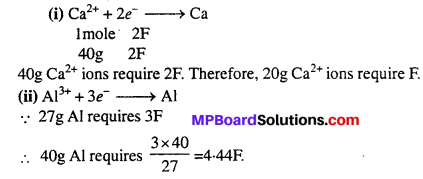
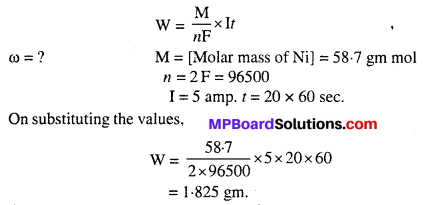
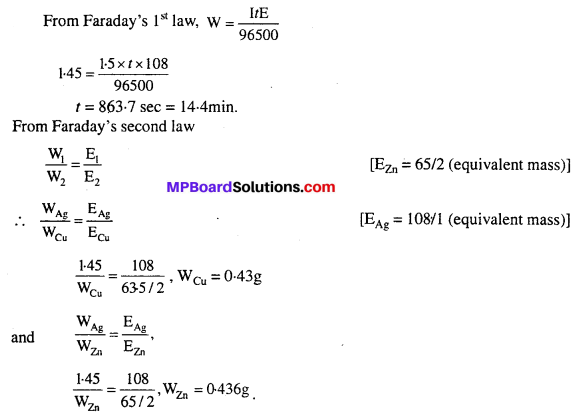
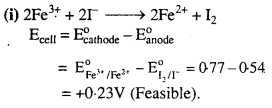
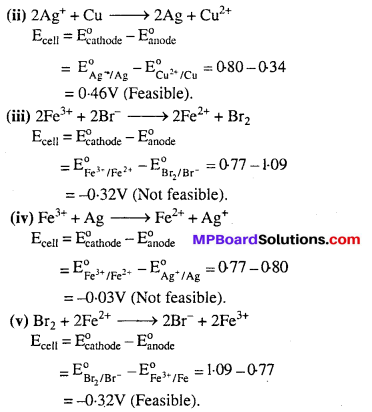
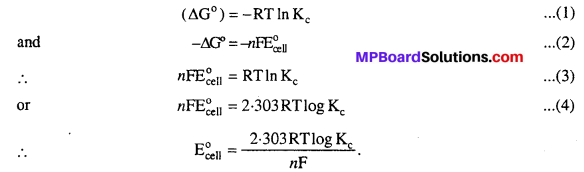
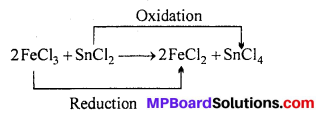
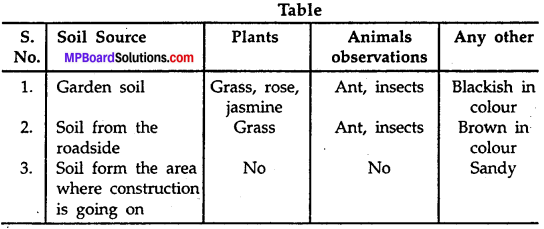
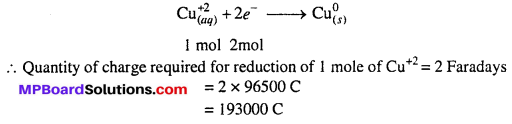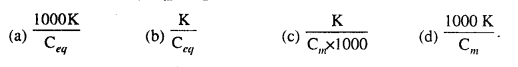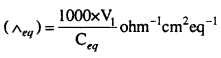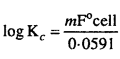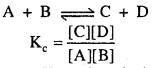MP Board Class 6th Science Solutions Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups
Sorting Materials into Groups Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
Name five objects which can be made from wood?
Answer:
The five objects which can be made from wood:
- Chair
- Table
- Door
- Bullock cart
- Plough.
Question 2.
Select those objects from the following which shine: Glass bowl, plastic toy, steel spoon, cotton shirt?
Answer:
Glass bowl, steel spoon.
Question 3.
Match the objects given below with the materials from which they could be made. Remember, an object could be made from more than one material and a given material could be used for making many objects?

Answer:
Book – Paper; Tumbler – glass; Chair – wood; Toy – plas – tics; Shoes – leather.
Question 4.
State whether the statements given below are True or False.
- Stone is transparent, while glass is opaque.
- A notebook has lustre while eraser does not.
- Chalk dissolves in water.
- A piece of wood floats on water.
- Sugar does not dissolve in water.
- Oil mixes with water.
- Sand settles down in water.
- Vinegar dissolves in water.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True.
![]()
Question 5.
Given below are the names of some objects and materials:
Water, basket ball, orange, sugar, globe, kpple and earthen pitcher,
Group them as:
- Round shaped and other shapes.
- Eatables and non – eatables.
Answer:
- Round shaped and other shapes: Basket ball, orange, globe, apple, earthen pitcher.
- Eatables and non – eatables: Water, sugar.
Question 6.
List all items known to you that float on water? Check and see if they will float on an oil or kerosene?
Answer:
Paper, ice, oil, wax and dried leaves. All of these items floats on water and they sink in oil and float on kerosene.
Question 7.
Find the odd one out from the following:
- Chair, Bed, Table, Baby, Cupboard.
- Rose, Jasmine, Boat, Marigold, Lotus.
- Aluminium, Iron, Copper, Silver, Sand.
- Sugar, Salt, Sand, Copper sulphate.
Answer:
- Baby
- Boat
- Sand
- Copper sulphate.
![]()
Projects and Activities
Activity 1.
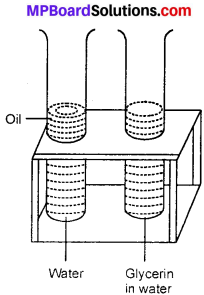
Given on experiment to show that glycerin or lime juice is soluble in water but not edible oil?
Answer:
Necessary materials – Glycerin or like juice, water, edible oil, two test tubes. Take two test – tubes half filled with water on test – tube stand. In one of the test tube add 5 to 6 drops of glycerin or lime juice and in second test tube add little edible oil. Shake them well and then let them remain on stand for about 5 minutes.
After 5 minutes, it is observed that glycerin dissolves in water. But in other test tube two distinct layers are seen, upper layer is that of the edible oil and lower one is of water. This shows that glycerin is soluble in water but edible oil is insoluble in water.
Activity 2.
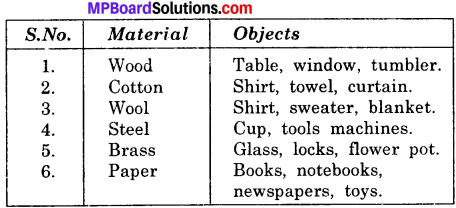
List some materials each of which can be used to make different kinds of object:
Answer:
Activity 3.
List five objects each of which is made different kinds of materials?
Answer:
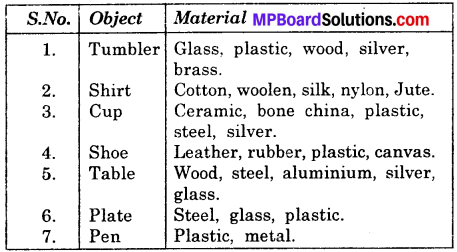
Activity 4.
Give an experiment to show that sugar is soluble in water but not chalk powder?
Answer:
Take two test – tubes containing water. Take a teaspoonful of sugar and chalk powder. Add the two in separate test – tubes. Shake the test – tubes and observe. In first test – tube sugar dissolves completely with no left over at the bottom. In second test – tube chalk powder does not dissolve but settled at the bottom (Fig.). This shows that sugar is soluble in water but not chalk powder.
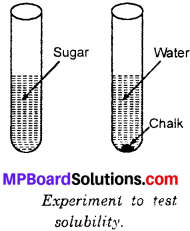
Activity 5.
Make a table to show that mixing of different solid materials in water?
Answer:
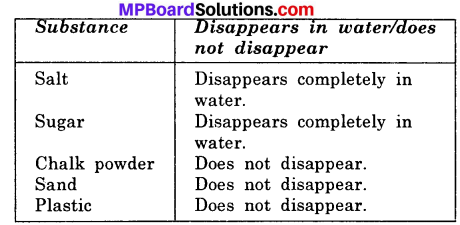
Activity 6.
Make a table to show that solubility of some common liquids in water?
Answer:
Solubility of some common liquids in water:
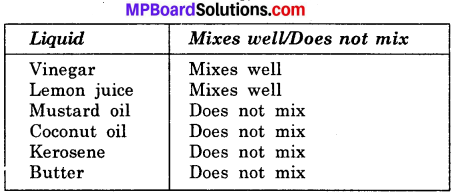
Sorting Materials into Groups Intex Questions:
Question 1.
Boojho wants to know, whether we found some materials that were used for making more than one type of an object?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 2.
Boojho suggests that we also check if the liquids that we used in Activity 6 mix well with some liquid other than water? Peheli is curious to known whether gases also dissolve in water?
Answer:
Some gases are soluble in water whereas others are not. For example, oxygen gas dissolved in water is very important for the survival of animals and plants that live in water.
Sorting Materials into Groups Additional Important Questions
Sorting Materials into Groups Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question (a)
All things are made of:
(a) Materials
(b) Things
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Materials
Question (b)
Wax and plastics are in water?
(a) Soluble
(b) Insoluble
(c) Miscible
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Insoluble
![]()
Question (c)
Chalk powder is in water?
(a) Soluble
(b) Insoluble
(c) Miscible
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Insoluble
Question (d)
A liquid containing a dissolved material is called:
(a) Soluble
(b) Solubility
(c) Solution
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Solution
Question (e)
Common salt is ……………………… in water?
(a) Soluble
(b) Insoluble
(c) Miscible
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Soluble
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the Blanks:
- A sugar syrup is a ……………………
- Sand is …………………. in water.
- Lemon juice is ………………….. in water.
- Materials which can be compressed or scratched easily are called ……………………….
- Materials which are difficult to compress are called ………………………..
- Iron, copper, aluminium and gold are examples of …………………………
- Those substances or materials, through with things can be seen are called ………………………….
- The materials through which objects can be seen, but not clearly, are known as ………………………..
Answer:
- Solution
- Insoluble
- Soluble
- Shoft
- Hard
- Metals
- Translucent
- Transparent.
![]()
Question 3.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
- Metals are good conductors of heat.
- Water is a bad conductor of electricity but if salt is dissolved in water, it becomes good conductor.
- Disprine tablet is insoluble in water.
- Iron is a magnetic material.
- Glass and air are transparent materials.
- Sands are soluble in water.
- Wax floats in water.
- Mustard oil is not miscible with water.
- Iron nails float in water.
- Gases are soluble in water.
- Coconut oil is not miscible with water.
- Stone is opaque while glass is transparent.
- Wood and plastics are good conductor of heat.
- We are able to see through opaque substances.
- Sand settles down in water.
- All metals are good conductors of heat.
- All gases are good conductors of heat.
- A substance which allows the heat to pass is conductor.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True.
Question 4.
Match the items in Column A with items in Column B:

Answer:
(i) – (b)
(ii) – (e)
(iii) – (a)
(iv) – (c)
(v) – (d)
Question 5.
In the given below group of words one is odd and rest are similar. Write down the odd qualities of them?
- Bus, motor cycle, cycle, bullock – cart.
- Pen, chalk, pencil, paper.
- Lemon, banana, ma ngo, ‘gulab jamun’.
- Hen, lizard, pigeon, crow.
- Tumbler, jug, mug, spoon.
Answer:
- Bullock – cart
- Paper
- Gulab jamun
- Lizard
- Spoon.
Question 6.
Answer the riddle:
Sometimes I am hard and chill Sometimes I run down the hill But I am always present in air Who am I?
Answer:
Water.
Sorting Materials into Groups Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is matter?
Answer:
Any thing which has mass and occupies space is called matter.
Question 2.
Write the definition of classification?
Answer:
The process of grouping and sorting objects is called classification.
Question 3.
Write down the names of two natural substances which are used to make cloth?
Answer:
Cotton and silk.
![]()
Question 4.
Name five things made up of plastic?
Answer:
- Chair
- Table
- Bucket
- Comb
- Toys.
Question 5.
List five things which are made up of same material?
Answer:
Shirt, towel, curtain, bed – sheet and trousers are made up of same material i.e., cotton.
Question 6.
Classify the following into natural and man-made substances: cotton, plastic, rubber, soil, petrol, diesel.
Answer:
Natural substance: Cotton, rubber, soil.
Man – made substances: Plastic, petrol, diesel.
Question 7.
Plastic is a man – made material. Give five more examples of man – made materials?
Answer:
Glass, steel, ceramic, thermocole and polythene.
Question 8.
Coal is a naturally occurring material. Write the names of five naturally occurring materials?
Answer:
Wood, cotton, jute, rubber and leather.
Question 9.
Name any four materials that can be used to make the school bag?
Answer:
School bag can be made from cotton (natural), nylon (man-made), leather (natural), jute (natural).
![]()
Question 10.
Name three material from which following things could be made:
- Table
- Bucket
- Glass
- Toys
Answer:
- Table: Wood, steel, aluminium, silver and glass.
- Bucket: Plastic, steel.
- Glass: Ceramic, bone china, steel, plastic and silver.
- Bowl: Steel, ceramic, bone china and brass.
- Chair: Wood, steel, aluminium silver and glass.
Question 11.
Give one example of solids which have the properties listed:
- Solids which are hard.
- Solids which are soft.
- Solids which are soluble in water.
- Solids which are insoluble in water.
- Solids which have colour.
- Solids which are colourless.
- Solids whose shape can easily changed.
- Solids which have smell.
- Solids which break easily.
- Solids which sink in water.
- Solids which float on water.
- Solids through which we can see.
- Solids through which we cannot see.
Answer:
- Stone, wood
- Butter
- Sugar, salt
- Chalk, sand
- Clothes
- Ice, colourless glass
- Clay, plastercin.
- Flowers, camphour.
- Glass
- Stone
- Wood piece.
- Glass
- Wall.
![]()
Question 2.
Name the liquids which have following properties:
- A colourless liquid.
- A liquid which has smell.
- A liquid in which sugar dissolves.
- A flammable liquid.
- A non – flammable liquid.
- Apair of liquids which are unmixable with each other
- A pair of liquids which are mixable with each other.
- A liquid that floats on water.
- A liquid that sinks in water.
- A liquid which has some colour.
Answer:
- Water
- Kerosene
- Water, milk
- Petrol
- Water
- Mustard oil and water
- Water and milk
- Petrol
- Mercury
- Mustard oil is yellow in colour.
Question 13.
Write the names of different things made by ghee, water, sugar?
Answer:
Ghee. It is used for sweets and different products of eating. Water. It is used for drinking, bathing, harvesting, etc. Sugar. It is used to sweeten milk, tea, sweets, etc.
![]()
Question 14.
Write names of four different things made from cotton?
Answer:
The different things made from cotton are shirt, towel, curtain, bed sheets, etc.
Question 15.
Divide the following items according to their solubility in water:
- Sugar
- Glass
- Particles of wood
- Salt
- Honey
- Rubber
- Soap
- Caustic soda
- Chalk
- Urea.
Answer:
Solubility in water:
- Sugar
- Salt
- Honey
- Soap
- Caustic soda
- Chalk
- Urea.
Question 16.
Does coconut oil get dissolved in kerosene oil?
Answer:
No.
![]()
Question 17.
List five opaque and five transparent materials?
Answer:
Opaque materials:
Cardboard, wooden piece, metal sheet and wall.
Transparent materials:
Glass, air, water, thin polythene, cellophane paper.
Question 18.
List five objects which are made from transparent material?
Answer:
Substances made from transparent material are
- Glass tumbler, cellophane sheet, ballons (coloured or colourless), car window, mask of transparent plastic sheet.
Question 19.
List five liquids that are transparent?
Answer:
- Water
- Alcohol
- Kerosene
- Purified mustard oil
- Glycerine.
Question 20.
List five objects made from opaque material?
Answer:
- Wooden chair
- Leather bag
- Plastic handle
- Iron almirah
- Cardboard box.
![]()
Question 21.
Why does wood float on water but stone sink?
Answer:
Wood floats on water because it is lighter than water whereas a piece of stone sinks in water. It is heavier than water.
Sorting Materials into Groups Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
If you have objects similar in all respects, can you classify them in different groups?
Answer:
No, it is not possible to classify similar objects. Classification can only be done when objects have some similar and some dissimilar properties in them.
Question 2.
Why do we need to classify objects?
Answer:
There are millions of objects around us. These are of different size, shape and different in any ways. It is not easy to study each of them. Thus for easy and better understanding, we need to classify them.
![]()
Question 3.
A bag can be made from jute, a naturally occurring material or from nylon, a man-made material. List five more things that can be made from natural as well as man – made material?
Answer:
- Tumbler – Copper and glass.
- Suitcase – Iron and plastic (P.V.C.)
- String – Cotton/jute and nylon.
- Pen – Aluminium and plastic.
- Shoes – Cloth/leather and plastic.
Question 4.
What is a solution?
Answer:
The matter which dissolves is called solute. A liquid in which solute gets dissolved is called solvent. When solute and solvent mix together it is called solution.
Question 5.
What is transparency? Find out the transparent and opaque substances from the following: Glass, plastic, wood, oil, paper, water, iron.
Answer:
The materials through which we can see the outside view are called transparent material. For example, water, glass. This property of such materials is called transparency.
Transparent substances:
Glass, water.
Opaque substances:
Plastic, wood, iron.
![]()
Question 6.
Mention three materials which are soluble and three which are insoluble in water?
Answer:
Materials soluble in water are:
- Salt
- Sugar
- Washing soda.
Materials insoluble in water are :
- Sand
- Chalk powder
- Coconut oil.
![]()
Question 7.
On what basis are the various objects grouped?
Answer:
The various objects can be grouped on the basis of their properties like:
- Colour
- Size
- Hardness or softness
- Natural or man – made,
- Solid, liquid or gas,
- Living or non – living
- Plant or animal
- Material they have made up of
- Simple substance or mixture of many substances.
Sorting Materials into Groups Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
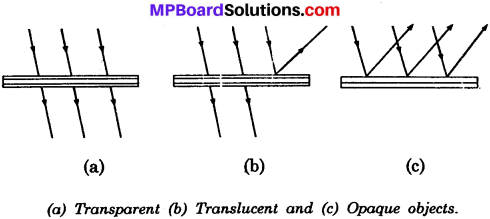
What are transparent, translucent and opaque objects?
Answer:
Transparent objects are those objects through which light passes across completely. We can see across them in figure. For example, glass, water, cellophane paper etc. Translucent objects are those objects which allow only a part of light falling on them to pass while they reflect the rest of the light.
We can see only faintly across them. For example, grinded glass, butter paper, turbid water, etc. Opaque objects are those objects which do not allow the light to pass through them. They reflect all the light falling on them. For example, card – board, an iron sheet, aluminium foil, etc.