MP Board Class 6th Science Solutions Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and their Surroundings
The Living Organisms and their Surroundings Text Book Exercises
Question 1.
What is a habitat?
Answer:
The place where a plant or an animal lives is called its habitat.
Question 2.
How are cactus adapted to survive in a desert?
Answer:
Cactus plants lose very little through transpiration. The leaves in desert plants are either absent, very small, or they are present in the shape of spines. This helps in reducing loss of water from the leaves through transpiration. The photosynthesis in these plants is usually carried out by the stems. The stem is also covered with a thick waxy layer, which helps to retain water. Cactus plants have roots that go very deep into the soil for absorbing water.
![]()
Question 3.
Fill up the blanks:
- The presence of specific features, which enable a plantor an animal to live in a particular habitat, is called …………….
- The habitats of the plants and animals that live on land are called ……………. habitat.
- The habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called ……………. habitat.
- Soil, water and air are the ……………. factors of habitat.
- Changes in our surroundings that make us respond to them, are called …………….
Answer:
- Adaptations
- Terrestrial
- Aquatic
- Abiotic
- Stimuli.
Question 4.
Which of the things in the following list are non – living? Plough, Mushroom, Sewing machine, Radio, Boat, Water hyacinth, Earthworm.
Answer:
Non – living things are plough, sewing machine, radio and boat.
Question 5.
Give an example of a non – living thing, which shows any two characteristics of living things?
Answer:
Clouds in the sky. They show two living characteristics. These are grow in size and move from one place to another place.
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the non – living things listed below, were once part of a living thing? Butter, Leather, Soil, Wool, Electric bulb, Cooking oil, Salt, Apple, Rubber.
Answer:
Butter, Leather, Wool, Cooking oil, Apple, Rubber.
Question 7.
List the common characteristics of the living things?
Answer:
The common characteristics of the living things are growth, movement, life cycle, nutrition (taking food), respiration, excretion, respond to stimuli, show movement, die and reproduction.
Question 8.
Explain, why speed is important for survival in the grasslands for animals that live there?
Answer:
There are few trees or places for animals to hide in the grassland habitats. The animals like lion or tiger prey other animals such as deer. The deer have very fast running speed to help them to run away from the predator’s speed is important for their survival in grassland habitats.
![]()
Projects And Activities
Activity 1.
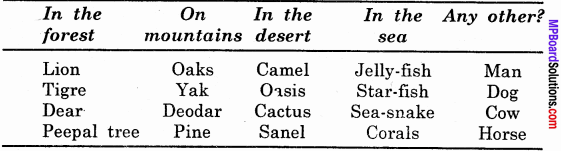
Prepare a table to show that animals, plants and other objects found in different surroundings.
Answer:
Animals, plants and’other objects found in different surroundings:
Activity 2.
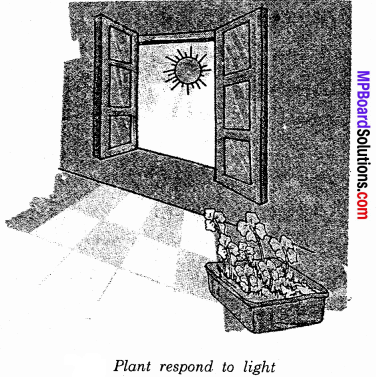
What is phototropism. Explain with a diagram.
Answer:
Phototropism is the growth of the plant shoot to the sources of light. Take a potted plant with erect stem. Keep the plant in dark room in which the source of the light should be on any one side. Observe the plant after a weak. We see that the shoot of the plant has bent towards the source of light as shown in figure.
Activity 3.
What is its name and habitat?
Answer:

Answer:
- “Penguin.”
- Habitat: Polar regions.
The Living Organisms and their Surroundings Additional Important Questions
The Living Organisms and their Surroundings Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question (i)
In which of the following thing, life activities are carried out –
(a) Chain
(b) Stone
(c) Banyan
(d) Plastic
Answer:
(c) Banyan
Question (ii)
prepare their own food –
(a) Plants
(b) Things
(c) Creatures
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Creatures
Question (iii)
…………… gives eggs.
(a) Cat
(b) Cow
(c) Hen
(d) Dog
Answer:
Question (iv)
Which one is not a noctural animal –
(a) Owl
(b) Camel
(c) Cockroach
(d) Bat
Answer:
(b) Camel
![]()
Question (v)
Pond is an example of habitat.
(a) Aquatic
(b) Desert
(e) Terrestrial
(d) Oceans.
Answer:
(a) Aquatic
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The place where the animals live is called …………….
- Hydra is fnuni in ……………
- Cactus is the plant found in ……………
- …………… is an añimal which gives eggs.
- …………… is a non – flower plant.
- A group of similar organisms is called …………….
- The world of living organisms is divided into and …………….
- …………….. are both living and non – living.
- There are some sea animals like dolphins and whales that do not have ………………
- Changes in our surrondings that makes us respond to them, are called ………………
Answer:
- Habitat
- Pond water
- Desert
- Snake
- Fungi
- Species
- Plant, animal
- Viruses
- Gills
- Stimuli.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
- Reproduction is a common feature of living and nonliving.
- The process of give birth to young ones is called as reproduction.
- Every living being responds to external stimuli. This property is called as response.
- The plants and animals that live on land are said to live in terrestrial habitats.
- Breathing is part of a process called respiration. Animals and plants are abiotic components.
- Abiotic components are also known as physical factors.
- Zizyphus is an aquatic plant.
- Many plants reproduce through seeds.
- There is wide variety of organisms present in different habitats.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True.
Question 4.
Match the items of Column A with Column B:

(i) (c)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (a)
(iv) (b)
(v) (f)
(vi) (e)
The Living Organisms and their Surroundings Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is an organisms?
Answer:
All living creatures of various kinds are organisms.
Question 2.
Name some animals which lay eggs?
Answer:
Frog, snakes, birds, etc. lay eggs.
Question 3.
Name animals which give birth to their young ones.
Answer:
Woman, cow, monkey, etc. give birth to their young ones.
Question 4.
What are biotic components?
Answer:
Plants and animals are biotic components.
Question 5.
What are abiotic components?
Answer:
Water, air, light, soil and heat are abiotic components.
![]()
Question 6.
How do plants obtain their food?
Answer:
Plants prepare their own food in their green leaves with carbon – di – oxide, water, minerals and sunlight.
Question 7.
How do the plants prepare their food?
Answer:
Plants take carbon – di – oxide from air water and sunlight. They prepare their food with the help of these and leave out oxygen.
Question 8.
Give example of organisms who do not need light and live underground?
Answer:
Earthworm, cockroach, rats and termites, etc. live in. burrows and are active at night.
Question 9.
Some names of living things are given below. Divide them in two groups (i) giving eggs, (ii) giving birth to young ones. Cockroach, Cat, Dog, Bird, Cow, Lizard, Parrot, Crow, Horse?
Answer:
- Living being which lay eggs are cockroach, bird, lizard, crow and parrot.
- Living being which give birth to young ones are cat, dog, cow and horse.
Question 10.
What is the food of a frog?
Answer:
Small insects.
Question 11.
What is the food of fishes?
Answer:
lt feeds up micro plants and aquatic insects.
Question 12.
What is the scientific name of human being?
Answer:
Homo – Sapines.
Question 13.
Name any three desert animals?
Answer:
Lizard, camel, snake.
Question 14.
Name any two desert plants?
Answer:
Kikar, cactus.
Question 15.
Name any two aquatic animals?
Answer:
Fish, coral.
![]()
Question 16.
Name three non – living things in a pond?
Answer:
Water, mud and air.
Question 17.
Name two living organisms in a pond?
Answer:
Frog and fish.
Question 18.
Name some animals which are found at mountains?
Answer:
Snow – bear, musk deer, wolf and water fowl.
Question 19.
How is light essential for plants?
Answer:
Plants prepare their own food in the presence of light.
Question 20.
Where do you find yak?
Answer:
At mountains.
Question 21.
What kind of trees do you see on Himalayan mountains?
Answer:
Pines, deodars, oaks.
Question 22.
What is adaptation?
Answer:
The presence of specific features or certain habits, which enable a plant or an animal to live in its surroundings is called adaptation.
Question 23.
What is excretion?
Answer:
As a result of various chemical (metabolic) reactions taking place in the body of cells certain harmful toxic substances are constantly formed. Removal of these toxic substances from j the body is termed as excretion.
![]()
Question 24.
Define respiration with the help of chemical equation?
Answer:
The process in which the oxidation of absorbed food is takes place by the 02 which is inhaled by breathing and energy is released out is called respiration. Chemical equation of nutrition is as follows:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 673 kcal (Energy)
Question 25.
Where will you find the birds?
Answer:
We find the birds on the branches of trees.
Question 26.
Name the habitat of monkey and cactus?
Answer:
The habitat of monkey is trees while the habitat of cacutus is desert.
The Living Organisms and their Surroundings Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are biotic components? Name some abiotic components.
Answer:
Plants and animals are part of biotic components. In addition, there are small organisms like fungi and bacteria in the habitat, which cannot be seen with naked eyes. These are called micro – organisms. They are also a part of biotic components of different habitat. Some abiotic components are rocks, soil, air and water.
Question 2.
Define terrestrial habitats and aquatic habitats.
Answer:
The plants and animals that live on .land are said to live in terrestrial habitats. For example; forests, grasslands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions. On the other hand, the habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitats. For example, lakes, rivers and oceans, etc.
There are large variations in forests, grasslands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions located in different parts of the world. This is true for all aquatic habitats as well.
![]()
Question 3.
Define mountain habitats. Also explain tree of a mountain habitat?
Answer:
Mountain habitats are normally very cold and windy. In some areas, snowfall may take place in winters also. There is a large variety of plants in the mountain regions. These trees are normally cone shaped and having sloping branches. The leaves of some of these trees are like needle. This helps the rainwater and snow to slide off easily. There could be trees with shapes very different from these that are also present on mountains: They have different type of adaptations to survive on the mountains.
Question 4.
List some common features of the living and non – living?
Answer:
Common features of living and non – living are:
- All of them have mass, shape, and they occupy space.
- They are made up of structural units.
- The structural units of living and non – living are called molecules respectively.
Question 5.
In what ways living things differ from non – living things?
Answer:
The living things differ from non – living in the following ways:
All the living are characterized by movement, execution respiration intake of food, reproduction and sentivity towards such, heat and sound.
Question 6.
What do you understand by life cycle and life span of the living things?
Answer:
In living things life starts with a single cell which developes to a mature plant or full grown animal and finally grows old. This whole cycle is called the life cycle. Life span is the time period for which animals grow till they die. This time varies from a few minutes to hundreds of years. Life span of bacteria is short and the life of span a banyan tree may be even hundred of years.
Question 7.
‘All living things respond to external stimuli’. Explain.
Answer:
An important character of plants and animals is their response to external stimuli that is touch, fight, sound, water, chemicals or smell. Plants grow in the direction of fight. Earthworm moves away from fight and saline medium. Cockroaches five in dark corners.
Question 8.
How can you say that plants respond to stimulus?
Answer:
Plants like animals respond to stimulus. For example, the shoot grow towards fight and root grow towards water. The touch – me – not plant shows the most clear example as its leaves drops on touching.
![]()
Question 9.
How do plants differ from each other?
Answer:
Plants differ from each other in their habitat, food habits, structure, shape of leaves, type of flower, type of fruit, etc. Some plants five in water, others in marshes and still others on land. Some plants are green, others are non – green, some plants have their body divided into stem, root or leaf but in others there is no stem, root or leaf.
Question 10.
What is photosynthesis?
Answer:
Photosynthesis is the process by which the green plants manufacture their own food from carbon dioxide and water in presence of sunlight. In the process they produce oxygen also.
![]()
Question 11.
Name five plants and five animals whose habitat is pond.
Answer:
Pond is the habitat for variety of plants and animals.
Plants found in pond:
Spirogyra (algae), water lily, hydrilla, water hyacinth, sundew, bladder wort. Sundew and bladder wort are insectivorous plants.
Animals found in pond:
Frog, fish, trutles, ducks, snail, kingfisher, etc.
Question 12.
How does reproduction take place in plants and creatures?
Answer:
Every adult living being has the capability to give birth to child like itself. For example, adult cat gives birth to its young ones, and they grow and become adult. The reproduction in plants take place when the seeds sowed in the soil get germinated, sprout out and a sapling is born. Gradually it grows up and become a plant. In case of some of the plants, Certain portion is put under the soil.
![]()
Question 13.
How is the growth in plants different from growth in animals?
Answer:
The growth in plants is a continuous process. It occurs throughout their life. In animals the growth occurs only for a limited period of time. For example, in human growth takes place only in the first twenty years of life.
Question 14.
Why is the process of excretion important for living?
Answer:
As a result of metabolism various toxic substances are continuously formed. These wastes (carbon dioxide, ammonia compounds, other salts) if allowed to accumulate in the body (cells), would disturb the chemical composition of the protoplasm and produce toxic effects, crippling the life activities. Hence their elimination is most important. This is done by the process of excretion.
The Living Organisms and their Surroundings Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the surroundings in sea and desert regions?
Answer:
In the sea, plants and animals are surrounded by saline (salty) water. Most of them use the air dissolved in water.
There is very little water available in the desert. It is very hot in the day time and very cold at night in the desert. The animals and plants of the desert live on the desert soil and breathe air from the surroundings. The sea and the desert are very different surroundings and we find very different kind of plants and animals in these two regions.

For example, a fish and a camel. There are so many kinds of fish. All the ones shown here have the streamlined shape. This shape helps them move inside water. Fish have slippery scales on their bodies. These scales protect the fish and also help in easy movement through water. Fish have flat fins and tails that help them to change directions and keep their body balance in water. Gills present in the fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water.

The body structure of a camel helps it to survive in desert conditions. Camel have long legs which help to keep their bodies away from the heat of the sand. They excrete small amount of urine, their dung is dry and they do not sweat. Since camels lose very little water from their bodies, they can live for many days without water.

We see that the features of a fish help it to live inside water and the features of a camel help it to survive in a desert.
Question 2.
Define acclimatisation?
Answer:
There are some changes that can happen in an organism over a short period of time to help them adjust to some changes in their surroundings. For instance, if we live in the plains and suddenly go to high mountain regions, we may experience difficulty in breathing and doing physical exercise for some days. We need to breathe faster when we are on high mountains.
After some days, our body adjusts to the changed conditions on the high mountain. Such small changes that take place in the body of a single organism over short periods, to overcome small problems due to changes in the surroundings, are called acclimatisation. These changes are different from the adaptations that take place over thousands of years.
![]()
Question 3.
How animals living in mountain regions adapt themselves? Is there any change in surroundings?
Ans. Animals living in the mountain regions are also adopted to the conditions there. They have thick skin or fur to protect them from cold. For example, yaks have long hair to keep them warm. Snow leopard has thick fur on its body including feet and toes. This protects its feet from the cold when it walks on the snow. The mountain goat has strong hooves for running up the rocky slopes of the mountains.


As we go up in the mountainous regions, the surroundings change and we see different kinds of adaptations at different heights.
Question 4.
Discuss the features of lion and deer that help them to survive in forests or grasslands?
Answer:
A lion lives in a forest or a grassland and is a strong animal that can hunt and kill animals like deer. It is light brown in colour. Lions have long claws in their front legs that can be withdrawn inside the toes. It’s light brown colour helps it to hide in dry grasslands when it hunts for prey (animals to eat). The eyes in front of the face allow it to have a correct idea about the location of its prey.

A deer is another animal that lives in forests and grasslands. It has strong teeth for chewing hard plant stems of the forest. A deer needs to know about the presence of predators (animals like lion that make it their prey) in order to run away from them and not become their prey.
It has long ears to hear movements of predators. The eyes on the side of its head allow it to look in all directions for danger. The speed of the deer helps them to run away from the predators. There are many other features of a lion, a deer or other animals and plants that help them to survive in their habitat.
![]()
Question 5.
Which life activities take place in livings being? Explain every activities in three to four sentences.
Answer:
The life activities take place in living being are as follows:
1. Nutrition:
Nutrition is very much essential for living beings for growth and for sustaining life. Every living being takes food in some or other form which provides nutrients to its body.
2. Respiration:
The process of respiration takes place in every living being. There can not be a life without respiration. Generally, the respirations is called as breathing. Exhaling and inhaling are the two steps of respiration.
3. Excretion:
To extrete urine and other harmful material out of body is the most important characteristics of living being. The harmful things like urine, stools, sweat and carbon – di -oxide, etc. are excreted through excretory organs of living beings.
4. Reproduction:
Every adult living being has the capability to give birth to child like itself.
5. Growth:
When we sow seed, it germinates, sprout out, gradually grows and it becomes adult. In this way, the growth takes place in every living being and this process is called growth.
6. Movement and Speed:
Movement and speed is one of the important property of living things. Animals move from one place to another in search of food or to save themselves from enemies. Like animals, no movement takes place in case of plants but despite remaining stationary at one place, they do their movements for procurring sunlight.
7. Response:
Every living being is sensational to the external stimulus. For example, during winter we wear woolen clothes.
Question 6.
What do you mean by growth?
Answer:
Growth means an increase in the size, weight or volume of an organism. It is permanent change in a living organism. The growth in animal is limited only upto the primary stages of life. In plants, the growth is unlimited and continues upto the last stage of life.

Question 7.
Discuss the reproduction in animals.
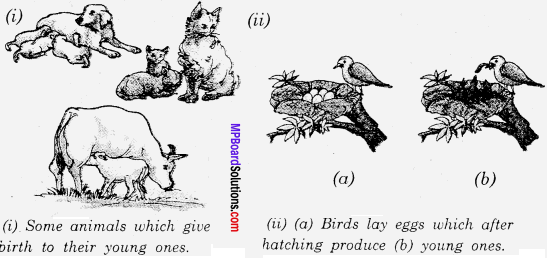
Answer:
Animals reproduce their own kind. The mode of reproduction may be different, in different animals. Some animals produce their young ones through eggs. Some animals give birth to the young ones. [See figure (i)] Many birds lay their eggs in the nest. Some of the eggs may hatch and young birds come out of these. [See figure (ii)]
Question 8.
Discuss the reproduction in plants.
Answer:
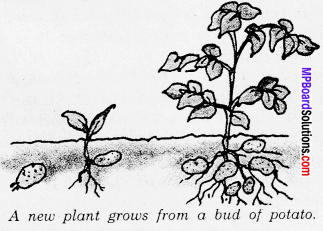
Plants also reproduce. Like animals, plants also differ in their mode of reproduction. Many plants reproduce through seeds. Plants produce seeds, which can germinate and grow into new plants. [See figure (i)]
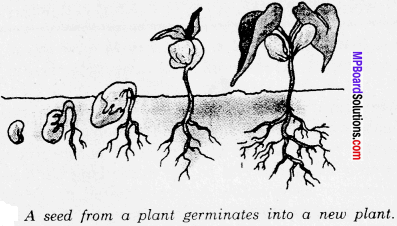
Some plants also reproduce through parts other than seeds. For example, a part of a potato with a bud, grows into a new plant. [See figure (ii)] Plants also reproduce through cuttings.