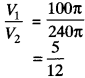MP Board Class 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 13.8
Assume π = \(\frac{22}{7}\), unless stated otherwise.
![]()
Question 1.
Find the volume of a sphere whose radius is
(i) 7 cm
(ii) 0.63 m
Solution:
(i) Here, radius (r) = 7 cm
∴ Volume of the sphere

Thus, the required volume is 1.05 m3 (approx.)
Question 2.
Find the amount of water displaced by a solid spherical ball of diameter
(i) 28 cm
(ii) 0.21 m
Solution:
(i) Diameter of the ball = 28 cm

Question 3.
The diameter of a metallic ball is 4.2 cm. What is the mass of the ball, if the density of the metal is 8,9 g per cm3.
Solution:
d = 4.2 cm
⇒ r = 2.1 cm
Density (D) = 8.9 gm/cm3
Volume of metallic ball = \(\frac{4}{3}\) x \(\frac{22}{7}\) x 2.1 x 2.1 x 2.1 = 38.808 cm3
Mass = D x V
= 8.9 x 38.808
= 345.3912 gm.
![]()
Question 4.
The diameter of the moon is approximately one – fourth of the diameter of the earth. What fraction of the volume of the earth is volume of the moon?
Solution:
Let d and d be the diameter of moon and earth respectively.
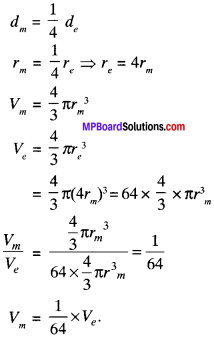
Question 5.
How many liters of milk can hemispherical bowl of diameter 10 J cm hold?
Solution:
d = 10.5 cm
r = 5.25 cm
Volume of the hemisphere = \(\frac{2}{3}\) x \(\frac{22}{7}\) x 5.25 x 5.25 x 0.25
= 303.18 cm3
= 0.303 l
Question 6.
A hemispherical tank is made up of an iron sheet 1cm thick. If the inner radius is 1 m, then find the volume of the iron used to make the tank.
Solution:
t = 1 cm
r1 = 1 m = 100 cm
r2 = r1 + t = 100 + 1 = 101 cm
Outer volume of tank (V2) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) πr22
Inner volume of tank (V1) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) πr13
Volume of iron = Outer volume – inner volume

= 0.06348 ml
Question 7.
Find the volume of a sphere whose surface area is 154 cm2.
Solution:
Surface area = 154 cm2
Surface area of sphere = 4πr2
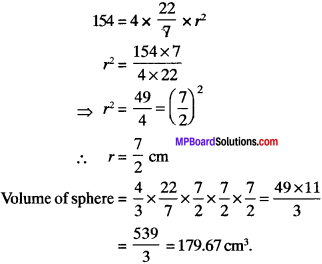
Question 8.
A dome of a building is in the from of a hemisphere. From inside, it was White – washed at the cost of ₹ 498.96. If the cost of white-washing is ₹ 2.00 per square meter, find the
(i) inside surface area of the dome.
(ii) volume of the air inside the dome.
Solution:
(i) Cost = ₹ 498.96
Rate = ₹ 2 per m2
Inside surface area = \(\frac{498.96}{2}\) = 249.48 m2
Inside curved surface area = 2πr2

Question 9.
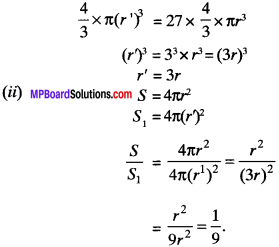
Twenty seven solid iron spheres, each of radius r and surface area S are melted to form a sphere with surface area S’. Find the
(i) radius r’ of the new sphere
(ii) ratio of S and S’.
Solution:
Let V and be the volume of old and new sphere respectively
(i) Volume of new sphere = 27 x volume of old sphere
V1 = 27 x V
Question 10.
A capsule of medicine is in the shape of a sphere of diameter 3.5 mm. How much medicine (in mm3) is needed to fill this capsule?
Solution:
d = 3.5 mm
r = 1.75 mm
Volume of medicine needed to fill the capsule
= \(\frac{4}{3}\)πr3
= \(\frac{4}{3}\) x \(\frac{22}{7}\) x 1.75 x 1.75 x 1.75
= 22.458 mm3
= 22.46 mm3 (Approx.)