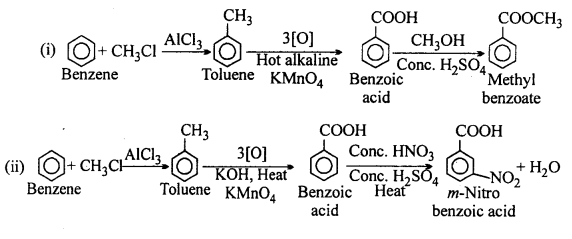
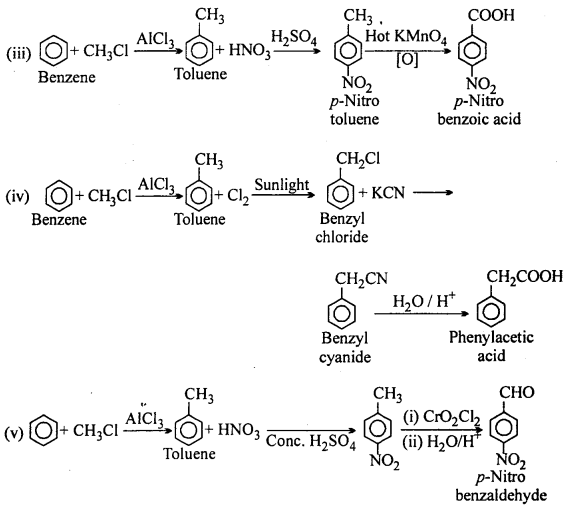
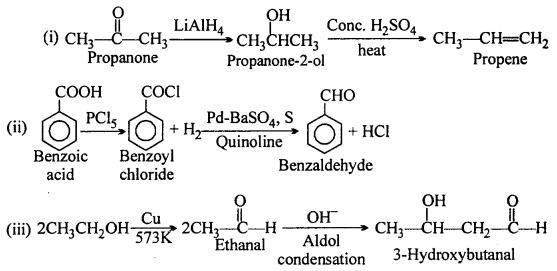
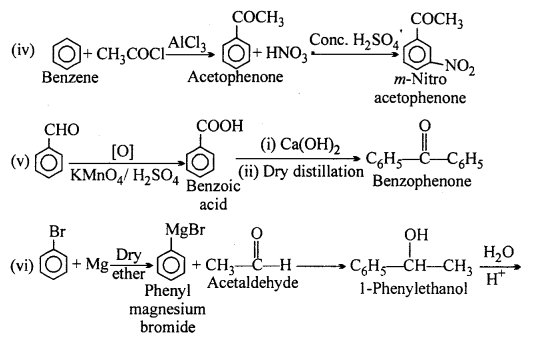
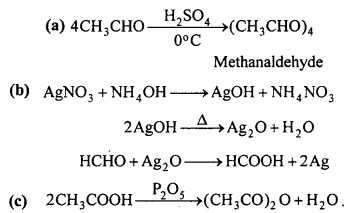
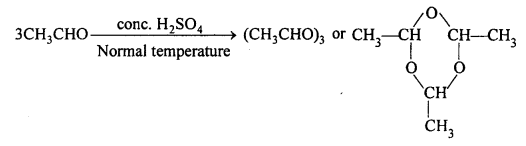
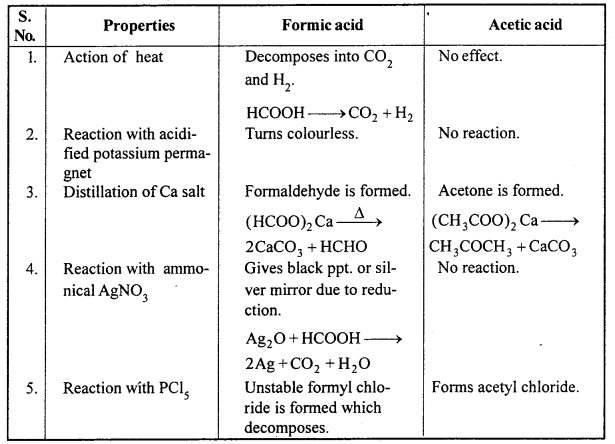
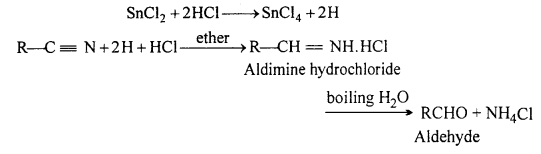
MP Board Class 12th Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Issue and Redemption of Debentures
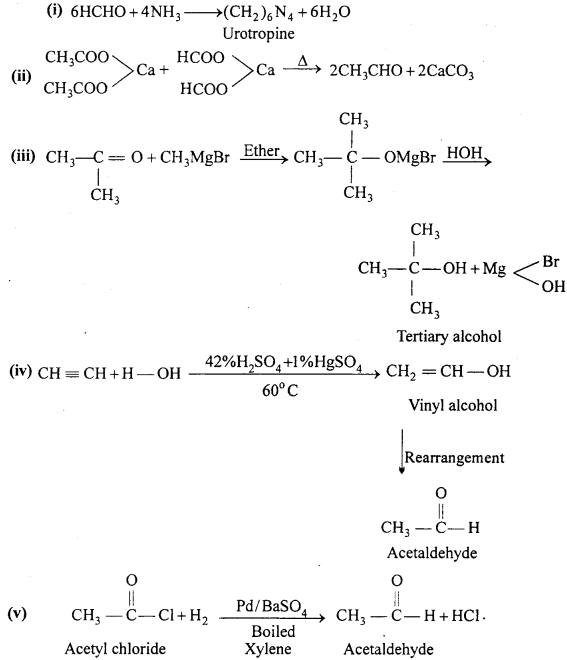
Issue and Redemption of Debentures Important Questions
Issue and Redemption of Debentures Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
X Ltd. bought assets worth Rs. 28,80,000. It issued debentures of Rs. 100 each at 4 % discount as purchase consideration. Number of debentures to be issued:
(a) 30,000
(b) 28,800
(c) 32,000
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) 30,000
Question 2.
Convertible debentures cannot be issued at discount if:
(a) They are to be converted immediately
(b) They are not to be converted immediately
(c) None of these.
Answer:
(a) They are to be converted immediately
Question 3.
Discount on issue of debentures will be shown in balance sheet under the heading:
(a) Profit / Loss statement
(b) Other non-current Assets
(c) Debenture Account
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Other non-current Assets
Question 4.
Excess of assets over liabilities at the time of purchasing a business is transferred to:
(a) General Reserve
(b) Capital Reserve
(c) Seller’s Account
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Capital Reserve
Question 5.
Own debentures means those debentures which the company:
(a) Issue to its promoters
(b) Issue to its director
(c) Purchase in open market as investment
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Purchase in open market as investment
Question 6.
Profit on cancellation of owned debentures is transferred to:
(a) Profit & Loss statement
(b) Debenture Redemption Reserve
(c) Capital Fund
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Capital Fund
![]()
Question 7.
When debentures are redeemed out of profit, then an equal amount is transferred to:
(a) General Reserve
(b) Debenture Redemption Reserve
(c) Capital Fund
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Debenture Redemption Reserve
Question 8.
In Debenture Redemption Reserve, Profit on the sale of Investment is credited to :
(a) Profit & loss statement
(b) Debenture Redemption Reserve Account
(c) General Reserve Account
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Profit & loss statement
Question 9.
Debentures can be redeemed by:
(a) Purchase in market
(b) Conversion into shares
(c) Change in Debenture
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 10.
Interest allowed on debenture is:
(a) Fixed
(b) Conversion into shares
(c) Accumulating
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Fixed
Question 11.
Balance of Debenture Redemption Reserve account is transferred after the redemption of all the debentures:
(a) Capital Reserve
(b) General Reserve
(c) Profit & Loss Appropriation A/c
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) General Reserve
![]()
Question 12.
Debenture holders come under the category of: (MP 2010,13,15)
(a) Owners
(b) Creditors
(c) Debtors
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Creditors
Question 13.
Debentures which may be transferred by more delivery:
(a) Secured
(b) Bearer
(c) Ordinary
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Bearer
Question 14.
The unpaid calls of debentures is called as:
(a) Calls in arrears
(b) Calls in advance
(c) Prepaid calls
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Calls in arrears
Question 15.
The fixed liability of a company is to pay to debenture:
(a) Profit
(b) Interest
(c) rent
(d) Commission.
Answer:
(b) Interest
Question 16.
Income from debentures is:
(a) Fixed
(b) Not fixed
(c) More
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Fixed
Question 17.
For the company, discount on issue of debenture is a: (MP 2009 Set A)
(a) Fictitious asset
(b) Liabilities
(c) Loss
(d) Real asset.
Answer:
(a) Fictitious asset
Question 18.
Kinds of debentures is/are :
(a) One
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Two
Answer:
(c) Four
![]()
Question 19.
Period of payment of internet on debenture is:
(a) 3 months
(b) 6 months
(c) 1 years
(d) Any time
Answer:
(b) 6 months
Question 20.
The amount of discount on issue of debenture is:
(a) Capital loss
(b) Revenue loss
(c) Capital expenditure
(d) Revenue expenditure.
Answer:
(a) Capital loss
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- Payment to debentures is done in the of company.
- The debentures which are redeemed first before paying any other type of debentures
are called - Debenture holders does not interfere in of company. (MP 2013, IS, 17)
- Debentures are generally issued for
- Generally interest on debenture is paid after expiry of a period of months. (MP 2009 A)
- Redemption of debenture means of the amount of debenture by the company.
- Creditors are company’s
- Debentures which can be changed into shares are called (MP 2014)
- Debentures is a written of debt. (MP 2016)
Answer:
- life time
- first debentures
- management
- cash
- six
- payment or redemption
- first debentures
- convertible debentures
- acknowledgement.
![]()
Question 3.
Match the following

Answer:
- (e) Registered debentures
- (d) Secured debentures (MP 2013)
- (c) Convertible debentures (MP 2013)
- (b) Redeemable debentures (MP 2014)
- (a) Preferred
- (f) Debenture. (MP 2011)
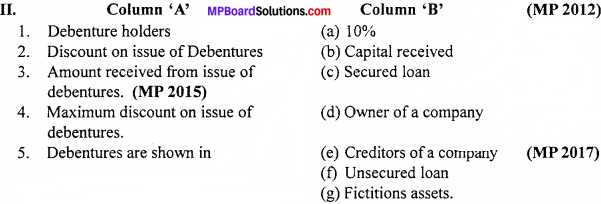
Answer:
- (e) Creditors of a company (MP 2017)
- (g) Fictitions assets.
- (b) Capital received
- (a) 10%
- (c) Secured loan
![]()
Question 4.
Write true or false:
- A debenture is a written document issued with the company’s seal acknowledging a debt.
- Debentures are part of owner’s equity.
- Interest paid on debentures is paid out of the company’s profit.
- Debentures cannot be issued at discount more than 10% of its face value.
- Redeemable debentures are those debentures which are paid after a specific period.
- Fixed debentures are also known as irredeemable debentures.
- Debentures cannot be converted into shares.
- Debentures cannot be issued at premium.
- A pledged security is an assistance security.
- Loss on issue of debenture is a revenue loss.
- Debenture holders are the owners of a company.
- Debenture holders received interest at a fixed rate.
- When calls amount is not received in debentures, then it is forfeited.
- Debentures are also issued for other consideration apart from cash. (MP 2013)
- Company’s debenture is generally transferable. (MP 2009 Set A)
- Debenture holders get dividend at fixed rate. (MP 2010)
- Interest is paid on debentures only in case of profit.
- Debenture holders are called share holders of a company. (MP 2011,15)
- Mortgaged debentures are called secured debentures. (MP 2016)
- The nature of debentures is that of short period loan. (MP 2016)
- Debenture can be redeemed on premium. (MP 2017)
Answer:
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the answer in one word/sentence:
- Name the document which either creates a debt or acknowledges it.
- Name the debentures which may be redeemed only at the time of winding up. (MP 2010)
- Purchase consideration – Net Assets = ?
- Issue of debentures of Rs. 100 at Rs. 125 and the difference 25 is called as.
- What are those debentures called whose name are registered in the company’s register? (MP 2009 Set A)
- Name the debentures which can be converted into shares. (MP 2010)
- What are those debentures called which are transferred by more delivery.
- How many debenture will be issued @ Rs. 100 each when a company purchased a building at a cost of 5 lakhs ? (MP 2011)
- Issue of debentures of Rs. 100 at Rs. 95 and the differences of Rs. 5 is called as. (MP 2013)
- Documents issued for long-term loan are called.
Answer:
- Debentures
- Irredeemable debentures
- Goodwill
- Premium
- Registered debentures
- Convertible debentures
- Bearer debentures
- 5000 debentures
- Discount
- Debenture.
![]()
Issue and Redemption of Debentures Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by debenture ?
Answer:
Debenture is a written certificate for taking loan from the public by the company on which the company put its seal and interest is paid at a predetermined rate on a fixed date.
Question 2.
What do you mean by bearer debentures ?
Answer:
The debentures which are transferable by simply delivery are called bearer debentures. The payment of it is made to the holder of it. No provision is maintained for the issue of such debentures.
Question 3.
What do you mean by Redeemable debentures ?
Answer:
The debentures which are repayable after a stipulated period or after a fixed date is called redeemable debentures.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Irredeemable debentures ?
Answer:
The debentures which are not redeemable during the lifetime of the company are called irredeemable debentures.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you mean by Secured debentures ?
Answer:
The debentures that are issued against the security, some specific assets or all the assets of the company are known as secured debentures. The assets undercharged cannot be sold without the consent of the debenture holders or till the time such debentures are re¬deemed completely.
Issue and Redemption of Debentures Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by debentures ? When can debentures be issued ?
Answer:
The word debenture is derived from the Latin word ‘Debere’ which means to owe. The term debenture is used to signify the acknowledgement of a debt given under the seal of the company and containing a contract for the repayment of the principal sum at a specified date and for the payment of interest at a fixed rate until the principal sum is repaid.
Whenever a company needs funds for a long period it can issue, debenture on the security of its assets, as an acknowledgement of debt from the public. It can be done in open market and applications can be invited. The person who buys debentures is called debenture holder.
Question 2.
Explain advantages of debentures to the company.
Answer:
Following are the advantages of issuing debenture :
1. Sufficient funds are raised : At the event of need of additional capital, a company may raise sufficient fund through issuing of debentures to the public.
2. No intervention in management: A debenture holder has no right to intervene in the management of the company since they do not enjoy voting right.
3. Fixed rate of interest: The rate of interest to be allowed on debentures is fixed at the time of issuing debentures. Hence, a company may make appropriate arrangement to pay interest in advance.
4. More dividends to shareholders : Due to issuing of debentures to full fill the need of additional capital, the shareholders may get more dividend since paying of interest to debenture holders costs cheaper than paying dividend, had the company issued additional shares to cater the need of additional capital.
5. Convenience in repayment: A company may conveniently arrange for the repayment of debentures to be made after a specific period of time.
![]()
Question 3.
How many types of debentures are there ? Any four.
Answer:
The following are the types of debentures :
- Redeemable debenture
- Irredeemable debenture
- Bearer debenture
- Registered debenture
- Mortgaged debenture
- Unsecured debenture
- Convertible debenture
- Non-convertible debenture.
Question 4.
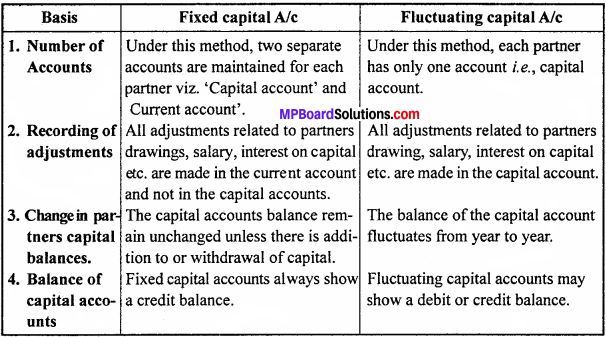
Differentiate between a shareholder and a debenture holder.
Answer:
The differences between a shareholder and a debenture holder:
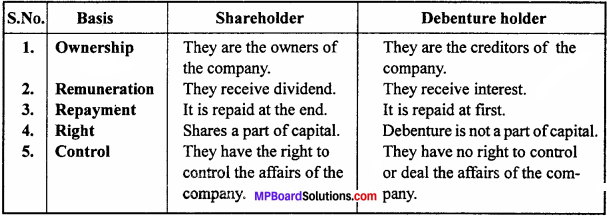
Question 5.
Explain secured and unsecured debentures.
Answer:
1. Secured debentures:
The debentures that are issued against the security, some specific or all the assets of the company are known as secured debentures. In other words, such debentures create charge on the assets of the company. Sometimes such charge may be a floating charge on all assets of the company. The assets undercharge cannot be sold without the consent of the debenture holders or till the time such debentures are redeemed completely.
2. Simple, naked or unsecured debentures:
Such debentures are not issued against the security of the assets of the company. Since, no security is placed for issuing such debentures, they are known as simple, naked or unsecured debentures. The holders of unsecured debentures come under the category of unsecured creditors. From the point of view of security, such debentures are very risky since on such debentures the company gives mere promise to pay the interest and to repay the principal sum when it is matured.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you mean by convertible and non-convertible debentures ?
Answer:
From Convertibility Point of View :
1. Convertible debentures:
The debentures for which the holders are given option to convert them into preference or equity shares within a stipulated period at a prescribed rate of exchange are called convertible debentures. Such debentures are popular among the companies because it may provide a permanent important source of capital.
2. Non-convertible debentures:
The debentures for which the holders have no option to convert into preference or equity shares are known as non convertible debentures. Generally, high rate of interest is allowed on such debentures. Such debentures are entirely redeemed on the date of their maturity.
Question 7.
Explain the methods of redemption of debentures.
Answer:
The method of redemption of debentures are as follows :
- Lump sum Payment method
- Annual installment payment method
- Purchase in the open market.
- Conversion method
- Under the below mentioned condition, these rules are not applicable.
- Where the maturity period of debentures is not more than 18 months
- Where the debentures are issued to the authorized company.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the essential characteristics of debentures.
Answer:
The essential characteristics of debentures are :
- A debenture is a certificate of debt.
- The company acknowledges the debt to the holders of the debentures by issuing debenture certificate.
- Debenture is a convenient means of external borrowings.
- A debenture includes debenture, stock, bonds or any of the security.
- A debenture contains the provision for payment of interest at regular intervals on fixed dates.
- A debenture contains the provision for repayment of the principal sum on due date.
Question 9.
What are the things kept in mind while redemption of debenture.
Answer:
Following things are kept in mind while redeeming the debenture :
- Redemption fund should be made.
- The amount of that fund utilize only that way what ever is redemption fund is created for.
- It is compulsory for each and every company to deposit 50% amount issued amt.
- Time of redemption amount should be arranged.
Question 10.
State the meaning of ‘Debentures issued as a collateral security’.
Answer:
The term collateral security means additional or secondary security in addition to the primary security. Sometimes, when a company takes loan from a financial institution, then besides the primary security, the company may issue debenture for additional security (as collateral security). The under who receives debenture as collateral security debenture is not entitled for interest on these debentures.
If any default is made by the company in paying back the principal amount or in interest on the loan, then the lender has the right to recover his dues from the amount the sale of primary security. But, if the primary security is not sufficient to recover the amount of the debt, then the debentures issued as collateral may be used for recovery of the remaining amount.
Question 11.
What do you mean by issue of debentures on discount and redemption on premium ?
Answer:
In this situation the company issue debentures at lesser than its face value but redeems them at higher than its face value. In this case company incurs loss both at the time of issue and at the time of redemption. The entries are as follows:
Bank A/c – Dr.
Discount on Issue of Debenture A/c – Dr.
Loss on issue of Debenture A/c
To Debenture A/c
To premium on Redemption of deb. A/c (Being issue of Debenture at discount and repayable at premium).
![]()
Issue and Redemption of Debentures Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the types of debentures. Explain any five.
Answer:
A company may issue following types of debentures:
- Redeemable debentures.
- Irredeemable debentures
- Registered debentures
- Simple debentures
- Bearer debentures
- Mortgaged or Secured debentures
- Convertible debentures
- Collateral debentures
- Right debentures.
1. Registered Debentures:
The debentures which are entered in the register of the company and are payable only to the registered holders are known as registered debentures. The interest on these debentures is payable to the registered holder. Such debentures cannot be transferred by mere delivery.
2. Bearer Debentures:
Such debentures can be transferred merely by delivery with-out any legal formalities. There are payable to the bearer or holder.
3. Redeemable Debentures:
The debentures which are repayable after a fixed period are called redeemable debentures.
4. Simple or Naked Debentures:
The debentures which have no security of payment of the principal and interest are called simple or naked debentures.
5. Right Debentures:
If a company issues debentures after 2nd August, 1979, first of all the existing shareholders have a right to subscribe. Such debentures are known as right debentures.
![]()
Question 2.
Differentiate between debenture and share.
Answer:
Differences between share and debenture:
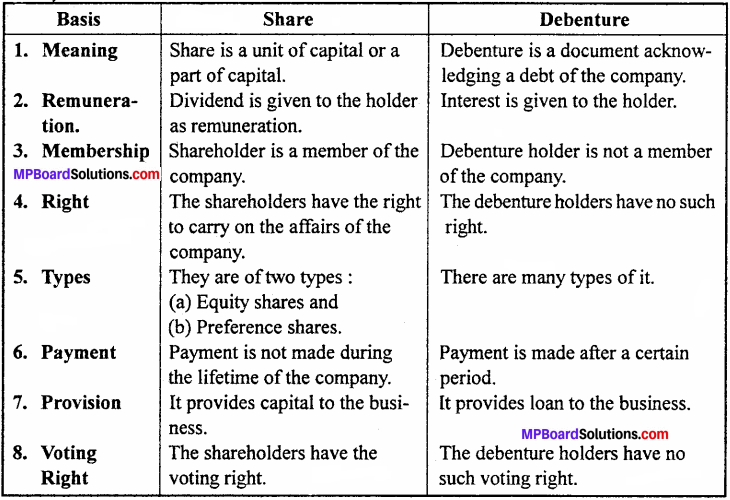
Question 3.
Mention the advantages of issue of debentures to the company.
Answer:
Following are the advantages of issuing debentures:
1. Sufficient funds are raised:
At the event of need of additional capital a company may raise sufficient fund through issuing of debentures to the public.
2. No intervention in management:
A debenture holder has no right to intervene in the management of the company since they do not enjoy voting right.
3. Fixed rate of interest:
The rate of interest to be allowed on debentures is fixed at the time of issuing debentures. Hence, a company may make appropriate management to pay interest in advance.
4. More dividends to shareholders:
Due to issuing of debentures to full fill the need of additional capital, the shareholders may get more dividend since paying of interest to debenture holders costs cheaper than paying dividend, had the company issued additional shares to cater the need of additional capital.
5. Convenience in repayment:
A company may conveniently arrange for the repayment of debentures to be made after a specific period of time.
Question 4.
What is issue of debentures at par, at premium or at discount? Show the journal entries in each case.
Answer:
1. Issue of debentures at par:
When the debentures are issued at the face value of the debenture, it is called issue of debentures at par. For example, debenture of Rs. 100 is issued at the same value.
Journal Entry
Bank Account – Dr.
To Debenture Account
(Being cash received on debenture issue)
2. Issue of debentures at premium:
When the debentures are issued more than its face value, it is said to be issue of debentures at premium. For Example, Debentures of Rs. 100 is issued for Rs. 120. Here, Rs. 20 is premium. Generally the premium amount is collected along with allotment.
Journal Entry
Debenture Allotment A/c – Dr.
To Debenture A/c To Debenture Premium A/c (Being the debenture issued at premium)
3. Issue of debentures at discount:
When the debentures are issued less than its face value is called issue of debentures at a discount, e.g., Debenture of Rs. 100, issued for Rs. 90. Here, Rs. 10 is discount.
Journal Entry
Debenture Allotment A/c – Dr.
Debenture Discount A/c – Dr.
To Debenture A/c
(Being the debenture issued at discount)