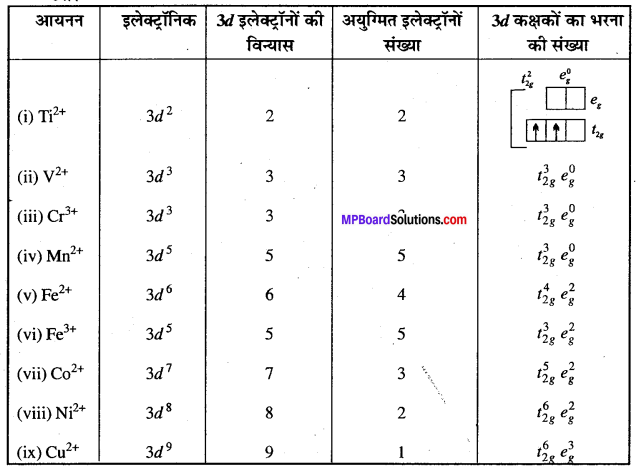
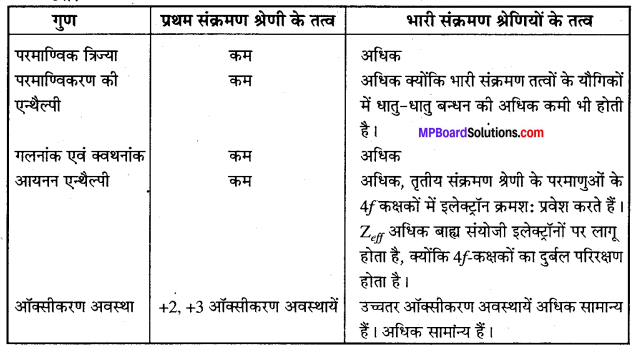
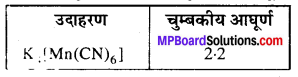
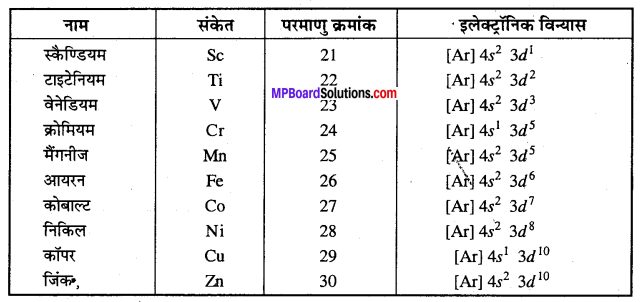
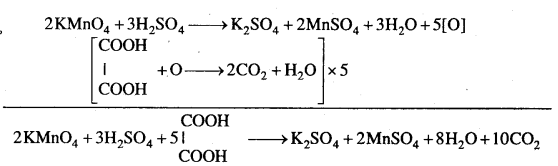
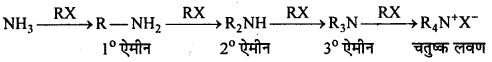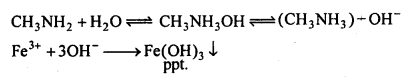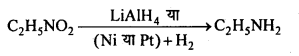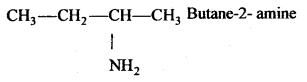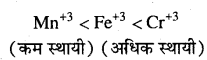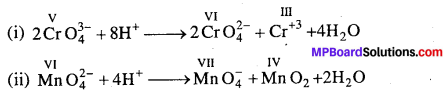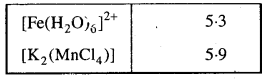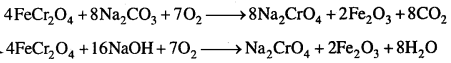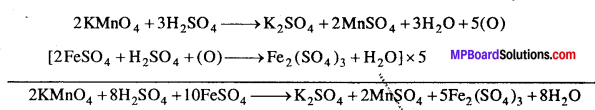MP Board Class 12th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 8 Controlling
Controlling Important Questions
Controlling Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Controlling is which level of management function :
(a) First
(b) Second
(c) Middle
(d) Last
Answer:
(d) Last
Question 2.
Control is related to :
(a) Result
(b) Work
(c) Effects
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(a) Result
Question 3.
Planning and Control are :
(a) Completely different
(b) Adverse to each other
(c) Similar to each other
(d) Interrelated activities.
Answer:
(d) Interrelated activities.
Question 4.
Out of the following which is not a technique of control:
(a) Exceptional control
(b) Budgetary control
(c) Cost control
(d) Punishable control.
Answer:
(d) Punishable control
Question 5.
Control is:
(a) Negative process
(d) Positive process
(c) Re-formative process
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Re-formative process
Question 6.
What is the first step of controlling:
(a) Budget preparation
(b) To lay down proportion
(c) Evaluation of performance
(d) Identification of deviations.
Answer:
(a) Budget preparation
Question 7.
What is the aim of control:
(a) To estimate production
(b) Arrangement of financial resources
(c) Evaluation of actual performance
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(c) Evaluation of actual performance
Question 8.
Control Process is :
(a) Continuous
(b) Primary
(c) Planning
(d) Essential.
Answer:
(a) Continuous
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
- The work of……………….. is to see whether the works are in conformity to plans or not.
- ………………..is forward looking……………….. and is backward looking.
- In control process it is……………….. that all the work is processing/done as per plans.
- Effective control is related to ………………..
- In control standard work is compared with………………..
- ………………..steps are taken in controlling process.
- In control process……………….. points are marked.
- Control is useful in controlling ………………..
- Control process of business enterprise is helpful for……………….. operations of business.
Answer:
- Control
- Planning, Controlling
- Evaluating test
- Results
- Actual work,
- Corrective
- Weak
- Wastage
- Skilled.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the answer in one word/sentence :
- In controlling actual performance is compared with.
- Name the remedial measures taken to correct deviations in process of control.
- Write the technique of control.
- Name the technique of control in which the exceptional works are only informed to managers ?
- Which technique of control is adopted for departments related with finance ?
- To determine the work standard is which step of control ?
- Write one advantage of control by exception.
- What is Budgeting ?
- What do you mean by control through budgeting ?
- On what function of management control depends ?
Answer:
- Standard performance
- Corrective action
- Auditing
- Exceptional control
- Auditing
- To determine the work standard is the 1st step of control
- By control by exception time is saved
- Budgeting is a process by which budget is controlled.
- by controlling through budgeting we mean the comparison between the budget provision and the actual goals set
- control depends on planing
Question 4.
Write true or false :
- Control is the primary function of management.
- In control actual performance is compared with standard performance.
- Control is the last function of management.
- Control provides security from risk.
- Control does not need at all levels of management.
- Deviation is always positive.
- Control should be rigid.
- Control is both positive and negative.
- Control is a continuous process.
- Control can be done for present and future activities only.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True.
Question 5.
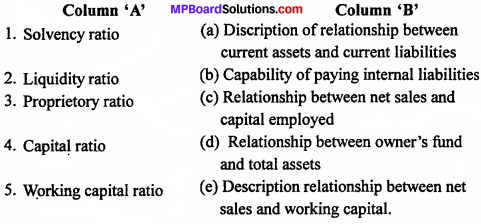
Match the columns :

Answers:
- (e)
- (c)
- (b)
- (a)
- (d)
- (g)
- (f)
- (j)
- (h)
- (i)
Controlling Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
“Planning is of no use without control.” Explain.
Answer:
Planning and controlling both are interdependent and interrelated activities. They are complementary and supplementary to each other.
The close relationship between planning and controlling can be justified on the following points:
- Planning is the origin of controlling
- Both are interrelated
- Planning is theoretical whereas controlling is practical.
Question 2.
What is control by exception ?
Answer:
A good control system should focus managerial attention on exceptional deviations. This is called ‘Control by exception’. It means if things are going smoothly, management should not interfere. Management should interfere only in exceptional circumstances.
Question 3.
Why is control incomplete without planning ?
Answer:
Control is fully dependent upon planning because it is the work of controlling to see whether the work is in conformity to plans or not, if not give directions for correction.
![]()
Question 4.
What is deviation in control ?
Answer:
The difference between actual performance and standard performance is deviation in control.
Question 5.
Ravi Ltd. wants to produce stapler pins in huge quantity. As per the policy of the company 44% of the production can be spoiled. Since last 5 lots 8 to 10% production is spoiled. The reason is the repair in the machine. What will be your suggestion for corrective action ?
Answer:
Current machine repair must be monitored or new machine must be purchased.
Question 6.
Why is control a blank exercise without planning ?
Answer:
Control is fully dependent upon planning because it is the work of controlling to see whether the work is in conformity to plans or not, if not give directions for correction.
Question 7.
What is feedback in control ?
Answer:
A feedback is a common and powerful tool of control process. It helps to take the system output into consideration, which enables the system to adjust the performance by corrective actions.
Question 8.
Define control.
Answer:
Definitions : According to Henri Fayol, “In an undertaking, control consists in verifying whether everything occurs in conformity with the plan adopted, the instructions issued and the principles established.”
Question 9.
Why do you need control ?
Answer:
In the current scenario of industrial revolution technological advancement, market and taste of customers are frequently changing, In this era the management has to work efficiently and effectively to meet the qualitative and quantitative standards. Therefore, control is must.
Question 10.
What is physical standard proportion ?
Answer:
Physical standard proportion includes number of tasks, labour, hours and other physical units.
Question 11.
What is monetary standard proportion ?
Answer:
Monetary standard proportion includes per unit cost, per unit sale, labour expenses and distribution expenses etc.
Question 12,
What do you mean by budget ?
Answer:
A budget is a financial plan for a defined period of time, usually a year, it may also include planned sales, volumes and revenues, resource quantities, cost and expenses, assets, liabilities and cash flows.
Question 13.
How does control improves the future plans ?
Answer:
Control improves future plans by suggestions from past experiences.
Question 14.
What is Budgetary control ?
Answer:
Budgets are quantitative statements of objectives, plans and programmed of an organization. Budgetary control regulates, all these important aspects for better functioning
Question 15.
How are planning and control interrelated and how does they provide to each other ?
Answer:
Relationship Between Planning and Control: Planning and controlling both are interdependent and interrelated activities. They are complementary and supplementary to each other.
The close relationship between planning and controlling can be justified on the following points:
- Planning is the origin of controlling
- Both are interrelated
- Planning is theoretical whereas controlling is practical
- Planning is meaningless without controlling and controlling is blind without planning
- Controlling ensures realizing planned goals efficiently and provides basis for improvement in future plans
- Planning is looking ahead and controlling is looking back.
Interrelation between planning and controlling can be understood from the following
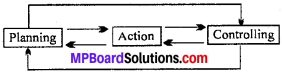
Question 16.
What do you understand by negative and positive deviation ?
Answer:
Negative Deviation : This occurs when the actual performance is less than the standard preformance.
Positive Deviation : This occurs when the actual performance is more than the standard performance.
Question 17.
How can control helpful to curtail the dishonest attitude of employees ?
Answer:
Controls can keep constant or steady watch on those employees and can be helpful to curtail dishonest behavior of employees.
![]()
Question 18.
Write one point of difference between planning and control.
Answer:
Planning is forward looking and controlling is backward looking.
Question 19.
Give two examples of qualitative standards in the control process.
Answer:
- Relationship with employees
- Ability of management.
Question 20.
Why should proportion/standard flexible and can be changed anytime ?
Answer:
The internal and external environment keeps changes very frequently so the standards must be flexible.
Question 21.
What is the last step of process of control ?
Answer:
Taking corrective action in the last step of process of control.
Question 22.
What do you mean by management information mechanism ?
Answer:
Management information mechanism is a technique which provide information and assistance to managerial decisions.
Question 23.
“Control is universal.” Explain why ?
Answer:
Control is universal because it is found at all levels of management. Controlling work is neither related to top level nor to lower level but it is required at all levels. In all organizations (Religious, Social, Political etc.) the need of control is felt.
![]()
Question 24.
Why is it said that planning is essential for control ?
Answer:
Determination and establishing standards are the first step of control. The object
of establishing standard is to know what consideration are expected from any work and how and through whom the consideration will be achieved. For all this planning is essential.
Question 25.
What do you mean by control ?
Answer:
Control is related to checking whether everything occurs in conformity with the standards stipulated in the plan. It measures and evaluates performance and brings to light the variations if any.
Question 26.
Write names of any four specific methods of control.
Answer:
The four methods are :
- Budget control
- Cost control
- Production control
- Quality control
- Material control.
Question 27.
What are the general methods of control ?
Answer:
General methods of control:
- Actual inspection
- Control through auditing
- Control through motivation
- By sending notices
- Return on investment.
Question 28.
Why is control backward looking ?
Answer:
Control is backward looking because in control we see the performance backward which is already performed by the workers and its comparison is done through plan
Question 29.
What is the relation between planning and controlling ?
Answer:
Planning and controlling both are interdependent and interrelated activities. They are complementary and supplementary to each other.
The close relationship between planning and controlling can be justified on the following points :
- Planning is the origin of controlling.
- Both are interrelated.
- Planning is theoretical whereas controlling is practical.
![]()
Question 30.
What is control through example ?
Answer:
Under this system of control, the manager himself places an example before his employees by being punctual, working for specific period, good behavior etc. This method is very effective.
Question 31.
Explain the cost control.
Answer:
By exercising cost control as per unit production cost can be ascertained and can find out the method of minimizing the cost in future so as to complete with the other items in the market, e.g., cost raw material, labour cost, direct expenses and indirect expenses etc.
Question 32.
What does control ensure ?
Answer:
Control ensures whether the actual work is going on according to the targets ! determined or not.
Question 33.
How is control full of objectives ?
Answer:
Control is full of objectives because it ensures whether the predetermined objectives of organizations are fulfilled or not by effective and efficient utilization of resources.
Controlling Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain two aspects of control.
Answer:
The two aspects of control are :
- Political control
- Managerial control
1. Political control means to inspect the impact and implementation of rules and plans of the organization.
2. Managerial control means to focus on the managerial and other activities of the organization.
Question 2.
What are points that should be kept in mind while preparing standards/proportion ?
Answer:
- Standards must be capable of measuring,
- Standard should be such which can be achieved with some efforts.
- Standards should be easy and clear.
- Standards must be flexible.
- While setting standards the deviation limits must be specified.
Question 3.
Explain, briefly, the features of a good control system.
Answer:
A good control system must fulfill the following requirements :
1. Suitability: The control system should be appropriate to the nature and need of the organization. A control system that is good to small organization may be inadequate for a big organization.
2. Objectivity : The control system should focus on the objectives of the organization. The determination of standard measurement of performance and corrective actions thereby, should be objective and impersonal. Subjective and arbitrary control cannot be effective. .
3. Simplicity: A good control system should be clear, easy to understand and operate. Unless the control system is understood fully by those responsible for its operation, it cannot be successful.
4. Economical: A good control system is one which is economical in terms of time and money. Small units may not be able to afford huge cost of control.
5. Flexible : A good control system must be flexible because business conditions are not stable. If the system of control can work only on the basis of one specific plan, it becomes useless if the plan breaks down and another has to be substituted. According to Theo Haimann, “A good control system must keep pace with continuously changing pattern of a dynamic business world. ”
6. Promptness : The control system should be such that actual result and all deviations from standards are quickly reported to the concerned officers. Delay in reporting will make control ineffective. Speed is also required in initiating the corrective actions.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the meaning of control process.
Answer:
Control is a universal and important function of management. It is the power to direct, order or restrain. Managerial control seeks to achieve conformity to plan as closely as possible. It is applied to all activities of the organization like purchases, sales, finance, marketing, personnel management etc.
Meaning: Control is the most important element of management. It is concerned with verifying whether actions are in conformity with the standard stipulated in the plan. It measures and evaluates performance and brings to light the variations, if any, for the purpose of necessary action by the management and to prevent the recurrence of such variations in future. Controlling as a function of management means the measurement and correction of performance of activities of subordinates in order to make sure that enterprise objectives and plans devised to attain them are accomplished.
Question 5.
How should a newly appointed foreman should manage the process of control ?
Answer:
A newly appointed foreman should manage the process of control:
- Setting of Standard/Proportion.
- Measurement of performance.
- Comparison of actual performance with standard performance:
- Analysis of deviation.
Question 6.
The ideal control system inspects every aspect of performance. Explain.
Answer:
An ideal control system is one which focuses on important aspect of performance. There may be thousands of jobs related to control but the prime focus must be control on the prime aspects as it is difficult to control all. If we keep controlling all the aspects then we face the problem of control delay, increase in cost and the important points are neglected.
Question 7.
Write the advantages of control by exception.
Answer:
Advantages of control by exception :
- It concentrates attention of managers towards important things.
- It differentiates between the important and ordinary problems.
- It saves the efforts of managers.
- There is no wastage of time and energy of managers in solving daily problems.
![]()
Question 8.
What do you mean by control ? How does control stimulates action ?
Answer:
Meaning of control:Control is related to checking whether everything occurs in conformity with the standards stipulated in the plan. It measures and evaluates performance and brings to light the variations if any
Control stimulate action : An effective control system stimulates action by spotting the variations from the original plan and highlighting them for the people who can set things right. Control helps in detecting the deviation and their causes. It enables the management to act quickly.
Question 9.
What things should be kept in mind while determine standards ?
Answer:
While determining standards following things should be kept in mind :
- Standard should be accurate.
- Standard should be lawful.
- Determined standard should be able to acquire.
- Standard should be according to planning.
- Standard should be such which can be measured.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the setting up standards as first step of control.
Answer:
Determination and establishment of standards are the first step of control. The object of establishing standard is to know what consideration are expected from any work and how and through whom the consideration will be achieved. What will be different levels of activating in work and what will be the expenditure ? For all this, a policy is prepared, which is called planning, without planning and policies, work cannot be estimated and standards cannot be established. In this way, for control planning is important.
Question 11.
Controlling is a Dynamic Process”. How its help in achieving the objectives ?
Answer:
Controlling involves view of standard as well a corrective action which may lead to changes in other managerial functions. The control system has to be adapted to the changing conditions and requirement of organization.
Controlling ensures that results of operations conform as closely as possible, to the predetermined objectives. Every organization draw up a plan of action at periodical intervals. The plan indicates the expected behavior and activities of people working in different units of the organization. By keeping a close watch over performance at various levels, controlling tries to correct the deviation between actual results and desired results. Mistakes are located promptly and appropriate remedial actions are initiated. Thus, it helps in achieving the objectives laid down in the plan of action.
![]()
Question 12.
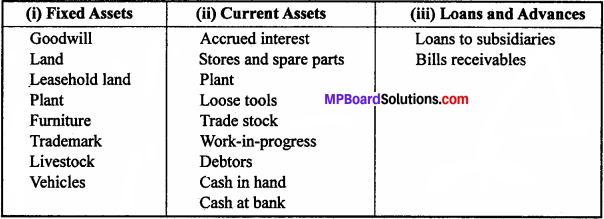
Define Net Working Capital.
Answer:
Net Working Capital: It represents the excess of current assets over current liabilities. Current assets include cash in hand, cash at bank, stock, debtors, bills receivables etc. while current liabilities consists of accounts payable, outstanding bills payable, bank overdraft, and outstanding expenses etc. Net working capital is a qualitative concept and it reveals the soundness of current financial position. Working capital may be classified as follows:
- Permanent or regular working capital
- Temporary or variable working capital
- Seasonal working capital and
- Special working capital.
Controlling Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1
Describe the salient features of control.
Or
Explain main characteristics of control.
Answer:
1. Control is a management function : Controlling work is done by the line officer and line officer may take advice and help from different experts and colleagues.
2. At all levels of management: Controlling work is neither related to top level nor to the lower level but it is required at all levels. At top level, controlling work is done by the chief manager and at the lower level foreman or other officer does the work of control.
3. Continuous process : Control is a regular activity, required at all levels. It is not an activity in isolation. The management has to be continuously vigilant to ensure that the management is in the right track. If control is withdrawn midway, then it may affect performance and subsequently, the efficiency of the organization.
4. Control is futuristic or Forward looking : The object of control is to wipe away present errors and defects so that no hindrance or defect may arise in future. Necessary steps are to be taken for this before hand. Whatever, faults have occurred in the past, should be examined and care is taken so that it should not be repeated in future.
Question 2.
“Planning and controlling are interrelated.” Explain.
Answer:
Relationship Between Planning and Control: Planning and controlling both are interdependent and interrelated activities. They are complementary and supplementary to each other.
The close relationship between planning and controlling can be justified on the following points:
- Planning is the origin of controlling
- Both are interrelated
- Planning is theoretical whereas controlling is practical
- Planning is meaningless without controlling and controlling is blind without planning
- Controlling ensures realizing planned goals efficiently and provides basis for improvement in future plans
- Planning is looking ahead and controlling is looking back.
Interrelation between planning and controlling can be understood from the following
1. Controlling without planning is blind: Control uses the standards of performance provided by planning as a base of evaluation and comparison.
2. Planning without controlling is meaningless : Controlling monitors the progress of plans implemented, discovers deviation and initiates corrective measures to ensure that activities conform to plans.
3. Planning seeks consistent, integrated and articulated programmed while controlling seeks to compel events to conform to plans.
4. Planning involves thinking and analysis to prescribe and appropriate course of action while controlling checks it prescribed decisions have been translated into desired action and verifies their accuracy and objectivity.
Conclusion : To conclude we can say that planning based on facts makes controlling easier and effective and controlling improves future planning. Therefore, planning is a prerequisite for controlling and the two are inseparable twins of management.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the limitations of control.
Answer:
Though control is essential in every organization, it does suffer from limitations. The following are the main limitations :
1. External factors : Though an effective external control is possible, the management virtually cannot exercise any control over external factors such as government policies, technological changes etc. All these affect planning.
2. Expensive: Control requires deputation of large personnel at various level to analyse deviations. This become an expensive affair for small organization.
3. Problems in fixing standards : There are various areas in management like employee morale, R & D, customer reactions, human relations etc. where standards for performance cannot be set in quantitative terms. In the absence of standards, control is ineffective.
4. Resistance : It is an accepted fact that control techniques are always looked upon as an interference in work by subordinates. Hence, full cooperation for effective control may not be obtained from the subordinates.Thus, these are some of the limitations of control
Question 4.
What are the types of standard ?
Answer:
Types of standard : Standards can be divided into the following parts :
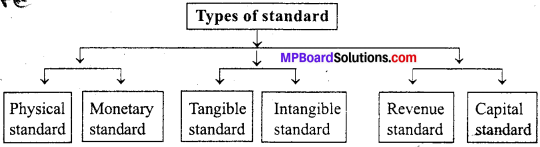
1. Physical standard : In it, determination of work is made about per hour, per day, per week, per unit etc.
2. Monetary standard : In it, standard is determined about per unit labor cost, per unit material cost, per unit factory cost. These standards can be measured in money.
3. Tangible standard : In it, standard is determined about per day production cost, per article production cost, per day production quantity and standard of fixed units.
4. Intangible standard : In it, to increase the morale of employees, to increase efficiency and to appreciate good work etc. are determined. Intangible standards cannot be measured in quantity. It can be felt by experience.
5. Revenue standard : In it, such standards are included which can be measured in terms of sales value, e.g., for transport company, income per passenger.
6. Capital standard : The standard capital ratio is two units of capital to one unit of borrowing. Standard of it in capital expenditures are determined for this different ratios are
determined as current ratio, ratio of loan with the owners capital etc. The capital standard should be increased or decreased looking to the size, nature of business.
Question 5.
What are various core areas of control and its methods ?
Answer:
The core areas of control are :
- Policy control: Real policy and control policy always vary which leads to deviation.
- Employee control: Management gets divided into sub-section management departments to have control on employees.
- Wage and salary control: Management controls the wage and salary of employees through the evaluation of their work.
- Capital control : The prime task of control is to monitor whether the usage of capital is for achieving the goal or not. If not then corrective measures are taken.
- Cost control: Control on various production departments to check and have optimum utilization of resources results in cost control.
- Inventory control: In production sufficient inventory must be available. There usage, purchase and storage must be properly monitor and corrective actions must be taken.
- Comprehensive control: Under this all the plans are collectively.
Question 6.
What are the various principles of control ?
Answer:
The various principles of control are :
- Principle of security of goal: Control process should be such which understands the difference between plans and actual deviation of tasks and take corrective actions.
- Principal of ability: Control process should be such which should be in expensive and should also take care of subordinates without hampering the image and confidence of management.
- Principle of priority : Control process should prioritize the activities and should focus on the important activities. If there is any deviation then they must be rectified.
- Principle of responsibility : Control is the responsibility of management and it cannot be taken lightly.
- Principle of flexibility : Control process must have lot of flexibility to amend easily if need be.
- Principle of revaluation : For effective control the control process must evaluated at regular intervals to incorporate the changing situations.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the essential factors of effective control system ?
Answer:
Essential Factors of Efficient Control System : Following are the essential factors of efficient control system:
1. Suitability : The control system must suit the requirements of an organization. It should be designed after considering the nature, size and functions of organization.
2. Flexibility : The control system should have the flexibility to adjust itself to the changing requirements of the organization. It should not be very rigid and strict.
3. Simple and understandable : The controlling system must be simple and easily understandable to the officials and employees of organization. Controlling system can be effectively applied if it is simple and understandable.
4. Economical: Controlling system should be economical with regard to time and money. It should be within the means of the enterprises.
5. Efficient control techniques: An effective and efficient control system should use efficient control techniques. Through these techniques the uncertainties in business can be easily tackled
Question 8.
Explain the methods of control.
Answer:
(A) General methods :
1. Actual inspection : By actual inspection we mean actual inspection of worker’s performance by taking rounds, visiting the departments.
2. Control through auditing : Internal or external auditing of certain accounts and books are necessary. By auditing we mean stock in going and incoming inventory, fixed assets books, cost accounting etc.
3. Control through motivation : This method is the best method of control. By motivating the labour, the sincere labour is encouraged to do more and more work.
4. By sending notices: Management can be controlled by sending notices, circulars, orders to subordinates for coordinating their work and establishing control thereby.
5. Return on investment (ROI): Return on investment is another wily used management control method of all. It is aimed of measuring profit as return on the capital employed for production. It uses a number of financial variables to arrive at the return on investment.
6. Control by policies : Policies are also one of the sources of control. Policies are
pre-determined for performance of activities. The employees work according to these policies. By these policies the employees get full opportunity to seek direction and they work within their own limits. Thus, control is observed by policies also.
7. Control by exception: Under this method, the controller or manager concentrates only on the exceptional circumstances and tries to remove them. Exceptions are activities which are not supposed to be done i.e., the activities should not be out of the area of activity of the employee. In management, control by exception has been imparted universal acceptance.
8. Control by example : This is specific example of control. The manager, in his leadership role, himself becomes a model example of the employees’ work and behaviour. The ideal behaviour of the manager becomes a ‘norm’ for the employees to follow, which in other words, means that the employees will behave in accordance with the example set by the manager. This method is called control by example.
9. Control by records and reports : The management scrutinizes the records and reports called from various branches from time to time. After scrutiny, the concerned branch or branches are issued necessary instructions or directions. Thus control is observed by scrutinizing the records and report of the concerned branches or offices.
10. Control by fixing of limitation: In an organization, area of activity or operation of an employee is fixed. It is necessary to obtain prior permission of the higher officials to work beyond the area of operation. This permission is granted in the interest of the organization only when it is found necessary. In this way, control is observed over the subordinates.
11. Control by disciplinary action : Disciplinary action along with criticism of an employee is a negative aspect of control. This has an adverse effect on the moral of the employee, reduces his efficiency and initiative. Even so. this method, at times, becomes necessary as a weapon of the last resort. This method is applied to those employees who do not improve in their efficiency in spite of use of all positive methods. This method should, however, be adopted only in instances of serious lapses or shortcomings.
12. Control by written order : Under this method the employees are served with written notice or memorandum. Sometimes, demi-official (D.O.) letters are also issued with instructions to bring improvement in their working using simple and clear language.
13. Control by other methods : In addition to above methods, control is adopted by additional budget, break-even analysis, ratio analysis, self-control, charts and tables, indices etc.
(B) Specific methods:
1. Budgetary control: It is a traditional form of control and it is a widely used device in management. Budgets are used to control the day today operations of an enterprise.
2. Cost control : By exercising cost control the per unit production cost can be ascertained and can find out the method of minimizing the cost in future.
3. Break even analysis: The relationship of sales and expenses is depicted by a break even point chart. This chart shows the volume at which revenues exactly covers expenses.
4. Quality control: The best quality product of same grade and size can be produced at a cheaper rate. Such attractive goods will capture the market.
5. Production control : Under production control, all the activities involved in production are controlled in such a manner that the work of production is accomplished within the fixed time. In production control, control measures like the quality of goods, quantity, cost etc. are also adopted. In production control, the following two factors are kept in mind :
(a) When, how much and by which methods goods are to be produced
(b) Whether production is being accomplished as per per-determined plans or not ?
6. Material control: In cost of production, materials form a major portion. Therefore, the availability of the best material and minimum cost is very essential. Less than required quantity or more than required quantity of material are both considered unsuitable. Whereas production will be affected in the absence of required quantity of material, in case of excess of material, a part of capital! will remain idle. “Therefore, observing required control over all activities of material management is material control.
![]()
Question 9.
What is controlling ? Explain its importance.
“Controlling is a continuous activity in an organization.”
Answer:
controlling is a continuous or never-ending process. According to Koontz and O’ Donnell, “Just as the navigator continually takes a planned action, so should the business manager continually take to reading to assure himself that his enterprise or department is on course. ” Controlling never stops. Planning and controlling are two interrelated functions are reinforce each other. Control follows a definite pattern and time-table, month after month and year after year on a continuous basis.
The following are the points due to which control has a great importance :
1. Increasing size of business: At present the size of business is increasing day by day, from sole trader to partnership, from partnership to company. One man cannot control such big organization. So it is necessary to take help from others, therefore, control is necessary to see that no type of irregularity creeps into the organization.
2. Motivation for efficient employee : Efficient employee always welcomes control system because he gets a good opportunity for good work and finds his way to progress. He may be appreciated by managers for good work and so an employee is motivated towards work.’ ‘
3. For complete discipline : Discipline is necessary for any enterprise. To maintain discipline, control is very necessary. So, it can be said where there is control, discipline will come automatically. In the absence of control, indiscipline arises and hence morale of good employees hampers.
4. Helpful in future planning : Through controlling process, managers get full knowledge about the limitations of their objects and their efficiency. On the basis of this knowledge, it becomes easier for managers to prepare future planning. Through the process of controlling, managers get very important information about targets which may be useful in preparing future planning. .
5. Aids efficiency : Basically, control is concerned with ensuring that all activities proceed as per plans. Hence, it brings about efficiency in the organization.
6. Decrease in risk : Generally business and risk cannot be segregated but limitation and obstacles of business can be fully controlled. If it is done, then risk of business may be minimized to a great extent.
7. Helpful in coordination : Coordination has an important place in management, where control is best, the discipline will be best and in the presence of discipline, coordination becomes easier.
8. Helpful in decentralization : Decentralization (Dispersion) of authority is essential in big enterprises. Management cannot delegate authority without ensuring controls management must retain control in its hands to make sure whether authority is being used properly.
9. Helps in further planning : Planning and control are closely related. While planning is forward-looking, control is backward looking. Good control enables to analyse causes for deviations, and if required alter the plans according to circumstances. Thus, control is essentially a review of work done, whereas planning drafts the course of future action. Thus, control helps in further planning.
10. Highlights deviations : Since control is basically a review of past actions, it highlights any deviation while implementing work. This is primarily done by comparing with the standards set. Constant review of actions definitely proves beneficial for the organization.


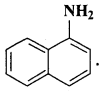

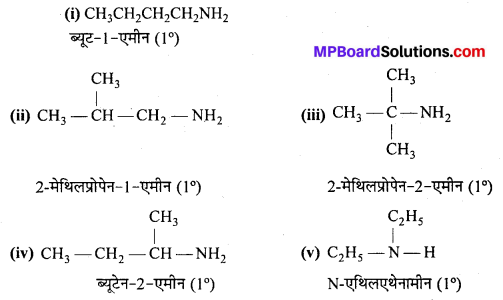
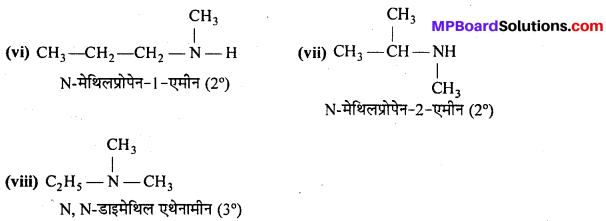
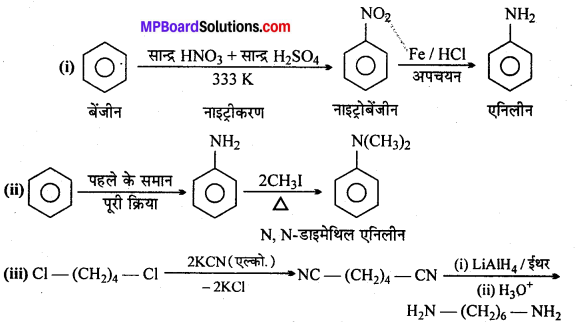
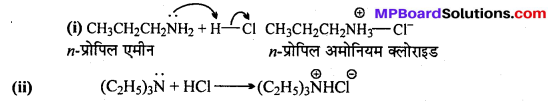
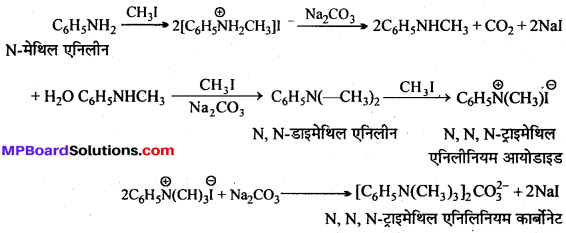
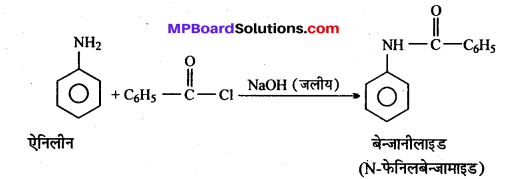

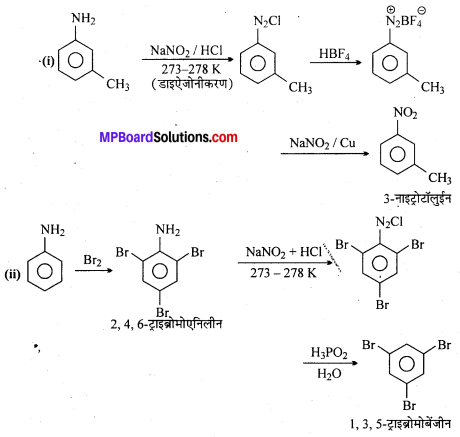
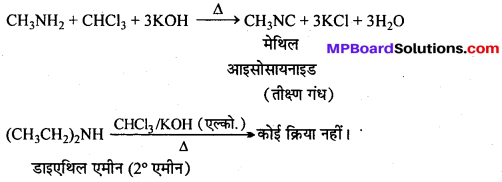
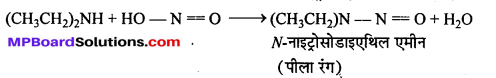
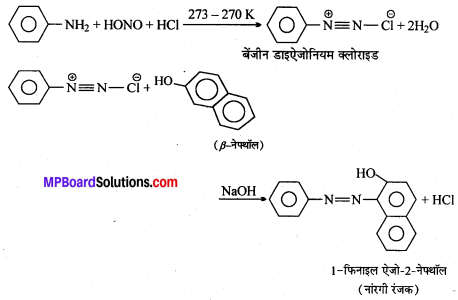
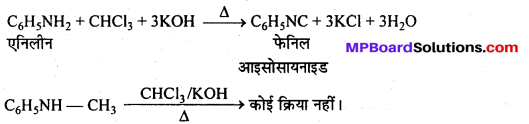
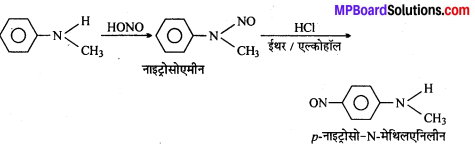
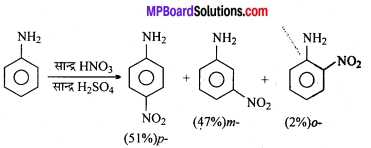
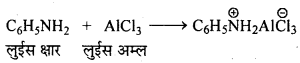
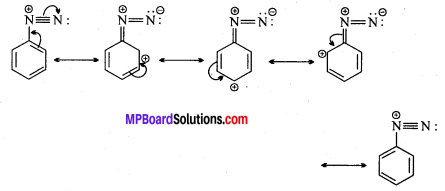
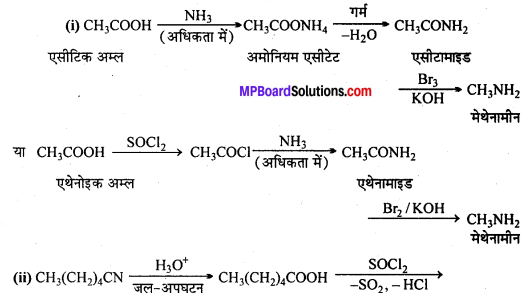
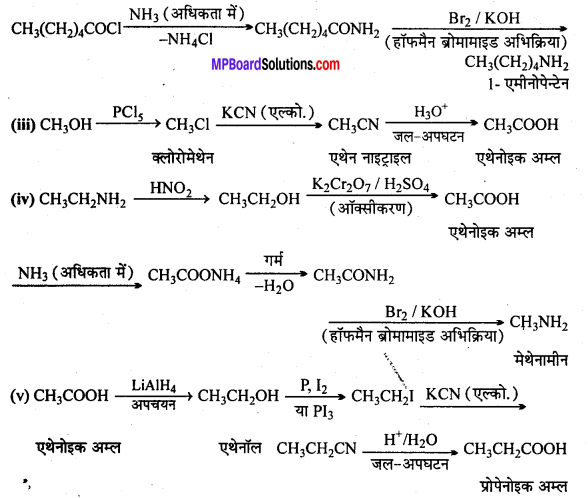
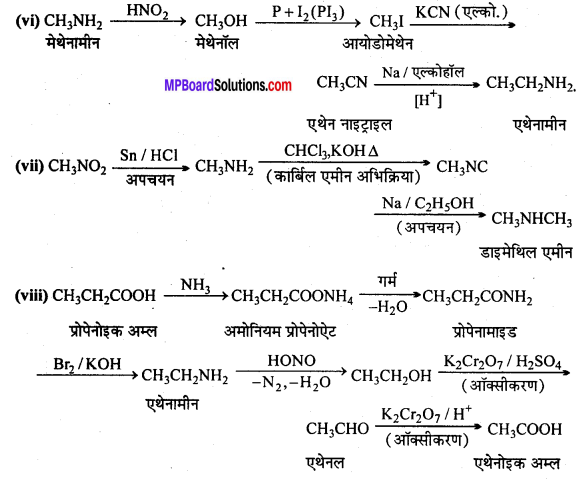
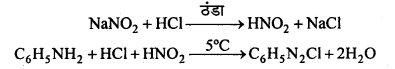
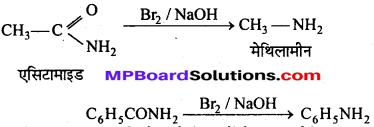
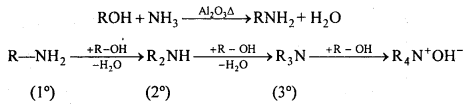
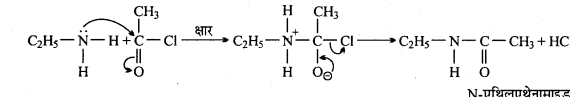
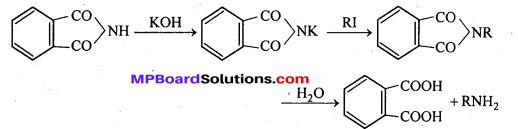
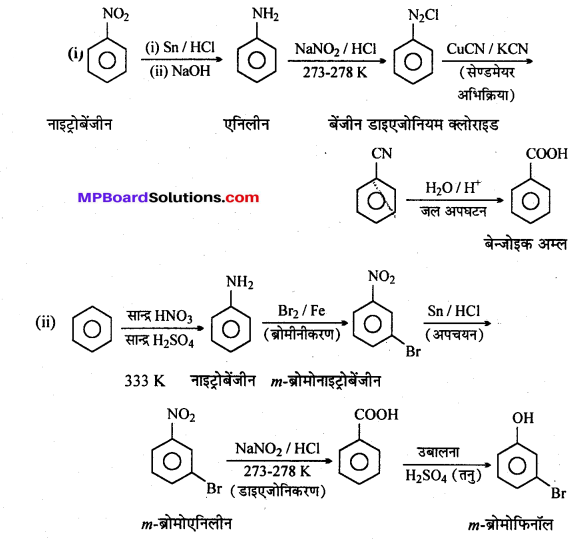
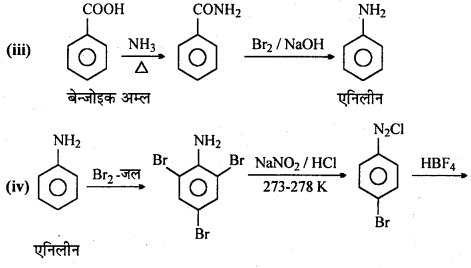
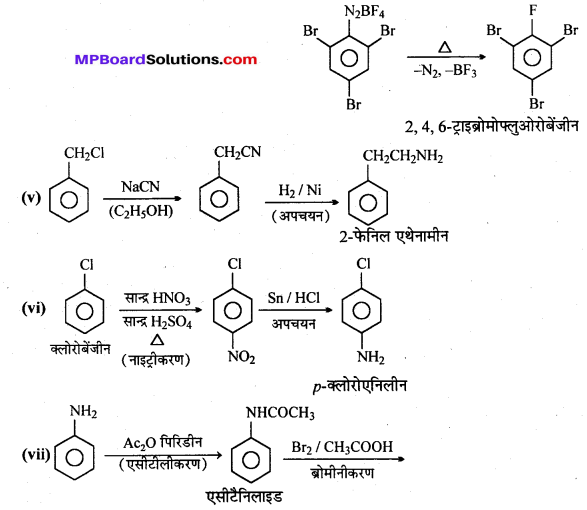
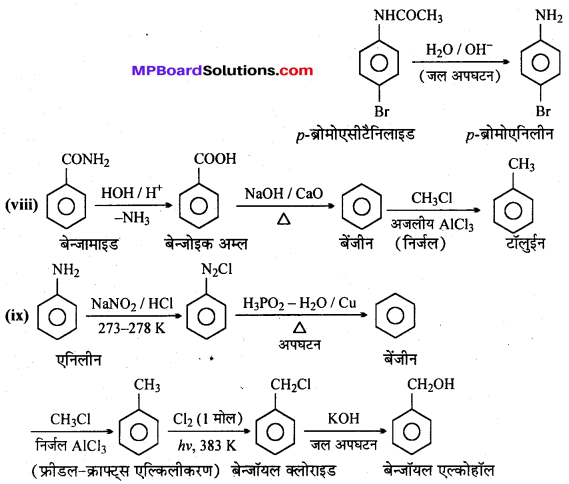
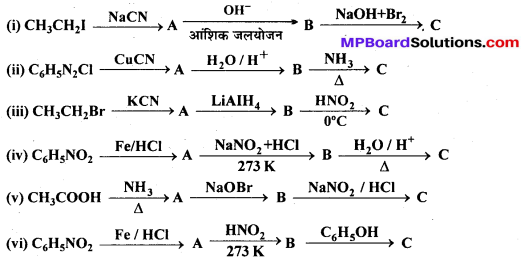
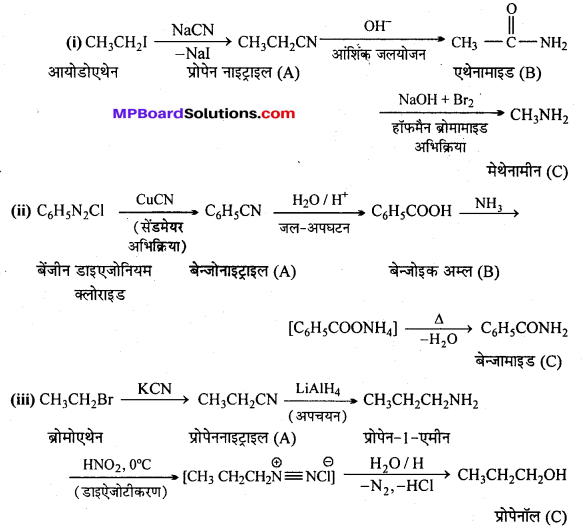
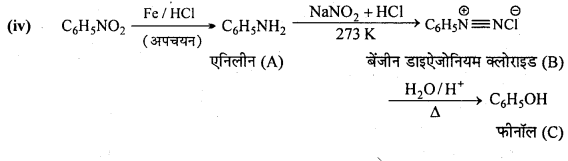
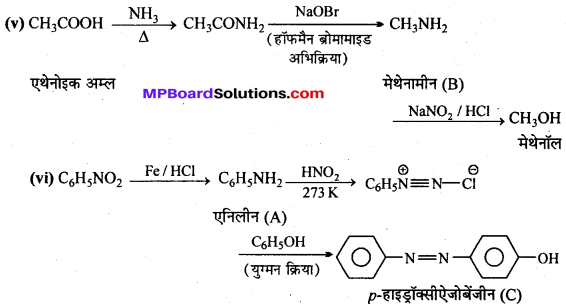
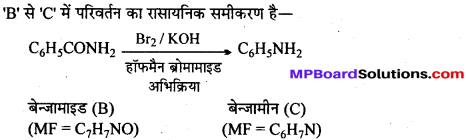
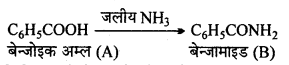
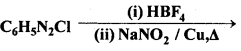
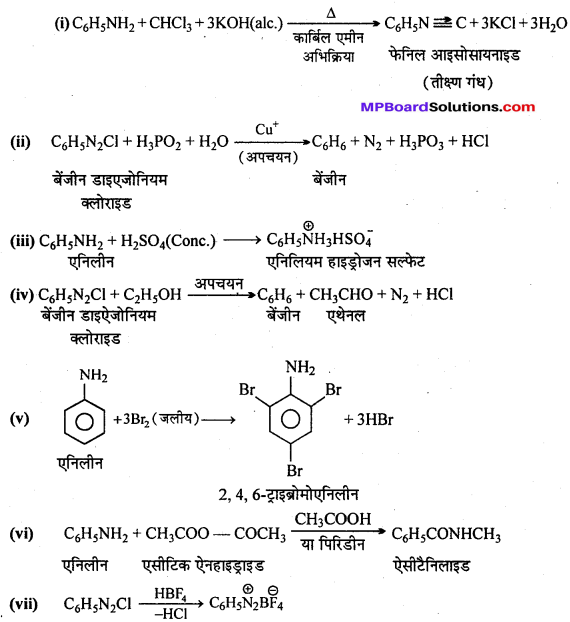
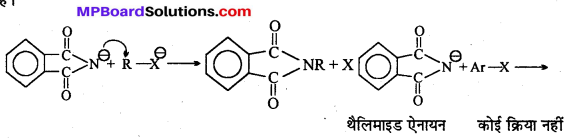
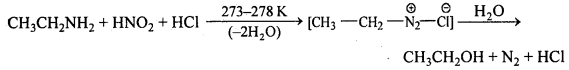
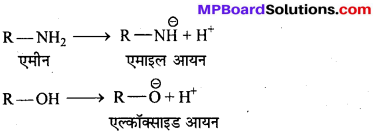
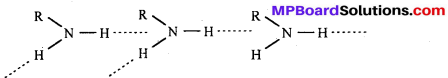
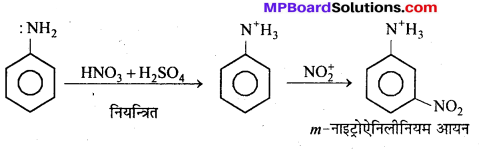
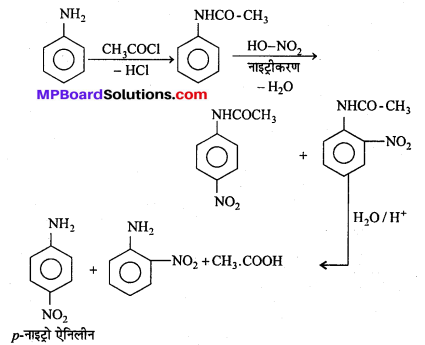
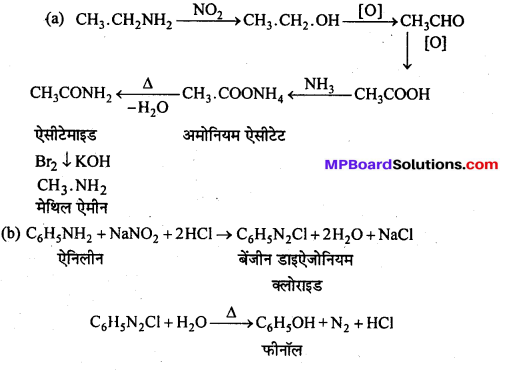
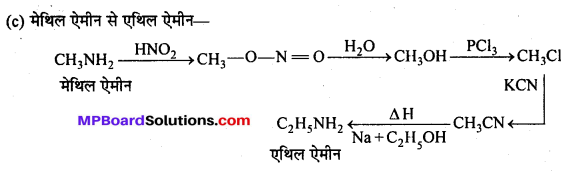
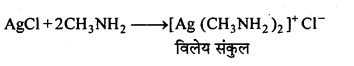
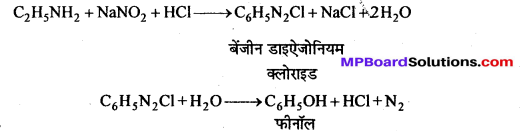
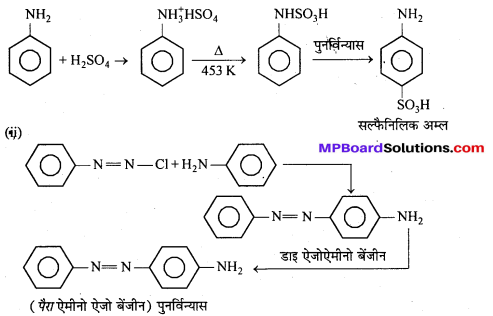
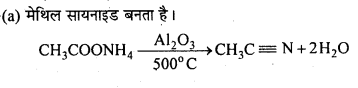
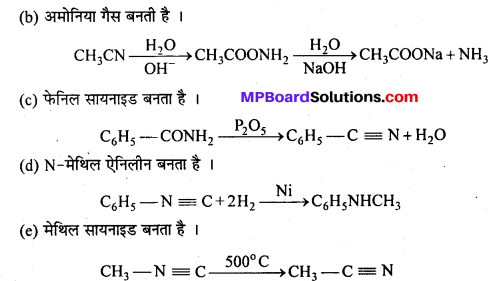
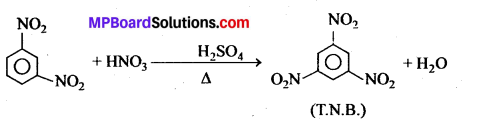
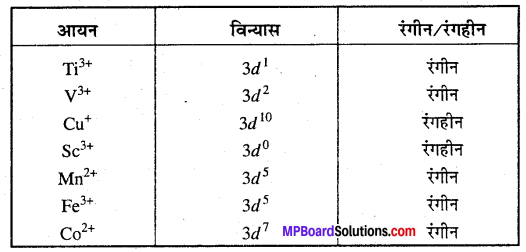
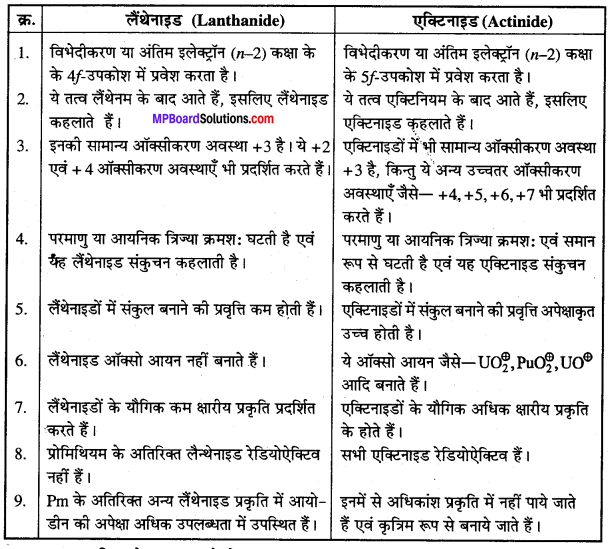
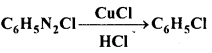 अभिक्रिया है
अभिक्रिया है


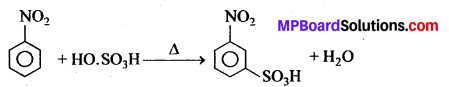
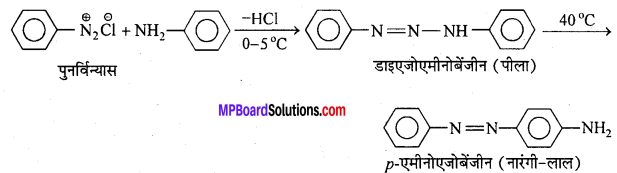
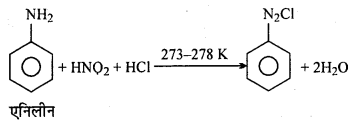
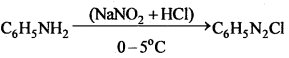 अभिक्रिया का नाम है। 0-5°C
अभिक्रिया का नाम है। 0-5°C उक्त अभिक्रिया का नाम लिखिए।
उक्त अभिक्रिया का नाम लिखिए।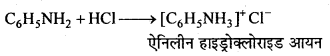
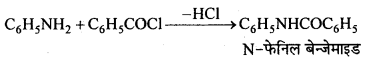
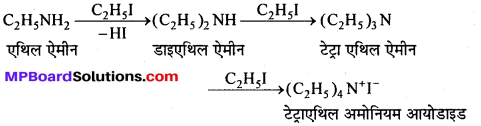
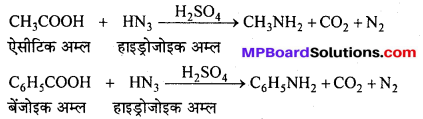
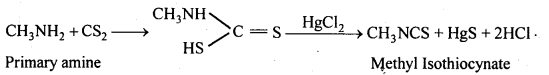
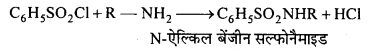
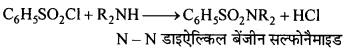
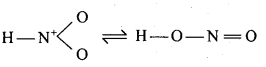
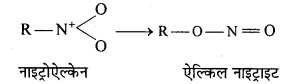
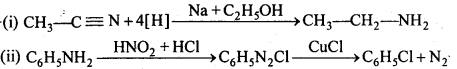
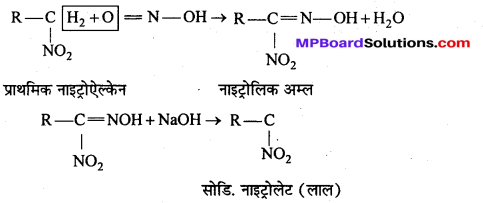
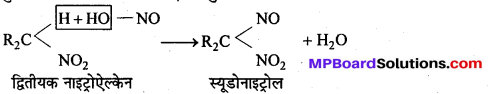
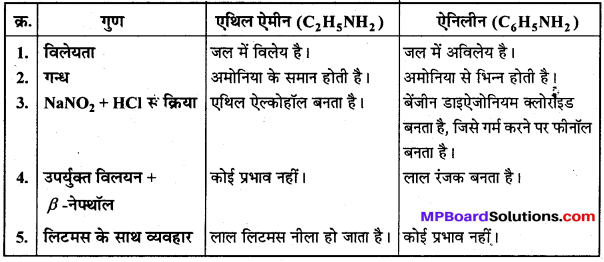
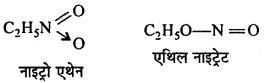
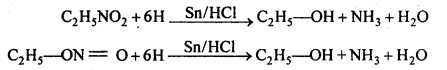
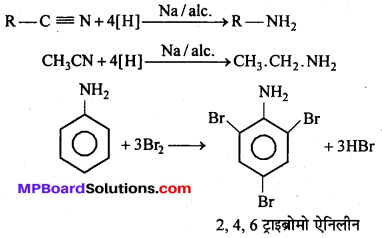
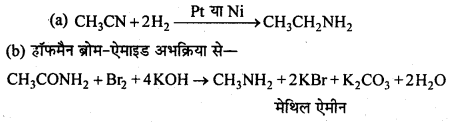
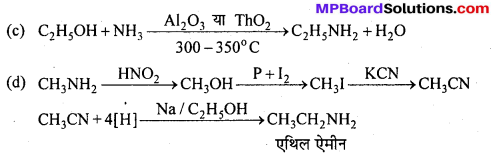
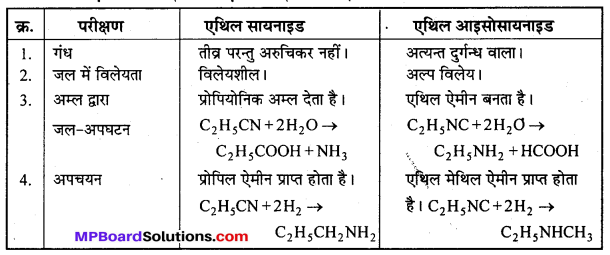
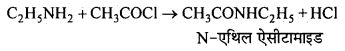
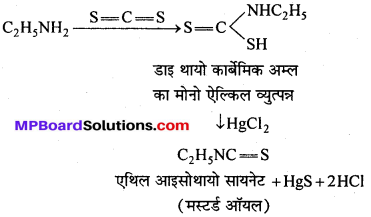
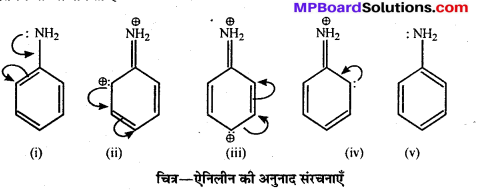
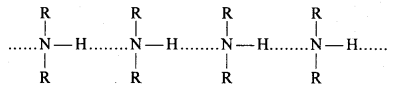
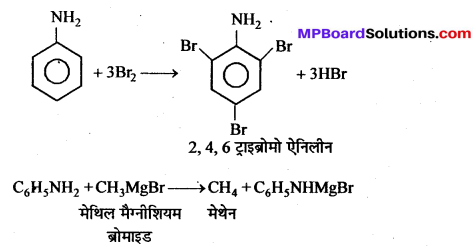
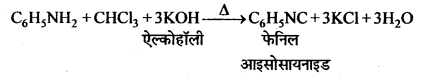
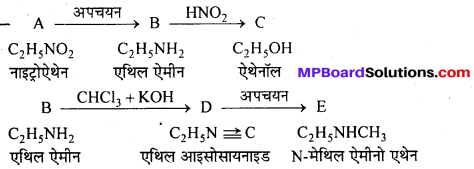
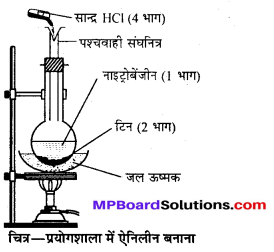
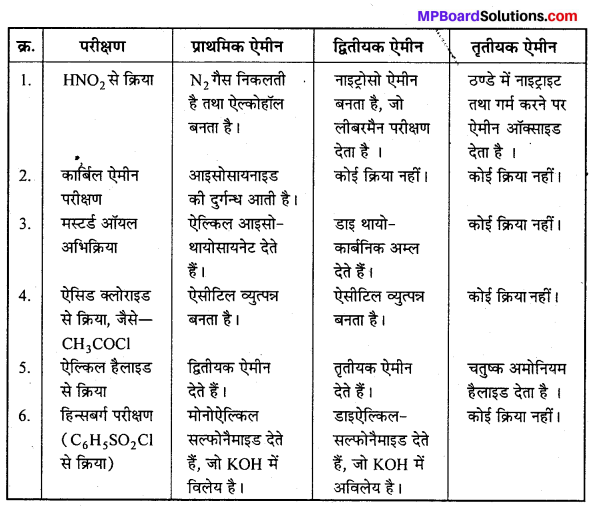
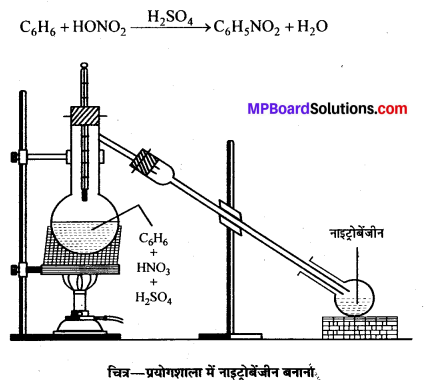
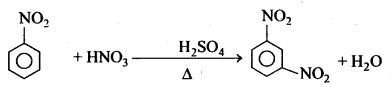
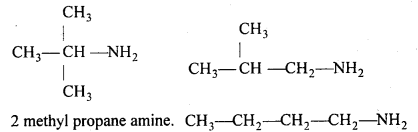
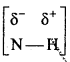 बन्ध उपस्थित होते हैं, जिससे ऐमीन में हाइड्रोजन बन्ध द्वारा अणुओं का संगुणन हो जाता है । इसी कारण इनका क्वथनांक समतुल्य अणुभार वाले ऐल्केन से अधिक होता है।
बन्ध उपस्थित होते हैं, जिससे ऐमीन में हाइड्रोजन बन्ध द्वारा अणुओं का संगुणन हो जाता है । इसी कारण इनका क्वथनांक समतुल्य अणुभार वाले ऐल्केन से अधिक होता है।