MP Board Class 12th Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Accounting for Share Capital
Accounting for Share Capital Important Questions
Accounting for Share Capital Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Maximum number of members in a private company is:
(a) 20
(b) 30
(c) 10
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) 10
Question 2.
Owners of company are:
(a) Shareholders
(b) Debenture holders
(c) Directors
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Shareholders
Question 3.
While issue the shares the rate of discount should not be more than:
(a) 5%
(b) 10%
(c) 6%
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) 10%
Question 4.
On calls in arrears according to Article A, the interest may be charged per annum:
(a) 5%
(b) 6%
(c) 10%
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) 5%
![]()
Question 5.
On calls paid in advance interest may be charged annum according to article A:
(a) 5%
(b) 8%
(c) 6%
(d) 7%.
Answer:
(c) 6%
Question 6.
Shares on which interest and repayment of money is paid after preference shares are:
(a) Preference shares
(b) Equity shares
(c) Rights share
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Equity shares
Question 7.
The capital beyond which a company cannot issue shares:
(a) Paid Capital
(b) Called up capital
(c) Authorised capital
(d) Issued capital.
Answer:
(c) Authorised capital
Question 8.
When excess application is received than the shares to be issued:
(a) Under subscription
(b) Over subscription
(c) Incomplete subscription
(d) Complete subscription.
Answer:
(b) Over subscription
Question 9.
Part of issued capital without receipt, a public Ltd. company cannot issue shares:
(a) Over subscription
(b) Minimum subscription
(c) Incomplete subscription
(d) Complete subscription.
Answer:
(b) Minimum subscription
![]()
Question 10.
Shares can be forfeited:
(a) For non payment of call amount
(b) Due to absence in meeting
(c) Due to inability of paying bank loan
(d) Due to montage of shares as securities.
Answer:
(a) For non payment of call amount
Question 11.
Balance of share forfeiture account is transferred to:
(a) General Reserve
(b) Capital Redemption Reserve
(c) Capital Reserve
(d) Revenue Reserve.
Answer:
(c) Capital Reserve
Question 12.
Written notice regarding forfeiture of shares should be given to the shareholder before:
(a) 21 days
(b) 14 days
(c) 7 days
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) 14 days
Question 13.
Part of Issued capital called from shareholder only on the liquidation of a company:
(a) Capital Reserve
(b) Authorized capital
(c) Reserve capital
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Reserve capital
![]()
Question 14.
Proposal related to forfeiture of shares is passed in:
(a) Share holder’s meeting
(b) Debenture holder’s meeting
(c) Creditor’s meeting
(d) Director’s meeting.
Answer:
(d) Director’s meeting.
Question 15.
Before the forfeiture of shares, company must serve a notice to shareholders before:
(a) 21 days
(b) 14 days
(c) 7 days
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) 14 days
Question 16.
When the company is being liquidated, a part of issued capital is demanded from shareholders, it is called:
(a) Authorized capital
(b) None of these.
(c) Capital gain
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Capital gain
Question 17.
When premium amount is not received in forfeiture of shares, share premium account is:
(a) Debited
(b) Credited
(c) Not written
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Debited
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- …………… get first dividend of a company.
- When amount to be paid in calls is paid before it is called ……………
- That part of authorized capital issued or offered to public for subscription is ……………
- A company is said to be …………… if it receives applications for a large number of shares as compared to the shares offered to public for subscription.
- Minimum subscription is mentioned in ……………
- Cancellation of share allotted and forfeiture of amount paid is called ……………
- As per company Law Board, a company is regarded as on …………… person.
- Shares have …………… value while stock have no …………… value.
- When a shareholder voluntarily surrender his share to the company, it is known as ……………
- Share forfeiture account is shown in …………… side of Balance sheet.
- Notice regarding forfeiture of shares must be given to the shareholders before ……………
days. - When forfeited shares are re-issued at discount, the …………… account is debited.
- When the articles contain no provision related to forfeiture of shares, the company can forfeit shares by passing a …………… resolution.
- To the absence of provisions for forfeiture of shares in articles of association a company may forfeit shares by passing a resolution.
- When a shareholder find its difficult to pay the amount due on calls shares held by him as such he may …………… the shares at his possession.
- Balance of share forfeiture A/c is shown in …………… side of balance sheet.
- The balance of …………… is utilized to write off preliminary expenses, discount on debentures, etc.
Answer:
- Preference
- Advance
- Issued capital
- Over subscription
- Prospectus
- Forfeiture of shares
- Artificial
- Face, Face
- Surrender of shares
- Liability
- 14
- Share forfeiture
- Special
- Special
- surrender
- liability
- capital reserve.
![]()
Question 3.
Match the columns:

Answer:
- (b) Equity shareholders
- (c) Over subscription
- (e) Under subscription
- (a) Preference shareholders
- (d) Unpaid calls account
- (f) At time of dissolution. (MP 2015)

Answer:
- (e) Forfeiture of shares.
- (c) Shares issued at premium
- (b) Shares issued at discount
- (a) Surrender of shares
- (d) Capital reserve account
Question 4.
Write true or false:
- Rate of dividend is fixed in preference shares.
- There are more chances of speculation in equity shares.
- According to table A, a company cannot call more than 25% of the nominal value of shares at a time.
- Between two calls there should be a difference of not less than 15 days.
- If shares of Rs. 100 are issued at Rs. 110 then it is said that shares are issued at discount. .
- After forfeiture of shares the responsible shareholder becomes free from remaining amount.
Premium is a type of capital gain. - After reissue of forfeited shares balance of share forfeited A/c is transferred to Reserve capital A/c.
- The discount allowed on the reissue of forfeited shares should never exceed the amount actually forfeited on such shares.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the answer in one word / sentence:
- Name the part of issued capital without the receipt of which share cannot be allotted.
- Name the company if at least 51% of its paid up capital is owned by the central or State governments or both.
- Name the company which has acquired more than half number of other company’s share. On which shares rate of dividend is not fixed ?
- Name the capital which the company does not issues in whole life of company.
- When a shareholder fails to pay the amount called by the company on shares held then the process of cancellation is called ?
- How are capital losses written off ?
- What is the issue of forfeited shares to public for subscription called ?
- Who proposes for the forfeiture of shares ?
Answer:
- Minimum subscription
- Government companies
- Holding companies
- Equity shares
- Reserve capital
- Share forfeiture
- Capital reserve
- Reissue of shares
- Board of Directors.
![]()
Accounting for Share Capital Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by share capital ?
Answer:
The total capital of a company is divided into small units. One unit is called as share and the total amount of the shares are called as share capital. Normally company issue share certificate and get this amount.
Question 2.
What is share ?
Answer:
The capital of a company can be divided into different units with different value, which are known as shares. They are the part of total capital.
Question 3.
What is share certificate ?
Answer:
Share certificate means the certificate issued by a company to its shareholders in which numbers of shares. Purchased its value is written along with the shareholder’s name.
Question 4.
What is equity shares ?
Answer:
They are also known as ordinary shares or risk shares. They get dividend only after paying the dividend or preference shares. If after paying dividend on preference shares, no profit is left, no dividend will be paid on equity shares.
Question 5.
What do you understand by the term ‘Sweet share’ ?
Answer:
Those shares which are issued by the company to its employees and officers at a discounted rate to encourage them to work devotion ally for the betterment of the company are called ‘sweet shares’. Such shares cannot be sold by the holders for at least one year.
![]()
Question 6.
Write two characteristics of equity shares.
Answer:
- Equity shareholders enjoy voting right over the others.
- On such shares dividend is not fixed.
Question 7.
Write any two merits of equity shares.
Answer:
- Equity shareholders are actual s owners of company.
- Shareholders have a full control over management of company.
Question 8.
Define preference shares.
Answer:
Preference shares are the shares on which a fixed rate of dividend is payable before anything is payable to the equality shareholders.
Question 9.
What do you mean by call in arrear ?
Answer:
The amount which is due on shareholders and which is called up by the company but shareholders could not paid till the fixed date (due date) then, such amount is called calls in Arrear.
Question 10.
What do you mean by authorised capital ?
Answer:
Authorised capital refers, to that capital which is stated in the memorandum of association. This is the maximum amount of capital which the company will have during its lifetime unless it is increased. It must be distinctly shown in the balance sheet of the company under the head ‘Share Capital’. It is also known as nominal capital or registered capital.
Question 11.
What do you mean by ‘Issued capital’ ?
Answer:
Issued capital refers to that part of authorised capital which is issued to public for subscription or sale. Issued capital is generally less than authorised capital or at the most, it may be equal to it but can never be more than authorised capital.
Question 12.
What do you mean by ‘Under subscription’ ?
Answer:
Under subscription means subscription by public for a number of shares which is smaller than the number of shares offered by the company for subscription. For example, when a company offers 20,000 shares of Rs. 10 each for public subscription, but the public applies for 19,000 shares such a situation is called ‘Under subscription’.
Question 13.
What is allotment of share ?
Answer:
After getting application from the specified person and institution then distribution of the shares is done on the basis of Application received this is called as allotment of shares.
![]()
Question 14.
What is prorata Allotment ?
Answer:
Prorata allotment:
In case of over subscription of shares, the directors allot small number of shares to the applicants. In other words, the directors accept the applications partially. In such cases the excess of application money is utilized against the amount due to allotment and future calls by the transferring the excess amount from the share application account. Thus, when the company allots shares proportionately or rationally to all the applicants, it is known as prorata allotment.
Question 15.
What is dividend ?
Answer:
When the company distributes a part of its profit on a certain rate to its share-holder, it is called dividend. The rate of dividend is fixed for preference shareholders while this facility is not available for equity shareholders. They get their dividend when the company make profit.
Question 16.
Define Company.
Answer:
Section 1 (i) of Indian Companies Act of 1956, defines a company as “Company formed and registered under this Act or an existing company.” An existing company means a company formed and registered under any of the former companies acts.
Question 17.
What do you mean by issue of shares at par ?
Answer:
When the shares of a company are issued at their nominal value (face value), then those are called issue of shares at par. For example if a share of Rs. 100 is issued for Rs. 100, then it is known as issue of shares at par.
![]()
Question 18.
What do you mean by issue of shares at premium ?
Answer:
When the shares are issued at a price higher than its face value, it is called issue at premium. From the issued price, the face value of the share is subtracted and the difference excess amount is the premium.
Question 19.
What do you mean by issue of shares at discount ?
Answer:
When the shares are issued at a price less than its face value, it is called issue at discount. For example : If a share of Rs. 100 is issued at Rs. 90 then it is issued at discount and the difference (Rs. 100 – Rs. 90) is the amount of discount i.e., Rs. 10.
Question 20.
What do you mean by forfeiture of shares ?
Answer:
If any shareholder falls to pay the amount due on allotment or any calls within the specified period, the company may cancel them. This is known as forfeiture of shares. In this condition, the amount already paid is taken over by the company.
Question 21.
What do you mean by reissue of forfeiture shares ?
Answer:
When the company reissues the forfeited shares it is known as ‘Reissue of for-feited shares.’ It can be done at par, at premium or at a discount.
Question 22.
What do you understand by surrender of shares ?
Answer:
When the shareholder voluntarily wants to gaining up the rights of being a share-holder and surrenders all his shares (Share certificates) to the company, then it is known as surrender of shares. The accounting of such surrender is alike forfeiture of shares.
![]()
Question 23.
What is ‘Reserve Capital’ ?
Answer:
That part of issued capital which is called from the shareholders on the event of dissolution of the company is called Reserve capital. This capital cannot be issued for issuing Bonus shares or writing off capital losses.
Question 24.
What is ‘Capital Reserve’ ?
Answer:
A Reserve fund created out of capital profit other than normal profit of the business is called capital reserve. It is displayed on the liabilities side of company’s Balance sheet. This fund can be utilized for issuing Bonus shares and writing off capital losses of the company.
Question 25.
Is there any provision of cancellation of forfeiture order ?
Answer:
The Articles of Association provides the Board of Directors, the right to forfeiture the shares of defaulting shareholders. The same article also provides the right to Board of Directors for cancellation of forfeiture order only if the defaulting shareholder pay all his previous dues along with interest and any penalty imposed on him.
Question 26.
Why reissue of forfeited shares are not called allotment ?
Answer:
Allotment is made only for ‘Primary’ and new issue of shares. But forfeited shares are existing shares (old). So, these can be reissued only.
![]()
Accounting for Share Capital Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write any four characteristics of a company.
Answer:
Following are the four characteristics of a company:
- Legal, artificial personality: A company is established by the company law and it has independent legal existence.
- Voluntary association: Any person by purchasing the shares of a company can become its member.
- Limited liability: The liability of each member is limited to the extent of the paid value of his shares.
- Representative arrangement: The representatives of the members look after the management of the company, these representatives are called ‘Directors’ of the company.
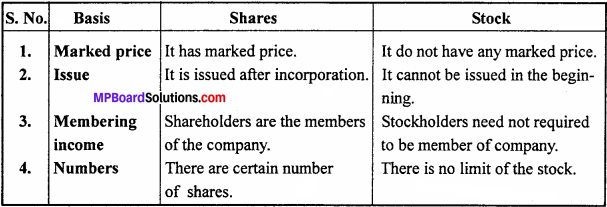
Question 2.
Differentiate between Shares and Stock. (Three points).
Answer:
Question 3.
What are the characteristics of preference shares ?
Answer:
The following are the characteristics of preference shares:
- The rate of dividend on these type of shares is fixed in advance
- The dividend on these shares are paid first
- The shareholders of these shares have no voting right
- The income on these shares are limited and fixed
- At the time of winding up a company preference shareholders paid first.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain any three types of preference shares. (CG 2005 Set A, Supple 13)
Answer:
1. Cumulative preference shares:
If on such shares in any year dividend is not paid due to less profit, as such in the next year the unpaid arrears of dividend shall be paid before making payment to the holders of any other class of shares.
2. Non – cumulative preference shares:
On these shares, the dividend is paid at a fixed percentage but the arrears of dividend, the dividend shall not accumulate in the coming years.
3. Convertible preference shares:
The holders of such shares have a right to get their preference shares converted into equity shares within a certain period.
Question 5.
Write any three merits of preference share. (CG 2010 Set C, Imp., Supple 13)
Answer:
Following are the three merits of preference share :
- Easy in management: These shareholders have no right to take part in company’s management. So, only limited persons are involved in management which is a favor for the company.
- Good sources of income: It is better for those shareholders who want a fixed and regular income.
- First preference in profit and payment: On these shares the profit is paid first and in the same way in the case of winding up, the share capital of preference shareholder is paid first.
Question 6.
Write any three demerits of equity shares.
Answer:
The following are the three demerits of equity shares :
- Uncertainty of dividend: It is not suitable for those person who require regular income, because in this shares the income is irregular and uncertain.
- Payment of dividend: Payment of dividend is made on these shares only after the payment on preference shares.
- Final payment: In this the shareholders get the payment only at the time of winding up of the company.
![]()
Question 7.
Write three demerits of preference shares.
Answer:
The three demerits of preference shares are:
- Fixed charge: They receive dividend at fixed rate every year. Hence, the burden on account of preference dividend is fixed on the company.
- No right in the management: The preference shareholders do not enjoy the right to participate in the administration or management of the company.
- Less dividend: In the years of excessive profits, the preference shareholders receive less profit as compared to those of equity shares.
Question 8.
What is calls in advance ?
Answer:
Sometimes the share amount is paid in advance before the call money becomes due, such type of advance is called call paid in advance. Articles ‘A’ of companies act gives permission regarding it, according to this articles interest will be allowed @ 6% p.a.
Question 9.
What is over-subscription ?
Or
What do you understand by over-subscription ?
Answer:
A company according to its own requirement issues shares. Sometimes company receives applications for a large number of shares than offered by it for subscription. In such case, the work of allotment of shares by directors becomes difficult because all the applicants cannot be allotted on the basis of their applications. In this case, the directors will allot only those shares which are issued by the company. Hence, allotment will be made on the basis of terms decided in the meeting of directors.
Question 10.
What is minimum subscription ?
Answer:
Minimum subscription is that minimum part of the issued capital which is necessary to raise by the way of issue of shares to meet the following expenses:
- To pay-off the necessary assets purchased for the company.
- To pay-off the preliminary expenses and commission to under-writers for sale of shares.
- The amount sufficient as working capital.
- To pay the loan taken for the purchase of necessary assets and for meeting the preliminary expenses.
- An amount necessary for any other purpose.
![]()
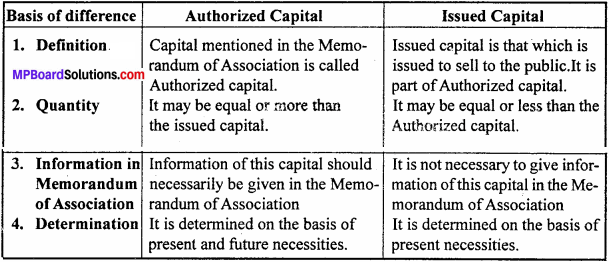
Question 11.
Write the difference between Authorized Capital and Issued Capital.
Answer:
Question 12.
Briefly explain the types of share capital.
Or
Discuss the kinds of capital of a company.
Answer:
Share capital means the capital raised by a company by the issue of shares. From the accounting point of view, the different kinds of share capital are as follows:
1. Authorised capital:
It is the capital which the company can raise from the public by the issue of shares. It is the maximum amount. It is stated in the memorandum of association. It is separately shown in the balance sheet. It is also known as nominal capital or registered capital. It is the capital on which the company is registered.
2. Issued capital:
It is the part of the authorised capital, that the company offered to the public for subscription.
3. Subscribed capital:
It is that portion of capital issued, which has actually subscribed by the public. It may be equal or less than the issued capital but never be more than the issued capital.
4. Called – up capital:
The company doesn’t require the full value of the shares they subscribed for at one instalment. Thus, the portion of the subscribed capital, which the share¬holders are called to pay is known as ‘Called-up Capital’.
5. Uncalled capital:
That part of the capital which is not called by the company from the shareholders is known as ‘Uncalled Capital’.
6. Paid – up capital:
It is that part of called-up capital, which is actually paid by the shareholders, is called ‘Paid-up capital’.
7. Reserve capital:
Sometimes, a company by means of a special resolution, decides that its uncalled capital will not be called-up; during its existence and that would be avail-able as an additional security to its creditors in the event of its liquidation. This capital is termed to be reserve capital.
![]()
Question 13.
When a company can issue its shares at a discount, what journal entries are passed in this regard ?
Answer:
Under section 79 of the companies Act of 1956, a company can issue shares at a discount subject to the following conditions:
- The company is completed one year of its business.
- The issue of shares at a discount has been authorised by the shareholders in a general meeting of the company and also has been sanctioned by the court.
- The rate of discount must not exceed 10% of the face value of the shares which is permitted by the Company Law Board. The maximum rate has to be specified by the share holders resolution permitting the issue.
- The shares are issued within two months of the date on which the issue is sanctioned by the Company Law Board or within such extended time as the board may allow.
- Shares to be issued at a discount must be of a class already issued.
Journal Entry:
When shares are issued at discount
Share Allotment A/c – Dr.
Discount on Issue of Shares A/c – Dr.
To Share Capital A/c
Question 14.
Discuss the procedure of issue of shares.
Answer:
Following steps are taken by a public company for the issue of shares:
1. Issue of prospectus:
The company issues a prospectus by which it invites public to subscribe to its shares. The prospectus describes the profitability and soundness of the business of the company to attract the investing public.
2. Receipt of application:
All application and the amount of share application money must be deposited by the public in a Company’s Scheduled Bank. After the last day for receipt of share applications the bank sends all applications to the company.
3. Allotment of shares:
The directors of the company have the right to accept application wholly or partially or reject it. Those who are allotted shares are sent ‘Letters of Allotment’ and those who are not allotted shares they are sent ‘Letters of Regret’ along with a cheque for the refund of application money.
![]()
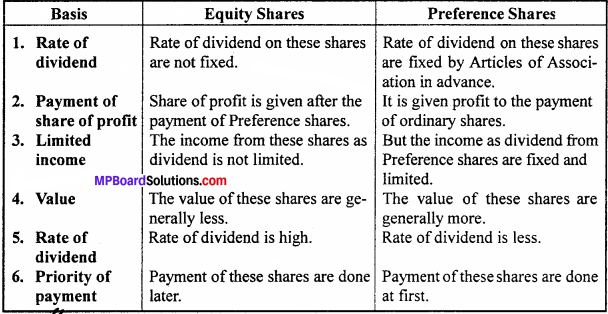
Question 15.
Differentiate between equity shares and preference shares. (Any 4)
Answer:
Differences between equity shares and preference shares:
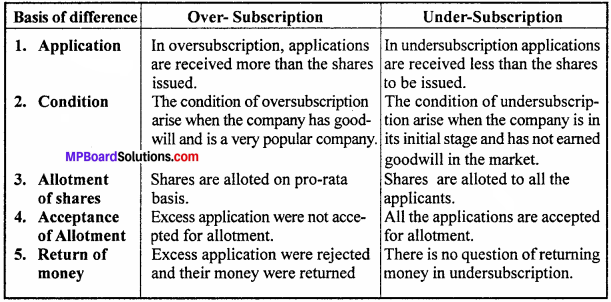
Question 16.
Write the difference between over subscription and under subscription.
Answer:
Difference between Over subscription & Under subscription:
Question 17.
What is forfeiture of shares ?
Answer:
If any shareholder fails to pay the amount due on allotment or calls within a specified period, the company may cancel them and the amount paid is taken over by the company. This is called forfeiture of shares.
The following conditions must be satisfied for the forfeiture of shares:
- The power to forfeit the shares must be given in the Articles of Association
- If the procedure of forfeiture is not given in the articles, table ‘A’ should be followed
- There should be default in payment of any allotment or call money by the shareholder
- Notice must be given to the respective shareholder for 14 days in advance
- The Board of Directors must pass a resolution for such forfeiture.
![]()
Question 18.
Explain the legal procedure of forfeiture of shares.
Answer:
The following are the legal provisions regarding forfeiture of shares:
- Shares can be forfeited only when the default is made by the shareholders in payments of a valid call
- Shares can be forfeited only if the power is expressly given by the Articles of the company
- If provisions are not made in.the Article of the company, then by passing a special resolution company can forfeit the shares
- The written notice of 14 days mentioning about forfeiture of shares must be given to the shareholders
- The share can be forfeited on the basis of the resolution passed by the board of directors.
Question 19.
Explain the procedure of forfeiture of shares.
Or
What steps are necessary for forfeiture of shares ?
Answer:
Following are the methods of forfeiture of shares:
1. Preparation of list: Firstly a list of defaulting shareholders is produced by the company secretary in the meeting of the board of directors.
2. Notice for payments: The board of directors orders to serve notice for payment of unpaid calls and interest.
3. Issued reminder: After the issue of above notice if shareholders unable to pay the call money then the board of directors orders again to serve final notice for payment.
4. Passing a resolution for forfeiture of the shares: If the final notice gets no response, the board will then pass a resolution for forfeiture of the shares and the share holders concerned will be intimated of the decision asking them to return to the company the share certificate issued to him on allotment of shares.
![]()
Question 20.
Describe the effects of forfeiture of shares.
Answer:
Rights and duties of defaulter shareholder w hen share is forfeited will be affected in the following way:
- Cancellation of membership:
At the time of forfeiture of shares, the membership of defaulter shareholder is cancelled. - Responsibility of payment:
Till the date of forfeiture of shares, the shareholders is responsible for the payment of balance amount. - No right on dividend:
The defaulter shareholder who’s shares are forfeited have no right on dividend.
Question 21.
Explain the reissue of forfeited shares.
Answer:
Company has full right to reissue the forfeited shares at proper time. Issue of forfeited shares to public is called reissue of share. There can be reissued at par, at discount or at premium.
Question 22.
Can the forfeited shares be reissued at discount ? Explain.
Answer:
Forfeited shares can be reissued at discount. Board of directors have the right to reissue the forfeited shares at discount, but the amount of discount on reissue should not exceed the amount forfeited on those shares. Thus, discount on reissue can be given maxi-mum up to the amount forfeited and not more than that.
![]()
Question 23.
Distinguish between Capital Reserve and Reserved Capital.
Answer:
Differences between capital reserve and reserved capital:
Capital Reserve:
- It can be utilized only in writing-off the capital losses.
- It is shown in the liability side of balance sheet.
- It is represents the amount which has already been received.
Reserved Capital:
- It can be utilized only at the time of liquidation of that company.
- It is not shown in the book of account.
- The amount of reserved capital is not received till the time of liquidation.
Question 24.
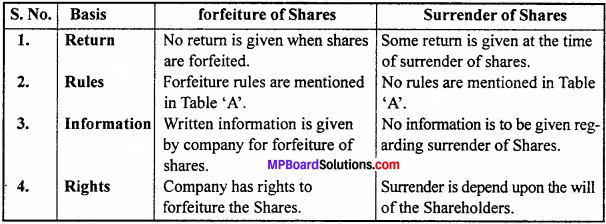
Differentiate between forfeiture of Shares and Surrender of Shares.
Answer:
Differences between forfeiture of Shares and Surrender of Shares:
Accounting for Share Capital Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Show journal entries for the reissue of forfeited shares.
Answer:
Forfeited shares can be reissued at par, at premium or at discount. Journal entries on all the above cases is given below:
(1) Reissue of Forfeited Shares at Par:

(2) Reissue of Forfeited shares at Discount:

(3) Reissue of Forfeited Shares at Premium:

(4) When the balance of Forfeited Shares A/c is transferred to Capital Reserve:
