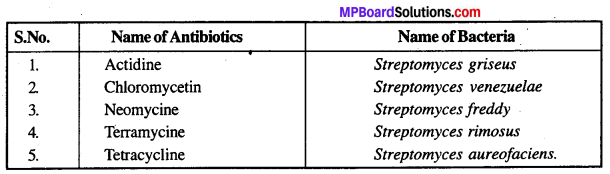
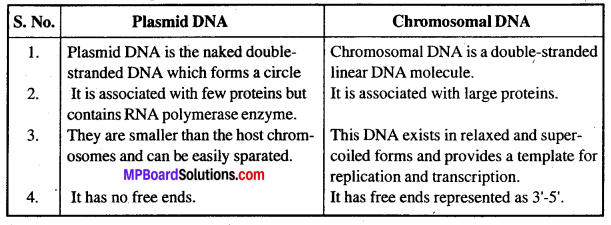
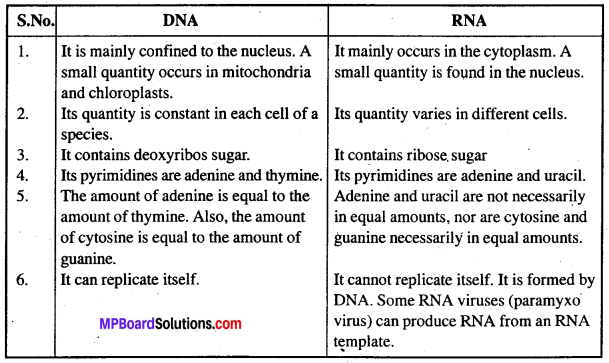
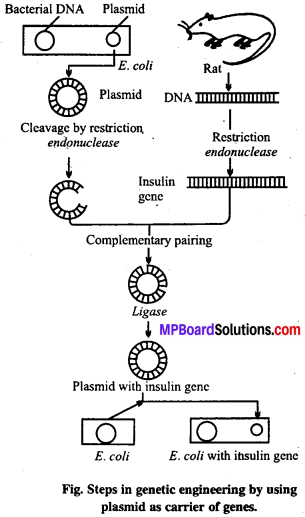
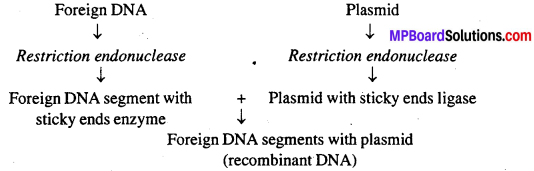
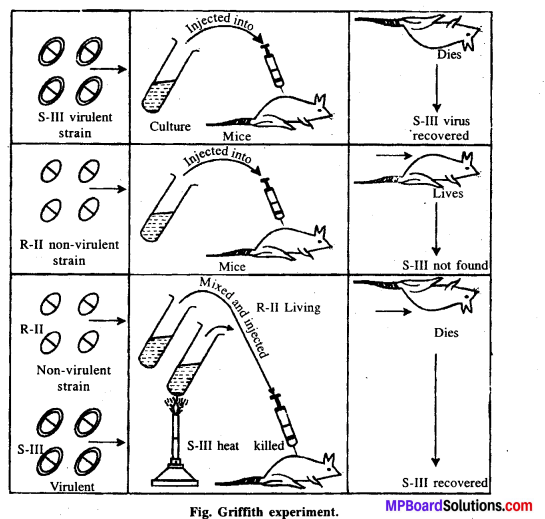
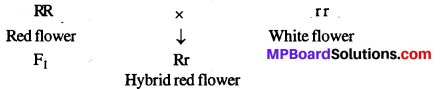
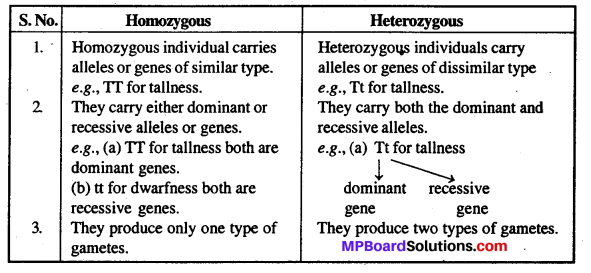
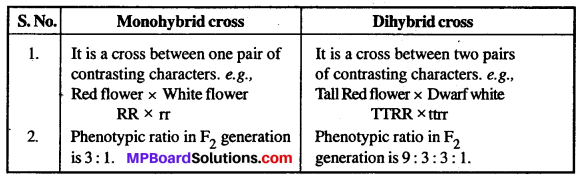
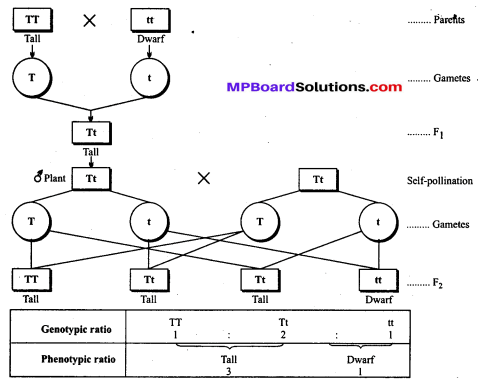
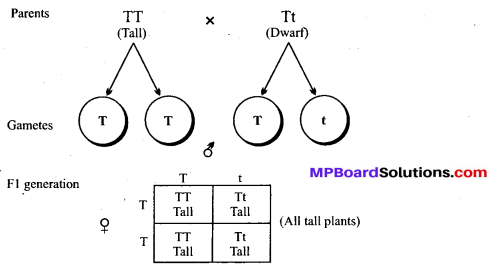
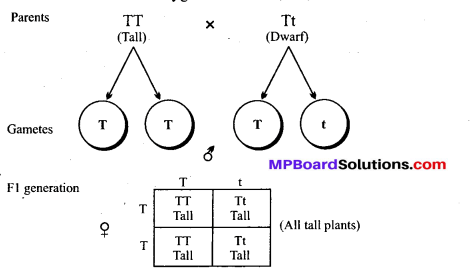
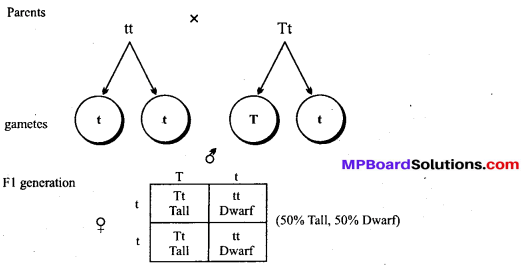
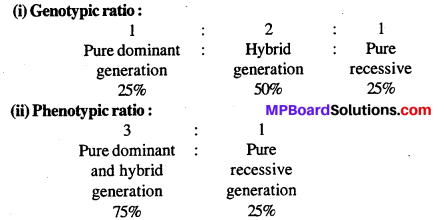
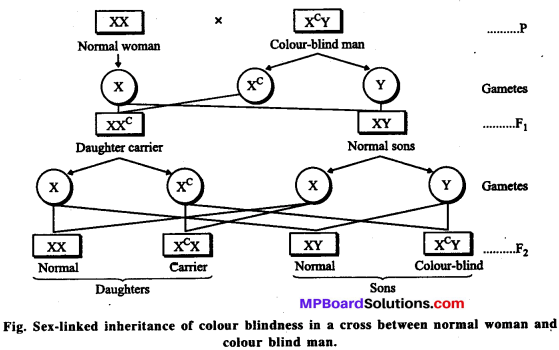
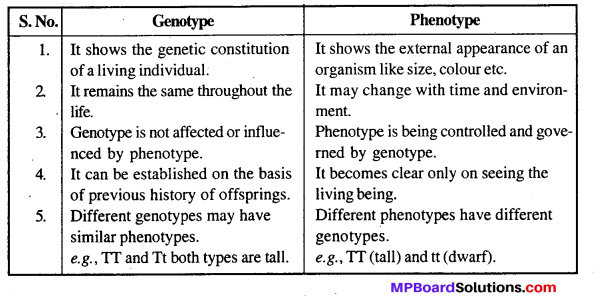
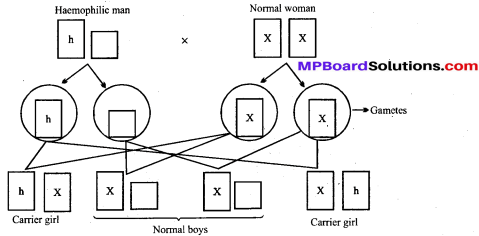
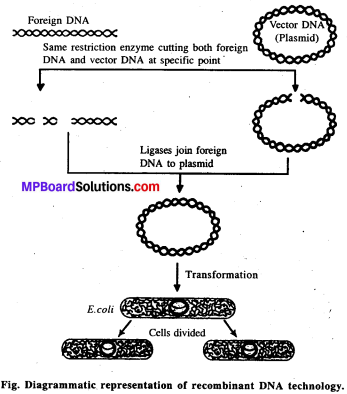
MP Board Class 12th Biology Solutions Chapter 8 मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग
मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग NCERT प्रश्नोत्तर प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
कौन-से विभिन्न जन स्वास्थ्य उपाय हैं, जिन्हें आप संक्रामक रोगों के विरुद्ध रक्षाउपायों के रूप में सुझाएँगे।
उत्तर
संक्रामक रोगों की रोकथाम के लिए हम निम्नलिखित उपाय सुझाएँगे
- संक्रामक रोगों के प्रति टीकाकरण (प्रतिरक्षीकरण) कार्यक्रमों का आयोजन करना।
- खाने और पानी आपूर्ति के संसाधनों का स्वच्छ रख-रखाव रखने के लिए लोगों एवं प्रशासन को प्ररित करना।
- रोग और शरीर के विभिन्न प्रकार्यों पर उनके प्रभाव के बारे में जागरूकता लाना।
- रोगवाहकों (वेक्टर्स) पर नियंत्रण रखने के उपायों जैसे-गंदगी के ढेर और गंदे पानी को इकट्ठा न होने देना।
- अपशिष्टों का समुचित निपटारा करना ताकि वातावरण स्वच्छ बना रहे।
प्रश्न 2.
जैविकी के अध्ययन ने संक्रामक रोगों को नियंत्रित करने में किस प्रकार सहायता की
उत्तर
जीव विज्ञान में हुई प्रगति से हमें संक्रामक रोगों से निपटने के लिए कारगर हथियार मिल गये हैं। टीका (Vaccine) के उपयोग और प्रतिरक्षीकरण कार्यक्रमों से चेचक, डिफ्थीरिया, न्यूमोनिया और टिटनेस जैसे-अनेक संक्रामक रोगों का काफी हद तक नियंत्रित कर लिया गया है। जैव प्रौद्योगिकी के उपयोग से नए-नए और अधिक सुरक्षित वैक्सीन बनाये जा रहे हैं। प्रतिजैविकों एवं अन्य दूसरी औषधियों की खोज ने भी संक्रामक रोगों का प्रभावी ढंग से उपचार करने में हमें सक्षम बनाया है।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित रोगों का संचरण कैसे होता है
(1) अमीबता
(2) मलेरिया
(3) एस्केरिसता
(4) न्युमोनिया।
उत्तर
(1) अमीबता-मानव की वृहत् आंत्र में पाए जाने वाले एंटअमीबा हिस्टोलिटिका नामक प्रोटोजोअन परजीवी से अमीबता (अमीबिएसिस) या अमीबी अतिसार होता है । कोष्ठबद्धता (कब्ज), उदरीय पीड़ा और ऐंठन, अत्यधिक श्लेषमल और रक्त के थक्के वाला मल इस रोग के लक्षण हैं । घरेलू मक्खियाँ इस रोग की शारीरिक वाहक हैं और परजीवी को संक्रमित व्यक्ति के मल से खाद्य और खाद्य पदार्थों तक ले जाकर उन्हें संदूषित कर देती हैं । मल पदार्थ द्वारा संदूषित पेयजल और खाद्य पदार्थ संक्रमण के प्रमुख स्रोत हैं।
(2) मलेरिया- प्लाज्मोडियम नामक एक बहुत ही छोटा-सा प्रोटोजोअन मलेरिया के लिए उत्तरदायी है। प्लाज्मोडियम की विभिन्न जातियाँ (प्ला. वाइवैक्स, प्ला. मेलिरिआई और प्ला. फैल्सीपेरम) विभिन्न प्रकार के मलेरिया के लिए उत्तरदायी हैं। इनमें से प्लाज्मोडियम फैल्सीपेरम द्वारा होने वाला दुर्दम (मेलिग्नेंट) सबसे गंभीर है और यह घातक भी हो सकता है। मादा एनाफीलिज मच्छर मानव में इस रोग का संचारण करती है।
(3) एस्केरिसता-आंत्र परजीवी ऐस्केरिस से ऐस्केरिसता (ऐस्केरिएसिस) नामक रोग होता है। आंतरिक रक्तस्राव, पेशीय पीड़ा, ज्वर, अरक्तता और आंत्र का अवरोध इस रोग के लक्षण हैं। इस परजीवी के अण्डे संक्रमित व्यक्ति के मल के साथ बाहर निकल आते हैं और मिट्टी, जल, पौधों आदि को संदूषित कर देते हैं। स्वस्थ व्यक्ति में यह संक्रमण संदूषित पानी, शाक-सब्जियों, फलों आदि के सेवन से हो जाता है।
(4) न्युमोनिया- स्ट्रेप्टोकोकस न्युमोनी और हीमोफिलस इंफ्लुएंजी जैसे जीवाणु मानव में न्युमोनिया रोग के लिए उत्तरदायी हैं । इस रोग में फुप्फुस के वायुकोष्ठ संक्रमित हो जाते हैं । संक्रमण के फलस्वरूप वायुकोष्ठों में तरल भर जाता है जिसके कारण सांस लेने में गंभीर समस्याएँ पैदा हो जाती हैं। ज्वर, ठिठुरन, खाँसी और सिरदर्द आदि न्युमोनिया के लक्षण हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
जल-वाहित रोगों की रोकथाम के लिए आप क्या उपाय अपनायेंगे?
उत्तर
पानी के द्वारा संचारित होने वाले कुछ मुख्य रोग हैं-टाइफॉइड, अमीबता, ऐस्केरिसता आदि। इन रोगों की रोकथाम के लिए
- पानी को उबाल कर या फिल्टर करके पीना चाहिए। पीने के पानी को साफ बर्तन में ढंककर रखें।
- जलाशयों, कुंडों और मलकुंडों और तालाबों की समय-समय पर सफाई करनी चाहिए।
- मलेरिया और फाइलेरिया जैसे रोगों के रोगवाहकों और उनके प्रजनन की जगहों का नियंत्रण खत्म कर देना चाहिए। इसके लिए आवासीय क्षेत्रों में और उसके आस-पास पानी को जमा नहीं होने देना चाहिए। शीतलयंत्रों (कूलर) की नियमित सफाई, मच्छरदानी का प्रयोग, मच्छर के डिंबकों को खाने वाली गंबुजिया जैसी मछलियाँ डालनी चाहिए।खाइयों, जलनिकास क्षेत्रों और अनूपों (दलदलों) (स्वंप्स) आदि में कीटनाशकों के छिड़काव किए जाने चाहिए। इसके अतिरिक्त दरवाजों और खिड़कियों में जाली लगानी चाहिए ताकि मच्छर अन्दर न घुस सकें।
प्रश्न 5.
डी. एन. ए. वैक्सीन के संदर्भ में ‘उपयुक्त जीन’ के अर्थ के बारे में अपने अध्यापक से चर्चा कीजिए।
उत्तर
जीवाणु या खमीर में रोगजनक की प्रतिजनी पॉलीपेप्टाइड का उत्पादन पुनर्योगज डी. एन. ए. (Recombinant DNA) प्रौद्योगिकी से होने लगा है इसे उपयुक्त जीन (Suitable gene) कहा जाता है। इस विधि से बड़े पैमाने पर उत्पादित टीकों की प्रतिरक्षीकरण की उपलब्धता बढ़ गयी है। उदाहरण के लिए खमीर से बनने वाला यकृतशोथ B(Hepatitis B) इसी प्रकार का टीका है।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
प्राथमिक एवं द्वितीयक लसीकाओं के अंगों के नाम बताइए।
उत्तर
- प्राथमिक लसिका अंग–अस्थिमज्जा एवं थाइमस ग्रंथि।
- द्वितीयक लसिका अंग-प्लीहा, लसिका ग्रंथियाँ, टॉन्सिल, परिशेषिका एवं क्षुद्रांत के पेयर पेंच आदि।
प्रश्न 7.
इस अध्याय में निम्नलिखित संकेताक्षर इस्तेमाल किये गये हैं। इसका पूरा रूप बताइए
(1) एम. ए. एल. टी.
(2) सी. एम. आई.
(3) एड्स
(4) एन. ए. सी. ओ
(5) एच. आई. वी।
उत्तर

प्रश्न 8.
निम्नलिखित में भेद कीजिए और प्रत्येक के उदाहरण दीजिए। (NCERT)
(1) सहज (जन्मजात) और उपार्जित प्रतिरक्षा
(2) सक्रिय और निष्क्रिय (अक्रिय) प्रतिरक्षा।
उत्तर
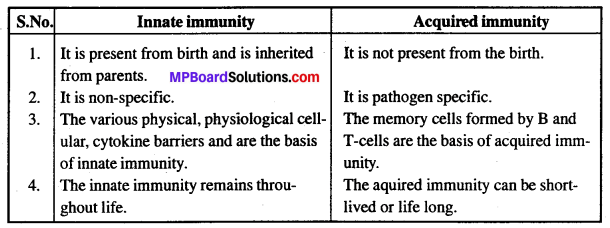
(1) सहज (जन्मजात) और उपार्जित प्रतिरक्षा में अंतर
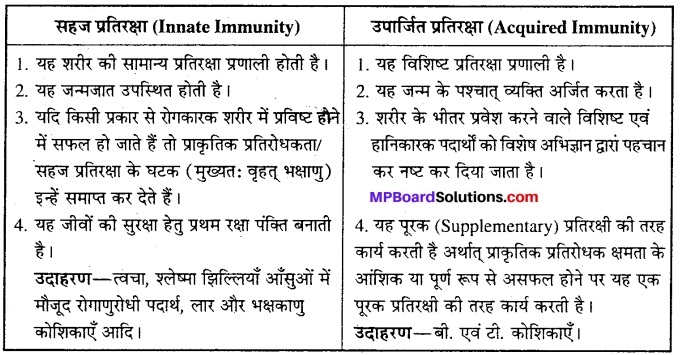
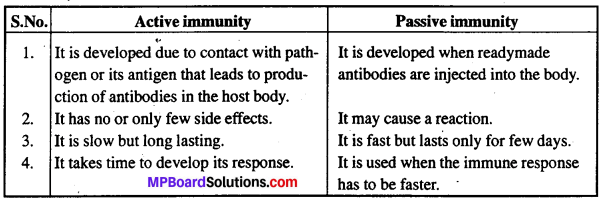
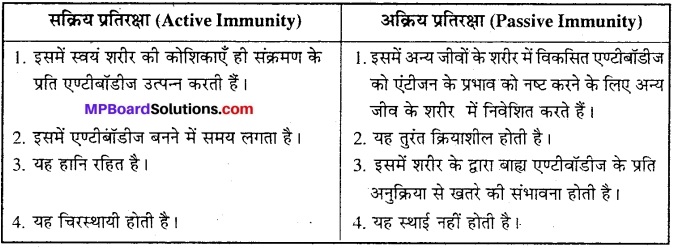
(2) सक्रिय एवं अक्रिय प्रतिरक्षा में अंतर
प्रश्न 9.
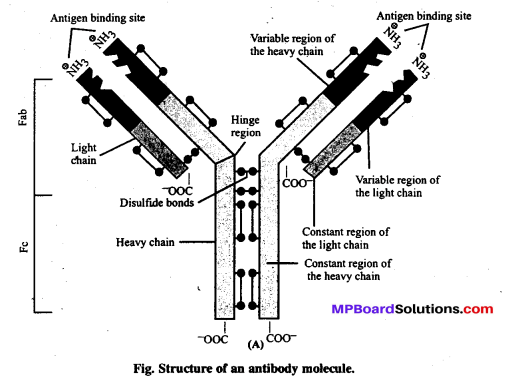
प्रतिरक्षी (प्रतिपिंड) अणु का अच्छी तरह नामांकित चित्र बनाइए।
उत्तर
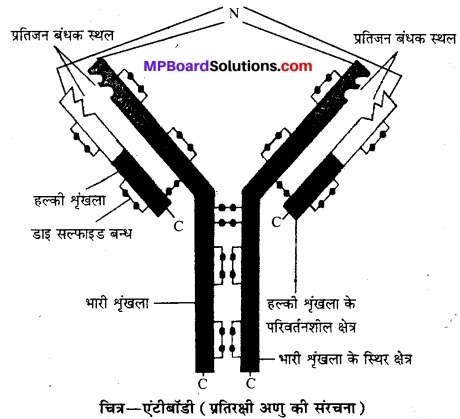
प्रश्न 10.
वे कौन-से विभिन्न रास्ते हैं जिनके द्वारा मानव प्रतिरक्षा न्यूनता विषाणु (HIV) का संचारण होता है।
अथवा
रक्त संचरण से फैलने वाले आज के भयावह रोग का नाम दो लक्षण तथा मुख्य रोकथाम के उपाय लिखिए।
अथवा
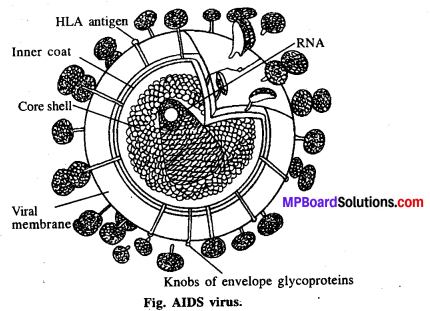
एड्स सर्वप्रथम कहाँ पाया गया ? इसके कारण, संचरण, लक्षण एवं रोकथाम के उपाय समझाइए।
अथवा
एड्स क्या है ? इसके फैलने के कारण लिखिए।
उत्तर
एड्स (AIDS) का पूरा नाम एक्वायर्ड इम्यून डेफीसिएन्सी सिण्ड्रोम (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) है। इसका पता सर्वप्रथम अमेरिका में सन् 1981 में लगा। यह रक्त संचरण, जननिक संसर्ग एवं माता से शिशु में फैलने वाला लैंगिक संसर्गजन्य रोग है, जिसमें रोगी की रोग प्रतिरोधात्मक क्षमता नष्ट हो जाती है। कारण यह ह्यूमन इम्यूनो विषाणु (HIV = Human Immuno Virus) के कारण होता है। एड्स रोग अथवा HIV का संचरण निम्न प्रकार से होता है
- एक से अधिक स्त्रियों से सहवास।
- संदूषित सीरिंज का प्रयोग।
- दूषित रक्त का आदान-प्रदान
- अंग प्रत्यारोपण।
- कृत्रिम वीर्य सेचन तकनीक का उपयोग।
- गर्भ के समय माता से बच्चे में।
रोग के लक्षण-AIDS के संक्रमण के फलस्वरूप अन्य लिम्फोसाइट्स को सक्रिय करने वाली सहायक “T” कोशिकाओं की संख्या में भारी कमी आती है। उग्र रूप से पीड़ित अधिकांश व्यक्ति तीन वर्ष के भीतर ही अन्य संक्रमणों या कैंसर के कारण मर जाते हैं। इससे मस्तिष्क को भारी क्षति पहुँचती है और वह अपनी स्मृति को खो देता है।
उपचार- अभी तक इस रोग के निवारण के लिए कोई उपचार नहीं है। एक बार यह रोग होने पर उस व्यक्ति का बचना असम्भव है फिर भी प्रतिरक्षा उत्तेजन विधि द्वारा शरीर में इस विषाणु की निरोधक कोशिकाओं की संख्या में वृद्धि की जा सकती है।
नियंत्रण-AIDS को फैलाने से रोकने के लिए निम्नलिखित उपाय काम में लाने चाहिए
- लोगों को AIDS के घातक परिणामों की जानकारी देना चाहिए।
- इन्जेक्शन लगाने वाली सीरिंज को एक बार प्रयोग करने के बाद फेंक देना चाहिए।
- रुधिर देने वाले व्यक्तियों, प्रत्यारोपण के लिए वृक्क, यकृत, नेत्र का कॉर्निया, वीर्य या वृद्धि हॉर्मोन का दान करने वाले व्यक्तियों तथा गर्भधारण करने वाली स्त्रियों का निरीक्षण अनिवार्य रूप से कराना चाहिए।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
वह कौन-सी क्रियाविधि है जिससे एड्स विषाणु संक्रमित व्यक्ति के प्रतिरक्षा तंत्र का ह्रास करता है।
उत्तर
HIV का द्विगुणन एवं रोगजनकता-संक्रमित व्यक्ति के शरीर में आ जाने के बाद विषाणु वृहद् भक्षकाणु (मेक्रोफेज) में प्रवेश करता है जहाँ उसका आर. एन. ए. जीनोम, विलोम ट्रांसक्रिप्टेज एन्जाइम (Reverse transcriptase enzyme) की सहायता से प्रतिकृतीकरण (Replication) द्वारा विषाणु डी. एन. ए. (Viral DNA) बनता है। यह विषाणु DNA परपोषी कोशिका के डी. एन. ए. में समाविष्ट होकर संक्रमित कोशिकाओं को विषाणु कण पैदा करने का निर्देश देता है ।
वृहद् भक्षक विषाणु उत्पन्न करना जारी रखते हैं और एक HIV फैक्टरी की तरह कार्य करते हैं। इसके साथ ही HIV सहायक टी-लसीकाणुओं (TH) में घुस जाता है, प्रतिकृति बनाता है और संतति विषाणु पैदा करता है। यह क्रम बार-बार दोहराया जाता है। जिसकी वजह से संक्रमित व्यक्ति के शरीर में सहायक टी-लसिकाणुओं की संख्या में उत्तरोत्तर कमी होती है।
इस अवधि के दौरान बार-बार बुखार एवं दस्त आते हैं तथा वजन घटता है। अचानक टी-लसिकाणुओं की संख्या में गिरावट के कारण व्यक्ति जीवाणुओं, विशेष रूप से माइक्रोबैक्टीरियम, विषाणुओं, कवकों यहाँ तक कि टॉक्सोप्लाज्मा जैसे परजीवियों के संक्रमण का शिकार हो जाता है। रोगी में इससे प्रतिरक्षा न्यूनता हो जाती है और वह इन संक्रमणों से अपनी रक्षा करने में असमर्थ हो जाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 12.
प्रसामान्य कोशिका से कैंसर कोशिका किस प्रकार भिन्न है ?
उत्तर
हमारे शरीर में कोशिका वृद्धि और विभेदन अत्यधिक नियंत्रित और नियमित है। कैंसर कोशिकाओं में ये नियामक क्रियाविधियाँ टूट जाती हैं। प्रसामान्य कोशिकाएँ ऐसा गुण दर्शाती हैं जिसे संस्पर्श संदमन (कॉन्टेक्ट इनहिबिशन) कहते हैं और इसी गुण के कारण दूसरी कोशिकाओं से उनका संस्पर्श उनकी अनियंत्रित वृद्धि को संदमित करता है। ऐसा लगता है कि कैंसर कोशिकाओं में यह गण खत्म हो गया है। इसके फलस्वरूप कैंसर कोशिकाएं विभाजित होना जारी रख कोशिकाओं का भंडार खड़ा कर देती हैं जिसे अर्बुद (ट्यूमर) कहते हैं।
अर्बुद दो प्रकार के होते हैं- सुदम (बिनाइन) और दुर्दम (मैलिग्नेंट)। सुदम अर्बुद सामान्यतया अपने मूल स्थान तक सीमित रहते हैं, शरीर के दूसरे भागों में नहीं फैलते तथा इनसे मामूली क्षति होती है। दूसरी ओर दुर्दम अर्बुद प्रचुरोद्भवी कोशिकाओं का पुंज है जो नवद्रव्यीय नियोप्लास्टिक कोशिकाएँ कहलाती हैं ये बहुत तेजी से बढ़ती हैं और आस-पास के सामान्य ऊतकों पर हमला करके उन्हें क्षति पहुँचाती हैं।
प्रश्न 13.
मेटास्टैसिस का क्या मतलब है ? व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर
अर्बुद कोशिकाएँ सक्रियता से विभाजित और वर्धित होती है जिससे वे अत्यावश्यक पोषकों के लिए सामान्य कोशिकाओं से स्पर्धा करती हैं और उन्हें भूखा मारती हैं। ऐसे अर्बुदों से उतरी हुई कोशिकाएँ रक्त द्वारा दूरदराज स्थलों पर पहुँच जाती हैं और जहाँ भी ये जाती हैं नये अर्बुद बनाना प्रारंभ कर देती हैं। मेटास्टैसिस कहलाने वाला यह गुण दुर्दम अर्बुदों का सबसे डरावना गुण है।
प्रश्न 14.
ऐल्कोहॉल/ड्रग के द्वारा होने वाले कुप्रयोग के हानिकारक प्रभावों की सूची बनाएँ।
उत्तर
ड्रग और ऐल्कोहॉल के तत्कालिक प्रतिकूल प्रभाव अंधाधुंध व्यवहार, बर्बरता और हिंसा के रूप में व्यक्त होते हैं । ड्रगों की अत्यधिक मात्रा से श्वसन-पात (रेस्पाइरेटरी फेल्योर), हृदय पात (हॉर्ट-फेल्योर) प्रमस्तिष्क रक्तस्राव (सेरेब्रल हेमरेज) के कारण समूर्छा (कोमा) और मृत्यु हो सकती है। ड्रगों का संयोजन या ऐल्कोहॉल के साथ उनके सेवन का आमतौर पर यह परिणाम अति मात्रा होती है।
युवाओं में ड्रग और ऐल्कोहॉल दुरूपयोग के सबसे सामान्य लक्षण शैक्षिक क्षेत्र में प्रदर्शन में कमी, बिना किसी स्पष्ट कारण के स्कूल या कॉलेज से अनुपस्थिति, व्यक्तिगत स्वच्छता के रूचि में कमी, विनिर्वतन, एकाकीपन, अवसाद, थकावट, आक्रमणशील और विद्रोही व्यवहार, परिवार और मित्रों से बिगड़ते संबंध, शौक की रुचि में कमी, सोने और खाने की आदतों में परिवर्तन, भूख और वजन में घट-बढ़ आदि हैं।
ड्रग/ऐल्कोहॉल के कुप्रयोग के दूरगामी परिणाम भी हो सकते हैं। अगर कुप्रयोगकर्ता को ड्रग/ऐल्कोहॉल खरीदने के लिए पैसे नहीं मिलें तो वह चोरी का सहारा ले सकता/सकती है। ये प्रतिकूल प्रभाव केवल ड्रग/ ऐल्कोहॉल का सेवन करने वाले तक सीमित नहीं रहता। कभी-कभी ड्रग/ऐल्कोहॉल अपने परिवार या मित्र आदि के लिए भी मानसिक और आर्थिक कष्ट का कारण बन सकता/सकती है।
जो अंत:शिरा द्वारा ड्रग लेते हैं उनको एड्स और यकृतशोथ-बी जैसे गंभीर संक्रमण होने की संभावना अधिक होती है। गर्भावस्था के दौरान ड्रग एवं ऐल्कोहॉल का उपयोग गर्भ पर प्रतिकूल प्रभाव डालता है। महिला खिलाड़ियों द्वारा उपचयी स्टेरॉइडों के सेवन के अनुषंगी प्रभावों में पुस्त्वन, बड़ी आक्रमकता, भावदशा में उतार-चढ़ाव, अवसाद, असामान्य आर्तव चक्र, मुँह और शरीर पर बालों की अत्यधिक वृद्धि, भगशेफ का बढ़ जाना, आवाज का गहरा होना शामिल हैं। पुरुष खिलाड़ियों में मुँहासे, बढ़ी आक्रामकता, भावदशा में उतार-चढ़ाव, अवसाद, वृषणों के आकार का घटना, शुक्राणु उत्पादन में कमी, यकृत और वृक्क की संभावित दुष्क्रियता, वक्ष का बढ़ना, समयपूर्व गंजापन, प्रोस्टेट ग्रंथि का बढ़ना आदि शामिल है।
![]()
प्रश्न 15.
क्या आप ऐसा सोचते हैं कि मित्रगण किसी को ऐल्कोहॉल/ड्रग सेवन के लिए प्रभावित कर सकते हैं? यदि हाँ, तो व्यक्ति इससे कैसे अपने आप को बचा सकता है ?
उत्तर
ड्रग, ऐल्कोहॉल एवं धूम्रपान के प्रति व्यक्ति किशोर अवस्था में आकर्षित होते हैं। ऐसी प्रवृत्ति से किशोरों को रोकना होगा, क्योंकि चिकित्सा से रोकथाम (बचाव) ज्यादा अच्छा होता है। इसके लिए माता-पिता .और अध्यापकों का विशेष उत्तरदियित्व है। यहाँ दिए गए कुछ उपाय किशोरों में ऐल्कोहॉल एवं ड्रग के कुप्रयोग के रोकथाम तथा नियंत्रण के लिए विशेष रूप से कारगर होंगे
1. माता-पिता/अभिभावकों से सहायता लेना-माता-पिता और समकक्षियों से फौरन मदद् लेनी चाहिए, ताकि वे उचित मार्गदर्शन कर सकें। निकट और विश्वसनीय मित्रों से भी सलाह लेते रहना चाहिए। युवाओं की समस्या को सुलझाने के लिए समुचित सलाह से उन्हें अपनी भावनाओं को अभिव्यक्त करने में सहायता मिलेगी।
2. संकट के लक्षणों की पहचान-माता-पिता और अध्यापकों को चाहिए कि वे बच्चों में खतरों के संकेतों को पहचाने और ध्यान दें। मित्रों को भी चाहिए कि वे ड्रग या ऐल्कोहॉल लेते देखने पर उन्हें रोकें या उनके अभिभावकों को सूचित करें। इसके बाद बीमारी को पहचानने और उसके पीछे छिपे कारणों का पता लगाने के लिए उचित उपाय करने होंगे। यह क्रिया समुचित चिकित्सकीय उपाय करने के लिए उपाय करने होंगे। यह क्रिया समुचित चिकित्सकीय उपाय करने में सहायता प्रदान करेगी।
3. व्यावसायिक और चिकित्सकीय सहायता लेना-जो व्यक्ति दुर्भाग्यवश ड्रग और ऐल्कोहॉल के कुप्रयोग रूपी दलदल में फंस गया है उसकी सहायता के लिए उच्च योग्यता प्राप्त मनोवैज्ञानिकों की उपलब्धता और व्यसन छुड़ाने तथा पुनः स्थापना कार्यक्रमों हेतु काफी सहायता उपलब्ध है।
4. शिक्षा और परामर्श -समस्याओं और दबावों का सामना करने और निराशाओं तथा असफलताओं को जीवन का एक हिस्सा समझकर स्वीकार करने की शिक्षा एवं परामर्श उन्हें देना चाहिए। यह भी उचित होगा कि बालक की ऊर्जा को खेलकूद, पढ़ाई, संगीत और पाठ्यक्रम के अलावा दूसरी स्वस्थ गतिविधियों की दिशा में भी लगाना चाहिए।
प्रश्न 16.
ऐसा क्यों है जब कोई व्यक्ति ऐल्कोहॉल या ड्रलेना शुरू कर देता है तो उस आदत से छुटकारा पाना कठिन होता है ? अपने अध्यापक से चर्चा कीजिए।
उत्तर
सबसे महत्वपूर्ण बात यह है कि ऐल्कोहॉल और ड्रग की अंतर्निहित व्यसनी प्रकृति है, लेकिन व्यक्ति इस बात को समझ नहीं पाता। ड्रगों और ऐल्कोहॉल के कुछ प्रभावों के प्रति लत, एक मनोवैज्ञानिक आशक्ति है। जो व्यक्ति को उस समय भी ड्रग एवं ऐल्कोहॉल लेने के लिए प्रेरित करने से जुड़ी है जबकि उनकी जरूरत नहीं होती या उनका इस्तेमाल आत्मघाती है। ड्रग के बार-बार उपयोग से हमारे शरीर में मौजूद ग्राहियों का सह्य स्तर बढ़ जाता है।
इसके फलस्वरूप ग्राही, ड्रगों या ऐल्कोहॉल की केवल उच्चतर मात्रा के प्रति अनुक्रिया करते हैं, जिसके कारण अधिकाधिक मात्रा में लेने की लत पड़ जाती है। लेकिन एक बात बुद्धि में बिल्कुल स्पष्ट होनी चाहिए कि इन ड्रग को एक बार लेना भी व्यसन बन सकता है। इस प्रकार, ड्रग और ऐल्कोहॉल की व्यसनी शक्ति उन्हें इस्तेमाल करने वाले/वाली को एक दोषपूर्ण चक्रा में घसीट लेते हैं, जिनसे इनका नियमित सेवन (कुप्रयोग) करने लगते हैं और इस चक्र से बाहर निकलना उनके बल में नहीं रहता। किसी मार्गदर्शन या परामर्श के अभाव में व्यक्ति व्यसनी (लती) बन जाता है और उनके ऊपर आश्रित होने लगता |
![]()
प्रश्न 17.
व्यसन के प्रमुख कारणों का वर्णन कीजिए।
अथवा
आपके विचार से किशोरों को ऐल्कोहॉल या ड्रग के सेवन के लिए क्या प्रेरित करता है और इससे कैसे बचा जा सकता है ?
उत्तर
व्यसन के प्रमुख कारण-
1. उत्सुकता-संचार माध्यमों के विज्ञापन व्यक्ति को नशीले पदार्थों को जानने की उत्सुकता पैदा करते हैं जिसके कारण सेवन करता है।
2. उत्तेजना एवं अपूर्व आनंद की प्राप्ति-कुछ मादक द्रव्य उत्तेजक प्रकृति के होते हैं। ये उन युवाओं को जिन्हें शारीरिक क्षमता की चाह होती है आकर्षित करते हैं। इसके सेवन से अद्भुत आनंद की प्राप्ति होती है। इसकी वास्तविक धारणा यह है कि इन दवाओं के सेवन से शारीरिक एवं मानसिक दुर्बलता आती है।
3. अधिक कार्यक्षमता की इच्छा-ऐसी भ्रान्ति है कि मादक द्रव्यों के सेवन से व्यक्ति में स्फूर्ति आती है और वह अधिकाधिक शारीरिक एवं मानसिक कार्य कर सकता है, इसी कारण कुछ नशीली दवाओं तथा मादक द्रव्यों का सेवन युवाओं द्वारा किया जाता है, किन्तु वास्तविकता यह है कि इस प्रकार के पदार्थ शारीरिक एवं मानसिक क्षमता को कम करके थकान बढ़ाते हैं।
4. कल्पना लोक की सैर-कुछ मादक द्रव्य वास्तविक दुनिया से व्यक्ति को पृथक् कर देते हैं जिससे इन्हें क्षणिक आनन्द की प्राप्ति होती है और व्यक्ति को नई सौन्दर्य भावना एवं आनन्द का अनुभव होता है। इन क्षणिक सुखों की प्राप्ति के लिए व्यक्ति नशीली दवाओं तथा पदार्थों का सेवन करते हैं जिनकी देखा-देखी परिवार के छोटे सदस्य भी नशीले पदार्थों का सेवन करने लगते हैं।
5. सामाजिक दबाव-कभी-कभी ऐसा भी होता है कि किसी समारोह में नशीली दवाओं के सेवन हेतु किसी नये व्यक्ति पर बार-बार दबाव डाला जाता है। इस दबाव के कारण कमजोर इच्छा शक्ति वाले व्यक्ति इन दवाओं का सेवन कर लेते हैं और आनन्द की अनुभूति होने पर वे बार-बार इनका सेवन प्रारम्भ कर देते हैं।
6. निराशाओं एवं चिन्ता से छुटकारा-चूँकि मादक पदार्थ व्यक्ति को वास्तविक परिस्थिति से दूर कर देते हैं और वह नशे में डूबकर अपने दुःख दर्द को कुछ समय के लिये भुला देता है। इस कारण वह दुःखों को अस्थाई रूप से भुला देने के लिए नशीले पदार्थों का सेवन करने लगता है, लेकिन यह तरीका व्यक्ति को कायर बनाकर उसमें मुकाबला करने की शक्ति को कम करता है।
7. पारिवारिक इतिहास-अनेक परिवारों में बड़े सदस्य खुलेआम नशीले पदार्थों का सेवन करते हैं जिनकी देखा-देखी परिवार के छोटे सदस्य भी नशीले पदार्थों का सेवन करने लगते हैं।
8. व्यापारिक प्रचार एवं असामाजिक तत्व-कई बार दवा कम्पनियों के विज्ञापन भी नशीले पदार्थों के सेवन की ओर किशोरों तथा युवाओं को आकर्षित करते हैं। कुछ असामाजिक तत्त्व भी बालक-बालिकाओं को । फुसलाकर उन्हें नशीले पदार्थों का आदी बना देते हैं और बाद में उनसे गैर-कानूनी कार्य करवाते हैं।
मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग अन्य महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्नोत्तर
मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
1. सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए
प्रश्न 1.
पोलियो, डिफ्थीरिया एवं टिटेनस से बचाव हेतु उपयोगी टीका है
(a) B.C.G.
(b) D.P.T.
(c) M.M.R.
(d) S.T.D.
उत्तर
(b) D.P.T.
प्रश्न 2.
रोग समाप्त हो जाने के बाद शरीर में उत्पन्न रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता कहलाती है
(a) सक्रिय प्रतिरक्षण
(b) निष्क्रिय प्रतिरक्षण
(c) (a) और (b) दोनों
(d) उपर्युक्त में से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर
(a) सक्रिय प्रतिरक्षण
प्रश्न 3.
कैंसर का संबंध होता है
(a) ऊतकों की अनियंत्रित वृद्धि से …
(b) बुढ़ापे से
(c) ऊतकों के नियंत्रित विभाजन से
(d) उपर्युक्त में से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर
(a) ऊतकों की अनियंत्रित वृद्धि से
प्रश्न 4.
चेचक के विरुद्ध टीका लगाने का अभिप्राय है
(a) जन्तुओं द्वारा प्राप्त W.B.Cs. का
(b) अन्य जन्तुओं से उत्पन्न प्रतिरक्षियों का
(c) प्रतिरक्षियों का
(d) दुर्बल किये गये चेचक विषाणु का।
उत्तर
(d) दुर्बल किये गये चेचक विषाणु का।
प्रश्न 5.
सिफिलिस एक लैंगिक प्रसारित रोग है, जो उत्पन्न होता है
(a) पैस्टुला द्वारा
(b) लेप्टोस्पाइरा द्वारा
(c) ट्रिपेनिमा पेलाइडम द्वारा
(d) विब्रियो द्वारा।
उत्तर
(c) ट्रिपेनिमा पेलाइडम द्वारा
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
प्रतिरक्षी होता है
(a) एक अणु जो एक विशेष प्रतिजन को ही नष्ट करता है
(b) W.B.Cs. जो जीवाणु का भक्षण करते हैं
(c) स्तनी के R.B.Cs. का स्रावण
(d) न्यूक्लियस का घटक।
उत्तर
(a) एक अणु जो एक विशेष प्रतिजन को ही नष्ट करता है
प्रश्न 7.
एलर्जी का एक रूप है
(a) दमा
(b) पीली आँखें
(c) टाइफॉइड
(d) गलफुल्ली
उत्तर
(a) दमा
प्रश्न 8.
मानव में AIDS विषाणु कैसे प्रवेश पाता है
(a) भोजन से
(b) चुम्बन से
(c) जल से
(d) खून से।
उत्तर
(d) खून से।
प्रश्न 9.
टीकों की खोज का श्रेय किसे जाता है
(a) एलेक्जेण्डर फ्लेमिंग
(b) एडवर्ड जेनर
(c) लुई पाश्चर
(d) राबर्ट कोच।
उत्तर
(b) एडवर्ड जेनर
प्रश्न 10.
रुधिर में होने वाला कैंसर है
(a) कार्योनोमा
(b) सारकोमा
(c) लिम्फोमा
(d) ल्यूकेमिया।
उत्तर
(d) ल्यूकेमिया।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
हिपेटाइटिस-B सतह प्रतिजन है
(a) शुद्ध प्रतिजन टीका
(b) आनुवंशिक टीका
(c) पुनर्योगज टीका
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
उत्तर
(c) पुनर्योगज टीका
प्रश्न 12.
एड्स परीक्षण जाना जाता है
(a) एलिसा
(b) आस्ट्रेलियन एण्टीजन
(c) HIV परीक्षण
(d) उपर्युक्त में से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर
(c) HIV परीक्षण
प्रश्न 13.
लिवर कैंसर का कारण है
(a) शराब
(b) तम्बाकू
(c) उपर्युक्त दोनों
(d) कोई नहीं।
उत्तर
(a) शराब
प्रश्न 14.
प्रोब का उपयोग है
(a) अंगुली छापन में
(b) जीन के पृथक्करण में
(c) रोगजनकों की पहचान में
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी में।
उत्तर
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी में।
प्रश्न 15.
मोनोक्लोनल एण्टीबॉडीज़ का उपयोग है
(a) रुधिर समूहों की पहचान में
(b) रोगजनकों की विश्वसनीय पहचान में
(c) कैंसर की विश्वसनीय पहचान में
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी में।
उत्तर
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी में।
प्रश्न 16.
भ्रूण संबंधी असमान्यताओं का अध्ययन कहलाता है
(a) ट्राइकोलॉजी
(b) टेरेन्टोलॉजी
(c) ट्रामैटोलॉजी
(d) टर्मिटोलॉजी।
उत्तर
(b) टेरेन्टोलॉजी
प्रश्न 17.
गर्भ के दौरान महिलाओं द्वारा थैलिडोमाइड के उपयोग से भ्रूण में होने वाला रोग कहलाता
(a) वैजाइनल कार्सिनोमा
(b) माइक्रोसिफैली
(c) फोकोमेलिया
(d) वाइरीलिज्म।
उत्तर
(c) फोकोमेलिया
प्रश्न 18.
ऐसा रासायनिक पदार्थ जिसके उपयोग से अनुभव या प्रेरणा ग्रहण करने की शक्ति समाप्त हो जाती है उसे कहते हैं
(a) शामक
(b) एनाल्जेसिक
(c) एस्थेटिक
(d) उत्तेजक।
उत्तर
(c) एस्थेटिक
प्रश्न 19.
अफीम को पौधे के किस भाग से प्राप्त किया जाता है
(a) पत्तियों से
(b) फल से
(c) बीजों से
(d) छाल से।
उत्तर
(b) फल से
प्रश्न 20.
सर्वाधिक घातक हेल्युसिनोजेन है
(a) अफीम
(b) मार्फीन
(c) L.S.D
(d) हेरोइन।
उत्तर
(c) L.S.D
![]()
प्रश्न 21.
चाय में पाया जाने वाला उत्तेजक पदार्थ है
(a) टेनिन
(b) कोकीन
(c) कैफीन
(d) फ्रेक।
उत्तर
(c) कैफीन
प्रश्न 22.
निम्न में से कौन एक औपिएट नारकोटिक है
(a) बरबीचुरेट
(b) मार्फीन
(c) एम्फोटेमाइन
(d) L.S.D
उत्तर
(b) मार्फीन
प्रश्न 23.
मन परिवर्तन करने वाली औषधि है
(a) साइकोट्रापिक
(b) हेल्यूसिनोजेन्स
(c) बरबीचुरेट्स
(d) उत्तेजक।
उत्तर
(a) साइकोट्रापिक
2. रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए
1. रोगों का जर्म सिद्धांत ………………. ने दिया था।
2………………. आनुवंशिक अभियांत्रिकी द्वारा निर्मित प्रथम मानव इंसुलिन है।
3. AIDS……………… संचारित रोग है।
4. गोनोरिया ……………… के द्वारा होता है।
5. कैंसर के लिये उत्तरदायी जीन को ………………. कहते हैं।
6. रक्त के कैंसर को ………………. कहते हैं। मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग
7. हिपेटाइटिस रोग …………….. के द्वारा होता है।
8. आदर्श टीका ………………. नहीं होना चाहिए।
9. …………… में रोग जनक जीवित अवस्था में होते हैं।
10. ………………. रक्त कैन्सर कहलाता है।
11. आसवित पेय में ………….. से अधिक एल्कोहॉल होता है।
12. रोगजनक की श्रेष्ठ जैव तकनीक ………………. है।
13. विश्व रेडक्रॉस दिवस ……………….. को मनाया जाता है।
14. नशीले पदार्थ के मिश्रण को. …………….. कहते हैं।
15. बेंजोडाइएजोपिन्स एक ……………….. औषधि है।
16. विश्व मानसिक स्वास्थ्य दिवस ……………… को मनाया जाता है।
17. एल. एस. डी. नामक औषधि को ………….. नामक कवक से प्राप्त किया जाता है।
18. बिना निद्रा के शारीरिक तनाव एवं व्यग्रता से मुक्त करने वाली औषधियों को …………….. कहते
19. भ्रूण की आकारिकीय असामान्यताओं का अध्ययन ……………….. कहलाता है।
20. महिलाओं की वृद्धि दर ……………….. वर्ष बाद रूक जाती है।
21. मैथुन द्वारा संचारित रोग ……………….. कहलाते हैं।
उत्तर
- राबर्ट कोच
- ह्यूम्यूलिन
- लैंगिक रूप से
- निसेरिया गोनोरी
- ओन्कोजीन
- ल्यूकेमिया,
- विषाणु
- रोगजनक तथा विषाक्त
- जीवित टीकों
- ल्यूकेमिया
- 20 %,
- टीकाकरण
- 8 मई
- कॉकटेल
- सायकोट्रापिक
- 10 दिसम्बर
- क्लेविसेप्स परप्यूरिया
- कुलाइजर्स
- टेकैन्टोलॉजी
- 20
- यौन संबंधी रोग।
3. सही जोड़ी बनाइए
I. ‘A’ – ‘B’
1. विश्व रेडक्रॉस दिवस – (a) इरीथ्रोजाइलॉम कोका
2. विश्व स्वास्थ्य दिवस – (b) पैपावर सोमेनीफेरम
3. विश्व तम्बाकू निषेध दिवस – (c) क्लैवीसेप्स परप्यूरिया
4. कोकेन – (d) 31मई
5. अफीम – (e) 8 मई
6. एल.एस.डी – (f) 7 अप्रैल।
उत्तर
1. (e), 2. (1), 3. (d), 4. (a), 5. (b), 6. (c).
II. ‘A’ – ‘B’
1. एड्स – (a) हापज सिम्प्लेक्स
2. जेनाइटल हीज – (b) हीमोफिलस ड्यूक्रेयई
3. सिफलिस – (c) नैजेरिया गोनोरिया
4. कैन्फ्रॉइड – (d) यौन संक्रमित रोग
5. गोनोरिया – (e) ट्रेपोनेमा पैलीडम।
उत्तर
1. (d), 2. (a), 3. (e), 4. (b), 5. (c).
III. ‘A’ – ‘B’
1. AIDS – (a) विषाणुरोधी प्रोटीन
2. प्रतिजैविक – (b) जैव युद्ध
3. इन्टरफेरॉन – (c) B.C.G
4. एन्थैक्स – (d) S.T.D
5. T.B. – (e) एलेक्जेण्डर फ्लेमिंग।
उत्तर
1. (d), 2. (e), 3. (a), 4. (b), 5. (c).
IV. ‘A’ – ‘B’
1. AIDS – (a) टीकाकरण
2. रोग निरोध – (b) ई. कोलाई से प्राप्त इन्सुलिन (मानव निर्मित इन्सुलिन)
3. किण्वन – (c) एण्टी रेट्रोवायरल
4. ह्यूम्यूलिन – (d) यीस्ट
5. मोतीझरा – (e) जीवाणु रोग।
उत्तर
1. (c), 2. (a), 3. (d), 4. (b), 5. (e).
4. एक शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए
1. रोगों का जर्म सिद्धान्त किसने दिया था ?
2. मलेरिया परजीवी के वाहक का नाम लिखिये।
3. आनुवंशिक अभियांत्रिकी द्वारा निर्मित इन्सुलिन का नाम लिखिये।
4. HIV का पूरा नाम लिखिये।
5. डिप्थीरिया, पोलियो एवं कुकुर खाँसी के वैक्सीन का नाम लिखिए।
6. ओपियम का स्रोत क्या होता है ?
7. उत्तेजक पदार्थ के दो उदाहरण दीजिए।
8. तम्बाकू में पाये जाने वाले हानिकारक रासायनिक यौगिक का नाम लिखिए।
9. L.S.D. के स्रोत का नाम लिखिए।
10. किन्हीं चार शामक औषधियों के नाम लिखिए।
11. ट्रंक्वीलाइजर का एक उदाहरण भी दीजिए।
12. मनुष्य के विचार एवं भावनाओं को परिवर्तित करके भ्रम की स्थिति पैदा करने वाली औषधियों को क्या कहते हैं?
उत्तर
- रॉबर्ट कोच
- प्लाज्मोडियम
- ह्यूम्यूलिन
- ह्यूमन इम्यूनोडेफीसिएन्सी वाइरस
- DPT वैक्सीन,
- पैपावर सोमेनीफेरम
- कैफीन, कोकीन
- निकोटिन
- क्लैवीसेप्स परप्यूरिया (कवक)
- (i) हेक्साबार्बिटॉल, (ii) मीथोहेक्सीटॉल, (iii) वेलियम, (iv) ऑक्साजेपाम
- फिनोथियोजीनेस
- बार्बीचुरेट्स।
मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
मलेरिया परजीवी के वाहक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
मादा एनाफिलीज मच्छर।
प्रश्न 2.
HIV का पूरा नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
ह्यूमन इम्यूनो-डेफिसियेंसी वाइरस।
प्रश्न 3.
डिफ्थीरिया, पोलियो एवं कुकुर खाँसी से बचाव हेतु लगाये जाने वाले टीके का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
D.PT. वैक्सीन एवं पोलियो वैक्सीन
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
ELISA का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
एन्जाइम लिन्क्ड इम्यूनो सॉर्बेन्ट असे।
प्रश्न 5.
कीमोथैरेपी से किस रोग का इलाज किया जाता है ?
उत्तर
कैन्सर का।
प्रश्न 6.
ओपियम का स्रोत क्या होता है?
उत्तर
अफीम।
प्रश्न 7.
उत्तेजक पदार्थों के तीन उदाहरण लिखिए।
उत्तर
कैफीन, कोकीन, एम्फीमाइन्स!
प्रश्न 8.
तम्बाकू में पाये जाने वाले हानिकारक रासायनिक यौगिक का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
निकोटिन।
प्रश्न 9.
LSD के स्रोत का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
क्लैविसेप्स परप्यूरिया
प्रश्न 10.
ट्रैकुलाइजर का एक उदाहरण भी दीजिये।
उत्तर
फेनोथाइएजीन।
प्रश्न 11.
मनुष्यं के विचार एवं भावनाओं को परिवर्तित करके भ्रम की स्थिति पैदा करने वाली औषधियों को क्या कहते हैं ?
उत्तर
सायकोडेलिक।
प्रश्न 12.
HIV संक्रमण से होने वाली बीमारी कौन-सी है ?
उत्तर
AIDSI
प्रश्न 13.
एड्स का परीक्षण किसके द्वारा किया जाता है ?
उत्तर
ELISA परीक्षण द्वारा।।
प्रश्न 14.
वर्तमान में देश के विभिन्न भागों में चिकनगुनिया रोग की पुष्टि हुई है। इस रोग के लिए उत्तरदायी वाहक (वेक्टर) का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
चिकनगुनिया रोग के लिए वेक्टर का नाम एडीज मच्छर है।
प्रश्न 15.
प्रतिरक्षा कितने प्रकार की होती है ? नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
प्रतिरक्षा दो प्रकार की होती है, जिन्हें क्रमशः सहज तथा उपार्जित प्रतिरक्षा कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 16.
वयस्क कृमि वुचेरिया शरीर में कहाँ पाया जाता है ?
उत्तर
वयस्क कृमि लिम्फ ग्रंथियाँ व लिम्फ मार्ग में पाया जाता है।
प्रश्न 17.
अर्बुद कितने प्रकार के होते हैं ? नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
अर्बुद दो प्रकार के होते हैं-
- सुदम (बिनाइन) और
- दुर्दम (मैलिग्नेंट)।
प्रश्न 18.
एड्स रोग से शरीर को कौन-सी प्रमुख हानि होती है ?
उत्तर
एड्स रोग में शरीर की रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता नष्ट हो जाती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 19.
गुटका सेवन करने वाले व्यक्ति के जबड़े की मांसपेशियाँ कठोर हो जाने के कारण उसका जबड़ा ठीक से नहीं खुलता है। संभावित रोग का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर
सबम्यूकस फाइब्रोसिस रोग होता है।
प्रश्न 20.
डी. पी. टी. (DPT) टीके का पूरा नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
डिफ्थीरिया पटुंसिस टिटेनस।
प्रश्न 21.
कैंसर में दी जाने वाली दवाओं व उपचार के पार्श्व प्रभाव (Side effect) बताइए।
उत्तर
बालों का झड़ना एवं एनीमिया ।
प्रश्न 22.
NAC का पूरा नाम बताइए।
उत्तर
नेशनल एड्स कंट्रोल ऑर्गेनाइजेशन।
प्रश्न 23.
मरीजुआना किस पौधे का सत्व (Extract) है ? नाम बताइए।
उत्तर
भांग (केनाविस सेटाइवा)।
प्रश्न 24.
अफीम, मार्फीन, हेरोइन, पेथीडीन तथा मेथेडॉन को सामूहिक रूप से क्या कहते
उत्तर
ओपिमेट नार्कोटिक्स।
प्रश्न 25.
मैरी मैलॉन का उपनाम क्या है ?
उत्तर
मैरी मैलॉन का उपनाम “टाइफॉइड मैरी है।
प्रश्न 26.
मनुष्य के शरीर में प्रवेश करने के बाद HIV जिन दो कोशिकाओं को गुणित करता है, उनके नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
मैक्रोफेजेज तथा सहायक T-लिम्फोसाइड्स।
प्रश्न 27.
न्यूमोनिया रोग में शरीर के कौन से अंग संक्रमित होते हैं ?
उत्तर
फुफ्फुस (Lungs) के वायुकोष्ठ (Alveoli) संक्रमित होते हैं।
प्रश्न 28.
तीव्र ज्वर, भूख की कमी, पेट में दर्द तथा कब्ज से पीड़ित लक्षणों के आधार पर चिकित्सक किस प्रकार पुष्टि करेगा कि व्यक्ति को टाइफॉइड है, अमीबिसिस नहीं?
उत्तर
टाइफॉइड रोग की पुष्टि विडाल परीक्षण के द्वारा की जाती है।
प्रश्न 29.
एल. एस. डी. (LSD) का पूरा नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
लाइसार्जिक अम्ल डाइएथिल एमाइड्स।
![]()
प्रश्न 30.
कैंसर उत्पन्न करने वाले विषाणु क्या कहलाते हैं ?
उत्तर
कैंसर उत्पन्न करने वाले विषाणु अर्बुदीय विषाणु (ओन्कोजेनिक वाइरस) कहलाते हैं।
प्रश्न 31.
विशिष्ट इम्यूनिटी को प्राप्त करने के लिए आवश्यक दो मुख्य कोशिकाओं के समूहों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
- T-लिम्फोसाइट्स
- B-लिम्फोसाइट्स।
प्रश्न 32.
लसीकाभ अंग किसे कहते हैं ?
उत्तर
वे अंग जिनमें लसीकाणुओं की उत्पत्ति, परिपक्वन एवं प्रयुरोद्भवन होता है, लसीकाभ अंग कहलाता है।
मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
मेटास्टेसिस का क्या मतलब है ? व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर
अर्बुद कोशिकाएँ सक्रियता से विभाजित और वर्धित होती हैं जिससे वे अत्यावश्यक पोषकों के लिए सामान्य कोशिकाओं से स्पर्धा करती है और उन्हें पोषण के अभाव में रखती हैं। ऐसे अर्बुदों से उतरी हुई कोशिकाएँ रक्त द्वारा दूरदराज स्थलों पर पहुँच जाती हैं और जहाँ ये भी पहुँचती हैं नये अर्बुद बनाना प्रारंभ कर देती है। मेटास्टेसिस कहलाने वाला यह गुण दुर्दम अबुंदों का सबसे खतरनाक गुण है।
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित को परिभाषित कीजिए
(1) प्रतिरोधकता
(2) वैक्सीन
(3) इन्टरफेरॉन
(4) टीकाकरण।
उत्तर
(1) प्रतिरोधकता-प्रत्येक जीव में रोगों से लड़ने या बचाव की क्षमता पायी जाती है। जीवों की रोगों से लड़ने की इस क्षमता को प्रतिरोधकता या प्रतिरक्षा कहते हैं।
(2) वैक्सीन-ऐसी औषधि जिसमें किसी रोग के कमजोर रोग कारक जीव होते हैं तथा उसका उपयोग रोग के प्रति प्रतिरोधकता को उत्पन्न करने में किया जाता है, उसे ही वैक्सीन कहते हैं। उदाहरण-पोलियो वैक्सीन।
(3) इन्ट फेरॉन-हमारी कोशाओं से बने ऐसे प्रोटीन जो विषाणुओं तथा कुछ दूसरे पदार्थों के कोशिका में प्रवेश करने से बनते हैं। इन्टरफेरॉन कहलाते हैं। ये रोगाणुओं व विषाणुओं के प्रभाव को नष्ट कर रोगों से बचाते हैं।
(4) टीकाकरण-टीकाकरण वह उपाय है जिसके द्वारा किसी जीव में किसी रोग के प्रति उपार्जित प्रतिरोधकता पैदा की जाती है।
प्रश्न 3.
जन्मजात एवं अर्जित प्रतिरोधकता में अन्तर लिखिए।
उत्तर
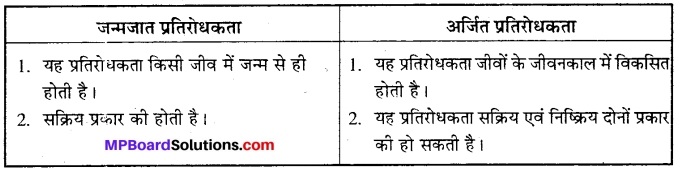
प्रश्न 4.
स्वप्रतिरोधकता किसे कहते हैं ?
उत्तर
स्व प्रतिरोधकता (Auto-immunity)-वह प्रतिरोधकता जो जीवों में अपनी ही रचनाओं के खिलाफ पैदा हो जाती है, स्व-प्रतिरोधकता कहलाती है। यह प्रतिरोधकता कई बीमारियों को पैदा कर देती है। ये बीमारियाँ इस बात पर निर्भर करती हैं कि शरीर कि रचना के प्रति प्रतिरोधकता विकसित हुई है।
उदाहरणस्वरूपयदि शरीर में R.B.Cs. के प्रति प्रतिरोधकता विकसित हुई है, तो यह अपनी ही R.B.Cs को नष्ट करके ऐनीमिया रोग पैदा करती है, लेकिन यदि पेशी कोशिकाओं के प्रति प्रतिरोधकता विकसित हो जाए तो यह पेशी कोशिकाओं को नष्ट करके शरीर में कमजोरी पैदा करती है। इसी प्रकार यदि यकृत कोशिकाओं के प्रति प्रतिरोधकता विकसित होती है, तो यह यकृत कोशिकाओं को नष्ट करके हिपेटाइटिस रोग पैदा करती है, अतः स्व-प्रतिरोधकत. डिजनरेटिव बीमारियों को पैदा करती है।
प्रश्न 5.
एलर्जन क्या है ? एलर्जी किस प्रकार उत्पन्न होती है ?
उत्तर
एलर्जी उत्पन्न करने वाले पदार्थों को एलर्जन कहते हैं। एलर्जन का प्रारम्भिक उद्भासन शरीर में अति संवेदनशीलता उत्पन्न करता है लेकिन एलर्जी उत्पन्न नहीं करता है। शरीर बाद में प्राथमिक प्रतिरक्षित अनुक्रिया विकसित कर लेता है, जिसमें B कोशाएँ प्रतिरक्षा उत्पन्न करती हैं किन्तु लगातार आक्रमण से कई बार प्रतिरक्षियाँ परास्त हो जाती हैं। इस संघर्ष मे हिस्टामाइन नामक रसायन शरीर में उत्पन्न होकर द्वितीयक प्रतिरक्षित अनुक्रिया अथवा एलर्जी उत्पन्न करता है, इसे वीभत्स खुराक कहते हैं। इससे त्वचा पर खुजली, दरारें, आँखों से पानी निकलना, हाँफना, छींकना, सूजन आदि लक्षण दिखायी पड़ते हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
B-कोशिका एवं T-कोशिका क्या है ?
अथवा
T-कोशिका क्या है?
उत्तर
श्वेत रुधिर कोशिकाएँ (लिम्फोसाइट्स) शरीर प्रतिरक्षात्मक तन्त्र की मुख्य कोशिकाएँ होती हैं। शरीर प्रतिरक्षात्मक तंत्र की लिम्फोसाइट्स दो प्रकार की होती हैं, जिन्हें B-कोशिका एवं T-कोशिका कहते हैं। ये दोनों कोशिकाएँ भ्रूणीय अवस्था में यकृत कोशिकाओं और वयस्क अवस्था में अस्थिमज्जा की कोशिकाओं द्वारा बनती हैं। रे दोनों कोशिकायें परिपक्व होने के बाद शरीर के रुधिर एवं लसीका के साथ परिसंचरित होती रहती हैं । T-कोशिकाएँ कोशिकीय प्रतिरक्षा तथा B-कोशिकाएँ प्रतिरक्षियों के निर्माण करने का कार्य करती हैं।
प्रश्न 7.
D.P.T. का टीका किन-किन रोगों से बचाव करता है ? प्रत्येक बीमारी के रोग कारक का नाम लिखिये।
उत्तर
यह टीका निम्नलिखित तीन बीमारियों से बचने के लिए लगाया जाता है
- डिफ्थीरिया
- कुकुर खाँसी
- टिटेनस।
रोगकारक का नाम जीवाणु
- डिफ्थीरिया – कोर्नीबैक्टीरिया डिफ्थेरी
- कुकुर खाँसी – बोर्डेटेला पुर्टसिस (जीवाणु)
- टिटेनस – क्लॉस्ट्रीडियम टिटैनी।
प्रश्न 8.
सुजननिकी किसे कहते हैं ?
उत्तर
सुजननिकी (Eugenics)-सुजननिकी वह विधि है, जिसके द्वारा भावी मानव पीढ़ी को आनुवंशिक आधार पर सुधारने का प्रयास किया जाता है। आजकल यह जीव विज्ञान की एक शाखा का रूप ले चुकी है। सुजननिकी में मानव सुधार के लिए दो कार्य किये जाते हैं। पहले कार्य द्वारा शारीरिक तथा मानसिक रूप से स्वस्थ व्यक्तियों को प्रजनन के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 9.
एलर्जी क्या है ? इसके कारणों को समझाइए।
अथवा
एलर्जी का प्रतिरक्षात्मक तन्त्र से क्या संबंध है ?
उत्तर
जब हमारे शरीर में ऐसा पदार्थ प्रवेश करता है, जिसके प्रति उच्च प्रतिरोधक क्षमता का विकास हो गया है, तब अचानक तीव्रता से हमारे शरीर में प्रतिरोधात्मक क्रियाएँ होने लगती हैं, जो पूरे शरीर में शोथ, जलन, खुजली या दाने के रूप में दिखाई देती हैं, इन्हीं सभी क्रियाओं को एक साथ एलर्जी कहते हैं। अतः एलर्जी हमारे शरीर में उच्च प्रतिरोधकक्षमता का प्रतीक है। धूल तथा परागकणों, सौन्दर्य प्रसाधनों, विविध रसायनों तथा रोगकारकों के कारण एलर्जी के लक्षण दिखाई देते हैं।
प्रश्न 10.
टीकाकरण प्रतिरक्षा में किस प्रकार उपयोगी है ?
उत्तर
टीकाकरण वह उपाय है जिसके द्वारा किसी जीव में किसी रोग के प्रति प्रतिरोधकता को पैदा किया जाता है। इस तकनीकी में कमजोर रोगकारक जीव को शरीर में प्रवेश करा दिया जाता है तब शरीर का प्रतिरक्षात्मक तंत्र प्रेरित होकर इस रोगकारक के प्रति प्रतिरक्षियों का निर्माण करके रोगप्रतिरोधात्मक क्षमता का विकास कर लेता है, और जब वास्तविक रोगाणु शरीर में प्रवेश करते हैं तब ये प्रतिरक्षी उसे नष्ट कर देते हैं और रोग से जीव की रक्षा हो जाती है। रोगकारकों या रोगाणुओं के कृत्रिम रूप से प्रवेश कराने वाले कारक को टीका कहते हैं। आजकल बच्चों को पोलियो, टिटेनस, डिप्थीरिया, कुकुर खाँसी, चेचक आदि के टीके लगाये जाते हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
औषधि व्यसन क्या है ? इसके क्या कारण होते हैं ?
उत्तर
शारीरिक तथा मानसिक रूप से नशीली दवाओं एवं नशीले पदार्थों पर निर्भरता व्यसन (Addition) कहलाता है।
सामाजिक दबाव या उत्सुकतावश नशीले पदार्थों का सेवन करके उत्तेजन तथा रोमांच का अनुभव होता है। व्यक्ति तीव्र इच्छा शक्ति के अभाव में लगातार सेवन करता है और एक समय ऐसा आता है कि वह चाहकर भी नहीं छोड़ पाता इस स्थिति को व्यसन कहते हैं। इसके प्रमुख कारण हैं-
- उत्सुकता
- उत्तेजना एवं अपूर्व आनन्द की प्राप्ति
- अधिक कार्यक्षमता की इच्छा
- कल्पना लोक की सैर
- सामाजिक दबाव
- निराशाओं और चिन्ता से छुटकारा
- पारिवारिक इतिहास
- व्यापारिक प्रचार एवं असामाजिक तत्व
- दर्द से आराम
- स्वर्गलोक की सैर।
प्रश्न 12.
शामक एवं ट्रैकुलाइजर्स में क्या अन्तर है ?
उत्तर
शामक एवं ट्रैकुलाइजर्स में अन्तर.
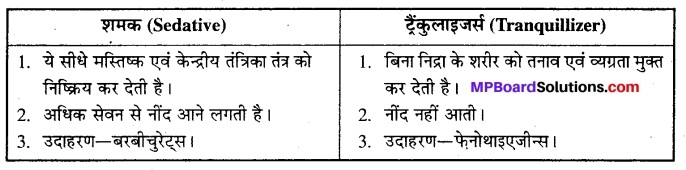
प्रश्न 13.
L.S.D. के स्रोत का नाम लिखिए। इसके कुप्रभावों का भी उल्लेख कीजिए।
उत्तर
लाइसर्जिक एसिड डाइएथिलेमाइड (L.S.D.) हल्का नशीला पदार्थ जो मस्तिष्क पर अस्थायी असर डालता है। इसे क्लेविसेप्स परप्यूरिया नामक कवक के वर्धा भाग से प्राप्त किया जाता है। ये कवक राई के पौधे में एर्गाट (Ergot) नामक बीमारी पैदा करता है। इससे राई के बाल के दानों में इस कवक के तन्तु गुच्छे के रूप में विकसित होते हैं इसे एर्गाट कहते हैं। एर्गाट को एकत्रित कर इसके अर्क से L.S.D. प्राप्त करते हैं।
प्रभाव-मनुष्य के मस्तिष्क पर प्रभाव डालता है जिससे उसके व्यवहार तथा रहन-सहन के तरीकों में काफी परिवर्तन आ जाता है। रक्त चाप बढ़ जाता है। गर्भवती महिला ज्यादा प्रयोग करें तो गर्भपात भी हो सकता है।
प्रश्न 14.
मानव शरीर एवं समाज पर ऐल्कोहॉल के प्रभावों का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर
मानव शरीर व समाज पर ऐल्कोहॉल के प्रभाव-
- मस्तिष्क नियंत्रण की शक्ति समाप्त हो जाती है।
- गलत-सही सोचने की क्षमता खत्म हो जाती है। मस्तिष्क की अक्रियता में सारे संबंध भूल जाता है।
- ज्यादा सेवन से आमाशय, हृदय, यकृत, वृक्क एवं अन्य अंगों की पेशियाँ कमजोर हो जाती हैं।
- रोग प्रतिरोधक शक्ति समाप्त हो जाती है ।
- ऐल्कोहॉल के आदी व्यक्ति की पुतलियाँ फैल जाती हैं ।
- कुछ दिनों बाद प्रायः व्यक्ति अपराधिक प्रवत्ति का हो जाता है।
प्रश्न 15.
व्यसन के प्रत्याहारी लक्षणों का संक्षिप्त में वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर
व्यसन के प्रत्याहारी लक्षण इस बात का संकेत देते हैं कि व्यक्ति औषधि/एल्कोहॉल व्यसन के अंतिम दौर में है तथा अब उसकी शरीर और अधिक औषधि सेवन/ऐल्कोहॉल के उपयोग के लायक नहीं रह गया है। ये लक्षण हैं
- शरीर में कंपकपी होनी (Tremois)
- मिचली आना (Nausea)
- उल्टी होना (Vomiting)
- कमजोरी लगना (Weakness)
- अनिद्रा (Insomnia)
- उत्कंठा (Anxiety)
प्रश्न 16.
साइकोट्रापिक औषधि किसे कहते हैं ?
उत्तर
साइकोटापिक औषधियाँ-ऐसी औषधियाँ मुख्यत: मनुष्य की चिन्तन शक्ति एवं मानसिक प्रक्रिया को प्रभावित करती हैं। इनके सतत् उपयोग से व्यक्ति के व्यवहार, होशो-हवाश एवं बोधगम्यता में परिवर्तन हो जाता है। अतः इन्हें मनोदशा परिवर्तक औषधि भी कहा जाता है। इन औषधियों के लगातार सेवन से व्यक्ति उनका आदी हो जाता है, वह इन औषधियों पर पूर्ण रूप से निर्भर हो जाता है तथा इनके उपयोग के बिना नहीं रह पाता है।
प्रश्न 17.
शामक औषधियाँ क्या हैं ये कितने प्रकार की होती हैं ? इनके प्रभाव लिखिए।
उत्तर
शामक औषधियाँ- इसके अंतर्गत ऐसी औषधियों को सम्मिलित किया गया है जो सीधे मस्तिष्क अर्थात् केन्द्रीय तंत्रिका तंत्र को निष्क्रिय कर देती हैं। ये शरीर को निश्चिन्त, सुस्त तथा स्वतंत्र कर देती है। इनकी अधिक मात्रा में सेवन से नींद आने लगती है। निद्रा उत्पन्न करने वाली इन औषधियों को हिप्नोटिक्स भी कहा जाता है। उदाहरण-बरबीचुरेट्स एवं बेन्जोडाइएजोपिन्स।
1. बरबीचुरेट्स- यह संश्लेषित औषधि होती है जिसे बरबीचुरिक अम्ल से तैयार किया जाता है। इनके प्रयोग से व्यक्ति हतोत्साहित हो जाता है तथा उसे नींद आ जाती है। इसी कारण इन्हें निद्राकारी पिल्स भी कहते हैं। ये व्यक्ति की क्रियात्मक सक्रियता तथा चिन्ता या उत्कंठा को कम करती है। यह निद्रा लाती है। इनके लगातार उपयोग से व्यक्ति इनका आदी हो जाता है। व्यक्ति को इनकी आदत से छुटकारा दिलाना कठिन हो जाता है। लम्बी अवधि तक इसके प्रयोग से व्यक्ति की याददाश्त कम होने लगती है। हकलाकर बोलने लगता है। उदाहरण-हेक्साबारबिटॉल, मीथोहेक्सीटॉल।
2. बेन्जोडाइएजोपिन्स-ये प्रति उत्कंठात्मक या एन्टी-एन्जाइटी औषधियाँ होती हैं। इनके उपयोग से नींद आती है। उदाहरण–वेलियम, डाइएजोपॉम आदि।
प्रश्न 18.
इन्टरफेरॉन क्या है ?
उत्तर
इन्टरफेरॉन जन्तु की जीवित कोशाओं द्वारा उत्पन्न वे शक्तिशाली विषाणु प्रतिरोधी पदार्थ हैं जो वाइरल रोगों के कारण उत्पन्न होते हैं। ये विषाणु के प्रथम संक्रमण के बाद उत्पन्न होते हैं तथा विषाणु के द्वितीय आक्रमण से जीव की रक्षा करते हैं। ये विषाणु रोगों की रोकथाम ठीक उसी तरह करते हैं जिस प्रकार प्रतिजैविक जीवाणु रोगों की रोकथाम करते हैं लेकिन जन्तु इन्टरफेरॉन मानवों पर प्रभावी नहीं है। जैव तकनीकी को सहायता से इन्हें मानव शरीर से बाहर भी व्यवसायिक स्तर पर प्राप्त किया जा सकता है।
मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
कैंसर क्या है ? कैंसर के प्रकार लिखिए तथा कैंसर रोग के प्रमुख कारण लिखिए।
अथवा
कैंसर रोग होने के कारण प्रस्तुत करते हुए इस रोग के लक्षण लिखिए।
उत्तर
जब कोशिका विभाजन एवं कोशिका वृद्धि असामान्य होती है, तो इसके कारण ट्यूमर का निर्माण होता है, जिसे कैंसर कहते हैं। अत: कैंसर एक प्रकार की असंगठित ऊतक वृद्धि की बीमारी है, जो कोशिकाओं में अनियन्त्रित विभाजन तथा विकास के कारण होती है। जिन कोशिकाओं की अनियन्त्रित वृद्धि के कारण कैंसर होता है, उन्हें नियोप्लास्टिक (Neoplastic) कोशिकाएँ कहते हैं। कैंसर के प्रकार (Types of Cancer)-कैंसर को निम्नलिखित भागों में विभाजित किया गया है1. सार्कोमास (Sarcomas).-संयोजी ऊतक का कैंसर है। 2% व्यक्तियों में यह रोग होता है।
2. कासनोमास (Carcinomas)-यह कैंसर एपिथीलियम कोशिकाओं में होता है। स्तन ग्रन्थि, फेफड़ा, आमाशय एवं अग्नाशय कैंसर। 85% कैंसर इसी प्रकार का होता है।
3. लिम्फोमास (Cancer of Lymphatic Tissue)-यह लसीका ऊतकों में पाया जाने वाला कैंसर है। इस प्रकार के कैंसर में लसीका गाँठे (Lymph nodes) तथा प्लीहा (Spleen) अधिक मात्रा में (Lymphocytes) बनाती है।
4. ल्यूकेमियास (Leukemias)–यह रुधिर कोशिकाओं में पाया जाता है। इसे रुधिर कैंसर भी कहते हैं। उपर्युक्त प्रकारों के अलावा भी कुछ विशेष प्रकार के कैंसर पाये जाते हैं, जो निम्नलिखित हैं
(a) मेलेनोमास (Melanomas)–वर्णक कोशिकाओं का कैंसर।
(b) ग्लियोमास (Gliomas)-तंत्रिका कोशिका का कैंसर।
(c) टीरेटोमास (Teratomas)-यह कोशिका विभाजन एवं भ्रूणीय विकास से संबंधित है। कैंसर के कारण-कैंसर उत्पन्न करने वाले भौतिक व रासायनिक कारकों को कार्सिनोजेन कहते हैं। कैंसर के प्रमुख कारक या कारण निम्नानुसार हैं
- धूम्रपान के कारण मुख व फेफड़ों का कैंसर होता है। इसी प्रकार सुपारी तथा कुछ दूसरे रसायन भी कैंसर पैदा करते हैं।
- ज्यादा उम्र में हॉर्मोनल सन्तुलन बिगड़ने के कारण भी कैंसर होता है।
- कुछ विषाणुओं के संक्रमण के कारण भी कैंसर होता है।
- उत्परिवर्तन के कारण भी कैंसर पैदा होता है।
- सूर्य की अल्ट्रावायलेट किरणें, प्रदूषक तथा रेडियोऐक्टिव किरणें भी कैंसर पैदा करती हैं।
कैंसर के लक्षण-कैंसर के प्रमुख लक्षण निम्नानुसार होते हैं
- किसी घाव का 7 भरना तथा असाधारण और बार-बार रक्तस्राव का होना या अन्य स्राव का निकलना। विशेषकर स्त्रियों में मासिक धर्म बन्द हो जाने के बाद प्रायः ऐसा होना
- बिना दर्द के असाधारण गाँठ या शरीर के किसी भी भाग का बढ़ जाना विशेषकर स्त्रियों के स्तन में गाँठ पड़ जाना या असाधारण वृद्धि होना।
- गले की खराबी या गले का रोग जो ठीक होने तथा भरने का नाम न ले।
- ‘पाखाने तथा मूत्र विसर्जन की आदतों में परिवर्तन होना।
- बार-बार अपच होना तथा खाने की चीजों को निगलने में परेशानी होना
- मस्सों एवं तिल (Wart and mole) के रंग तथा आकार में अचानक परिवर्तन का होना ।
- किसी भी अल्सर का इलाज के बाद भी ठीक न होना।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
प्रतिरक्षात्मक तंत्र क्या है ? मनुष्य के प्रतिरक्षात्मक तंत्र के विभिन्न घटकों एवं उनकी भूमिकाओं का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर
प्रतिरक्षात्मक तंत्र–एक विशेष श्वेत रुधिर कोशिकाएँ या ल्यूकोसाइट्स जिन्हें लिम्फोसाइट्स कहते हैं, शरीर प्रतिरक्षात्मक तन्त्र की मुख्य कोशिकाएँ होती हैं। प्रतिरक्षात्मक तन्त्र की लिम्फोसाइट्स दो प्रकार की होती हैं, जिन्हें B-कोशिका और T-कोशिका कहते हैं। ये दोनों कोशिकाएँ भ्रूणीय अवस्था में यकृत कोशिकाओं और वयस्क अवस्था में अस्थिमज्जा की कोशिकाओं द्वारा बनती हैं। इनमें से T-कोशिकाएँ कोशिकीय प्रतिरक्षा और B-कोशिकाएँ प्रतिरक्षियों के निर्माण के लिए जिम्मेदार होती हैं। दोनों ही कोशिकाएँ ऐण्टिजनों से प्रेरित होकर ही अपने-अपने कार्यों को करती हैं।
(1) B-calfahratti a fucsaiti ho ufar ufafchal (Mechanism or Action of B-cells to Antigens)-जब कोई ऐण्टिजन शरीर द्रव (रुधिर एवं लसीका) में प्रवेश करता है तब B-कोशिकाएँ इससे प्रेरित होकर प्रतिरक्षियों का निर्माण करती हैं। मानव शरीर में हजारों प्रकार के ऐण्टिजन के लिए अलग-अलग हजारों प्रकार की विशिष्ट B-कोशिकाएँ पाई जाती हैं। जब कोई B-कोशिका ऐण्टिजन के संपर्क में आती है, तो यह प्रेरित होकर तेजी से गुणन करके बहुत-सी एक क्लोन (Clone) प्लाज्मा कोशिकाओं का निर्माण करती हैं, इस एक क्लोन की अधिकांश कोशिकाएँ लगभग एक सेकण्ड में 2000 प्रतिरक्षी अणुओं का निर्माण करती हैं। B-कोशिकाओं में प्रतिरक्षियों के उत्पादन की यह क्षमता इन कोशिकाओं के विकास एवं परिपक्वन के दौरान उपार्जित लक्षणों के एकत्रित होने के कारण भ्रूणीय अवस्था में ही बनती है।
(2) T-calforcatuit on tfucwatato ufà ufaisher (Mechanism or Action of T-cells to Antigens)-T-कोशिकाएँ भी B-कोशिकाओं के ही समान एक क्लोन T-कोशिकाओं के उत्पादन के द्वारा ऐण्टिजनों के प्रति प्रतिक्रिया व्यक्त करती हैं। प्रत्येक T-कोशिका एक विशिष्ट ऐण्टिजन से संबंधित होती है। इसलिए हमारे शरीर में विशिष्ट प्रकार के ऐण्टिजनों के लिए अलग-अलग T-कोशिकाएँ 4-5 वर्ष या इससे अधिक समय तक जीवित रहती हैं। T-कोशिकाओं द्वारा उत्पादित एक क्लोन कोशिकाएँ, एण्टिजन की प्रतिक्रिया की दृष्टि से जनक T-कोशिका के समान होती हैं, लेकिन ये विभिन्न कार्यों को करती हैं। ये निम्न प्रकार की हो सकती हैं
(i) मारक T-कोशिकाएँ (Killer T-cells = KT-cells)-ये ऐण्टिजन को सीधे आक्रमण के द्वारा नष्ट करती हैं। इसके लिए ये कुछ ऐसे रसायनों का स्राव करती हैं, जो भक्षकाणुओं (Phagocytes) को आकर्षित करके इन्हें ऐण्टिजनों के तेजी से भक्षण के लिए प्रेरित करती हैं। ये दूसरी T-कोशिकाओं को आकर्षित करने के लिए भी कुछ रसायनों का स्राव करती हैं। T-कोशिकाएँ ऐण्टिजनों के प्रति इन क्रियाओं को व्यक्त करने के लिए शरीर के उन स्थानों पर जाती हैं, जहाँ पर ऐण्टिजनों का आक्रमण होता है।
(ii) सहायकT-कोशिकाएँ (Helper T-cells = HT-cells)-ये वेT-कोशिकाएँ हैं, जो B-कोशिकाओं को प्रतिरक्षियों के निर्माण के लिए प्रेरित करती हैं।
(iii) दाबक T-कोशिकाएँ (Suppressor T-cells = ST cells)-ये वे T-कोशिकाएँ हैं, जो प्रतिरक्षात्मक तन्त्र द्वारा अपने ही शरीर की कोशिकाओं पर आक्रमण करने से रोकती हैं। इनमें से कुछ कोशिकाएँ एक निश्चित ऐण्टिजन के लिए याददाश्त कोशिकाओं का भी काम करती हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
तंबाकू धूम्रपान के हानिकारक प्रभावों का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर-
तंबाकू धूम्रपान के हानिकारक प्रभाव
(1) यह केन्द्रीय तंत्रिका तंत्र तथा तंत्रिकीय आवेग के संचरण के मार्ग को प्रभावित करता है। कम मात्रा में इसका उपयोग मस्तिष्क के विभिन्न केन्द्रों को उत्तेजित करता है, परन्तु इसका लम्बा उपयोग तन्त्रिका-तन्त्र की क्रियाशीलता को कम करता है।
(2) यह एड्रीनेलीन के स्राव को प्रेरित करके रक्त दाब तथा हृदय गति को बढ़ाता है। रक्त दाब को बढ़ाकर यह हृदय की बीमारियों को उत्तेजित करता है।
(3) गर्भवती महिलाओं में धूम्रपान, भ्रूण के विकास को रोकता है।
(4) तम्बाकू के धुएँ में कार्बन मोनोऑक्साइड (CO), एरोमैटिक हाइड्रोकार्बन तथा सार भी पाया जाता है। CO रुधिर की O2, संवहन क्षमता को कम करती है। हाइड्रोकार्बन कैन्सर को प्रेरित करते हैं । इस कारण तम्बाकू चबाने वालों में मुँह तथा धूम्रपान करने वालों में गले एवं फेफड़ों का कैन्सर अधिक होता है।
(5) तम्बाकू का किसी भी रूप में प्रयोग लार तथा आमाशयी रसों के अधिक स्रावण को प्रेरित करता है, जिससे आमाशय में अम्लीयता बढ़ जाती है, फलत: आहार नाल में अल्सर का खतरा बढ़ जाता है और श्लेष्मा की अवशोषणशीलता कम हो जाती है। व्यक्ति अल्पपोषण, भूख एवं कब्ज का शिकार हो जाता है।
(6) धूम्रपान वृक्कों की क्रियाशीलता पर प्रतिकूल प्रभाव डालता है। यह पेशियों एवं कंकाली ऊतकों को शिथिल करके व्यक्ति को दुर्बल बनाता है। इसके सेवन से व्यक्ति की उम्र घटती जाती है। इसके प्रयोग से ब्रोंकाइटिस तथा एम्फीसेमा (Emphysema) नामक रोग भी होता है।
(7) तम्बाकू के लगातार सेवन से स्वादेन्द्रीय कम संवेदनशील हो जाती है तथा मुँह व गला हमेशा सूखा रहता है। इससे घ्राण शक्ति भी कमजोर हो जाते हैं, क्योंकि श्लेष्मा के ऊपर लार की एक स्तर जमा हो जाती है।
प्रश्न 4.
पुनर्वासन पर टिप्पणी लिखिए।
उत्तर
औषधि एवं ऐल्कोहॉल व्यसन से ग्रसित व्यक्ति का अपनी पूर्व अवस्था, अर्थात् स्वस्थ अवस्था या सामान्य स्वास्थ्य वाली अवस्था में वापस आ जाना ही पुनर्वासन कहलाता है। पुनर्वासन हेतु व्यक्ति की नशाखोरी की आदत को धीरे-धीरे समाप्त करने का प्रयास किया जाता है। व्यक्ति में औषधि व्यसन के प्रत्याहारी लक्षणों (Withdrawal symptoms) के उपचार हेतु प्रारंभ में उन्हें निस्तब्धकारी औषधियाँ (Tranquillizers) देकर ठीक किया जाता है, परन्तु यह औषधि निर्भरता का अल्पावधि उपचार (Short term treatment) ही होता है।
व्यसन से ग्रसित व्यक्ति के दीर्घकालीन उपचार (Long term treatment) हेतु औषधि उपचार के साथसाथ व्यवहारात्मक शिक्षा भी देना आवश्यक होता है, ताकि व्यक्ति इन औषधियों के कुप्रभावों को समझ सके तथा स्वयं ही औषधि निर्भरता छोड़ने का प्रयास करने लगे। इस कार्य हेतु सम्बन्धियों (Relatives), दोस्तों एवं चिकित्सकों के द्वारा उनका मनोवैज्ञानिक (Psychological) एवं सामाजिक उपचार (Therapy) आवश्यक होता है। लोगों को ऐसे व्यक्तियों के साथ सहानुभूति रखते हुए उन्हें इनके कुप्रभावों की जानकारी देनी चाहिए तथा उनकी औषधि निर्भरता को धीरे-धीरे समाप्त करना चाहिए।
औषधि व्यसन से ग्रसित व्यक्ति के पुनर्वासन के दौरान व्यक्ति को पर्याप्त मात्रा में भोजन, विटामिन्स, इलेक्ट्रोलाइट्स (Electrolytes) आदि पदार्थ भी देने चाहिए। चूँकि सामान्यतः यह देखा गया है कि व्यसन से ग्रसित कोई व्यक्ति अचानक औषधि सेवन बन्द कर देता है तो उसके मस्तिष्क में CAMP (Cyclic adenosine monophosphate) का स्तर बढ़ जाता है जो कि एक प्रत्याहारी लक्षण (Withdrawal symptom) है। ऐसे रोगी को विटामिन-C देने से CAMP का स्तर नियंत्रित रहता है तथा व्यक्ति में प्रत्याहारी लक्षण उत्पन्न नहीं हो पाते हैं।















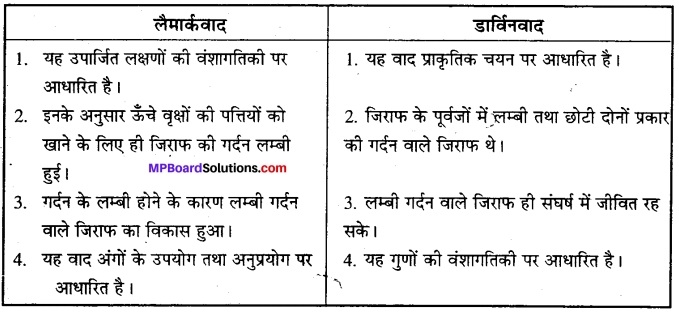
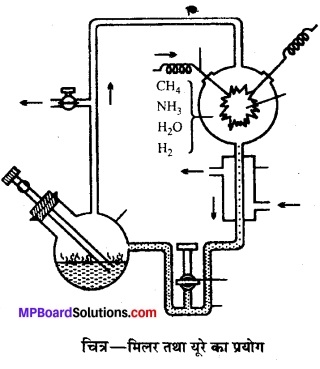
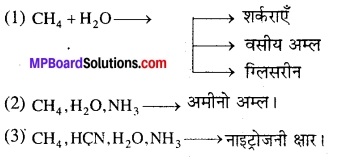
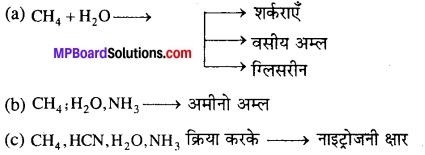

 Answer:
Answer: