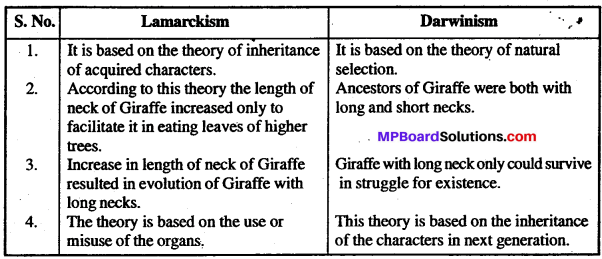
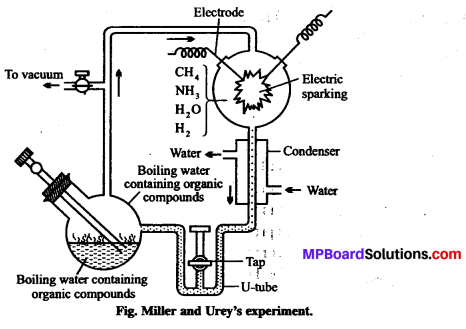
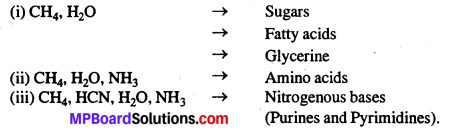
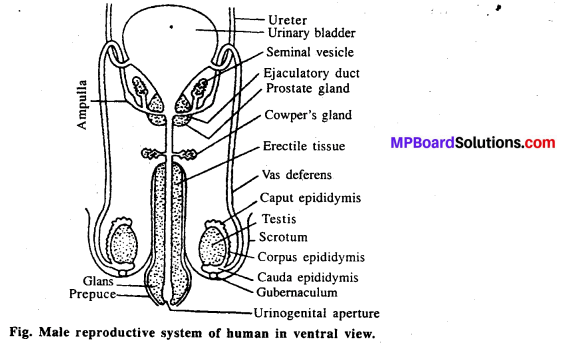
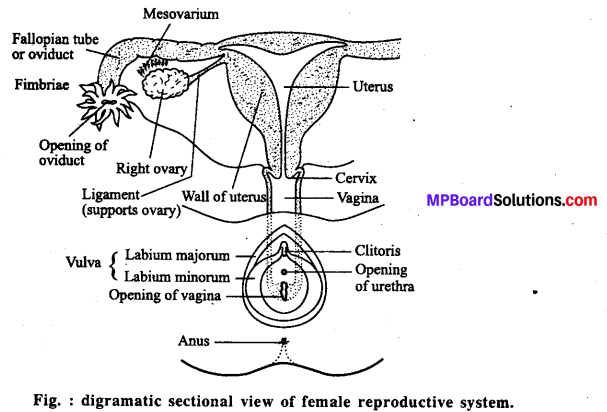
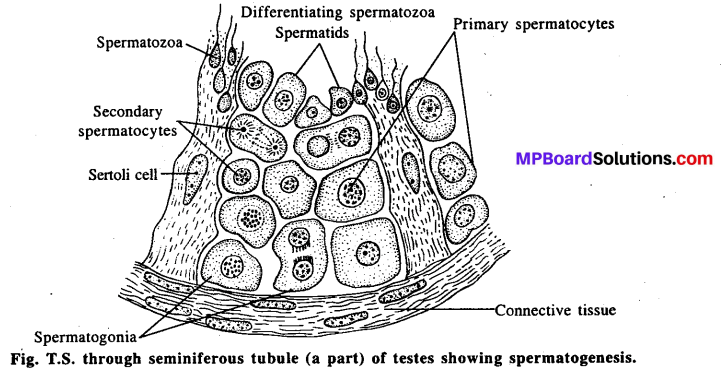
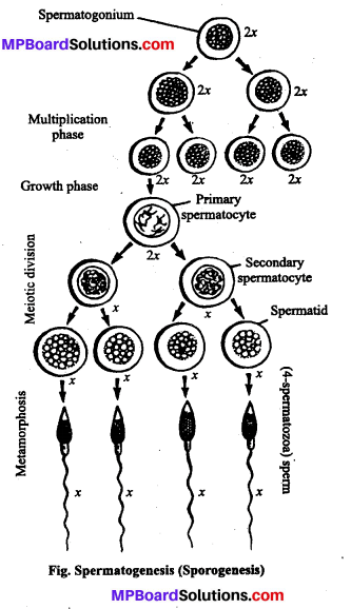
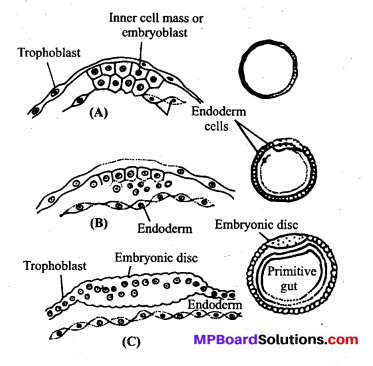
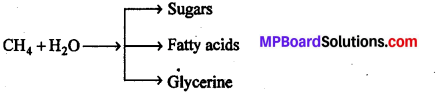MP Board Class 12th Biology Solutions Chapter 4 जनन स्वास्थ्य
जनन स्वास्थ्य NCERT प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
समाज में जनन स्वास्थ्य के महत्व के बारे में अपने विचार प्रकट कीजिए।
उत्तर
जनन स्वास्थ्य का तात्पर्य जनन के सभी पहलुओं जैसे शारीरिक, भावनात्मक, व्यावहारिक तथा सामाजिक स्वास्थ्य से है। दुनिया में भारत पहला ऐसा देश है जिसने राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर जननात्मक स्वस्थ समाज को प्राप्त करने की कार्य योजनाएँ बनाई हैं। इन कार्यक्रमों को परिवार कल्याण के नाम से जाना जाता है। इनकी शुरूआत 1951 में (परिवार नियोजन के नाम से) हुई थी। जनन संबंधित और आवधिक क्षेत्रों को इसमें सम्मिलित करते हुए बहुत उन्नत व व्यापक कार्यक्रम फिलहाल ‘जनन एवं बाल स्वास्थ्य सेवा कार्यक्रम (आ.सी.एच.)’ के नाम से प्रसिद्ध है। इन कार्यक्रमों के अंतर्गत् जनन संबंधी विभिन्न पहलुओं के बारे में लोगों में जागरूकता पैदा करते हुए और जननात्मक रूप से संबंध समाज तैयार करने के लिए अनेक सुविधाएँ एवं प्रोत्साहन दिए जा रहे हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
जनन स्वास्थ्य के उन पहलुओं को समझाइए, जिस पर आज के परिदृश्य में विशेष ध्यान देने की जरूरत है
उत्तर
जनन स्वास्थ्य प्राप्ति के लिए विभिन्न कार्य-योजनाओं के सफलतापूर्वक क्रियान्वयन के लिए मजबूत संरचनात्मक सुविधाओं, व्यावसायिक विशेषज्ञता तथा भरपूर भौतिक सहारों की आवश्यकता होती है। लोगों को जनन संबंधी समस्याओं जैसे-सगर्भता (Pregnancy), प्रसव (Parturition), यौन संचारित रोगों, गर्भपात (Abortion), गर्भ निरोधकों, आर्तव चक्र संबंधी समस्याओं, बांझपन (Infertility) आदि के बारे में चिकित्सकीय सहायता देने के लिए बेहतर तकनीकों एवं नई कार्य योजनाओं को क्रियान्वित करने की भी आवश्यकता है ताकि लोगों की अधिक सुचारु रूप से देखभाल और सहायता की जा सके।
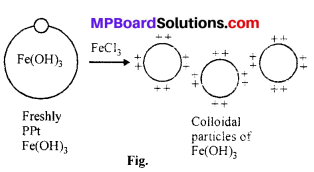
बढ़ती “मादा भ्रूण हत्या” की कानूनी रोक के लिए ऐम्नियोसेंटेसिस (Amniocentesis) जैसे लिंग परीक्षण पर वैधानिक प्रतिबंध तथा व्यापक बाल प्रतिरक्षीकरण (टीकाकरण) आदि कुछ महत्वपूर्ण कार्यक्रमों को शामिल किया गया है। जनन संबंधी विभिन्न अनुसंधानों को बढ़ावा देने के लिए हमारे देश की सरकारी एजेंसियाँ सतत् क्रियाशील हैं। लखनऊ स्थित केन्द्रीय औषध अनुसंधान संस्थान (Central Drug Research Institue CDRI) ने “सहेली” नामक गर्भनिरोधक गोली का निर्माण किया है। यौन संचारित रोगों की सही जाँच तथा देखभाल और लगभग सभी जनन स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं हेतु विकसित चिकित्सा सुविधाओं के होने से बेहतर समाज एवं जनन स्वास्थ्य के संकेत प्राप्त हो रहे हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
क्या विद्यालयों में यौन शिक्षा आवश्यक है ? यदि हाँ तो क्यों ?
उत्तर
हाँ, विद्यालयों में यौन शिक्षा आवश्यक है, ताकि छात्र/छात्राओं को यौन संबंधी विभिन्न पहलुओं के बारे में फैली हुई भ्रान्तियों एवं यौन संबंधी गलत धारणाओं से छुटकारा मिल सके। बच्चों को जनन अंगों, किशोरावस्था एवं उससे संबंधित परिवर्तनों, सुरक्षित और स्वच्छ यौन क्रियाओं, यौन संचारित रोगों एवं एड्स की जानकारी देना विशेष रूप से किशोर आयु वर्ग में जनन संबंधी स्वस्थ जीवन बिताने में सहायक होती है।
प्रश्न 4.
क्या आप मानते हैं कि पिछले 50 वर्षों के दौरान हमारे देश के जनन स्वास्थ्य में सुधार हुआ है? यदि हाँ तो इस प्रकार के सुधार वाले कुछ क्षेत्रों का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर
जी हाँ, पिछले 50 वर्षों के दौरान हमारे देश के जनन स्वास्थ्य क्षेत्र में सुधार हुआ है। निम्न क्षेत्रों में हुए सुधार को आसानी से देखा जा सकता है
- यौन संबंधी मामलों के बारे में बेहतर जागरुकता आयी है।
- चिकित्सकीय देख-रेख में होने वाले प्रसवों की संख्या में वृद्धि हुई है।
- प्रसवोत्तर देखभाल बेहतर हुई है।
- मातृ मृत्यु-दर (MMR) में गिरावट आई है।
- शिशु मृत्यु-दर (IMR) में गिरावट आई है।
- यौन संचारित रोगों की सही जाँच-पड़ताल तथा देखभाल व उपचार बेहतर हुआ है।
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि दर पर रोक लगी है।
कुल मिलाकर सभी यौन समस्याओं हेतु बढ़ी हुई चिकित्सा सुविधाओं का होना समाज के बेहतर जनन स्वास्थ्य की ओर संकेत देता है।
प्रश्न 5.
जनसंख्या विस्फोट के कौन-से कारण हैं ?
उत्तर
शीघ्र एवं अनियमित जनसंख्या वृद्धि को जनसंख्या विस्फोट कहा जाता है।इसके प्रमुख कारण निम्नलिखित हैं
- रोगों व महामारियों पर नियंत्रण
- कृषि का विकास
- संचार व आवागमन के साधन
- उच्च जन्मदर
- निम्न मृत्युदर
- मनुष्य का वर्ष भर मैथुनकाल होना।
प्रश्न 6.
क्या गर्भ-निरोधकों का उपयोग न्यायोचित है ? कारण बताइए।
उत्तर
भारत में जनसंख्या वृद्धि-दर अत्यधिक होने के कारण राष्ट्रीय संकट उत्पन्न हो गया है। अतः गर्भ निरोधकों का उपयोग न्यायोचित है। इसके उपयोग से परिवार को सीमित किया जा सकता है एवं उनकी सुविधाओं में वृद्धि की जा सकती है। इन गर्भ निरोधकों के उपयोग से यौन संचारित रोगों (STDs) से बचा जा सकता है। इसके साथ ही दो संतानों के बीच अन्तराल भी रखा जा सकता है।जनसंख्या वृद्धि को कम करके परिवार, समाज व देश की समृद्धि में सहयोग कर सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 7.
जनन ग्रंथि को हटाना, गर्भ निरोधकों का विकल्प नहीं माना जा सकता है, क्यों?
उत्तर
जनन ग्रंथियाँ सन्तान उत्पन्न करने वाले अंग हैं । वृषण में शुक्राणुओं तथा अण्डाशय में अण्डों का निर्माण होता है। गर्भ निरोधक के लिए स्वस्थ अंगों को शरीर से हटाना उचित नहीं है। इससे मानसिक, शारीरिक स्वास्थ्य संबंधी समस्याएँ उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं। जबकि गर्भ निरोधक विधियाँ सुलभ होती हैं एवं उनका कोई बुरा प्रभाव भी शरीर पर नहीं पड़ता है। इनका आसानी से प्रयोग भी किया जा सकता है। जरूरत पड़ने पर इसे हटाया भी जा सकता है। जनन ग्रंथि को हटाना एक जटिल प्रक्रिया है, कानून हमें इसकी आज्ञा भी नहीं देता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
उल्बवेधन एक घातक लिंग निर्धारण (जाँच) प्रक्रिया है, जो हमारे देश में निषेधित है। क्या यह आवश्यक होना चाहिए ? टिप्पणी कीजिए।
उत्तर
बढ़ती मादा भ्रूण हत्या की कानूनी रोक के लिए उल्बवेधन (Amniocentesis) जाँच (भ्रूणीय लिंग निर्धारण), लिंग परीक्षण पर वैधानिक प्रतिबंध उचित है क्योंकि यह एक खतरनाक प्रवृत्ति है। कई बार ऐसा देखा जाता है कि यह पता चलने पर कि भ्रूण मादा (लड़की) है, चिकित्सीय सगर्भता समापन (Medical termination of pregnancy) कराया जाता है, सामान्य भाषा में इसे गर्भपात (Abortion) कहा जाता है। यह पूरी तरह गैर-कानूनी है। इस प्रकार की प्रवृत्ति से बचना चाहिए क्योंकि यह माता एवं बच्चा (भ्रूण) दोनों के लिए खतरनाक है । इससे समाज में पुरुष एवं महिलाओं की संख्या का अनुपात भी बिगड़ सकता है। जिससे वैवाहिक तथा स्वास्थ्य संबंधी समस्याएँ भी उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं।
प्रश्न 9.
बन्ध्य दम्पत्तियों को संतान पाने हेतु सहायता देने वाली कुछ विधियाँ बताइए।
उत्तर
यदि दंपत्ति बच्चा पैदा करने में अक्षम है तथा ऐसे दोष को ठीक करने का इलाज संभव न हो तो कुछ विशेष तकनीकों के द्वारा उन्हें बच्चा पैदा करने में सहायता की जा सकती है, ये तकनीकें सहायक जनन प्रौद्योगिकी (ART) कहलाती हैं।
1. पात्रे निषेचन (Invitro fertilization IVF)-
इस विधि में अण्डाणु का निषेचन शरीर से बाहर लगभग शरीर के भीतर जैसी स्थिति में कराया जाता है। इसके पश्चात् स्त्री में भ्रूण स्थानान्तरण (Embryo transfer, ET) कराया जाता है।
- युग्मनज डिंबवाहिनी स्थानान्तरण (Zygote intrafallopian transfer ZIFT)-इस प्रक्रिया में प्रारंभिक भ्रूण को 8 ब्लास्टोमियर तक की अवस्था में स्त्री की डिंबवाहिनी या फैलोपियन नलिका में अग्रिम परिवर्धन के लिए स्थानांतरित किया जाता है।
- आन्तर गर्भाशयी स्थानान्तरण (Intrauterine transfer IUT)-जब भ्रूण को 8 ब्लास्टोमियर से अधिक अवस्था पर परिवर्तन हेतु स्त्री के गर्भाशय में स्थानान्तरित किया जाता है तो इसे IUT कहते हैं । यदि किसी स्त्री में गर्भधारण नहीं हो पाता है तो उसकी सहायता के लिए पात्रे निषेचन अर्थात् अन्य स्त्री के भीतर ही निषेचन कराने के बाद भ्रूण को उस स्त्री में स्थानान्तरित किया जा सकता है।
- टेस्ट ट्यूब बेबी (Test tube baby)-इस विधि में दाता स्त्री के अण्डे को दाता पुरुष शुक्राणु से प्रयोगशाला में परखनली के भीतर (स्त्री शरीर के बाहर) निषेचन कराया जाता है तथा निश्चित समय तक अनुरूपी परिस्थितियों में परिवर्धन के बाद अग्रिम परिवर्धन हेतु स्त्री के गर्भाशय में स्थानान्तरित कर दिया जाता है। इस विधि द्वारा जन्मे बच्चे को “टेस्ट ट्यूब बेबी” कहते हैं।
2. युग्मक आन्तर फैलोपीयन स्थानान्तरण (Gamete intrafallopian transfer GIFT)-
जिन स्त्रियों में अण्डाणु उत्पन्न नहीं होता है किन्तु इनमें निषेचन और भ्रूण परिवर्धन के लिए उचित वातावरण होता है उनमें यह विधि अपनायी जाती है। इसमें एक दाता स्त्री से अण्डाणु लिया जाता है तथा उस स्त्री को फैलोपीयन नलिका में स्थानांतरित कर दिया जाता है।
3. आन्तर कोशिकीय शुक्राणु निक्षेपण (Intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection)-
प्रयोगशाला में भ्रूण बनाने के लिए इस प्रक्रिया में शुक्राणु को सीधे ही अण्डाणु में अंत:क्षेपित कर दिया जाता है।
4. कृत्रिम वीर्य सेचन (Artificial insemination AI)-
यदि पुरुष-स्त्री को वीर्य सेचित करने में अक्षम हो अथवा उसके वीर्य में शुक्राणुओं की संख्या कम हो तो ऐसी अवस्था में यह तकनीक अपनायी जाती है। इस विधि में पति अथवा एक स्वस्थ दाता का वीर्य कृत्रिम रूप से स्त्री की योनि में प्रविष्ट कर दिया जाता है। जब कृत्रिम विधि से वीर्य को गर्भाशय में प्रविष्ट किया जाता है तो इसे गर्भाशय वीर्य सेचन (Intra-uterine insemination IUI) कहते हैं।
5. परपोषी मातृत्व (Host mothering)-
इस विधि में भ्रूण को प्राकृतिक माता से निकालकर एक अन्य स्त्री धात्रेय माता (Foster mother) में रोपित कर दिया जाता है। धात्रेय माता में यह भ्रूण जन्म तक अथवा अस्थायी रूप से निश्चित समय तक वर्धित होता है। जिसके बाद इन्हें पुनः मूल माता में या अन्य किसी स्त्री में रोपित कर दिया जाता है। यह तकनीक ऐसी स्त्रियों के लिए लाभदायक है जिनमें भ्रूण बन तो जाता है किन्तु पूर्ण परिवर्धन के समय तक ये इसे रख नहीं पाती हैं।
प्रश्न 10.
किसी व्यक्ति को यौन संचारित रोगों की चपेट में आने से बचने के लिए कौन-से उपाय अपनाने चाहिए?
उत्तर
यौन संचारित रोगों से बचाव (Protection from Sexually Transmitted Diseases)यौन संचारित रोगों से बचाव हेतु निम्न बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए
- किसी अनजान व्यक्ति या बहुत से व्यक्तियों के साथ यौन संबंध न रखें।
- मैथुन के समय हमेशा कंडोम का इस्तेमाल करें।
- संक्रमित व्यक्ति का रुधिर किसी अन्य व्यक्ति को न चढ़ाया जावे।
- पहले से उपयोग किये गये इंजेक्शन व सुईयों का प्रयोग न करें।
- समलैंगिकता से बचें।
- यदि कोई आशंका है तो तुंरत ही प्रारंभिक जाँच के लिए किसी योग्य चिकित्सक से मिलें और रोग की पहचान होने पर पूरा इलाज करावें।
प्रश्न 11.
निम्न वाक्य सही है या गलत, व्याख्या सहित बताइए
(क) गर्भपात स्वतः भी हो सकता है। (सही/ गलत)
उत्तर
गलत, सामान्य परिस्थितियों में गर्भपात नहीं होता। किसी दुर्घटनावश या स्वैच्छिक रूप से गर्भसमापन (गर्भपात) होता है।
(ख) बंध्यता को जीवनक्षम संतति न पैदा कर पाने की अयोग्यता के रूप में परिभाषित किया गया है और यह सदैव स्त्री की असामान्यताओं/दोषों के कारण होती है।(सही/गलत)
उत्तर
गलत, बंध्यता हमेशा स्त्री की असामान्यताओं/ दोषों के कारण नहीं होती, कभी-कभी पुरुष भी बंध्यता के लिए दोषी होता है।
![]()
(ग) एक प्राकृतिक गर्भ निरोधक उपाय के रूप में शिशु को पूर्णरूप से स्तनपान कराना सहायक होता है। (सही/गलत)
उत्तर
सही, शिशु को पूर्णरूप से स्तनपान कराने से अण्डोत्सर्ग नहीं होता है। अतः आर्तव चक्र (Menstrual cycle) भी नहीं होता है, जिसके कारण गर्भ की संभावनाएँ समाप्त हो जाती हैं। किन्तु यह विधि शिशु के जन्म के अधिकतम 6 माह तक कारगर है।
(घ) लोगों के जनन स्वास्थ्य के सुधार हेतु यौन संबंधित पहलुओं के बारे में जागरुकता पैदा करना एक प्रभावी उपाय है।(सही/गलत)
उत्तर
सही, क्योंकि ऐसा करने से लोगों की जनन स्वास्थ्य की समस्याएँ समाप्त अथवा कमतर हो जाती हैं।
प्रश्न 12.
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों को सही कीजिए
(क) गर्भ निरोधक के शल्य क्रियात्मक उपाय युग्मक बनने को रोकते हैं।
उत्तर
युग्मक बनने से नहीं, बल्कि युग्मकों के परिवहन को रोकते हैं।
(ख) सभी प्रकार के यौन संचारित रोग पूरी तरह उपचार योग्य हैं।
उत्तर
हिपेटाइटिस-B, एड्स एवं जननिक हर्पिस का उपचार नहीं होता।
![]()
(ग) ग्रामीण महिलाओं के बीच गर्भ निरोधक के रूप में गोलियाँ (पिल्स) बहुत अधिक लोकप्रिय
उत्तर
ग्रामीण महिलाओं में गर्भ निरोधक के रूप में गोलियाँ (पिल्स)लोकप्रिय नहीं हैं । ग्रामीण महिलाओं को यौन शिक्षा की आवश्यकता है।
(घ) ई. टी. तकनीकों में भ्रूण को सदैव गर्भाशय में स्थानान्तरित किया जाता है।
उत्तर
ई. टी. तकनीकों में 8 ब्लास्टोमियर से ज्यादा अवस्था वाले भ्रूण को गर्भाशय में स्थानान्तरित किया जाता है। जबकि 8 ब्लास्टोमियर से कम अवस्था वाले भ्रूण को अण्डवाहिनी में स्थानान्तरित किया जाता है।
जनन स्वास्थ्य अन्य महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्नोत्तर
जनन स्वास्थ्य वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
1. सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए-
प्रश्न 1.
स्त्रियों के शरीर से फैलोपियन ट्यूब को अलग करना कहलाता है
(a) वैसेक्टोमी
(b) ट्यूबेक्टोमी
(c) ओवरीक्टोमी
(d) कैस्ट्रेशन।
उत्तर
(b) ट्यूबेक्टोमी
प्रश्न 2.
आबादी की सर्वाधिक वृद्धि का प्रमुख कारण है
(a) कम मृत्यु दर
(b) जन्मदर में वृद्धि
(c) अकाल न पड़ना
(d) युद्ध कम होना।
उत्तर
(a) कम मृत्यु दर
प्रश्न 3.
बड़े शहरों में अधिक जनसंख्या का कारण है
(a) शिक्षा के अवसर
(b) उपलब्ध भौतिक सुविधाएँ
(c) अधिक आय के स्रोत
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
उत्तर
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
प्रश्न 4.
जनसंख्या घनत्व अधिक है____
(a) यू.एस.ए. में
(b) भारत में
(c) चीन में
(d) जापान में।
उत्तर
(c) चीन में
प्रश्न 5.
AIDS रोग फैलता है
(a) बैक्टीरिया से
(b) प्रोटोजोआ से
(c) वाइरस से
(d) फंगस से।
उत्तर
(c) वाइरस से
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
यौन संक्रमित रोगों के कारक होते हैं
(a) विषाणु
(b) जीवाणु
(c) प्रोटोजोआ
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
उत्तर
(a) विषाणु
प्रश्न 7.
भारत में जनसंख्या की गणना की गई थी
(a) सन् 1891
(b) सन् 1947
(c) सन् 1950
(d) सन् 1961.
उत्तर
(a) सन् 1891
प्रश्न 8.
निम्न में से जन्मदर को नियंत्रित करने की विधि
(a) TUD
(b) GIFT
(c) MIF
(d) IVEET
उत्तर
(a) TUD
प्रश्न 9.
एल्कोहॉल से सर्वाधिक प्रभावित अंग है
(a) यकृत
(b) सेरीब्रम
(c) सेरीबेलम
(d) हृदय।
उत्तर
(a) यकृत
प्रश्न 10.
विश्व की जनसंख्या वृद्धि दर है
(a) 2.4%
(b) 2%
(c) 3%
(d) 4%.
उत्तर
(b) 2%
2. रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए
1. मानव जनसंख्या का सांख्यिकीय अध्ययन ………………. कहलाता है।
2. माल्थस के अनुसार जनसंख्या में ………………. वृद्धि होती है जबकि खाद्य उत्पादन में ……………….. वृद्धि होती है।
3. किसी समष्टि में एक निश्चित अवधि में जीवों का आना और बाहर जाना ………………. कहलाता
4. शुक्राणु नली को काटकर बन्द करना ………………. कहलाता है।
5. स्थलीय जीवों के जनसंख्या घनत्व के लिये स्थान के क्षेत्रफल को ……………… से प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
6. जन्मदर एवं अप्रवासन जनसंख्या घनत्व में ………………. करते हैं।
7. संशोधित जन्मदर ……………… जन्मदर से अधिक होती है।
8. जनसंख्या आकार को नियन्त्रित करने वाले कारक को …………….. कहते हैं।
9. जैव सूचकांक = ( ………………. / मृत्युदर) x 1000.
10. बालिकाओं में बालकों की अपेक्षा ……………. परिपक्वता आती है।
11. भारत पहला देश है जिसने …………………… स्वास्थ्य देखभाल को ………………….में सामाजिक लक्ष्य के रूप में लाया।
12. RCH भारत में .. ……………. में लाया गया।
13. एम्नियोसेन्टेसिस में लिंग निर्धारण …………. गुणसूत्र के निरीक्षण द्वारा लाया गया।
14. प्रसव के ठीक बाद महिलाएँ …… अनार्तव (मासिक धर्म amoeriorrhoea) का अनुभव करती हैं।
15. LNG-20 ……………….. स्रावी IUD है।
उत्तर
- डेमोग्राफी
- बीजगणितीय, अंकगणितीय
- प्रवासन
- वैसेक्टोमी
- द्विविमा (m2)
- वृद्धि,
- अशोधित
- धनात्मक अवरोधक
- जन्मदर
- जल्दी
- प्रजनन, सन् 1951
- सन् 1997,
- लिंग
- स्तनपान संबंधी
- हॉर्मोन।
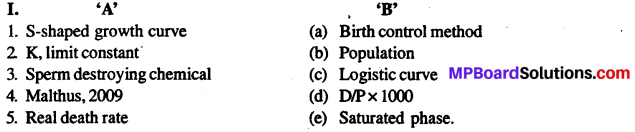
3. सही जोड़ी बनाइए
‘A’ – ‘B’
1. S-आकृति वक्र – (a) जन्म नियंत्रण विधि
2. kसीमा स्थिरांक – (b) जनसंख्या
3. शुक्राणु नाशक रसायन – (c) लॉजिस्टिक वक्र
4. माल्थस 2009 – (d) D/Px1000
5. वास्तविक मृत्युदर – (e) संतृप्ति अवस्था।
उत्तर
1.(c), 2.(e), 3.(a), 4. (b), 5.(d).
‘A’ – ‘B’
1. माल्थस – (a) कॉपर-टी
2 वैसेक्टोमी – (b) लिंग परीक्षण
3. ट्यूबेक्टोमी – (c) सेन्सस
4. जनगणना – (d) जनसंख्या पर निबंध
5. एम्निओसेण्टेसिस – (e) पुरुष
6. आई.ग.सी.डी. – (f) स्त्री या जनसंख्या नियंत्रण।
उत्तर
1.(d),2.(e),3. (1), 4.(c), 5.(b), 6.(a).
4. एक शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए
1. दो ऐसे कारण दीजिए जिनसे जनसंख्या अनियन्त्रित रूप से बढ़ जाती है।
2. IUCD का पूरा नाम लिखिए।
3. मानव जनसंख्या का अध्ययन क्या कहलाता है?
4. माला D और N में कौन-सा रासायनिक गर्भ-निरोधक पाया जाता है ?
उत्तर
- (i) कम उम्र में विवाह, (ii) शिक्षा
- इन्ट्रायूरिक कन्ट्रासेप्टिव डिवाइसेस
- डेमोग्राफी (Demography)
- एस्ट्रोजन एवं प्रोजेस्टीरॉन हॉमोन।
जनन स्वास्थ्य अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
परिवार नियोजन को अब किस नाम से जाना जाता है ?
उत्तर
परिवार नियोजन को अब “परिवार कल्याण” के नाम से जाना जाता है।
प्रश्न 2.
सेन्ट्रल ड्रग रिसर्च इन्स्टीट्यूट (CDRI) कहाँ अवस्थित है।
उत्तर
लखनऊ (उत्तरप्रदेश) में स्थित है।
प्रश्न 3.
कंडोम के उपयोग के कोई एक लाभ लिखिए।
उत्तर
कंडोम यौन संचरित रोगों से बचाव करता है।
प्रश्न 4.
हफ्ते में एक बार लेने वाली गर्भनिरोधक गोली का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
“सहेली”
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
IUCD काशब्द विस्तार बताइए।
उत्तर
इन्ट्रा यूटेराइन कॉन्ट्रासेप्टिव डिवाइस।
प्रश्न 6.
STD का सम्पूर्ण रूप लिखिये।
उत्तर
यौन संचारित रोग (Sexually Transmitted Diseases)।
प्रश्न 7.
विवाह की वैधानिक आयु स्त्री और पुरुष के लिए क्या सुनिश्चित है ?
उत्तर
स्त्री की आयु 18 वर्ष तथा पुरुष के लिए 21 वर्ष सुनिश्चित है।
प्रश्न 8.
दो STD के नाम लिखिए जो संदूषित रक्त से संचारित होते हैं।
उत्तर
(a) एड्स
(b) हिपेटाइटिस-BI
प्रश्न 9.
लैंगिक संपर्क से होने वाले कोई दो रोग बताइए।
उत्तर
- सूजाक (Gonorrhoea)
- सिफलिस (Syphilis)
प्रश्न 10.
HIV एवं AIDS का सम्पूर्ण रूप लिखिए।
उत्तर
- HIV—ह्यूमन इम्यूनोडेफीसिएन्सी वाइरस।
- AIDS- एक्वायर्ड इम्यूनोडेफीसिएन्सी सिन्ड्रोम।
प्रश्न 11.
ZIFT का पूरा नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर
युग्मनज अन्तः डिम्बवाहिनी स्थानान्तरण (Zygote Intra-fallopian Transfer)।
प्रश्न 12
पुरुष में नसबंदी की शल्य क्रिया का क्या नाम है ?
उत्तर
वैसेक्टोमी (Vasectomy)।
प्रश्न 13.
दो ऐसे कारण दीजिये जिनसे जनसंख्या अनियन्त्रित रूप से बढ़ जाती है।
उत्तर
रोगों का नियंत्रण, कृषि का विकास।
प्रश्न 14.
मानव जनसंख्या का अध्ययन क्या कहलाता है ?
उत्तर
डेमोग्राफी।
प्रश्न 15.
माला D और N में कौन-सा रासायनिक गर्भ निरोधक पाया जाता है ?
उत्तर
एस्ट्रोजन एवं प्रोजेस्ट्रॉन।
प्रश्न 16.
एम्नियोसेण्टेसिस विधि द्वारा किसका परीक्षण किया जाता है ?
उत्तर
भ्रूण का लिंग परीक्षण।
प्रश्न 17.
किसी इकाई क्षेत्रफल में पाई जाने वाली मानव संख्या कहलाती है ?
उत्तर
जनसंख्या घनत्व।
जनन स्वास्थ्य लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
परखनली शिशु कैसे प्राप्त किये जा सकते हैं ?
उत्तर
स्त्रियाँ जब गर्भधारण करने योग्य नहीं होती हैं, उस स्थिति में परखनली शिशु तकनीक का उपयोग किया जाता है। स्त्रियों के अनिषेचित अण्डाणु को ऐण्टिसेप्टिक स्थिति में निकाला जाता है। इस अण्डाणु को परखनली में लेकर शुक्राणु द्वारा निषेचन (Fertilization) की क्रिया कराते हैं । निषेचित अण्डाणु से विदलन क्रिया द्वारा 32 कोशिकीय अवस्था वाला भ्रूण बनता है, जिसे ब्लास्टोसिस्ट (Blastocyst) कहते हैं। इस 32 कोशिकीय भ्रूण का रोपण स्त्रियों के गर्भाशय में कर दिया जाता है जहाँ पर इस भ्रूण का अगला विकास होता है और शिशु बनता है जिसे ‘टेस्ट ट्यूब बेबी’ कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
गिफ्ट (GIFT) क्या है ?
उत्तर
GIFT-इसका पूरा नाम गैमीट इन्ट्रा फैलोपियन ट्रान्सफर (Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer) है । यह गर्भ निरोधन की आधुनिक तकनीक है। इस तकनीक में शुक्राणु कैथेटर (Catheter) में संगृहीत कर लिया जाता है। वाश स्विम तकनीक (Wash swim up technique) द्वारा शुक्राणुओं को अण्डाणु के पीछे कैथेटर में संगृहीत किया जाता है। यह सम्पूर्ण क्रिया स्त्रियों की फैलोपियन नलिका में होती है। निषेचन क्रिया शुक्राणुओं की संख्या कम होने से पूर्ण नहीं हो पाती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
ट्यूबेक्टोमी और वैसेक्टोमी को समझाइये।
उत्तर
ट्यूबेक्टोमी-इसमें स्त्री की अण्डवाहिनी को काटकर बाँध दिया जाता है। जिससे अण्डाणु गर्भाशय में नहीं आ पाते और निषेचन नहीं हो पाता। इसे ट्यूबेक्टोमी कहते हैं। यह परिवार नियोजन की एक विधि है। वैसेक्टोमी-यह भी परिवार नियोजन की एक विधि है जो पुरुषों द्वारा अपनाई जाती है। इसमें पुरुष की शुक्राणु नलिका को काटकर बाँध दिया जाता है जिससे शुक्राणु स्खलन के समय नहीं निकलते और निषेचन नहीं हो पाता। यह क्रिया वैसेक्टोमी कहलाती है।
प्रश्न 4.
एम्नियोसेण्टेसिस क्या है ?
उत्तर
एम्नियोसेण्टेसिस भ्रूण परीक्षण की एक तकनीक है जिसमें सर्जिकल सुई द्वारा मादा के गर्भाशय से एम्नियोटिक द्रव को शरीर से बाहर निकाला जाता है और एम्नियोटिक द्रव में उपस्थित फोयटस कोशा का संवर्धन किया जाता है और इसका गुणसूत्रीय परीक्षण करके निम्न बातों का पता लगाया जाता है
- गुणसूत्रीय असामान्यता, जैसे-डाउन सिण्ड्रोम, फिलोडेल्फिया सिण्ड्रोम एवं एडवर्ड सिण्ड्राम।
- उपापचयी अनियमितताएँ, जैसे- PKU, क्रिटेनिज्म, एल्केप्टोन्यूरिया।
- लिंग भ्रूण के परीक्षण में इसका उपयोग किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 5.
मानव जनसंख्या वृद्धि के सामाजिक कारण समझाइये।
उत्तर
मानव जनसंख्या वृद्धि के प्रमुख सामाजिक कारण निम्नलिखित हैं
- समाज का अशिक्षित होना ।
- निम्न सामाजिक स्तर का होना।
- समाज में विभिन्न प्रकार की कुरीतियाँ होना।
- विभिन्न प्रकार की सामाजिक मान्यताएँ ।
- कम उम्र में विवाह करना, क्योंकि उम्र के पूर्वार्द्ध में प्रजनन क्षमता अधिक होती है।
- निम्न सामाजिक स्तर के कारण मनोरंजन का अभाव होना।
- सामाजिक मान्यताएँ जैसे-पुत्र रत्न की प्राप्ति से मोक्ष मिलता है
- सामाजिक पिछड़ापन।