MP Board Class 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Circles Ex 10.2
Question 1.
Recall that two circles are congruent if they have the same radii. Prove that equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centers.
Solution:
We have a circles having its centers at O and O’ two equal chords AB and CD such that they subtend ∠AOB and ∠COD respectively at their centers, i.e. at O and O’.
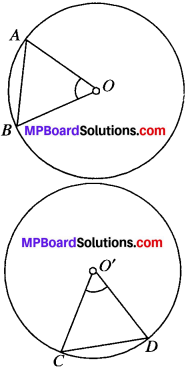
We have to prove that
∠AOB = ∠CO’D
Now, in ∆AOB and ∆CO’D, we have
AO = CO’ [Radii of the same circle]
BO = DO’ [Radii of the same circle]
AB = CD [Given]
∆AOB = ∆CO’D [SSS criterion]
Their corresponding parts are equal.
∴ ∠AOB = ∠CO’D
![]()
Question 2.
Prove that if chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centers, then the chords are equal.
Solution:
We have circles having their centers at O and O’, and its two chords AB and CD such that
∠AOB = ∠CO’D
we have to prove that
AB = CD
In ∆AOB and ∆COO’D, we have:
AO = CO’ [Radii of the same circle]
BO = DO’ [Radii of the same circle]
∠AOB = ∠CO’D [Given]
∆AOB = ∆CO’D [SAS criterion]
Their corresponding parts are equal, i.e.,
AB = CD.