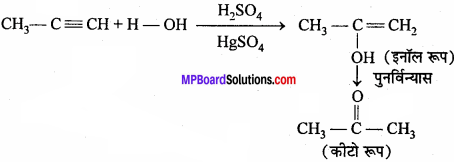
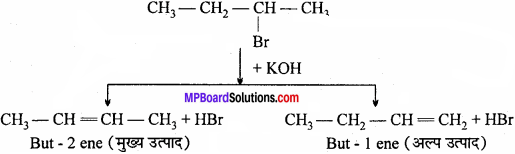
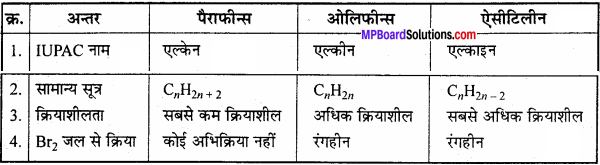
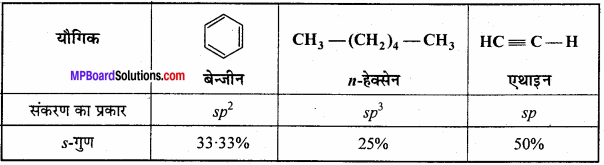
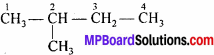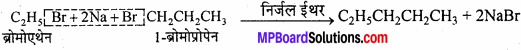MP Board Class 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Important Questions
Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which is used in DNA cultivation :
(a) Allesa
(b) Bloting technique
(c) PCR
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) PCR
Question 2.
Which is stained by Ethidium bromide :
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) Protein
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) DNA
Question 3.
(a) Bacteria
(b) Virus
(c) Yeast
(d) Plant cell.
Answer:
(a) Bacteria
![]()
Question 4.
Plasmids are:
(a) Circular
(b) Extra – nuclear
(c) Vector
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 5.
Resistant gene found in pBR 322 :
(a) Ampicillin
(b) Tetracycline
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 6.
Eco RI is :
(a) A virus
(b) A bacteria
(c) A restriction enzyme
(d) A cyanobacteria.
Answer:
(c) A restriction enzyme
Question 7.
Plasmid and cosmid are :
(a) DNA vector
(b) RNA vector
(c) A bacteria
(d) A virus.
Answer:
(c) A bacteria
Question 8.
When stablised, bio technical department by Indian government :
(a) 1948
(b) 1985
(c) 1986
(d) 1987.
Answer:
(c) 1986
Question 9.
Who gave the name plasmid :
(a) Jacob and Monod
(b) Laderberg
(c) Ruth senger
(d) Khurana.
Answer:
(b) Laderberg
Question 10.
What is vector DNA :
(a) Breaker of DNA
(b) Cutter of DNA
(c) Transfer in DNA in one
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Transfer in DNA in one
Question 11.
RI plasmid is obtained from :
(a) E. coli
(b) Yeast
(c) Agrobacterium
(d) Rhizobium.
Answer:
(c) Agrobacterium
Question 12.
pBR 322 is :
(a) Bacteria
(b) Virus
(c) Plasmid
(d) Recombinant protein.
Answer:
(c) Plasmid
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- …………….. is used for DNA staining.
- …………….. joins DNA segments.
- …………….. are small sized cloning vectors.
- In …………….. disturbed genes can be replaced by proper genes.
- Small segments of DNA are moved to …………….. pole through power steering.
- PCR is first discoverd by ……………..
- …………….. bacteria is responsible for tumor formation.
- …………….. enzyme is used in PCR.
- …………….. is used for gene transfer in dicot.
- …………….. is done by electrophorasis.
- …………….. DNA polymerase is also activeted in high temperature.
- Sticky ends of helpfull in the function of …………….. enzyme.
Answer:
- Ethidium bromide
- DNA ligase
- Cosmid
- Gene therapy
- Distant
- Kary muilis
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Taq polymerase
- Ti plasmid
- Isolation of DNA segment
- Taq DNA polymerase
- DNA Ligase.
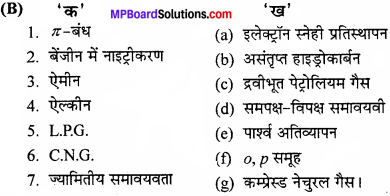
Question 3.
Match the followings:

Answer:
- (c)
- (a)
- (b)
- (e)
- (d)
![]()
Question 4.
Write the answer in one word/sentances:
- Biomolecule that destroy viruses and produce immunity in human being.
- Name of the first cloned animal.
- Where does CCMB situated?
- What kind of charge found in DNA segment?
- Name the technique in which seperate DNA segments.
- Name the molecular scissors.
- Write the full name of PCR.
- Which metal is used in gene gun method?
- Who discover the enzyme restriction?
- What is meant by GM organism?
- Write the full name of FEB.
Answer:
- Interferon
- Dolly
- Hyderabad
- Negative
- Bio power steering
- Re – striction, enzyme
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Tungstun or Gold
- Werner Arber
- Genetically Modified organism
- European Federation of Biotechnology.
Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which enzyme is used for isolation of target gene?
Answer:
Restriction endonuclease is used for isolation of target gene.
Question 2.
Which DNA polymerase is active in high tempereature?
Answer:
Taq DNA polymerase is active in high temperature.
Question 3.
Name three restriction endonuclease enzyme.
Answer:
- EcoRI
- Hind II
- Hind III.
Question 4.
Write full form of PCR. Which enzyme is used in?
Answer:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
- Taq DNA is used in PCR.
Question 5.
What is bacteriophage?
Answer:
Viruses, they are infected to bacteria are called Bacteriophage.
Question 6.
First recombinant DNA was formed in.
Answer:
In bacteria Salmonella typhimurium.
Question 7.
What is molecular scissors?
Answer:
Restriction enzyme is called molecular scissors.
![]()
Question 8.
Where does Hind II cuts the DNA molecule?
Answer:
It cuts the DNA molecule at a specific 6 base pair sequence.
Question 9.
What is the funtions of sticky ends?
Answer:
It helps enzyme DNA ligase.
Question 10.
Which type of charge found in DNA?
Answer:
Negative charge.
Question 11.
How does ethidium bromide cause DNA to fluorescence in electrophoresis?
Answer:
The most commonly used stain for detecting DNA is ethidium bromide.
Question 12.
What is electrophoresis?
Answer:
Electrophoresis is a technique used in laboratories in order to separate micromolecules based on size.
Question 13.
Give the function of circular DNA which is found in bacterial cell.
Answer:
It works as a vector.
Question 14.
Name the technique in which we should isolate DNA segment.
Answer:
Electrophoresis.
Question 15.
Name two antibiotic restriction gene which is found in plamid pBR 322.
Answer:
Ampicillin and Tetracycline.
![]()
Question 16.
What is plasmid?
Answer:
A plasmid is a small DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from a chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently.
Question 17.
What is DNA ligase?
Answer:
DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiesterbond.
Question 18.
What is C – DNA?
Answer:
C – DNA is a single stranded RNA. C – DNA is often used to clone eukaryotic genes in prokaryotes.
Question 19.
What is Ti – plasmid?
Answer:
Ti or tumour inducing plasmid is a plasmid that is a part of the genetic equipment that Agrobacterium tumifaciens use to transduce their genetic material to plants.
Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
From what you have learnt, can you tell whether enzymes are bigger or DNA is bigger in molecular size? How did you know?
Answer:
DNA is bigger in molecular size than enzymes. Because DNA is a long double stranded molecule which can go up to a few meters in length when stretched end to end but enzymes although variable in size, would still be smaller than the DNA.
Question 2.
What would be the molar concentration of human DNA in a human cell? Consult your teacher.
Answer:
The average molecular weight of a nucleotide in human DNA is 130.86. The molecular weight of human DNA will therefore be 6 x 109 nucleotides (based on the human genome project) x 130.86 = 784.56 x 109 gm/mol. The molar concentration of DNA can be calculated accordingly.
The molarity can be calculated as
Molar concentration = \(\frac { No. of molecules}{ Molecular weight }\)
Question 3.
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No, of eukaryotic cells do not have restriction endonucleases. All the restriction endonucleses have been isolated from the various strains oi bacteria arid they arc also named according to the genus and species of prokaryotes. The first letter of the enzyme comes from the genus and the second two letters come from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they have been isolated.
![]()
Question 4.
Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks ?
Answer:
Shake flask are used for growing microbes and mixing the desired materials on a small scale in the laboratory. However, the large-scale production of a desired biotechnological product requires large stirred tank bioreactors.
Besides better aeration and mixing properties, bioreactors have the following advantages:
- It has an oxygen delivery system.
- It has a foam control, temperature and pH control system.
- Small volumes of culture can be withdrawn periodically.
Question 5.
Name the scientist who discovered artificial DNA synthsizing method.
Answer:
The Nobel prize in physiology 1968 was awarded jointly to Robert W. Holley, Hargobind Khorana and M. Nirenberg for their interpretation of the genetic code.
Question 6.
What is gene manipulation or genetic engineering? Explain it.
Answer:
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification is the direct manipulation of an organisms genes using biotechnology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes and across species boundaries to produce improved organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA.
It may also mean extracting DNA from another organisms genome and combining it with the DNA of that individual. Genetic engineering is used by scientists to enhance or modify the characterstics of an individual organisms genetic engineering can be used to produce plants that have a higher nutritional value or can tolerate exposure to herbicides.
Question 7.
Write application of genetic engineering in crop improvement.
Answer:
Genetic engineering has placed an important role in improvement of plant production. There are following applications of genetics in plant improvement.
- Production of polyploidy crops.
- Hybridization : Hybridization is used to produce plants with, desirable traits.
- Transgenic plants : It helps a lot in improving the yield and quality of crops.
- Insect and herbicides resistant plants are engineered.
Question 8.
Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
Answer:
A recombinant DNA is made in the pachytene stage of prophase I by crossing over during meosis cell division. Recombination nodules are visible in synaptonemal complex in pachytene sub stage. Crossing over occurs in this time between chromatids than recombinant DNA is formed.
![]()
Question 9.
Can you think and answer how a reporter enzyme can be used to monitor transformation of host cells by foreign DNA in addition to a selectable marker?
Answer:
Reporter enzyme can differentiate recombinants from non – recombinants on the basis of their ability to produce a specific colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of the enzyme β – galactosidase. (MPBoardSolutions.com) This results into inactivation of the enzyme which is referred to as insertional inactivation. The presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue – coloured colonies if the plasmid in the bacteria does not have an insert. The presence of the insert results in insertional inactivation of β – galactosidase and the colonies do not produce any colour. These are identified as recombinant colonies.
Question 10.
Make a chart (with diagrammatic representation) showing a restriction enzyme, the substrate DNA on which it acts, the site at which it cuts DNA and the products it produces.
Answer:
The substrate DNA on which a restriction enzyme acts :
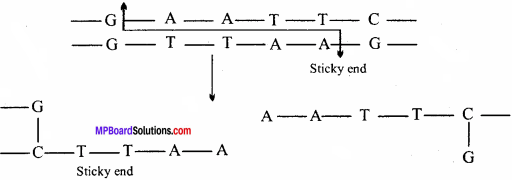
Question 11.
Write the uses of animal cloning.
Answer:
Applications (Uses) of Animal cloning :
- By this technique desired genotypes of any organism can be conserved.
- It produces organisms with better characters.
- Endangered plant and animal species can be conserved by this technique.
- Animals with good quality of milk and protein can be produced.
Question 12.
Write applications of genetic engineering in medical field.
Answer:
- The hereditary diseases like colour – blindness, haemophilia which are caused by recessive genes therapy.
- Substances like vitamins, hormones, amino acids and antibiotics can be synthe – sized in bacteria by introducing the genes which code these substances.
- Production of insulin : It is a medicine used for the treatment of diabetes. It is produced by gene splicing.
- Hepatitis – B vaccine : Hepatitis – B is a viral disease of liver, today this vaccine is prepared with the help of genetic engineering.
Question 13.
What do you understand by gene bank? What are its significances?
Answer:
Gene bank:
The institution which conserves the genes of the organisms is called as gene bank. The genetic material (DNA) found in the cells of organisms are conserved in gene banks. The best measure of conserving genes is to conserve endangered organisms. The tissues or cells of organisms are also conserved in gene banks.
Significance:
Genes stored in gene bank are used for the production of improved varieties of species and for scientific tests.
![]()
Question 14.
What do you understand by gene cloning? What are its significance?
Or
What is gene cloning? Write its importance.
Answer:
Gene cloning:
It is a process in which DNA of an organism is cut into smaller DNA fragments by the use of restriction endonuclease enzymes. Each DNA fragment is introduced into a bacterial, yeast, insect, plant or animal cell. The cells are grown on a suitable medium under suitable conditions. Each cell containing a particular DNA fragment multiplies to give rise a group of cells, all containingthe same foreign DNA.
These groups of cells are known as clone of cells. These copies of DNA resulting from the multiplication or recombinant DNA are called as cloned DNA and the process is known as gene cloning,
Significance:
- Useful hereditary characters are obtained by this process.
- Many diseases are cured by this process.
- Many medicines are synthesized with the help of this process.
- This process should also be used in eugenics.
Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Long Answer Type Questions
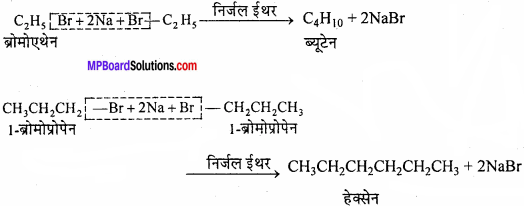
Question 1.
Collect 5 examples of palindromic DNA sequences by consulting your teacher. Better try to create a palindromic sequence by following base – pair rules.
Answer:
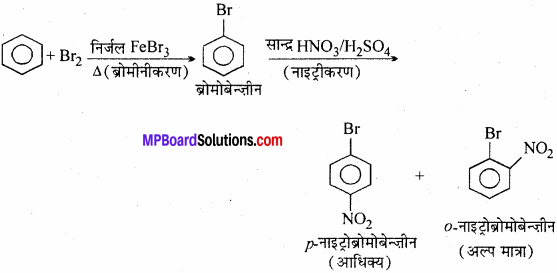
Some palindromic DNA sequences and the restriction enzymes which act on them are:
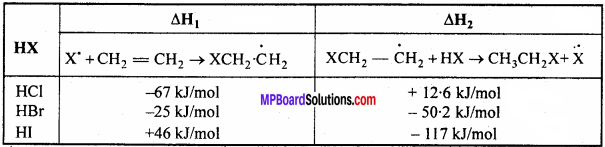
1. 5′ – AGCT – 3 Alul (Arthrobacter lutens)
3′ – TCGA – 5′
2. 5′ – GAATTC – 3’EcoRI (Escherichia coli)
3′-CTTAAG-5′
3. 5′- AAGCTT – 3’HindIII (Haemophilus influenzae)
3′ – TTCGAA – 5′.
4. 5′ – GTCGAC – 3’SalI (Streptomyces albus)
3′ – CAGCTG – 5′
5. 5′ – CTGCAG – 3’PstI (Providencia stuartii)
3′ – GACGTC – 5′.
Question 2.
Describe briefly the followings :
- Origin of replication
- Bioreactor
- Downstream processing.
Answer:
1. Origin of replication:
Origin of replication (ori) is a sequence on the chromosome, form where replication starts and any place of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells. This sequence also controls the copy number of the linked DNA. So, if we want to recover many copies of the target DNA it should be linked to the ‘ori’ site and should be cloned in a vector whose origin supports high copy number.
2. Bioreactor:
Bioreactor is large vessels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products, individual enzymes, etc., using microbial, plant, animal or human cells. (MPBoardSolutions.com) A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired production levels by providing optimum growth conditions of temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen, etc.
3. Downstream processing:
Downstream processes include separation and purification, formulation with suitable preservatives, etc. which are collectively referred to as downstream processing. Such formulation has to undergo through clinical trials as in case of drugs. Strict quality control testing for each product is also required. The downstream processing and quality control testing vary from product to product.
Question 3.
Explain briefly:
- PCR
- Restriction enzymes and DNA
- Chitinase.
Answer:
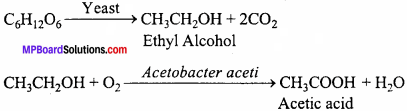
1. PCR:
PCR stands for polymerase chain reaction, a method of amplifying fragments of DNA. This method can make multiple copies of even a single DNA fragment or the gene of interest in a test tube. The reaction ntixture requires:
- Double – stranded DNA fragment (gene of interest).
- Primers – small chemically synthesized oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of this DNA.
- The special thermostable DNA polymerase (isolated from a bacterium, Thermus aquaticus), that does not denature and remain active even at high temperature.
Unwinding of two strands of DNA by heating the sample at 92 – 94°C helps primers to get positioned on the exposed nucleotides as per base pairing rules. DNA polymerase recognizes primes as ‘start’ tags and begins to extend the primes using the free nucleotides provided in the reaction and the genomic DNA as template. With each round of reactions, the DNA doubles.
2. Restriction enzymes and DNA:
These enzymes are used in genetic engineering to cut the large DNA molecule into smaller fi agments. When DNA from two different sources are cut by the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments have the same kind of’sticky – ends’ and these can be joined together (end – to – end) using DNA ligases. This new DNA created by joining fragments, from two different sources/genomes together is recombinant DNA.
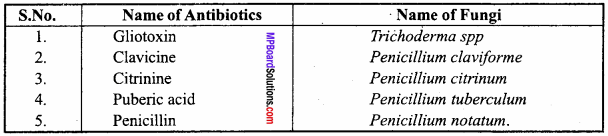
3. Chitinase:
Chitinase is an enzyme that breaks down chitin, a component of fungal cell wall. It is useful for isolating the fungal cell DNA.
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss with your teacher and find out how to distinguish between :
- Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA
- DNA and RNA
- Exonuclease and Endonuclease.
Answer:
1. Distinguish between Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA :
Plasmid DNA:
- Plasmid DNA is the naked double – stranded DNA which forms a circle
- It is associated with few proteins but contains RNA polymerase enzyme.
- They are smaller than the host chromosomes and can be easily sparated.
- It has no free ends.
Chromosomal DNA:
- Chromosomal DNA is a double – stranded linear DNA molecule.
- It is associated with large proteins.
- This DNA exists in relaxed and super – coiled forms and provides a template for replication and transcription.
- It has free ends represented as 3′ – 5′.
2. Distinguish between DNA and RNA :
DNA:
- It is mainly confined to the nucleus. A small quantity occurs in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
- Its quantity is constant in each cell of a species.
- It contains deoxyribos sugar.
- Its pyrimidines are adenine and thymine.
- The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of thymine. Also, the amount of cytosine is equal to the amount of guanine.
- It can replicate itself.
RNA:
- It mainly occurs in the cytoplasm. A small quantity is found in the nucleus.
- Its quantity varies in different cells.
- It contains ribose sugar
- Its pyrimidines are adenine and uracil. Adenine and uracil are not necessarily in equal amounts, nor are cytosine and
- guanine necessarily in equal amounts.
- It cannot replicate itself. It is formed by DNA. Some RNA viruses (paramyxo virus) can produce RNA from an RNA template.
3. Distinguish between Exonuclease and Endonucleases:
Exonucleases are nucleases which cut off the nucleotides from the 5′ or 3′ ends of a DNA molecule, whereas endonucleases are nucleases which cleave the DNA duplex at any point except at the ends.
Question 5.
Describe the useful and harmful effects of genetic engineering.
Or
Give importance and uses of DNA recombinant technique.
Or
Describe the Genetic engineering. Write the importance of it in human life.
Answer:
The branch of molecular genetics in which we can manipulate or transplant the genes or the genetic material or DNA according to our will is called gene manipulation or genetic engineering. The main objective of genetic engineering is to synthesize recombinant DNA (formed of the DNA segments of two different organisms).
The useful and harmful effects of genetic engineering are as follows :
(A) Useful effects or Utility:
1. Industrial uses:
Various types of substances such as vitamins, hormones and antibiotics can be-synthesized in bacteria by introducing genes that code these substances. In this way, bacteria can function as living factories for the synthesis of these substances. Humulin (human insulin) is synthesized by this method.
2. Treatment of diseases:
A new system of medicines, gene therapy may develop to cure several genetic disorders such as haemophilia, colour-blindness, etc. Also many inborn meta¬bolic disorders due to defective genes such as alkaptonuria, phenylketonuria, etc. can be cured.
3. Use in agriculture:
The genes for N2 fixation found in symbiotic bacteria Rhizo – bium leguminosarum or blue-green algae may be transferred to the major food crops, increases food production without using expensive fertilizers. Thus, we can save millions of rupees spent otherwise on fertilizers and manures to boost food production.
4. Changes in the structure and expression of genes:
We can obtain new plants, animals having traits tailored according to our will.
(B) Harmful effects:
- Normal harmless bacteria can be transformed into cancer causing forms thus ushering a new era of biological warfare.
- During experiments, it is quite possible to obtain super viruses for which we might have no defence.
- By the use of recombinant DNA, the bacteria may be made resistant to antibiotics.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the mechanism of recombinant DNA technology in genetic engineering by using plasmid as carrier of genes.
Answer:
Mechanism of Recombinant DNA Technology : Mechanism of recombinant DNA technology involves the following steps :
1. Isolation of desired gene or functional DNA segment:
From the eukaryotic cell desired DNA segment is isolated with the help of enzyme restriction endonuclease. Now this segment of DNA is known as foreign DNA.
2. Transfer of DNA segment from one organism to other:
Plasmid is an extra chromosomal circular DNA found mostly in bacteria over and above the main genome. When bacteria multiplies the plasmid DNA also multiplies along with the chromosomal DNA. These plasmids can be easily isolated from the bacterial cell with the help of restriction endonucleases. Plasmid serves as a vector for transferring the foreign DNA into a suitable recipient.
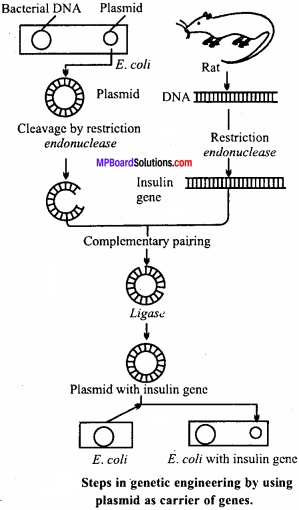
Foreign DNA and plasmid sliced with the help of endonucleases has free sticky ends through which they join each other with complementary base pairing with the help of enzyme DNA ligase. Thus, a recombinant DNA is formed,
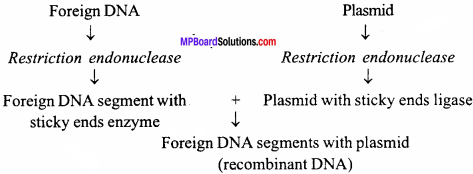
Such a recombinant DNA when introduced into a recipient bacterium (transformation), it replicates and expresses itself, within the bacterial cell, the recombinant DNA molecule replicates along with the endogenous DNA of the host cell and produces copies of cloned DNA. This process is known as gene cloning. The cloned recombinant DNA produced in large quantities’can be isolated, purified and analysed.
Question 7.
Describe the role of genentic engineering in artificial synthesis of human insulin.
Answer:
- Aldric and his supporter prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to the A and B chains of human insulin.
- Sticky ends were produced in the E.coli plasmid and the insulin gene by treating them both with the same restriction endonucleases.
- These two are then joined together by the enzyme DNA ligase.
- The bacteria are then grown in sterilised bioreactors in the appropriate growth medium.
- The chain A and B are produced separately, extracted and purified.
![]()
Question 8.
What is clone? Give its preparation, extraction and purification.
Answer:
An organism or cell or group of oiganisms, produced a sexually from an ancestor, to which they are genetical.
1. Gene cloning : Following steps are used by gene cloning :
(i) Preparation of gene:
DNA extracted from an organism, with the gene of interest is cut into gene size pieces with restriction enzyme.
(ii) Insertion into vector:
Bacterial plasmids are cut with the same restriction enzyme. Plasmids are small circles of DNA in bacterial cells that are naturally present in addition to the bacterial other DNA.
(iii) Transformation of host cells:
The recombinant plasmids are then transferred into bacteria using either electroporation. The plasmid are small enough to pass through the holes into the cells. However rather than using electricity to create holes in the bacterium, it is done by alternating the temperature between hot and cold.
The bacteria is grown on a culture dish and allowed to grow into colonies. All the colonies on all the plates are called a gene library.
2. Plant cloning:
Plant tissue culture is a method of propagation that has been sprouting in popularity throught as an altemative.to cloning. Plant can be cloned artificially using tissue culture. (MPBoardSolutions.com) Vegetative propagation works because the end of the cutting forms a mass of non specialized cells called a callus, the callus will grow divide and form various specialized cells eventually forming a new plant.
Question 9.
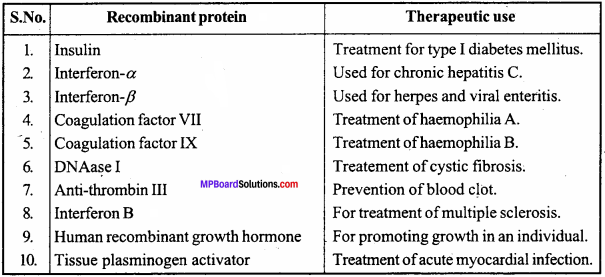
Can you list 10 recombinant proteins which are used in medical practice? Find out where they are used as therapeutics (use the internet).
Answer: