MP Board Class 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease
Human Health and Disease Important Questions
Human Health and Disease Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Syphilis is caused by :
(a) Tryponema
(b) Leptospira
(c) Pasturelia
(d) Vibro.
Answer:
(a) Tryponema
Question 2.
AIDS is caused by :
(a) Blood cancer
(b) H1N1
(c) Bacterium
(d)TMV.
Answer:
(b) H1N1
Question 3.
Which one is not cancer :
(a) Leukemia
(b) Glaucoma
(c) Carcinoma
(d) Sarcoma.
Answer:
(b) Glaucoma
![]()
Question 4.
First organic acid produced through the process of fermentation :
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Lactic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Butyric acid.
Answer:
(d) Butyric acid.
Question 5.
Vaccines produced by genetic engineering is :
(a) Hepatitis B
(b) Herpes virus
(c) Malarial vaccines
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Question 6.
The vitamins produced by activity of microbes are :
(a) Vitamin B2
(b) Vitamin B12
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Vitamin B2,B12 and Vitamin C.
Answer:
Question 7.
Enzyme used in manufacture of detergent is :
(a) Proteases
(b) Amylases
(c) Rennet
(d) Lipase.
Answer:
(d) Lipase.
Question 8.
Common human interferons are :
(a) Leukocytic interferon – α
(b) Fibroblastic interferon – β
(c) Immune interferon – γ
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(c) Immune interferon – γ
Question 9.
Which of the following is used in genetic engineering :
(a) DNA – polymerase
(b) Nuclease
(c) Restriction endonuclease
(d) RNA – polymerase.
Answer:
(b) Nuclease
Question 10.
Yeast is used in preparation of:
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Cheese
(c) Curd
(d) Ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
(d) Ethyl alcohol.
Question 11.
Germinating barley seeds are used in the preparation of:
(a) Cheese
(b) Wine
(c) Beer
(d) Lactic acid.
Answer:
(d) Lactic acid.
Question 12.
‘Syphilis’ is a sexually transmitted disease caused by :
(a) Treponema pallidum
(b) Leptospira
(c) Pasturelia
(d) Vibrio.
Answer:
(d) Vibrio.
Question 13.
The immunity obtained after the body has recovered from a disease is :
(a) Active immunity
(b) Passive immunity
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Passive immunity
![]()
Question 14.
Vaccination used for protection from Polio, Diptheria and Tetanus : (MP 2015)
(a) BCG
(b) DPT
(c) MMR
(d) STD.
Answer:
(b) DPT
Question 15.
AIDS test is known us : (MP 2017)
(a) Australian antigen
(b) ELISA
(c) Thyroid test
(d) pH test.
Answer:
(b) ELISA
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- AIDS is an example of ………………….. transmitted disease.
- Genes responsible for cancer are called …………………..
- ………………….. is known as blood cancer.
- ………………….. is first human made insulin by genetic engineering.
- Hepatitis B disease is caused by …………………..
- Asthma is a type of …………………..
- ………………….. is the transfer of human organs from a donor to a recipient.
- Nutrient deficiency disease is caused by …………………..
- Plague vaccine is discovered by …………………..
- ………………….. is the full name of AIDS.
- Gonorrhea disease is caused by …………………..
- L.S.D. is found by ………………….. fungi.
- Typhoid is caused by …………………..
- ………………….. is found in Klinefelter syndrome.
Answer:
- Sexually
- Oncogene
- Leukemia
- Humulin
- Virus
- Allergy
- Organ transplantation
- Less nutrition
- Dr. Haffkine
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
- Nesseria gonorrhoeae
- Clavicepspurpurea
- Saltnonalatyphi,
- One extra chromosme.
Question 3.
Match the followings:
I.

Answer:
- (d)
- (e)
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
- (f)
II.

Answer:
- (e)
- (c)
- (d)
- (b)
- (a)
Question 4.
Write answer in one word/sentences:
- Name the vector of malarial parasite.
- Give full name of HIV.
- Give the name of harmful chemical compound of tobacco.
- Give one example of sedative drugs.
- Name the disease which is transmitted from one person to another is called.
- When is AIDS day celebrated?
- Who prescribed the word AIDS first time?
- Name the branch that aims at improving the genetic quality of a human population.
- Write the name of virus which causes cancer.
- Give the name of one edible yeast.
- Name the disease which is treated by chemotherapy.
- What is the name of antiviral protein?
- Who gave the Germ theory of disease?
- What is the reason of syphilis?
Answer:
- Plasmodium
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Nicotine
- Benzodiazopines
- Infectious disease
- 1 December
- Edward Jenner
- Eugenics
- Oncogenic virus
- Ashby a gossypii
- Cancer
- Interferon
- Robert Koch
- Sexual contact.
Human Health and Disease Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are lymphoid organs?
Answer:
Lymphoid organs are certain organs, in which lymphocytes can differentiate and proliferate.
Question 2.
What is the name of drug which converts thoughts and feelings of human and causes fear?
Answer:
Psychedelic drugs.
Question 3.
Which disease is caused by transmission of HIV?
Answer:
AIDS.
Question 4.
Name the method which is used in the diagnosis of AIDS.
Answer:
ELISA Test.
![]()
Question 5.
In different parts of the country Chikungunya is clarified. Name the carrier of this disease.
Answer:
Chikungunya is spread through bites from A. aegypti mosquitoes.
Question 6.
Name the types of Immunity.
Answer:
Immunity is two types:
Innate immunity
Acquired immunity.
Question 7.
Where is Wuchereria found?
Answer:
Filarial worms Wuchereria is found in lymph vessels.
Question 8.
Name the types of tumours.
Answer:
Tumours are of two types : Benign and Malignant.
Question 9.
What harm does AIDS cause in humans?
Answer:
Immune power of the body is decreased by AIDS.
Question 10.
When inability to open the mouth because human chewing areca nuts in betel quid or its variants (gutkha) and jaw muscles become hard. Give the name of possible disease.
Answer:
Submucous fibrasis disease.
Question 11.
Name the full form of DPT.
Answer:
Diphtheria, Pertussis and Tetanus.
Question 12.
What is the side effects of cancer treatment?
Answer:
Hair falling and Anemia.
Question 13.
What is the full form of NAC?
Answer:
National AIDS Control Organization.
Question 14.
Which plant extract is called marijuana?
Answer:
Cannabis sativa.
Question 15.
Name combine form of the poppy, morphine, heroin, pethidine and methedrine.
Answer:
Meconium.
Question 16.
What is the second name of Mary Mallon?
Answer:
The second name of Mary Mallon is Typhoid Mary.
Question 17.
Name the cells which are multiplied by HIV when it enters the human body.
Answer:
Macrophages and helper T – lymphocytes.
Question 18.
Which body organs are affected by Pneumonia?
Answer:
Lungs and Alveolies are affected.
![]()
Question 19.
What is the confirmation test of Typhoid?
Answer:
Typhoid fever can be confirmed by Widal test.
Question 20.
Write the full form of LSD.
Answer:
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide.
Question 21.
Which viruses are responsible for cancer?
Answer:
Oncogenic viruses have cancer – causing viral oncogenes.
Human Health and Disease Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the various public health measures which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious disease ?
Answer:
The common preventive measures are as follows :
- Education – People should be educated about communicable diseases to protect themselves from such diseases.
- Vaccination – People should get vaccination on time to avoid infection.
- Sanitation – The sanitation condition should be improved to avoid infection from polluted water, contaminated food, etc.
- Eradication of vectors – The breeding places of vectors should be destroyed and adult vectors should be killed by suitable methods.
- Sterilisation – The patient’s surroundings and articles of use should be completely sterilised so as to reduce the chances of infection.
Question 2.
Explain what is meant by metastasis?
Answer:
Metastasis is the spread of cancerous cells through migration from one tissue to other tissue and organs resulting in formation of secondary tumour. Malignant tumour is a mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic cells. They grow rapidly and invade surrounding unaffected normal cells assues. Cells get sloughed off from such tumour and migrate to distant sites through blood. A new place of infection is thus, established and a new tumour is formed. This property is called metastasis.
Question 3.
Define the following:
- Immunity
- Vaccine
- Interferon
- Vaccination.
Answer:
1. Immunity : The capacity of any organism to fight with the disease and causal organisms is known as immunity. The immunity is due to B and T cells.
2. Vaccine : The chemical substances which protect our body by disease causing organisms are called vaccines.
3. Interferon : Interferon is an antiviral protein which is produced within animal cells due to stimulus produced after viral infection and which prevents the infection and multiplication of other viruses.
4. Vaccination : Vaccination is the process by which resistance against specific disease is created in any living organism.
Question 4.
Distinguish between Inborn and Acquired immunity.
Answer:
Differences between Inborn and Acquired immunity are:
Inborn immunity:
- This immunity is present by birth.
- It is a kind of active immunity.
Acquired immunity:
- This immunity helps in the expansion of life span of organism.
- This immunity is of both type active immunity and passive immunity.
Question 5.
What is auto – immunity?
Answer:
This is an abnormality which sometimes develop in the immune system of the body. Instead of destroying foreign molecules, it starts attacking the body’s own cells leading to serious consequence. Such diseases are called autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases depend on the type of self – antigen involved. If the self-antigens are R.B.Cs. then the body destroys its own R.B.Cs. resulting in chronic anaemia. When the self – antigen is a muscle cell, it results in destruction of its own muscles resulting in severe weakness, when the self-antigens are liver cells, it results in chronic hepatitis.
Question 6.
What is allergens? What cause the allergy to produce?
Answer:
Allergy is the condition of hypersensitivity of the body against certain substances or to a physical or chemical agent allergens. When antigen antibody reaction takes place in the body, it results allergy. Sufficient antibodies will not be produced in lacking of proper immune system. The allergens combine with the antibody bound mast cells, which causes the cell to burst releasing histamine. It results inflammatory responses in the body. Allergy may be caused by a medicine, cosmetics and other substances like, pollen grains, dust particles etc.
![]()
Question 7.
What is B – cells and T – cells? Explain it.
Answer:
B – lymphocytes or B – cells produce an army of protein called antibodies in blood. In response to pathogens, T – lymphocytes or T – cells help B – cells to produce antibodies, immune response are produced by these two types of lymphocytes.
Question 8.
Which types of diseases are protected by D.P.T. vaccine? Write the name of pathogens for each disease.
Answer:

Question 9.
What is eugenics?
Answer:
Eugenics:
The branch of biology which deals with the study of improvements of human race is called eugenics.
Importance:
- Development of selective reproduction in similar species
- Transfer of genetic materials in various organisms
- Development of GM food and GM crops
- Gene cloning
- Gene therapy, etc.
Question 10.
How vaccination is important in immunity?
Answer:
Vacc, nation is the process of introduction of weakened or inactivated pathogens or proteins (vaccine) into a person so, provide protection against the disease. Vaccination provides immunisation after a time gap. Due to immunisation our body produces antibodies against the vaccine and develops the ability to neutralise pathogens during actual infection. Nowadays different types of vaccine which gives in children like polio, tetanus, deptheria, pertusis, small pox etc.
Question 11.
What is drug addiction? What are its causes?
Answer:
Addiction is most common problem of our youths because they start to take different types of drugs and alcoholic beverages due to various reasons. It makes them habitual and dependent on them. Addiction is the habitual, psychological and physiological dependence on a substance or practice which is beyond voluntary control. A person who is habituated to a substance or a practice especially harmful one, is called drug addiction.
Its causes are:
- Curiosity
- Fun and Stimulation
- Will of doing more work
- Feeling of freeding
- Temporary escape from the life problems.
Question 12.
Write down the differences between sedative and tranquilizer.
Answer:
Differences between Sedative and Tranquilizer :
Sedative:
- These drugs depress the activities of central nervous system.
- A person sleeps more after taking excess drugs.
- Example: Barbiturates.
Tranquilizer:
- These drugs lessen tension and do not induce sleep.
- They do not sleep.
- Example: Phenothiazines.
Question 13.
Give the name of source of LSD. Give its effects also.
Answer:
LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide):
It is a crystalline amidated alkaloid which is obtained from the sclerotium of ergot fungus Claviceps purpurea, pathogen of ergot disease of rye. LSD causes horrible dreams, hallucinations, chronic psychosis and damage the brain. LSD was tried as treatment for alcoholism, neurosis and cancer patients. LSD brings about chromosomal and foetal abnormalities. Pathological condition caused by LSD abuse or by eating grain affected by ergot is called ergotism.
Question 14.
Describe the effect of alcohol on human body and society.
Answer:
The effects of alcohol on human body and society are :
- It effects the central nervous system.
- Persons is incapable of differentiating what is right and what is wrong.
- Taking excess of alcohol weakens heart, lungs, liver and other parts of the body.
- Pupil of eye expands on taking excess of alcohol.
- This increases the criminal activities in human beings.
Question 15.
Write withdrawal symptoms of addiction.
Answer:
Withdrawal symptoms from addiction:
When a drug dependent person fails to get the drug, he feels severe physical and psychological disturbances. These are called withdrawal symptoms. It includes tremors, nausea, vomiting, weakness, insomnia, anxiety run fits, decreased appetite, restlessness, elevated blood pressure, rapid heartbeat and epilepsy. These symptoms indicates that the body of addict person is unable to further use of intoxicant and they should stop it immediately.
Question 16.
Describe about the psychotropic drugs.
Answer:
These drugs effect on thinking power, mental processes, continuous use of these drugs, bring change in human behaviour, consciousness and perception. So, they are called mood altering drugs. The person becomes addict by the use of these drugs and cannot live without these drugs.
Question 17.
What are sedative? What are its types? Write its effect.
Answer:
Sedative:
Drugs which directly depress the brain and central nervous system are included in this group. They make the body free from anxiety and lethargic. The excessive use leads to sleep. Sleep causing drugs are also called Hypnotics.
It is of two types:
- Barbiturates and
- Benzodiazepines.
1. Barbiturates : It is a sedative and tranquilizer. It supresses brain’s activity and creates a feeling of relaxation, drowsiness and sleepiness.
2. Benzodiazepines : These drugs are commonly prescribed to help relieve anxiety in people who have anxiety disorder or another mental illness where anxiety is a symptom. They are very addictive.
![]()
Question 18.
What is interferon?
Answer:
Interferon:
Interferon is an antiviral protein which is produced within animal cells due to stimulus produced after viral infection and which prevents the infection and multiplication of other viruses.
Question 19.
How is a cancerous cell different from a normal cell?
Answer:
Cancer cell is different from normal cells in the sense that it:
- Looses the property of contact inhibition.
- Continues to grow and divide.
- Produces masses of cells called tumours.
Question 20.
In which way has the study of biology helped us to control infectious diseases?
Answer:
Study of biology helps us to diagnose the pathogen in following ways:
- The life – cycle of many pathogens studied.
- Alternate and reservoir hosts are known.
- The mechanisms of transmission of disease is known.
- The protective measures are suggested against disease and pathogens based an above studies.
- Suitable medicines against infectious disease are suggested.
- The preparation of vaccines against many pathogens also entitle the use and study ofbiology.
Question 21.
How does the transmission of each of the following diseases take place:
- Amoebiasis
- Malaria
- Ascariasis
- Pneumonia.
Answer:
- Amoebiasis : Through faecal-oral route.
- Malaria : Through the bite of female Anopheles mosquito.
- Ascariasis : Through taking contaminated food and water.
- Pneumonia : Droplets from the sputum of the patient.
Question 22.
What measure would you take to prevent water – borne diseases?
Answer:
To prevent water borne diseases, following measures are required:
- Drinking water should he clean, free from contamination. This could be achieved by filtration, boiling or sedimentation and chemical treatment of water.
- Water resources/ reservoirs should be periodically de – contaminated / disinfected.
- Water should not be allowed to stand for long to become breeding pools.
- Standards practices of hygiene should be strictly maintained in public catering.
Question 23.
Discuss with your teacher what does ‘a suitable gene’ mean, in the context of DNA vaccines.
Answer:
The term ‘suitable gene’ refers to that specific segment of DNA which forms immunogenic protein, such genes can be cloned and then integrated with vector for introducing into an individual to be immunised for certain disorder producing a particular vaccine against the pathogens.
Question 24.
Name the primary and secondary lymphoid orgAnswer:
Answer:
Primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and thymus. Secondarylymphoid organs are spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix
Question 25.
The following are some well known abbreviations, which have been used in this chapter. Expand each one to its full form:
- MALT
- CMI
- AIDS
- NACO
- HIV.
Answer:
- MALT : Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue.
- CMI : Cell Mediated Immunity.
- AIDS : Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
- NACO : National AIDS Control Organisation.
- HIV : Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
Question 26.
How are allergies related to the body’s immune system?
Answer:
Allergy is the condition of hypersensitivity of the body against certain substances or to a physical or chemical agent allergens. When antigen antibody reaction takes place in the body, it results allergy. Sufficient antibodies will not be produced in lacking of proper immune system. The allergens combine with the antibody bound mast cells, which causes the cell to burst releasing histamine. It results inflammatory responses in the body. Allergy may be caused by a medicine, cosmetics and other substances like pollen grains, dust particles, etc.
Question 27.
Differentiate the following and give examples of each:
- Innate and Acquired immunity.
- Active and Passive immunity.
Answer:
1. Differences between innate and acquired immunity:
Innate immunity:
- It is present from birth and is inherited from parents.
- It is non – specific.
- The various physical, physiological cellular and cytokine barriers are the basis of innate immunity.
- The innate immunity remains throughout life.
Acquired immunity:
- It is not present from the birth.
- It is pathogen specific.
- The memory cells formed by B and
- T – cells are the basis of acquired immunity.
- The aquired immunity can be short – lived or life long.
2. Differences between active and passive immunity:
Active immunity:
- It is developed due to contact with pathogen or its antigen that leads to production of antibodies in the host body.
- It has no or only few side effects.
- It is slow but long lasting.
- It takes time to develop its response.
Passive immunity:
- It is developed when readymade antibodies are injected into the body.
- It may cause a reaction.
- It is fast but lasts only for few days.
- It is used when the immune response has to be faster.
Question 28.
Draw a well – labelled diagram of an antibody molecule.
Answer:
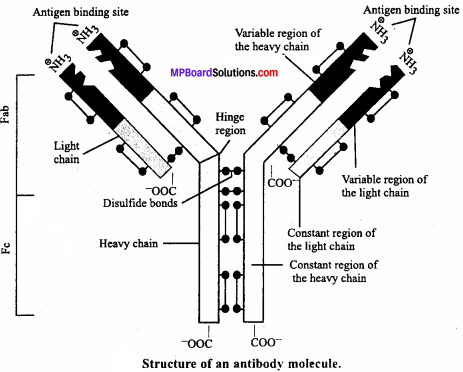
Human Health and Disease Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is cancer? Write the names of two types of cancer and causes of cancer.
Answer:
Cancer:
When tumours are formed due to unorganized and uncontrolled division of cell, then it is called cancer.
Types of Cancer:
Cancer is not a single disease but a complex of many diseases. Today about 200 distinct types of cancer have been recognized. These are grouped into main types:
- Carcinomas
- Sarcomas
- Lymphomas and
- Leukemias.
1. Carcinomas:
The tumours which are made up of epithelial cells of ectodermal or endodermal origin are called carcinomas, example solid tumours in nerve tissues and in tissues of body surfaces or their attached glands. It includes breast, skin, cervical and brain carcinomas.
2. Sarcomas:
The tumours which are made up of connective tissue cells of mesodermal origin are called sarcomas, example solid tumours growing from connective tissues, bones, cartilages and muscles. It constitutes only about 2% of human cancers.
3. Lymphomas:
Cancers in which there is excessive production of lymphocytes by the lymph nodes and spleen are called lymphomas, example Hodgkin’s disease. It constitutes about 5% of human cancers.
4. Leukemias:
It is cancer of blood characterized by excessive number of W.B.Cs. (or leucocytes) in the blood (neoplastic growth). These cells invade into bone – marrow, lymph nodes and the spleen. It is more frequent in the children of age group 5 to 7 years but it can occur at any age. Acute leukemia causes death. It has no sure remedy. It constitute about 4% of human cancers.
Causes of Cancer:
Physical and Chemical factors which cause cancer are called as carcinogens. Main causes of cancer are as follows:
- Smoking causes mouth and lung cancer.
- Radiations, such as X – rays, ultraviolet rays and other ionizing radiations cause cancer.
- Viruses may cause cancer.
- Chemical substances such as Nicotine, caffeine, products of combustion of coal and oil, polycyclic hydrocarbons may cause cancer.
Symptoms of Cancer:
There are some symptoms of cancer which must be kept in mind:
- Any lump or thickening in the tissue especially in breast, tongue or lip.
- A wound that is not healing.
- Any sudden change in mole or warts.
- Persistent indigestion and difficulty in swallowing things.
- Regular cough and hoarseness in sound.
- Unusual weight loss.
- A change in bowel habits.
- Any ulcer that does not get well.
- Bleeding in vagina at times other than the menstruation.
- Non – injury bleeding from the surface of the skin, mouth or any other opening of the body.
![]()
Question 2.
What is AIDS? Write down its causes, transmission and symptoms.
Or
Write the name, two symptoms and important preventive measures of today’s dreadening disease spread through blood transfusion.
Or
Where is AIDS reported for the first time ? Describe the causes, method of transmission and control measures of this disease.
Answer:
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) disease is discovered for the first time in America in the year 1981.
Causes of Disease:
This disease is caused by the infection of a vims known as HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Vims).
Transmission:
It is transmitted through sexual contact, homosexuality, contaminated needles, blood transfusion, dmgs, artificial insemination and organ transplantation etc.
Symptoms of Disease:
It is characterized by showing swollen lymph nodes, fever, loss of weight. The person loses the immunity against the infection. In this disease, the number of helper T-cells are reduced.
Treatment:
No suitable drug is available so far against this disease. Only anti – viral cells may increase in the number by immune stimulation method.
Control:
The following measures are advised to prevent spreading of disease:
- Providing health education and explain the hazardous effects of AIDS.
- Do not reutilize the used syringe. Throw it away or destroy it.
- The blood of donor person and organs of transplantation like kidney, liver, cornea of eyes, growth hormones would be carefully examined before use.
- Sexual contact with many people must be avoided.
Question 3.
What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency in the immune system of the infected person ?
Answer:
The virus enters macrophages after getting into the body of individual where RNA forms viral DNA by reverse transcription. The viral DNA gets incorporated in the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viral copies. The newly produced virus particles attack helper T – cells and thus, the number of T-cells decrease. Since, the helper T-cel Is are essential for functioning of immune system, the person suffers from various diseases due to dificient immune system.
Question 4.
List the harmful effects caused by alcohol/drug abuse.
Answer:
The adverse effects of drugs and alcohol abuse are:
- Low to moderate doses can cause reckless behaviour, vandalism and violence depression, fatigue, weight fluctuations, etc.
- Excessive doses of drugs may lead to coma and death due to respiratory failure, heart failure or cerebral haemorrhage.
- A combination of different drugs or alcohol mixed with drugs, results in overdosing and even death.
Question 5.
Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
Answer:
Yes, friends can influence one to take drugs and alcohol. A person can take the following steps for the prevention of themself against drug abuse:
- By avoiding under peer pressure as everyone has their own field of interest which should be respected by there teachers and family. One should not experiment with alcohol for curiosity and fun.
- Avoid the company of friends who take drugs.
- Seek help from parents and peers. A child should not pushed beyond his/her threshold limits.
- Take proper knowledge and counselling about drug abuse. Devolve your energy in other extra-curricular activities.
- Seek immediate professional and medical help from psychologists and psychiatrists if symptoms of depression and frustration become apparent.
- Get rid of the problem completely and lead, perfectly normal life by increasing their will power.
Question 6.
Why is that once a person starts taking alcohol or drugs, it is difficult to get rid of this habit? Discuss it with y.our teacher.
Answer:
It is difficult to get rid of this habit, because these substances are addictive and one starts having unpleasant feelings or withdrawal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, shivering, muscle twitching, excessive perspiration, muscular and abdominal cramps. Mind loses control and all one can think of is taking the addictive substance. That is why resisting the temptation/pressure for the first time is the only way to avoid getting into the addictive habit and committing a slow suicide.
![]()
Question 7.
In your view what motivates youngsters to take to alcohol or drugs and how can this be avoided ? .
Answer:
Probably the ‘motivation’ comes from:
- Curiosity to experience the effect.
- Foolishness to try to prove oneself in front of the peers.
- Wrongly taking it as an excuse to escape from reality.
- Wrong thinking that one time ‘try’ is not going to do any harm.
But youngsters who are strong willed, who understand its ill effects and who are satisfied with their academic and other achievements and who don’t want to waste their precious life, don’t fall for this kind of ‘Motivation’.
Question 8.
What is immune system? Describe various components of immune system of man and its role.
Answer:
The Immune System or Immunity (A Specific Defence Mechanism):
The ability of an organism to resist the pathogen Or development of disease resistance is known as immunity and the study of immunity is called immunology, while the infected person with no disease is called immune. The most peculiar characteristic of immune system is that it can differentiate the self (body’s own cells) and non-self (foreign microbes).
Cells of the Immune System:
Lymphocytes are the type of W.B.Cs. or Leucocytes which are chief cells of immune system of body. There are two types of lymphocytes that promote cellular immunity and humoral immunity. Both of these types of lymphocytes are derived from lymphocyte stem cells in the bone – marrow in the embryo.
1. T – cells of lymphocytes:
These cells eventually migrate to the lymphoid tissue. Before doing so, the lymphocytes first migrate to thymus gland and are processed in the gland, hence called T – lymphocytes or T – cells. These are responsible for cellular immunity. There are following types of T – cells :
(i) Killer T – cells:
Killer T – cells or KT – cells directly attack and destroy antigen. In doing so, they move to the site of invasion and produce some chemical that attracts and stimulate phagocytes to feed more voraciously on antigen.
(ii) Helper T – cells:
Helper T – cells or HT – cells stimulate B – cells to produce more antibody.
(iii) Suppressor T – cells:
Suppressor T – cells or ST – cells keep entire immune system to attack on the own body cell.
Mode of action of T – cells to antigens:
T – cells are antigen specific (each T – cell recognizes a specific antigen and different types of T – cells are stimulated by different types of antigens). When a T – cell is stimulated by specific antigen, T – lymphocytes divide rapidly to form a clone of T – cells called lymphoblasts. T – cells live for 4 – 5 years or even longer. T – cells of a clone are morphologically similar but they perform different functions. According to their functions, their are three classes of T – cells, i.e., killer T – cells, helper T – cells and suppressor T – cells.
2. B – cells of lymphocytes:
The other population of lymphocytes which produces antibodies are processed in some unknown area, possibly liver or spleen. This population was firstly discovered in birds in which processing occurs in the bursa of fabricus, a structure not found in mammals. For this reason they are called as B – cells or B – lymphocytes. They are responsible for humoral immunity.
Mode of action B – cells to antigens:
Once a B – cells is activated by the antigen, it multiplies very fast and forms a clone of plasma cells. Most of these produce antibody at a tremendous rate of 2,000 molecules per second. These antibodies circulate in the lymph to fight the antigen. So, forming humoral immune system. B – cells are short lived and are replaced by new cells from the bone – marrow after every few days.
The capacity of B – cells to produce specific antibodies is acquired during its development and maturation.
![]()
Question 9.
Describe the harmful effects of tobacco smoking.
Answer:
Effect of chewing and smoking tobacco:
The chewing and smoking of tobacco affects us in the following ways:
1. It affects the route of the transfer of nerve impulse and central nervous system. In low concentration nicotine stimulates conduction of nerve impulse but long – term use reduces the activity of nervous system.
2. Nicotine stimulates the release of adrenaline leading to high blood pressure. Increased blood pressure due to smoking enhances the risk of heart diseases.
3. It retards foetal growth in pregnant women.
4. The smoke of tobacco contains aromatic hydrocarbons and tar along with carbon monoxide (CO). Carbon monoxide reduces oxygen carrying capacity of the blood. Hydrocarbons induces cancer. Due to these reasons tobacco chewing person suffer from mouth cancer and smokers suffer from throat and lung cancers.
5. The use of tobacco in any form stimulates the secretion of saliva and gastric juices due to which acidity is increased in stomach. It may cause ulcers in the wall of stomach. The absorption capacity of mucous membrane of stomach also decreases. Thus, person get suffered from hyponutrition, loss of appetite and constipation.
6. Smoking also affects the activity of kidneys.
7. Nicotin relaxes the muscular and skeletal tissues due to which person becomes weak.
8. Long – term smoking may also cause diseases like bronchitis and emphysema.
9. Smoking reduces immunity of the body.
10. Lips of smokers may become dark coloured. Teeth and fingers get stained. The breath becomes foul.
MP Board Class 12th Biology Important Questions