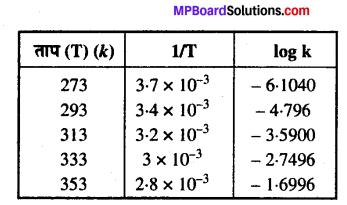
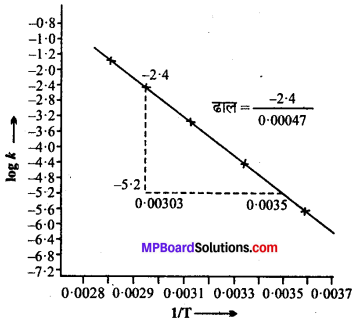
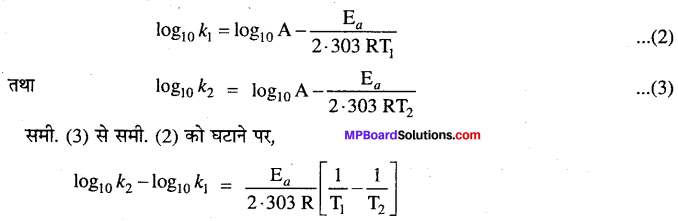
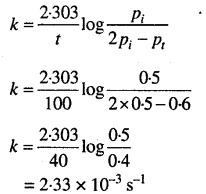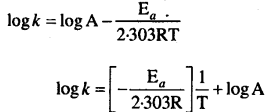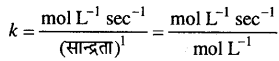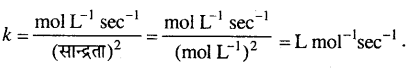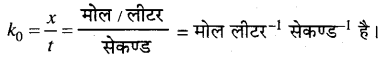MP Board Solutions for 12th General English Reading Comprehension Unseen Passages Questions and Answers aids you to prepare all the topics in it effectively. You need not worry about the accuracy of the Madhya Pradesh Board Solutions for 12th English as they are given adhering to the latest exam pattern and syllabus guidelines.
You Can Download MP Board Class 12th English Solutions Questions and Answers Notes, Summary, Lessons: Pronunciation, Translation, Word Meanings, Textual Exercises. Enhance your subject knowledge by preparing from the Chapterwise MP Board Solutions for 12th English and clarify your doubts on the corresponding topics.
MP Board Class 12th General English Unseen Passages
Kick start your preparation by using our online resource MP Board Solutions for 12th General English Unseen Passages Questions and Answers. You can even download the Madhya Pradesh Board Class 12th English Solutions Questions and Answers for free of cost through the direct links available on our page. Clear your queries and understand the concept behind them in a simple manner. Simply tap on the concept you wish to prepare in the chapter and go through it.
Comprehension’ शब्द
‘Comprehend’ से बना है। ‘Comprehend’ का अर्थ ‘समझना’ होता है। Comprehension Test का अभिप्राय विद्यार्थी को अंग्रेजी के दिए हुए passage के अर्थ को समझने की योग्यता की परीक्षा लेना है। अत: अंग्रेजी का कोई अपठित passage देकर कुछ प्रश्न पूछे जाते हैं जिनके उत्तर उस passage में से ही देने होते हैं। Passage के अर्थ को समझ लेने पर प्रश्नों के उत्तर देना कठिन नहीं होता है। अतएव passage को ध्यानपूर्वक पढ़कर ही उत्तर देना चाहिए।
सभी उत्तरों का विद्यार्थी के अपने शब्दों में होना आवश्यक नहीं है।
“Students can obtain the answer to (several of the) questions by copying the relevant part or parts of the text.”
इस प्रश्न को ऐसे हल करें :
- Express yourself in a clear and coherent manner. Your language should be simple and correct, while your expression need be forceful.
अपने विचारों को सुस्पष्ट एवं सुसम्बद्ध विधि से प्रकट करो। तुम्हारी भाषा सरल और सही हो, जबकि अभिव्यक्ति प्रभावशाली। - Use small and simple sentences.
छोटे तथा साधारण वाक्यों का प्रयोग करो। - You can state your answer in more than one sentence as long as you keep to the point.
तुम जब तक अपने सन्दर्भ की सीमा में रहो, अपने उत्तर को एक से अधिक वाक्यों में लिख सकते हो। - The answer should be neither too long nor too short.
उत्तर न तो ज्यादा लम्बा होना चाहिए न ज्यादा छोटा। - Do not add any new ideas of your own unless you are asked to do so.
जब तक निर्देशित न किया जाय तब तक कोई नया मत या विचार अपनी तरफ से मत जोड़ो। - Read the passage carefully two or three times.
गद्यांश को दो या तीन बार पढ़ो। - Try to grasp the general sense of the passage.
गद्यांश का सामान्य अर्थ ग्रहण करने की कोशिश करो।
Solved Examples
Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions given below them:
1. The Jataka Stories recount the many previous births of the Buddha in human and animal lives. In all there are 547 stories, originally told by the Buddha to his disciples. They were written down in Pali Language around 400 B.C. and absorbed into the Buddhist Canon not long ago after his death. The stories show the progression of his lives through many incarnations, gradually acquiring the wisdom, selflessness and thoughtfulness which eventually lead to enlightment. In each birth he performed some meritorious deed to bring him spiritual progress. Here is one of his stories.
A hare once lived in the forest with his animal friends, the jackal, the otter and the monkey. The animal respected the hare as he was wise and gentle. One day he said that they should all fast and give whatever food they gathered to whoever needed it. So the monkey found ripe mangoes, the jackal found a Lizard and a pot of milk and the otter found a fish. But the hare could not find any food and vowed that if anyone is hungry, he would offer him his own body. His tremendous vow was heard by the earth herself, who told Sakka, Lord of the devas. He decided to test the hare.
Sakka entered the forest disguised as a beggar and asked hare for food. Please eat my body’ the hare replied without hesitation.
So Sakka built fire and the hare willingly ran into the flames. Feeling no pain, he rose up to heaven. In gratitude, Sakka drew an image of hare on the moon for everyone to see and remember the hare’s selfless sacrifice. [2016]
Unseen Passage For Class 12 Mp Board Questions:
(A) Jataka stories are related to the previous incarnations of
(i) Lord Krishna (ii) Mahaveer (iii) Dattatraya (iv) Gautam Buddha.
(B) The stories are written in Language.
(i) Sanskrit (ii) Pali (iii) Prakrit (iv) Awadhi.
(C) The wise animal was
(i) Monkey (ii) Otter (iii) Hare (iv) Jackal.
(D) Sakka entered the forest in disguise of
(i) a beggar (ii) a monk (iii) a fakir (iv) a peasant.
(E) The Jataka Stories contain stories. [1]
(i) 547 (if) 457 (iii) 754 (iv) 745.
(F) Word previous relates to [1]
(i) Present (ii) Past (iii) Future.
(G) Monkey found as food to be given to needy person. [1]
(i) Bananas (ii) Guavas (iii) Ripe mangoes (iv) Oranges.
(H) The Jataka stories were written in [1]
(i) 400 A.D. (ii) 400 B.C. (iii) 420 A.D. (iv) 420 B.C.
(I) What reward did Sakka give to hare for his self-sacrifice? [2]
(J) What do the Jataka Stories show? [2]
Answers:
(A) (iv)
(B) (ii)
(Q) (ii)
(D) (i)
(E) (i)
(F) (ii)
(G) (iii)
(H) (ii)
(I) Sakka drew an image of hare on the moon for everyone to see and remember the hare’s selfless sacrifice.
(J) The Jataka stories show the progression of Buddha’s lives through many incarnations gradually acquiring the wisdom, selflessness and thoughtfulness which eventually lead to enlightenment.
2. The “Pench National Park” [Mogliland] is one of famous National parks in the world. It is in between Nagpur and Jabalpur city. There is also the center point of India. It is on the road National Highway 07. We can reach Kanyakumari from Kashmir by this road. Park is also known as “Mogliland” because of the “Jungle boy”-“Mogli” named later. The history of Seoni district and gazette says about a “miracle” which is related with the Jungle boy and the herd of dangerous wild animals. The boy was^born at Chorgarthiya village now it is very near to the park in Seoni district, M.P. One day when the little innocent boy of [1]8 months was a sleeping out side of the hut, her mother left him and went to her fields. The herd of animals came there and lifted the innocent for their dinner. With the help of history and gazette of Seoni and friends to “Rudyard Kipling”, an Australian novel writer, wrote the famous “Jungle book” novel. Its main script based on Mogli’s true life.
Mogli the hero of the famous Jungle book grew up among .dangerous herd of animals. He ate, ran, jumped, made sounds and helped them with human skills. We have seen in a Television serial in 1989. History says he lived with animals round about 24 years. We know very well that human has great affection to several animals but it is “One and only “miracle” in the modem world” that “animal brought up a human”. Why they give time to grow up? Why did they not eat the boy? It is wonderful. So Pench National Park called the Mogliland because he passed his life and acted like animal in the area. MP’s Ex. Forest Minister, Lt. Harbansh Singh who was very devoted to the children of schools and education, worked a lot for Mogliland and started a program named ‘Mogli Utsav’ for school students of MP in [2002].
“Save animals life”. [2015]
Mp Board English Unseen Passage Questions:
(A) Gazette means:
(i) a book (ii) question paper (iii) government documents (iv) paper for printing.
(B) Mogliland is situated between Nagpur and city.
(i) Indore (ii) Jabalpur (iii) Gwalior (iv) Bhopal.
(C) Write the verb form of the word ‘wonderful’:
(i) Wonder (ii) Wonderful (iii) Wander (iv) Wonderfully.
(D) Pench National Park is known as :
(i) Mogliland (ii) Landmark (iii) England (iv) Island.
(E) “Rudyard Kipling,” wrote a novel its name is :
(i) A history (ii) The Jungle book (iii) Paikbook (iv) Book of Australia.
(F) Who had lifted the innocent child Mogli?
(i) Tiger (ii) Dogs (iii) A herd of animals (iv) Fox.
(G) Select the correct alternative that is the opposite of the word ‘pet’
(i) tame (ii) wild (iii) loving (iv) homely.
(H) Who started Mogli Utsav? Who was forest Minister then?
(i) Harbans Singh (ii) Randheer Yadav (iii) Mr. V. Niranjan (iv) Deepak Saxena.
(J) Who is the hero of the famous novel ‘The Jungle Book’?
(K) Why is “The Pench National Park” called Mogliland?
Answers:
(A) (iii)
(B) (ii)
(Q (i)
(D) (i)
(E) (ii)
(F) (iii)
(G) (ii)
(H) (i)
(I) The hero of the famous novel ‘The Jungle Book’ is Mogli.
(J) The Pench National Park is called Mogliland because Mogli passed his life and acted like animal in that area.
3. How did man discover salt? We are not sure. Perhaps, the cattle of Stone Age tribesmen found and fed on* salt licks or salt rocks. Their masters may have carried pieces of the salt rock to their caves. Salt springs were found to provide a more constant supply of salt. Villages grew around these springs. Man cut down trees for fuel for evaporating water to obtain salt. In China, the early human settlements were near salt pans on the Yellow River. Everywhere in the world, salt production has been going on for thousands of years. The ancient Greeks and Romans included salt in the offerings they made to their gods. The preservative quality of salt made it a specially fitting symbol of enduring fidelity. The word salt was used in phrases conveying high esteem and honor, in ancient and modem languages. In English, the expression, “the salt of the earth”, describes a person greatly respected by the community.
It was considered a prestigious item of commerce and civilizations flourished because of it. The sea has always been man’s most important source of salt supply. When oceans recede, salt ponds and salt marshes are left behind.
The Romans were famous roadbuilders. One of their roads called the Salt Route, built around 400 B.C. exists even today. In those days, salt from Rome was carried along this road to central Italy. The early Egyptians were supplied with salt from swamps at the mouth of the Nile. [2014]
Mp Board Class 12 English Book Solution Questions:
(A) What is the meaning of ‘prestigious’? [1]
(i) having respect (ii) religious (iii) business (iv) necessary.
(B) The noun form of the word‘describe’ is : [1]
(i) describe (ii) description (iii) described (iv) redescribe.
(C) The opposite of the word ‘modem’ is : [1]
(i) new (ii) early (iii) ancient (iv) recent.
(D) The of the tribesmen may have carried salt to their caves. [1]
(i) servant (ii) master (iii) friend (iv) neighbour.
(E) The constant supply of salt was made by : [1]
(i) salt springs (ii) rivers (iii) forests ‘ (iv) early man.
(F) The early Egyptians used to get salt from swamps at the mouth of [1]
(i) Nile river (ii) sea (iii) Yellow river (iv) salt rocks.
(G) In those times, around the springs, grew. [1]
(i) cities (ii) villages (iii) roads (iv) forests.
(H) ‘The salt of the earth’ means : [1]
(i) a person greatly respected in the society (ii) the salt that we get from salt springs (iii) the salt offered to gods (iv) a person not respected in the society.
(I) Why do you think salt is very important since early days? Mention two points. [2]
(J) How was the ‘Salt Route’ important for the Romans? [2]
Answers :
(A) (i)
(B) (ii)
(C) (iii)
(D) (ii)
(E) (i)
(F) (i)
(G) (ii)
(H) (i)
(I) Salt is very important since early days because :
(i) the cattle of Stone Age tribesmen were fed on salt licks,
(ii) salt has preservative quality.
(J) The ‘salt route’ was important for the Romans because in those days salt from Rome was carried along this road to central Italy.
4. Garbage is a great environmental hazard. It comes from various sources used paper, tiffin packings, plastic bags, ice-cream wrappers, bottle caps, fallen leaves from trees and many more.
Garbage makes the premises ugly, unkempt and breeds diseases. A lot of trash that is thrown away contains material that can be recycled and
reused such as paper, metals and glass which can be sent to the nearest recycling centre or disposed of to the junk dealer. It also contains organic matter such as leaves which can enrich soil fertility. A compost pit can be made at a convenient location where the refuse can be placed with layers of soil and an occasional sprinkling ofVater. This would help decomposition to make valuable fertilizer. This would also prevent pollution that is usually caused by burning such organic waste. [2013]
The Spectrum Textbook General English Class 12 MP Board Questions:
(A) The main sources of Garbage in present conditions : [1]
(i) Household things (ii) Plots and other materials (iii) Water and liquid (iv) Plastic bags.
(B) Leaves can enrich fertility. I
(i) water (ii) soil (iii) air (iv) human body.
(C) The noun form of the word ‘recycled’ : [1]
(i) recycle (ii) recycling (iii) recycling (iv) to recycled.
(D) Give the meaning of ‘nearest’ : [1]
(i) closest (ii) closely (iii) fir (iv) far away.
(E) Give a great environmental hazard : [1]
(i) water pollution (ii) air pollution (iii) garbage (iv) all of these.
(F) Garbage makes premises: [1]
(i) clean (ii) beautiful (iii) ugly (iv) dry.
(G) We can dispose garbage to a : [1]
(i) Grocer (ii) Vendor (iii) Bookseller (iv) Junk dealer.
(H) Garbages can be reused by [1]
(i) re-selling (ii) recycling (iii) repairing (iv) renovating.
(I) What are the sources of garbages?. [2]
(J) Mention two things which help organic waste material to change into fertilizer in the compost pit. [2]
Answers :
(A) (i)
(B) (ii)
(C) (ii)
(D) (i)
(E) (iv)
(F) (iii)
(G) (iv)
(H) (ii)
(I) The sources of garbage are used paper, tiffin packings, plastic bags, ice-cream wrappers, bottle caps, fallen leaves from trees etc.
(J) (i) Layers of Soil
(ii) Sprinkling of water.
5. Old people say that childhood is the best part of life. They look back at their childhood and remember all its happy days, the jolly games, the fun they had at school, the sweets land cakes they used to eat, jokes they used to play and endless discussions they had among friends about almost every topic. Perhaps these old folks are right. And yet they forget many things that were not so pleasant in their childhood. There is a funny story that tells of a boy, who was crying because he had to go back to school after the holidays and the father scolded him and said, “Why, I only wish i could be a boy and go to school again. And all in a moment the father was little boy and his son was a grown-up man like his father. And the father, in the shape of a little boy, had to go to school, and I can tell you he did not like it at all. A child’s troubles may seem small to grown-ups but they are very big to him. [2017]
The Spectrum Textbook General English Class 12 Solutions MP Board Questions :
(A) What are the joys of childhood? [1]
(i) games, work hard and fun (ii) labor and work only (iii) eating cakes only (iv) games, fun eating sweets and cakes.
(B) Give the opposite of‘ forget’. [1]
(i) dark (ii) dull (iii) remember (iv) call.
(C) Would old people be happy, if they became children again? [1]
(i) Yes (ii) May be (iii) May not be (iv) No.
(D) What wish did the father make? [1]
(i) He had been a child again (ii) He would become an old-man (iii) He would become a young boy (iv) He would become a rich man.
(E) Givemeaningof‘little’. [1]
(F) Give Adjective form of (II and III form degree)—‘Good’. [1]
(G) Why was the boy crying? [1]
(i) He wanted a lollipop (ii) He did not want to go to school (iii) He had not done his home-work (iv) He was hurt.
(H) To whom does a child’s troubles seem big? [1]
(i) to a mother (ii) to a father (iii) to a child (iv) to a teacher.
(I) What were the things which were not pleasant in the childhood? [2]
(J) How does the author compare Childhood and old age? [2]
Answers :
(A) (iv)
(B) (iii)
(C) (iii)
(D) (i)
(E) Small.
(F) (II) form—Better (III) form—Best.
(G) (ii)
(H) (iii)
(I) Going back to school after holidays and getting scolding from parents were not pleasant in the childhood.
(J) To the author childhood is the best part of life as one looks back at life. It is so because people remember all the games, fun and lovely things but they forget many things that were not so pleasant.
6. Nationalism, of course is a curious phenomenon; which at a certain stage in a country’s history gives life, growth, strength and unity, but at the same time, it has tendency, to limit one, because one thinks of one’s own country as something different from the rest of the world. The perspective changes and one is continuously thinking of one’s own struggles and virtues and failure to the exclusion of other thoughts. The result is that the same nationalism, which is the symbol of growth for a people becomes a symbol of cessation of that growth in the mind. Nationalism, when it becomes successful, sometimes goes on spreading in an aggressive way and becomes a danger internationally. Whatever line of thought you follow, you arrive at the conclusion that some kind of balance must be found, otherwise, something that was good can turn into evil. Culture, which is essentially good, becomes not only static but aggressive and something that breeds conflict and hatred when looked at from a wrong point of view. How do you find a balance?, I do not know. Apart from political and economic problems of the age, perhaps [1] that is the greatest problem today; because behind it there is a tremendous conflict in the spirit of man and a tremendous search for something it cannot find. We turn to economic theories because they have undoubted importance.
It is folly to talk of culture or even of God when human beings starve and die. Before one can talk about anything else; One must provide the normal essentials of life to human beings. That is where economics comes in. Human beings today are not in the mood to tolerate this suffering and starvation and inequality when they see that the burden is not equally shared. Others gain profit while they only bear the burden. [2018]
Questions :
(A) Nationalism is a symbol of [1]
(i) pride (ii) humbleness (iii) growth (iv) culture.
(B) Culture is essentially good but becomes : [1]
(i) dynamic (ii) static (iii) worse (iv) rotten.
(C) We can find balance when we turn to : [1]
(i) economics (ii) history (iii) culture (iv) geography.
(D) The word ‘starve’ in the passage means : [1]
(i) to die of hunger (ii) poverty (iii) lack of strength (iv) diseases.
(E) According to Nehru; Nationalism is a …. phenomenon. [1]
(i) natural (ii) cultural (iii) curious (iv) ethical.
(F) What is the verb form of ‘conclusion’? [1]
(i) include (ii) conclude (iii) conclusive (iv) concludable.
(G) It is folly to talk of culture when : [1]
(i) human beings starve and die (ii) the burden is not equally shared (iii) culture becomes aggressive (iv) nationalism becomes successful
(H) The noun form of ‘tolerate’ is : [1]
(i) tolerance (ii) tolerable (iii) tolerably (iv) toleration.
(I) When does a society become static? [2]
(J) According to Nehru when is it folly to talk about culture or God? [2]
Answers :
(A) (iii)
(B) (ii)
(C) (i)
(D) (i)
(E) (iii)
(F) GO
(G) (i)
(H) (i)
(G) It is folly to talk of culture when :
(I) A society becomes static when it looks at culture from a wrong point of view.
(J) According to Nehru, it is folly to talk of culture or even God when human beings starve and die.
7. Man’s journey of life from childhood to old age is very charming and colorful. Youth is the most exciting period of man’s life, when it is time to grow and dream. A young man is frill of hope, energy and zeal. Nothing is difficult or impossible or dangerous for him. The old people say that youth is not daring but thoughtless. A young man bums the candle at both ends. He commits mistakes and learns only after burning his finger. Sometimes the young men misuse their freedom and thus invite difficulties by their foolish actions. They are full of strength, energy and enthusiasm. They become rebels and are no longer afraid of facing the forces of realities. A young man accepts the challenge of evil, difficulties and hardships, to win or lose the game of life is the mission of his career. He loves to lead an adventurous life and has a keen desire to build up a new world of his dream. But the period of youth does not last long. Soon it is followed by old age, when he regrets his past mistakes and failures. The weak old man feels helpless, depressed and disappointed. He becomes unfit for any adventure. But some fortunate old people never grow old and continue to feel young and active and make the most of even the last years of their lives. It will not be wrong to say that youth brings honour and old age commands respect.
Questions :
(A) Man’s journey of life from childhood to….is very charming and colorful. [1]
(i) Young age (ii) Old age (iii) Death
(B) Who is full of hope, energy and zeal? t
(i) A child (ii) An old man (iii) A young man.
(C) Who misuse their freedom? I
(i) Young men (iii) Women. (ii) Old men
(D) Youth is followed by : [1]
(i) Old age (ii) Death (iii) Neither of the above.
(E) Old age commands : [1]
(i) Admiration (iii) Halted. (ii) Respect
Find out words from the passage which mean :
(F) attractive. i
(G) goal. [1]
(H) dejected. [1]
(I) What is charming and colorful? [2]
(J) What is the most exciting period of man’s life? [2]
Answers :
(A) (i)
(B) (iii)
(C) (i)
(D) (i)
(E) (ii)
(F) charming
(G) mission
(H) depressed
(I) Man’s journey of life from childhood to old age is charming and colorful.
(J) Youth is the most exciting period of a man’s life.
8. Character is one of the greatest power in the world. In its noblest embodiment, it exemplifies human nature in its highest forms, for it exhibits man at his best.
Men of genuine excellence in very station of life-men of industry, of integrity, of high principle, of sterling honesty, of purpose command the spontaneous homage of mankind. It is natural to believe in such men, to have confidence in them, and to imitate them. All that is good in the world is upheld by them, and without their presence in it, the world would not be worth living in.
Although genius always commands admiration, character most secures respect. The former is more the product of brain power, the latter of heart power and in the long run it is the heart that rules in life.’ Men of genius stand to society in the relation of its intellect, as men of character of its conscience, and while the former are admired; the later are followed.
Great men are always exceptional men, and greatness itself is best comparative. Indeed, the range of most men in life is so limited that very few have the opportunity of being great. But each man can act his part honestly and honorably and to the best of his ability. He can use his gifts and not abuse them. He can strive to make the best of life. He can be true, just, honest and faithful, even in small things. In a word, he can do his duty in that sphere in which providence has placed him.
Questions :
(A) Which is one of the greatest powers in the world? [1]
(i) Conduct (ii) Character (iii) Neither of the above.
(B) Genius commands : [1]
(i) Admiration ’ (ii) Respect (iii) Criticism.
(C) What rules life in the long run? [1]
(i) Head (ii) Heart (iii) Body.
(D) Who are exceptional men? [1]
(i) Great men (ii) Brave men (iii) Rich men.
(E) Who are followed by others? [1]
(i) Men of conscience (ii) Men of character (iii) Men of strength.
(F) Give the opposite of the word ‘best’. [1]
(G) Give the noun form of the word ‘believe’. [1]
(H) Select the word from the passage which means ‘chance’. [1]
(I) What is the force of character? [2]
(J) What sort of men command the homage of mankind? [2]
Answers :
(A) (ii)
(B) (i)
(C) (i)
(D) (i)
(E) (ii)
(F) worst.
(G) belief.
(H) opportunity.
(I) Character is one of the greatest powers in the world. In its noblest embodiment, it exemplifies human nature in its highest forms, for it
exhibits man at his best.
(J) Man of genuine excellence in every sphere of life commands the homage of mankind.
We believe the information shared regarding MP Board Solutions for 12th English Unseen Passages Questions and Answers as far as our knowledge is concerned is true and reliable. In case of any queries or suggestions do leave us your feedback and our team will guide you at the soonest possibility. Bookmark our site to avail latest updates on several state board Solutions at your fingertips.