MP Board Class 9th Science Solutions Chapter 12 Sound
Sound Intext Questions
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 162
Question 1.
How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
Answer:
When an object vibrates, it allows the particles of the medium around it to vibrate. It exerts force on the adjacent particles and continue oscillating in all directions and one of it, hit our ear’s medium which creates sound. This process continues in the medium till the sound reaches your ear.
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 163
Question 1.
Explain how sound is produced by your school bell.
Answer:
When the bell rings, it continues to move forward and backward which creates vibration and simultaneously a series of compressions and rarefactions which produce a very loud sound.
![]()
Question 2.
Why are sound waves called mechanical waves?
Answer:
Sound waves needs medium to propagate therefore, they are called mechanical waves. Sound cannot travel in the absence of a medium. Sound waves are propagated through a medium because of the interaction of the particles present in that medium.
Question 3.
Suppose you and your friend are on the moon. Will you be able to hear any sound produced by your friend?
Answer:
No, because sound waves needs a medium through which they can propagate. And since there is no medium on the moon due to absence of atmosphere, one cannot hear any sound produced by his / her friend on the moon.
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 166
Question 1.
Which wave property determines.
- loudness
- pitch?
Answer:
- Amplitude determines loudness of a sound wave.
- Frequency determines pitch of a sound wave.
Question 2.
Guess which sound has a higher pitch: guitar or car horn?
Answer:
Guitar has a higher pitch than car horn, because sound produced by the strings of guitar has higher frequency and since pitch is proportional to frequency, pitch of guitar will be higher.
![]()
Question 3.
What are wavelength, frequency, time period and amplitude of a sound wave?
Answer:
- Wavelength: Wave length is the length between two consecutive peaks it is represented by Greek letter λ (lambda). Louder sound has shorter wavelength and softer sound has longer wavelength.
- Frequency: The number of sound waves produced in unit time is called the frequency of sound waves. Frequency is measured in seconds. Frequency is denoted by Greek letter v (nu). The SI unit of frequency is ‘hertz’.
- Amplitude: Amplitude of a wave is magnitude of maximum disturbance on either side of the normal position or mean value in a medium.
Question 4.
How are the wavelength and frequency of a sound wave related to its speed?
Answer:
Speed, wavelength, and frequency of a sound wave are related as follows:
Speed (ν) = Wavelength [λ] × Frequency (v)
⇒ ν = λ × v
Question 5.
Calculate the wavelength of a sound wave whose frequency is 220 Hz and speed is 440 m/s in a given medium.
Answer:
Given,
Frequency of the sound wave, v = 220 Hz
Speed of the sound wave, u = 440 ms-1
Putting the equations,
Speed = Wavelength (λ) × Frequency (v)
ν = λ × v
∴ λ = \(\frac { ν }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 440 }{ 220 }\) = 2 m
Hence, Wavelength = 2 m.
Question 6.
A person is listening to a tone of 500 Hz sitting at a distance of 450 m from the source of the sound. What is the time interval between successive compressions from the source?
Answer:
Given,
Frequency = 500 Hz
Distance = 450 m
Since, T = \(\frac { 1 }{ Frequency }\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 500 }\) = 0.002 sec.
Hence, person will listen the sound after every 0.002 sec.
Question 7.
Distinguish between loudness and intensity of sound.
Answer:
Intensity drives loudness of a sound. These both qualities of sound are proportional to each other. The amount of sound passing through a unit area per second represents intensity of a sound wave. While loudness is the response of the ear to the sound (amount received to pinna). The loudness of a sound is defined by its amplitude. The amplitude of a sound decides its intensity, which in turn is perceived by the ear as loudness.
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 167
Question 1.
In which of the three media, air, water or iron, does sound travel the fastest at a particular temperature?
Answer:
Sound travels the fastest in solids medium (here Iron) then in liquids (water) and it is the slowest in gases (air). Therefore, for a given temperature, sound travels as follows (decreasing order): ⇒ Iron > water >air.
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 168
Question 1.
An echo returned in 3s. What is the distance of the reflecting surface from the source, given that the speed of sound is 342 ms-1?
Answer:
Given,
Speed, v = 342 ms-1
Time, t = 3 s
Since, Distance = v × t
= 342 × 3 = 1026 m
Condition,
In fixed time interval, sound has to travel a distance that is twice the distance of the reflecting surface and the source.
Hence, the distance of the reflecting surface from the source = \(\frac { 1026 }{ 2 }\) m = 513 m.
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 169
Question 1.
Why are the ceilings of concert halls curved?
Answer:
Ceilings of concert halls are curved to:
- Enhance loudness and echo of sound created.
- Sound after reflection (from the walls) spreads uniformly in all directions.
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 170
Question 1.
What is the audible range of the average human ear?
Answer:
The audible range of an average human ear is between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Question 2.
What is the range of frequencies associated with
- Infrasound?
- Ultrasound?
Answer:
- Infrasound: frequencies less than 20 Hz.
- Ultrasound: frequencies more than 20,000 Hz.
Sound Intext Questions Page No. 172
Question 1.
A submarine emits a sonar pulse, which returns from an underwater cliff in 1.02 s. If the speed of sound in salt water is 1531 m/s, how far away is the cliff?
Answer:
Given,
Time taken by the sonar pulse to return, t = 1.02s
Speed of sound in salt water, v = 1531 ms-1
Distance of the cliff from the submarine = Speed of sound × Time taken
= 1531 × 1.02 m = 1561.62 m
Distance travelled by the sonar pulse during its transmission and reception in water
= 2 × Actual distance = 2d
Actual distance,
d = Distance of the cliff from the submarine / 2 = \(\frac { 1561 }{ 2 }\) = 780.31 m.
![]()
Sound NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
What is sound and how is it produced?
Answer:
Sound is a form of energy which is received at our ear pinna and gives the sensation of hearing. It is a vibration which propagates in air and developed by vibrating objects.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe with the help of a diagram, how compressions and rarefactions are produced in air near a source of sound.
Answer:
When vibration is produced by a body, it moves in backward and forward direction till the energy lasts. During forward movement it creates a region of high pressure. This region of high pressure is known as compressions. When it moves backward, it creates a region of low pressure. This region is known as a rarefaction. This is shown in figure given below.

Here,
C = compressions
R = rarefaction.
Question 3.
Cite an experiment to show that sound needs a material medium for its propagation.
Answer:
Arrange the instrument according to the picture given below:
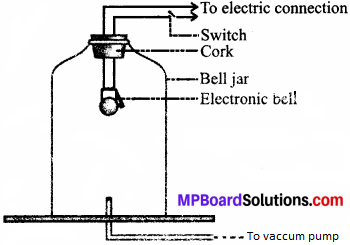
- Take an electric bell and an air tight jar with glass bell and connect it to a vacuum pump.
- Suspend the bell inside the jar, and press the switch of the bell.
Method: Now pump out the air from the glass jar. The sound of the bell will become fainter and after some time, the sound will not be heard. This shows that sound needs a material medium to travel.
Question 4.
Why is sound wave called a ‘longitudinal wave’?
Answer:
Sound wave is called longitudinal wave because the air particles vibrates parallel to the direction of propagation of sound wave,it is produced by compressions and rarefactions in the air.
Question 5.
Which characteristics of the sound helps you to identify your friend by his voice while sitting with others in a dark room?
Answer:
The quality of pitch and loudness of sound enables us to identify our friend by his voice.
![]()
Question 6.
Flash and thunder are produced simultaneously. But thunder is heard a few seconds after the flash is seen, why?
Answer:
Speed difference is the main reason of this happening. The speed of sound (344 m/s) is very less than the speed of light (3 × 108 m/s). A flash is seen before we hear a thunder because sound of thunder takes more time to reach the Earth as compared to light.
Question 7.
A person has a hearing range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. What are the typical wavelengths of sound waves in air corresponding to these two frequencies? Take the speed of sound in air as 344 ms-1.
Answer:
We know,
Speed (ν) = Wavelength × Frequency v
ν = λ × v
Given,
Speed of sound in air ν = 344 m/s (Given)
(i) For, v = 20 Hz
λ1 = \(\frac { ν }{ v }\)
= \(\frac { 344 }{ 20 }\) = 17.2 m
(ii) For, v = 20000 Hz
12 = \(\frac { ν }{ v }\)
= \(\frac { 344 }{ 20000 }\) = 0.172 m
Hence, for humans, the wavelength range for hearing is 0. 0172 m to 17.2 m.
Question 8.
Two children are at opposite ends of an aluminium rod. One strikes the end of the rod with a stone. Find the ratio of time taken by the sound wave in air and in aluminium to reach the second child.
Answer:
Velocity of sound in air= 346 m/s
Velocity of sound waves in aluminium 6420 m/s
Let length of rod be 1.
Time taken for sound wave in air, t1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ Velocity }\) in air.
Time taken for sound wave in aluminium, t2 = \(\frac { 1 }{ Velocity }\) in aluminium.
Therefore,
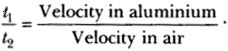
= \(\frac { 6420 }{ 346 }\) = 18.55.
Question 9.
The frequency of a source of sound is 100 Hz. How many times does it vibrate in a minute?
Answer:
Frequency =100 Hz. (Given)
This means the source of sound vibrates 100 times in one second.
Therefore, number of vibrations in 1 minute, i.e. in 60 seconds = 100 × 60 = 6000 times.
Question 10.
Does sound follow the same laws of reflection as light does? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, sound waves also follow the same laws of reflection as light wave do because:
- Angle of incidence of sound is always equal to that of angle of reflection of sound waves.
- The direction in which sound is incident, the direction in which it is reflected and normal all lie in the some plane.
![]()
Question 11.
When a sound is reflected from a distant object, an echo is produced. Let the distance between the reflecting surface and the source of
sound production remains the same. Do you hear echo sound on a hotter day?
Answer:
An echo is heard when the time for the reflected sound is just 0.1 s
Time taken = \(\frac { Total Distance }{ Velocity }\)
On a hotter day, due to lighter medium the velocity of sound is more then a colder day. Hence, sound wave will move faster and if time taken by echo is less than 0.1 sec it will not be heard.
Question 12.
Give two practical applications of reflection of sound waves.
Answer:
Two practical applications of reflection of sound waves are:
- Reflection of sound is used to measure the distance and speed of underwater objects. This method is known as SONAR.
- Working of a stethoscope is also based on reflection of sound. In a stethoscope, the sound of the patient’s heartbeat reaches the doctor’s ear by multiple reflection of sound.
Question 13.
A stone is dropped from the top of a tower 500 m high into a pond of water at the base of the tower. When is the splash heard at the top? Given, g = 10 ms-2 and speed of sound = 340 ms-1.
Answer:
Height of the tower, s = 500 m
Velocity of sound, v = 340 ms-1
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 ms-2
Initial velocity of the stone, u = 0 (since the stone is initially at rest)
Time taken by the stone to fall to the base of the tower t1,
According to the second equation of motion:
s = ut1 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) gt12
500 = 0 × t1 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 10 t12
t12 = 500
t1 = 10 s
Now, time taken by the sound to reach the top from the base of the tower, t2 = \(\frac { 500 }{ 340 }\) = 1.47 s.
Therefore, the splash is heard at the top after time, t Where, t = t1 + t2 = 10 + 1.47 = 11.47 s.
Question 14.
A sound wave travels at a speed of 339 ms-1. If its wavelength is 1.5 cm, what is the frequency of the wave? Will it be audible?
Answer:
Speed of sound, v = 339 ms-1
Wavelength of sound, λ = 1.5 cm = 0.015 m
Speed of sound = Wavelength × Frequency
ν = λ × v
∴ v = \(\frac { ν }{ λ }\)
= \(\frac { 339 }{ 0.015 }\)
= 22600 Hz.
The frequency range of audible sound for humans lies between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Since, the frequency of the given sound is more than 20,000 Hz, it is not audible.
Question 15.
What is reverberation? How can it be reduced?
Answer:
The repeated multiple reflections of sound in any big enclosed space is known as reverberation. The reverberation can be reduced by covering the ceiling and walls of the enclosed space with sound absorbing materials, such as fibre board, loose woollens, etc.
Question 16.
What is loudness of sound? What factors does it depend on?
Answer:
The effect produced in the brain by the sound of different frequencies is called loudness of sound. Loudness depends on the amplitude of vibrations. In fact, loudness is proportional to the square of the amplitude of vibrations.
Question 17.
Explain how bats use ultrasound to catch a prey.
Answer:
Bats produce high – pitched ultrasonic squeaks. These high – pitched squeaks are reflected by objects such as preys and returned to the bat’s ear. This allows a bat to know the distance of his prey.
![]()
Question 18.
How is ultrasound used for cleaning?
Answer:
Objects to be cleansed are put in a cleaning solution and ultrasonic sound waves are passed through that solution. The high frequency of these ultrasound waves detaches the dirt from the objects.
Question 19.
Explain the working and application of a SONAR.
Answer:
Sonar stands for Sound Navigation And Ranging. It is a device used to measure the depth, direction and speed of under – water objects such as submarines and ship wrecks with the help of ultrasounds and is also used to measure the depth of seas and oceans. An ultrasonic sound is produced and transmitted by the transducer (it is a device that produces ultrasonic sound) of the Sonar, which travels through sea water.
The echo produced by the reflection of this ultrasonic sound is detected and recorded by the detector, which is converted into electrical signals. The distance (d) of the under – water object is calculated from the time (t) taken by the echo to return with speed (v) is given by 2d = v × t.
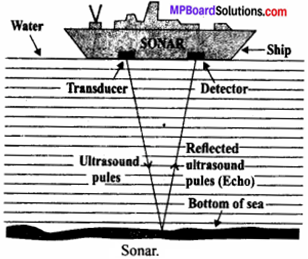
Question 20.
A SONAR device on a submarine sends out a signal and receives an echo 5 s later. Calculate the speed of sound in water if the distance of the object from the submarine is 3625 m.
Answer:
Given,
Time taken to hear the echo, t = 5 s
Distance of the object from the submarine, d = 3625 m
Total distance travelled by the sonar waves during the transmission and reception in water = 2d
Using formula:
Velocity of sound in water,
v = 2 \(\frac { d }{ t }\)
= 2 × \(\frac { 3625 }{ 5 }\) = 1450 ms-1.
Question 21.
Explain how defects in a metal block can be detected using ultrasound.
Answer:
Defects in metal blocks do not allow ultrasound to pass through them and they are reflected back. This fact is used to detect defects in metal blocks. Ultrasound is passed through one end of a metal block and detectors are placed on the other end. The defective part of the metal block does not allow ultrasound to pass through it. As a result, it will not be detected by the detector. Hence, defects in metal blocks can be detected using ultrasound.
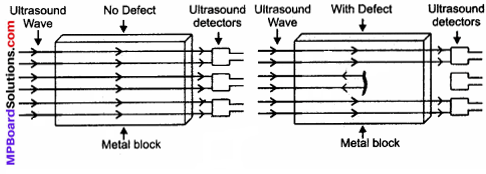
Question 22.
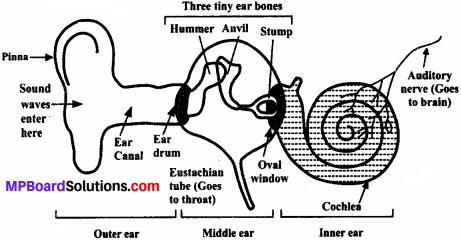
Explain how the human ear works.
Answer:
The human ear consists of three parts – the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear.
- Outer ear: It is also termed ‘pinna’. It collects the sound from the surrounding and directs it towards auditory canal.
- Middle ear: It is at the auditory canal where there is a thin membrane called eardrum or tympanic membrane. The sound waves set this membrane to vibrate. These vibrations are amplified by three small bones hammer, anvil and stirrup.
- Inner ear: When vibration reach the cochlea in the inner ear and are converted into electrical signals which are sent to the brain by the auditory nerve, and the brain interprets them as sound.
Sound Additional Questions
Sound Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following waves have no requirement of any medium to propagate?
(a) sound
(b) radio
(c) light waves
(d) none of above.
Answer:
(c) light waves
Question 2.
What kinds of waves are produced by sound?
(a) longitudinal only
(b) transverse waves only
(c) electromagnetic Waves
(d) both Longitudinal and Transversal.
Answer:
(a) longitudinal only
![]()
Question 3.
When a wave propagate, it transfers ___________ .
(a) energy only
(b) matter only
(c) both energy and matter
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(a) energy only
Question 4.
Note is a sound ___________ .
(a) of mixture of several frequencies
(b) of mixture of two frequencies only
(c) of a single frequency
(d) always unpleasant to listen.
Answer:
(a) of mixture of several frequencies
Question 5.
A key of a mechanical piano struck gently and then struck again but much harder this time. In the second case:
(a) sound will be louder but pitch will not be different.
(b) sound will be louder and pitch will also be higher.
(c) sound will be louder but pitch will be lower.
(d) both loudness and pitch will remain unaffected.
Answer:
(d) both loudness and pitch will remain unaffected.
Question 6.
Earthquake produces which kind of sound before the main shock wave begins ___________ .
(a) ultrasound
(b) Infrasound
(c) audible sound
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(b) Infrasound
Question 7.
Infrasound can be heard by ___________ .
(a) dog
(b) bat
(c) rhinoceros
(d) human beings.
Answer:
(c) rhinoceros
Question 8.
Before playing the orchestra in a musical concert, a sitarist tries to adjust the tension and pluck the string suitably. By doing so, he is adjusting ___________ .
(a) intensity of sound only.
(b) amplitude of sound only.
(c) frequency of the sitar string with the frequency of other musical instruments.
(d) loudness of sound.
Answer:
(c) frequency of the sitar string with the frequency of other musical instruments.
![]()
Question 9.
What we term to the number of oscillations completed in one second?
(a) time period
(b) velocity
(c) frequency
(d) wavelength.
Answer:
(c) frequency
Question 10.
Sound waves which can be propagate in solids are ___________ .
(a) Longitudinal only.
(b) Transverse only.
(c) Either longitudinal or transverse.
(d) Non mechanical waves only.
Answer:
(c) Either longitudinal or transverse.
Question 11.
In SONAR, we use ___________ .
(a) ultrasonic waves
(b) infrasonic waves
(c) radio waves.
(d) audible sound waves.
Answer:
(a) ultrasonic waves
Question 12.
Sound travels in air if ___________ .
(a) particles of medium travel from one place to another.
(b) there is no moisture in the atmosphere.
(c) disturbance moves.
(d) both particles as well as disturbance travel from one place to another.
Answer:
(c) disturbance moves.
Question 13.
When we change feeble sound to loud sound we increases ___________ .
(a) Frequency
(b) Amplitude
(c) Velocity
(d) Wavelength.
Answer:
(b) Amplitude
Question 14.
In the curve (Figure) half the wavelength is ___________ .
image
(a) AB
(b) BD
(c) DE
(d) AE
Answer:
(a) AB
Question 15.
The time taken to complete an osoillation ___________ .
(a) time period
(b) velocity
(c) frequency
(d) wavelength.
Answer:
(a) time period
Question 16.
The period of a vibrating body of frequency 100 Hz is ___________ .
(a) 100 seconds
(b) 10 seconds
(c) 0.1 second
(d) 0.01 second.
Answer:
(a) 100 seconds
![]()
Question 17.
Which of the following is SI unit of amplitude?
(a) metre
(b) s-1
(c) metre / second
(d) Hertz.
Answer:
(a) metre
Question 18.
The quantity λ is known as ___________ .
(a) wave velocity
(b) frequency
(c) wavelength
(d) wave number.
Answer:
(c) wavelength
Question 19.
Sound wave of which of the following frequency is an ultrasonic sound?
(a) 30 Hz
(b) 300 Hz
(c) 3000 Hz
(d) 30,000 Hz.
Answer:
(d) 30,000 Hz.
Question 20.
In which of the following, speed of the sound is maximum?
(a) air
(b) water
(c) steel
(d) kerosene.
Answer:
(c) steel
Sound Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How does sound travels in gases and liquids – as longitudinal or as transverse waves?
Answer:
As longitudinal waves.
Question 2.
Give examples of longitudinal waves.
Answer:
Sound waves.
Question 3.
What is speed of sound in air?
Answer:
At 0° C, it is 331 m/s. At 20°C, it is 341 m/s.
Question 4.
What is reverberation?
Answer:
The repeated reflection that results in the persistence of sound is called reverberation.
![]()
Question 5.
Among solids, liquids and gases sound travels faster in which medium?
Answer:
Sound travels the fastest in solids.
Question 6.
What is one Hz?
Answer:
Hz is the unit of frequency, called as Hertz. One Hertz is equal to one cycle per second.
Question 7.
What is ‘note’ of second?
Answer:
The sound produced due to a mixture of several frequency is called a note, it is pleasant to listen to.
Question 8.
What is pitch?
Answer:
The way our brain interprets the frequency of an emitted sound is called the pitch.
Sound Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Sound? Why it is important for us?
Answer:
Sound is a longitudinal mechanical wave. Sound has great importance in our daily life. It gives us a sensation of hearing. It makes it possible to communicate with other persons through speech.
Question 2.
What is a mechanical wave?
Answer:
A mechanical wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium when the particles of the medium set neighbouring particles into motion. The particles vibrating in turn do not move forward but the disturbance is carried forward.
Question 3.
What is a longitudinal wave?
Answer:
If the particles of a medium vibrate in a direction, parallel to or along the direction of propagation of wave, it is called longitudinal wave.
![]()
Question 4.
What type of waves can travel in vacuum? Give example(s).
Answer:
Electromagnetic waves can travel in vacuum. Sun light, x – rays are examples of electromagnetic waves.
Question 5.
Suppose you and your friend are on the Moon. Will you be able to hear any sound produced by your friend?
Answer:
No, we will not hear any sound on the Moon. The Moon does not have any atmosphere, since sound is a mechanical wave and requires a medium to travel.
Question 6.
What are the factors, speed of sound wave depends upon?
Answer:
Speed of the sound depends on the following factors:
- Inertial property of the medium (to store kinetic energy).
- Elastic property of the medium (to store potential energy).
- Temperature of the medium.
- Density of the medium.
- Humidity present in the medium (in air / gases).
Question 7.
Three persons A, B and C are made to hear a sound travelling through different mediums as given below:
| Persons | Medium |
| A | Iron Rod |
| B | Air |
| C | water |
Who will hear the sound first ? Why ?
Answer:
Person A will hear the sound first because sound travels the faster in solids than in liquids and gases.
Question 8.
If 20 waves are produced per second, what is the frequency in hertz?
Answer:
Number of waves per second is known as frequency.
∴ Frequency (v) = 20 Hz.
Question 9.
What is echo?
Answer:
The sound waves produced bounce back or gets reflected from the mountains or buildings and come to our ears, this reflected sound is known as Echo. To hear echo, the barrier reflecting the sound should be atleast at a distance of 17 metres.
![]()
Question 10.
What is infrasonic? Give an example.
Answer:
Sound having frequency less than 20 Hz is known as infrasonic sound or infrasonic. Waves produced during earthquake are infrasonic.
Sound Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Establish the relationship between speed of sound, its wave length and frequency. If velocity of sound in air is 340 m s-1, calculate:
- wavelength when frequency is 256 Hz.
- frequency when wavelength is 0.85 m.
Answer:
Derivation of formula ν = v λ
- 340 = 256 λ ⇒ λ = 1.33 m.
- 340 = v (0.85) ⇒ v = 400 Hz.
Question 2.
A girl is sitting in the middle of a park of dimension 12 m × 12 m. On the left side of it there is a building adjoining the park and on right side of the park, there is a road adjoining the park. A sound is produced on the road by a cracker. Is it possible for the girl to hear the echo of this sound? Explain answer.
Answer:
If the time gap between the original sound and reflected sound received by the listener is around 0.1 s, only then the echo can be heard. The minimum distance travelled by the reflected sound wave for the distinctly listening the echo, distance = velocity of sound × time interval;
= 344 × 0.1 = 34.4 m.
But, in this case the distance travelled by the sound reflected from the building and then reaching the girl will be (6 + 6 = 12 m), which is much smaller than the required distance. Therefore, no echo can be heard.
Sound Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
Question 1.
A key of piano is struck gently and then struck again but much harder this time. What will happen in the second case?
Answer:
In second case, the loudness will increase as this will increase the amplitude of vibration of string. Pitch and frequency will also increase in force or tension in the string.
![]()
Question 2.
At a hill station, a child could hear the echo of his voice after 0.2 s. But, when he went to the same place in the afternoon, he could not hear echo at all. What could be the reason?
Answer:
In afternoon, the temperature rises, therefore the speed of sound also increased. The reflected sound will take very less time to travel back and no echo is heard.
Sound Value Based Question
Question 1.
It is not advisable to construct houses near airports, inspite of that many new residential apartments are constructed near airports. Rajesh / Sumit files RTI and also complains the municipal office about the same.
- Why one should not reside near airport?
- Name other two places where there is noise pollution.
- What value of Rajesh is reflected in this act?
Answer:
- The landing and taking off of the air – planes causes lot of noise-pollution which may lead to deafness, high blood pressure and other health problems.
- The other two places where there is noise-pollution are residing near the heavy traffic routes and railway stations or lines.
- Rajesh shows participating citizen and moral responsibility values.