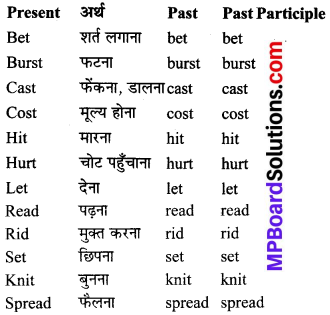
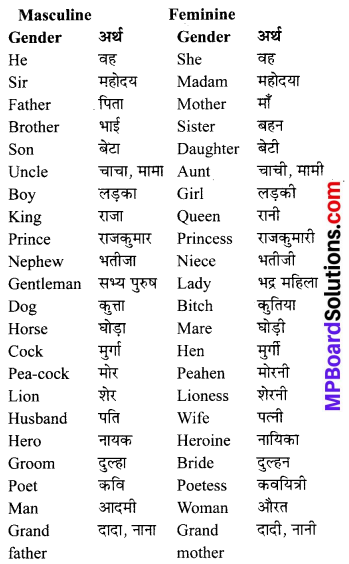
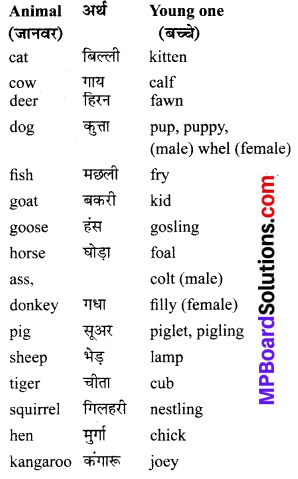
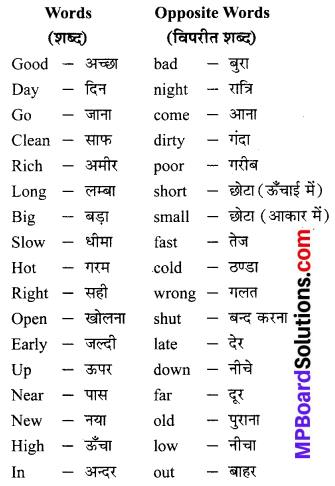
Students who wish to prepare the English Subject can rely on the MP Board Solutions for Class 6 English Chapter 8 Robin Hood and the Sheriff Questions and Answers prevailing. Become perfect with the concepts of Class 6 English Chapter 8 Robin Hood and the Sheriff Questions and Answers, Grammar, Summary, Notes, Guide, Pdf, by preparing you can score highest grade in your exams. Here, You Can Download MP Board Class 6 English Solutions. Detailed Solutions are provided to the concepts by experts keeping in mind the latest edition textbooks and syllabus.
MP Board Class 6th Special English Solutions Chapter 8 Robin Hood and the Sheriff
Ace up your preparation by referring to the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 8 Robin Hood and the Sheriff Questions and Answers and learn all the topics within. Click on the topic you want to prepare from the Class 6 English and prepare it easily. You can understand your strengths and weaknesses by learining the Questions and Answers in MP Board Solutions for Class 6 English PDF.
Robin Hood and the Sheriff Text Book Exercise
Word Power
(a) Make new words by using prefixes.
Example:
un – uneasy, unable.
(a, al, en, dis, im, in, un, mis)
Answer:
a : alike, affix
al : altogether, already
en : enforce, encourage
dis : disqualify, discontentment
in : impose, impossible
un : unseen, unknown
mis : misfortune, misconduct
(b) Make adverb as shown in the example.
Example:
near – nearly
second ………..
easy ………..
last ………..
quick ………….
happy ………..
kind ………..
loud ………..
slow ………….
Answer:
secondly
easily
lastly
quickly
happily
kindly
loudly
slowly
Comprehension
(a) Answer these questions
Class 6 English Chapter 8 Robin Hood And The Sheriff MP Board Question 1.
Why were the Sheriffs feared some persons?
Answer:
Some persons were afraid of Sheriffs because they used to hang a person on a little or no offence.
Robin Hood Was The Leader Of Rich Travellers MP Board Question 2.
Who were ‘outlaws’?
Answer:
Outlaws were the men who ran away from the cities for the fear of being punished the Sheriffs. There they joined the company of other men like them.
Robin Hood And The Sheriff MP Board Question 3.
How did the outlaws make their living?
Answer:
The outlaws used to rob the travellers on the highways. They also killed the deer in the forest to earn money and make their living.
Robin Hood Was The Leader Of Rich Travellers True Or False MP Board Question 4.
Why was Robin Hood a terror to the rich people?
Answer:
The rich people were afraid of Robin Hood, because he often robbed them of their money. He helped the poor with the booty.
Lesson 8 Robin Hood And The Sheriff MP Board Question 5.
How did the Sheriff show that he was very eager to catch Robin Hood?
Answer:
The Sheriff announced to give half of his wealth to the man who helped him to catch Robin Hood. It shows his eagerness to catch Robin Hood.
Robin Hood And The Sheriff Question Answer MP Board Question 6.
What was Robin Hood going to the town for?
Answer:
Robin Hood was going to the town with a view to meet and teach Sheriff a good lesson.
Question 7.
How did Robin Hood get into the disguise of a butcher?
Answer:
Robin Hood purchased meat, apron and a horse from a butcher. He wore his clothes and got into the disguise of a butcher.
Question 8.
Why didn’t the Sheriff allow Robin Hood to pay for the food and drinks?
Answer:
The Sheriff was the host. Therefore, he did not let Robin Hood pay for the dinner, for he was the Sheriffs guest.
(b) Answer these questions
Question 1.
‘Mr. Sheriff’ you have forgotten two things, Robin Hood said. When did Robin Hood say this? What two things had the Sheriff ‘forgotten’?
Answer:
The Sheriff had finished his dinner and was about to leave for his town. Then Robin Hood said these words. The things that Sheriff had forgotten were:
- he had to buy the animals.
- he had to pay for the dinner, he had enjoyed at the Green Wood Inn.
Question 2.
Why was the Sheriff not able to buy the animals?
Answer:
The Sheriff did not have enough money with him. Therefore, he was not able to purchase those animals.
Question 3.
When did Robin Hood let the Sheriff go?
Answer:
Robin Hood allowed the Sheriff to leave only after snatching all the money he had.
Question 4.
What did Robin Hood do when he and the Sheriff reached the highway?
Answer:
On reaching the highway, Robin Hood stopped and kicked the Sheriffs horse, which set it running as fast as it could.
(c) Tick (✓) for the correct statements and (✗) the incorrect statements.
- In olden days in England, the law was very cruel.
- The Sheriff were lawyers.
- Robin Hood was the leader of rich travellers.
- Robin Hood put on the butcher’s apron and took the load of meat to the town.
- The Sheriff was frightened while he rode out to Sherwood forest.
Answer:
- (✓)
- (✓)
- (✗)
- (✓)
- (✓)
Grammar in Use
(a) Read these sentences.
1. The Sheriff has been looking for a chance to catch me.
2. I have been living in this house since 1960.
The verb in italics are in the present perfect continuous tense.
They express actions/which took place over a period of time in the past and may possibly be continuing still.
For example the sentence – means;
Some time ago the Sheriff started looking for a chance to catch me.
He is still looking for a chance.
The sentence (2) means;
I started living in this hour in 1960.
I am still living in it.
Now express the meaning of each pair of sentences below in one sentence, using the present perfect continuous tense (has/have + been + verb – ing)
- These girls started learning French three years ago. They continue to learn French. (Use ‘for three years’).
- Shyam started doing his homework at 7”o clock. He is still doing it. (Use -‘Since’)
- It started raining at 5’o clock yesterday morning. It is still raining. (Use ‘Since’)
- Our English teacher started teaching in this school in 1964. (Use ‘Since’)
- “The poor Sheriff started waiting for me a long time ago.”
“He is still waiting for me” (Use ‘for a long time’).
Answer:
- These girls have been learning French for three years.
- Shyam has been doing his homework since To clock.
- It has been raining since 5’o clock yesterday morning.
- Our English teacher has been teaching in this school since 1964.
- The poor Sheriff has been waiting for me for a long time.
(b) Fill in the blanks with phrases given.
(as kindly as, as quickly as, as often as, as soon as, as fast as, as much as)
- Uma goes to pictures …………. her mother allows her.
- The boys decided to start for the picnic …………. possible.
- When the police arrived, the thief ran ………….. his legs could carry him.
- The teacher spoke to the child …………… she could, but the child kept on crying.
- “Type this letter ………….. you can. But don’t make any mistake.” said the officer to the typist.
- During the war people freely gave ……………. they could for the National Defence Fund.
Answer:
- as often as
- as soon as
- as fast as
- as kindly as
- as quickly as
- as much as
Let’s Write
Question 1.
Write down 10 sentences about Robin Hood on the basis of qualities listed above.
Answer:
- Robin Hood was an outlaw.
- He lived in the forest of Sherwood.
- He was the enemy of the rich and friend to the poor.
- He used to rob the cruel landlords to help the poor.
- He provided shelter to the people who suffered at the hands of the cruel, wicked and foolish Sheriffs.
- The Sheriff of that city was his bitter enemy and wanted to catch him.
- On hearing it, Robin Hood decided to teach him a lesson. At the end he renowned successful in his mission.
- Rich people were afraid of him but the poor loved him to the core of their hearts.
- He was kind and just.
- We appreciate him for his heroic deeds and adventurous nature.
Robin Hood and the Sheriff Word Meanings

Hope the data shared has shed some light on you regarding the MP Board Solutions of Class 6 English Chapter 8 Robin Hood and the Sheriff Questions and Answers. Do leave us your queries via the comment section and we will guide you at the earliest with help seeked. Stay connected with our website and avail the latest information in a matter of seconds.