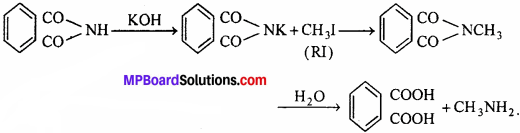
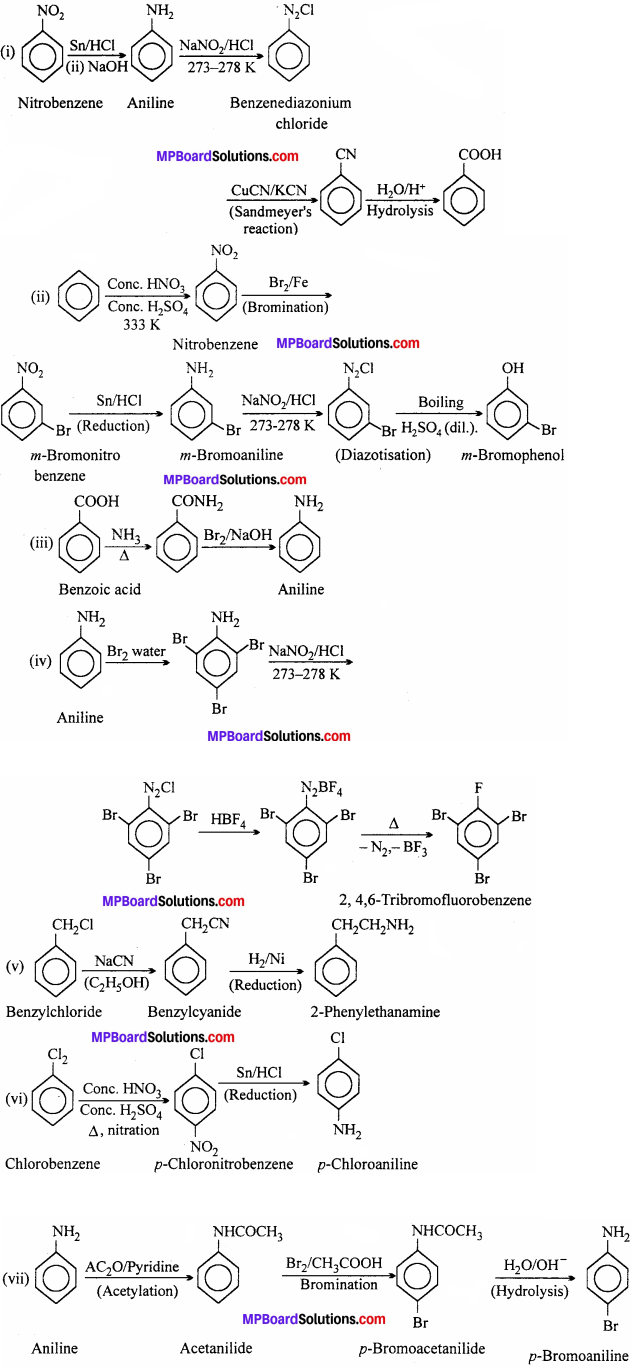
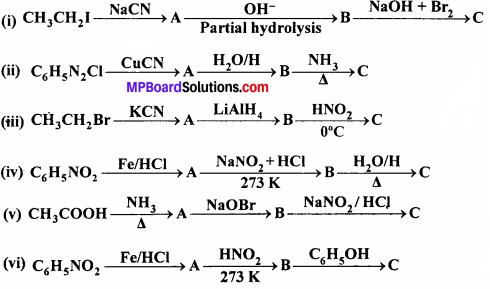
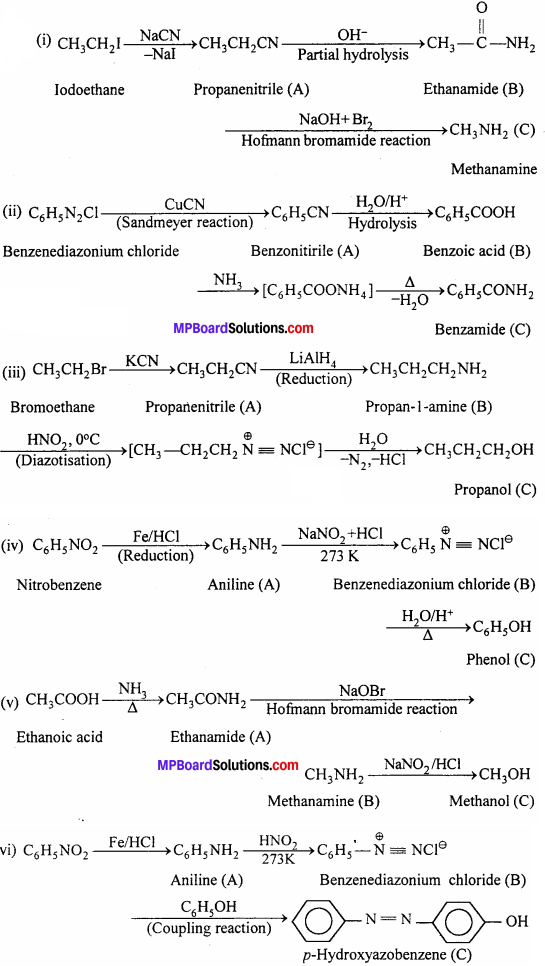
MP Board Class 12th Economics Important Questions Unit 6 राष्ट्रीय आय एवं संबंधित समुच्चय
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं संबंधित समुच्चय Important Questions
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं संबंधित समुच्चय वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए –
प्रश्न (a)
समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र के अध्ययन का विषय है –
(a) राष्ट्रीय आय का सिद्धांत
(b) उपभोक्ता का सिद्धांत
(c) उत्पादक का सिद्धांत
(d) इनमें से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर:
(a) राष्ट्रीय आय का सिद्धांत
प्रश्न (b)
निम्नलिखित में कौन-सा प्रवाह नहीं है –
(a) पूँजी
(b) आय
(c) निवेश
(d) मूल्य ह्रास।
उत्तर:
(a) पूँजी
![]()
प्रश्न (c)
राष्ट्रीय आय का मापन निम्नलिखित में किस विधि से किया जाता है –
(a) उत्पादन विधि
(b) आय विधि
(c) व्यय विधि
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
उत्तर:
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
प्रश्न (d)
प्राथमिक क्षेत्र में निम्नलिखित में कौन शामिल है –
(a) भूमि
(b) बन
(c) खनन
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
उत्तर:
(d) उपर्युक्त सभी।
प्रश्न (e)
एक वर्ष की राष्ट्रीय आय को जनसंख्या से भाग देने पर प्राप्त होती है –
(a) निजी आय
(b) व्यक्तिगत आय
(c) व्यक्तिगत व्यय योग्य आय
(d) प्रति व्यक्ति आय।
उत्तर:
(d) प्रति व्यक्ति आय।
![]()
प्रश्न (f)
उत्पादन करने वाले उद्यमों को बाँटा जाता है –
(a) दो क्षेत्रों में
(b) तीन क्षेत्रों में
(c) चार क्षेत्रों में
(d) पाँच क्षेत्रों में।
उत्तर:
(b) तीन क्षेत्रों में
प्रश्न 2.
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए –
- कृषि को …………………………….. क्षेत्र में शामिल किया जाता है।
- पीगू ने कल्याण को ………………………….. भागों में बाँटा है।
- चीनी उत्पाद अर्थव्यवस्था के …………………………………. क्षेत्र में सम्मिलित होता है।
- भारत में राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना का कार्य …………………………….. करता है।
- एक लेखा वर्ष की अवधि में देश की भौगोलिक सीमाओं के अंतर्गत उत्पादित अन्तिम वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं के योग को …………………………….. कहते हैं।
- …………………………. आय देश के आर्थिक विकास का सूचक होती है।
उत्तर:
- प्राथमिक
- दो
- द्वितीयक
- केन्द्रीय सांख्यिकीय
- GDP
- राष्ट्रीय।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
सत्य /असत्य बताइये –
- भारत की प्रति व्यक्ति आय विकसित देशों की तुलना में काफी कम है?
- काले धन ने देश में समानान्तर अर्थव्यवस्था को जन्म दिया है?
- भारत की राष्ट्रीय आय में सर्वाधिक योगदान द्वितीयक क्षेत्र का है?
- प्राथमिक क्षेत्र में विद्युत्, गैस एवं जलापूर्ति को सम्मिलित किया जाता है?
- उपहार के रूप में प्राप्त आय को राष्ट्रीय आय में सम्मिलित किया जाता है?
- पुरानी वस्तुओं की बिक्री से प्राप्त आय को राष्ट्रीय आय में शामिल नहीं किया जाता है।
उत्तर:
- सत्य
- सत्य
- असत्य
- असत्य
- असत्य
- सत्य।
प्रश्न 4.
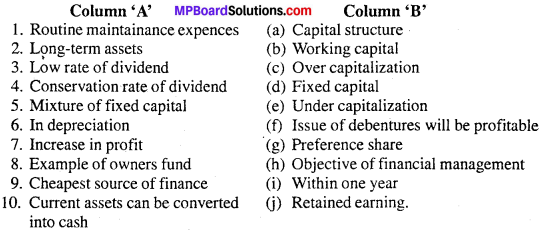
सही जोड़ियाँ बनाइये –

उत्तर:
- (e)
- (a)
- (d)
- (c)
- (b)
प्रश्न 5.
एक शब्द/वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिये –
- भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था के कौन – से क्षेत्र का राष्ट्रीय आय में सर्वाधिक योगदान है?
- अंतिम स्टॉक एवं प्रारंभिक स्टॉक में अन्तर कहलाता है?
- राष्ट्रीय आय का अध्ययन किस अर्थशास्त्र में किया जाता है?
- राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि किस बात की सूचक होती है?
- राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना वर्ष में कितनी बार की जाती है ?
- वर्ष में कौन – सी वस्तुओं व सेवाओं के मौद्रिक मूल्य को कुल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद में जोड़ा जाता है?
उत्तर:
- तृतीयक
- स्टॉक में परिवर्तन
- समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में
- आर्थिक प्रगति की
- एक बार
- अंतिम।
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं संबंधित समुच्चय अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र क्या है?
उत्तर:
वह अर्थशास्त्र जिसमें व्यक्तिगत स्तर पर आर्थिक समस्याओं का अध्ययन एवं विश्लेषण किया जाता है व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र कहलाता है। जैसे – एक व्यक्ति, एक परिवार, एक इकाई, एक उत्पादक आदि।
प्रश्न 2. समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र क्या है?
उत्तर:
समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र वह आर्थिक प्रणाली है जिसमें आर्थिक समस्याओं का अध्ययन एवं विश्लेषण अर्थव्यवस्था के स्तर पर किया जाता है। जैसे – सम्पूर्ण अर्थव्यवस्था, समग्र उत्पादन, समग्र विनियोग आदि।
![]()
प्रश्न 3. आर्थिक इकाई क्या है?
उत्तर:
आर्थिक इकाई का आशय उन व्यक्तियों या संस्थाओं से है जो आर्थिक निर्णय लेते हैं। उदाहरण के लिये, उपभोक्ता निर्णय लेता है, क्या एवं कितना उपभोग करना है? एक उत्पादक निर्णय लेता है कि किन वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं का, कितनी मात्रा में उत्पादन करना है। वह आर्थिक इकाई या अभिकर्ता एक निवेशक भी हो सकता है जो यह निर्णय लेता है कि उसे कब, कहाँ एवं कितनी मात्रा में धन का विनियोजन करना है। सरकार भी आर्थिक इकाई के रूप में निर्णयकर्ता हो सकती है कि अधिकतम लोक कल्याण एवं देश के आर्थिक विकास में कैसे निर्णय लिये जायें ताकि आर्थिक विकास के लक्ष्य को प्राप्त किया जा सके।
प्रश्न 4.
उपभोक्ता वस्तुएँ किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
मानवीय आवश्यकताओं की संतुष्टि के लिये प्रत्यक्ष रूप से उपभोग करने की प्रतिसालग्न वस्तुएँ ही उपभोक्ता वस्तुएँ कहलाती हैं। उदाहरण के लिये, दूध, सब्जी, गेहूँ, चावल का उपभोग आदि।
प्रश्न 5.
पूँजीगत वस्तुओं से क्या तात्पर्य है?
उत्तर:
उत्पादन की प्रक्रिया में ऐसी स्थिर परिसंपत्तियाँ जिनका बार – बार प्रयोग होता है पूँजीगत वस्तुएँ कहलाती हैं। इन्हें टिकाऊ उपभोग उत्पादक वस्तुओं के नाम से भी जाना जाता है। प्लांट एवं मशीनरी पूँजीगत वस्तुएँ हैं जिनका प्रयोग उत्पादन में बारंबार किया जाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
अंतिम वस्तुओं से आपका क्या आशय है?
उत्तर:
अंतिम वस्तुओं काय उन:
से है जो उपभोक्ता एवं निवेशक द्वारा वस्तु के अंतिम प्रयोग के लिये उपलब्ध होती है। उदाहरण के लियं उपपाक्ताओं द्वारा उपभोग के लिये एवं उत्पादकों द्वारा निवेश के लिये जो वस्तुएँ अंतिम तौर पर उपलब्ध होती हैं उन्हें अंतिम वस्तुएँ कहते हैं। दूसरे शब्दों में, जब कोई वस्तु अंतिम प्रयोगकर्ता के पास पहुँच जाती है तो उसे अंतिम वस्तु कहा जाता है जिसका अंतिम प्रयोग केवल उपभोक्ता या निवेश होता है।
प्रान 7.
मध्यवर्ती वस्तुओं से आप क्या समझते हैं?
उत्तर:
मध्यवर्ती वस्तुओं का आशय ऐसी वस्तुओं से है जो किसी लेखावर्ष में उत्पादन में कच्चे माल के रूप में उपयोग के लिये अथवा पुनः बिक्री के लिये खरीदी जाती है । मध्यवर्ती वस्तुओं को राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना में शामिल नहीं किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 8.
प्रवाह एवं स्कंध (Flow and Stock) की अवधारणा को समझाइये?
उत्तर:
प्रवाह चर के अन्तर्गत:
प्रवाह एक ऐसी मात्रा है जिसे उचित समयावधि जैसे घंटे, दिन, सप्ताह, मास, वर्ष आदि के आधार पर मापा जाता है। उदाहरण के लिये, व्यय, बचत, पूँजी निर्माण, ब्याज, पूँजीह्रास, मुद्रा की पूर्ति में परिवर्तन आदि। स्कंध (स्टॉक) वह मात्रा है जो किसी निश्चित समय बिन्दु पर मापी जाती है। उदाहरण के लिये, विदेशी ऋण, ऋण की मात्रा, संपत्ति, उपस्कर आदि।
![]()
प्रश्न 9.
सकल निवेश (Gross Investment) से क्या आशय है?
उत्तर:
सकल निवेश से तात्पर्य पूँजीगत वस्तुओं जैसे:
मशीनों, भवनों, उपकरणों के स्कंध में वृद्धि से है जो भविष्य में अर्थव्यवस्था की उत्पादन क्षमता को बढ़ाते हैं। किसी अर्थव्यवस्था में उत्पादन क्षमता में भौतिक पूँजी के स्कंध में होने वाली वृद्धि, पूँजी निर्माण कहलाती है। अतः अर्थव्यवस्था की उत्पादन क्षमता को बढ़ाने वाला निवेश, सकल निवेश कहलाता है। सकल निवेश में से ह्रास को घटाकर शुद्ध निवेश ज्ञात किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 10.
मूल्यह्रास किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
अचल संपत्तियों के निरंतर उपयोग के कारण इन परिसंपत्तियों के मूल्य में आने वाली शनैःशनैः कमी ही मूल्यह्रास कहलाती है। सामान्य टूट – फूट एवं अप्रचलन के कारण स्थायी संपत्तियों के मूल्य में गिरावट को स्थायी पूँजी का उपभोग कहते हैं। राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना के लिये सकल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद में से ह्रास को घटाया जाता है।
प्रश्न 11.
आय के चक्रीय प्रवाह (Circular flow of Income) से आपका क्या आशय है?
उत्तर:
आय के चक्रीय प्रवाह से आशय मुद्रा एवं पदार्थ तथा सेवाओं के निरंतर प्रवाह से है। आय का चक्रीय प्रवाह अर्थव्यवस्था के प्रमुख क्षेत्रों जैसे परिवार, फर्म, सरकारी क्षेत्र से जुड़ा रहता है। उदाहरण के लिये, फर्मे पहले आय सृजित करती हैं तत्पश्चात् ये आय परिवारों में साधन सेवायें प्रदान करने के लिये वितरित की जाती हैं और अंत में वही आय फर्मों के पास वापस आ जाती है। यही आय का चक्रीय प्रवाह कहलाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 12.
आय का चक्रीय प्रवाह किन सिद्धांतों पर निर्भर करता है?
उत्तर:
आय का चक्रीय प्रवाह दो मूल सिद्धांतों पर निर्भर होता है –
- विनिमय की प्रक्रिया में उपभोक्ता द्वारा किया गया खर्च विक्रेताओं द्वारा प्राप्त की गई राशि के बराबर होता है।
- वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं का प्रवाह एक दिशा की ओर होता है जबकि मौद्रिक भुगतानों का प्रवाह विपरीत दिशा की ओर होता है इसी कारण आय का चक्रीय प्रवाह उत्पन्न होता है।
अतः वास्तविक प्रवाह का अर्थ पदार्थों एवं सेवाओं के प्रवाहों से है जबकि मौद्रिक प्रवाह का आशय साधन भुगतान एवं उपभोग व्यय से है।
प्रश्न 13.
राष्ट्रीय आय क्या है?
उत्तर:
एक देश के सामान्य निवासियों द्वारा देश के अंदर व देश के बाहर अर्जित साधन आय का योग ही राष्ट्रीय आय कहलाती है एक वर्ष में उत्पादित सभी अंतिम वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं के मौद्रिक मूल्य को राष्ट्रीय आय कहते हैं।
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं संबंधित समुच्चय लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं प्रति व्यक्ति आय में अन्तर स्पष्ट कीजिए?
अथवा
राष्ट्रीय आय तथा प्रति व्यक्ति आय से क्या आशय है?
राष्ट्रीय आय तथा प्रति व्यक्ति आय में अन्तर बताइए?
उत्तर:
राष्ट्रीय आय:
एक वर्ष में उत्पादित समस्त वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं के मौद्रिक मूल्य का योग राष्ट्रीय आय कहलाती है।
प्रति व्यक्ति आय:
जब कुल राष्ट्रीय आय में कुल जनसंख्या से भाग दिया जाता है तो प्रति व्यक्ति आय प्राप्त होती है।
राष्ट्रीय आय और प्रति व्यक्ति आय में अन्तर –
राष्ट्रीय आय:
- किसी देश के समस्त उत्पादकों के वास्तविक उत्पादन का योग राष्ट्रीय आय कहलाता है।
- राष्ट्रीय आय में प्रति व्यक्ति आय शामिल होती है।
- राष्ट्रीय आय विकास का प्रतीक है।
प्रति व्यक्ति आय:
- एक व्यक्ति विशेष द्वारा विभिन्न स्रोतों से प्राप्त उत्पादन का योग राष्ट्रीय आय कहलाता है।
- प्रति व्यक्ति आय राष्ट्रीय आय का एक भाग है।
- प्रति व्यक्ति आय राष्ट्रीय आय का एक भाग है।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र के दृष्टिकोण से अर्थव्यवस्था के चार प्रमुख क्षेत्रकों का वर्णन कीजिए?
उत्तर:
किसी अर्थव्यवस्था को समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र के दृष्टिकोण से जिन चार भागों में विभाजित किया गया है वे निम्न हैं –
1. परिवार क्षेत्र:
जिन वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं का उपभोग उपभोक्ताओं द्वारा किया जाता है उसे परिवार क्षेत्र कहते हैं। इस क्षेत्र में परिवार क्षेत्र के उत्पादन के घटकों का स्वामी भी परिवार होता है।
2. उत्पादक क्षेत्र:
इस क्षेत्र में उन सभी घटकों को सम्मिलित किया जाता है जो उत्पादन की क्रिया में संलग्न रहते हैं। वे सभी इकाइयाँ जो उत्पादन का कार्य करती हैं उन्हें अर्थव्यवस्था के उत्पादक क्षेत्र में सम्मिलित किया जाता है वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं का उत्पादन जिन फर्मों के द्वारा किया जाता है उनके द्वारा उत्पादन के साधनों जैसे भूमि, श्रम, पूँजी, संगठन एवं साइज (क्षेत्र) किराया देकर प्राप्त किया जाता है।
3. सरकारी क्षेत्र:
कल्याणकारी सेवाओं को बनाये रखने का काम सरकार का है। वैसे तो सरकार का कार्य कानून और व्यवस्था को बनाये रखना है किन्तु सरकार सार्वजनिक क्षेत्र के लिये एक उत्पादक की तरह भी कार्य करती है।
4. विदेशी क्षेत्र:
‘इसमें शेष विश्व को सम्मिलित किया जाता है। इसे Rest of the world’ कहते हैं। इसके अन्तर्गत घरेलू अर्थव्यवस्था का विश्व के अन्य देशों के मध्य पूँजी के प्रवाह तथा आयात – निर्यात को शामिल किया जाता है।
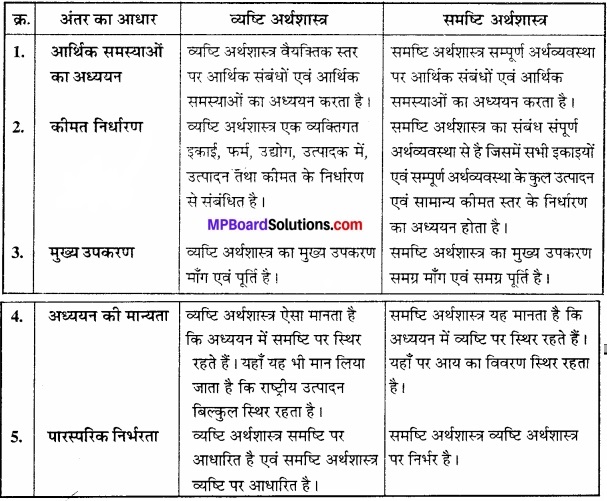
प्रश्न 3.
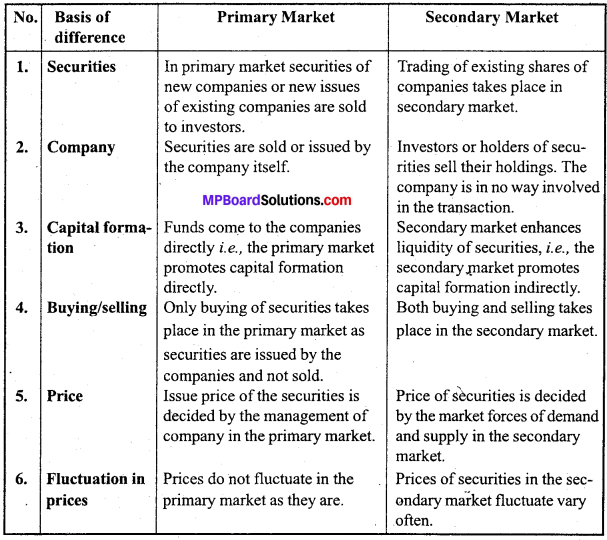
व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र एवं समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में अन्तर स्पष्ट कीजिए?
उत्तर:
व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र एवं समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में अन्तर –
प्रश्न 4.
स्टॉक तथा प्रवाह से क्या समझते हैं? स्टॉक तथा प्रवाह में तीन अन्तर बताइए?
उत्तर:
स्टॉक तथा प्रवाह:
स्टॉक वह मात्रा है जिसे किसी समय विशेष पर मापा जाता है जबकि प्रवाह वह मात्रा है जिसे विशेष समयावधि में मापा जाता है। जैसे एक निश्चित तिथि पर देश में मुद्रा की मात्रा स्टॉक है तथा एक वित्त वर्ष में जो व्यय है वह प्रवाह कहलाता है।
स्टॉक तथा प्रवाह में अन्तर –
स्टॉक:
- स्टॉक वह मात्रा है, जिसे किसी समय विशेष पर मापा मापा जाता है।
- स्टॉक का कोई समयकाल नहीं होता।
- स्टॉक एक स्थैतिक अवधारणा है।
- कुछ चरों की स्टॉक अवधारणाएँ नहीं होती। कुछ चरों की केवल प्रवाह अवधारणाएँ होती हैं। जैसे – आयात – निर्यात।
प्रवाह:
- प्रवाह वह मात्रा है, जिसे विशेष समयावधि में मापा जाता है।
- प्रवाह का समयकाल होता है।
- प्रवाह एक प्रावैगिक अवधारणा है।
- कुछ चरों की केवल प्रवाह अवधारणाएँ होती हैं। जैसे – आयात – निर्यात।
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं राष्ट्रीय पूँजी में अन्तर बताइए?
उत्तर:
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं राष्ट्रीय पूँजी में अन्तर –
राष्ट्रीय आय:
- राष्ट्रीय आय एक समयावधि जैसे – एक वर्ष की होती है – अतः यह एक प्रवाह होती है।
- राष्ट्रीय आय में सेवाएँ शामिल होती हैं।
- राष्ट्रीय आय में पूँजीगत तथा उपभोग दोनों वस्तुएँ शामिल होती हैं।
- राष्ट्रीय आय, राष्ट्रीय पूँजी को प्रभावित करती है।
- आर्थिक क्रियाएँ राष्ट्रीय आय को प्रभावित करती हैं।
राष्ट्रीय पूँजी:
- राष्ट्रीय पूँजी किसी समय विशेष पर होती है, एक स्टॉक है।
- राष्ट्रीय पूँजी में सेवाएँ शामिल नहीं होती हैं।
- राष्ट्रीय आय में केवल पूँजीगत वस्तुओं को शामिल शामिल होती हैं।
- राष्ट्रीय पूँजी, राष्ट्रीय आय का कारण होती है।
- एक निश्चित समय में राष्ट्रीय पूँजी स्थिर होती है।
प्रश्न 6.
सन् 1929 की विश्वव्यापी मंदी को समझाइये?
उत्तर:
सन् 1929 में विश्वव्यापी मंदी ने संपूर्ण विश्व के विकासत देशों की अर्थव्यवस्था को चूर-चूर कर दिया। इस मंदी में उत्पादन तो था पर खरीदने वाले नहीं थे। सन् 1929 से सन् 1933 के मध्य संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में बेरोजगारी 3% से बढ़कर 25% तक बढ़ गई। अमेरिका के समग्र निर्गत में 33% की गिरावट आ गई। इसी दौरान सन् 1936 में जॉन मेनार्ड कीन्स ने एक पुस्तक प्रकाशित की ‘रोजगार, ब्याज एवं मुद्रा का सामान्य सिद्धांत’ इसी ने समष्टि अर्थव्यवस्था की नींव रखी।
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र एवं व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में परस्पर क्या निर्भरता है?
उत्तर:
समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में हम सम्पूर्ण अर्थव्यवस्था का एक इकाई के रूप में अध्ययन करते हैं एवं व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में हम अर्थव्यवस्था की छोटी – छोटी इकाईयों का अध्ययन करते हैं। दोनों एक – दूसरे के प्रतियोगी नहीं वरन् पूरक हैं। एक – दूसरे पर आश्रित हैं। उदाहरण के लिये, यदि व्यक्ति की आय बढ़ेगी तो राष्ट्रीय आय स्वतः बढ़ जायेगी परन्तु राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि हो रही है तो यह आवश्यक नहीं है कि प्रत्येक व्यक्ति की आय बढ़ रही हो। व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र की भाँति समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में भी सीमित साधनों के विवेकपूर्ण उपयोग एवं प्रबंधन की समस्या ही मुख्य समस्या है। समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र में व्यक्तिगत हित की अपेक्षा सार्वजनिक हित एवं सामाजिक कल्याण पर अधिक बल दिया जाता है। समष्टि अर्थशास्त्र एवं व्यष्टि अर्थशास्त्र राधा एवं कृष्ण की भाँति है दोनों एक – दूसरे के बिना रह नहीं सकते। दोनों एक – दूसरे पर निर्भर हैं।
प्रश्न 8.
निम्नलिखित आँकड़ों से राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना कीजिए –
- वेतन – ₹ 6,000
- किराया – ₹ 2,000
- लाभ – ₹ 2,000
- ब्याज – ₹ 1,000
- उपभोग – ₹ 5,000
- सकल घरेलू विनियोग – ₹ 800।
हल: राष्ट्रीय आय = वेतन + किराया + लाभ + ब्याज
= 6,000 + 2,000 + 2,000 + 1.000
= ₹ 11,000।
प्रश्न 9.
निम्नलिखित आँकड़ों के आधार पर आय गणना विधि द्वारा राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना कीजिए –
मदें:

हल: राष्ट्रीय आय = वेतन एवं मजदूरी + ब्याज + किराया + लाभ
= 18,000 + 7,000 + 6,000 + 25.000
राष्ट्रीय आय = ₹ 56,000 करोड़।
प्रश्न 10.
निम्नलिखित आँकड़ों के आधार पर आय गणना विधि द्वारा राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना कीजिए –

हल: राष्ट्रीय आय = वेतन एवं मजदूरी + किराया/लगान + लाभ + ब्याज
= 30,000 + 10,000 + 50,000 + 10,000
राष्ट्रीय आय = ₹ 1,00000 करोड़।
प्रश्न 11.
निम्नलिखित आँकड़ों से राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना कीजिए –
- वेतन – ₹ 60,000
- किराया – ₹ 20,000
- लाभ – ₹ 20,000
- ब्याज – ₹ 10,000
- उपभोग – ₹ 50,000
- सकल घरेलू उत्पाद – ₹ 8,000
- मूल्यह्रास – ₹ 10,000
हल: राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना
सूत्र – राष्ट्रीय आय = वेतन + किराया + लाभ + ब्याज
= 60,000 + 20,000 + 20,000 + 10,000
राष्ट्रीय आय = 1,10,000.
प्रश्न 12.
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद की कोई चार विशेषताएँ लिखिए?
उत्तर:
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद की विशेषताएँ निम्न हैं –
- सकल राष्ट्र इस तथ्य को संकेत करता है कि सकल घरेलू उत्पाद (GDP) के मूल्य में घिसावट व्यय शामिल है।
- सकल घरेलू उत्पाद के मूल्य में दोहरी गणना से बचने के लिए केवल अंतिम वस्तुओं व सेवाओं के मूल्य को ही जोड़ा जाता है।
- पुरानी वस्तुओं की बिक्री से प्राप्त राशि इसमें नहीं जोड़ी जाती।
- इसके मूल्य में स्व – उपभोग के लिए किया गया उत्पाद तथा खुद – काबिज मकानों का आरोपित किराया शामिल होता है।
प्रश्न 13.
आय गणना विधि का चुनाव करते समय किन – किन बातों पर ध्यान देना आवश्यक है?
उत्तर:
आय गणना विधि का चुनाव करते समय निम्नलिखित बातों पर ध्यान देना चाहिए –
- गैर – कानूनी कार्यों से होने वाली आय को शामिल नहीं किया जाना चाहिए। जैसे – जमाखोरी, तस्करी. घूस से प्राप्त आय।
- पुरानी वस्तुओं की बिक्री से प्राप्त होने वाली आय को राष्ट्रीय आय में शामिल नहीं किया जाता है, किन्तु दलालों को मिलने वाला कमीशन राष्ट्रीय आय में जोड़ा जाता है।
- आकस्मिक रूप से मिलने वाली आय को शामिल नहीं किया जाना चाहिए। जैसे – लॉटरी से मिलने वाली आय।
- हस्तांतरित भुगतान, जैसे – पेंशन, छात्रवृत्तियाँ, बेरोजगारी भत्ता, सरकारी सहायता आदि को राष्ट्रीय आय में नहीं जोड़ा जाता।
- मृत्यु कर, उपहार कर, सम्पत्ति कर, अप्रत्याशित लाभों पर कर आदि को राष्ट्रीय आय में शामिल नहीं किया जाता, क्योंकि इन करों का भुगतान करदाता या तो अपने धन में से अथवा भूतकाल की बचत से करता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 14.
आय गणना प्रणाली के प्रमुख घटकों के बारे में लिखिए?(कोई पाँच)
उत्तर:
आय गणना प्रणाली के प्रमुख घटक निम्नलिखित हैं –
1. मजदूरी आय:
मजदूरी आय से तात्पर्य, उस आय से है जो श्रमिक को उनकी सेवाओं के बदले मौद्रिक या किस्त के रूप में प्राप्त होती है। इसमें समस्त कर्मचारियों के वेतन व मजदूरी, श्रमिकों को प्राप्त सामाजिक सुरक्षा योगदान, पेंशन, फण्ड, आवास, शिक्षा, मनोरंजन आदि की सुविधाओं को सम्मिलित किया जाता है।
2. गैर – मजदूरी आय:
भूमि के स्वामी, पूँजीपति तथा साहसी को किराया (लगान), ब्याज तथा लाभांश के रूप जो आय प्राप्त होती है, उसे गैर – मजदूरी आय कहते हैं। इसमें मिश्रित आय को भी सम्मिलित किया गया है।
3. परिचालन अधिशेष:
इसमें सार्वजनिक उद्योगों के परिचालन अधिशेष को सम्मिलित किया जाता है।
4. विदेशों से शुद्ध आय:
इसमें कर्मचारियों का शुद्ध पारिश्रमिक, सम्पत्ति के स्वामित्व एवं उद्यमशीलता से शुद्ध आय तथा निवासी कम्पनियों द्वारा विदेशों से शुद्ध प्रतिधारित आय को सम्मिलित किया जाता है।
5. स्व – उपभोग के लिए वस्तुएँ:
एक अर्थव्यवस्था में उत्पन्न सभी वस्तुएँ बाजार में बिकने के लिये नहीं आतीं बल्कि उसका एक भाग उत्थादक स्वयं के उपभोग के लिये अपने पास रख लेता है। अतः इस भाग का मौद्रिक मूल्य राष्ट्रीय आय में सम्मिलित किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 15.
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद के अंग कौन – कौन से हैं?
उत्तर:
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद से अभिप्राय किसी देश में एक निश्चित समयावधि में उत्पादित अन्तिम वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं के मूल्यों के योग से होता है –
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद के अंग:
- एक देश की घरेलू सीमा में एक निश्चित अवधि में उत्पादित अन्तिम वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं के मूल्य के योग को सकल घरेलू उत्पाद कहते हैं।
- वस्तुओं के उत्पादन में उपभोग एवं पूँजीगत वस्तुओं को शामिल किया जाता है।
- उपभोक्ता एवं पूँजीगत वस्तुओं को टिकाऊ एवं गैर – टिकाऊ वस्तुओं में विभक्त किया जाता है।
- निजी एवं सार्वजनिक दोनों क्षेत्रों के उत्पादन को लिया जाता है।
- अन्तिम वस्तुओं के उत्पादन को ही सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में शामिल किया जाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 16.
राष्ट्रीय आय की उत्पादन विधि को समझाइये?
अथवा
राष्ट्रीय आय गणना की मूल्य वृद्धि विधि की व्याख्या कीजिए?
उत्तर:
इस विधि के अन्तर्गत राष्ट्रीय आय ज्ञात करने के लिए हम या तो मूल्य वृद्धि ज्ञात कर लेते हैं या एक लेखा वर्ष में उत्पादित समस्त वस्तुओं व सेवाओं के मौद्रिक मूल्य का योग कर लेते हैं। इस योग को बाजार कीमतों पर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 17.
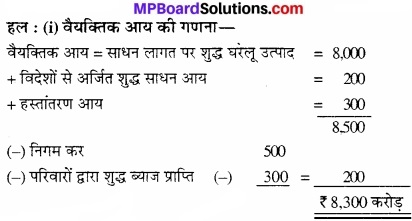
निम्नलिखित आँकड़ों से वैयक्तिक आय और वैयक्तिक प्रयोज्य आय की गणना कीजिए –
(₹ करोड़ में)
- कारक लागत पर निवल घरेलू उत्पाद – 8,000
- विदेशों से प्राप्त निवल कारक आय – 200
- अवितरित लाभ – 1,000
- निगम कर – 500
- परिवारों द्वारा प्राप्त ब्याज – 1.500
- परिवारों द्वारा भुगतान किया गया ब्याज – 1,200
- अंतरण आय – 300
- वैयक्तिक कर – 500
हल:
1. वैयक्तिक आय की गणना –
2. वैयक्तिक प्रयोज्य आय की गणना –

प्रश्न 18.
हजाम राजू एक दिन में बाल काटने के लिए ₹ 500 का संग्रहरण करता है। इस दिन उसके उपकरण में ₹ 50 का मूल्यह्रास होता है। इस ₹ 450 में से राजू ₹ 30 बिक्री कर अदा करता है। ₹ 200 घर ले जाता है और ₹ 220 उन्नति और नए उपकरणों का क्रय करने के लिए रखता है। वह अपनी आय में से ₹ 20 आयकर के रूप में अदा करता है। इन पूरी सूचनाओं के आधार पर निम्नलिखित में राजू का योगदान ज्ञात कीजिए –
- सकल घरेलू उत्पाद।
- बाजार कीमत पर निवल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद।
- कारक लागत पर निवल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद।
- वैयक्तिक आय।
- वैयक्तिक प्रयोज्य आय।
हल :
ΣRi = ₹ 500
स्थायी पूँजी का उपयोग = ₹ 50
बिक्री कर = ₹ 30
प्रतिधारित आय = ₹ 220
घर ले जाई गई आय = ₹ 200
आयकर = ₹ 20
(a) बाजार कीमत पर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद (GDP at Market Price) में योगदान
= बाल काटने के लिए प्राप्त आगम
= ₹ 500
(b) बाजार कीमत पर शुद्ध राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद (NNP at Market Price) में योगदान
= बाजार कीमत पर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद – स्थायी पूँजी का उपभोग
= ₹ 500 – ₹ 50 = ₹450
(c) साधन लागत पर शुद्ध राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद में योगदान
= बाजार कीमत पर शुद्ध राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद – शुद्ध अप्रत्यक्ष कर
-₹ 450 – ₹ 30 = ₹420
(d) वैयक्तिक आय = साधन लागत पर शुद्ध राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद में योगदान – अवितरित लाभ
= ₹ 420 – ₹ 220
= ₹ 200
(e) वैयक्तिक प्रयोज्य आय = वैयक्तिक आय – प्रत्यक्ष कर
= ₹ 200 – ₹ 20
= ₹ 180
अतः
- ₹ 500
- ₹ 450
- ₹ 420
- ₹ 200
- ₹ 180.
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं संबंधित समुच्चय दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
राष्ट्रीय आय के महत्व को पाँच बिन्दुओं में स्पष्ट कीजिए?
अथवा
राष्ट्रीय आय का महत्त्व लिखिए। (कोई चार)
उत्तर:
राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना का निम्नलिखित महत्व है –
1. आर्थिक विकास का मापदण्ड:
जिन देशों की राष्ट्रीय आय अधिक होती है वह आर्थिक दृष्टि से विकसित माने जाते हैं तथा जिन देशों की राष्ट्रीय आय कम होती है, वह पिछड़े हुए देश माने जाते हैं।
2. जीवन – स्तर का सूचक:
जिस देश में प्रतिव्यक्ति राष्ट्रीय आय जितनी अधिक होती है, वहाँ के नागरिकों का जीवन – स्तर प्राय: उतना ही ऊँचा होता है।
3. तुलनात्मक अध्ययन में सहायक:
राष्ट्रीय आय के अध्ययन से विभिन्न देशों की कुल तथा प्रतिव्यक्ति आय की तुलनात्मक जानकारी उपलब्ध हो जाती है।
4. आर्थिक कल्याण का मापक:
यदि अन्य बातें समान रहें तो राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि होने पर आर्थिक कल्याण भी बढ़ जाता है तथा राष्ट्रीय आय में कमी होने पर आर्थिक कल्याण भी कम हो जाता है।
5. आर्थिक नीति के निर्माण में सहायक:
राष्ट्रीय आय के आँकड़े किसी देश की आर्थिक नीति के निर्माण में भी सहायक होते हैं। इन आँकड़ों से सरकार को रोजगार, साख, बचत तथा विनियोग संबंधी मामलों में आर्थिक नीति बनाने में सहायता मिलती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद तथा सकल राष्ट्रीय आय में अंतर स्पष्ट कीजिए?
उत्तर:
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद एवं सकल राष्ट्रीय आय में अंतर –
क्र. सकल घरेलू उत्पाद:
- सकल घरेलू उत्पाद का आशय एक देश की घरेलू सीमा के अंदर उत्पादित कुल अंतिम निवासियों द्वारा उत्पादित)कुल अंतिम वस्तुओं वस्तुओं व सेवाओं के कुल मौद्रिक मूल्य से है।
- सकल घरेलू उत्गद एक भौगोलिक धारणा है।
- इसका संबंध देश के घरेलू सीमा से है।
- GDP = P(G) + P(S)
- यदि विदेशों से प्राप्त आय ऋणात्मक है तो इसका मूल्य GNP के मूल्य से अधिक होगा। मूल्य GDP के मूल्य से अधिक होगा।
सकल राष्ट्रीय आय:
- सकल राष्ट्रीय आय से आशय एक राष्ट्र के निवासियों द्वारा उत्पादित कुल अंतिम वस्तुओं वस्तुओं व सेवाओं के कुल मौद्रिक मूल्य से है।
- सकल राष्ट्रीय आय एक राष्ट्रीय धारणा है।
- इसका संबंध देश के सामान्य निवासियों से है।
- GNP = GDP + NFIA
- यदि विदेशों से प्राप्त आय धनात्मक है, तो इसका मूल्य GDP के मूल्य से अधिक होगा।
प्रश्न 3.
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं निजी आय में अन्तर स्पष्ट कीजिए?
उत्तर:
राष्ट्रीय आय एवं निजी आय में अन्तर –
राष्ट्रीय आय:
- राष्ट्रीय आय में केवल आय भुगतान शामिल किए जाते हैं।
- राष्ट्रीय आय में निजी एवं सार्वजनिक दोनों क्षेत्रों में सृजित आय को शामिल किया जाता है।
- राष्ट्रीय आय एक देश के सामान्य निवासियों की आय होती है।
- राष्ट्रीय आय = घरेलू साधन आय + विदेशों से प्राप्त शुद्ध साधन आय।
निजी आय:
- निजी आय में आय भुगतान तथा हस्तान्तरण भुगतान दोनों शामिल किये जाते हैं।
- निजी आय में केवल निजी क्षेत्र की आय को शामिल किया जाता है।
- निजी आय निजी क्षेत्र के लोगों की आय होती है।
- निजी आय में राष्ट्रीय ऋणों पर ब्याज के भुगतान को शामिल किया जाता है।
- निजी आय = घरेलू साधन आय + घरेलू उत्पाद से प्राप्त शुद्ध साधन आय से सरकारी क्षेत्र को प्राप्त आय + समस्त चालू हस्तान्तरण + विदेशों से प्राप्त शुद्ध साधन आय।
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
भारत में राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि की धीमी गति के किन्हीं पाँच कारणों का वर्णन कीजिए?
अथवा
भारत की राष्ट्रीय आय कम होने के कारणों को लिखिए?
उत्तर:
भारत में राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि की धीमी गति के प्रमुख कारण निलिखित हैं –
1. जनसंख्या में वृद्धि:
राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि की धीमी गति का सबसे प्रमुख कारण हैं, जनसंख्या में तीव्र वृद्धि। जनसंख्या में तीव्र वृद्धि के कारण राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि की दर धीमी हो गई है।
2. कृषि पर निर्भरता:
देश की 71% जनसंख्या अभी भी कृषि में लगी हुई है। जबकि औद्योगिक क्षेत्रों में केवल 12% जनसंख्या लगी है एवं सेवा क्षेत्र में केवल 17% जनसंख्या लगी है। इसलिए राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि की गति धीमी है।
3. पूँजी की कमी:
देश में पूँजी की कमी राष्ट्रीय आय में धीमी वृद्धि का एक प्रमुख कारण रही है पूँजी की कमी का कारण लोगों की बचत करने की इच्छा एवं शक्ति तथा विनियोग की प्रेरणा का कम होना है।
4. तकनीकी पिछड़ापन:
भारत के तकनीकी पिछड़ेपन के कारण उत्पादन में परम्परागत रीतियों का प्रयोग किया जाता है जिसके कारण उत्पादकता का स्तर निम्न बना रहता है। इससे कृषि व औद्योगिक दोनों क्षेत्रों में लोगों की आय कम रहती है।
5. आय का असमान वितरण:
भारत में राष्ट्रीय आय का वितरण बहुत असमान है। इसी असमानता का प्रमुख कारण सरकार की दोषपूर्ण कर नीति है।
प्रश्न 5.
भारत में राष्ट्रीय आय की वृद्धि हेतु पाँच आवश्यक सुझाव दीजिए?
अथवा
भारत में राष्ट्रीय आय को बढ़ाने के चार सुझाव दीजिए?
उत्तर:
भारत की राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि हेतु प्रमुख सुझाव निम्नलिखित हैं –
- प्राकृतिक साधनों का उचित उपयोग: देश की राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि के लिये यह आवश्यक है कि प्राकृतिक साधनों का उचित उपयोग किया जाये।
- जनसंख्या की वृद्धि पर नियंत्रण: देश की राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि के लिये यह आवश्यक है कि यथासंभव बढ़ती हुई जनसंख्या की दर को कम किया जाय।
- बचतों को प्रोत्साहन एवं पूँजी – निर्माण: देश की राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि के लिये घरेलू बचतों को प्रोत्साहित किया जाना चाहिऐतथा उन बचतों को पूँजी-निर्माण में बदल दिया जाना चाहिए।
- कृषि का आधुनिकीकरण करना: कृषि उत्पादन बढ़ाने के लिये कृषि का आधुनिकीकरण आवश्यक है। कृषि के आधुनिकीकरण से उत्पादन बढ़ेगा। फलतः देश की राष्ट्रीय आय भी बढ़ेगी।
- साहसियों को पर्याप्त सुविधाएँ एवं प्रेरणाएँ: राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि के लिये सरकार को चाहिये कि वह उद्योग स्थापित करने वाले साहसियों को पर्याप्त सुविधाएँ दें तथा उनको उत्पादन करने के लिये प्रोत्साहित करें।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
बंद अर्थव्यवस्था एवं खुली अर्थव्यवस्था में अन्तर बताइए?
उत्तर:
बंद अर्थव्यवस्था एवं खुली अर्थव्यवस्था में अन्तर –
बंद अर्थव्यवस्था:
- जब किसी देश का अन्य दूसरे देशों से कोई आर्थिक संबंध आर्थिक संबंध नहीं होती है, तो उसे बंद अर्थ – व्यवस्था कहते हैं।
- बंद अर्थव्यवस्था में सकल घरेलू उत्पाद एवं राष्ट्रीय आय दोनों एक समान होते हैं।
- बंद अर्थव्यवस्था एक काल्पनिक अर्थव्यवस्था है।
- बंद अर्थव्यवस्था में पूँजी-निर्माण नगण्य होता है।
- बंद अर्थव्यवस्था में उपभोग एवं विनियोग दोनों उत्पादन के बराबर होते हैं।
खुली अर्थव्यवस्था:
- जब किसी देश का अन्य दूसरे देशों से आर्थिक संबंध स्थापित हो जाता है, तो उसे खुली अर्थव्यवस्था कहा जाता है।
- खुली अर्थव्यवस्था में राष्ट्रीय आय एवं घरेलू आय में अन्तर होता है।
- खुली अर्थव्यवस्था एक वास्तविक अर्थव्यवस्था है।
- खुली अर्थव्यवस्था में उपभोग तथा विनियोग का योग उत्पादन से अधिक भी हो सकता है और कम भी।
प्रश्न 7.
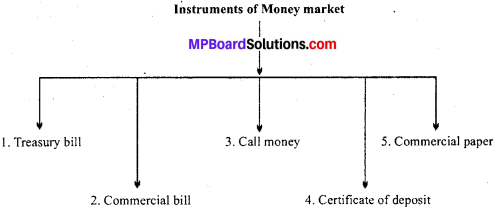
राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना विधियाँ कौन – सी हैं?
अथवा
राष्ट्रीय आय मापने की विधियों की विवेचना कीजिए?
उत्तर:
1.आय गणना विधि:
इस विधि में सभी साधनों द्वारा प्राप्त आय को जोड़ा जाता है अतः इसे प्राप्त आय गणना विधि भी कहते हैं। इस विधि में एक वर्ष में व्यक्ति या व्यावसायिक उपक्रमों द्वारा प्राप्त विशुद्ध आय को ज्ञात किया जाता है, उनका योग ही राष्ट्रीय आय होता है। इस योगफल में अनुत्पादक आय को शामिल नहीं किया जाता है।
2. व्यय गणना विधि:
इस विधि में लोगों में व्यय और बचत को जोड़कर राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना की जाती है)। इस विधि के अनुसार किसी देश की कुल राष्ट्रीय आय लोगों के कुल उपभोग एवं बचतों के बराबर होती है।
3. मिश्रित गणना विधि:
इस प्रणाली का प्रयोग डॉ. व्ही. के. राव ने किया है) इसमें उत्पादन विधि व आय विधि दोनों का मिश्रित प्रयोग करने राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना की जाती है। यह विधि भारत में राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना हेतु सफल विधि मानी गयी है।
4. उत्पादन गणना विधि:
इस विधि में एक वर्ष के अन्तर्गत देश में स्थित सारे उद्योगों, व्यवसायों, कृषि कार्य द्वारा समस्त उत्पादित वस्तुओं का मूल्य जोड़ दिया जाता है, इससे से कच्चे माल का मूल्य, मशीनों का ह्रास तथा प्रतिस्थापना आदि का मूल्य घटाकर वास्तविक राष्ट्रीय आय ज्ञात कर लिया जाता है। इस प्रणाली का प्रयोग करते समय वस्तुओं और सेवाओं के मूल्य की दोहरी गणना से बचना चाहिए। विदेशों को भुगतान में दिये जाने वाले चरण एवं ब्याज की राशि घटाते हुए प्राप्त होने वाले ऋण एवं ब्याज की आय को जोड़कर राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना करनी चाहिए।
5. सामाजिक लेखांकन विधि:
इस विधि का आविष्कार प्रो. रिचर्ड स्टोन ने किया है। इसमें देश की समस्त जनसंख्या को कई वर्गों जैसे उत्पादन संस्थाएँ, वित्तीय संस्थाएँ, बीमा एवं सामाजिक सुरक्षा संस्थाएँ, अंतिम उपभोक्ता वर्ग एवं अन्यों में बाँट दिया जाता है, इनमें प्रत्येक वर्ग के कुछ व्यक्तियों की आय ज्ञात करके उसका औसत निकालकर उस वर्ग के व्यक्तियों की संख्या से गुणा कर दिया जाता है। इस प्रकार सभी वर्ग के व्यक्तियों की आय ज्ञात करके इन्हें जोड़कर कुल राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना कर ली जाती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
एक किसान ने ₹ 500 का कपास स्वतः उत्पादित करके कपड़ा मिल को बेचा। कपड़ा मिल ने कपड़ा तैयार करके ₹ 600 में रेडीमेड गारमेंट फैक्ट्री को बेचा। रेडीमेड गारमेंट फैक्ट्री ने ड्रेसेज तैयार करके ₹ 1000 में एक स्टोर को बेच दिया। स्टोर मालिक ने ₹ 1200 में ड्रेसों को उपभोक्ताओं को बेचा?
प्रत्येक फर्म द्वारा की गई मूल्य वृद्धि सकल मूल्य वृद्धि ज्ञात कीजिए?
हल:
किसान, कपड़ा मिल, रेडीमेड गारमेंट फैक्ट्री, स्टोर द्वारा की गयी मूल्य वृद्धि निम्न प्रकार होगी
1. किसान द्वारा मूल्य वृद्धि = कपड़ा मिल को कपास का विक्रय
= ₹ 500
2. कपड़ा मिल द्वारा मूल्य वृद्धि = रेडीमेड गारमेंट फैक्टरी को कपड़ा का विक्रय – किसान से कपास का क्रय – विक्रय
= 600 – ₹ 500 = 100
3. रेडीमेड गारमेंट फैक्टरी द्वारा = स्टोर को ड्रेसेज का विक्रय मूल्य – कपड़ा मिल से कपास का क्रय – मूल्य
= 1000 – 600 = ₹ 400
4. स्टोर द्वारा मूल्य वृद्धि = अंतिम उपभोक्ताओं को विक्रय मूल्य – रेडीमेड गारमेंट फैक्टरी से ड्रेसेज का क्रय मूल्य
= 1200 – 1000 = ₹ 200
कुल मूल्य वृद्धि = किसान + कपड़ा मिल + रेडीमेड गारमेंट फैक्ट्री + स्टोर द्वारा मूल्य वृद्धि।
= ₹ 1200।
प्रश्न 9.
पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था की प्रमुख विशेषतायें क्या हैं? लिखिये?
उत्तर:
पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था में सामान्यतया निम्न प्रमुख विशेषताएँ दृष्टिगोचर होती हैं –
1.स्वतंत्र माँग एवं पूर्ति बल से कार्यान्वित-पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था में एक बाजार इतना संपन्न होता है कि वह क्रेताओं एवं विक्रेताओं के परस्पर संबंध को जन्म देता है। यही कारण है कि पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था का बाजार स्वतंत्र माँग एवं पूर्ति बल से कार्यान्वित होता है।
2. माँग एवं पूर्ति की सापेक्षिक शक्तियों से मूल्य निर्धारण:
इस बाजार में वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं की कीमतें माँग तथा पूर्ति की बाजार शक्तियों द्वारा निर्धारित होती हैं।
3. उपभोक्ता बाजार का सम्राट:
पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था में उपभोक्ता प्रमुख होता है। उसकी आय, आदत, प्राथमिकताओं के अनुसार ही उत्पादों का क्रय करके वह अधिकतम संतुष्टि प्राप्त करता है तथा उत्पादक भी उन्हीं वस्तुओं का उत्पादन करते हैं जिनके उत्पादन से उन्हें अधिकतम लाभ की प्राप्ति होती है। उत्पादक के लिये उपभोक्ता पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था में बाजार का सम्राट है अतएव माँग के विरुद्ध उत्पादक उत्पादन नहीं कर सकता है।
4. पूँजी संचय को बढ़ावा:
पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था में उत्पादन के साधनों में पूँजी को सर्वाधिक महत्व दिया जाता है एवं मुख्य साधन के रूप में देखा जाता है इसलिये पूँजी के संचय की प्रवृत्ति को बढ़ावा मिलता है।
5. सरकारी हस्तक्षेप नहीं:
पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था में उत्पादकों के निर्णयों में सरकार का कोई हस्तक्षेप नहीं होता है। सरकार बाजार की माँग एवं पूर्ति की अंतक्रिया में कोई हस्तक्षेप नहीं करती है। सरकार कानून व्यवस्था एवं प्रतिरक्षा के रख – रखाव पर अपना ध्यान केन्द्रित करती है।
6. स्वामित्व एवं प्रबंधन निजी हाथों में – पूँजीवादी अर्थव्यवस्था में उत्पादन के साधनों पर स्वामित्व निजी हाथों में होता है। यहाँ तक कि उसका प्रबंधन भी पूँजीपतियों के हाथों में होता है। एक उत्पादक निर्णय लेने में स्वतंत्र होता है। लाभ पर अधिकार भी उत्पादक का होता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 10.
राष्ट्रीय आय से संबंधित समुच्चय के अन्तर्गत सकल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद (GNP), सकल घरेलू उत्पाद (GDP), शुद्ध घरेलू उत्पाद (NDP) को बाजार मूल्य एवं साधन लागत पर समझाइये?
उत्तर:
1.सकल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद (GNP):
सकल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद से आशय देश के सामान्य निवासियों द्वारा घरेलू भौगोलिक सीमा के अन्दर एवं देश के बाहर अर्जित की गई आय से है। जब सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में विदेशों से प्राप्त शुद्ध साधन आय को जोड़ दिया जाता है तो उसे सकल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद कहा जाता है। इसे निम्न समीकरण द्वारा भी समझाया जा सकता है GNP = GDP + NFIA (Net Factor Income from Abroad) या सकल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद = सकल घरेलू उत्पाद + विदेशों से प्राप्त शुद्ध साधन आय या GNP = GDP + X – M भी होता है।
सकल राष्ट्रीय उत्पाद की गणना में मूल्य ह्रास को नहीं घटाया जाता है। इसकी गणना स्थिर मूल्यों के आधार पर भी की जा सकती है। विशेषकर सामाजिक सुरक्षा, पेंशन, वृद्धावस्था पेंशन, बेरोजगारी भत्ता, पूँजीगत वस्तुओं के क्रय – विक्रय इत्यादि को इसकी गणना में शामिल नहीं किया जाता है। साथ ही जिन सेवाओं का कोई मौद्रिक मूल्य नहीं होता उसे भी इसकी गणना में सम्मिलित नहीं किया जाता है। कालाबाजारी एवं तस्करी से बेची एवं खरीदी जाने वाली वस्तुओं को भी शामिल नहीं किया जाता है।
2. सकल घरेलू उत्पाद (GDP):
किसी देश की भौगोलिक सीमाओं के अन्दर एक वर्ष की अवधि में, उत्पादित समस्त अंतिम वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं के मौद्रिक मूल्य जिसमें विदेशों से प्राप्त आय को सम्मिलित नहीं । किया जाता है सकल घरेलू उत्पाद कहते हैं। इसकी गणना साधन लागत पर एवं बाजार मूल्य पर की जाती है।, इसे निम्न समीकरणों की सहायता से स्पष्ट किया जा सकता है –
GDP = C + 1
GDP = (P x Q) + (P x S)
GDP = C + Cg + I + Lg
सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में हस्तांतरण आय एवं गैर कानूनी क्रियाओं से प्राप्त आय को शामिल नहीं किया जाता है। पुरानी पूँजीगत वस्तुओं की बिक्री को भी इसकी गणना में शामिल नहीं किया जाता है।
(अ) बाजार मूल्य पर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद:
उत्पादित अंतिम वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं का सकल मूल्य लिया जाता है। उत्पादित वस्तु की मात्रा के साथ उत्पादित वस्तु के मूल्य का गुणा किया जाता है।
GDPMP = P (Q) + P (S)
(ब) साधन लागत पर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद:
उत्पादन के प्रत्येक साधन विशेष की प्राप्त आय उसकी आय कहलाती है जिनका योग करके सकल घरेलू उत्पाद की गणना की जाती है। उत्पादकों के लिये साधनों का पुरस्कार लागत कहलाती है।
GDPfc = Net factor income (Domestic factor – Income) + Depreciation Expenses.
अर्थात् साधन लागत पर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद = बाजार मूल्य पर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद – परोक्ष कर उत्पाद + सरकारी सहायता
स्थायी मूल्यों पर गणना:
स्थायी मूल्यों पर भी सकल घरेलू उत्पाद की गणना की जा सकती है। स्थायी मूल्यों की सहायता से अनुमानित मूल्य ज्ञात किया जा सकता है। इसे वास्तविक घरेलू आय भी कहा जाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
उत्पादन गणना विधि को अपनाने पर कौन – कौन सी कठिनाइयों का सामना करना पड़ता?
उत्तर:
उत्पादन गणना विधि को अपनाने पर निम्नांकित कठिनाइयों का सामना करना पड़ता है –
- यह निश्चित करना कठिन होता है कि कौन – से पदार्थों को अंतिम माना जाए तथा कौन – से पदार्थों को मध्यवर्ती या कच्चा माल माना जाए।
- मूल्य हास का सही अनुमान लगाना कठिन है, क्योंकि पूँजीगत पदार्थों के मूल्य में कमी अनेक कारणों से हो सकती है।
- अनेक उत्पादक क्रियाओं को उत्पादन की मात्रा में सम्मिलित नहीं किया जाता है।
- उत्पादन के सभी क्षेत्रों से संबंधित सही आँकड़े, उपलब्ध न होना।
- दोहरी गणना की संभावना सदैव बनी रहती है, जिससे सही माप नहीं हो पाती है।