In this article, we will share MP Board Class 10th Social Science Book Solutions Chapter 12 Indian Constitution Pdf, These solutions are solved subject experts from the latest edition books.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Solutions Chapter 12 Indian Constitution
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Text book Exercises
Objective Type Questions
Mp Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Question 1.
Multiple Choice Questions
(Choose the correct answer from the following)
Chapter 12 Social Science Class 10 Question (i)
The constitution is –
(a) Form of government
(b) Government of country
(c) Documents of rules
(d) Fundamental Rights and laws
Answer:
(c) Documents of rules
Indian Constitution Class 10 Mp Board Question (ii)
Which of the following is not a speciality of the Indian constitution –
(a) Parliamentary form of government
(b) Federal Government
(c) Free and impartial Judiciary
(d) Unwritten Constitution
Answer:
(d) Unwritten Constitution
Indian Constitution Class 10 Question (iii)
How many Fundamental duties have been indicated in the Constitution –
(a) 5
(b) 14
(c) 18
(d) 10
Answer:
(a) 5
![]()
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 12 Question 2.
Fill in the blanks: (MP Board 2011, 2013)
- Chairman of the Constituent Assembly was …………
- Dr.B.R. Ambedkar was chairman of constitutional ………..
- The newly drafted Constitution was adopted by the constituent assembly on …………
- The right of equality is one of the ……………. describe in the Constitution.
Answer:
- Rajendra Prasad
- Drafting Committee
- 26 Nov 1949
- Rights
Social Science Class 10 Chapter 12 Question 3.
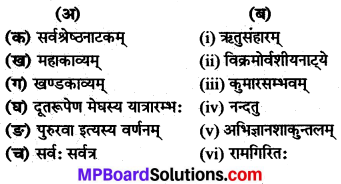
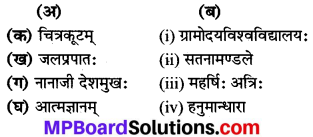
Match the coloumn:

Answer:
(a) (iv)
(b) (ii)
(c) (v)
(d) (i)
(e) (iii).
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Indian Constitution 10th Class Chapter 12 Question 1.
What is a constitution?
Answer:
Constitution may be said to be a document which contains laws, rules and regulations for proper governemnt of a country.
The Constitution Of India Class 10 Chapter 12 Question 2.
Who is the protector of Fundamental Rights in India?
Answer:
Supreme Court (Judiciary).
Define Constitution Class 10 Chapter 12 Question 3.
When fundamental duties were added in the Constitution?
Answer:
According to the 42th Amendment in 1976 the fundamental duties were added in the Constitution of India.
Mp Board Class 8 Social Science Chapter 12 Question 4.
In whose guidance the Independence Bill was drafted?
Answer:
Lok Manya Bal Gangadhar Tilak.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Short Answer Type Questions
10th Social Science Match The Following Chapter 12 Question 1.
What is the importance of Constitution? (MP Board 2010)
Answer:
Constitution is needed for properly running the government and clearly defining the roles and functions of the legislature, judiciary and administration so also for ensuring a balance and coordination amongst them. In the absence of Constitution there is a strong possibility of conflicts between different organs of the Government and at times even a situation of anarchy may arise Fundamental rights and duties of citizens are also specified in the Constitution. It can be said that Constitution is the very base of Government.
![]()
Mp Board Class 8 Social Science Solution Chapter 12 Question 2.
Write an introductory note on Constituent Assembly?
Or
Give the introduction of Constitution Assembly? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
The formation of Constituent Assembly was the result of the ‘Swaraj Bill’ prepared under the directions of Lokmanya Bal Gangadhar Tilak in 1895, the statement of Mahatma Gandhi on 5 January, 1922 that, “Indian Constitution shall be as per the wishes of the people of India”, the National Convention of February 1924 under the Chairmanship of Tej Bahadur Sapru and the demand in the Patna Convention of Swaraj Dal in May 1934.
The members of the Constituent Assembly could not be elected directly by adult franchise therefore as a practical solution provincial Assemblies were utilised as election bodies.
Question 3.
Who were the prominent members of the Constituent Assembly from Madhya Pradesh?
Answer:
Important members of the Constituent Assembly from the existing provinces viz. Central Province a Berar, Central India region (Bhopal, Gwalior, Indore and Rewa) were Pandit Ravishankar Shukla, Seth Govind Das, Hari Vishnu Kamat, Ghanshyam Singh Gucch, Gopikrishan Vijayvargiya, Radhavallabh Vijayvargiya and Thakur Lai Singh.
Question 4.
What do you understand by Directive Principales of the State Policy?
Or
What do you mean by Directive Principles of State Policy? Write. (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
Directive Principles of the State Policy:
In the fourth part of the Constitution, fundamental principles of Governance have been described, these are known as directive principles. The principles are guidelines for political, social and economic programmes for modem democracy. Although these principles cannot be directed by any court to be enforced but they are fundamental in the good Governance of the country. Through these directive principles an attempt has been made to set up a welfare state in India.
Question 5.
What is importance of Preamble in the Constitution?
Answer:
In the Preamble of the Constitution the framers of the Constitution have incorporated the objectives of the Constitution, so also values and ideals. This is called the essence or spirit of the Constitutions, it is the resolve and feelings of the framers of the Constitution.
In the very beginning of the Preamble it has been indicated that the Constitution has been framed as per the wishes of the people and ultimate powers vest in the people. It has been stated that India shall be sovereign, democratic republic. As per the 42nd Constitutional amendment; India was declared as a socialist and secular state.
Question 6.
Explain the meaning of Socialist and Secular. (MP Board 2009, 2013)
Answer:
Socialism and Secular:
By a socialist state is meant that the Indian economy shall be based on socialistic pattern of society. Minimum basic needs of every Indian shall be fulfilled. Socialism as per the Indian conditions shall be adopted. The ideal of secularism has been cherished in the Constitution. It means that the state shall protect the interests of all religious beliefs but will not have any particular religion as state religion. The state shall not discriminate citizens on the basis of religion. Every citizen is free to follow its religion and beliefs.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Additional Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Choose the correct answer from the following
Question (i)
Cabinet Mission Plan came to India in –
(a) 1942
(b) 1944
(c) 1946
(d) 1948.
Answer:
(b) 1944
Question (ii)
Indian Constitution is divided into –
(a) 20 Parts
(b) 21 Parts
(c) 22 Parts
(d) 23 Parts.
Answer:
(c) 22 Parts
Question (iii)
How many articles are there in Indian constitution –
(a) 320
(b) 345
(c) 370
(d) 395
Answer:
(d) 395
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
- The first draft on Constitution was submitted to the President of the Constituent Assembly on …………..
- The first meeting of Constituent Assembly was held on 9 December………….
Answer:
- 21 February, 1948
- 1946
Question 3.
True and False type questions:
- The demand for Constituent Assembly was related with National Movement.
- Indian Constitution had 395 Articles at the time of final submission.
- Supreme Court is the protector of fundamental rights? (MP Board 2009)
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee of Constitution? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- False
Answer in One – Two Words or One Sentence:
Question 1.
What did the citizens obtain by enjoying fundamental rights?
Answer:
The citizens can live independent and progressive life by enjoying fundamental rights.
Question 2.
How has Abraham Lincoln defined democracy?
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln defined democracy, as that it is government of the people, by the people and for the people.
Question 3.
When was the first meeting of the Constituent Assembly held?
Answer:
First meeting of the Constituent Assembly was held on 9 December, 1946.
Question 4.
Who was elected the Chairman for first meeting of the Constituent Assembly?
Answer:
Dr. Sacchidanand Sinha.
![]()
Question 5.
When was new constitation passed and adopted?
Answer:
The new constitution was passed and adopted on 26 November, 1949.
Question 6.
Which plan is the basis of Indian constitution.
Answer:
By 42nd Amendment (1976).
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Universal adult franchise?
Answer:
The Constitution has given the right to vote to all its adult citizens. By adult franchise is meant that every adult citizen has a right to vote on attainment of a definite age. In the Constitution this right is given to all citizens who attain the age of 18 years, irrespective of their religion, race, caste, sex or place of the person.
Question 2.
What do you mean by a soverign state?
Answer:
The country will decide its own foreign and domestic policies. It is not under any foreign rule and it can have its own policies of behaviour at the international level.
Question 3.
When did the new constitution was adopted?
Answer:
The new Constitution was passed and adopted on 26 November, 1949. Certain provisions of the Constitution in respect of citizenship, election and interim Parliament were adopted with immediate effect and remaining provisions became effective from 26 January, 1950, which was called as the date of promulgation of the Constitution.
Question 4.
What did Dr. B.R Ambedkar say about the Constitution of India?
Answer:
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar said about the Indian Constitution:
It is the bulkiest in the world. Here people of different religions and classes live. Detailed description of all this is given in the constitution of the country.
Question 5.
Explain the right of speech and freedom of expression?
Answer:
The right to freed on grants certain freedoms to the Indians. One such freedom is right to state one’s views and express them. But this freedom is to be exercised within the framework of public order, decency, sovereignty etc.
Question 6.
Explain the right to constitutional remedies?
Answer:
Right to constitutional remedies is one of the important fundamental rights. According to this right, the courts are required to protect the fundamental rights from any encroachment. For this, the courts have the power to issue writs. Habeas Corpus, Prohibition, Quo Warranto, Mandamus, Certiorari.
Question 7.
Why Fundamental Rights are incorporated in the Indian Constitution?
Answer:
The incorporation of fundamental rights in the Constitution is a matter of great significance. This shows that how important and sacred fundamental rights have been considered and how they are thought to be so Fundamental that they have been incorporated in the Constitution.
Question 8.
Why the Indian citizen should follow the Fundamental Duties?
Answer:
The Indian citizen follows and should follow fundamental duties because –
- Duties constitute part of the constitution and as such possess legal states.
- They have to enjoy rights and hence should follow duties.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the right to equality?
Answer:
Right to equality has been explained in Articles 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18. The kind of equality in the constitution is given as under –
- Equality before law and equal protection of law.
- Prohibition of discrimination on grounds of caste, creed, colour, sex, region or any one of them.
- Equal opportunities to all, based only on qualifications.
- Abolition of untouchability.
- Abolition of all title except academic and military.
Question 2.
What rights are received from the right against exploitation?
Answer:
The following rights are received from the right against exploitation –
- Prohibition of bonded labour.
- Prohibition of Adivasis system.
- Prohibition of employment of children below the age of 14 in any hazardous beings.
- Prohibition of trafficing in human beings.
Question 3.
Distinguish between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles?
Answer:
- The Fundamental Rights are enforceable while the Directive Principles are not enforceable.
- The Fundamental Rights are in the form of injustiction on the state while the Directive Principles are in the form of directives to the state.
- The Fundamental Rights are rights of the citizens the Directive Principles are the duties of the state.
- The Fundamental Rights lay the foundations of political democracy while the Directive Principles, of economic democracy.
- The Fundamental Rights are, by and large, negative whereas the Directive Principles are positive in character.
Question 4.
What do you mean by the Federal Form of Government?
Answer:
Federal Form of Government As per the First Schedule of the Constitution, India is a federation of States. Thus federal form of Government has been set up in India. The powers of Government are not Centralized at one place and are divided between the Center and the States and both have independence in their respective jurisdictions.
The Constitution is written and rigid to a considerable extent and it is supreme. The Supreme Court is the protector of the Constitution. Supreme Court has also the powers to interpret the Constitutional provisions and decide Constitutional disputes arising between the Center and the States.
Question 5.
Discribe the salient features of Indian Constitution?
Answer:
Salient Features of Indian Constitution are:
- Written and the largest Constitution.
- Mix of rigidity flexibility.
- Sovereign Republic.
- Socialist and secular republic.
- Parliamentary system.
- Federal system.
- Free and impartial judiciary.
- Fundamental rights and basic duties.
- Directive principles of state policy.
- Universal adult franchise.
Question 6.
Indian Constitution is the matrix of flexibility and rigidity. Explain?
Answer:
A Constitution is termed as rigid or flexible on the basis of the procedure adopted for its amendment. If the constitution can be adopted by a simple procedure followed for framing simple laws it is termed as flexible but if a special procedure is needed for amendment then it is termed as rigid or inflexible.
There are three procedures of amendments in the Indian Constitution. Certain provisions can be amended by a simple majority, some provisions can be amended by specific majority and certain important ones can only be amended by specific majority and consent of atleast 50 per cent number of states. Thus it is a mix of flexibility and rigidity.
Question 7.
How many types of Constitution can be there?
Answer:
The fathers of Indian Constitution consulted and took useful provisions from Constitutions of several countries. The directive principles have been taken from the Constitution of Ireland. The idea of Fundamental Rights has been taken from the Constitution of United States of America. The concept of Federation of states (Federal form of Government) is taken from Canadian Constitution.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 12 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the characteristics of the Fundamental Rights and Duties in Indian Constitution? (MP Board 2011, 2013)
Or
Describe the fundamental duties of citizen of India? (MP Board 2009)
Or
Describe the fundamental rights and citizen? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
The Fundamental Rights are as follows:
- Right to equality.
- Right to freedom.
- Right against exploitation.
- Right to freedom of religion.
- Cultural and educational rights.
Fundamental Rights and Duties:
For alround development of the citizens, fundamental rights are essential. There is a provision for fundamental righjts for the citizens. In case they are violated, a citizen has the right to approach the High Court or Supreme Court. During the period of Emergency these Fundamental Rights can be suspended.
The provision of Fundamental Duties of the citizens have been added in the Constitution by an amendment (42nd Amendment of the Constitution, 1976). Ten fundamental duties have been specified in the Constitution.
Fundamental Duties:
It shall be the duty of every citizen of India.
1. To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag and the National Anthem.
2. To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom.
3. To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India.
4. To defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so.
5. To promote harmony and spirit of common brotherhood amongst all the people of India transcending religious, linguistic and regional or sectional diversities, to renounce practices derogatory to the dignity of women.
6. To value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture.
7. To protect and improve the natural environment including forest, lakes, rivers and wildlife and to have compassion for living creatures.
8. To develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform.
9. To safeguard public property and to abjure violence.
10. To strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity so that the nation constantly rises to higher levels of endeavor and achievement.
Question 2.
Discuss any four features of the Indian Constitution?
Or
Describe the main features of Indian constitution? (MP Board 2009)
Or
Describe the Parliamentary and Federal System of the Government?(MP Board 2009)
Or
Write any five features of Indian constitution? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
The constitution of India is the lengthiest constitution. Accordingly it possesses certain important features. Some of these can be discussed as under:
1. Federal Form of Government:
The Constitution does possess all the formal requisites of a federation written constitution, rigidity of the constitution, decentralisation, powerful judiciary. But it can change into a unitary system during emergency.
2. Parliamentary System:
The Present of India is constitutional head whereas the council of Ministers is the real. All the ministers are collectively responsible in the Lok Sabha. The ministers work as a team they swim, and sink together.
3. Abolition of Untouchability:
The constitution abolishes untouchability. Untouchability is declared against law and against the constitution.
4. Universal Adult Franchise:
The universal adult franchise has been guaranteed by the constitution. Every citizen, irrespective of any caste, creed, colour or sex, has the right to vote and participate in administration.
Question 3.
Mention some of the Directive Principles of State Policy?
Answer:
- The state would prohibit concentration of material and natural resources in the hands of the few.
- Public assistance to the poor, the aged and the helpless.
- Right to work and to education.
- Equal wages for equal work, for both men and women.
- Organising and empowering the Village Panchayats to make them units of self – government.
- Promoting cottage and small scale industries in the rural, areas.
- Enacting prohibition.
- Prohibiting the slaughter of the cows and those animals which give milk.
- Organising agriculture on scientific lines and promoting animal husbandry.
- Providing free and compulsory education to the children below 14 years within a period of ten years.
- Uniform civil code for the whole country.
- Separation of executive from judiciary.
- Protection of monuments of national importance.
- Promoting world peace and security, cooperation and arbitration.
- Giving economic and educational assistance to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes and other weaker sections of the society.
Question 4.
Explain briefly to the Drafting Committee for the preparation of Indian Constitution?
Answer:
Drafting Committee:
Drafting of the Constitution was not an easy task, therefore different sub committees were formed to facilitate drafting of the Constitution. 10 sub – committees were relating to matters of procedure and 8 sub – committees related to matters of facts. Important sub – committees were Rules, Business and Drafting Committee, Steering Committee, Committee on Fundamental Rights Union Powers Committee, Minority Rights Sub-committee, etc.
To give final shape to the reports and suggestions of the above sub – committees a drafting Committee under the chairmanship of Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar was formed. Other members of this Committee were N. Gopalswami Ayangar, Aladi Krishna Swami Aiyyar, Sayyad Mohammad Sadullah, K.M. Munshi. B.L. Mittra and D.P. Khaitan subsequently B.L. Mittra and D.P. Khaitan were replaced by N. Madhavan Rao and T.T. Krishnamachari. The Draft Constitution was submitted to the President of the Constituent Assembly on 21 February, 1948. Thereafter detailed discussions were held in the Constituent Assembly.
Question 2.
Discuss the cultural base of Indian Constitution.
Answer:
The framers of the Constitution were aware of the fact that the life of the people of a country is closely associated with the culture and rich heritage of the country the identity of a country is not on the basis of political organisation or beliefs but on the basis of the culture, traditions, beliefs and feelings of nationality.
Indian Constitution is not merely a political document but much more than that. It contains the culture and National Values in it. In the manuscript of the Constitution, the rice cultural and national heritage of the country has been depicted through representative pictures. These pictures depict the traditions from Mohan – jodaro and Vedic period to the period of Freedom Movement.
These pictures are of the bull seal of Mohan – jodaro period, Lord Ram returning with Sita in the ‘Pushpak Viman’ after victory of Lanka, preaching of Gita by Sri Krishan to Arjuna, Lord Buddha, Mahavir Swami, Akbar and in the background Mughal architecture, Shivaji, Guru Govind Singh, Tipu Sultan, the historical Dandi March of Mahatma Gandhi, the Himalayas the Indian ocean etc.