MP Board Class 7th Social Science Model Question Paper
Choose the correct alternative from the options given below:
Question 1.
Ibn Battutah visited India during the reign of:
(a) Muhammad bin Tuglaq
(b) Razia Sultan
(c) Alauddin Khilji
(d) Ibrahim Lodi
Answer:
(a) Muhammad bin Tuglaq
Question 2.
The main occupation of the people during the Mughal period was:
(a) agriculture
(b) timber industry
(c) foreign trade
(d) None of die above.
Answer:
(a) agriculture
Question 3.
The Museum of Man of Madhya Pradesh is situated at:
(a) Indore
(b) Jabalpur
(c) Bhopal
(d) Ujjain
Answer:
(c) Bhopal
Question 4.
The unit of air pressure is:
(a) Millimeter
(b) mill bar
(c) milligram
(d) centimeters
Answer:
(b) mill bar
![]()
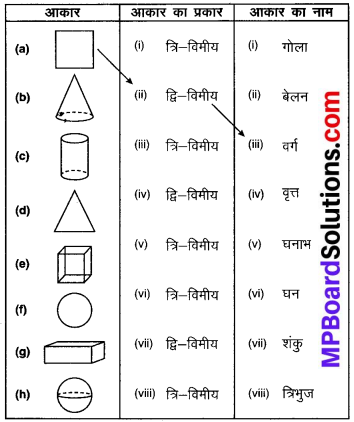
II. Match the columns:

Answer:
1. (c) Taiga
2. (a) Statue of Gomteshwara
3. (d) Desart
4. (b) President
III. Fill in the blanks:
- Fishes are found in abundance in the ……………
- The total number of members of the MP Vidhan Sabha is …………..
- ………….. is die autobiography of Babur.
Answer:
- ocean
- 230
- Tuzak-i-Babri.
Question 4.
Mention the literary sources of the medieval period.
Answer:
A great variety of literary sources of the medieval period are available like writings on palm leaves and birch bark.
Question 5.
Write the names of any three members of the Constituent Assembly.
Answer:
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad
- Pt JawaharLal Nehru
- Acharya Kripalani
Question 6.
Name the movements of the earth.
Answer:
- Rotation
- Revolution
Question 7.
Give examples of the Chola architecture.
Answer:
The imposing gateways to the temple known as ‘gopurams’ were the special features of the chola architecture. The walls of temples were covered with sculpture and with scenes depicting both gods and men.
![]()
Question 8.
Write in brief the religious policy of Akbar.
Answer:
Akbar followed a policy of broad religious toleration. He gave full religious freedom to the people. In 1564 he abolished the Jiazyah which was sometimes used by the ulema to humiliate the,non – Muslims. He abolished the pilgrim’s tax. He gathered at his court a band of talented people and in his Ibadat Khana people of the religions Christian, Zoroastrians, Hindus, Jains even athiests gathered. He set up a new religion which was compounded of many existing religions. This new religion was known as Din-i- Illahi.
Question 9.
Write the important rights of a child.
Answer:
Important Rights of a child are:
- Right to live
- Right to education
- Right of protection against exploitation
- Freedom of expression.
Question 10.
Differentiate between weather and climate.
Answer:
Weather:
- Weather is a short duration atmospheric condition.
- Weather represents the atmospheric condition of small area.
- The weather can change many times in a day.
- In the weather of one sea – son any one element is prominent.
Climate:
- Climate is a long duration atmospheric condition.
- Climate represents the wide area of atmo – spheric condition.
- The climate does not change for long periods.
- In one type of climate one or many seasons we there.
Question 11.
What is mixed farming?
Answer:
In mixed forming, cattle are also reared along with crops.
![]()
Question 12.
What are the qualifications required to become the member of Vidhan Sabha?
Answer:
The qualifications required to become die member of Vidhan Sabha:
- He must be a citizen of India.
- He must have completed the age of 25 years.
- He must not hold any post of profit under the State or Central Government.
- He must not be mentally unstable or bankrupt
Question 13.
Shivaji had the abilities of an able administrator. Justify.
Answer:
Shivaji was not only a great general but also a good administrator of top order. Shivaji’s administration was of high order which inspired by ideals of public welfare. Though Shivaji was all in all, in all matters, he kept a committee of 8 persons to advise him on the affairs of the state. This committee came to be known as Ashta Pradhan. This was file main feature of Shivaji’s administration.
The main source of income was the tax on the land which amounted to two – fifths of file land produce. Chauth and Sardeshmukhi were also levied on those living outside Maratha kingdom. Chauth was one fourth of the tax which farmers paid such kingdoms by their peasants. Sardeshmukhi was over and above this tax.
It was one tenth of the total revenue, from which these taxes were collected, remained free from the Maratha looting’s and attacks. For the smooth and efficient administration, Shivaji divided his kingdom into a number of provinces known as prants, and each prant into districts and parganas. In this way Shivaji proved himself as an able administrator.
Or
Describe the progress made in the field of language, literature and science during the Sultanate period.
Answer:
Language, literature and scientific progress during the Sultanate period are:
- The temples and mosques were the primary educational centers. In some places, primary schools were also established.
- There were provisions for higher education.
- The main language was Persian. Many Persian words began to be used in Indian languages.
- A new language Urdu developed during this period, which was a mixture of Hindi and Persian language.
- During Sultanate period the regional languages flourished and excellent literary work was created.
- In some Hindu Kingdoms like Vijayanagar Sanskrit was the court language. Various Sanskrit books were translated in various Indian as w ell as Arabic and Persian languages also.
- With the introduction of paper, the oldest available texts were reproduced during fins period throughout the country.
Medicines:
During the Sultanate period Maulana Badmddin, Maulana Sadruddin and Azimuddin were famous physicians. Machandra and Jog were famous surgeons.
Question 14.
Describe the powers of the president of India.
Answer:
The powers of file President –
- The President appoints the Prime Minister. On file advice of the Prime Minister, he also appoints others Ministers.
- He is the chief executive of the country. He appoints the Governors of the States, Chief Justice and Judges of the Supreme Court and die High Court.
- He also appoints the Chairman and die members of the National Human Rights Commission.
- He can issue ordinance when the parliament is not in session. This ordinance is as good as a law.
- The President has the power to grant pardon, reprieve, or remission of punishment or commute death sentence.
Or
Write the freedoms given to the citizens of India.
Answer:
- Freedom to express thoughts.
- Freedom to move freely.
- Freedom to live and settle in any part of India.
- Freedom to take up any job anywhere in India.
![]()
Question 15.
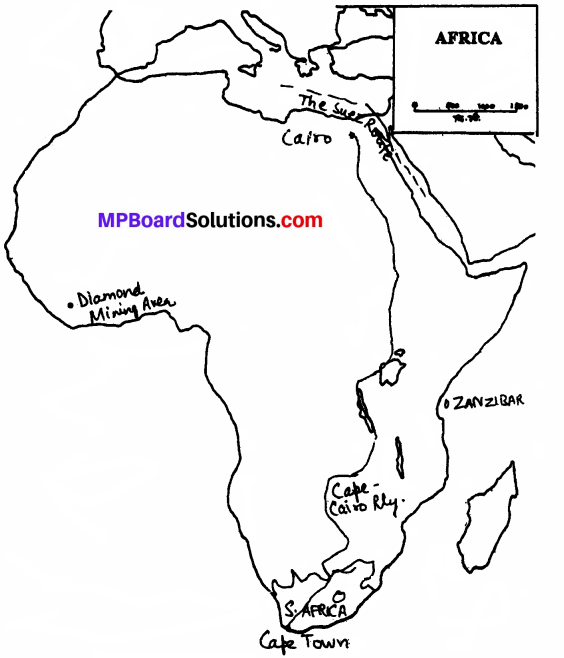
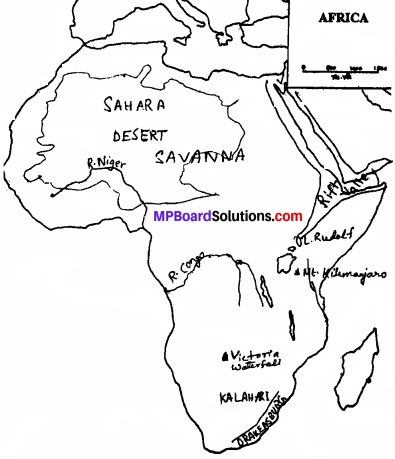
Describe the physical features of the continent of Africa.
Answer:
Africa is avast continent from north:
south extending between 37° 14’ N to 34°50’ S latitude. The major part lies within the tropical zone. In fact it is the most tropical of all the continents. There are marked variations in the distribution of rainfall. For example, near the equator, rain falls all the year round, but in die Sahara desert it does not fall at all. Near the Equator there is only one season,’ the hot wet summer but in the northern and the southern parts of Africa climate varies.
There are regions in the South Africa where rain occurs in the winter. There are regions where rain occurs only in summers. Vegetation of Africa – The rainfall is uneven in Africa. The belt lying along the equator on both has hot and wet climate. It rains almost daily and there is only one season – the hot wet summer season. Due to abundance of heat and moisture most of die region is covered with thick forest which is known as the tropical rain forest.
Or
Describe the climate and wild life of Europe.
Answer:
In the Western Europe the climate is marine type. In this climate die winters are cool not cold, and the summers are warm and not hot. Winters are foggy. The rainfall is well distributed all over the year and the temperature is equable. Such climate is found in Central and Eastern Europe. This part of the continent is far from die moderating influence of the westerlies and the ocean. It has Continental climate where it is extreme hot in summer, cold in winter.
The range of temperature is very great Rainfall is moderate. In southern European countries surrounding the Mediterranean the winters are warm and summers are dry. In the summer the region comes under the influence of sub-tropical high pressure belt It, combined with off-shore winds rales any possibility of rain.
In the winter the region comes under the influence of the rain bearing westerlies. In the region situated in the North of Arctic Circle the summers are brief, days are long and warm. The sun is visible at night also. For die major part of the year the region is covered with snow. Precipitation is much less and it is in the form of snow only. This type of climate is known as Tundra climate.
Question 16.
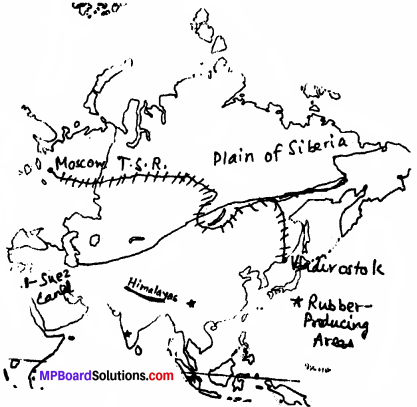
Mark the following in the map of Asia
- Himalayan mountains
- The Siberian plains
- Rubber producing area
- Trans-Siberian Railway
- Suez Canal.
Answer: