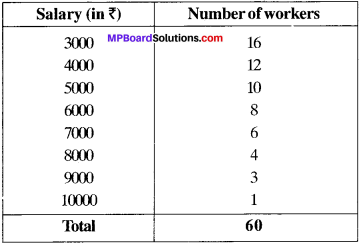
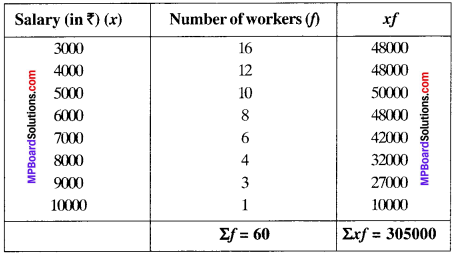
MP Board Class 10th Special Hindi सहायक वाचन Solutions Chapter 5 भगिनी निवेदिता (संस्मरण, प्रवाजिका आत्मप्राणा)
भगिनी निवेदिता अभ्यास
संस्मरण
प्रश्न 1.
स्वामी विवेकानन्द से निवेदिता की मुलाकात कब, कहाँ और कैसे हुई? (2013, 17)
उत्तर:
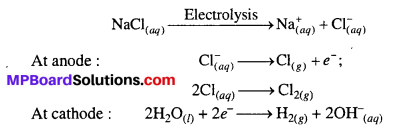
स्वामी विवेकानन्द से निवेदिता की मुलाकात सन् 1893 के शिकागो के विश्वधर्म सम्मेलन में हई स्वामीजी लन्दन अपने मित्रों के आग्रह पर आये थे यहीं पर मार्गरेट (निवेदिता) ने स्वामीजी के प्रवचन सुने और अपना आदर्श मान लिया।
प्रश्न 2.
स्वामी जी के साथ हिमालय यात्रा में निवेदिता को क्या अनुभव हुए?
उत्तर:
स्वामीजी के साथ हिमालय यात्रा में निवेदिता पैदल ही चलीं। मार्ग में वे पटना, वाराणसी, लखनऊ, पंजाब, रावलपिण्डी, बारामुला होते हुए कश्मीर पहुँचे। उन्होंने पहली बार भारत की पवित्र भूमि पर पाँव रखा था।
भारत के पवित्र तीर्थस्थान गाँव, पर्वत, नदियाँ तथा भारत के श्रद्धालुओं से मिलने का अवसर उन्हें प्राप्त हुआ।
वे अमरनाथ की दुर्गम यात्रा पर स्वामी जी के साथ अकेली ही गयीं इस यात्रा के पश्चात् उनकी जीवन शैली में बहुत बड़ा परिवर्तन आ गया। वे स्थान-स्थान पर व्याख्यान देने लगीं। उन्होंने शिक्षा के उत्थान के लिए अपनी अदम्य शक्ति लगायी और निरन्तर प्रयास किया कि सभी महिलाएँ शिक्षित हो जायें। उनका कहना था यह सम्पूर्ण देश तुम्हारा है और देश को तुम्हारी आवश्यकता है। अतः अपने मूल्यवान समय को देश के हित के लिए लगाओ।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
अमरनाथ यात्रा से भगिनी निवेदिता को भारत को समझने में किस प्रकार सहायता मिली?
उत्तर:
अमरनाथ यात्रा से भगिनी निवेदिता को भारत के रहन-सहन, खान-पान एवं वेश-भूषा की पर्याप्त जानकारी मिली। स्थान-स्थान पर रुकने से वहाँ के लोगों की बोली और विचारों से अवगत हुई।
भगिनी निवेदिता भारत के ज्ञान,दर्शन,संस्कृति व परम्पराओं से परिचित हुईं। वे यहाँ की संस्कृति और सभ्यता से इतना अधिक प्रभावित हुईं कि उन्होंने स्वयं को भारत की माटी में ही एकाकार (समाहित) कर लिया।
उन्होंने यहाँ महिलाओं के आचार-व्यवहार व रहन-सहन तथा वात्सल्यपूर्ण व्यवहार को देखा। यात्रा के दौरान उन्होंने प्रकृति का अपूर्व आनन्द लिया। उनका कहना था कि भारत में जितनी शान्ति है, उतनी अन्य कहीं नहीं वास्तव में इस देश की सभ्यता एवं संस्कृति, दुनिया को एक नई रोशनी प्रदान करने वाली है। यहाँ के प्रत्येक दृश्य एवं संस्कार अपनी अलौकिक छटा विकीर्ण कर रहे हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
कलकत्ता में फैले प्लेग के समय निवेदिता ने किस प्रकार सेवा की?
उत्तर:
निवेदिता ने 13 नवम्बर, सन् 1896 को कलकत्ता (कोलकाता) में अपने निवास स्थान के समीप एक बालिका विद्यालय की स्थापना की, लेकिन अगले वर्ष जैसे ही निवेदिता को कलकत्ता (कोलकाता) में प्लेग फैलने का समाचार मिला, वे अपने सभी शिष्यों के साथ टोली बनाकर रोगियों की सेवा में जुट गयीं। वे रात-दिन भूखी-प्यासी रहकर और अपनी चिन्ता छोड़कर रोगियों की चिकित्सा में निःस्वार्थ भाव से जुटी रहती थीं। रोगियों की सेवा के उपरान्त उन्हें हार्दिक प्रसन्नता प्राप्त होती थी। उन्हें रोगियों से पर्याप्त स्नेह और आदर मिलता था। उनके विषय में जिला चिकित्सा अधिकारी ने एक रिपोर्ट में लिखा है-
“निवेदिता अपने आराम, स्वास्थ्य, भोजन तक की चिन्ता न कर गन्दी बस्तियों में घूमती रहीं।”
इस प्रकार निवेदिता ने निःस्वार्थ भाव से रोगियों की सेवा की।
प्रश्न 5.
स्त्री शिक्षा पर निवेदिता के विचार स्पष्ट कीजिये। (2018)
उत्तर:
निवेदिता जब भारत आयीं, उस समय उनके मन में एक विद्यालय स्थापित करने की भावना ने जन्म लिया। अतः सन् 1896 में 13 नवम्बर को उन्होंने अपने घर के पास बालिका विद्यालय की स्थापना की थी, माँ ने इस विद्यालय का विधिवत् उद्घाटन किया। इस विद्यालय में लड़कियों को पढ़ने-लिखने के अतिरिक्त चित्रकारी, मिट्टी का काम भी सिखाया जाता था। उनको इस कार्य में अपूर्व सुख की अनुभूति होती थी। लगभग छः माह बाद धनाभाव के कारण विद्यालय चलाने में असुविधा हुई। अतः धन संग्रह के लिए वे पुनः विदेश गयीं और वहाँ उन्होंने देखा कि विदेशों में भारतवासियों की झूठी और घृणित तस्वीर प्रस्तुत की जा रही है। विशेषकर भारत की स्त्रियों की निन्दा की जा रही है। उन्होंने स्त्रियों की उचित स्थिति को व्यक्त किया।
प्रारम्भ में बालिका विद्यालय में कोई भी अपनी बालिका को नहीं भेजना चाहता था, लेकिन निवेदिता ने अपनी सेवा तथा सरल चित्तवृत्ति के द्वारा लोगों के मन को आकर्षित किया और लोगों ने अपनी बालिकाओं को विद्यालय भेजना शुरू कर दिया।
धीरे-धीरे विद्यालय बढ़ने लगा और आज भी यह विद्यालय सुव्यवस्थित रूप से चल रहा है।
प्रश्न 6.
भारतीय स्त्रियों के कौन-कौन से गुणों ने निवेदिता को प्रभावित किया? (2015)
उत्तर:
भारतीय स्त्रियों के निम्नलिखित गुणों ने निवेदिता को प्रभावित किया-
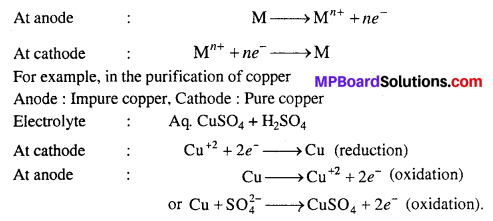
(1) ममतामयी माँ :
निवेदिता ने भारत की महिलाओं को आदर्श माँ के रूप में पाया। वात्सल्य भाव की जो छवि भारत की स्त्रियों में पायी जाती है,वह अन्यत्र दुर्लभ है। वे वास्तव में ममता और प्रेम से परिपूर्ण हैं।
(2) आदर्श पत्नी :
निवेदिता ने भारत की स्त्रियों को आदर्श पत्नी के रूप में पाया। माँ-बाप तथा सास-ससुर की सेवा का जो आदर्श भाव यहाँ की महिलाओं में है, वह अन्य कहीं नहीं है। वह अपने पति की रक्षा के लिए अपने प्राणों का भी बलिदान कर देती हैं।
(3) वीरता की साक्षात् प्रतिमूर्ति :
भारत की स्त्रियाँ वीरता की साक्षात् मूर्ति हैं। रानी लक्ष्मीबाई और अहिल्याबाई इसका साक्षात् उदाहरण हैं। वास्तव में यहाँ की महिलाएँ देश की रक्षा के लिए अपने प्राणों को न्योछावर करने वाली हैं।
(4) दया और सद्भावना :
भारत की स्त्रियों में दया और सद्भावना अधिक है। यह बात निवेदिता ने यहाँ की स्त्रियों के सम्पर्क में आकर ही जानी भारत आने के बाद ही उन्हें स्त्रियों के समुचित गुणों का सही रूप में ज्ञान हुआ। वास्तव में भारत की महिलाएँ धन्य हैं। अतः किसी विद्वान ने उचित ही कहा है-
“यत्र नार्यस्तु पूज्यन्ते रमन्ते तत्र देवता।”
![]()
भगिनी निवेदिता महत्त्वपूर्ण वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
भगिनी निवेदिता बहु-विकल्पीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
भगिनी निवेदिता पर लिखा गया ‘संस्मरण’ के लेखक हैं- (2011)
(क) अजहर हाशमी
(ख) प्रवासिका आत्मप्राणा
(ग) डॉ.श्यामसुन्दर दुबे
(घ) डॉ. यतीन्द्र अग्रवाल।
उत्तर:
(ख) प्रवासिका आत्मप्राणा
प्रश्न 2.
निवेदिता ने गुरु मान लिया था
(क) दयानन्द को
(ख) रामानुजाचार्य को
(ग) विवेकानन्द को
(घ) रामानन्द को।
उत्तर:
(ग) विवेकानन्द को
प्रश्न 3.
भगिनी निवेदिता का वास्तविक नाम था (2009)
(क) मार्गरेट थेचर
(ख) मिस वीन्स
(ग) मार्गरेट एलिजाबेथ नोबुल
(घ) लिली।
उत्तर:
(ग) मार्गरेट एलिजाबेथ नोबुल
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति
- उनकी लन्दन में एक संन्यासी …………… से भेंट हुई।
- समुद्री यात्रा पर उन्होंने अपने ……………. से बहुत कुछ सीखा।
- वे भारत को महान ………….. का देश कहा करती थीं।
- कलकत्ता में …………. फैला था। (2016)
उत्तर:
- विवेकानन्द
- गुरु
- महिलाओं
- प्लेग।
सत्य/असत्य
- निवेदिता भारत आकर अप्रसन्न थीं।
- निवेदिता गीता का निरन्तर अध्ययन करती थीं।
- रामकृष्ण शारदा मिशन भगिनी निवेदिता बालिका विद्यालय आज भी चल रहा है।
- भगिनी निवेदिता संस्मरण नहीं है। (2010)
उत्तर:
- असत्य
- सत्य
- सत्य
- असत्य
![]()
सही जोड़ी मिलाइए

उत्तर:
1. → (ग)
2. → (ख)
3. → (क)
एक शब्द/वाक्य में उत्तर
- निवेदिता नाम का क्या अर्थ है?
- शिक्षा के लिए धन एकत्र करने उन्हें कहाँ जाना पड़ा?
- अपने विद्यालय में उन्होंने क्या चलाना सीखा?
उत्तर:
- समर्पण
- विदेश
- चरखा।