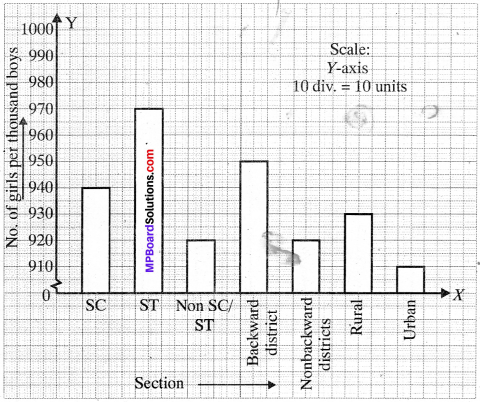
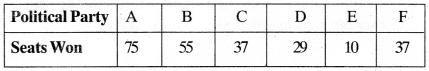
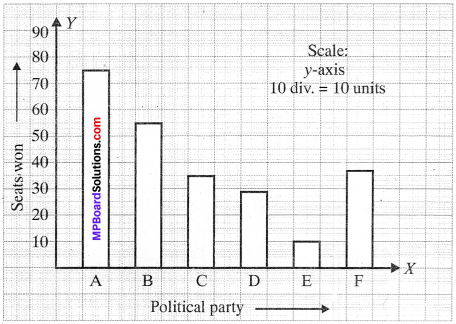
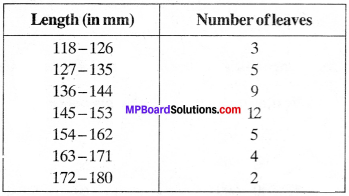
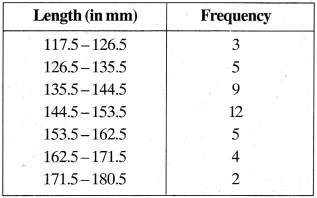
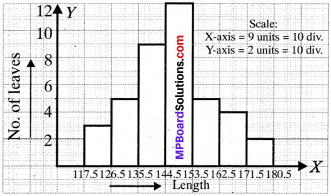
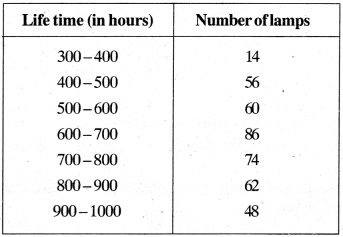
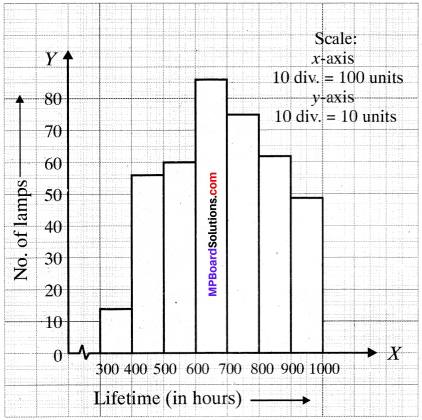
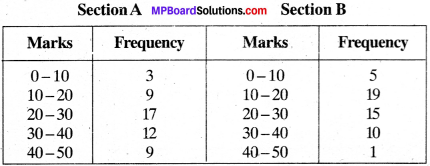
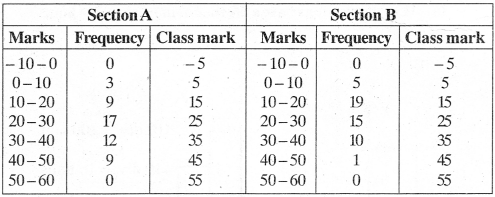
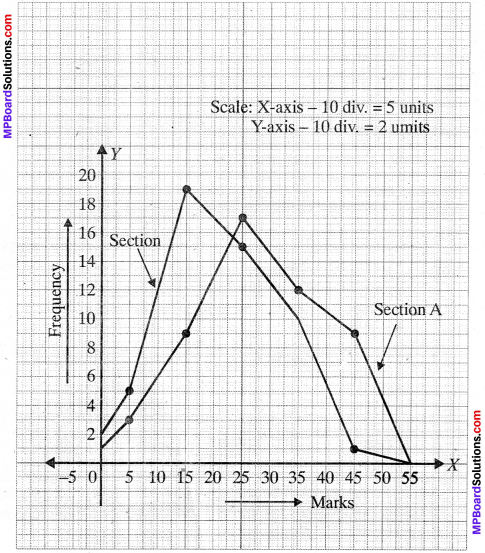
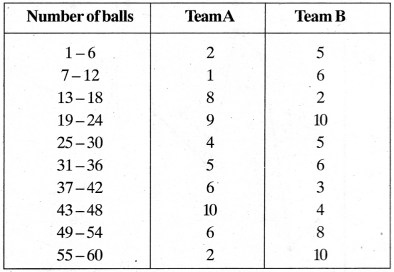
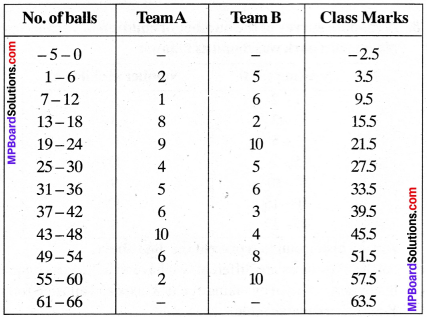
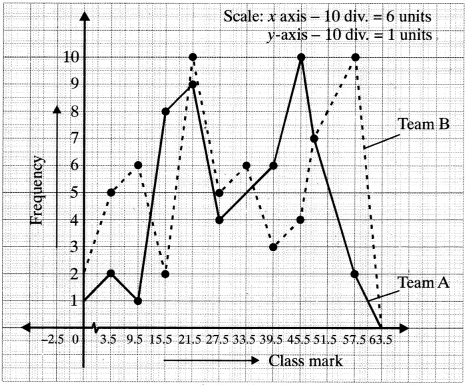
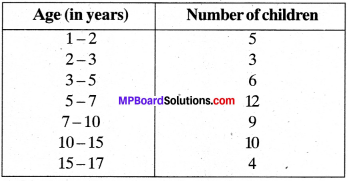
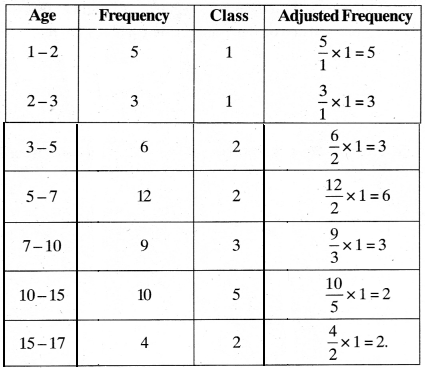
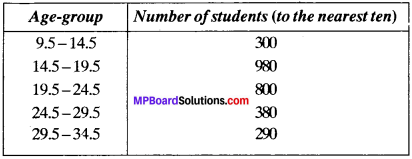
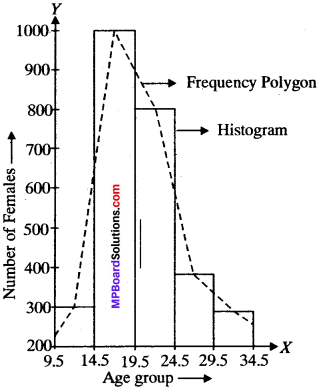
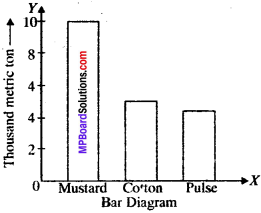
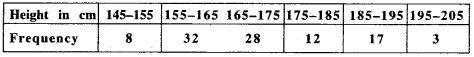
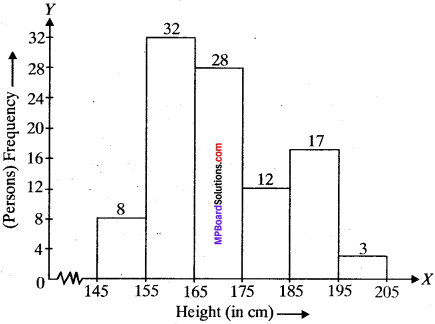
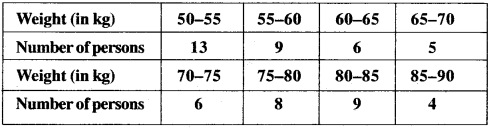
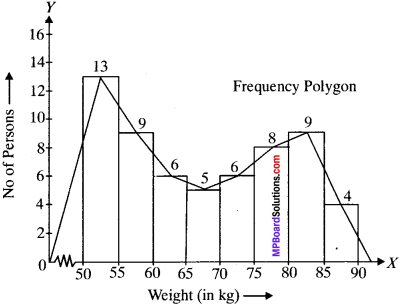
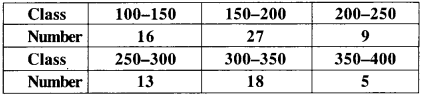
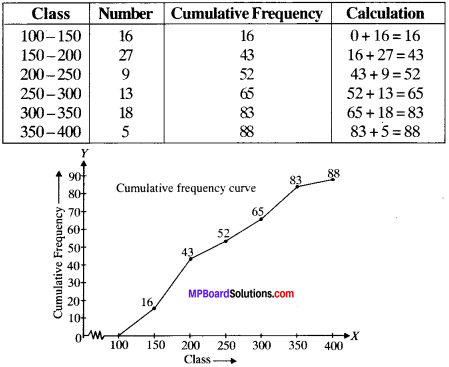
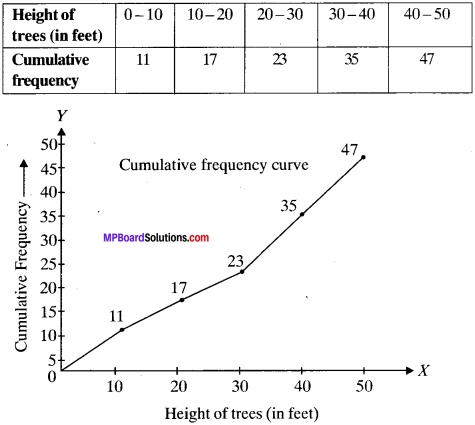
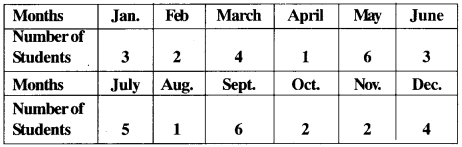
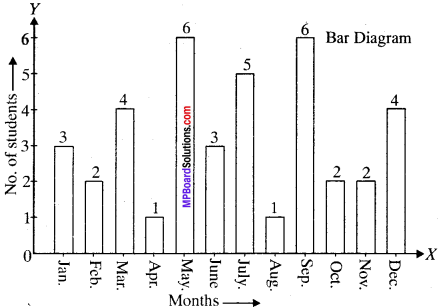
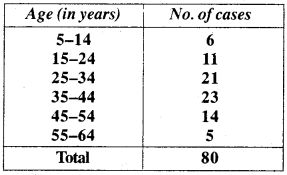
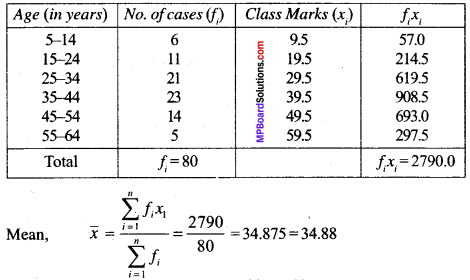
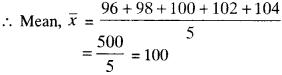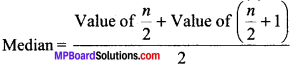MP Board Class 11th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 2 Forms of Business Organisation
Forms of Business Organisation Business Important Questions
Forms of Business Organisation Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The structure in which there is separation of ownership and management is called –
(a) Sole proprietorship
(b) Partnership
(c) Company
(d) AH business organization.
Answer:
(c) Company
Question 2.
The karta in Joint Hindu Family business has –
(a) Limited liability
(b) Unlimited liability
(c) No liability for debts
(d) Joint liability.
Answer:
(b) Unlimited liability
Question 3.
In a co – operative society, the principle followed is –
(a) One share one vote
(b) One man one vote
(c) No vote
(d) Multiple votes.
Answer:
(b) One man one vote
Question 4.
The board of directors of a joint stock company is elected by –
(a) General public
(b) Government bodies
(c) Shareholders
(d) Employees.
Answer:
(c) Shareholders
Question 5.
The maximum number of partners allowed in the banking business are –
(a) Twenty
(b) Ten
(c) No limit
(d) Two.
Answer:
(b) Ten
![]()
Question 6.
Profits do not have to be shared. This statement refers to –
(a) Partnership
(b) Joint Hindu Family business
(c) Sole proprietorship
(d) Company.
Answer:
(c) Sole proprietorship
Question 7.
The capital of a company is divided into number of parts each one of which are called –
(a) Dividend
(b) Profit
(c) Interest
(d) Share.
Answer:
(d) Share.
Question 8.
The Head of the Joint Hindu Family business is called –
(a) Proprietor
(b) Director
(c) Karta
(d) Manager.
Answer:
(c) Karta
Question 9.
Provision of residential accommodation to the members at reasonable rates is the objective of –
(a) Producer’s cooperative
(b) Consumer’s cooperative
(c) Housing cooperative
(d) Credit cooperative.
Answer:
(c) Housing cooperative
Question 10.
A partner whose association with the firm is unknown to the general public is called –
(a) Active partner
(b) Sleeping partner
(c) Nominal partner
(d) Secret partner.
Answer:
(d) Secret partner.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- …………… are business practise which are desirable form the point of new of society.
- …………… is to persue those policies which are desirable for values of society.
- Business ethics depends on welfare of ……………
- Maximum social welfare in business shows …………… responsibility.
- Business owes some …………… towards society
- Moving vehicle causes …………… pollution.
- ………….. gives partnership birth.
- The first objective of cooperative society is called ……………
- The partner who invested capital only but not take a part in management is called ……………
- The life of sole tradership is ……………
- The liabilities of chief (owner) of Hindu undivided family are …………… on the contrary the liabilities of its members are ……………
- In sole tradership does have …………… capacity.
- ………….. only can take a part of JHF.
- For selecting any kind of business is …………… most important factor.
- The limit in Rs. of small scale industries is ……………
- We need type of business for large scale production and distribution ……………
- Minimum number of members are required for company ……………
- For public company …………… minimum number of members are required.
- ………….. company does not issue share capital.
- For every proposal of company …………… having voting right.
- The first preference has been given for paying dividend …………… shares.
- The small parts of capital of every company is called ……………
- The debenture required for mortgage of asset is called ……………
- To making Memorandum of Association is ……………
- To making Article of Association for Joint Stock Pvt. Ltd. company is ……………
- For purchasing share / debenture company issued its …………… for inviting public.
- Memorandum of Association of a company is …………… charter.
- In the absence of Article of Association the rules and regulations followed by company is ……………
- In Memorandum of Association of company the rights and …………… are written.
- Company incorporated in it ……………
- …………… is a important document of a company.
- …………… is the evidence of existence of company.
- Company is a …………… person.
- Registration of company is called …………… company.
- The persons which construct a company is called ……………
- In place of prospectus …………… can issued.
- In Memorandum of Association at least …………… person’s sign is compulsory.
Answer:
- Business ethics
- Business responsibility
- Business
- Social
- Society,
- Air
- Compromises
- For provide service
- Inactive partner.
- Uncertain,
- Unlimited, limited
- For making contract
- Who can take birth in family
- Financial
- One crore
- Company
- Two
- Three
- Private
- Equity
- Preference,
- Shares
- Mortgage debenture
- Compulsory
- Not compulsory
- Prospectus
- Non – convertible
- Table – A
- Object
- Company Act. 1956
- Memorandum of Association
- Incor – poration
- Artificial
- Incorporation
- Promoter
- Substitute prospectus
- Seven.
![]()
Write true or false:
- Co – operative society was originated in England and Germany.
- In partnership responsibility of members are limited.
- Registration of partnership is compulsory.
- Secracy in sole tradership is always profitable.
- Registration of sole tradership is compulsory.
- Chief of Hindu family is called Karta.
- Company is a word of French language.
- Public company do not issued prospectus.
- Equity share capital is included ownership capital.
- Public deposit is a medium term source of finance.
- Debenture holder is included in ownership capital.
- Preference shares do not have the right of getting dividend.
- After getting maturity then member of family can become partner of family business. First company act
- was passed in India on 1850.
- The having one member can never be company.
- There is no risk in sole tradership.
- Partnership deed defines oral agreement among partners.
- Public sectors main aim is not to earn profit.
- Private company start business after obtaining the certificate of incorporation.
- Alteration in Article of Association is easy.
- When company became existence the work of promoter ends.
- Company can alter in memorandom of association by passing a ordinance.
- M.O.A. is a important document of company.
- Private company start business instantly after getting certificate of incorporation.
- Article of Association is compulsory.
- A.O.A. is second important document of company.
- For registration of company prospectus of company is compulsory.
- Table – A can be the subsitute of A.O.A.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True.
Question 4.
Question (A)
Match the columns:

Answer:
1. (b)
2. (a)
3. (c)
4. (d)
5. (f)
6. (h)
7. (e)
8. (g)
9. (j)
10. (i)
11. (1)
12. (k)
13. (p)
14. (o)
15. (n)
16. (m)
17. (r)
18. (q)
19. (t)
20. (s)
21. (v)
22. (u).
Question (b)

Answer:
1. (c)
2. (b)
3. (d)
4. (a)
5. (j)
6. (e)
7. (f)
8. (g)
9. (h)
10. (i)
![]()
Question (C)

Answer:
1. (e)
2. (c)
3. (b)
4. (a)
5. (d)
Question 5.
Give answer in one word/sentence:
Question 1.
Write name of that form of organization in which there is only one owner.
Answer:
Sole proprietorship.
Question 2.
By what name head of joint Hindu family is called?
Answer:
Karta.
Question 3.
Two necessary requirements for formation of Joint Hindu Family.
Answer:
- Minimum two male members,
- Should have some ancestral property.
Question 4.
Write the nature of liability of sole trade.
Answer:
Unlimited liability.
Question 5.
The document prepared in partnership?
Answer:
Partnership Deed.
Question 6.
Who appoint Board of Directors in the joint stock company?
Answer:
Shareholders.
Question 7.
Can minor be admitted in the partnership firm?
Answer:
As per Partnership Act 1932 minor cannot be admitted but he can be admitted to share profits of the firm.
Question 8.
How many minimum member are required for public undertaking?
Answer:
7 members.
![]()
Question 9.
Which company shares are transferable?
Answer:
Public company.
Question 10.
Give two examples of public company.
Answer:
- MTNL and
- BHEL.
Question 11.
Write two profits of multinational companies.
Answer:
Profits:
- Foreign investment,
- Creation of employment opportunity.
Question 12.
What do you understand by minimum and maximum in case of public company?
Answer:
It is related to members minimum seven and maximum no limit.
Question 13.
How many minimum members are required in joint Hindu family?
Answer:
Minimum two.
Question 14.
By which Act. JHF is governed?
Answer:
By JHF Act, 1956.
Question 15.
Which systems are included in JHF business?
Answer:
- Diabhag system
- Mitakshara system.
Question 16.
Karta of JHF have what status with decisions?
Answer:
Freedom to take decisions.
Question 17.
Which business can be started without registration?
Answer:
Sole trade.
Question 18.
Who is responsible for profit and loss in sole trade?
Answer:
Sole proprietor.
Question 19.
How partnership firm gets started?
Answer:
By contract.
Question 20.
How many maximum number of members are required for banking business?
Answer:
10.
Question 21.
What kind of liability each partner have in partnership firm?
Answer:
Unlimited.
Question 22.
In which type partnership agreement can be made?
Answer:
Written or Oral.
Question 23.
What is cooperative society Act?
Answer:
Cooperative society Act, 1912.
Question 24.
What is objective of cooperative society?
Answer:
Mutual cooperation or Help.
![]()
Question 25.
How many maximum number of members can be there in cooperative society?
Answer:
100.
Question 26.
Whose name is mentioned in common seal of company?
Answer:
Company’s name.
Question 27.
Which company cannot sell its shares to general public?
Answer:
Private company.
Question 28.
What is Amended Company Act?
Answer:
Company Act, 2013.
Forms of Business Organisation Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
For which of the following types of business do you think a sole proprietorship form of organization would be more suitable and why?
- Grocery store
- Medical store
- Legal consultancy
- Craft centre
- Internet cafe
- Chartered accountancy firm.
Answer:
Sole proprietorship will be most suitable in case of a Grocery store as in this case, initial business setting – up costs are not very high, the legal requirements are minimum and the scale of operations is small. Besides, direct personal contact is needed with the customers in the case of a grocery store and hence, sole proprietorship where there is a single person who owns and manages the business may be more suitable as he would be able to know his customers well and thus serve them better.
Or,
For which of the following types of business do you think a partnership form of organizations would be more suitable and why?
- Grocery store
- Medical store
- Legal consultancy
- Craft centre
- Internet cafe
- Chartered accountancy firm.
Answer:
Partnership form of organizations would be most suitable for all Internet cafe as this business needs greater capital investment and varied skills. It can come into existence easily through a legal agreement by putting an agreement between the prospective partners into place whereby they agree to carry out the business of the firm and share risks. There is no compulsion with respect to registration of the firm. In case of lack of demand closure of the firm too is not difficult. Further the partners are jointly and individually liable for payment of debts which does not put the liability on one person as in sole proprietorship.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the following terms in brief?
- Perpetual succession
- Common seal
- Karta
- Artificial person.
Answer:
1. Perpetual Succession:
Company is a legal entity separate of its owners or members. It can be brought to an end only by law as it is created by the law. It will only cease to exist when a specific procedure for disclosure called winding up, is completed. Members may come and go but the company continues to exist through consecutive succession of old members by new members on a continuous basis.
2. Common Seal:
A company is a creation of law and exists independent of its members Company is thus considered to be an artificial person who acts through its Board of Directors, When the Board of Directors enters into an agreement with others. It indicates the company’s approval through a common seal. The common seal is the engraved equivalent of an official signature.
3. Karta:
The head of the Hindu Joint Family who is the eldest member and controls the Joint Hindu Family business which is a specific form of business organization found only in India is called Karta. Joint Hindu Family business refers to a form of organization where in the business is owned and carried on by the members of the Hindu Undivided Family (HUF). It is governed by the Hindu Law.
4. Artificial Person:
A company is called an artificial person because just like natural persons, a company can own’ property, incur debts, borrow money, enter into contracts, sue and be sued but unlike them it cannot breathe, talk, walk, eat, etc. A company is a creation of law and exists as an artificial person independent of its members.
Question 3.
Give the meaning of Joint Hindu Family?
Answer:
Joint Hindu family business is a type of business organization in which all the members of the family work under the control of the head of the family.
Question 4.
Give the meaning of private company?
Answer:
The private company is such company which restrict its members from transferring their shares to others and number of members ranges from 2 to 50 and it cannot invite public for subscription of shares.
Question 5.
What is public company?
Answer:
The company which is not a private company is called as public company. Hence, number of members of the public company will be according to the capital of the company. There is no restriction the sale and purchase of shares. The company can invite public for issue and subscriptions of shares.
Question 6.
Can a minor can be member of JHF?
Answer:
Yes, a minor can be member of JHF on the basis of the birth.
Question 7.
Is establishment of sole trade if difficult and expensive?
Answer:
No, for establishment of sole trade there is no need of having big expenditure. It is very easy to establish the sole trade without any legal formalities. By small capital also it can be started. In this the owner is free to take decisions.
Question 8.
Is sole trades liability is limited?
Answer:
No, liability of the sole trade is not limited upto the capital invested by him but his liability is unlimited i.e., personal assets of his can also be used for defraying his debts.
![]()
Question 9.
Is only Karta of JHF have unlimited family?
Answer:
Yes, only Karta of JHF have unlimited liability and remaining other member liability is upto limit of their shares in the JHF.
Question 10.
How objective of cooperative society is different from the objective of Joint stock company?
Answer:
Cooperative society is run for welfare of society and its members, but not at cost of loss. They also earn profit but it is in very less quantity.
Question 11.
Explain partner by Estoppel.
Answer:
If any person is not a partner of the firm but according to his behaviour other partner of the firm assume him as a partner and have faith on him is called as partner by Estoppel.
Question 12.
Define partnership?
Answer:
Indian partnership Act, 1932 Sec (4):
“Partnership is the relation between parsons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them active for all.”
Question 13.
Define cooperation?
Answer:
According to Seligman:
“Cooperation is its technical sense means, abandon – ment of competition among distribution and production and elimination of middlemen of all kinds.”
Question 14.
Compare position of minor in JHF and partnership firm?
Answer:
On the basis of birth only the membership in JHF is adhered. Hence, minor from birth only becomes the member of the JHF. But in partnership minor cannot be admitted as partner as it has no power of making contract but he can be admitted to share only profits of the firm.
Question 15.
How cooperative society present the ideal of democracy and secularism?
Answer:
In cooperative society people become member by its own and leave the firm by its own. Any person belonging to any caste, creed, colour or race can be its member if it is having general interest. In cooperative society Elected Management committee is responsible for doing its work as assigned by cooperative society. All the members have equal rights, Although what ever amount of capital they have invested.
Question 16.
What is minimum and maximum no. of members of sole trade?
Answer:
The minimum and maximum no. of members of sole trade is one only.
Question 17.
When the establishment of sole trade is essential?
Answer:
Following establishment can be made of sole trade:
- Less capital requirement e.g. cottage industry.
- Which can be managed with simple qualification e.g. gardening and farming.
- Those firms where individual attention is required e.g. watch repair.
- Those firms whose local area is limited and demand of commodity is limited e.g. vegetables and fruits etc.
Question 18.
If registration is optional, why do partnership firms willingly go through this legal formality and get themselves registered ? Explain.
Answer:
Registration of partnership firm means recording of the firm’s name and its relevant prescribed particulars, in the Register of firms kept with the Registrar of firms. It provides conclusive proof of the existence of a partnership firm. It is optional for a partnership firm to get registered still most of the partnership firms voluntarily get themselves registered as in case of non – registration, the firm has to face the following consequences:
- A partner of an unregistered firm cannot file, file suit against the firm or other partners.
- The firm cannot file a suit against third parties.
- The firm cannot file a case against the partners.
Hence, to avoid these disadvantages, partnership firms register themselves.
Question 19.
By which Act partnership is governed?
Answer:
By Indian partnership Act. 1932.
Question 20.
Is sole proprietorship have limited or unlimited liability?
Answer:
In sole trade there is unlimited liability which exist of the sole proprietor. Some business debts are not only cleared by the business assets but also by the personal assets of sole proprietor.
![]()
Question 21.
What is partnership deed?
Answer:
An agreement between two or more persons in writing, duly stamped and registered between the persons to enter into and form a partnership firm is called as partnership deed.
Question 22.
Explain the statement “Partnership takes birth with the agreement”?
Answer:
Birth of partnership takes place by the contract among the partners. Therefore, in the partnership deed in is very important to mention the mode of business operation, distribution of profit and loss, capital contribution by the partners etc. So that incase of any dispute things can be settled accordingly.
Question 23.
Why farmers cooperative society is constituted?
Answer:
Farmers cooperative society is constituted in order to make the farmers to get agricultural implements at the discounted rates to their members.
Question 24.
By which act the cooperative societies are registered?
Answer:
Cooperative societies are registered under cooperative society Act, 1912.
Question 25.
What is promotion?
Answer:
According to Gesternberg “Promotion may be defined as discovery of business opportunities and the subsequent organization of funds, properties and management ability into a business concern for the purpose of making profits there from”.
Forms of Business Organisation Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are different forms of business organization? Write its name.
Answer:
Followings are the different forms of business organization:
- Sole trade
- Joint Hindu family business
- Partnership
- Co – operative Society
- Joint stock company.
Question 2.
Write three disadvantages of sole trade?
Answer:
The three disadvantages of sole trade are:
1. Limited capital:
In sole trade the quantity of capital is small. So for the capital proprietor has to depend upon the loan given by family members, friends, relatives etc.
2. Limited talent:
In sole trade as the capital talent also remains limited to the skill of the proprietor. Any proprietor have lot of skill but cannot be perfect in all sections of the trade.
3. Limited goodwill:
Generally the goodwill of the sole trades remains same in comparison to the other forms of business organization.
Question 3.
How does a co – operative society exemplify democracy and secularism? Explain.
Answer:
The word co – operative means working together with others for a common purpose. The co – operative society is a voluntary association of persons, who join together with the motive of welfare of the members. The membership of a co – operative society is voluntary. A person is free to join a co – operative society and can also leave anytime without any compulsion. The decision making power in a co – operative society lies in the hands of an elected managing committee.
Every member has one vote and this right to vote gives the members a chance to elect the members of the managing committee. All these features lend the co – operative society a democratic character further, the membership of a co – operative society is open to all. Irrespective of their religion caste and gender.
Question 4.
Who is manager of the joint Hindu family? What are his rights?
Answer:
Joint Hindu family is managed and controlled by the eldest member of the family who is called as karta. Only Karta have the legal rights to enter in contract with others and outsiders. Karta only takes the decisions of the family.
Question 5.
Can a minor be partner in a firm? If yes, then explain main rights of a minor in brief?
Answer:
Minor refers to a person who is below 18 years of age and is incompetent to enter into contract but with the consent of all other partners he can be admitted into a partnership firm as per section – 30 and partnership Act. He will enjoy only profits but he will not bear losses.
Minor has following Rights in the firm:
1. Right to get profit:
A minor has the right to share in firms assets and profits of the firms as decided at the time of admission.
2. Right to inspect the firms book:
A minor has the right to inspect the books of the firm.
Question 6.
Explain social importance of sole trade.
Answer:
Following is the social importance of the sole trade.
1. Arranging professional education:
Sole trader can inform necessary information regarding the profession to the proper person and educate them.
2. Providing employment:
Sole trader cannot do whole work at the own but he can also appoint some persons and can create employment opportunities.
3. Reasonable price:
Sole trader open his shop near by the customer place and hence make goods available at the reasonable price to them.
4. Easy sole:
Sole trader reduces the problem of sale of the goods and sell commodity in small quantity to the customers.
Question 7.
“Sole trade is best in the world.” Discuss.
Answer:
India is a developing country where population increase is the major problem. For the proper development in each and every sector there is need of growth in small industries, agricultural industries. Hence, organization like sole trade only can solve this type of problem.
Sole trade is best in world because:
- Trading of artful goods.
- Ornaments and trading of similar nature.
- Trading of small and cottage industries.
- Such trade where personal supervision is almost required.
- Such trade where minimum capital is required and where there is no need to expand its area.
![]()
Question 8.
Write characteristics of J. H. F business.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of J. H. F business:
1. Family business:
It is totally a family business because in this business only the members of the family are involved. Whether the members are adult or minor, they have the right to become a member of the business as per the Hindu Inheritance Act 1956.
2. Operation of business:
The responsibility of the management of business affairs rests with the head of the family or senior citizen of the family in case of acute illness of the head of the family. Only they are competent and possess the right to enter into contract.
3. Registration of business:
Unlike company and partnership firms, the registration of J. H. F. business is not essential. It is free from all legal formalities and it is managed and controlled under Hindu Law.
4. Membership:
As soon as the male child takes birth, he becomes the member of the business. In ‘Dayabhag’ system, women can also become member under some specific situations because Hindu Inheritance Act, 1956 has given the right to women to become a member of the J. H. F.
5. Liabilities:
The liabilities of the members of the family is limited to their share of assets but the liability of the head of the family is unlimited. The liabilities of the business cannot be discharged with the personal property of the members.
Question 9.
What do you understand by public company?
Answer:
Public company is that company which is not a private company and which do not have any restriction as per memorandum of association as is there in private company. In other words public company is that company which do not restricts:
- Transfer of shares
- Members are not limited to 50
- Invites public for issue of shares and debentures.
Question 10.
Explain the advantages the one person company.
Answer:
Following are the advantages of OPC:
1. Limited liabilities:
OPC have the facility of limited liability which means the liability is limited upto the capital invested in the company.
2. Good alternative of risks sole proprietorship business OPC is getting popularity as one of the good alternative against the sole tradership.
3. Sole share holder:
In OPC only one shareholder is there hence, he is the whole sole owner of the company.
Question 11.
Write advantages of consumer cooperative store.
Answer:
Followings are the advantages of consumer cooperative stores:
1. Goods available at reasonable price:
They purchase goods from the producers and sell them directly to their members.
2. Good quality goods:
These stores sell good quality at cheaper prices. They do not have any adulteration.
3. EIimination its middlemen:
Since there stores purchase goods directly from the producers it eliminates the middlemen and hence, goods are available at cheaper prices.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain special privileges of the private company?
Answer:
Following privileges and exemptions are given to a private company as compared to a public Ltd. company under companies act.
1. Number of members:
The minimum number of members required for establishment of a private company is two, whereas for a public Ltd. company is seven.
2. Allotment of shares:
The clause of minimum subscription is not applicable to a private company for allotment of shares.
3. Submission of prospectus:
A private company need not has to file a prospectus or statement in lieu of prospectus with the registrar.
4. Issue of share capital:
Further issue of shares may not be offered to the existing members rather it is open to all.
5. Issue of shares and debentures:
There is no legal restriction on issue of shares or debentures.
Question 13.
What are the rules applicable in the absence of the partnership deed?
Or, How profit and loss is distributed, interest on capital and drawings is treated in the absence of the partnership deed?
Answer:
If partnership deed is not there then rules given in Indian partnership Act, 1932 is applicable automatically which are as under:
- Profit and loss among the partners will be distributed equally.
- No salary or remuneration will be given to any partner.
- Even partner has right to participate in working of the firm.
- Interest on capital will not be given and interest on drawings will not be changed.
- If loan is given by any partner to the firm then he will get Int. @6% p.a.
- Each and Every partner have the right to inspect the books of the firm.
Question 14.
Give six names of Indian companies which are under private sector?
Answer:
Indian companies under private sector are:
- Automotive Manufactures Pvt. Ltd.
- Cargill India Pvt. Ltd.
- Chromous Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- Destin Laboratories r Pvt. Ltd
- Karvy Computer Share Pvt. Ltd.
- Chiragagri Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
- Parle Products Pvt. Ltd.
- Samsung India Electronics Pvt. Ltd.
- V.K. Global Publication Pvt. Ltd.
- Yamaha motor Pvt. Ltd.
Question 15.
Write the name of Indian companies which are under public sector?
Answer:
Indian companies under public sector are:
- Apollo Hospital
- Axis Bank
- Bajaj Auto
- Canara Bank
- Dish TV
- DLF
- Educomp
- Gitanjali Gems
- GMR Infra
- HDFC Bank
- Hero Motocorp
- HUL
- Infosys,
- ITC
- Jet Airways
- Jindal Steel
- JSW Energy
- LIC Housing
- MRF
- NDTV
- NTPC
- Oil India
- ONGC
- Pantaloon
- Reliance Industries Ltd.
Forms of Business Organisation Long Answer Type Questions – I
Question 1.
Why people give more importance to have sole trade irrespective of limitations of size and available resources?
Answer:
It is because of following advantage of sole trade:
1. Easy to start and dissolve:
The sole tradership firm can be easily started at any time without any typical formalities. Similarly, he can put an end to it without following much of legal formalities.
2. Devotion in work:
A sole trader works will full zeal and devotion because:
- The success of business depends on his hard labour.
- He will be solely entitled for all the business profit.
- He chooses the business of his choice and so he works with full interest.
3. Freedom of occupation:
A sole trader can start any type of legal business according to his will. There is no legal binding upon him for starting a business.
4. Secrecy:
The activities of the trader remain secret. His business policies and trade secrets are not disclosed to others, therefore, he can maximize his profits by maintaining topmost secrecy of his business operations.
5. Prompt decisions:
A sole trader is the king of his own will, for any decisions. He is not required to consult or seek the permission of anybody. Therefore, the decisions in the firm are taken by him very promptly. Thus, spontaneous or on the spot decisions in the business often give fruitful results.
6. Personal contact:
A sole trader always keeps personal contacts with different parties in his business activities. Every consumer often comes in his personal contact.
![]()
Question 2.
What do you understand by sole trade firm? Write its characteristics.
Answer:
Sole trading is that form of business organization which is started and run by one person who bears profits and losses of it. Following characteristics are there of the sole trade:
1. Freedom of business:
A sole trader is free to choose a business of his convenience and choice. Before choosing a business, he keeps in mind the profit yielding capacity of the business. If there is any legal restriction on trading of any goods then he has to seek permission from the government or local authorities. Such liberty of business does not exists in other type of business organization, i.e., partnership and company.
2. Full control:
Since sole trader is the owner of the business, full control of the business is in the hands of proprietor and he is liable for all managerial activities related to the business. That is why Gesternberg has stated, “He owes all and risk all.”
3. Unlimited liability:
The sole trader arranges for the total capital for his business. The liability of bearing the losses lies with him only. No doubt, he enjoys the profits also, but the liability towards the total creditor is also to be borne by the single proprietor. In case, if business assets are insufficient to meet business debts, then private assets are attached to business for clearing the debts of the business.
4. No separate existence:
The sole trading concern has no legal existence independent of its owner.
5. Sole ownership of capital:
Since the arrangement of the total capital is done by the single person, therefore, he owns the total capital even if it is increased due to an additional profits earned by him during the course of business activities.
6. No legal formalities:
Unlike the limited companies, a sole trader is free from any legal formalities to be complied with in respect of the formation of his firm. Therefore, time gap is not created due to legal formalities in respect of the establishment of the business.
Question 3.
Write advantages of J.H.F.
Answer:
The main advantages of J.H.F. business are as follows:
1. No legal formalities:
Like sole trade, a J.H.F. business can be established without and regal formalities. It can be started and dissolved any time with the consent of the members of the family.
2. Liberty of business:
The head of the family of J.H.F. business has full freedom to choose a business of his choice. He does not has to consult or take permission from anybody to commence a business.
3. Freedom of decision:
Like sole trade, the liability of the business rests with a single person, i.e., the head of the family. He may or may not consult the other members before taking any decision. This helps him in taking quick decision and fructify the golden opportunities in the business. Such freedom does not exit in other forms of business organizations except sole trade business.
4. Management and operation:
The management and operation of the business affairs is in the hand of the head of the family. At times, he may take suggestions or seek help of operation and management of his business. For example, when the head of the family is going Abroad or for an outing few days, when the head falls sick or he is undergoing a long medical treatment, then he can bestow the responsibility on the shoulders of the most capable member temporarily.
5. Direct contact with customers:
Just like the sole trader, the head of J.H.F. business remains in regular contact with the customers and so he can observe and analyse the taste and demand of the consumers and try to provide them maximum satisfaction.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the merits/profits from the partnership.
Answer:
Merits of Partnership:
1. Ease of Formation and Closure:
A partnership firm can be formed with minimal legal formalities by an agreement between the prospective partners whereby they agree to carry out the business of the firm and share risks. Registration of the firm is also not compulsory. Closure of the firm can be done easily too.
2. Varied Expertise and Effective Decisions:
The partners can look after different , functions according to their areas of expertise. This reduces the burden of work on individual partners and leads to more effective decisions.
3. More Capital:
In partnership the capital is contributed by many partners. Thus, larger amount of funds are available as compared to a sole proprietor to undertake additional operations when needed.
4. Risk Sharing:
All the partners share the risks involved in running a partnership firm. This reduces the anxiety burden and stress on individual partners.
5. Secrecy:
A partnership firm is not legally required to publish its accounts and
submit reports. Hence, it can maintain confidentiality of information relating to its operations.
Question 5.
Mention limitation or demerits of the partnership.
Answer:
Limitations of Partnership:
1. Unlimited Liability:
The partners of a firm have unlimited liability. Personal as¬sets may be used for repaying debts if the business assets are insufficient. Further, the partners are jointly and individually liable for payment of debts. Hence, if some partners are unable to pay the debt proportionate to their share, the others will have to repay the entire debt causing excessive burden on them.
2. Unlimited Resources:
Partnership firms usually do not operate on a large scale as there is a restriction on the number of partners and hence, contribution in terms of capital investment remains insufficient for business expansion beyond a point.
3. Conflicts Decision:
Making authority in a partnership is shared by all the partners. Difference in opinion may thus lead to conflicts between partners. Decisions of one partner are binding on other partners and a wrong decision by one may result in financial problem for all others. If a partner decides to leave the firm due to conflicts this can result in termination of partnership as there is a restriction on transfer of ownership.
4. Lack of Continuity: Partnership comes to an end with the death, retirement. Insolvency or Lunacy of any partner it may result in lack of continuity if the remaining partners do not enter into a fresh agreement to continue the business.
Question 6.
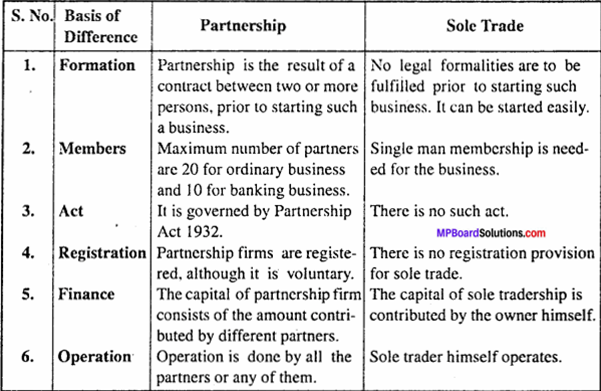
Differentiate between partnership and sole trade.
Answer:
Differences between Partnership and Sole Trade:
Question 7.
Write five features of the cooperative society?
Answer:
The chief characteristics of a cooperative societies are as follows:
1. Voluntary association:
In cooperatives the membership is voluntary, any person of 18 years of age living in the same area or busy in same profession or having the common objectives can become the member of association. There is no compulsion either to become its member or to continue its membership. The members can leave the cooperative association at any time at their own will.
2. Capital:
Contributing a marginal amount any person can become the member of the cooperative society. Normally a single person cannot buy shares exceeding 10% of the total paid – up capital or shares worth Rs. 1,000.
3. Equality:
The principle of “One man one vote” is adopted in the cooperatives, this is applied throughout irrespective of capital investment or services rendered by any member.
4. Democratic management:
With the cardinal principle of equality, the management of a cooperative organization becomes more democratic in character. The cooperative functions in each locality, so almost all the members can attend the meetings to elect their representatives to manage the day to day affairs of the organization.
5. Cash sales:
Cooperative business safely undertakes all the transactions in cash. Cash sale avoids risk of loss, caused by the practice of debts.
Question 8.
Write objectives of opening cooperative society in the school.
Answer:
Followings are the objectives of opening cooperative society in the school:
1. Reasonable rate:
In order to provide goods at reasonable rate to the students.
2. Good quality:
Making availability of good quality goods for the students.
3. Security of goods:
In order to fulfill the needs of customers making goods availability and also secured.
4. End of monopoly:
In order to end the monopoly of the producers.
5. Economy:
Development of thrift in students and to provoke the habit of serving.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the kinds of companies.
Answer:
There are two types of companies:
(a) Private company:
According to Sec. 31 (1) (iii), private company is one:
- Where the number of members range from 2 – 50.
- Which restricts its members from transferring their shares to others.
- In which the word ‘private’ is added at the end of its name.
(b) Public company:
A public company has the following characteristics:
- The minimum number of members in a Public Ltd. Co. is 7 and the maximum is unlimited.
- Such company does not restricts the transfer of its shares.
- It generally invites the common public to subscribe for its shares.
Such companies apply the term Ltd. at the end of their names.
Question 10.
Write the characteristics of one man company.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of one man company:
1. Only one person is required:
Only one parson is required are the establishment of this kind of company.
2. Like private company:
One person company existence is like private company. It means that all the exemptions and privileges are available for them also.
3. Nomination:
The main person of the UPC has to nominate on person so that in case of death or illness of the main person. The business can be going on without any interruption.
4. Joint holder:
All the shares of the company is jointly holded by one person only. But two person can also be acting as joint holder.
5. Limited liability:
OPC have limited liability as in case of the company it debt is to be cleared then it will up to the availability of the assets of the firm.
Question 11.
Write the importance of the promoters.
Answer:
Promoters plays very important role, in the economic and social development of the country. Now a days the role of companies are going on increasing, but for its formation, promoters plays very important role. The relation of the company and promoters depend on the faith. Risk of formation of the company also lies on the promoters only. If the promoter is successful in his work then the income of the company goes on increasing and if not then company may bear loss. Hence, promoters are called as the backbone of the company. Hence, in short the role of promoters can be depicted as
- They convert ideas and imaginations into reality.
- Promoter lead to capital formation in the country.
- They lead to establishment of new companies and extension of the old companies.
- The praise new inventions and convert them into reality.
- Helpful in the utilization of natural resources.
![]()
Question 12.
What is prospectus? Write its objectives.
Answer:
A prospectus is an invitation to the members of the public, anyone who brings his money and applies in due from to buy shares or debentures of the company. A private company is prohibited from making any invitation to the public to subscribe for shares or debentures of the company [Sec. 3(1) (iii)] of the Company’s Act. Sec. 2(36) of the act defines prospectus as, “Prospectus means any document prescribed or issued and includes any notice, circular, advertisement or other document inviting deposits from the public or inviting offers from the public for the subscription or purchase of any shares or debentures of a body corporate”.
Objects of the issue of Prospectus:
A prospectus is issued for the following objectives:
- An invitation to buy shares or debentures of the company.
- To bring to the notice of the public that the new company has been formed.
- To convince the public that the investment of the public would remain safe.
- A director’s declaration about the company’s policy and their liabilities.
The allotment of shares must be over within 120 days from the date of issue of the prospectus.
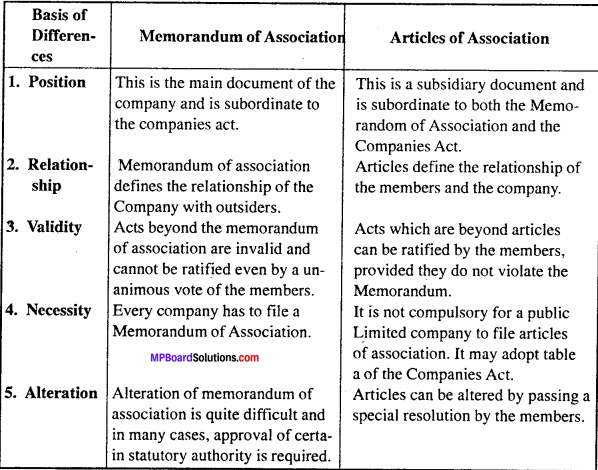
Question 13.
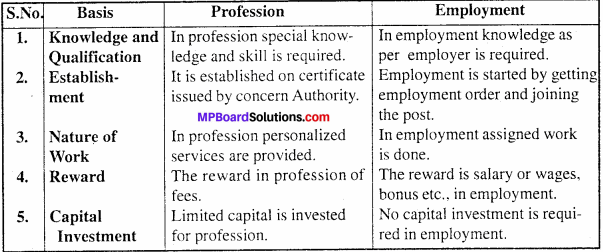
Distinguish between ‘Memorandum of Association’ and ‘Articles of Association’?
Answer:
Differences between Memorandum of Association and Article of Association:
Question 14.
The business assets of an organization amount to 50,000 but the debts that remain unpaid are 80,000. What course of action can the creditors take if,
1. The organization is a sole proprietorship firm.
2. The organizations is a partnership firm with Anthony and Akbar as partners. Which of the two partners can the creditors approach for repayment of debt? Explain giving reasons.
Answer:
1. The organization is a sale proprietorship firm sale proprietors have unlimited liability. This implies that the owner is personally responsible for payment of debts in case the assets of the business are not sufficient to meet all the debts. As such the owner’s personal possessions such as his/her personal car and other assets could be sold for repaying the debt.
Example:
In the given case the total debts that remain unpaid are 80,000 but the organizational assets amount to 50,000 only. In such a situation the creditors can demand from the proprietor to pay 30,000 from his/her personal sources even. If he/she has to sell his/her personal property to repay the firm’s debts.
2. The organization is a partnership firm with Anthony and Akbar as partners. The partners of a firm have unlimited liability. Personal assets may be used for repaying debts in case the business assets are insufficient. As the total debts that remain unpaid are 80,000 but the organizational assets amount to 50,000 only, the creditors can demand from both or any of the partners.
Anthony and Akbar to pay 30,000 from their personal sources even if they have to sell their personal property to repay the firm’s debts.
Question 15.
What points are to be kept in mind while selection of the business?
Answer:
Following points are to be kept in mind while selection of the business:
- Simplicity of organization
- Capital availability
- Loan requirement
- Managerial rights
- Transfer of ownership
- Scope of extension
- Work area
- Charge in work
- Government control
- Tax.
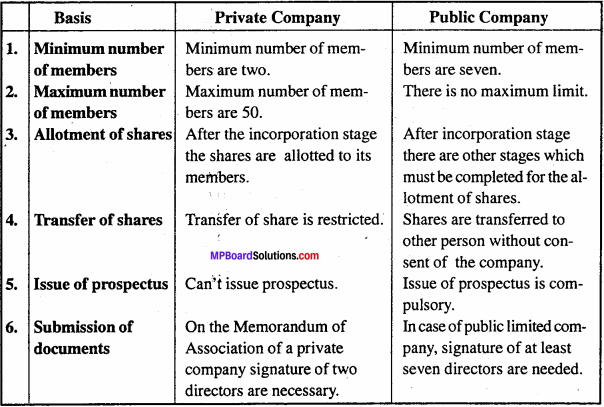
Question 16.
Differentiate between Private and Public company.
Answer:
Differences between Private and Public companies:
Forms of Business Organisation Long Answer Type Questions – II
Question 1.
What do you understand by a sole proprietorship firm? Explain its features and merits.
Answer:
Sole proprietorship refers to a form of business organization which is owned, managed and controlled by an individual who is the recipient of all profits and bearer of all risks. The word “sole” implies “only” and “proprietor” refers to “owner”. Hence, a sole proprietor is the only owner of a business. This form of business is particularly common in small scale business and areas of personalized services.
Features of Sole Proprietorship:
1. Formation and Closure:
Very few legal formalities are required to start a sole proprietary business, except in the fields where’a license is required. Closure of the business can also be done easily.
2. Unlimited liability:
Sole proprietors have unlimited liability. This implies that the owner is personally responsible for payment of debts in case the assets of the business are not sufficient to meet all the debts.
3. Sole Risk Bearer and Profit Recipient:
The sole proprietor bears the risk of failure of business all alone and also receives all the business profits which are a reward for his risk bearing.
4. Control and Decision Making:
The sole proprietor has the absolute right to run the business and make all decisions regarding the business without any interference from others. He is the king in. all aspects.
Merits of Sole Proprietorship:
1. Prompt Decision Making:
The decision making is prompt under sole proprietor-ship. As there is considerable degree of freedom in making business decisions and there is no need to consult others. This results in timely capitalization of market opportunities.
2. Confidentiality:
All the information related to business operations is kept confidential and secrecy is maintained as the sole decision making authority rests with the proprietor. A sole proprietor is also no bound legally to publish firm’s accounts.
3. Direct Incentive:
The sole proprietor receives all the business profits as a reward for bearing the business risk he/she is the single owner and does not need to share profit. This provides an incentive to the sole proprietor to work hard.
4. Sense of Accomplishment:
There is a sense of personal satisfaction involved in working for oneself. It insure a sense of accomplishment and confidence in the individual.
![]()
Question 2.
Why partnership is not so popular in comparison to the sole trade? Explain its features and limitations.
Answer:
In partnership the profit is distributed among the partners of the firm. It is operated either by all or any one of them acting for all. Partnership came into existence because of the demerits of the sole trade.
Following are the features/profits of the partnership:
1. Simple to start and end:
Partnership can be started and ended with the consent of all the partners. It is also not compulsory to get the firm registered.
2. Balance decision:
Partner normally do that work only in which they are specialized and so they get it profit.
3. Risk share:
Risk or loss is also distributed among all in the pre – decided ratio by the partners. So no partner is overloaded with risk or loss.
4. Secrecy:
It is not necessary to get the books of account to be published and hence, secrecy is maintained.
5. Personal look:
All managerial work is done normally by the partners only hence, there is total control on the employees.
Limitations of partnership:
1. Unlimited liability:
The biggest demerit of partnership business is unlimited liability. Partners always fear that their personal property will be utilized to pay off the business debt.
2. Limited capital:
The resources and capital invested in the firm are larger but it is compared to the capital of the sole tradership, the amount of capital and resources are not very large.
3. Lack of public confidence:
A partnership can’t enjoy public confidence because of the absence of legal formalities, and due to lack of publicity of its affairs.
4. Lack of continuity:
If any partner dies, retires, gets insolvent or insane then partnership cause to an end.
5. Limited ability:
A partnership may not be able to provide requisite organizing power and technical skill.
6. Difficulty in transfer of interest:
A partner can’t transfer his interest in the firm without the consent of the other partners. Until such time the funds invested by one partner in the business are blocked at least temporarily.
Question 3.
Explain main principles of cooperation.
Answer:
Fedrick Nicholson, while stating the principles of cooperation has said, “The work which cannot be done by a single person, can be done with the mutual cooperation and help from all. Those physical resources can be achieved which are available only to the rich people and in this way every person can develop his own natural talents.” Cooperation has certain principles. They are as follows:
- It is a voluntary association.
- Cooperative organization is set up to fulfil some economic purposes.
- Every work is done in a economical way.
- Each member has equal rights.
- In cooperative organization all the decisions are taken by the majority of members, therefore in election and in routine working of the business activities democratic pattern is fully adopted.
- Members’ interest are protected.
- The formation of cooperative is based on principle of “First serve then profit.”
- All members work with mutual cooperation and help.
![]()
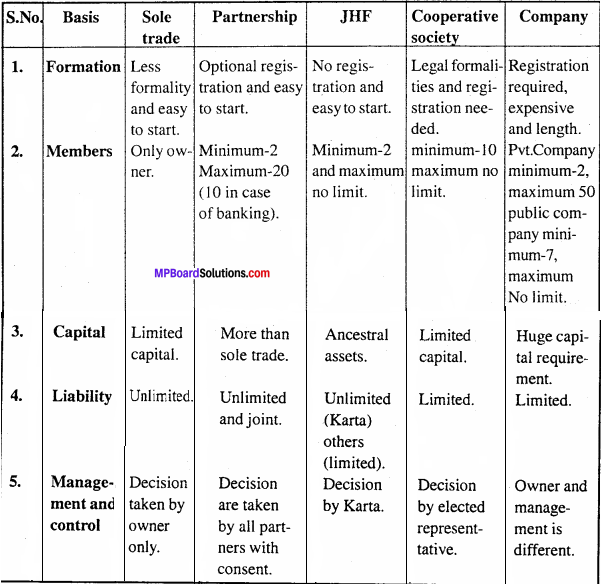
Question 4.
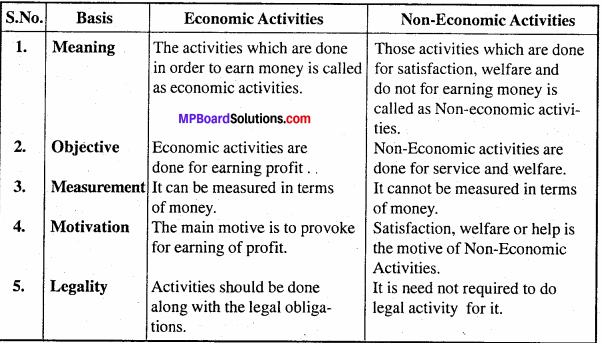
Differentiate among different forms of business organization.
Or,
Explain any four difference between cooperative society and company.
Answer:
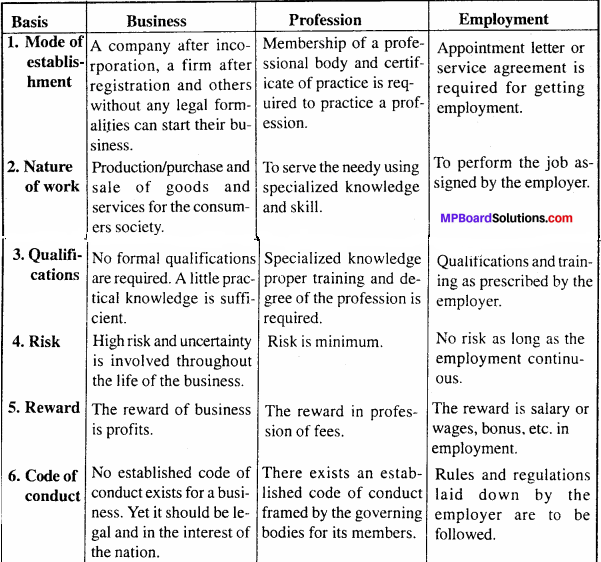
Differences between different firms of business organization:
Question 5.
Why is it important to choose an appropriate form of organization?
Discuss the factors that determine the choice of form of organization?
Answer:
After studying various terms of business organizations it is evident that each form has certain advantages as well as disadvantages.The important factors determining the choice of organization are discussed below:
1. Cost and Ease of starting business:
Sole proprietorship is started easily as far as initial business setting up costs and legal requirements are concerned. In case of partnership also, the advantage of less legal formalities and lower cost is there because of limited scale of operations. Registration is compulsory in case of co – operative societies and companies. Formation of a company involves a lengthy and expensive legal propedure.
2. Liability:
In case of sole proprietorship and partnership firms, the liability of the owners/partners is unlimited. This may result in payment of debt from personal assets of the owners. In Joint Hindu family business, only the Karta has unlimited liability.
3. Continuity:
The continuity of sole proprietorship and partnership firms is affected by events such as death, insolvency or insanity of the owners. However, such factors do not affect the continuity of business in the case of organizations like, Joint Hindu Family business, co – operative societies and companies.
4. Managerial Ability:
It is difficult for a sole proprietor to have expertise in all functional areas of business. In other forms of organizations like partnership and company, there is division of work among the members which allows the managers to specialize in specific areas, leading to better decision making.
5. Capital Requirements:
For large scale operations, company form is the most suitable as large amount of funds can be arranged by issuing shares. In this form, for medium and small sized business, one can opt for partnership or sole proprietorship. Capital requirements for expansion can also be met more easily in company form.
6. Degree of Control:
Sole proprietorship provides direct control over operations and absolute decision making power. But if the owners want to share control for more effective decision making, partnership or company form of organization can be adopted. In company form of organization, professionals are appointed to manage the affairs of a company as there is complete separation of ownership and management.