MP Board Class 9th Special Hindi सहायक वाचन Solutions Chapter 9 प्रेरणा दीप (पौराणिक कथा संदर्भ, संकलित)
प्रेरणा दीप अभ्यास
बोध प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
रामायण के रचयिता कौन हैं?
उत्तर:
रामायण के रचयिता महर्षि बाल्मीकि हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
नदी के तट पर किस पक्षी का जोड़ा था?
उत्तर:
नदी के तट पर क्रौञ्ज पक्षी का जोड़ा था।
प्रश्न 3.
बाल्मीकि के शिष्य का नाम क्या था? बताइए।
उत्तर:
बाल्मीकि के शिष्य का नाम भारद्वाज था।
प्रश्न 4.
राम के वंश का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर:
राम के वंश का नाम सूर्यवंशी इक्ष्वाकु था।
प्रश्न 5.
कौरव सेना के सेनानायक का नाम क्या था?
उत्तर:
कौरव सेना के सेनानायक का नाम भीष्म पितामह था।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
युधिष्ठिर कौरव की सेना में क्यों गये थे?
उत्तर:
युधिष्ठिर कौरव की सेना में भीष्म पितामह एवं अन्य गुरुजनों के चरण स्पर्श करने तथा उनसे आशीर्वाद लेने गये थे।
प्रश्न 7.
बाल्मीकि ने निषाद को क्या और क्यों अभिशाप दिया?
उत्तर:
बाल्मीकि ने निषाद को यह अभिशाप दिया कि “तू अब आने वाले समय में कभी भी प्रतिष्ठा (सम्मान) को प्राप्त नहीं कर सकेगा। क्योंकि तूने कामासक्त क्रौञ्ज के जोड़े में से नर क्रौञ्च का वध कर दिया है।”
प्रश्न 8.
बाल्मीकि को ध्यान के समय ब्रह्मा जी ने दर्शन देकर क्या कहा?
उत्तर:
बाल्मीकि जब ध्यान लगाकर बैठे हुए थे तभी सृष्टि के रचयिता ब्रह्माजी ने दर्शन देकर उनसे कहा-“ऋषिवर मेरी ही इच्छा वाणी अनायास आपके मुँह से निकली और श्लोक रूप में इसलिए निकली है कि आप अनुष्टुप् छन्दों में रामचन्द्र के सम्पूर्ण चरित्र का वर्णन कीजिए। श्रीराम कथा संक्षेप में आप नारदजी से सुन ही चुके हैं। मेरे राम, लक्ष्मण, सीता और राक्षसों का गुप्त अथवा सब वृत्तान्त आपकी आँखों के सामने आ जाएगा, होगा वह भी दिखाई पड़ेगा। अतः जो आप लिखे यथार्थ और सत्य होगा। इस प्रकार आपकी लिखित रामायण इस लोक में अमर हो जायेगी।”
प्रश्न 9.
श्रीकृष्ण ने अर्जुन को अपने विराट स्वरूप में क्या दिखलाया?
उत्तर:
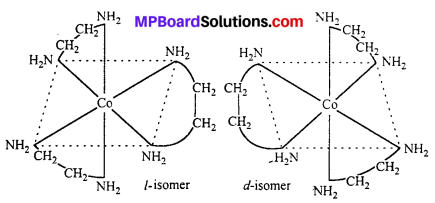
श्रीकृष्ण ने अर्जुन को अपना विराट स्वरूप दिखलाया जिसे देखकर अर्जुन काँप उठे। उन्होंने देखा कि एक विशाल अग्नि-ज्वाला, जिसमें चारों ओर से कीड़े-मकोड़े आते हैं और समाकर भस्म हो जाते हैं। उसी तरह समस्त कौरव भी कृष्ण के मुख में समा रहे हैं। इसे देखकर अर्जुन का मोह भंग हो गया और उन्होंने भगवान कृष्ण की वन्दना की।
प्रश्न 10.
माता सत्यवती से भीष्म ने क्या प्रतिज्ञा की थी?
उत्तर:
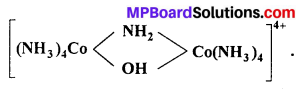
माता सत्यवती से भीष्म ने प्रतिज्ञा की थी कि वे राजा के पक्ष में रहेंगे तथा उसी की ओर से युद्ध करेंगे। लेकिन धर्म और सत्य की सदैव विजय होती है अतः विजयी पाण्डव ही होंगे।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
तमसा नदी की प्राकृतिक सुन्दरता का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर:
तमसा नदी का प्राकृतिक सौन्दर्य बहुत मनोहारी था। इस समय बसन्त ऋतु का आगमन हो चुका था। नदी का जल अत्यन्त स्वच्छ एवं पवित्र था। यहाँ तक कि उसका तल भी स्पष्ट नजर आ रहा था। जल के किनारे पक्षी बैठे थे तथा उसमें मछलियाँ तैर रही थीं। नदी के किनारे हरे-भरे जंगल थे। कुछ पक्षी तो पेड़ों पर बैठे थे तथा कुछ नदी के किनारे। कुछ पक्षी नदी के जल में अपनी चोंच डुबोकर पानी पी रहे थे। इस प्रकार इस प्राकृतिक सौन्दर्य का आनन्द लेते हुए पक्षी विचरण कर रहे थे।
प्रश्न 12.
नारद जी की वाणी याद आने पर बाल्मीकि ने नारद जी से क्या पूछा ? तथा नारद जी ने क्या उत्तर दिया? लिखिए।
उत्तर:
एक बार बाल्मीकि जी निषाद को दिये गये कठोर शाप की चिन्ता में मग्न थे कि उसी समय उन्हें नारद जी की वाणी याद आयी। उन्होंने नारद जी से पूछा था-“हे देवर्षि, मुझे किसी ऐसे पुरुष का नाम बताइये जो गुणवान, बलवान एवं धर्मात्मा हो, जो सत्य पर दृढ़ रहता हो, अपने वचन का पक्का हो, सबका हित करने वाला हो, विद्वान हो और जिससे बढ़कर सुन्दर कोई दूसरा न हो।”
इस प्रश्न को सुनकर नारदजी ने कहा था कि मैं ऐसे एक ही पुरूष को जानता हूँ। वे इक्ष्वाकु वंश के राजा दशरथ के पुत्र राम हैं। वे सब तरह से गुणवान और रूपवान हैं और जब क्रोध करते हैं तब डर के मारे देवता और दानव भी काँप उठते हैं।
प्रश्न 13.
श्रीकृष्ण का कर्मयोग संक्षिप्त में समझाइए।
उत्तर:
युद्ध क्षेत्र में जब अर्जुन ने देखा कि कौरव सेना तथा पाण्डव सेना दोनों में ही उनके आत्मीय एवं परिवारीजन हैं और वे दोनों ही एक-दूसरे को राज्य प्राप्ति के लिए मारने को उद्यत हैं तो अर्जुन दु:खी हो जाते हैं और अपना गाण्डीव धनुष रथ में एक तरफ रखकर रथ के पिछले भाग में बैठ जाते हैं।
जब श्रीकृष्ण ने अर्जुन की इस मोह ग्रसित दशा को देखा तो उन्होंने अपना विराट स्वरूप दिखाकर अर्जुन का मोह भंग किया तत्पश्चात् उन्होंने अर्जुन को कर्मयोग का उपदेश देते हुए कहा कि आत्मा अजर और अमर है। इसलिए हे अर्जुन! तुम शोक मत करो तथा युद्ध करो।
प्रश्न 14.
कुरुक्षेत्र में खड़ी सेनाओं का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर:
कुरुक्षेत्र में ग्यारह अक्षौहिणी सेना कौरवों की ओर थीं ओर सात अक्षौहिणी सेना पाण्डवों की ओर थीं। दोनों सेनाएँ आमने-सामने व्यूह-रचना के तरीके से खड़ी थीं। कौरव सेना के प्रधान सेनापति भीष्म पितामह थे तथा पाण्डव सेना के आगे धनुर्धारी अर्जुन थे। अर्जुन के रथ का नाम नंदिघोष था जिसके सारथी स्वयं भगवान श्रीकृष्ण थे। कौरव सेना के सेनापति भीष्म पितामह के रथ के साथ ही रथी दुःशासन था तथा थोड़ी दूरी पर मुक्ताओं से जड़ित सुन्दर रथ पर कौरवराज दुर्योधन था। पास ही गुरू द्रोणाचार्य और अश्वत्थामा थे। इस प्रकार कौरवों एवं पाण्डवों की अपार सेना एक अद्भुत रोमांचकारी दृश्य उपस्थित कर रही थी।