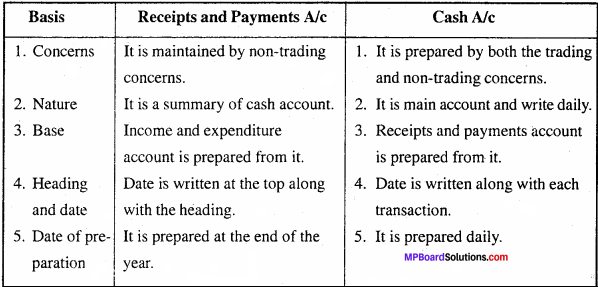
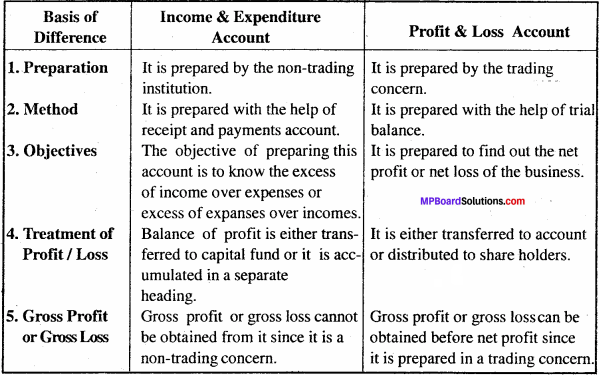
MP Board Class 12th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 5 Organization
Organization Important Questions
Organization Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Out of the following, which is not a part of delegations :
(a) Accountability
(b) Authority
(c) Responsibility
(d) informal organization.
Answer:
(d) informal organization.
Question 2.
A network of social relationship that arise relationship due to interaction at work is called:
(a) Formal organization
(b) Informal organization
(c) Denaturalization
(d) Delegation.
Answer:
(b) Informal organization
Question 3.
Organization cannot be seen as :
(a) As a work of management
(b) As a structure of relationship
(c) As a process
(d) As an enterprise instinct
Answer:
(d) As an enterprise instinct
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a part of organization:
(a) Division of work
(b) Work structure
(c) Formation of work and departments
(d) provide leadership
Answer:
(d)provide leadership
Question 5.
Which of the following does not follow the scalar chain :
(a) Formal structure
(b) Informal structure
(c) Functional structure
(d) Divisional structure
Answer:
(b) Informal structure
Question 6.
Group of activities on the basis of product line Is a part of:
(a) Decentralized organization
(b) Divisional organization
(c) Functional organization
(d) Centralized organization
Answer:
(b) Divisional organization
![]()
Question 7.
A tall structure has a :
(a) Narrow span of management
(b) Wide span of management
(c) No span of management
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Narrow span of management
Question 8.
Grouping of a activities on the basis of functions line is a part of:
(a) Delegated organization
(b) Divisional organization
(c) Functional organization
(d) Autonomous organization
Answer:
(c) Functional organization
Question 9.
Centralization refers to :
(a) Retention of decision making authority
(b) Dispersal of decision making authority
(c) Creating division of profit centers
(d) Opening new centers or branches
Answer:
(a)Retention of decision making authority
Question 10.
Span management refers to :
(a) Number of managers
(b) Length of term for which a manger is appointed
(c) Number of subordinates under a superior
(d) Number of members in top management.
Answer:
(b) Length of term for which a manger is appointed
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- ……………….establishes cordial relation between labour and capital.
- Organization formed according to goods produced by them is called …………..
- The transfer of right in limited form to the members is called …………..
- Distribution of rights and duties of an enterprise at the lowest level is called ……………
- Rights and duties are clearly described in ……………organization.
Answer:
- Organization
- Departmental, Organization
- Delegation
- Decentralization
- Formal
Question 3.
Write the answers in one word/sentence :
- Granting authority and responsibility regarding a specific job to subordinates.
- A systamatic dispersion of authority at all levels of department.
- Big organization is divided into small administrative unit.
- Authority is delegated not responsibility.
- That form of organization which is developed due to mutual relations.
- That organization which is based on rules and procedures.
- In functional organization what type of relation is shown ?
- When does management of organization comes in the process of management ?
- Which step is departmental organization ?
- In informal organization what type of relations is there among members ?
Answer:
- Authority
- Decentralization
- Divisional organization
- Authority
- Informal organization
- Informal organization
- Authority and subordinates
- After planning
- Second step
- Friendly relation.
Question 4.
Write true or false :
- Establishment of organization is done by lower level of management.
- Organization gives birth to corruption.
- Delegation of authority means assigning work to others.
- Accountability is the obligation to carry out responsibility.
- Organization in management is as important as structure of bones in human body.
Answer
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True.
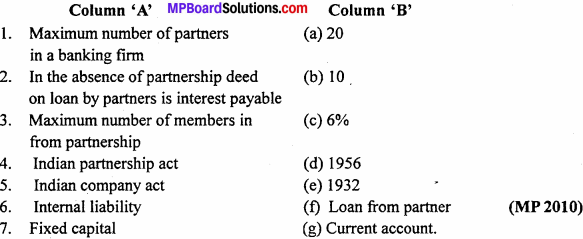
Question 5.
Match the columns

Answer:
1. (e)
2. (a)
3. (b)
4. (c)
5. (d)
![]()
Organization Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
After which function of management organizing function comes ?
Answer:
Organizing function comes after planning.
Question 2.
How does a strong organization increases job satisfaction among the workers ?
Answer:
A strong organization increases job satisfaction among the workers by assigning them work according to their ability.
Question 3.
How can repetition stopped in an organization ?
Answer:
Right person at the right job.
Question 4.
Why is a big task divided into smaller parts ?
Answer:
Because of the following reasons:
- To reduce the burden of work load
- To avail the ability of specialized employees
- To avoid from repetition of tasks.
Question 5.
What do you understand by divisional ?
Answer:
When a big organization is divided into small administrative units for managing effectively it is called divisional.
Question 6.
How is the word organizing used ?
Answer:
Organization is used in two forms :
- Organizational Structure and
- Functional structure.
Question 7.
What is delegation of authority ?
Answer:
Delegation of authority merely means the granting of authority to subordinate to operate within prescribed limits.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the meaning of authority responsibility accountability relationship.
Answer:
Authority responsibility relationship means the relationship which explains from whom an individual will receive orders and to whom he will be accountable or answerable while performing a particular task.
Question 9.
What is expansion of management ?
Answer:
Expansion of management means organizing the deployment of employees or managing tasks.
Question 10.
How is informal organization formed ?
Answer:
The structure is a result of social interaction between employees of similar interests.
![]()
Organization Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is delegation of authority ?
Answer:
Granting authority and responsibility regarding specific job to the subordinates is called as delegation of authority. Delegation of authority is an art of granting certain ordinary, routine and exact authorities to competent subordinates so that they can perform the work as per instructions efficiently. It is an important element of organization. Delegation of authority is based upon the principle of division of work.
Question 2.
What is line organization ?
Answer:
Line organization is the oldest form of organization. Business or industry structure with self contained departments. Authority travels downwards from top and accountability upwards from bottom along the chain of command and each department manager has control over his or her departments affairs and employees.
Question 3.
What do you mean by organization ?
Answer:
Organization means a group of people having a certain object. It involves coordinating the employees activities in an efficient manner for accomplishing the objectives of the enterprise. The success of an enterprise totally depends on how powerful the organization is.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the merits of committee organization.
Answer:
The merits of committee organization are as follows :
- Committee organization promotes cooperation
- Quick decisions can be taken in important cases
- Policy matters and problems can be solved easily
- Coordination can easily be exercised in different departments with the help of committees.
Question 5.
Give a definition of organization.
Answer:
According to Prof. L. Haney, “Organization is a harmonious adjustment of specialized parts for the accomplishments of some common purpose or purposes.”
According to D.W.R. Spriegal, “Organization is the structural relationship between the various factors in an enterprise”.
Question 6.
Where is line organization suitable ?
Answer:
Those organizational units where employees are less in number. Production is of general type and employees are disciplined, here line organization is suitable.
Question 7.
How does organization help in improving the morale of employees ?
Answer:
In an effective organization, the employees are well aware of their rights, duties and responsibilities and therefore they understand the objectives of the enterprise quite well. This helps them to develop the feelings of sincerity, participation and cooperation thereby increasing their morale.
Question 8.
How organization stops repetition of work ?
Answer:
By assigning specific work to specific person repetition is avoided in organization.
Question 9.
Write the main characteristics of line organization.
Answer:
The main characteristics of line organization are :
- The orders flow from top to bottom i.e. in downward direction.
- orders are passed by officers.
Question 10.
Write the various forms of organization.
Answer:
According to nature and size, an organization has following forms :
- Line organization
- Line and staff organization
- Functional organization
- Committee organization.
![]()
Question 11.
Discuss the objectives or importance of organization.
Answer:
1. Economy in production : The main object of organization is to bring economy in production. It means production of goods at minimum cost.
2. Economy in time and labour : In organization, best machines, equipments and best methods are applied and so enough time and labour of the work are saved.
3. Cordial relations between labour and capital: To establish relation between labour and management is one of the object of organization. For this, the best entrepreneur is appointed to safeguard the interest of the labour and capital.
4. Spirit of service : Due to social consciousness, the object of every businessman is to serve first then profit. So, every organization in present time has the object to serve.
Question 12.
Throw light on the importance of organization.
Answer:
1. Effective formulation of policies : Policies are framed by the administration of any enterprises or organization. It is the work of the management to formulate all policies. Once the policies are framed, the organization (normally, a group of people) executes these policies. A strong organization ensures reliable policies. So, organization has great importance for effective formulation of policies.
2. Encouragement to specialization : Specialization is based upon the principle of division of labour. If the employees are grouped according to their efficiency, then the work will be carried-out efficiently. This division of work enhances the spirit of employees. Specialization is encouraged due to the number of employees.
3. Increase in managerial efficiency : Priority is given to coperaion, coordination and discipline in a sound organization. So, the work is done at the earliest. Due to earliest disposal of work, new planning is again framed by the top management or administration so the work remains in the continuous process. In this way due to the expansion of managerial work, managerial efficiency progress in a rapid way.
4. Fillip to growth : It can be known from the history of old and big organization that their growth has become possible due to organization. The main maxim for the growth of healthy and sound business is only organization.
5. To work systematically : In organization every person performs his duty systematically as it is clearly directed in the organization about the execution of work.
6. Prevents corruption : There is no any place corruption in a sound organization.
Question 13.
“Organization increases the capacity of production”. Explain.
Answer:
In a sound and organization employees work with full devotion and so production of the enter process increases. Now techniques and machines developed in the enterprise increases the efficiency of employees which will result is large scale production.
Question 14.
What is project organization ?
Answer:
Project organization is that system in which a working team is constituted for specific production or to provide services.
Question 15.
What are the disadvantages of line organization ?
Answer:
Disadvantages of line organization are as follows :
(i) There is a good scope for favouritism as the highest officer has the authority. There is a possibility that he promotes or appoints his favourites.
(ii) The-modem industry is so complex that it is not possible for a single person to perform all the work efficiently. It is not possible for the department head to be specialized in very field. Hence, there is a lack of specialization in this method.
Question 16.
What is line and staff organization ? Write its four characteristics.
Answer:
The line is the chain of command that extends from board of directors through the various delegation and re-delegations of authority and responsibility to the point where
the primary activities of the company are performed. They are directly engaged in producing or selling of goods and services and provide advices also characteristics :
- Order and responsibility moves from top to bottom in this organization.
- Both the working thinking and giving suggestions are separate in it.
- To assist the line officers employees are appointed.
- The specialists work as a staff member only.
Question 17.
Mention the advantages of line organization.
Answer:
Advantages : The advantage of line organization are as follows :
- Every member of the organization knows his responsibilities and duties.
- There is strong discipline because the subordinates knows their rights and control area.
- In this type of organization, adjustment can be made according to the needs, i.e., there is flexibility.
- The subordinates cannot runaway from their duties because they are not able to put their responsibilities on others.
Question 18.
What do you mean by committee organization ?
Answer:
Committee organization is that system in which a specific group is formed to perform administrative work committee is a group of persons. They are allotted some functions in such a way that they will perform the function collectively. The head of this committee is called the president.
Question 19.
What are the reasons of distributing works in small parts ?
Answer:
Work is distributed into small parts due to following reasons :
- To reduce the pressure of work
- To have advantage of profit
- To divide the work in such a way so that repetition should not be there.
Question 20.
What do you mean by divisional organization ?
Answer:
When a big organization is divided into small administrative unit for managing effectively, it is called divisional organization.
Question 21.
Write the four advantages of territorial organization.
Answer:
The four advantages of territorial organization are as follows :
- It provides effective span at control.
- Expansion of business in various regions becomes easy.
- It facilitates in economy is rent and labour.
- It provides opportunity of giving training to managers.
Question 22.
“By top level organization the efficiency of Administration increases.” Explain.
Answer:
Formal organization is top level organization. Formal organization is established for general objectives. Organization structure is determined by top level. In it authority and responsibility are clearly defined. Formal organization aims at achieving predetermined objectives. Every individual belongs to one work group only and works under one superior. So by top level organization the efficiency of administration increases.
![]()
Question 23.
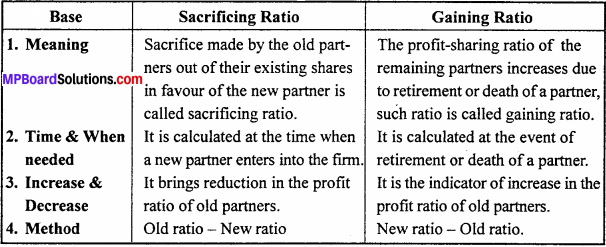
Distinguish between divisional and functional organization.
Answer:
The differences between divisional and functional organization :
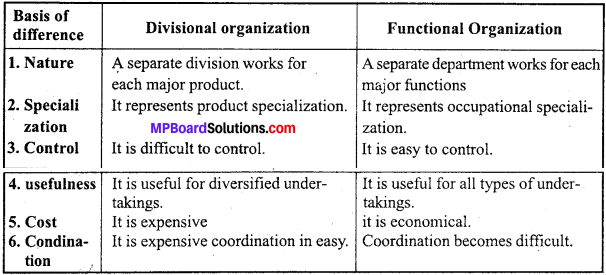
Question 24.
What is the relation between formal and informal organization ?
Answer:
Informal organization is a part of formal organization. In formal organization the worker complete their work with the help of each other. They consult each other due to this friendly relationship is maintained. On the basis of friendship a network of informal organization in formed. This network is called informal organization. Thus formal organization gives birth to informal organization. So we can say that formal organization and informal organization are interrelated.
Question 25.
“Organization increases managerial efficiency.” How ?
Answer:
The best organization increases managerial efficiency. The best and effective organization helps in achieving objectives easily. The best organization means good employees, workers and management. Better environment helps in the efficiency of organization. Increase in managerial efficiency is because of specialization in an organization. A good organization provides training to its employees. These qualified and trained people make full utilization of various resources.
Question 26.
What are the characteristics of informal organization ?
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of informal organization :
- These type of organizations are formed spontaneously.
- These organization have common interest.
- It is a voluntary organization.
- These organizations have no concern with manual and charts.
- These organization can be legal or illegal.
- It is a part of formal organization.
- In these organization the relationship is based upon personal understanding.
Organization Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between formal and informal organization.
Answer:
Differences between Formal and Informal Organization :
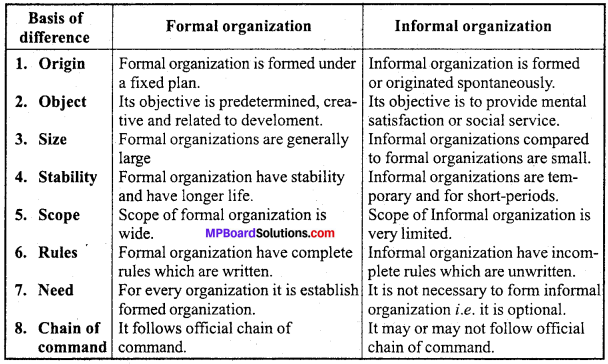
Question 2.
What is formal organization ? Explain any four features.
Answer:
The different types or forms of organizations are classified on various basis. One of the type is formal and informal organization.
Formal organization : It is an official structure of activities, roles and authority relationship which is planned and executed by management for achieving organizational objectives. In this organization every individual belongs to one work group only and works under one superior only. It follows official chain of command.
Characteristics of formal organization : Following are the characteristics of formal organization:
- This type of organization is established for general objectives.
- Organization structure is determined by top level.
- Authority and responsibility are clearly defined in formal organization.
- The relationship.is determined according to the jobs and its nature.
- Formal organization aims at achieving predetermined objectives.
- Every individual belongs to one work group only and works under one superior.
- In this type of organization policies, procedures and plans are written.
![]()
Question 3.
What is informal organization ? Explain its characteristics/features.
Answer:
Informal Organizations: Informal organization is the result of working together and social interactions. It has no predetermined purpose. It achieves social satisfaction. In this type of organization there is no prescribed channel of communication. There are no set or fixed rules in this organization. The examples of this organization are relationship between travellers, players, pilgrims, etc.
Definitions :
(1) According to Keith Davis, “Informal organization is that network of personal and social relationships which is not established or required by formal organizations.”
(2) According to C. I. Barnard, “Organization is informal when aggregate inter-personal relationships are without conscious joint purpose.”
Characteristics of informal organization : The characteristics of informal organization are as follows:
- These type of organizations are formed spontaneously.
- These organizations have common interest.
- It is a voluntary organization.
- These organizations have no concern with manuals and charts.
- In this organization the relationship is based upon personal understanding.
- These organizations can be legal and illegal.
- It does not have a clear and well defined structure.
- It emerges to meet the social and cultural needs of the members of the organization.
- It is a part of formal organization.
- The rules and regulations in this organization is not in writing.
- It may or may not follow official chain of command.
Question 4.
What do you mean by delegation of authority ? What are its elements ?
Ans.
Delegation of authority: Granting authority and responsibility regarding specific job to subordinates is called delegation of authority.
The process or elements of delegation are as follows :
1. Assigning of duty : The first and important element of delegation is assigning of duty or task or responsibility. Before the task is assigned, the superior must:
- Determine the results expected from subordinates
- Identify the tasks to be assigned
- Define the tasks to be assigned. The original officer gives less important or routine duties to subordinates while the original officer should himself perform the important, complicated and secret work.
2. Granting of authority : Without authority nobody is going to perform the duties. Thus for completion of work it is necessary to grant authority along with assigning of duties. In the words of Koontz O’Donnell, “Actually the authority vested in a managerial position is the right to use discretion, the right to create and maintain an environment for the performance of individual working together in a group. Thus all needed authorities should be delegated for the fulfilment of a responsibility.
3. Creation of responsibility : Responsibility means holding an individual answerable for final results. Delegation is an art of getting work done effectively not escaping from responsibility to superiors. According to Allen, “Accountability or responsibility is the obligation to carry out responsibility and exercise authority in terms of performance standard established.”
Acceptability of delegation. A person can accept or reject an assigned task. If the delegated authority rejects the task then the delegated management with assign it to another capable employee therefore acceptability of delegation is important.
4. Evaluation and control of internal activities : It is the last step of the process of organizing every subordinate is responsible for the task assigned by his or her authority. Higher authorities evaluate the deployed tasks to their subordinates assures its process and avail the power of authority.
![]()
Question 5.
What is decentralization ? Explain its advantages.
Answer:
Meaning : Decentralization is the opposite of centralization which means systematic delegation or dispersal of authority at all levels of management and in all departments of the organization. In this process subordinates are given more role and importance in the management and organization. It is the top level management which decides introduction of decentralization in the organization.
Definition : The major definitions of decentralization are as follows :
1. Everything that goes to increase the importance of the subordinates role is decentralization. —Henri Fayol.
Following are the Importance or advantages of decentralization:
1. Quick decision making: Since the workload of managers at top level is reduced so they are free to make decisions which are speedy in nature,
2. Reduces the burden of managers: The most important benefit of decentralization is that it reduces the burden of managers at top level. The work is assigned by the managers to the subordinates which brings relief to the top level management.
3. Motivates subordinates : Managers or the top level management authorises the subordinates to take decisions independently which increases their morale and motivates them towards the betterment of organization.
4. Democratic management: Decentralization facilitates democratic management. It shares authority and responsibility between managers. It also avoids concentration of power.
5. Helps in facing competition : Today’s competition can be faced effectively only when a person is able to take and implement decisions. This can be performed only when the authority and responsibility of decisions is provided by organization. Thus decentralization helps to face competition effectively.
6. Training and Development: Through decentralization training and development is automatically directed or followed. Decentralization helps in providing training to subordinates and makes them specialised in their work.
7. Incentives to workers : Decentralization provides job satisfaction to workers by giving them independence and participation in the activities of organization which increases the morale of employees.
Question 6.
Distinguish between divisional and functional organization.
Answer:
Question 7.
Explain the various advantages and disadvantages of formal organization.
Answer:
Formal organization : It is an official structure of activities, roles and authority relationship which is planned and executed by management for achieving organizational objectives. In this organization every individual belongs to one work group only and works under one superior only. It follows official chain of command.
Characteristics of formal organization : Following are the characteristics of formal organization:
- This type of organization is established for general objectives.
- Organization structure is determined by top level.
- Authority and responsibility are clearly defined in formal organization.
- The relationship is determined according to the jobs and its nature.
- Formal organization aims at achieving predetermined objectives.
- Every individual belongs to one work group only and works under one superior.
- In this type of organization policies, procedures and plans are written.
Merits of formal organization : Following are the merits of formal organization :
- Objectives can be easily achieved through this organization.
- There is unity of order and direction in this organization.
- Stability persists in this organization. .
- There is easy and effective coordination and control over activities.
- Responsibilities are fixed in case of failures.
- There is clear determination of duties, authorities and responsibilities.
- In this type of organization reasonable and balanced division and subdivision of activities.
- Advantages of specialization and division of work can be achieved.
- All activities are performed according to rules and regulations.
- The resources are utilized up to the maximum extent in these organizations.
Demerits of formal organization : Following are the demerits of formal organization:
- There is lack of flexibility in these organizations.
- In these organizations there is always problem of control and coordination.
- Red farism develops in this organization.
- There is lack of initiative informal organization.
- Sometimes power and authority is misused. .
- Formal work and communication is not having importance in this organization.
![]()
Question 8.
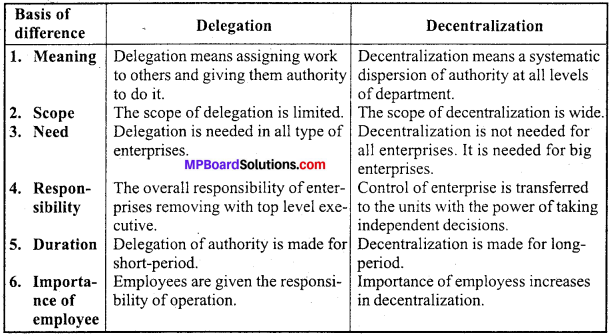
Differentiate between Delegation and Decentralization.
Answer:
Differences between Delegation and Decentralization :

Question 9.
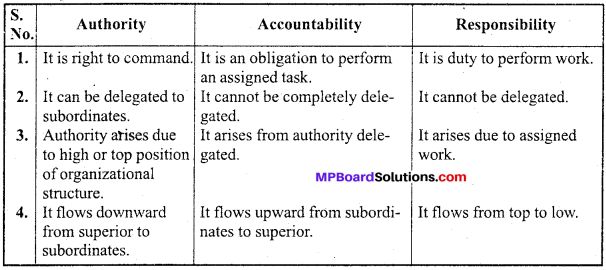
Distinguish between Authority and Accountability.
Answer:
Differences between Authority and Accountability :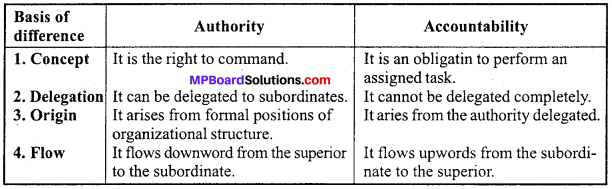
Question 10.
Write the essentials of good organization structure.
Answer:
Essentials of good organization structure :
1. Clear lines of authority : There must be a clear line of authority running from the top to bottom of the organization. It is achieved through delegation by step from the highest executive to the lowest worker having the least responsibility and no authority over others. Failure to clarify the line of authority result in friction, politics and inefficiencies.
2. Adequate delegation of authority : Every person in the organization must get adequate authority to meet his obligations according to situations. Authority is vested in the top most executive and is delegated to his subordinates wherever necessary to meet their obligations. If sufficient authority is not delegated, the top most executive or the person vesting the authority, faces various problems such as bottle-neck in decision-making, delay in decision implementation, pressure on higher level and less motivation to subordinates. These all problems hamper the growth of the organization.
3. Minimum managerial levels : The managerial level in an organization should be kept minimum as far as possible. The greater the number of levels, the larger the chain of command and the longer the time in travelling the message up and down. Though the number of levels is not certain, yet it serves as guide-line.
4. Unity of direction : Every person in the organization should be directed only by one boss as far as possible relating to a single major function. Multiplication of direction may create confusion and may lead to role conflict.
5. Application of Ultimate Responsibility : The authority flows from superior to subordinate along with the responsibilities. The higher level manager is not relieved of his responsibilities for the acts delegated to the subordinates. He is responsible for his own duties and the duties of his subordinates.
6. Span of Control: Span of control refers to the number of subordinates a manager can directly supervise. There is a limit on this number but it cannot be applied universally because several factors such as nature of superior and that of a subordinates, communication techniques, etc. affect the span of control.
7. Simplicity : Taking into account the essential network but leaving no room for confusion and ambiguity the organization structure should be designed as simple as possible. Too many levels or communication channels, or committees, or multiple of command or too much coordination often create more problems rather to solve them.
Question 11.
Describe the objects of organization.
Answer:
1. Economy in production : The main object of organization is to bring economy in production. It means production of goods at minimum cost.
2. Economy in time and labour : In organization, best machines, equipment and best methods are applied and so enough time and labour of the work are saved.
3. Cordial relations between labour and capital : To establish relation between labour and management is one of the object of organization.
Safeguard the interest of the labour and capital.
4. Spirit of service : Due to social consciousness, the object of every businessman is to serve first then profit. So, every organization in present time has the object to serve.
Question 12.
Describe characteristics of project organization.
Answer:
- This system is adopted to perform any specific project
- After completion of the project its existence ends
- Working team is constituted with persons of special ability.
Question 13.
Explain briefly the process of organization.
Or
Method of organization.
Answer:
Following are the steps of organization :
1. Establishment of objectives: The first step of organization structure is establishment of objectives. In the object of organization, those activities should be clearly explained for which organization is built.
2. Determination of activities : The second step in organization is determination of activities and its division. While dividing activities the organizational objectives must be kept in mind.
3. Grouping of activities : The next step involves grouping of activities as purchases, sales, advertisement, marketing, production etc. Different departments are set up for that purpose.
4. Allocation of work : It involves allocation of work on the basis of skills and specialization of employees. The principle of right job for right person is followed while allocating work to employees.
5. Delegation of authority : It is not possible to execute activities without authority. Therefore along with work, the authority is also delegated to the employees.
6. Coordination : For coordination, employees and officers are introduced to each other and everybody’s working place, work, right, duties and relation to each other are specifically mentioned.
Question 14.
Describe the characteristics of organization.
Answer:
1. Organization is a group of people : One person cannot be defined as organization. So, there should be at least two or more persons. There is no restriction on maximum number.
2. Specific objective : Any good organization has specific objectives. A gathering of people without a purpose is not an organization.
3. Division of work : For efficiently achieving goals, the work at hand should be divided and delegated. For example, the activities of an organization may be divided under purchase, sales, finance, personnel, production, etc,
4. Universal existence : Organization exists universally, irrespective of size of the company. All spheres or fields of society like politics, business, schools, families, etc. have organization though the objective may be different.
5. Leadership and formal relations : Organization is also characterized by the presence of leadership and formal relations among the members of the group.
6. Effective communication and coordination : An efficient organization necessitates effective communication as a requisite element. Proper communication and coordination between various levels of the organization results in easy execution of work.
Question 15.
“Write the characteristics, advantage and disadvantage of informal organization.
Answer:
Characteristics of informal organization : The characteristics of informal organization are as follows:
- These type of organizations are formed spontaneously
- These organizations have common interest
- It is a voluntary organization
- These organizations have no concern with manuals and charts
- In this organization the relationship is based upon personal understanding
- These organizations can be legal and illegal
- It does not have a clear and well defined structure
- It emerges to meet the social and cultural needs of the members of the organization
- It is a part of formal organization
- The rules and regulations in this organization is not in writing
- It may or may not follow official chain of command.
![]()
Advantages of informal organization : Following are the advantages of informal organization:
- It removes the weakness of formal organization
- It is an effective means of communication
- Through this organization the spirit of cooperation and coordination develops
- It provides social status and sense of satisfaction
- Employees are motivated towards work.
Disadvantages of informal organization : Following are the disadvantages of informal organization:
- Illegal activities are encouraged in these organizations
- These organizations create confusions by spreading rumours
- High level management is generally opposed by this organization
- Some of these organizations are against democracy and secularism
- These organizations are generally have short life.
Conclusion : Generally all organizations have some merits and demerits. Informal organization is complementary to formal organization
Question 16.
Write the principles of organization.
Answer:
Golonel Lyndall Urwick has given following principles :
1. Principle of objectives: The objective of an enterprise should be the objective of whole organization, because every organizational aims at achieving aims of an enterprise. Objectives should be made clear at every level.
2. Principle of specialization : Every person has got particular quality of doing particular work. One person should be allotted one work only this will increases his ability of doing that particular work.
3. Principle of coordination : The main aim of organization should be to maintain coordination among various elements, through which objectives can be achieved.
4. Principle of authority : Authority should not be vested in one hand, but it should be distributed accordingly. So that workers take interest in the work and a feeling of responsibility also arises.
5. Principle of continuity : According to time and requirement, changes should be done. In other words, an organization should be flexible, otherwise it would not be successful. One should recognize the speed of time.
6. Principle of responsibility: After assigning authority, care of responsibility should also be taken. This increases the desire of working more and quality of work. Every worker should be well aware that he is responsible to whom.
7. Principle of definition : Every employee should be made well aware of his duties and responsibilities. Every duty, position etc. in every organization should be clearly prescribed in writing, which helps in quick achievements of goals.
8. Principle of uniformity: There should be uniformity in authority and responsibility given to various officers. But there should be no dispute between authority of two officers which will result in indiscipline and lead to delay of work.
9. Principle of span of control: Area of control of each manager should be restricted, this results in better performance and it becomes easy to carry and complete work. ‘Urwick’ has said that “Maximum a person can handle five to six persons”. According to the nature of business, control should be restricted.
10. Principle of balance : Balance should be made between different units of an organization. Balance increase discipline in the management of a business and helps in the success of the organization.
11. Principle of unity of command : A worker takes orders from his superior boss only and not from others, he is answerable to his boss only. If he has two boss, then confusion will be created and if he listens to one boss and not other, this will create conflict. Therefore, unity of command is necessary for success.
12. Principle of simplification : Organizers should make such policies which are simple, easy, understood by everyone and impressive. If the elements of an organization or policies are not simple, it will create problem.
13. Other principles: Some modem principles showed by experts are :
- Principle of efficiency
- Principle of unity of objectives
- Principle of participation
- Principle of formality
- Principle of inspection and balance
- Principle of surety
- Principle of transferring ownership.
![]()
Question 17.
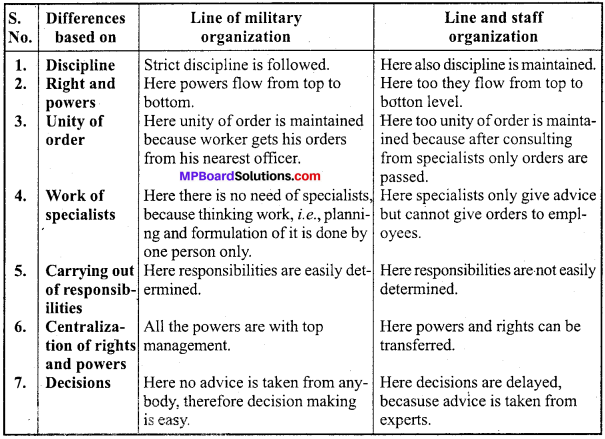
Distinguish between line of organization and staff organization.
Answer:
differences between Line and Staff organization :
Question 18.
Distinguish among authority, responsibility and accountability.
Answer:
Differences among Authority, Responsibility and Accountability.