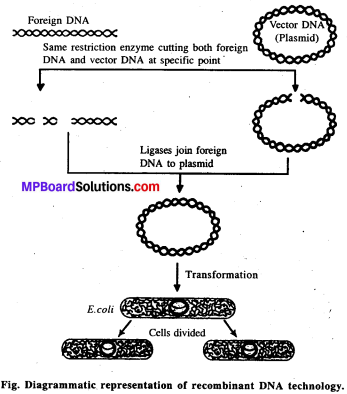
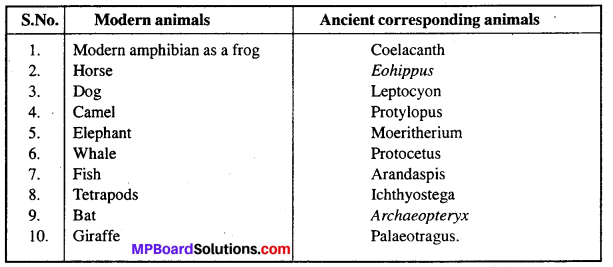
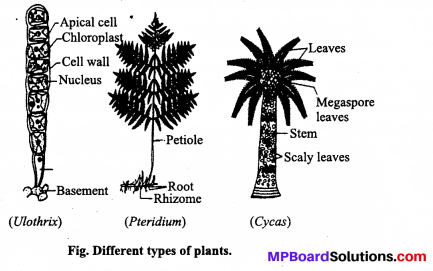
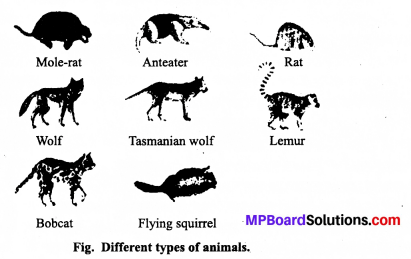
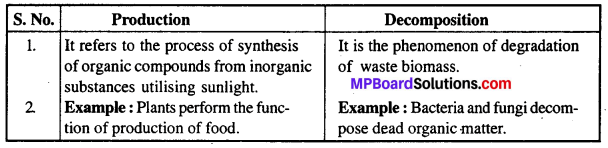
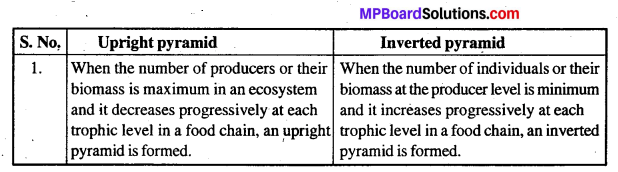
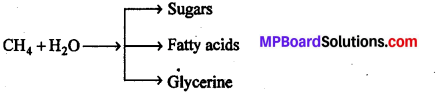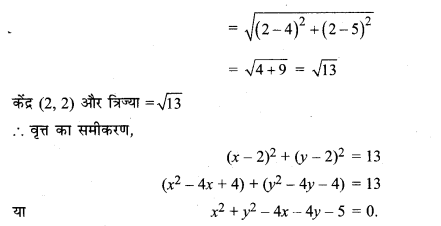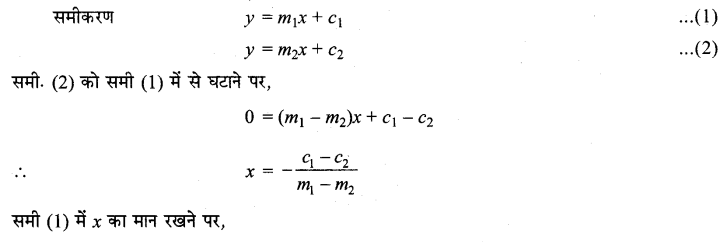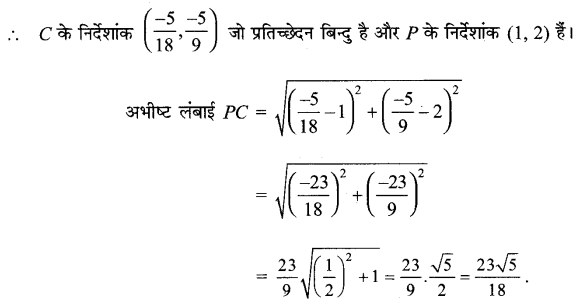MP Board Class 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 11 शंकु परिच्छेद Ex 11.3
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों 1 से 9 तक प्रत्येक दीर्घवृत्त में नाभियों और शीर्षों के निर्देशांक, दीर्घ और लघु अक्ष की लंबाइयाँ, उत्केंद्रता तथा नाभिलंब जीवा की लम्बाई ज्ञात कीजिए।
प्रश्न 1.
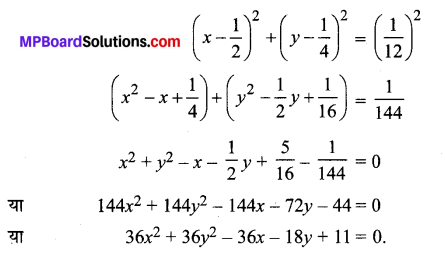
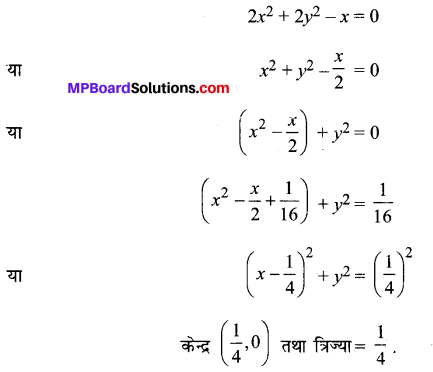
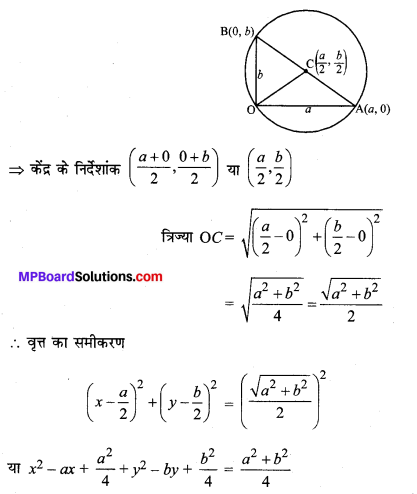
\(\frac{x^{2}}{36}+\frac{y^{2}}{16}\) = 1
हल:

प्रश्न 2.
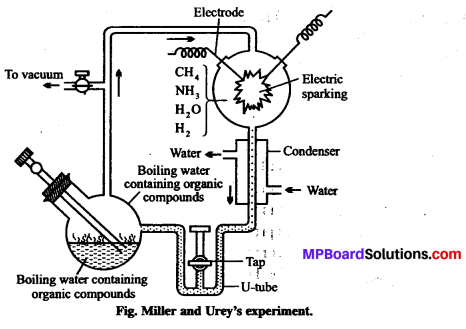
\(\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{25}\) = 1
हल:

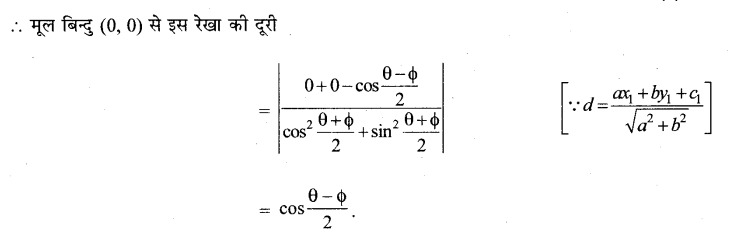
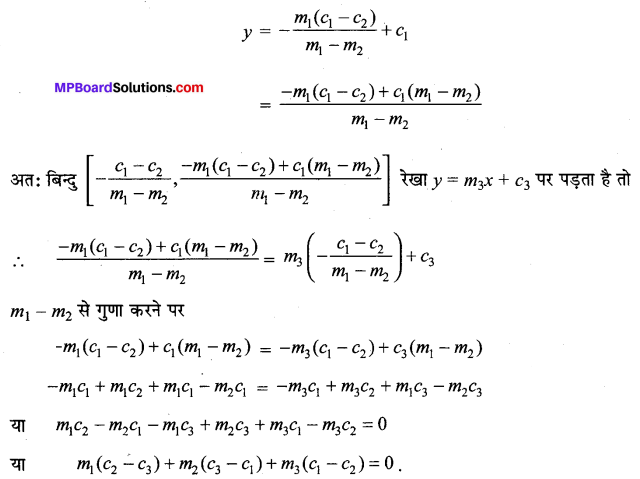
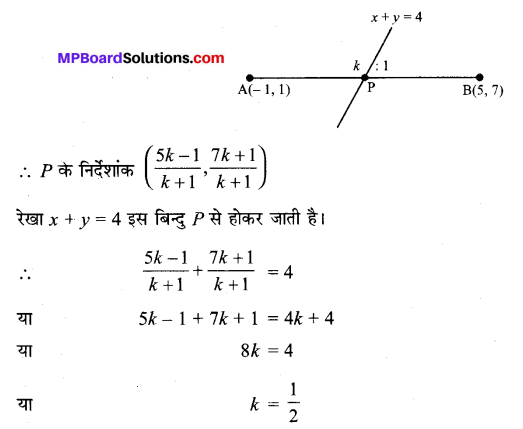
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 2a = 2 × 5 = 10
लघु अक्ष की लंबाई = 2b = 2 × 2 = 4
उत्केंद्रता = e = \(\frac{c}{a}=\frac{\sqrt{21}}{5}\)
नाभिलंब जीवा की लंबाई = \(\frac{2 b^{2}}{a}=\frac{2 \times 4}{5}=\frac{8}{5}\).
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
\(\frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}\) = 1
हल:
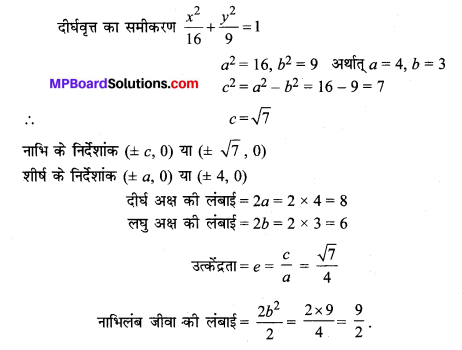
प्रश्न 4.
\(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{100}\) = 1
हल:
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण \(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{100}\) = 1
∴ a2 = 100, b2 = 25
∴ a = 10, b = 5
∴ c2 = a2 – b2 = 100 – 25 = 75
∴ c = 5\(\sqrt{3}\)
नाभि के निर्देशांक (0, ± c) या (0, ± 5\(\sqrt{3}\))
शीर्षों के निर्देशांक (0, ± a) या (0, ± 10)
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 2a = 2 × 10 = 20
लघु अक्ष की लंबाई = 2b = 2 × 5 = 10
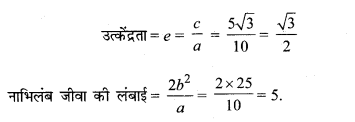
प्रश्न 5.
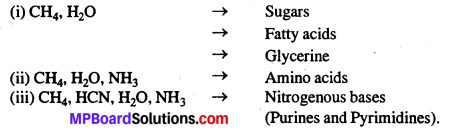
\(\frac{x^{2}}{49}+\frac{y^{2}}{36}\) = 1
हल:
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण \(\frac{x^{2}}{49}+\frac{y^{2}}{36}\) = 1
∴ a2 = 49, b2 = 36
∴ a = 7, b = 6
दीर्घ अक्ष, x-अक्ष के अनुदिश है
c2 = a2 – b2 = 49 – 36 = 13
c = \(\sqrt{13}\)
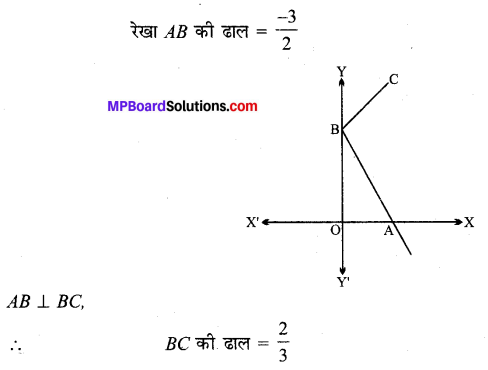
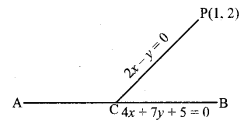
नाभियों के निर्देशांक (± c, 0) या (± \(\sqrt{13}\), 0)
शीर्षों के निर्देशांक (± a, 0) या (± 7, 0)
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 2a = 2 × 7 = 14
लघु अक्ष की लंबाई = 2b = 2 × 6 = 12
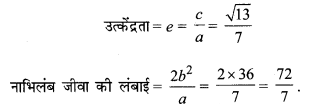
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
\(\frac{x^{2}}{100}+\frac{y^{2}}{400}\) = 1
हल:
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण \(\frac{x^{2}}{100}+\frac{y^{2}}{400}\) = 1
∴ a2 = 400, b2 = 100
∴ a = 20, b = 10
c2 = a2 – b2 = 400 – 100 = 300
∴ c = 10\(\sqrt{3}\)
दीर्घ अक्ष, y- अक्ष के अनुदिश है
नाभियों के निर्देशांक (0, ± c) या (0, ± 10\(\sqrt{3}\))
शीर्षों के निर्देशांक (0, ± a) या (0, ± 20)
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 2a = 2 × 20 = 40
लघु अक्ष की लंबाई = 2b = 2 × 10 = 20
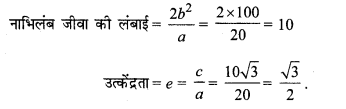
प्रश्न 7.
36x2 + 4y2 = 144.
हल:
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण 36x2 + 4y2 = 144
या \(\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{36}\) = 1
∴ a2 = 36, b2 = 4
∴ a = 6, b = 2
∴ c2 = a2 – b2 = 36 – 4 = 32
∴ c = 4\(\sqrt{2}\)
दीर्घवृत्त का अक्ष, y-अक्ष के अनुदिश है
नाभियों के निर्देशांक (0, ± c) या (0, ± 4\(\sqrt{2}\))
शीर्षों के निर्देशांक (0, ± a) या (0, ± 6)
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 2a = 2 × 6 = 12
लघु अक्ष की लंबाई = 2b = 2 × 2 = 4

प्रश्न 8.
16x2 + y2 = 16.
हल:
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण 16x2 + y2 = 16
या \(\frac{x^{2}}{1}+\frac{y^{2}}{16}\) = 1
∴ दीर्घवृत्त का अक्ष, y-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
a2 = 16, b2 = 1
∴ a = 4, b = 1
c2 = a – b2 = 16 – 1 = 15
∴ c = \(\sqrt{15}\)
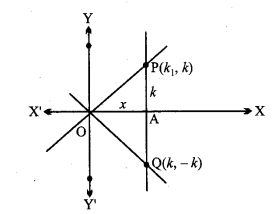
नाभियों के निर्देशांक (0, ± c) या (0, ± \(\sqrt{15}\))
शीर्षों के निर्देशांक (0, ± a) या (0, ± 4)
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 2a = 2 × 4 = 8
लघु अक्ष की लंबाई = 2b = 2 × 1 = 2

![]()
प्रश्न 9.
4x2 + 9y2 = 36.
हल:
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण 4x2 + 9y2 = 36
या \(\frac{x^{2}}{9}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}\) = 1
दीर्घ अक्ष, x-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
∴ a2 = 9, b2 = 4
∴ a= 3, b = 2
c2 = a2 – b2 = 9 – 4 = 5
∴ c = \(\sqrt{5}\)
नाभियों के निर्देशांक (± c, 0) या (± \(\sqrt{5}\), 0)
शीर्षों के निर्देशांक (± a, 0) या (± 3,0)
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 2a = 2 × 3 = 6
लघु अक्ष की लंबाई = 2b = 2 × 2 = 4
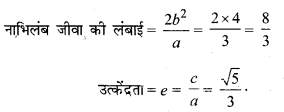
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों 10 से 20 तक प्रत्येक में, दिए प्रतिबंधों को संतुष्ट करते हुए दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण ज्ञात कीजिए।
प्रश्न 10.
शीर्षों (± 5, 0), नाभियाँ (± 4, 0).
हल:
a = 5, c = 4, c2 = a2 – b2
या 16 = 25 – b2
∴ b2 = 25 – 16 = 9
और a2 = 25
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण,
\(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}\) = 1
प्रश्न 11.
शीर्षों (0, ± 13), नाभियाँ (0, ± 5).
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष, y-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
∴ c = 5, a = 13, c2 = a2 – b2
∴ 25 = 169 – b2
∴ b2 = 169 – 25 = 144,
और a2 = 132 = 169
∴ दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण
\(\frac{x^{2}}{144}+\frac{y^{2}}{169}\) = 1
प्रश्न 12.
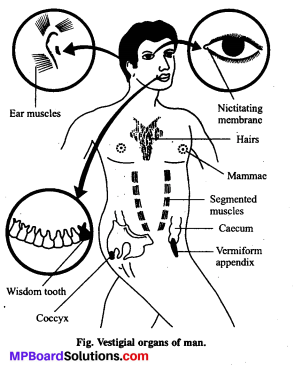
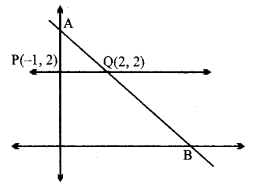
शीर्ष (± 6, 0), नाभियाँ (± 4, 0).
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष x-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
a= 6, ∴ a2 = 36, c = 4
c2 = a2 – b2 या 16 = 36 – b2
∴ b2 = 36 – 16 = 20
∴ दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण
\(\frac{x^{2}}{36}+\frac{y^{2}}{20}\) = 1.
![]()
प्रश्न 13.
दीर्घ अक्ष के अंत्य बिन्दु (± 3, 0), लघु अक्ष के अंत्य बिन्दु (0, ± 2).
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष x-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
a = 3, b = 2, ∴ a2 = 9, b2 = 4
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण,
\(\frac{x^{2}}{9}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}\) = 1
प्रश्न 14.
दीर्घ अक्ष के अंत्य बिन्दु (0, ± \(\sqrt{5}\)), लघु अक्ष के अंत्य बिन्दु (± 1, 0).
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष, y-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
a = \(\sqrt{5}\), b = 1, ∴ a2 = 5, b2 = 1
दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण,
\(\frac{x^{2}}{1}+\frac{y^{2}}{5}\) = 1
प्रश्न 15.
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 26, नाभियाँ (45, 0).
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष, x-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
और 2b = 26, ∴ b = 13 या a2 = 169,
c = 5, c2 = 25 = a2 – b2 = 169 – b2
∴ b2 = 169 – 25 = 144
अतः a2 = 169, b2 = 144
∴ दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण,
\(\frac{x^{2}}{169}+\frac{y^{2}}{144}\) = 1.
प्रश्न 16.
दीर्घ अक्ष की लंबाई = 16, नाभियाँ (0, ± 6).
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष, y-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
2b = 16, ∴ b = 8 या b2 = 64,
c = 6, c2 = 36,
c2 = a2 – b2
या 36 = a2 – 64
∴ a2 = 64 + 36 = 100
∴ दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण
\(\frac{x^{2}}{64}+\frac{y^{2}}{100}\) = 1
प्रश्न 17.
नाभियाँ (± 3, 0), a = 4.
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष, x-अक्ष के अनुदिश है।
∴ c = 3, a = 4
अब c2 = a2 – b2
या 9 = 16 – b2
∴ b2 = 16 – 9 = 7
∴ दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण,
\(\frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{7}\) = 1
![]()
प्रश्न 18.
b = 3, c = 4, केन्द्र मूल बिन्दु पर, नाभियाँ x-अक्ष पर है।
हल:
दीर्घ अक्ष, x-अक्ष के अनुदिश है
c2 = a2 – b2
16 = a2 – 9
a2 = 16 +9 = 25
∴ दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण,
\(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}\) = 1
प्रश्न 19.
केंद्र (0, 0) पर, दीर्घ अक्ष y-अक्ष पर और बिन्दुओं (3, 2) और (1, 6) से जाता है।
हल:

प्रश्न 20.
दीर्घ अक्ष,x-अक्ष पर और बिन्दुओं (4, 3), (6, 2) से जाता है।
हल:
मान लीजिए दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1

∴ दीर्घवृत्त का समीकरण,
\(\frac{x^{2}}{52}+\frac{y^{2}}{13}\) = 1