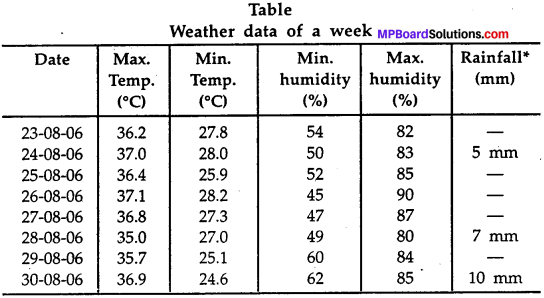
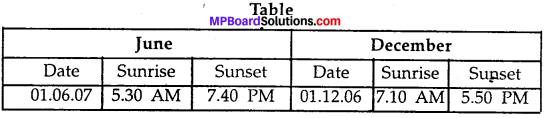
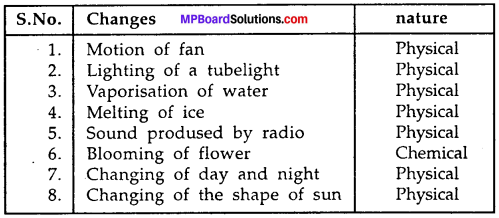
Get Updated MP Board Solutions for Class 7 Special English Revision Exercises 2 Questions and Answers in PDF Format and download them free of cost. These are provided as per the latest exam pattern and syllabus. Access the topics of Chapter wise and communication skills, grammer part through the direct links available depending on the need. You can Download MP Board Class 7 English Solutions and can score highest grade in examination. Clear all your queries on the Mp Board Solutions for Class 7 English Chapter 21 Tansen Questions and Answers Subject by using the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for existing.
MP Board Class 7th Special English Solutions Revision Exercises 2
If you are eager to know about the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for Class 7 English you will find all of them here. You can identify the knowledge gap using these MP Board Solutions for English PDF and plan accordingly. Don’t worry about the accuracy as they are given after extensive research by people having subject knowledge along side from the latest English Syllabus.
Comprehension
Question 1.
Where does the poet breathe a song?
Answer:
The poet breathe’s a song into the air.
Question 2.
Why is Shravan Kumar famous?
Answer:
Shravan kumar is famous for his devotion and obedience to his blind parents.
Question 3.
What is a talking machine? What is a ‘talkie’?
Answer:
A talking machine is one that can talk. The modem gramophone is simply an improvement on this talking machine. A ‘talkie’ is a talking picture. This is the modern cinema.
Question 4.
Why did the Americans turn off their electric lights for a while when Edison died?
Answer:
Edison had invented the electric light. Therefore, when Edison died, the Americans turned off their electric lights for a while as a mark of respect to the wonderful inventor.
Question 5.
What kind of life did Sri Ramakrishna live as a temple priest?
Answer:
As a temple priest Sri Ramakrishna spent all his time in the service of ‘Kali’ the Divine Mother whom he worshipped out of religious duty. He lived a happy and a deeply religious life. He spent days and nights in prayer. He led a very hard life. He often went without food and water and ruined his health.
Question 6.
Why is quarrelling in the name of religion foolish?
Answer:
All the religions lead to the same goal. They also teach the same truth. In fact, people worship the same God under different names. Therefore, quarrelling in the name of religion is foolish.
Question 7.
What do you understand by the lines “till …….began No, time to wait?
Answer:
The smile appears in the eyes before it reaches the mouth. It takes a few moments. But the poet has no time even to view that smile.
Question 8.
What words and phrases did Anand fail to understand?
Answer:
The words and phrases which Anand failed to understand are = Cross, boiling of blood, get, novel.
Question 9.
Whom do the villagers give credit for their prosperity?
Answer:
The villagers give credit to God (who sends rain)
Question 10.
What is the best of all for the country people?
Answer:
The country faith is the best of all for the country-people.
Word Power
A. Choose the correct words to complete the sentences.
- She is very ………. to me. (deer/dear)
- He has a very bad eye ………… (sight/site)
- The ………… was bright that day. (Son/sun)
- He went inside the temple to ………… to god. (prey/pray)
- He saved the ………. from the hunter. (dear/deer).
Answer:
- dear
- sight
- sun
- pray
- deer.
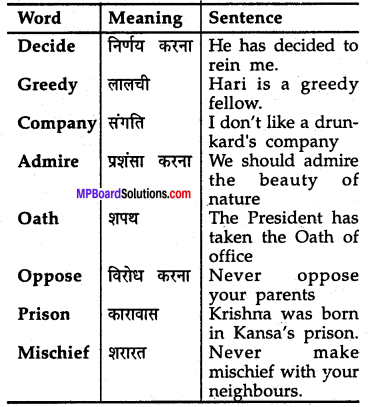
B. Match the words in column (A) with the meaning given in column (B)

Answer:
1. → (b)
2. → (d)
3. → (a)
4. → (e)
5. → (c)
Grammar in Use
A. Rearrange the words in the following sentences and rewrite them to make meaningful sentences:
- the/bet/is/What/?/
- surprised/very/am/I/./
- committed/a/blunder/he/./
- archer/great/a/was/Dashrath/./
- jobs/lost/Edison/many/./
Answer:
- What is the bet?
- I am very surprised.
- He committed a blunder.
- Dashrath was a great archer.
- Edison lost many jobs.
B. Use the prefix ‘dis’ in the words given below and fill in the blank space, trust obey honest similar like
- We should never ………. our elders.
- People of ……….. nature never come together.
- I ………. eating kachori.
- Mr. Natawarlal is a ………… man.
- Don’t ………… a priest.
Answer:
- disobey
- dissimilar
- dislike
- dishonest
- distrust
Let’s Write
1. Write five sentences about the wood.
2. Write ten sentences on Shravan Kumar. Take the help of the clues, obedient, devoted, dutiful, pilgrimage, forest, put aside, thirsty, old and blind, river.
3. Write a paragraph on gramophone.
4. You are a cricket player of your school team. Give a set of three or four rules of the game using ought to and ought not to.
5. Write a message to your friend stating that as you didn’t attend the school that day and you want him to send the homework for English given by the teacher.
Answer:
1. The wood :
The wood is a place of beasts. We find many trees in the wood. The trees provide us fuel, food and fruit. Rishis live in the wood. They practise penance there.
2. Shravan Kumar was a devoted and obedient son. He used to carry his old and blind parents for pilgrimage. One day he was passing through the forest around Ayodhya. His parents asked him to bring water. Shravan took a pot. He went to Saryu river to bring water. His pot produced a gurgling sound. King Dashrath drought him to be a big animal. He shot an arrow. It pierced shravan’s chest. Shravan asked Dashrath to give water to his parents just then he died.
3. Edison invented the first talking machine. It looked very funny. However, it could talk. It was a new machine. The modern gramophone or record player is an improvement on the talking machine. The present day telephones and wireless sets are also talking machines. We can play the records on the gramophone of our choice and hear songs. The modem cinema is called a talkie due to the same.
4.Three or four rules of the game-
- The bowler ought not to cross the crease- line while bowling.
- The bowler ought not to throw the ball above chest height of the batsman.
- We ought to obey the orders of the umpire.
- We ought to play a fair game.
5. Class Room Activity in School
We believe the information shared regarding MP Board Solutions for Class 7 English Chapter 21 Tansen Questions and Answers as far as our knowledge is concerned is true and reliable. In case of any queries or suggestions do leave us your feedback and our team will guide you at soonest possibility. Bookmark our site to avail latest updates on several state board Solutions at your fingertips.