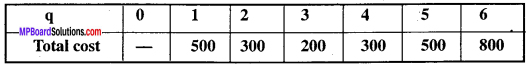
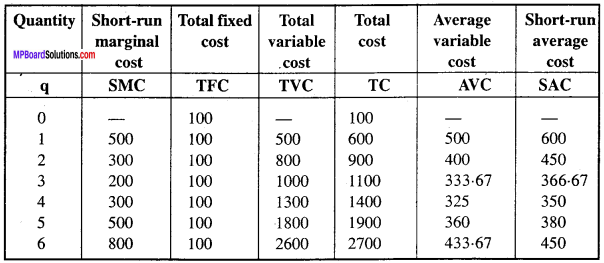
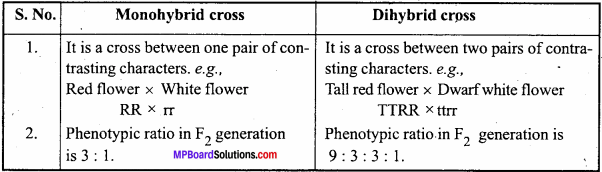
MP Board Class 12th Hindi Swati Solutions गद्य Chapter 7 मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? (निबंध, रामनारायण उपाध्याय)
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? अभ्यास
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
रामनारायण उपाध्याय की अधिकांश रचनाओं के निर्माण का आधार क्या है?
उत्तर:
रामनारायण उपाध्याय ने आम जनता के स्नेह दर्द एवं भाषा को लेकर ही अधिकांश रचनाओं का निर्माण किया है।
प्रश्न 2.
गाँव के एकान्त जीवन में लेखक का सबसे बड़ा साथी कौन है?
उत्तर:
गाँव के एकान्त जीवन में लेखक का सबसे बड़ा साथी डाक है।
प्रश्न 3.
लेखक के गाँव से स्टेशन कितनी दूर था?
उत्तर:
लेखक के गांव से स्टेशन आठ मील दूर था।
प्रश्न 4.
सम्मान के विषय में लेखक की क्या मान्यता है?
उत्तर:
लेखक सम्मान का भूखा नहीं है परन्तु सम्मान के विषय में उसकी मान्यता है कि मनुष्य सम्मान अपने लिए या अपनी रचनाओं के लिए पा सकता है। अतः लेखक ने अपनी रचनाओं के लिए सम्मान चाहा है।
प्रश्न 5.
“लिखने के लिए मैंने कभी नहीं लिखा” इसका तात्पर्य एक वाक्य में लिखिए।
उत्तर:
दूसरों के आदेश पर लेखक ने न लिखकर अपनी इच्छा अर्थात् मन के चाहने पर लिखा है।
![]()
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
“मुझसे बड़ा तो मेरा नाम है।” लेखक ने ऐसा क्यों कहा है?
उत्तर:
लेखक जब किसी पत्र-पत्रिका में अपना नाम पढ़ता है, तो सोचता है कि “मुझसे बड़ा तो मेरा नाम है। जहाँ में नहीं जा सका, वहाँ वह पहुँचा है और जिनसे मैं नहीं मिल सका, उनसे वह मिला है। अनेक बड़े आदमियों से उसने मेरा परिचय कराया है।” अगर लेखक अपना नाम न बताये तो सम्पादक उसे कार्यालय में न घुसने दे और ट्रेन में अन्तरंग मित्र उसका बिस्तरबन्द हटाकर स्वयं लेट जाये। नाम की चिट ही कार्यालयों में जाने की आज्ञा देती है। सदा नाम बीच में आकर रक्षा करता है। इसी कारण लेखक ने नाम को बड़ा कहा है।
प्रश्न 2.
कभी-कभी प्रिय शब्दों का मोह त्यागकर लेखक उन्हें क्यों निकाल देता है?
उत्तर:
कभी-कभी प्रिय शब्दों का मोह त्यागकर लेखक को उन्हें इसलिए निकाल देना पड़ता है कि वे भाषा के प्रवाह में बाधक जान पड़ते हैं। उनके निकलते ही ऐसा लगता है कि प्रवाह अब सहज हो गया है और बात अब ठीक ढंग से कहीं गई है।
प्रश्न 3.
पुस्तक की पहली प्रति बिकने पर लेखक को क्या अनुभव हुआ?
उत्तर:
जिस दिन लेखक की पुस्तक की पहली प्रति बिकती है, तो लेखक को बड़ा सुख मिलता है। लेकिन पुस्तक का पूरा-पूरा मूल्य लेकर भी जब उसे किसी के हाथों सौंपता हूँ तो जाने क्यों लेखक के हाथ काँपने लगते हैं। मन अनायास ही गुनगुनाने लगता है-“अभी तक यह मेरी थी, अब तुम्हारी हुई। इसे सुख दोगे सुखी होगी, दुःख दोगे दुःखी होगी।”
प्रश्न 4.
बस में मिला गाँव का किसान लेखक को देखकर बार-बार क्यों हँसने लगा था?
उत्तर:
एक दिन लेखक बस में यात्रा कर रहा था तो बस में बैठा किसान लेखक को देखकर बार-बार हँसने लगा तो लेखक ने किसान से पूछा, “भाई तुम हँसते क्यों हो?” किसाने ने कहा, “एक दिन मेरी बच्ची स्कूल से एक किताब लाई थी। उसे पढ़कर मेरी स्त्री और बच्ची दोनों खुश हुए। आज आप दीखे तो मुझे उस पुस्तक की याद हो आई और मैं अपनी हँसी रोक नहीं पाया। सोचता हूँ, आप इतनी अच्छी किताब लिख कैसे लेते हैं कि जिसे पढ़कर मेरी स्त्री और लड़की दोनों खुश हों।”
प्रश्न 5.
लेखक के उदास होने पर पुस्तकें क्या कहती हैं?
उत्तर:
जब कभी लेखक का मन उदास होता है, कोई छोटी-सी बात मन को बेचैन कर जाती है, किसी घटना विशेष को लेकर तिलमिला उठता है, कोई समस्या सोने नहीं देती या चिन्ताओं से घिर जाता है तो ये पुस्तकें बुजुर्गों की तरह लेखक की पीठ को सहलाते हुए उसे ढाँढस बँधाती हैं तथा नजदीक आकर कान में पूछती है-“कहिए, किस बात की परेशानी है?” यह पुसतकें एक सच्चे दोस्त की तरह संग-साथ निभाती हैं।
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
पं. रामनारायण उपाध्याय किन-किन परिस्थितियों में लेखन करते हैं?
उत्तर:
“आप क्यों लिखते हैं” इस प्रश्न के उत्तर में उपाध्याय जी लेखन की परिस्थितियों का वर्णन करते हुए कहते हैं, “लगता है जैसे मैं नहीं लिखता वरन् कोई आता है और मुझसे अपनी बात लिखा ले जाता है।” बहुत बार चाहकर भी लेखक नहीं लिख पाता और कभी-कभी ऐसा जोश आता है कि रात में सोते से जागकर मन की बात लिख डालता है। विचार आते ही खाना, पीना,सोना,बैठना छोड़कर विचार का छोर पकड़कर रचना तैयार कर ली जाती है। इसके विपरीत कभी-कभी लेखक रचना को पूरी तरह मन में तैयार कर लेता है और मन की तस्वीर कागज पर उतरती चली जाती है।
उपाध्याय जी को लिखने के लिए किसी खास समय या बाह्य साधन की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है। जब भी मौज आती है, बिना किसी टेबल-कुर्सी या चाय की प्याली के खाली जमीन पर बैठकर पैर की सीट पर दफ्ती जमा लिखने में आनन्द आता है। हाँ, लिखते समय एकान्त की जरूरत होती है। लिखने के लिए लेखक को किसी के आदेश की आवश्यकता नहीं होती, वह खेत की मेड़ पर बैठकर खेतों को निहारते हुए लिख लेता है। स्टेशन से घर लौटते हुए आठ मील की दूरी तय करते हुए ही विचारों में लिख लेता है। नींद न आने पर रात्रि की शान्ति और आकाश के तारे लिखने में सहायता करते हैं। कोई अच्छी बात दूसरों तक पहुँचाने के लिए लेखक लिख लेते हैं। मनुष्यता पर प्रहार होने पर लिखना पं. जी का स्वभाव है। उपाध्याय जी स्वयं कहते हैं कि लेखन उनके जीवन का अविभाज्य अंग है, तो वह लोगों को आत्मसात करने के लिए भी लिखते हैं। साथ ही लेखक को आत्मदान का-सा सुख मिलता है। अन्त में, लेखक कहता है कि वह इसलिए लिखता है क्योंकि वह लिखे बिना नहीं रह सकता।
प्रश्न 2.
जब घर पर नई पुस्तक छपकर आती थी तो किस तरह का वातावरण निर्मित हो जाता था?
उत्तर:
जिस दिन घर पर नई पुस्तक छपकर आती थी उस दिन समूचे घर में उसी की धूम रहती थी। कोई आता है तो चेहरे की तरफ उसके मुख पृष्ठ को निहारता है,कोई उसके पृष्ठों को उलटने लगता है,कोई उसे बीच में ही पढ़ना शुरू कर देता है,कोई बड़ी शान से उसे अपनी बगल में दबाकर उधार माँगकर पढ़ने के लिए घर ले जाता है। नई पुस्तक स्वयं भी बच्चों की तरह उछल-कूद करने लगती है। कभी वह ताक या टेबल पर चढ़कर वहाँ से ताक-झाँक करती है। कभी रैक या अलमारी से मुँह निकालकर मुँह चिढ़ाती है, तो कभी बिस्तर की चादर में छिपकर चुनौती देती है कि अब ढूँढो तो जानूँ। कहने का अर्थ है कि उसे खुशी के कारण कहीं रखा जाता है और कभी कहीं। बच्चे शौक में उसे छिपा देते हैं। जिससे कोई उसे उधार माँगकर न ले जाए। इस प्रकार सम्पूर्ण घर का वातावरण एक अनोखी खुशी से भर जाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
लेखक अपनी पुस्तक की पर्याप्त रॉयल्टी किसे मानकर सन्तुष्ट होता है?
उत्तर:
एक दिन लेखक के एक मित्र ने पूछा कि आपको अपनी पुस्तक पर कितनी रॉयल्टी मिली? इस प्रश्न के उत्तर में लेखक को कोई ऐसा अंक नहीं मिला जिसे वह रॉयल्टी के बदले बता सके। किन्तु लोगों का प्यार,सम्मान,दूसरों की खुशी, ईमानदारी आदि उस नकद रॉयल्टी से कहीं अधिक है, जिसे लेखक स्वयं वर्णित करता है। पत्र के माध्यम से जीवन में लेखक को अपने भाई का स्थान देने वाली बहन, अस्पताल में मृत्यु शैया पर पड़ा नौजवान, जो लेखक की पुस्तक पढ़ने को बेचैन हैं,बस में मिलने वाला किसान,जो लेखक को देखकर इसलिए हँसता है कि लेखक ऐसी पुस्तकें कैसे लिख लेते हैं,जो उसकी पत्नी व पुत्री को खुशी देती हैं। रोटी में से पैसे बचाकर दफ्तर का बाबू पुरानी किताबें खरीद कर पढ़ता है,लड़का साइकिल का किराया नहीं लेता क्योंकि उपाध्याय जी उसके प्रिय लेखक हैं। इतने सारे पाठकों का असीम स्नेह, उनकी खुशी व कृतज्ञता लेखक की पुस्तकों की पर्याप्त रॉयल्टी है,जिसे पाकर लेखक अपार सन्तोष का अनुभव करता है।
प्रश्न 4.
“साहित्य में मैं स्नेह को बहुत मूल्य देता हूँ।” रामनारायण जी के इस कथन का आशय स्पष्ट कीजिए।
अथवा
रामनारायण उपाध्याय जी साहित्य में स्नेह को बहुत मूल्य क्यों देते हैं? (2009, 12)
उत्तर:
उपाध्याय जी के इस कथन का आशय है कि सबका स्नेह पाना बड़ा कठिन होता है। धन तो साधारण व्यक्ति भी थोड़े से परिश्रम से कमा लेता है और धन के बल पर समाज में सम्मान भी पा लेता है। इसके विपरीत स्नेह अमूल्य वस्तु है जो सबको नहीं मिलती। एक सच्चा साहित्यकार ही स्नेह, प्यार, ममता आदि पा सकता है। इस कारण रामनारायण जी लेखकों की मित्रता को पसन्द करते हैं। उन्हें धनवानों की संगति पसन्द नहीं। साधारण से साधारण साहित्यकार भी लेखक को आत्मीयता प्रदान करता है। उसका कारण है स्नेह। इसी कारण लेखक ने साहित्य में स्नेह को बहुत मूल्य दिया है।
प्रश्न 5.
“लिखना मेरे जीवन का अविभाज्य अंग है और अपने आपको अधिक से अधिक आदमियों के साथ आत्मसात करने के लिए ही लिखता है। लिखने में मुझे आत्मदान करने की तरह सुख मिलता है।” उक्त गद्यांश को पढ़कर पूछे गये प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए-
- पाठ और लेखक का नाम लिखिए।
- यह कथन किसके द्वारा कहा गया है?
- “आत्मदान” से यहाँ क्या तात्पर्य है?
उत्तर:
- पाठ का नाम-मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? लेखक का नाम-पं. रामनारायण उपाध्याय।
- यह कथन लेखक (पं. रामनारायण उपाध्याय) के द्वारा कहा गया है।
- आत्मदान का शाब्दिक अर्थ है-आत्मार्पण। दूसरों के सुख के लिए अपने सुखों का त्याग करना ही आत्मदान है जिसको करने पर अपनी ही आत्मा को अपार सुख मिलता है।
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? भाषा अध्ययन
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित प्रत्ययों से दो-दो शब्द बनाइए
ता, कार, वाला, पन, इक।
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए
घर, गंगा, कपड़ा, हाथ, मुंह।
उत्तर:
- घर – गृह, आलप।
- गंगा – जाह्नवी, सुरसरि।
- कपड़ा – वस्त्र, वसन।
- हाथ – हस्त, कर।
- मुँह – मुख, आनन।
प्रश्न 3.
दिये गये मुहावरों का वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए
मुंह चिढ़ाना, त्यौरियाँ चढ़ जाना, कसौटी पर कसना, हाथ काँपना, चैन न पड़ना।
उत्तर:
(i) शब्द – मुंह चिढ़ाना।
वाक्य प्रयोग :
चिड़ियाघर में बन्दर बच्चों को देखकर मुंह चिढ़ा रहे थे।
(ii) शब्द – त्यौरियाँ चढ़ जाना।
वाक्य प्रयोग :
कक्षा में अत्यधिक शोर सुनकर कक्षाध्यापक की त्यौरियाँ चढ़ गईं।
(iii) शब्द – कसौटी पर कसना।
वाक्य प्रयोग :
मित्रता करने से पूर्व व्यक्ति को कसौटी पर कसकर देख लेना श्रेयस्कर होता है।
(iv) शब्द – हाथ काँपना।
वाक्य प्रयोग :
तलाक प्रपत्र पर हस्ताक्षर करते समय पति-पत्नी के हाथ काँप उठे।
(v) शब्द – चैन न पड़ना।
वाक्य प्रयोग :
जब तक रमेश ने प्रोजेक्ट कार्य पूरा न कर लिया, उसे चैन न पड़ा।
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
इन शब्दों में से अंग्रेजी, हिन्दी, उर्दु और आंचलिक शब्दों को छाँटिए-
रायल्टी, इन्सान, पर्याप्त, इन्कार, पूर्व, किस्सा, झोला, खटिया, काबिल, स्टेशन, गर्व, टेबल, दफ्ती, झिझक, समूचा, राज, विभाग।
उत्तर:
अंग्रेजी शब्द – रायल्टी, स्टेशन, टेबल।
हिन्दी शब्द – पर्याप्त, पूर्व, गर्व, झिझक, समूचा, विभाग।
उर्दू शब्द – इन्सान, इन्कार, किस्सा, काबिल, दफ्ती,राज।
आंचलिक शब्द – झोला, खटिया।
प्रश्न 5.
नीचे दिए वाक्यों में निर्देशानुसार वाच्य परिवर्तन कीजिए
- लड़का गीत गाता है। (कर्म वाच्य)
- रमेश द्वारा नाटक खेला गया। (कर्तृ वाच्य)
- बालक छत से कूदते हैं। (भाव वाच्य)
- पक्षी आकाश में उड़ता है। (भाव वाच्य)
- कमला से कल पत्र लिखा जाएगा। (कर्तृ वाच्य)
- लड़का पुस्तक पढ़ता है। (कर्म वाच्य)
उत्तर:
- लड़के द्वारा गीत गाया जाता है।
- रमेश नाटक खेलता है।
- बालकों से छत से कूदा नहीं जाता है।
- पक्षी से आकाश में उड़ा जाता है।
- कमला कल पत्र लिखेगी।
- लड़के के द्वारा पुस्तक पढ़ी जाती है।
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? पाठ का सारांश
सुप्रसिद्ध निबन्धकार एवं लोक साहित्यविद् ‘पं. रामनारायण उपाध्याय’ की सक्षम लेखनी द्वारा लिखित प्रस्तुत निबन्ध ‘मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ?’ में लेखक ने अपने गाँव व घर को ही लेखन की प्रेरणा माना है। उनके अनुसार उनके आसपास के वातावरण ने ही उन्हें सरल व सहज विषयवस्तु उपलब्ध करायी है।
लेखक के अनुसार, साहित्य रचना के लिये जन-सम्पर्क ही सब कुछ हैं। चाहे वह सम्पर्क कॉफी हाउस में हो, सड़क पर हुआ हो, चाहे सब्जी खरीदते समय हुआ हो। ग्रामीण भाषा, गीत, खेत, दर्द से ही उनकी रचनाओं का निर्माण हुआ है। उन्हें सम्मान की भूख नहीं बल्कि स्नेह को बहुमूल्य मानते हैं। इसीलिये पत्र-व्यवहार को वे अधिक महत्व देते हैं। वह बताते हैं कि कभी-कभी लिखने का ऐसा जोश आता है कि सोते से जागकर लिखना शुरू कर देते हैं,खाना, पीना, घूमना, बात करना छोड़ देते हैं।
लिखने से पूर्व वे रचना का भाव मन में तैयार कर लेते हैं। फिर लिखने के लिए किसी बाह्य साधन,जैसे–मेज,कुर्सी, चाय की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है। जमीन पर बैठकर ही लिखने लगते हैं। बस एकान्त अनिवार्य है। वे कभी किसी के आदेश पर या सम्मान पाने के लिए नहीं लिखते हैं। वे तो इसलिए लिखते हैं, क्योंकि लिखना उनके जीवन का अविभाज्य अंग है। जब उनकी कोई नई पुस्तक आती है, तो घर खुशियों से भर जाता है। जब कोई पुस्तक बेची जाती है, तो लेखक को बड़ा दुःख होता है क्योंकि पुस्तक उनका सच्चा मित्र है।
साथ ही बुरे समय में बुजुर्गों की तरह ढाढस बँधाती है। वे अपने लिखने का उद्देश्य सत्य को प्रकट करना तथा मानवता का प्रसार करना मानते हैं। उनके लिए धनोपार्जन लिखने का उद्देश्य नहीं है। सबका असीम स्नेह ही उनकी पुस्तकों की रॉयल्टी है। वे अपने से बड़ा अपने नाम को मानते हैं। पुस्तकें ही लेखक के जीवन की सारी जिम्मेदारी को निभाना जानती हैं। पुस्तकें ही लेखक की छत हैं, और छाया हैं। इस प्रकार हम देखते हैं कि लेखक अपनी आत्म सन्तुष्टि के लिए ही लिखते हैं।
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? कठिन शब्दार्थ
राज = रहस्य। जिज्ञासु = जानने की इच्छा रखने वाला। शाश्वत = सदैव। कलेवर = शरीर। अधिकांश = अधिकतर। जीवन्त-संस्पर्श = सजीव सम्पर्क। अर्जन = कमाना। कतई = बिल्कुल अन्तरंग = घनिष्ठ। बाध्य = मजबूर। बाधक = रुकावट। निहारना = गौर से देखना। नीरवता = शान्ति। अविभाज्य = टुकड़े न होना। आत्मसात = घुलना-मिलना, अपने में मिलना। आत्मदान = आत्मार्पण। बजुर्ग = बड़े-बूढ़े। शिकस्त = टूट गया। सालता = दुखी, चुभना। अनायास = बिना कोशिश के। आकांक्षा = इच्छा। अनुगृहीत = जिस पर कृपा की गई हो, उपकृत। मरणासन्न = मरने वाला। सांत्वना = ढांढस। परिचित = जाना-पहचाना। समृद्ध = धनी। समक्ष = सामने। कृतज्ञता = एहसान।
![]()
मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ? संदर्भ-प्रसंग सहित व्याख्या
(1) गाँव के एकान्त जीवन में डाक मेरा सबसे बड़ा साथी है। किसी अन्तरंग मित्र के आने की तरह मैं उसकी प्रतीक्षा में रहता हूँ। डाक में मुझे अपने मित्रों के पत्रों का बड़ा मोह रहा है। मिलकर तो आदमी बाध्य होता है, तो बात करने के लिए, लेकिन बिना मिले भी जिनमें अपनों के लिये याद जगे, याद के उन चरणों में मैं श्रद्धा से नत हूँ। (2013)
सन्दर्भ :
प्रस्तुत पंक्तियाँ हमारी पाठ्य-पुस्तक के ‘मैं क्यों लिखता हूँ?’ नामक पाठ से उद्धृत हैं। इसके लेखक ‘पंडित रामनारायण उपाध्याय’ हैं।
प्रसंग :
एक सच्चे लेखक में अपने साथियों, मित्रों,पाठकों आदि से मिलने की तीव्र इच्छा रहती है। लेखक जिनसे मिल नहीं पाता, उन तक अपना प्रणाम व कृतज्ञता पहुँचाने का साधन मात्र पत्र हैं। पत्र डाक के माध्यम से आते-जाते हैं, इस कारण लेखक डाक को भी अपना सबसे प्रिय साथी मानता है।
व्याख्या :
लेखक कहता है कि गाँव के शान्त व एकांकी जीवन में उनका सबसे बड़ा साथी डाक है क्योंकि जब डाक आती है तो उसमें लेखक के लिए भी पत्र होते हैं। उन पत्रों को पाकर ऐसा लगता है। जैसे पत्र नहीं, पत्र भेजने वाला गले मिल रहा है। एक पत्र के लिए सारी दूरियाँ समाप्त हो जाती हैं। जैसे-हम किसी आने वाले मित्र की प्रतीक्षा बड़ी बेचैनी से करते हैं, उसी प्रकार लेखक भी डाक के आने की प्रतीक्षा बेचैन होकर करता है। जब कोई आमने-सामने प्रत्यक्ष रूप से मिलता है,तो दोनों वार्तालाप करने के लिए मजबूर होते हैं, लेकिन पत्र ऐसा साधन है, जिसमें व्यक्ति प्रत्यक्ष नहीं होता है,पर उसका वजूद पत्र में झलकता है जिससे विस्मृत स्मृतियाँ जागृत हो जाती हैं। लेखक इन्हीं यादों के चरणों में अपनेको उस व्यक्ति के प्रति नत-मस्तक हो जाता है। पत्र लिखने वाले की यादों के प्रति उसके मन में श्रद्धा रहती है।
विशेष:
- लेखक के लिए डाक एक सच्चे मित्र के समान है, तथा उसकी यादें ही उसका मिलन है।
- छोटे-छोटे वाक्यों में गम्भीर मार्मिकता है।
- संस्कृत शब्दावली के साथ भाषा में प्रवाह है।
- शैली आत्मकथात्मक है।
(2) मन में जब भी कोई नया विचार आता है, मेरा खाना, पीना, सोना, बैठना मुश्किल हो जाता है। और तब मैं उस विचार का एक छोर पकड़कर टहलने लगता हूँ। रुई को पीजने की तरह विचारों को धुनकर उनकी पोनी बना, मन के चरखे पर उससे तार निकालने में बड़ा आनन्द आता है और फिर जैसे कोई ताने-बाने से कपड़ा बुनता है, उसी तरह विचारों को बुनकर मेरी रचना तैयार हो जाती है।
सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
लिखने के लिए उद्यत लेखक ने बताया है कि जब लिखने का आवेग आता है तो नींद-प्यास सब उड़ जाती है, विचार भाषा में परिवर्तन होते जाते हैं।
व्याख्या :
लेखक उपाध्याय जी कहते हैं कि जब उनके मन में विचार उठते हैं तो उन विचारों को लिखित रूप देने के लिए उनका मन व्याकुल हो जाता है जिस कारण उनका खाना, पीना, सोना,बैठना आदि सब व्यर्थ हो जाता है। मात्र एक लगन रह जाती है कि शीघ्र-अति-शीघ्र इन विचारों को लिखित आकार दे दिया जाए। ऐसे में लेखक एक विचार को पकड़कर लिखना शुरू करता है। रुई से लेकर कपड़ा बुनने तक की घटनाओं का रूपक बाँधते हुए लेखक कहता है कि जिस प्रकार सर्वप्रथम रुई को धुनकर उसकी गन्दगी बाहर निकाली जाती है, रुई को मुलायम बनाया जाता है फिर उसकी हाथ द्वारा पूनी बनाकर चरखे से सूत कातते हैं।
उसके बाद सूत का ताना-बाना फर्मे पर चढ़ाकर कपड़ा बुना जाता है। ठीक उसी प्रकार जब मन में विचार आते हैं तो बुद्धि उन विचारों को छाँटकर शुद्ध विचारों की संग्रह रूपी पूनी बनाती है। मन रूपी चरखे पर उन विचारों को काता जाता है,सूत बनाया जाता है। विचारों के क्रमबद्ध संग्रह से एक रचना तैयार हो जाती है। वह रचना मन को आनन्दित करने वाली होती है।
विशेष :
- विचारों को साकार रूप देने का वर्णन किया है।
- रूपक के माध्यम से विचारों की गद्य विधा तक पहुँचने की स्थिति का परिचय दिया है।
- सरल भाषा के साथ आंचलिकता का प्रभाव है।
- शैली आत्मकथात्मक है।
![]()
(3) जब कभी मेरा मन उदास हो जाता है, कोई छोटी-सी बात मेरे मन को बेचैन कर जाती है, किसी घटना-विशेष को लेकर मैं तिलमिला उठता हूँ, कोई समस्या मुझे सोने नहीं देती या किन्हीं चिन्ताओं से मैं घिर जाता हूँ तब ये पुस्तकें किसी बुजुर्ग की तरह मेरी पीठ को सहलाते हुए मुझे ढाढ़स बँधाती आई हैं। (2010)
सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
अपनी पुस्तकों को अपना सच्चा साथी मानने वाले लेखक का मत है कि पुस्तकें मन की उदासी, चिन्ता, खिन्नता, बेचैनी को दूर करने वाली होती हैं। वे ही अधीर मानव को धैर्य प्रदान करती हैं।
व्याख्या :
लेखक उपाध्याय जी कहते हैं कि वे जब भी दुःखी होते हैं, उनके मन में मलिनता आती है और उनका मल व्याकुल हो उठता है। जब भी कोई घटना उन्हें बेचैन तथा उद्विग्न कर देती है,जब भी वे विभिन्न प्रकार की चिन्ताओं में फंस जाते हैं तब इन स्थितियों से वे परेशान हो जाते हैं। तब उन्हें शान्ति देने वालीं, उन्हें धीरज बँधाने वालीं, उनकी प्रिय पुस्तकें ही होती हैं। उनके पढ़ने से उन्हें व्याकुलता, खिन्नता, तिलमिलाहट, परेशानी आदि सभी से छुटकारा मिल जाता है। वे उनकी पीठ पर किसी संरक्षक (बुजुर्ग) की तरह हाथ फेरती हैं और धैर्य प्रदान करती हैं।
विशेष :
- दुःख में पुस्तकें धैर्य प्रदान करती हैं। ये संकट की साथी होती हैं।
- साहित्यिक खड़ी बोली का प्रयोग हुआ है।
- आत्माभिव्यंजक शैली को अपनाया गया