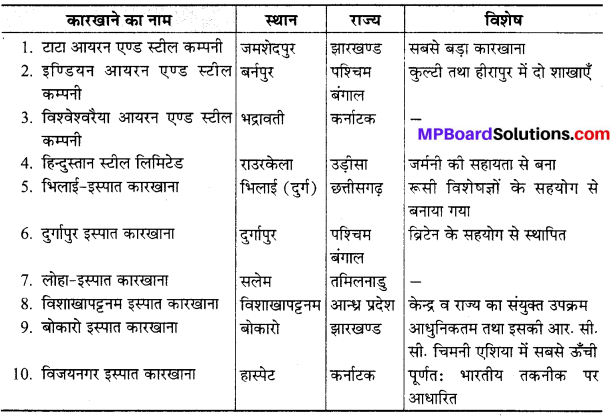
MP Board Class 10th Sanskrit Solutions Durva Chapter 18 महाराजः छत्रसालः (गद्यम्) (सङ्कलितम्)
MP Board Class 10th Sanskrit Chapter 18 पाठ्यपुस्तक के प्रश्न
Mp Board Class 10th Sanskrit Chapter 18 प्रश्न 1.
एकपदेन उत्तरं लिखत-(एक पद में उत्तर लिखिए)।
(क) छत्रसालस्य पितुः नाम किम्? (छत्रसाल के पिता का क्या नाम था?)
उत्तर:
श्रीचम्पतरायः (श्री चम्पतराय जी)
(ख) छत्रसालस्य जन्म कस्मिन् ग्रामे अभवत्? (छत्रसाल का जन्म किस गाँव में हुआ था?)
उत्तर:
ककरकचनयग्रामे (ककरकचनय गाँव में)
(ग) ‘बुन्देलकेसरी’ इति नाम्ना कः प्रसिद्धः? (‘बुन्देलकेसरी’ नाम से कौन प्रसिद्ध था?)
उत्तर:
छत्रसालः (छत्रसाल)
(घ) शिववीरः छत्रसालाय किं नामक कृपाणम् अयच्छत्? (शिववीर ने छत्रसाल को किस नाम की कृपाण दी?)
उत्तर:
‘भवानीति’ (भवानी)
(ङ) भूषणः कस्याः भाषायाः महाकविः आसीत्? (भूषण किस भाषा का महाकवि था?)
उत्तर:
हिन्दीभाषायाः (हिन्दी भाषा का)
Mp Board Class 10 Sanskrit Chapter 18 प्रश्न 2.
एकवाक्येन उत्तरं लिखत-(एक वाक्य में उत्तर लिखिए-)
(क) योद्धारः किमर्थं सर्वस्वं हुतवन्तः? (योद्धाओं ने किसलिए अपना सब कुछ जला दिया?)
उत्तर:
योद्धारः मातृभूमि पराधीनतापाशात् विमुक्तये सर्वस्वं हुतवन्तः। (योद्धाओं ने मातृभूमि को गुलामी के जाल से मुक्त करने के लिए अपना सब कुछ जला (बलिदान कर) दिया।
(ख) छत्रसालस्य जन्म कस्मिन् जनपदे अभवत्? (छत्रसाल का जन्म किस जनपद में हुआ?)
उत्तर:
छत्रसालस्य जन्म ‘टीकमगढ़’ जनपदे अभवत्। (छत्रसाल का जन्म टीकमगढ़ जनपद में हुआ।)
(ग) छत्रसालः कस्य शिष्यः आसीत्? (छत्रसाल किसका शिष्य था?)
उत्तर:
छत्रसालः स्वामिप्राणनाथस्य शिष्यः आसीत्।। (छत्रसाल स्वामीप्राणनाथ का शिष्य था।)
(घ) कान् पराजित्य छत्रसालः पन्नानगरं राजधानीम् अकरोत्? (किनको हराकर छत्रसाल ने पन्नानगर को राजधानी बनाया?)
उत्तर:
पन्नाजनपदस्य गोंडजातीयान् राज्ञः पराजित्य छत्रसालः पन्नानगरं राजधानीम् अकरोत्। (पन्नाजनपद की गोंड जाति के राजा को हराकर छत्रसाल ने पन्नानगर को राजधानी बनाया।)
(ङ) गुरुणा छत्रसालः केन उपाधिना विभूषितः? (गुरु के द्वारा छत्रसाल को किस उपाधि से विभूषित किया गया?)
उत्तर:
गुरुणा छत्रसालः ‘महाराज’ इत्युपाधिना विभूषितः (गुरु के द्वारा छत्रसालः “महाराज” नामक उपाधि से विभूषित किया गया।)
कक्षा 10 संस्कृत पाठ 18 MP Board प्रश्न 3.
अधोलिखितप्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि लिखत-(नीचे लिखे प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए)
(क) के के वीराः भारतस्वतन्त्रतायै मुगलैः सह अयुध्यन्? (कौन से वीरों ने भारत की स्वतन्त्रता के लिए मुगलों से युद्ध किया?)
उत्तर:
महाराजशिववीरः, महाराणाप्रतापः, राज्ञी लक्ष्मीबाई, वीरपुङ्गवा छत्रसालः प्रभृतयः अनेकाः वीराः भारतस्वतन्त्रतायै मुगलै, सह अयुध्यन्। (महाराज शिववीर, महाराणाप्रताप, रानी लक्ष्मीबाई, वीरश्रेष्ठ छत्रसाल आदि अनेक वीरों ने भारत की स्वतन्त्रता के लिए मुगलों से युद्ध किया।)
(ख) बाल्यकालादेव छत्रसालः किमर्थं प्रयतते स्म? (बचपन से ही छत्रसाल किसके लिए प्रयास कर रहा था?)
उत्तर:
बाल्यकालादेव छत्रसालः भारतमातरं मुगलशासनात् विमोक्तुं प्रयतते स्म। (बचपन से ही छत्रसाल भारतमाता को मुगल शासन से मुक्त करने का प्रयास कर रहे थे।)
(ग) छत्रसालस्य साहित्यिकं प्रेम कथं ज्ञायते? (छत्रसाल का साहित्यिक प्रेम कैसे पता चलता है?)
उत्तर:
छत्रसालः काव्यसाहित्यशास्त्रसम्मानार्थ भूषणमहाकवेः शिविकाम् अपि उतोलयत्। एतेन तस्य साहित्यिकं प्रेम ज्ञायते। (छत्रसाल ने काव्यसाहित्यशास्त्र के सम्मान के लिए महाकवि भूषण की पालकी को भी उठाया। इससे उनके साहित्यिक प्रेम का पता चलता है।)
Class 10 Sanskrit Chapter 18 प्रश्न 4.
प्रदत्तशब्दैः रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत (दिए गए शब्दों से रिक्त स्थान भरिए-)
(छत्रसालदशक, द्वयशीतिः, छत्रसालः, सूबेदारी, भवानी)
(क) मुगल शासकः इमं …………….. इति दातुम् ऐच्छत्।
(ख) शिववीरः तस्मै …………….. इति नामकं कृपाणं समर्पितवान्।
(ग) भूषणः …………….. इति काव्यरचनाम् अकरोत्।
(घ) भारतमातृभूः संरक्षकः …………….. आसीत्।
(ङ) छत्रसालः …………… वर्षपर्यन्तम् अजीवत्।
उत्तर:
(क) सूबेदारी
(ख) भवानी
(ग) छत्रसालदशक
(घ) छत्रसालः
(ङ) द्वयशीतिः।
Sanskrit Class 10 Chapter 18 Mp Board प्रश्न 5.
यथायोग्यं योजयत्-(उचित क्रम से जोड़िए-)

उत्तर:
(क) 3
(ख) 1
(ग) 2
(घ) 5
(ङ) 4
Class 10 Sanskrit Chapter 18 Mp Board प्रश्न 6.
निम्नलिखितक्रियापदानां धातुं, लकारं, पुरुष, वचनं च लिखत
(नीचे लिखे क्रियापदों के धातु, लकार, पुरुष और वचन लिखिए-)

उत्तर:

10th Class Sanskrit Book Mp Board प्रश्न 7.
अधोलिखितपदानां सन्धिविच्छेदं कृत्वा सन्धिनाम लिखत
(नीचे लिखे पदों के संधिविच्छेद करके सन्धिनाम लिखिए-)

उत्तर:

Class 10 Sanskrit Mp Board प्रश्न 8.
अधोलिखितपदानां समासविग्रहं कृत्वा समासनाम लिखत
(नीचे लिखे पदों के विग्रह कर समास का नाम लिखिए-)
(क) महाराजः
(ख) क्षेत्रपतिः
(ग) वीरपुरुषः
(घ) राष्ट्रभक्तिः
(ङ) यशः शरीरम्
उत्तर:

Mp Board Class 10th Sanskrit Solution प्रश्न 9.
उदाहरणानुसारं पर्यायशब्दान् लिखत
(उदाहरणानुसार पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए-.)
उदाहरणम् – केसरी (रिन्) – सिंहः
(क) स्वतन्त्रः
(ख) कृपाणः
(ग) युद्धम्
(घ) तनयः
(ङ) जन्मभूमिः
उत्तर:
(क) स्वतन्त्रः मुक्तिः
(ख) कृपाणः – खड्गः
(ग) युद्धम् – समीरः, संग्रामम्
(घ) तनयः – पुत्रः
(ङ) जन्मभूमिः – मातृभूमिः
Class 10th Sanskrit Mp Board प्रश्न 10.
रेखांकितपदान्याधृत्य प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत
(रेखांकित पदों के आधार पर प्रश्न बनाइए-)
(क) स्वातन्त्र्यनायकाः स्वकीयं सर्वस्वं हुतवन्तः। (स्वतन्त्रता के नायकों ने अपना सब कुछ जला दिया।)
उत्तर:
के स्वकीयं सर्वस्वं हुतवन्तः? (किन्होंने अपना सब कुछ जला दिया?)
(ख) छत्रसालः शिववीरं महाराजं मिलितवान्। (छत्रसाल शिववीर महाराज से मिला।)
उत्तर:
छत्रसालः कं महाजं मिलितवान्। (छत्रसाल किस महाराज से मिला?)
(ग) अयं बाल्यकालात एव भारतमातरं विमोक्तुं प्रयतते स्म। (यह बचपन से ही भारतमाता को मुक्त करने का प्रयास कर रहा था।)
उत्तर:
अयं कस्मात् एवं भारतमातरं विमोक्तुं प्रयतते स्म? (यह कब से ही भारत माता को मुक्त करने के प्रयास कर रहा था?)
(घ) छत्रसालः भूषणस्य शिविकाम् उत्तोलयत्। (छत्रसाल ने भूषण की पालकी उठाई।)
उत्तर:
छत्रसालः कस्य शिविकाम् उत्तोलयत्? (छत्रसाल ने किसकी पालकी उठाई?)
(ङ) ‘मऊसहानिया’ स्थले सः प्राणान् अत्यजत्। (‘मऊसहानिया स्थल’ पर उसने प्राण त्याग दिए।)
उत्तर:
कस्मिन् स्थले सः प्राणान् अत्यजत्? (किस जगह पर उसने प्राण छोड़े?)
योग्यताविस्तारः –
महाराजछत्रसालसादृशाः येऽन्ये स्वातन्त्र्यनायकाः मध्यप्रदेशे अभवत् तेषां नामानि लिखत।
महाराज छत्रसाल जैसे अन्य स्वतंत्रता सेनानियों के जो मध्यप्रदेश में हुए, नाम लिखो।
महाराजः छत्रसालः पाठ का सार
प्रस्तुत पाठ में ‘महाराज छत्रसाल’ का जीवन-चरित्र वर्णित किया गया है, जिससे छात्रों को बलिदान, पराक्रम और राष्ट्र-भक्ति की सीख मिल सके तथा वे भी ऐसे वीरों की भाँति अपने देश के लिए बलिदान की भावना उत्पन्न कर सकें।
महाराजः छत्रसालः पाठ का अनुवाद
1. सम्प्रति अस्माकं देशोऽयं स्वतन्त्रोऽस्ति। किन्तु स्वतन्त्रताप्राप्त्यै परतन्त्रताकालादेव समये-समये राष्ट्रभक्तैः अनेकैः वीरपुरुषैः स्वस्य जीवनस्य आहुतिरपि प्रदत्तेति। गौराङ्गवैदेशिकेश्यः पूर्वं यदा भारतदेशः मुगलैः आक्रान्तः आसीत् तदा मुमलैः सह ये पराक्रमशालिनः युद्धं कृतवन्तः तेषु महाराजशिववीरः, महाराणाप्रतापः, राज्ञीलक्ष्मीबाई, वीरः वाः छत्रसालप्रभृतयः अप्रतिमाः योद्धारः आसन्। एते मातृभूमिं पराधीनतापाशात् विमुक्तये स्वीयं सर्वस्वं हुतवन्तः।।
Sanskrit Class 10th Mp Board शब्दार्थाः :
सम्प्रति-इस समय-now;आक्रान्तः-अधिकार में किया हुआ-control; वीरपुङ्गवाः-वीरों में श्रेष्ठ-bravest; पाशात्-जाल में-snare, clutches.
कक्षा 10 संस्कृत पाठ 6 महाराणा प्रताप MP Board अनुवाद :
इस समय हमारा यह देश आजाद है। किन्तु स्वतन्त्रता प्राप्त करने के लिए गुलामी के समय से ही समय-समय पर अनेक राष्ट्रभक्त वीर-पुरुषों के द्वारा अपने जीवन की आहुति भी दी गई। विदेशी अंग्रेजों से पहले जब भारत देश पर मुगलों का अधिकार था तब मुगलों के साथ जिन पराक्रमशालियों ने युद्ध किए, उनमें से महाराज शिववीर, महाराणा प्रताप, रानी लक्ष्मीबाई, वीरों में श्रेष्ठ महाराज छत्रसाल आदि अनेक अद्वितीय योद्धा थे। इन्होंने मातृभूमि को गुलामी के जाल से मुक्त कराने के लिए अपना सर्वस्व जला दिया ‘समर्पित कर दिया।
Sanskrit 10th Class Mp Board English :
Brave patriots made sacrifices to liberate India during Mughal rule-heroic persons like Maharaja Shiv Veer, Maharana Pratap, Rani Laxmi Bai, bravest emperor Chhatrasala were unique soldiers- Sacrificed their all to seek freedom for country.
2. “बुन्देलकेसरी” इति विख्यातस्य छत्रसालस्य जन्म (1649) एकोनपञ्चाशदुत्तरषोडशशततमे ईस्वीये मध्यप्रदेशस्य ‘टीकमगढ़’ जनपदस्य मयूरपर्वतीयक्षेत्रे वर्तमानलिधौराविकासखण्डे “ककरकचनयग्रामे” अभवत्। छत्रसालस्य मातुर्नाम सारन्धादेवी पितु म च श्रीचम्पतरायः इत्यासीत्। अयं वीरः बाल्यकालादेव भारतमातरं मुगलशासनात् विमोक्तुं प्रयतते स्म। यथासमये एतदर्थम् एव छत्रसालः शिववीरमहाराजम् अपि मिलितवान्। तस्मै शिववीरोऽपि सर्वविधं साहाय्यं कर्तुं वचनम् अयच्छत्। तथा च स्वतन्त्रतायै योद्धं स्वाशीर्वादस्वरूपं “भवानीति” नामकं कृपाणम् अपि दत्तवान्।
शब्दार्थाः :
विमोक्तुम्-मुक्त करने के लिए-to liberate;प्रयतते-प्रयास कर रहा है-making efforts; सर्वविधम्-सब प्रकार की-of all sorts.
Sanskrit Class 10 Mp Board अनुवाद :
‘बुन्देलकेसरी’ नाम से विख्यात छत्रसाल का जन्म 1649 ई. में मट यप्रदेश के ‘टीकमगढ़’ जनपद के मयूर पर्वतीय क्षेत्र में वर्तमान में लिधौरा विकास खण्ड में “ककरकचनयग्राम में हुआ। छत्रसाल की माता का नाम सारन्धादेवी और पिता का नाम श्री चम्पतराय था। यह वीर बचपन से ही भारतमाता को मुगलों से मुक्त करने (कराने) के लिए प्रयास कर रहा था। उचित समय आने पर इसके लिए ही छत्रसाल, शिववीर महाराज से भी मिला। उसे शिववीर ने भी हर तरह की सहायता करने के लिए वचन दिया। और आजादी के लिए युद्ध करने के लिए अपने आशीर्वाद के रूप में ‘भवानी’ नाम की कृपाण भी दी।
Mp Board Class 10 Sanskrit Solution English :
Chhatrasala was known as Lion of Bundel–made efforts to liberate India from the trammels of the Mughals since childhood-met emperor Shiv Vira for the same and sought promise of help-Shiv Vira gave him a sword along with his blessings.
3. औरङ्गजेबस्य, अन्येषां राज्ञां च शक्ति अविगणय्य जनसहयोगेन छत्रसालः युद्धं कृतवान् विजयश्रियम् अपि अवाप्तवान्। असौ सेनानी सर्वप्रथमं युद्धे चित्रकूटात् गोपाचलनगरं (ग्वालियरम्) यावत् तथा च कालपीतः गढ़ाकोटा यावत् निजं प्रभुत्वं संस्थापयामास। अनन्तरं सः पन्नाजनपदस्य गोंडजातीयान् राज्ञः पराजित्य पन्नानगर राजधानीम् अकरोत्।
प्रसिद्धः स्वामिप्राणनाथः अस्य गुरुः आसीत्। प्रसन्नः गुरुः छत्रसालं “महाराज” इत्युपाधिना विभूष्य आशीर्वादं प्रदत्तवान्, यत्
राज्ये त्वदीये नृप! छत्रसाल! क्षोणिस्सदा कम्पमयी विभातु।
अश्वः त्वदीयः समियात् तु यत्र, भोस्तत्र साफल्यमवाप्नुहि त्वम्।।
Mp Board Solution Class 10 Sanskrit शब्दार्थाः :
अविगणय्य-बिना गणना करके-not caring (ignoring); अवाप्तवान्-प्राप्त किया-obtained; प्रभुत्वम्-शासक त्व-lordship; संस्थापयामास-स्थापित किया-established; विभूष्य-विभूषित करके- embellishing; क्षोणिः-पृथ्वी-earth; विभातु-प्रकाशित हो-shine; त्वदीयः-तुम्हारा-yours; समियात्-जाये-proceed, so; अवाप्नुहि-प्राप्त करो-ohtain.
Mp Board Class 10 Sanskrit Book Pdf अनुवाद :
औरङ्गजेब के और अन्य राजाओं की शक्ति की बिना गणना किए, जन सहयोग से छत्रसाल ने युद्ध किया और विजय भी प्राप्त की। इस सेनानी ने सबसे पहले युद्ध में चित्रकूट से गोपालनगर (ग्वालियर) तक तथा कालपीत गढ़ाकोटा तक अपना शासनत्व स्थापित किया। इसके बाद उसने पन्ना जनपद की गोंडीय जाति के राजा को हराकर पन्नानगर को राजधानी बनाया।
प्रसिद्ध स्वामीप्राणनाथ इनके गुरु थे। खुश होकर गुरु ने छत्रसाल को ‘महाराज’ की उपाधि से विभूषित कर आशीर्वाद दिया कि-“हे राजा छत्रसाल! तुम्हारे राज्य में कांपती हुई धरती सदा प्रकाशित हो। तुम्हारा घोड़ा जहाँ भी जाए, वहीं तुम सफलता प्राप्त करो।”
Class 10 Mp Board Sanskrit Solution English :
Ignored strength of Aurangzeb and others fought and won victory-Set up his rule from Chitrakoot to Gwalior and Kalpita Garhakata-defeated king of Pannagarh and made it his kingdom.
His guru Swami Pran Natl. embellished him with the title “Maharaja’ and blessed him to win victory wherever his horse happened to go.
4. यदा औरङ्गजेबः दक्षिणभारते व्यापृतः आसीत् तदा युद्धकौशलेन असौ बघेलखण्ड-मालव-राजस्थान-पञ्चाम्बुप्रदेशपर्यन्तं क्षेत्रं स्वाधिपत्ये कृतवान्। मुगलशासकः इमं मानिनं प्रान्ताधिपतित्वं “सूबेदारी” इति दातुम् ऐच्छत् तदा अयं न्यषेधयत्। एकदा महोबा-“जैतपुरनगरयोः मुगलशासने जाते सत्ययं पेशवाबाजीरावाय सहायतार्थम् एकं पत्रं प्रेषितवान्। बाजीरावसाहाय्येन सः पराजितं भूभागं विजितवान्। विजयेन आह्लादितोऽयं पेशवाबाजीरावम् औरसपुत्रमिव मत्वा विजितराज्यस्य तृतीयभागं तस्मै सहर्ष प्रदात्।”
Mp Board Sanskrit Book Solution Class 10 शब्दार्थाः :
व्यापृतः-व्यस्त-busy; न्यषेधयत्-मना कर दिया- refused; ऐच्छत्-इच्छा की-desired.
अनुवाद :
जब औरङ्गजेब दक्षिण भारत में व्यस्त था, तब युद्ध कौशल से इन्होंने बधेलखण्ड मालव, राजस्थान, पांच अम्बु प्रदेश तक के क्षेत्र पर अपना अधिकार किया। मुगलशासक ने इनका मान करने के लिए पान्तों का अधिपतित्व ‘सूबेदारी’ देनी चाही तो इन्होंने मना कर दिया। एक बार महोबा ने- “जैतपुरनगर से मुगलशासन होने पर सत्यय को पेशवा-बाजीराव की सहायता के लिए एक पत्र भेजा। बाजीराव की सहायता से उन्होंने हारा हुआ क्षेत्र जीत लिया। विजय से खुश होकर इन्होंने पेशवा बाजीराव को औरसपुत्र के समान मानकर जीते हुए राज्य का तीसरा भाग उसे खुशी से दे दिया।
English :
Won victory over many regions when Aurangzeb was busy in Southern India–Mughal emperor offered him ‘Subedari’ of certain provinces. He declined the offer.
Recaptured lost regions with the help of Bajirao offered one-third of won over kingdom of Bajirao, considering him as adopted son.
5. छत्रसालस्य शौर्यण, राष्ट्रभक्त्या, उदारतया च प्रभावितो हिन्दीभाषायाः महाकविः भूषणः “छत्रसालदशक” इति वीररसनिबद्धां काव्यरचनाम् अकरोत्। छत्रसालः काव्यसाहित्यशास्त्रसम्मानार्थं भूषणमहाकवेः शिविकाम् अपि उत्तोलयत्। द्वयशीतिवर्षस्य अवस्थायाम् एकत्रिंशदुत्तरसप्तदशशततमे (1731) खीस्ताब्दे दिसम्बरमासस्य चतुः तारिकायां “मऊसहानिया” इत्यस्य तालपरिसरे एषः क्षणभङ्गनिष्ठं शरीरम् अत्यजत्। अधुना सः पाञ्चभौतिकशरीरेण नास्ति परन्तु यशः शरीरेण सर्वदा अस्मान् भारतीयान् प्रेरयन् राष्ट्रभक्तिभावंच शिक्षयन् तिष्ठति एव। अयं देशः जन्मभूमिसंरक्षक्स्य महापराक्रमशालिनः छत्रसालस्य सदैव ऋणी अस्ति। विजयतेतरां महाराजः छत्रसालः।
शब्दार्थाः :
शिविकाम्-पालकी को-palanquin; उत्तोलयत्-उठाया-raised; क्षणभङ्गनिष्ठम्-क्षण भर में नष्ट होने वाला-transitory, fragile; शिक्षयन्-सिखाते हुए-teaching.
अनुवाद :
छत्रसाल के शौर्य, राष्ट्रभक्ति और उदारता से प्रभावित होकर हिन्दी भाषा के कवि भूषण ने ‘छत्रसालदशक’ नामक वीररस से युक्त काव्य की रचना की। छत्रसाल ने काव्यसाहित्यशास्त्र के सम्मान के लिए महाकवि भूषण की पालकी को भी उठाया। बयासी (82) वर्ष की आयु में सन् 1731 ई. में दिसम्बर मास की चार तारीख को ‘मऊसहानिया’ तालाब के परिसर में इन्होंने क्षणभर में नष्ट होने वाले शरीर को त्याग दिया। अब वह पञ्चभूत रूपी शरीर से नहीं हैं पर यश रूपी शरीर से हमेशा हम भारतीयों को प्रेरित करते हुए और राष्ट्रभक्ति का भाव सिखाते हुए रहेंगे। यह देश जन्मभूमि की रक्षा करने वाले महापराक्रमी छत्रसाल का हमेशा ऋणी रहेगा। महाराजा छत्रसाल विजयी हो।
English :
Bhushar composed a literary piece named ‘Chhatrasala Dashak’. Chhatrasala raised Bhushan’s palanquin to honour him.
Died at the age of 82. His heroic death will go on inspiring us with his patriotic feelings. The country will ever remain indebted to Chhatrasala.