In this article, we will share MP Board Class 10th Social Science Book Solutions Chapter 4 Transport, Communication and Foreign Trade Pdf, These solutions are solved subject experts from the latest edition books.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Solutions Chapter 4 Transport, Communication and Foreign Trade
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Text Book Exercise
Students can also download MP Board 10th Model Papers to help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Objective Type Questions
Transport Communication And Foreign Trade MP Board Question 1.
Multiple Choice Questions:
(Choose the correct answer from the following)
Transport Communication And Foreign Trade Meaning In Hindi MP Board Question (a)
How many railway zones are there in India:
(a) 9
(b) 16
(c) 14
(d) 15
Answer:
(b) 16
Mp Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Question (b)
Distance between two rails of the broad guage:
(a) 1676 mm
(b) 1000 mm
(c) 792 mm
(d) 1560 mm.
Answer:
(a) 1676 mm
Chapter 4 Sst Class 10 MP Board Question (c)
The Place associated with metro rails:
(a) Bengluru
(b) Ahmedabad
(c) Kolkata
(d) Bhopal.
Answer:
(c) Kolkata
Mp Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 9 Question (d)
The main gas pipeline transport is:
(a) Barauni – Haldia
(b) Barauni – Jalandhar oil pipeline
(c) Naharkatia – Barauni oil pipeline
(d) Hajira – Jagdishpur gas pipeline.
Answer:
(d) Hajira – Jagdishpur gas pipeline.
Chapter 4 Social Science Class 10 MP Board Question (e)
Port to reduce pressure on Bombay Port:
(a) Paradweep
(b) Haldia
(c) Nhava Sheva
(d) Kandla.
Answer:
(c) Nhava Sheva
Mp Board Class 10th Social Science Solution In English Question (f)
Communication facility in India for talking to people living abroad (foreign countries):
(a) B.P.T.
(b) I.S.D.
(c) S.T.D.
(d) W.L.L.
Answer:
(b) I.S.D.
Social Science Class 10 Mp Board Solutions Question (g)
Those consumers who do not have computer or internet, for them this communication system has been developed:
(a) Business mail
(b) Speed post
(c) E – Post
(d) E – Bill post.
Answer:
(c) E – Post
Mp Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 10 Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- Most safe and deed port on the Koromandal coast in Andhra Pradesh is …………………
- Letter boxes are installed in …………………………. cities for local letters.
- Useful channel for sorting and sending dam, available in the capital places of all the state capitals is …………………………….
- Short name of International network is ………………………… (MP Board 2009, 2011, 2013)
- Foreign trade means ……………………….. of goods between two countries.
- At the time of independence India’s foreign trade was having …………………….. position.
- In the import-export policy declared in 1992 made ……………………. very liberal.
Answer:
- Visakhapatnam
- big
- satellite station
- Internet
- exchange
- zero
- economy.
Chapter 4 Class 10 Social Science MP Board Question 3.
Match the Column:

Answer:
- (e)
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
- (d)
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 MP Board Question 1.
Which port has been developed 125 kilometres away from Kolkata?
Answer:
Haldia.
Class 10th History Chapter 4 Notes MP Board Question 2.
Where is headquarter of Indian Airlines?
Answer:
New Delhi.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 Notes MP Board Question 3.
What is main objective of Prime Minister’s village road scheme in India?
Answer:
The main objective of Prime Minister’s village road scheme is to connect all the villages having a population up to 500, to all weather roads.
Question 4.
What do you mean by transport and communication?
Answer:
The process of carrying man and material from one place to other place is called transport. The process of transmitting information from one person to other or from one place to other through different means is called as communication. It is transmission of message or information.
Question 5.
When the commercial (advertisements) service of Doordarshan was started?
Answer:
The commercial service of Doordarshan was started in 1976.
Question 6.
On which channel information about India’s social, cultural and economic sectors is shown to international viewers?
Answer:
‘D.D. India’ channel has been started for the viewers of international level.
Question 7.
What is present name of the radio broadcasting service?
Answer:
All India Radio and from 1957 it was called ‘Akashvani’.
Question 8.
By what name the educational channel of the ‘Doordarshan’ is mainly known?
Answer:
D.D. Gyan Darshan.
Question 9.
Name the main international naval routes of India?
Answer:
Following are the main international sea routes pass through India:
1. Singapore route:
This route is from Kolkata to shores of United States of America via Japan.
2. Australia route:
Chennai to Australia and Newzealand via Singapore.
3. Sues route:
Mumbai to Port Said and London.
4. Gape of Good hope route:
Mumbai, Mombasa to Europe and America.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by metro rail service?
Or
What do you mean by metro rail services? Write? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
For metro cities, there is a plan to develop metro railways. Metro Rail service is very fast and comfort service provided to the daily passengers. In India, the network of metro railways has been completed in Kolkata, Mumbai and Delhi. The father of Delhi Metro Rail Corporation is a veteran engineer named E. Sridharan under which the DMRC is working with world class work culture and infrastructure.
Question 2.
What are main hinderances of the internal navigational transport?
Answer:
The main hinderances are:
- Seasonal river flowing in nature.
- River level changeable in nature.
- Lack of proper planing and policy.
- Time taking transportation.
Question 3.
What is difference between a dock and a port?
Answer:
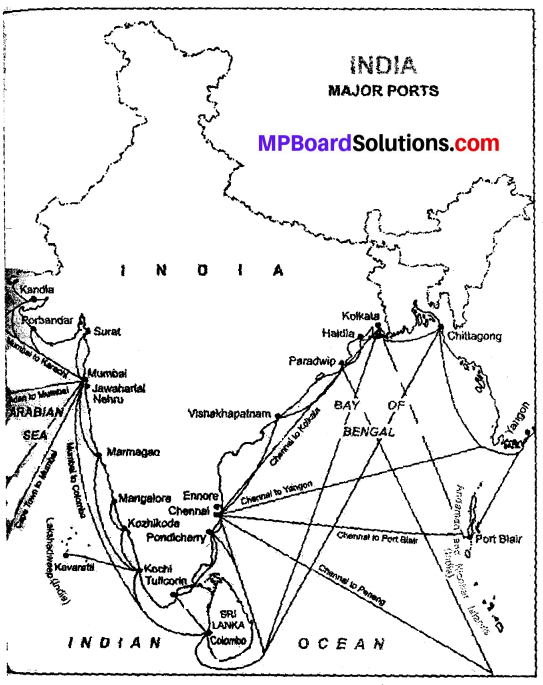
Ports and docks are the centres of shipping transport. There is difference between a port and a dock. Ports are meant for coming and going of ships, their stay, and there are resting facilities on the ports whereas docks are meant for loading in and unloading of goods from the ships. Ports are the locations where there is land and sea. There are 13 major and 184 small ports in India. Over 93% of the trade in India is carried out from these ports. They are main centres of trade and therefore called the getway of trade.
Question 4.
What is cellular phone?
Answer:
It is phone like a wireless set and is called mobile phone or cellular phone. You can carry it in your pocket and talk to anyone from there itself and receive outstation phone calls also. Up to the year 2006, the number of persons using this service were about 3.1 crores.
Question 5.
What is difference between telegram and fax?
Answer:
Telegram:
American scientist Tomas Alva Edison invented telegraph sending messages speedily became possible by telegrams. For this, telegram lines were installed on pillars. Messages were sent through these lines, with the help of electricity and code machines.
Fax:
Fax is a means of sending and receiving written messages. For this a fax machine is needed, which is connected to a telephone and the message is put into the machine. This machine prints that message on a paper at the receiving end. It also prints senders telephone number, address and time of the message.
Question 6.
What is meant by Internet?
Or
What do you mean by internet? (MP Board 2009, 2011)
Answer:
Internet is the short form of the Word International Network. With the help of this service a person can see an event happening in any country, contact persons and get desired information. Information and data can be obtained through lakhs of computer information centres in ones own language. In India ranks fourth in the world in respect of this facility. 4.5% of the country’s total population have access to the internet.
Question 7.
Describe the Indian Doordarshan service?
Answer:
The telecasting service on regular basis was started in India in the year 1965. In the year 1976 it was separated from ‘Akashvani’ and a separate organisation, ‘Doordarshan’ was set up. Now about more than 87% people of the country through 1042 transmitting stations can watch the programmes.
Number of centres preparing programmes is 20. During 1976 the advertisement service was started, and from 1982 telecasting of coloured programmes was started. D.D. 1 and D.D. 2 were started from Delhi. Thereafter, satellite channels in 11 regional languages were started.
From February 1987 morning service of ‘Doordarshan’ and from 26th January, 1989 afternoon service of the ‘Doordarshan’ have started to cater to the needs of all classes of viewers. For sports related activities D.D. Sports’ channel and for quality education, an educational channel viz. ’D.D. Gyan Darshan’ has been started.
Question 8.
What is meant by satellite communication service?
Answer:
Scientists have prepared mechanized satellites for the benefit of the society and they have been launched in the space with the help of rockets. These artificial satellites move around the Earth and transmit, through pictures and maps, information regarding weather, natural resources, army activities etc. Aryabhatt, Apple, IRS man made Satellites are examples of efforts made in this direction.
Question 9.
What is meant by foreign or international trade?
Or
Write any four characteristics of International Trade? (MP Board 2009, 2010, 2011)
Answer:
The foreign trade of a country consists of exports and imports. The excess of exports over imports refer to a surplus in balance of trade. A country always tries to have a surplus in its foreign trade. After independence, India’s foreign trade has undergone remarkable changes and is no longer confined to few countries and commodities. Along with these changes the following other characteristics can be mentioned about the foreign trade of India:
1. There has been substantial increase in imports on account of development needs of the economy.
2. The composition of imports has undergone a great change. The imports now consist of sophisticated machines, lubricants, oils and fertilizers which are essential for the country’s industrial and agricultural development.
3. There has been a change in the pattern of India’s exports. We do not export much of raw material and food group commodities any more as we did before independence.
4. The exports now cover wide range of items of agricultural and industrial sector of handicrafts, handloom, cottage and craft articles.
Question 10.
How is business affected by cultural diversity?
Answer:
Culturally all the countries of the world are different from each other. The religious beliefs life style, customs and traditions and tastes of the people of every country are different. Demand and production of every country are therefore different because of these diversities.
Cultural diversity of population also affects the trade of a country. There is a great demand for commodities of religious necessities as well as the articles of comfort and luxury in countries where diversity of population is more and the standard of living of the people there is normally.
Question 11.
What is meant by infrastructure of foreign trade?
Answer:
Infrastructure of foreign trade means the basic facility for export house, loading – unloading the goods, container’s facility, custom clearance facilities, stocking and air conditioning facilities and the maintenance of harbour, port and air aviation department along with the foreign trade policy.
Question 12.
Explain the difference between export promotion and import substitution?
Answer:
Export promotion and import substitution:
After achievement of independence, the quantum of imports in India have considerably increased but exports have not increased to expected extent. As a result, the position of balance of payments was adversely affected. The increasing deficits in the foreign trade on the one hand necessitated an increase in the exports and on the other hand a necessity was felt to reduce imports. Therefore, the policy of export promotion and import substitution was adopted to improve the balance of payment position.
Export promotion:
Under this, old and new exporters are encouraged to export more and more goods.
Import substitution:
Under this system, instead of importing things (from far off places) they are produced in any neighbouring country. So also efforts are made, to substitute imported goods by producing them indigenously.
Question 13.
What are main five items which are imported and five items which are exported?
Or
Write the names of any five main items which are imported and exported from India? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
India’s items of import or re – import:
India imports the following commodities from other countries:
Cereals and cereal preparations, copra, crude, rubber, raw wool, raw cotton, raw jute, crude oil and lubricants, animal and vegetable oil fats, fertilizers, chemical elements and compounds, medical and pharmaceutical products, plastic materials, paper, iron and steel machinery, transport equipment, defence equipment etc.
India’s items of export:
India exports the following items to other countries:
Jute manufactures, cotton fabrics, cotton yarn, iron ore, cakes, leather, engineering goods, chemicals, iron and steel, tobacco, cashew kernels, coffee, mica, sugar, manganese ore, art-silk fabrics, footwear, vegetable oils, pearls and precious and semi – precious stones.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How the means of transport are guiding factors for the progress of human civilization?
Answer:
The means of transport play an important role in providing a strong base to the economy, and promote sense of brotherhood and good feelings for the people of our country living in different regions, so also these means promote unity in the country. India is a vast country with diverse culture, different languages and cultural diversity therefore, there is always a threat to the national unity.
Transport facilities bring the people of different regions close to each other thus national integration is promoted since the efficient transportation system facilitates travelling from one region to the other and develop a sense of understanding between people of different regions. This helps in reducing differences at cultural and mental levels.
Means of transportation facilitate quick transport of goods and passengers regularly and reliably. The world has become small due to easy approachability and linking of countries through their respective markets. Means of transport are of a great help at the time of natural calamities like famines, flood, epidemics, earthquakes and shortage excess of rains.
Road transport is the one, which is within reach of most of the people of the country. Road transport is important and useful for short and medium distances. This mode of transport is also supplemental to rail, water and air transport system. Road transport facilities are multi purpose, cheap and reach to your door.
It is only through road transport that the agricultural fields are connected to markets, factories and the consumers. It is also possible to load goods from desired place and pick up from and drop passengers at the desired places. Through road transport education, thoughts, skills and knowledge can be reached to remote areas and villages. Roads help transport, all sorts of assistance during war time and at the times of famines, epidemics, wars, etc.
Question 2.
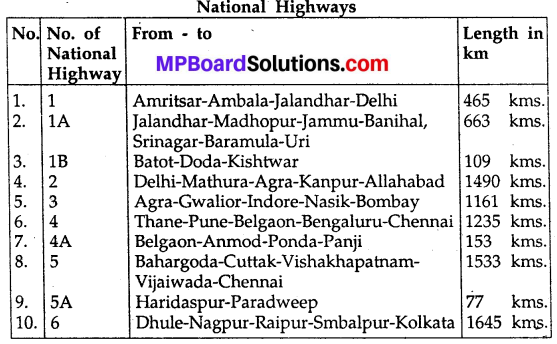
Describe the main National highways of India?
Answer:
These are constructed and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD) Government of India. These pucca roads join the capitals of different states of the country, big business and industrial centres, main ports and roads of the adjoining countries. The total length of National highway in India is 58,112 kilometres.
The share of National highways of India in terms of length is only 2% of the total length of roads of India but their share in the total transportation is 45 per cent. To boost up the economic development of the country the ‘National Highways Development Policy 1999’ was formulated, according to which a target of construction of about 14000 kilometres, 4/6 lane National highways by 2007. Some National highways of India are as follows:
Question 3.
The distribution of rail routes in India is unequeal. Explain?
Answer:
The rail routes in India have developed mostly in those areas which are economically more developed. This distribution is highly imbalanced.
More dense rail route areas:
This area is spread over the Northern India in Sutlaj – Ganges plains up to West Bengal. Important railway stations on this rail route are Ludhiana, Delhi, Kanpur, Lucknow, Allahabad, Varanasi, Asansol, Howrah, etc.
Dense rail route areas:
The peninsular plains and Southern plateau are included in this area. Main stations on this route are Ahmedabad, Vadodra, Chennai, etc.
Less dense areas:
These areas comprise the hilly, plateau, desert and marshy areas, forest and economically backward areas, sparsely populated areas etc. Here the transportation facilities are negligible. Rail routes have not been developed. In this category, fall the areas of Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Bastar area of Chhattisgarh and most parts of Orissa.
The Eastern and Western coastal area of India, are rugged and narrow therefore, the rail routes could not be developed adequately. On the eastern coast from Kanya Kumari coast to Howrah, the rail route is developed. On Western coastal area, Kokan Railway Corporation has been developed. On the Western Coastal area, with the setting up of Kokan Railways Corporation, 837 kilometres of rail track has been developed.
Question 4.
How are the means of communication very important in modem times? Explain?
Or
“The means of communication are very important in modem age.” Explain it? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
The means of communication in an economy work in the same way as the blood vessels work in the human body. The blood vessels carry blood to different part of body and keep it healthy and fit. Similarly, the communication system carries man and material from one place to other places thus keeping the socio – economic activities of the nation mobile all the time.
1. The world is said to be shrinking because now far – flung areas of country have come very close to each other because of fast means of communication.
2. For nation building and bringing about awareness among people with regard to policies and development programmes implemented in the country.
3. To encourage economic development of the country, develop social relations and cultural unity.
4. To bring together people from different walks of life at the international level.
5. The means of communication are of immense importance to our forces. The defence of the country depends upon the improved and fast means of transport and communication. They help and facilitate the movement of arms, ammunition and other supplies. Communication links are established to transmit the important messages and communications.
6. The means of communication have strengthened the bonds of national unity in India by social and cultural contacts between the various people of the country.
7. To provide information regarding war, accidents earthquake or any other type of emergency so that immediate help and relief can be arranged.
8. They are life lines also because through these means government is able to maintain law and order situation.
Question 5.
Doordarshan is the most useful medium of communication. Explain?
Or
Television is the most useful medium of communication. Explain it? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
The present era is the era of knowledge and information. Doordarshan has become a powerful source of information having the system of audio – vedio mechanism. Now – a – days in the means of communication Doordarshan has become very important because of following reasons:
- For nation building and bringing about awareness among people with regard to be picturing and practical development of programmes implemented in the country.
- To encourage the publicity of economic development of the country, develop social relations and cultural unity.
- To bring together people from different walks of life at the national and international level.
- To know about important events of the world through print and electronic media.
- To communicate with our friends and relatives living in dif¬ferent corners of the world.
- To provide information regarding war, accidents, earthquake or any other type of emergency so that immediate help and relief can be arranged.
Question 6.
Explain the contribution of foreign trade in the economic development and explain the factors that affecting the international trade?
Or
Write the main factors affecting international trade? (MP Board 2009, 2012)
Answer:
International trade of a country is the indicator of its economic progress. That country is considered ‘developed’ which has a sizeable share, per capital, at the international level. Those countries whose per capita trade is less are considered economically backward. The contribution of foreign trade in the economic development can be enumerated as under:
- Foreign trades makes a country self – dependent. Those commodities which are not available in the country due to unsuitable weather conditions, quality of land and other factors they can be made available through foreign trade.
- This promotes industrialisation. Raw material and sources of energy can be imported.
- Foreign trade increase possibilities of agricultural development, improved technology and seeds promote agricultural development.
- Foreign exchange is earned which is utilised for economic development.
- Foreign trade increases avenues of employment in industry and agricultural sector.
- It enables consumers to see a variety of things, and improve their living standard (by buying such things).
- It is possible to provide immediate relief to victims of floods, famine epidemics, earthquake etc., and save their lives by importing things or their requirement.
- Inflation can be controlled. Division of labour can be promoted, which is an indicator of economic development.
Factors affecting International Trade:
International trade is affected by many natural, economic, political and social reasons. Main factors affecting International trade are as under:
1. Location:
Those countries which are located on the Interna¬tional trade routes, commercially they progress easily.
2. Rugged sea coast:
The countries where sea coast is there the ports are very developed and they have adventurous and good sailors.
3. Natural resources:
The trade of a country is affected by the diversity of its natural resources. They include the climate, forests, cultivable land, agricultural crops, minerals etc. On these resources the production depends.
4. Economic development:
The level of economic development of different countries is not similar. Countries which are economically advanced their trade is more developed.
Question 7.
Explain the measures adopted to promote exports in India?
Answer:
Government efforts for export promotion:
1. Setting up of different organisations:
Government of India has set up Foreign Trade Institute Export Import Advisory Council, State Trading Corporation, Export Promotion Council, Cotton Textiles Corporation, Jute Corporation, Import – Export Bank to open new markets for export, for publicity of domestic goods in foreign countries and to extend facilities to exporters.
2. Trade promotion institute:
To ensure co – ordination between different institutions engaged in exports promotion and to provide necessary services to them a Trade Development Organisation has been set up.
3. Establishment of state trading corporation:
This corporation has been set up to export a variety of things, expand the existing market, and provide necessary facilities to the exporters.
4. Establishment of export houses:
This organisation has been set up to provide financial assistance to recognised organisations from the marketing development fund. There are seven export resource centers viz. Kandla (Gujarat), Santacruz (Maharashtra), Kocchi (Kerala), Chennai (Tamilnadu), Noida (Uttar Pradesh), Phalta (West Bengal), Vishakhapatanam (Andhra Pradesh).
Custom clearance facilities are availiable here.
5. Indian import – export bank:
This bank has been set up to promote imports and exports.
6. Green Card:
To accelerate the pace of exports the Government have issued green cards to institutions which are engaged in cent per cent exports.
7. Liberal licence system:
The government have declared a new import – export policy and made the licensing system very liberal, this has encouraged free trade.
Question 8.
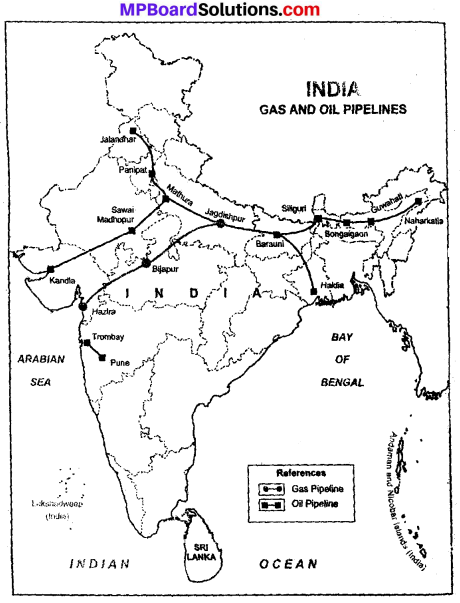
Indicate the following in the map of India:
Hajira-Jagdishpur pipeline, Vishakhapatanam, Milk pipeline, any two internal water transport routes, Area of the Border roads Development Board?
Or
Show Hajira-Jagdishpur gas pipeline on the given outline map of India? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Additional Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Multiple Choice Questions:
(Choose the correct answer from the following)
Question (a)
Which of the following is not the category of guage of Indian railways?
(a) Broad guage
(b) Metre guage
(c) Metro guage
(d) Narrow guage.
Answer:
(c) Metro guage
Question (b)
Where are the electric engines produced?
(a) Kolkata
(b) Ishapore
(c) Barackpore
(d) Chittaranjan.
Answer:
(d) Chittaranjan.
Question (c)
What is the road density in India (per sq. km)?
(a) 44 km
(b) 59 km
(c) 64 km
(d) 74 km.
Answer:
(a) 44 km
Question (d)
The first telex service started in Devanagri in India in:
(a) 1959
(b) 1969
(c) 1979
(d) 1989.
Answer:
(b) 1969
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- ……………….. looks after the roadways at the national level.
- ……………….. is the cheapest means of transportation.
- The goods which are sent from a country to other countries are known as ……………………
- ………………….. and ……………………. are the basis of international trade.
- The length of Amritsar – Ambala – Jalandhar – Delhi National Highway is …………………….
- ………………………. is the most expersive form of transpart.
- Milk is sent through ………………………. Pipeline from Anand to Ahmedabad. (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
- CPWD
- Waterways
- exports
- surplus, deficit
- 465 km
- Air transport
- Anand – Ahmedabad.
Question 3.
True and False type questions:
- The trade carried out between states, towns and village in called internal trade.
- Selling and sending goods and services to the foreign countries is called import.
- Transport and communication are the lifeline of any country.
- PIN code means the Postal Index Number.
Answer:
- True
- False
- True
- True.
Question 4.
Match the columns:

Answer:
1. (d)
2. (c)
3. (a)
4. (e)
5. (b)
Answer in One – Two Words or One Sentence
Question 1.
What do you mean by lifelines of the national economy?
Answer:
Means of transport and communication are called lifelines of the national economy.
Question 2.
What are the two major means of land transport?
Answer:
Roadways and Railways.
Question 3.
Why is transport a necessity?
Answer:
Transport is a necessity because it helps us in production and distribution of goods.
Question 4.
Name the areas where narrow guage has been laid in India?
Answer:
Narrow guage has been confined to only few hill stations.
Question 5.
What percentage of our people travel by second class?
Answer:
Over 96 per cent of passengers travel by second class.
Question 6.
Name the southern most railway station in India?
Answer:
Cape Comorin (Kanya Kumari).
Question 7.
Name the northern – most railway station in India?
Answer:
Jammu Tawi.
Question 8.
What is meant by export promotion?
Answer:
Export promotion means efforts to promote export.
Question 9.
What is import substitution?
Answer:
It is a device adopted by a country to produce those goods within the country which are imported from outside the country.
Question 10.
In which year the Indian Railway service started? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
1854.
Question 11.
What is the policy of Indian Railways regarding electrification?
Answer:
The rapid electrification of all the railway tracks.
Question 12.
Name the two super – fast trains of India?
Answer:
- Rajdhani Express
- Shatabdi Express.
Question 13.
What is the inland navigational potential in India?
Answer:
5200 kilometres.
Question 14.
Name the two navigational rivers of India?
Answer:
- Ganga
- Brahmaputra.
Question 15.
Up to which city would Ganga be used in navigation in due course?
Answer:
Up to Patna and in due course up to Allahabad.
Question 16.
Name the two main ports of the western coast of India?
Answer:
- Mumbai
- Nhava Sheva.
Question 17.
Name the four ports which have been developed recently.
Answer:
- New Mangalore
- Haldia
- Nhava Sheva
- Ennore.
Question 18.
How many major ports are there in India?
Answer:
Twelve.
Question 19.
Which is the major public sector enterprise of the central Government?
Answer:
Indian Railways.
Question 20.
What is the most important facility provided by the telephone service?
Answer:
Telex services.
Question 21.
Name means of mass communication?
Answer:
Means of mass communication are telephone, television, radio, films and internet.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the various forms of transport in land, water and air?
Answer:
The land transport network consists of road and railways. The waterways comprise of deep – sea, coastal and inland navigation. The air transport offers air travel through aeroplanes.
Question 2.
Name the width of railways in India?
Answer:
Indian railways consist of three types of guages:
- Broad gauge (1.69 metre)
- Metre gauge (1.00 metre)
- Narrow gauge (0.77 metre).
Question 3.
What are express or free highway?
Answer:
Express or freeways are national highways with 4 to 6 lanes meant to meet the requirement of fast traffic movement across the country.
Question 4.
What are three names of Express or Freeways?
Answer:
Golden Quadrilateral, North – South and East – West Corridors, Connectivity of 10 major ports with Golden Quadrilateral and the Corridors.
Question 5.
What is the total length of roads in India? How much of this length is surfaced?
Answer:
The total length of roads in India is 25 lakh kilometres. 57% of this length is surfaced.
Question 6.
What are the lifelines of a country?
Answer:
Means of transport and communication are the lifelines of a country. Means of transport include roads, railways, airways and waterways. Posts, telegraphs, telephone, telex, fax, radio, television, Internet and E-mail are important means of communication.
Question 7.
State the importance of border roads?
Answer:
Importance of Boarder Roads are:
- Border roads help us to guard and protect highly inhospitable terrain, relief and climatic conditions by our Jawans along our borders with Pakistan, China and Myanmar.
- They help in military supply of arms, ammunition and food to our military.
Question 8.
What does the total road length indicate?
Answer:
The total road length in India is 25 lakh kilometres on March 31, 2002. It indicates that road transport is the most important mode of transport of India of the total length 57% are surfaced roads.
Question 9.
In what way is television more useful than radio? Give one point?
Answer:
Television is more useful than radio because it gives live vision of the happenings along with audio sounds and commentary while radio provides only audio service.
Question 10.
What does ‘BOT’ stand for?
Answer:
BOT stands for Build, Operate and Transfer. It means that after realising cost and profit for certain period, the roads will be transferred to the government as their rightful owners.
Question 11.
What is mass communication?
Answer:
Mass communication means to communicate with several people at a time. It contains electronic media, doordarshan, radio, press and audio – visual media which plays a very vital role in creating awareness among the people about various programmes and policies.
Question 12.
What is export control?
Answer:
It is exercised by a country to regulate the export in respect of limited number of items whose supply position demands that their export should be regulated in the larger interest of the country.
Question 13.
What are the main objectives of India’s export and import policy?
Answer:
The major objectives of the new Import – Export Policy 1988 – 1991 are to stimulate industrial growth, promote efficient import sub – stitution and self – reliance.
Question 14.
List some factors affecting International Trade?
Answer:
Factors affecting International trade are:
- Location.
- Rugged sea coast.
- Natural Resource.
- Economic Development.
- Business policy.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
“Means of transport and communication are the lifelines nation”. Prove this statement? (MP Board 2009)
Or
Why are means of transport and communication called the lifelines of a country and its economy?
Answer:
Lifelines of a human being are his veins. They carry blood in all the parts of the body and keep them hale and hearty. Likewise means of transport and communication bring all the regions of a country closer and develop them equally. A country makes tremendous progress because of its developed means of transport and communication. Without these all the developmental activities will come to an end and the country would meet its doom.
Question 2.
Why is railway transport very important in our country?
Answer:
Importance of Railways in our country:
India is a vast country. Its both length and breadth exceeds 3,000 kilometres each. In such a country, means of transport is an imperative need that can carry men and material in bulk from one place to another. Roads, inland waterways and airways are unable to cope with this huge traffic. Railways are capable of fulfilling this requirement. They carry passengers and goods over long distances and in bulk.
Question 3.
What is Container Service? Write four characteristics of Container Service?
Answer:
Container Service is that railway service in which door – to – door freight service is provided. Its characteristics are as follows:
- It reduces transportation and delivery time of goods.
- It ensures greater security of goods and freedom from pilferage.
- It has proved more economic for both railways and its customers. .
- Thefts and robberies have no chance to be committed.
Question 4.
What is the importance of unsurfaced roads in India?
Answer:
Since independence unsurfaced roads have increased three times. This explains their importance.
- These roads open up the countryside to modern ways of living.
- Bullock – carts carry nearly 90 crore tonnes of goods from rural areas to urban areas over short distances. These bullock-carts run on unsurfaced roads and carry bulk of goods.
Question 5.
Distinguish between Transport and Communication?
Answer:
Transport:
- The movement of goods and passengers from one place to another is called transport.
- Rail Road, Sea and Air Route constitute the transport system.
Communication:
- The transmission of any message news and any idea from one place to other place is called communication.
- Postal letters, telephone, wireless, television etc. are the examples of means of communication.
Question 6.
In which part of India is air travel found more economical than road or rail transport?
Answer:
Air transport is more economical in the hilly areas of the country. Hills are not easily accessible to the people because of the rough and steep nature of the terrain. It is very difficult and in some case impossible to build long and strong roads or lay railway lines. Air transport makes it possible to reach such remotest places. Air transport is the fastest means of transport as such its importance to fulfill the needs of the Jawans in the border areas is still more important. Places like Leh and Tibbet can be easily accessible through these means.
Question 7.
What, in your opinion, is the policy of Indian Railways with regard to electrification?
Answer:
In 1854 the first electrified railway line was laid and traffic started on it in India. At that time the trains ran on locomotive (steam) engine. In course of time railways became very popular. They expanded by leaps and bounds. Side by side they created numerous problems specially of over – crowding and slow speed.
In order to remove these hindrances, electrification of railway tracks is the answer. It seems that there is a policy of the Indian Railways to get all the tracks electrified. A total of 13018 kms of railway tracks have been electrified by the end of 1996 – 1997. The day is not far away when we will see electric trains running on them.
Question 8.
Furnish two main facts about the importance of border roads for the defence of our country?
Answer:
Border roads maintain the supply line for our jawans on the frontiers irrespective of physical odds and extremely harsh climatic conditions as our international borders extend along Pakistan and China. Border roads join the border areas with the interior parts of the country, having links with National Highways. Hence they integrate the country into a well – knit entity.
Question 9.
Find out the facilities provided by the Indian Railways to the passengers?
Answer:
Facilities provided by the Indian railways to the passengers are:
- Reservation facilities by computers.
- Waiting – room facilities on the station.
- Return of ticket if a passenger has to postpone his/her journey.
- Lunch and dinner is supplied in the trains.
- Electrification of railway tracks.
- New tracks in new areas.
- Adoption of uni – gauge system. Conversion of metre gauge into broad guage.
- Replacement of steam engines by diesel and electric engines.
Question 10.
Differentiate between broad guage and narrow guage?
Answer:
Broad Guage:
- Broad Guage is the category of railway track which has width of 1.69 metres between the rails.
- 50% of the total length of the railway trackes in India consists of broad gauge.
- Example: Delhi – Kolkata Railway Track.
Narrow Guage:
- Narrow Guage is the category of Railway track which has 0.77 metre width between the rails.
- Narrow gauge railway tracks are found only in hilly areas.
- Example: Kalka-Shimla Railway Track.
Question 11.
Differentiate between river transport and road transport?
Answer:
River Transport:
- River Transport provides inland navigational facilities within the country. It is also called inland water transport.
- River transport is carried by boats and crafts or steamers.
- It is slow in speed.
- It is cheaper to maintain.
Road Transport:
- Road Transport is through roads within or outside the country through Kuchcha or Pucca roads.
- It is carried out by buses, trucks, lorries, carts, cars and two – wheelers.
- It is comparatively speedier than river transport.
- It is costlier to maintain.
Question 12.
Differentiate between port and harbour?
Answer:
Port:
- It is a point on the coast where ships can be tied up for anchor..
- In ports, ships load and unload commodities.
- Indented coasts provide natural ports.
- Port is mostly linked with a fertile and productive hinterland.
Harbour:
- It is in area of sea, providing safe entrance to ships.
- It gives protection to ships from waves and storms.
- River estuaries, bays provide natural harbours such as Mumbai.
- Harbour provides sufficient room for anchorage of ships.
Question 13.
What is meant by Inland waterways?
Answer:
The waterways that are found in the inner parts of a country in the form of rivers, lakes, canals are known as Inland waterways. These waterways include deep rivers, large lakes and streams. The inland waterways are the cheapest means of transport within a country. They are helpful in carrying the heavy and bulky goods from one place to another. In India, the rivers like the Ganges and the Brahmaputra serve the purpose of inland water transportation. Inland waterways save us from pollution.
Question 14.
Why are ports called the gateways of the world trade? Explain with examples?
Answer:
Ports are the places (gateways) through which our imports and exports pass. This gives us access to oceans. They provide links with other countries or far off places. They facilitate us to catch fish , and supplement our food needs.
Question 15.
What are the importance of print media?
Answer:
Importance of print media is as under:
- It gives us news about the world.
- It helps us know about various happenings in and around the world.
- Information about the government works and policies and programmes are obtained through print media.
- It also increases our education.
Question 16.
Describe the trade and its types?
Answer:
Trade is the exchanges of goods and services between persons, states and countries.
Types of Trade:
There are three types of trade:
1. Local Trade:
It is carried between people in villages, towns and cities.
2. State Level Trade:
It is carried out between two or more states. .
3. International Trade:
It is carried out between two or more countries. It may take place through sea, air or land routes.
Question 17.
Distinguish between internal and external (foreign) trade?
Answer:
Internal Trade and External Trade (Foreign Trade):
Internal Trade:
- Internal trade is carried out between the states, towns and villages within the territorial limits of a country.
- Goods like jute, cotton, sugar and tea, when traded between the places in our country it forms part of internet trade.
External Trade:
- Foreign trade is carried out between different countries. Thus exchange of goods and services among the different nations are known as foreign or external trade.
- The goods like jute, cotton, or machines, when traded between two countries, we call it external trade.
Question 18.
Why the policy of export promotion has been given preference over import substitution?
Answer:
Our present trade policy is known as export-led strategy or export – oriented and production – oriented import – export policy. The import substitution policy cannot be solely as we continue to import capital goods that are required for developmental purpose. Secondly India’s industrialisation has reached a stage of development where the process of import – substitution is nearly complete. The need today, therefore, is to give precedence to export promotion policy which is nothing but a mix of export promotion and import substitution policy. The efforts have been made to imporve the quality of export goods and reducing their cost.
Question 19.
Explain the re – export business?
Answer:
If a country, after importing certain items from other countries and exporting them again to the neighbouring countries, the process is called ’re – export. Re – export is done by a country to such countries who are not suitably located near the ports or those who cannot have favourable trade with other countries-owing to foreign exchange problems.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 4 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is contribution o’f agriculture and industry to the growth of Indian economy?
Answer:
Contribution to the growth of agriculture and industry:
The railways have contributed to the growth of agriculture and industry in the following ways:
1. Railways carry increased amount of fertiliser and foodgrains every year from the place of their production to the entire country.
2. Railways bring war material from all the parts of the country and take them to the every doors of industries where they are needed.
3. Railways ensure wider market for agricultural and industrial, product. Specially for industrial products, it is necessary to explore the new markets and take things to them.
4. Railways have played an important role in hauling coal, mineral ore, mineral oils and in promoting industries by helping in production as well as distribution.
5. The railways have helped in bringing the labour force from all the comers of the country. It has brought the people living in the far flung areas quite close to each other. It has helped in bringing national and emotional integration of the country.
6. Promotion of national integration and modernisation:
The Railways keep the people of different areas in contact with one another. They bring the people living in the far flung areas quite closer to each other. They are the carriers of views, culture and civilisation. They, thus play an important role in the national and emotional integration of the country. Through railways people keep link between various states and help in time of food shortage and natural calamities and other catastrophs.
Question 2.
Describe the means of communications of India?
Answer:
After independence the Means of Communication have made a great progress. The means of transport and communication have been called the lifelines of a country. The developed means of communication play a dominent role in industrial development of developing and developed countries. In India the importance of the means of communication has increased very much. Following are the chief communication services of India:
1. Post Offices and Postal Services:
It is the cheapest means of communication for the general public. The post cards, inland letters, envelops and the registered letters are the means of sending messages through post offices. In 1986 there were 128559 Post Offices in cities and 156825 in villages
2. Telegraphs:
In some post offices the messages are sent through telegrams. It reaches to all the places quickly. In 1986 there were 37425 telegraph offices in India.
3. Telephone:
A man can talk with another man all over the world without moving from his place. At the time of independence there were only 321 telephone exchanges in the country. This number has reached 11480 and the number of telephones has increased manifolds.
4. The Telex Services:
It is the post office service whereby subscribers hire the use of teleprinters. It is a typewriter exchange and one can exchange views through teleprinters. At present there are about 117 telex services. The first Devanagri telex service started in 1969.
5. Radio and Wireless:
Radio is very cheap and quick means of communication of news to the masses. India at present has 85 radio stations. About 90% of the population of India is getting benefit of this type of communication.
6. Television:
The television is viewing of distant objects or event by electrical transmission. It is the main source of recreation and obtaining news from different parts of the world. India at present has seven full – fledged television centres, five relay centres and INSAT stations and four SITE continuity centres. The T.V. programmes can have access only to 70% of the total population. In the main time efforts are being made to provide community viewing sets for villages.
7. The Insat (INSAT) Communication Services:
The apple INSAT is the first effort in the field of Insat communication service. After it INSAT – A and INSAT – B were projected in space. They can be used for communicating news. It is the first INSAT which is being utilised for communication and weather reports. INSAT – 1D has already been planned to be launched in space on 12th June, 1990. It will take the place of INSAT – 1B which is in its last step to complete its duration in space.
Question 3.
State the ways by which means of transport and communication help the growth of industries in India?
Answer:
The means of transport and communication are helpful in the industrial development pr growth in the following manner:
- They help in transporting raw material from place of their origin to that of industries.
- They are of great help in transporting the refined and finished products to the national as well as international markets.
- They are helpful in mobility of the labourers and in supplying the required information about the industries.
- They transport the raw material and labourers to the underdeveloped areas, and the backward areas and help in the industrial development.
- These means also help in reducing regional imbalances resulting in balanced development.
Question 4.
Give the importance of ‘means of transport’ in modern times.
Answer:
The means of transport are indispensable these days. The following facts prove this statement:
- They easily and quickly transport men and material from one place to another.
- They are helpful in supplying the consumer goods to the markets and consumers rapidly.
- They are helpful in supplying the raw material to the industries. Hence they contribute in the formation of capital and development of industries.
- They provide immediate relief in times of war, natural calamity, famine and flood.
- They are equally important for the security and defence of the country as they transport the armed forces as well as artillery to the battle fronts and border areas.
- Improved means of transport have made travel convenient.
- The developed means of transport have brought the people of the world closer to one another and have encouraged the sense of international brotherhood and oneness.
Question 5.
State two important facts supportive of the importance of National Highways in India?
Answer:
The total length of the National Highways in India as an Dec. 31, 2001 was 52000 kms accounting for only 2% of the totjal
road length. But they play an important role in the country because of the following:
- National Highways carry more than 45% of total road traffic.
- They carry large number of passengers from one place to another.
- They also carry military men and material to border areas from cantonments and vice versa.
- They have contributed a lot in reducing regional imbalances.
- They help in the national integration to a great extent.
Question 6.
Explain main export items of Indian Trade?
Answer:
The main export items of Indian trade are:
1. Jute Manufactures:
This item occupies an important place in India’s exports. Before partition it used to be India’s major foreign exchange earner. But now in the face of international competition, its share has declined much.
2. Tea:
Tea accounts for 5 per cent of India’s total exports U.K. and U.S.A. are the principal buyers of Indian tea.
3. Cotton Fabrics, Yam and Manufacture:
The share of cotton fabrics raw cotton in total exports of our country is about 4.5 per cent. The total value of cotton readymade garment exports have been to the tune of Rs. 3088.8 crores in the year 1987 – 1988.
4. Gems and Jewellery:
In terms of its share in export, it constitutes about 16.8 per cent of our total exports.
5. Leather and Leather Manufactures (including Footwear):
This is one of the traditional items of Indian exports. In the year 1987 – 1988 India exported goods worth Rs. 1148.5 crores.
6. Sugar:
Export of sugar preparation accounts for about 2.3 per cent total exports. It has emerged as an important items of our exports.
7. Iron – ore and Iron and Steel:
Our principal customer of iron ore is Japan. In the year 1987-88 we have exported iron-ore werth about Rs. 542.8 crores.
8. Machinery and Transport Equipment:
These goods are part of engineering goods which are exported by our country and are non-traditional goods. In the year 1985 – 1986 India has exported engineering goods worth Rs. 898/- crores.
Map Work
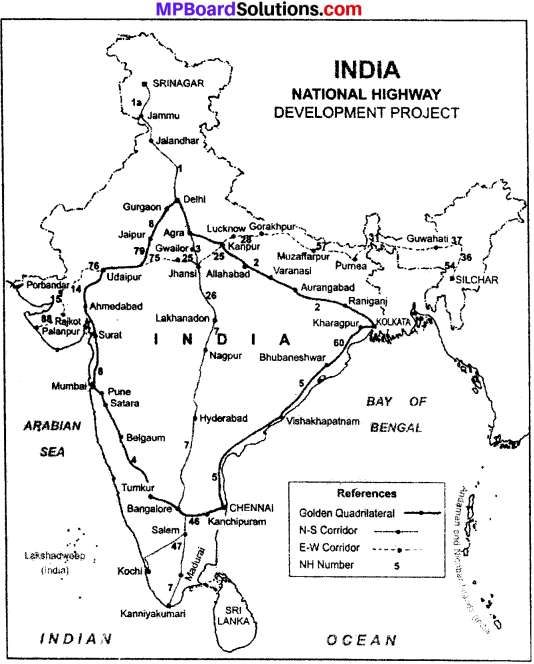
Question 1.
On an outline map of India, draw National Highways Development Projects?
Or
On an outline map of India, show Delhi – Jalandhar – Shrinagar National Highway? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
Question 2.
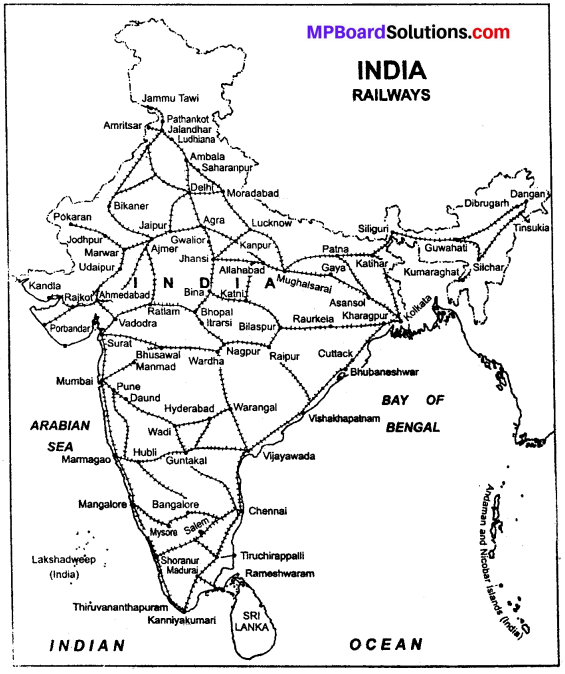
On an outline map of India, major routs of Indian Railways?
Or
On an outline map of India, show railway line from Delhi to Kolkata? (MP Board 2009)
Answer:
Question 3.
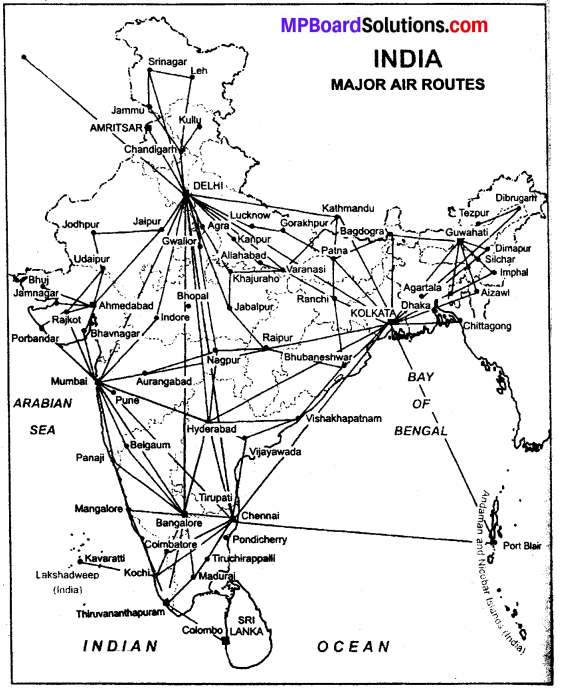
On an outline map of India, draw major air routes?
Or
On an outline map of India, show Santacruz Airport (Mumbai)? (MP Board 2009)
On an outline map of India, show Palam Airport (Delhi)? (MP Board 2009)
Answer: