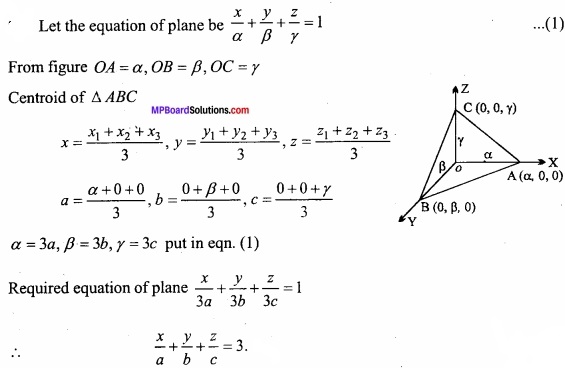
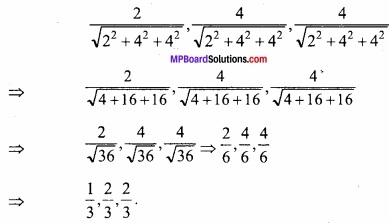
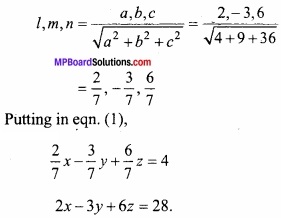
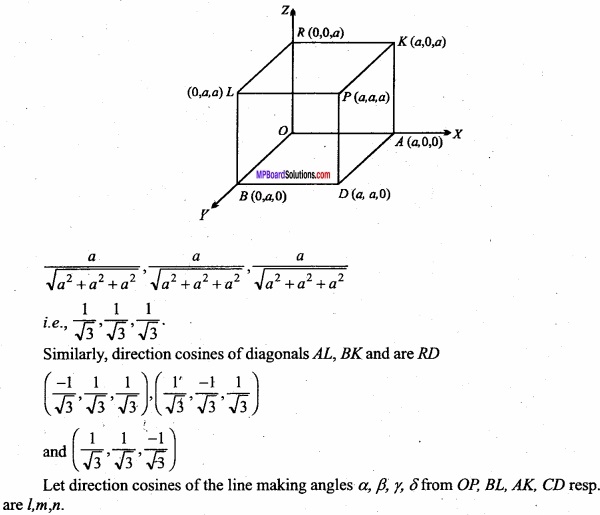
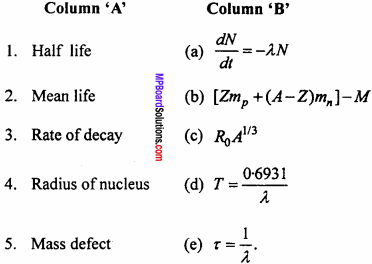
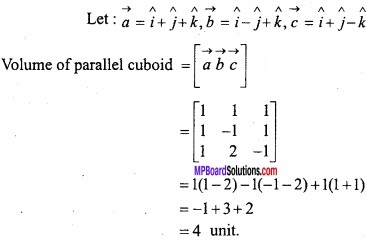
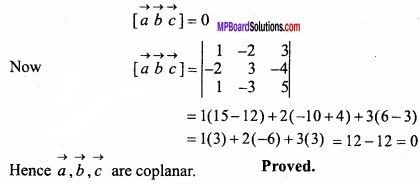
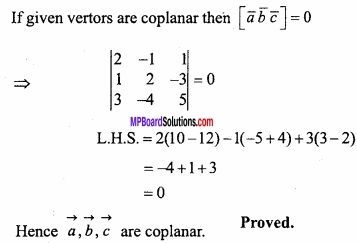
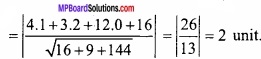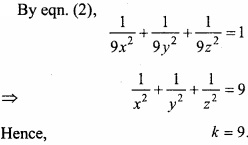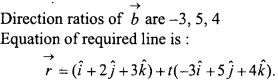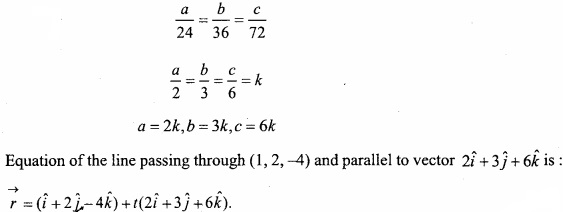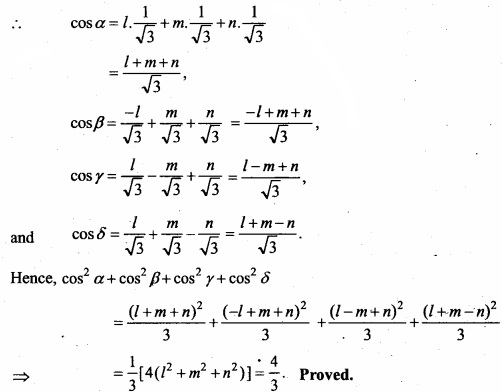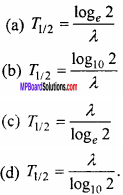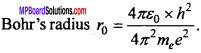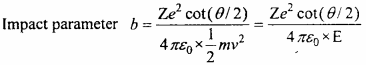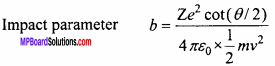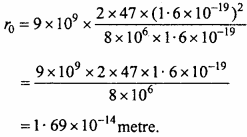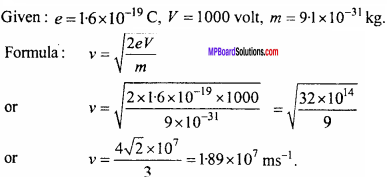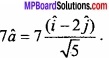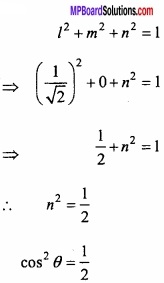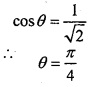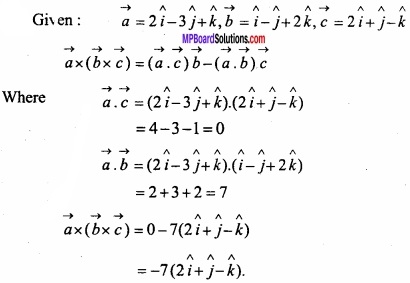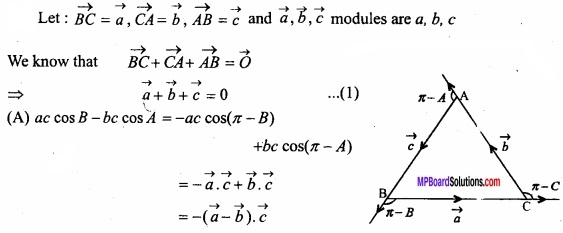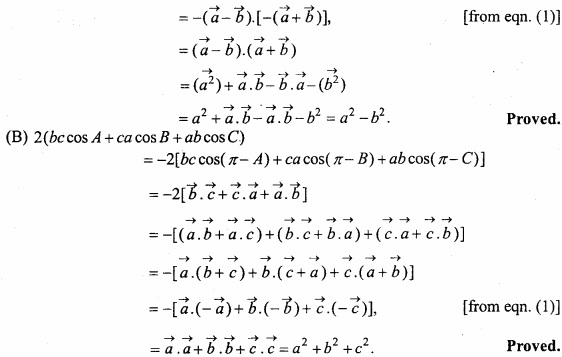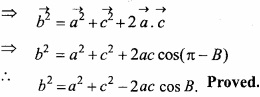MP Board Class 12th Maths Important Questions Chapter 12 Linear Programming
Linear Programming Important Questions
Linear Programming Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
At which point the value of 3x + 2y is maximum under the constraints x + y ≤ 2, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0:
(a) (0,0)
(b) (1.5, 1.5)
(c) (2, 0)
(d) (0,2).
Answer:
(c) (2, 0)
Question 2.
Variables of the objective function of linear programming problem are:
(a) negative
(b) zero or negative
(c) zero
(d) zero or positive.
Answer:
(d) zero or positive
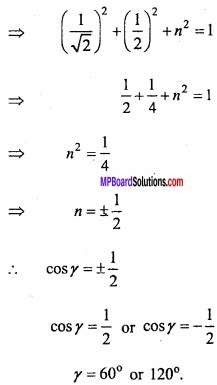
![]()
Question 3.
Consider the inequalities x1 + x2 ≤ 3, 2x1 + 5x2 ≥ 10, x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0, which of the following points like in a feasible region:
(a) (2, 1)
(b) (4, 2)
(c) (2, 2)
(d) (1, 2).
Answer:
(d) (1, 2)
Question 4.
In linear constraints the maximum value of objective function will be:
(a) at centre of feasible region
(b) at (0,0)
(c) at one of the vertices of the feasible region
(d) at the vertex which is situated at maximum distance from (0,0).
Answer:
(c) at one of the vertices of the feasible region
Question 5.
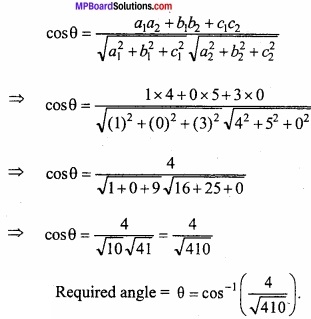
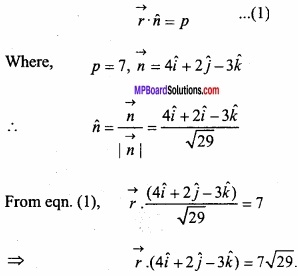
Under constraints x – 2y ≤ 6, x + 2y ≥ 0, x ≤ 6 maximum value of P = 3x + 4y is:
(a) 16
(b) 17
(c) 18
(d) 19.
Answer:
(c) 18
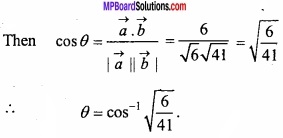
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The function whose maximum and minimum value is to be found subject to given linear constraints is called …………………………..
- The maximum or minimum value of objective function is called …………………………..
- The graph of x ≥ 0 is situated in the …………………… quadrant.
- The process of doing certain specified step in a given order is called …………………………….
- The common region determined by all constraints including the non – negative constraints x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 of a linear programming problem is called the ……………………. for the problem.
Answer:
- Objective function
- Optimum value
- First
- Programming
- Feasible region.
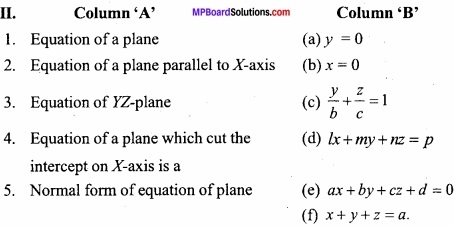
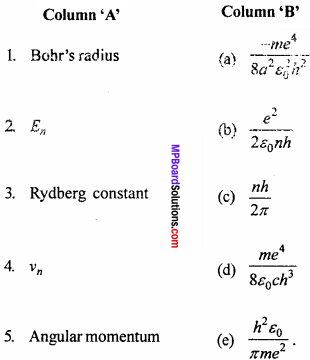
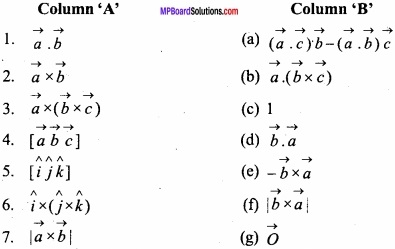
Question 3.
Match the Column:
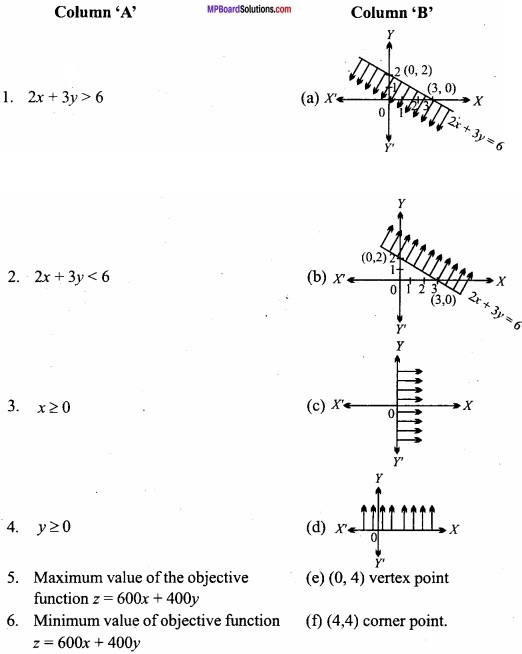
Answer:
- (b)
- (a)
- (d)
- (c)
- (f)
- (e).
Question 4.
Write True/False:
- If the variable x is such that its value lies between two fixed point a and b, then {x: a < x < b} is called closed interval.
- The function whose maximum or minimum value is to be found is called objective function.
- The set of values of the variables satisfying all constraints is called feasible solution of the problem.
- If the feasible region is void, then the problem has bounded solution.
- Graph of two or more than two equation is called linear inequation system.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False.
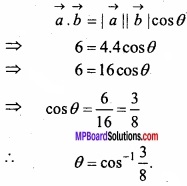
![]()
Question 5.
Write the answer in one word/sentence:
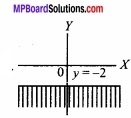
- Represent y ≤ – 2 graphically?
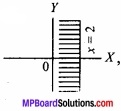
- Represent 2x – 4 ≤ 0 graphically?
- The graph of inequation x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 will be situated in which quadrant?
- What word is used for the maximum or minimum value of the objective function?
- P = 5x + 3y is an objective function. The coordinate of the vertices of feasible region are (3, 0), (12, 0), (0, 6). Write minimum value of objective function?
Answer:
1. 
2. 
3. First
4. Optimum value
5.15.
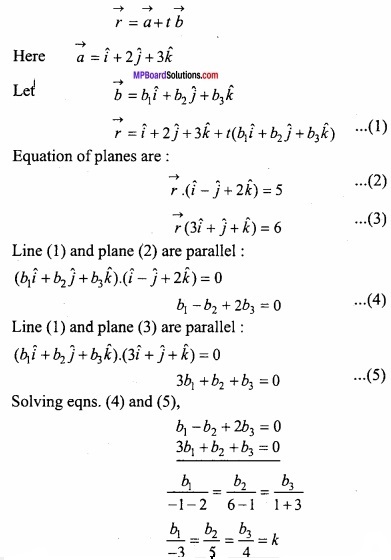
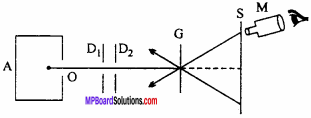
Linear Programming Long Answer Type Question – I
Question 1.
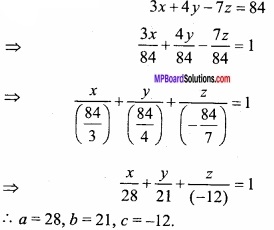
Find the maximum value of the function P = 2x + 3 y when the constraints are:
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0,x + 2y ≤ 10; 2x + y ≤ 14?
Solution:
Because of the constraints x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0, the graph of other linear inequation should be found on first quadrant only.
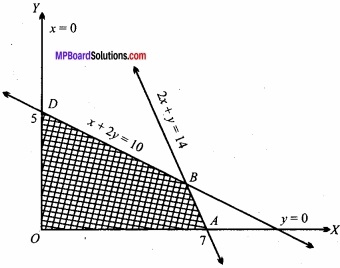
For x + 2y = 10, the table for values of x and y are given below:

For testing point (0, 0) the inequation x + 2y ≤ 10 therefore the region is towards origin 0 + 2 × 0 ≤ 10.
For 2x + y = 14 the table for the values of x and y are given below:
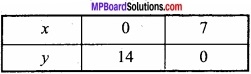
For origin (0, 0), 2x + y ≤ 14 is true because 2(0) + 0 ≤ 14. Therefore the region is towards the origin.
The required graph is the common region of the inequations shown by shaded portion OABD of the above graph whose vertices OABD the values of objective function P=2x + 3y is shown in the following table:
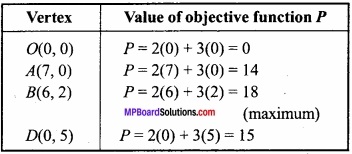
∴ The maximum value of P is 18 which is on point B (6, 2) for which x = 6, y = 2.
Question 2.
Find the minimum value of function P = x + y subject to constraints 3x + 2y ≥ 12, x + 3y ≥ 11, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0?
Solution:
Because x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 the graph of other constraints lies on first quadrant. They are
3x + 2y ≥ 12 ………………….. (1)
x + 3y ≥ 11 …………………… (2)
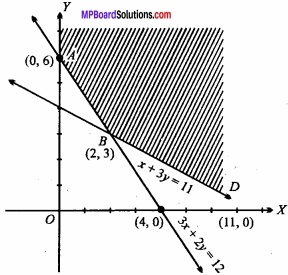
(i) For 3x + 2y = 12 the table for the values of x andy are given below:
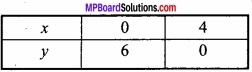
(ii) For x + 3y = 11 the table for the values of x and y are given below:
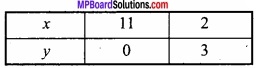
The testing point (0, 0) does not satisfy both the inequations because
3 (0) +2 (0) ≥ 12 which is false
0 + 3(0) ≥ 11 which is false
Therefore the possible region in an open region whose vertices are A, B, D. The calculation of objective function according to the fundamental extreme point theorem is as below:
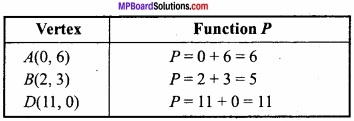
Therefore, minimum value of P is 5 when x = 2,y = 3.
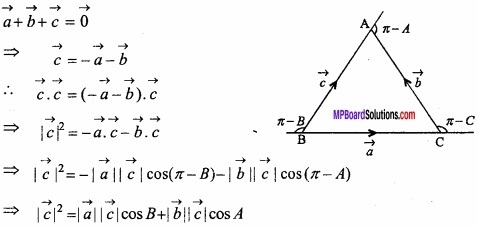
Question 3.
Show graphically the fixed region by the inequations given below:
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 2x + 5y ≤ 16, 2x + y ≤ 8?
and find the value of* andy for which the function P = 5x+ 4y has maximum value?
Solution:
2x + 5y ≤ 16 ……………………. (1)
and 2x + y ≤ 8 …………………………. (2)
\(\frac { 2x }{ 16 } \) + \(\frac { 5y }{ 16 } \) ≤ 1, [from inequation (1)]
⇒ \(\frac{x}{4}\) + \(\frac { y }{ \frac { 16 }{ 5 } } \) ≤ 1 ………………….. (3)
Similarly, \(\frac { 2x }{ 8 } \) + \(\frac { y }{ 8 } \) ≤ 1 [from inequation (2)]
⇒ \(\frac{x}{4}\) + \(\frac{y}{8}\) ≤ 1 ……………………….. (4)
The region x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 representing graphically the inequations (3) and (4),
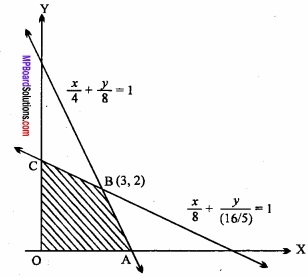
Lines \(\frac{x}{4}\) + \(\frac{y}{8}\) = 1
and \(\frac{x}{4}\) + \(\frac { y }{ \frac { 16 }{ 5 } } \) = 1
Intersects each other at the point B(4, 2). Hence OABC is the region bounded by the lines, where the coordinates of the points O, A, B, C are 0 (0, 0), A (4, 0), B (3, 2), C (0, \(\frac{16}{5}\) ) respectively
On the vertices the value of P = 5x + 4y will be following:
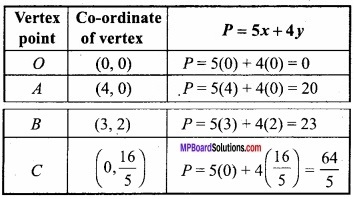
From the above table the maximum, value of P is 23 on the point B (3, 2).
Hence the value is maximum at x = 3 and y = 2.
Question 4.
If a young man rides his motorcycle at 25 km per hour, he has to spend Rs. 2 per km on petrol, if he rides it in a faster speed of 40 km per hour, the petrol cost increases to Rs. 5 per km. He has Rs. 100 to spend on petrol and wishes to find what is maximum distance he can travel within one hour. Express this as a linear program¬ming problem and then solve it?
Solution:
Let the distance travelled at 25 km/hour = x km.
And distance travelled at 40 km/hour = y km.
We wish to maximize z = x + y subject to the constraints
2x + 5y ≤ 100 …………………….. (1)
\(\frac{x}{25}\) + \(\frac{y}{40}\) ≤ 1
Now let us solve the linear programme in the following way:
As x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 we shall shade the solution set of the other inequalities in the first quadrant.
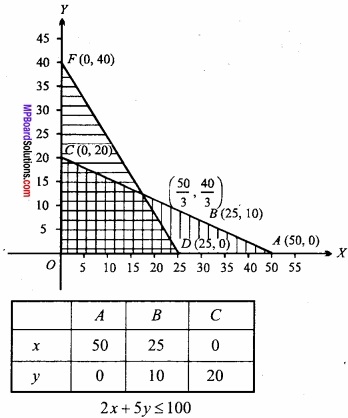
For, eqn. (1),
2x + 5y = 100
x = \(\frac{100 – 5y}{2}\)
Now the test point O (0, 0) makes the inequation (1) true so we shade the half plane containing (0, 0).
For eqn.(2), \(\frac{x}{25}\) + \(\frac{y}{40}\) ≤ 1
or 8x + 5y ≤ 200
⇒ 8x + 5y = 200
⇒ x = \(\frac{200-5y}{8}\)
Again the test point (0, 0) makes the inequality (2) true so we shade the half plane containing (0, 0).
The vertices of feasible region are
0(0,0), D (25, 0), G ( \(\frac{50}{3}\), \(\frac{40}{3}\) ) , C (0, 20)
Let us caluculate z = x + y at these points.
At D (25, 0) z = 25 + 0 = 25
At G ( \(\frac{50}{3}\), \(\frac{40}{3}\) ) z = \(\frac{50}{3}\) + \(\frac{40}{3}\) = 30
At C (0, 20) z = 0 + 20 = 20
Hence, Maximum z = 30 km at ( \(\frac{50}{3}\), \(\frac{40}{3}\) ).
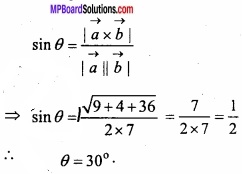
![]()
Question 5.
A manufacturer plants to install some new machines in his workshop. Type A machine costs Rs. 800 and occupies 3 square metre of floor space. Type B machine costs Rs. 1600 and occupies 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) square metres of space. He can spend Rs. 20,000 altogether and the space available is 30 sq. metres. Type A turns out 10 components per hour where as type B 15 per hour. Trade restrictions compel him to have at least 3 machines of type A and 4 machines of type B?
What is the maximum number of machines he can install? Which arrangement gives him the maximum output?
Solution:
Let us assume that he buys x machines of type A and y machines of type B. Taking on account the costs of the machines and the total money available 800x + 1600y ≤ 20,000
or x + 2y ≤ 25 ………………. (1)
Again using the conditions of the space available and the space required for the machines
3x + \(\frac{3}{2}\) y ≤ 30
2x + y ≤ 20 …………………….. (2)
Also using the trade restrictions on having two types of machines
x ≥ 3 ……………………….. (3)
y ≥ 4 ……………………. (4)
The number of machines he buys will be x + y and the total output (10x + 15y) per hour.
Let N = x+y ……………………. (5)
and O = 10x + 15y ……………………… (6)
Now our problem is to maximize (5) and (6) subject to constraints (1) to (4).
The shaded region is the feasible region. The comers of the feasible region are the points (3, 4), (8, 4), (5, 10) and (3, 11).
At the point (3, 4)
N = 3+ 4 = 7,O = 30+ 60 = 90
At the point (8,4)
N = 8+ 4 = 12, O = 80 + 60 = 140
At the point (5, 10)
N = 5 + 10 = 15, O = 50 + 150 = 200
At the point (3, 11)
N = 3 + 11 = 14, O = 30 + 165 = 195
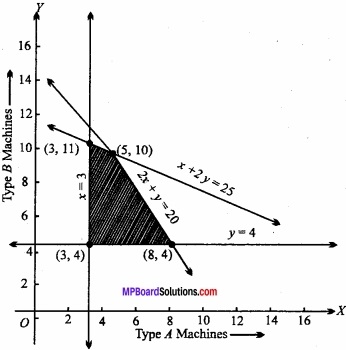
The maximum number of machines he can buy is 15. Also maximum output can be obtained by using 5 machines of type A and 10 machines of type B.
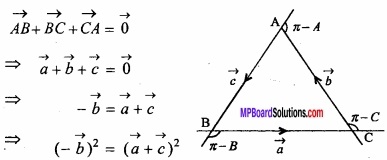
Question 6.
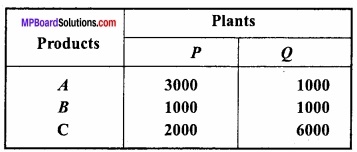
A soft drinks firm has two bottling plants one located at P and other at Q? Each plant produces three different soft drinks A, B and C? The capacities of two plants in number of bottles per day are as follows:
A market survey indicates that during the month of April there will be a demand for 24,000 bottles of A, 16,000 bottles of B and 48,000 bottles of C. The operating cost per day of running plants P and Q are respectively Rs. 6,000 and Rs. 4,000. Find graphi-cally how many days should the firm run each plant in April so that the production cost is minimized?
Solution:
Suppose that firm runs plant P for x days and plant Q for y days in April so the total operating cost of two plants is given by:
z = 6000x + 4000y (objective function)
As P plant produces 3000 bottles and Q plant produces 1000 bottles of drink A per day, so total production of drink A in the supposed period is
(3000x + 1000y) bottles
But there will be a demand for 24,000 bottles of this drink so the restriction 3000x + 1000y ≥ 24000 i.e., 3x + y ≥ 24
Similarly for the other two drink we have the constraints 1000x + 1000y ≥ 16000 i.e., x + y ≥ 16
2000 x + 6000 y ≥ 48000 i.e., x + 3y ≥ 24
Moreover x and y are non – negative. So x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Mathematically, the given problem now reduces to minimize
z = 6000 x – 4000 y (objective function)
Subject to the conditions
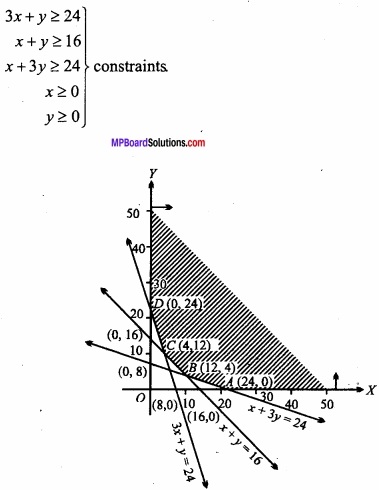
The graph of the system or inequations can be easily obtained arid is as shown in figure, As (x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 the graph has been drawn in the first quadrant only). The points in the region which is common shaded area unbounded above constitutes the graph of the system of inequations.
Now the minimum value of the cost function z = 6000 x + 4000 y
As at one of the points A (24, 0), B (12,4), C (4, 12) and D (0, 24).
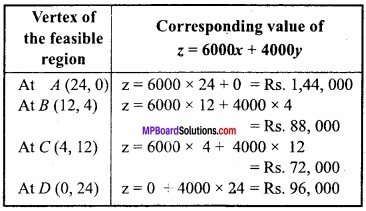
Hence P is minimum at x = 4 and y = 12. Therefore for minimum cost the firm P should run for 4 days and Q for 12 days.
Minimum cost will be Rs. 72,000.
![]()
Question 7.
A and B are the two tailor A earns Rs. 150 per day and B earns Rs. 200 per day? A can stich 6 shirts and 4 pants per day and B can stich 10 shirts and 4 pants per day? Formulate the above as a linear programming problem (L.P.P.) for minimizing the cost of at least 60 shirts and 32 pants? (CBSE 2005)
Solution:
Let, tailor works x days and tailor B works y day.
Hence, invest function is
Z = 150x + 200y
According to the function, tailor A, stich 6 shirts and B stich 10 shirts, for minimizing the cost of at least 60 shirts.
6x + 10 ≤ 60
and tailor A stich, 4 pants and B stich 4 pants, for minimizing the cost of at least 32 pants.
4x + 4y ≤ 32
and x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Similarly,
For minimizing invest function Z = 150x + 200y subject to the following contraints
6x + 10y ≤ 60
4x + 4y ≤ 32.
Note: For drawing the graph of constraints 6x + 10y ≤ 60, we will draw the graph of 6x + 1o y = 60.
\(\frac{6x}{60}\) + \(\frac{10y}{60}\) = 1
\(\frac{x}{10}\) + \(\frac{y}{6}\) = 1 ……………….. (1)
Line (1) cuts the intercepts 10 and 6 respectively with the coordinates axes.
i.e., By joining the points P(10,0) and Q( 0,6) get the graph of line 6x +10y = 60 easily.
Similarly draw the graph of 4x + 4y = 32
⇒ \(\frac{4x}{32}\) + \(\frac{4y}{32}\) = 1
⇒ \(\frac{x}{8}\) + \(\frac{y}{8}\) = 1 …………………….. (2)
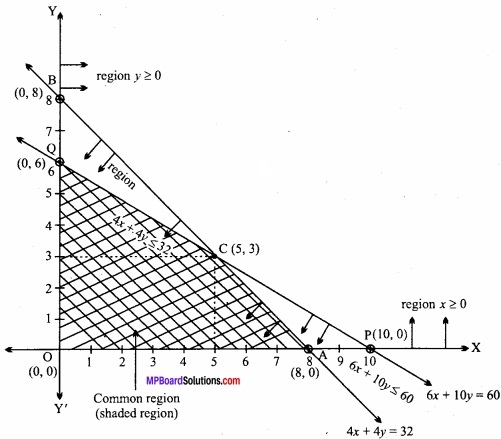
Line (2) cuts the intercepts 8, 8 with the coordinates respectively i.e., graph of line 4x + 4y = 32 can be find by joining the points A(8, 0) and B(0, 8).
(i) x ≥ 0, all points above and on the X – axis in the solution set.
(ii) y ≥ 0, all points above and on the Y – axis in the solution set.
(iii) Taking testing point O (0, 0) for finding the solution set of 6x + 10y ≤ 60 we have, 6 × 0 + 10 × 0 < 60
⇒ 0 < 60 , which is true.
Hence all points on the line 6x + 10y = 60 including all points near to the origin is the solution set of 6x +10y ≤ 60.
(iv) Similarly, solution set of 4x + 4y ≤ 32 towards to the origin and each point on the line 4x + 4y = 32.
Hence, the common region of x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 6x + 10y ≤ 60 and 4x + 4y ≤ 32 shown in above graph by shaded region.
i.e., the required region is OACQ whose corner points are O (0, 0), A (8, 0), C (5, 3) and Q (0, 6).
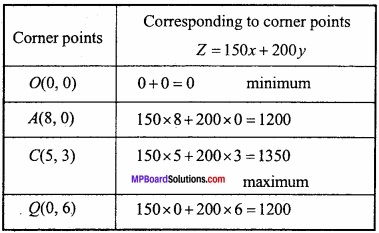
Minimum value of invest Z = 150x + 200y is 0 and maximum invest cost of Rs. 1350 is corresponding to point (5, 3).