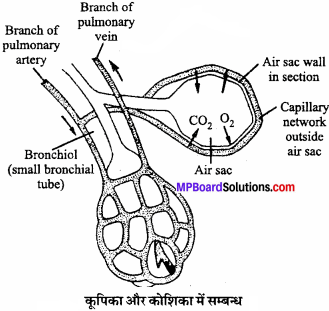
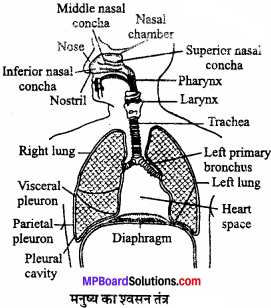
MP Board Class 11th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 9 Small Business
Small Business Important Questions
Small Business Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which is not included in small business –
(a) Business run by womens
(b) Cottage industries
(c) Khadi and rural industry
(d) Industry having investments up to 2 crore.
Answer:
(d) Industry having investments up to 2 crore.
Question 2.
Which is not the characteristics of small business –
(a) Unlimited work scope
(b) Free management
(c) Priority of workers
(d) Limited investment.
Answer:
(a) Unlimited work scope
Question 3.
In India the small business can be classified into how many categories on the basis of capital investment –
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d)5.
Answer:
(c) 2
Question 4.
Which is not the characteristics of cottage industry –
(a) Use of foreign technique in production
(b) They are organized by personal resources of the members
(c) Simple tools are used in it
(d) Small capital investment.
Answer:
(a) Use of foreign technique in production
Question 5.
India hasof small business undertakings –
(a) 95
(b) 92
(c) 90
(d) 94.
Answer:
(a) 95
Question 6.
In India small business units have ………….. position.
(a) 3rd
(b) 2nd
(0)4
(d) 1st.
Answer:
(b) 2nd
![]()
Question 7.
Investment limit in small business:
(a) 20 lakh
(b) 25 lakh
(c) 10 lakh
(d) 2 lakh.
Answer:
(b) 25 lakh
Question 8.
In India which norm is not used for the measurement of business units –
(a) Number of person engaged in the business
(b) Capital investment in the business
(c) Quantity of production
(d) Number of educated people in the business.
Answer:
(d) Number of educated people in the business.
Question 9.
How many goods are reserved for small business –
(a) 800
(b) 700
(c) 900
(d)500.
Answer:
(a) 800
Question 10.
NABARD was established in the year –
(a) 1982
(b) 1985
(c) 1984
(d) 1986.
Answer:
(a) 1982
Question 2.
Question (A)
- For establishing of small scale Industries …………….. is needed.
- Cottage industries are directey related with ……………. area.
- By cottage industries we can stop …………….. to leave die village.
- By small scale industries we can increase ……………….. development.
- For establishment of small and cottage industries government help ……………..
Answer:
- Finance
- Rural
- Rural public
- Economic
- Financially.
![]()
Question (B)
Fill in the blanks:
- First Industrial area established in 1956 in …………….
- District Industrial center established on …………….
- Problem of rural employment can be solved by development of …………….
- …………… is a base of Indian small scale industry ……………..
- In small scale industries there are ……………. chances in employment then large Scale Industries.
Answer:
- Okhal
- 1978
- Small scale industries
- Mixed economy
- More.
Question 3.
Write true or false:
- Small scale industries are smaller than cottage industries.
- Small scale industries are mainly established in village.
- For establishment of small scale industries we need huge amount of capital.
- For establishing cottage industries govt, do not provide any aid.
- Government step up for establishing small and cottage industries.
- Small scale industries are helpful in improving personal skill.
- National small scale industries corporation is established in 1955.
- There are more flexibility in small scale industries.
- Small scale industries are not able to produce foreign exchange.
- The series of small scale, medium scale is determined on the basis of invested capital.
Answer:
- False
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True.
Question 4.
Give answer in one word / sentence:
Question 1.
What is meaning of small business?
Answer:
A small business is an enterprise whose investment in plant and machinery is not more than 1 crore.
Question 2.
Name the four measures which are used for measurement of business undertaking?
Answer:
- Quantity of capital investment
- Value of production
- Quantity of production
- Number of labours.
![]()
Question 3.
Name four units included in the small business.
Answer:
- Small scale industries
- Subsidiary small industrial units
- Export based units
- Cottage industries.
Question 4.
Write two characteristics of small scale industries.
Answer:
The characteristics are:
- Labours are kept on wages
- Machines are run by electricity.
Question 5.
Write three examples of small scale industries.
Answer:
They are:
- Carpet making of Panipat
- Hosiery work of Ludhiana
- Scientific machine making industries of Ambala.
Question 6.
What is subsidiary small scale industries?
Answer:
Those units which sells their minimum 50% of their produce to those units which so far are called as patent units.
Question 7.
What are export oriented units?
Answer:
Those units which export their 50% or more of their produce is called as export oriented units.
Question 8.
What is cottage industry as per Treasury Commission?
Answer:
According to the Treasury Commission “any unit which is run by the members of the family on full time or part time basis is called as cottage industry”
Question 9.
Write any three characteristics of cottage industry.
Answer:
The Three characteristics of cottage industries are:
- They are run by the member of the family
- These units many labour run their unit in their house only.
- These units generally fulfill the local needs.
![]()
Question 10.
Write three problems of small business in India.
Answer:
The three problems are:
- Lack of finance
- Lack of distribution facilities
- Lack of skill labours.
Question 11.
Write different types of units established in rural, backward areas or mountaneous region?
Answer:
- Agriculture based units
- Cottage industries
- Khadi and rural undertakings.
Question 12.
Write three functions of the SIDBI?
Answer:
The three functions of the SIDBI are:
- Help in expansion of small scale industrial units.
- Providing loans at simple norms.
- Providing facilities of factoring.
Question 13.
What do you know about small business industrial ministry?
Answer:
This ministry takes decision for the progress and development of small business units. They also make programme and projects for them.
Question 14.
What do you know about agriculture and rural industry ministry?
Answer:
This ministry works as nodal agency for the khadi and rural industry, small and minor units etc. They also execute the Prime Minister Employment Opportunity Scheme. They also execute the different policy, projects etc. related to the agriculture and rural industry along with the medium of rural industries commission, handloom board, coir board and silk board etc.
Question 15.
Write the different help given by government in order to promote small industries?
Answer:
The different helps given by government in order to promote small industries are:
- To make industrial free horn selling
- To make provisions for making shade in the developed land
- For providing provision of 10 – 15% economic help in making of fixed assets.
Question 16.
Write two praises given by the government for small scale industries?
Answer:
- Along 800 commodities have been reserved for the small industries.
- Concession in production upto one crore.
Question 17.
Write full form of NABARD?
Answer:
National Agriculture and Rural Development Bank.
Question 18.
Which institution was established in 1982 for unified Fural development bank?
Answer:
NABARD
Question 19.
Name four institution which helps in promotion of small industries?
Answer:
- Commercial Bank
- Co – operative Bank
- National Agriculture and Rural.
Question 20.
Where is head office of NSIC?
Answer:
New Delhi.
![]()
Question 21.
Name the unit run by members of the family?
Answer:
Cottage industry.
Question 22.
Which industry is run both in village and urban areas?
Answer:
Cottage industry.
Question 23.
What is investment limit of small industries?
Answer:
10 crore.
Question 24.
What is full form of NSIC?
Answer:
National Small Industries Corporation.
Question 25.
What is full form of DIC?
Answer:
District Industrial Centre.
Small Business Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write meaning of small business.
Answer:
Small business is divided into following categories:
- Capital investment not more than 1 crore in the normal small business.
- Fixed capital should not be more than 25 lakh in the small undertakings.
- If subsidiary industries having fixed capital more than 1 crore will be considered as big but in this undertaking has to sell minimum 50% of their produce to the other under taking.
Question 2.
Write the objectives of fund scheme made for the progress of traditional industries.
Answer:
The objectives of fund scheme made for the progress of traditional industries are:
- To develop traditional industrial units in different parts of die country.
- To develop innovation and traditional skill.
- Helpful in the development of technology.
- To develop distribution possibilities.
- To create long term employment opportunities-
Question 3.
“Small business units are helpful in creation of employment opportunities”. Discuss.
Answer:
Unemployment problem is viscous problem in India. Labour based industries are required for creation of employment opportunities for the vast population of our country. Small business establishment lead to maximum employment opportunities where less capital and more labour can be employed. Small business can also provide business opportunities and self – employment to the lakhs of educated people of the country.
Question 4.
How small business is helpful in the balanced development of different regions of the country? Clarify.
Answer:
Small business units are established in those semi-urban areas which lead to the development of backward areas. Decentralization of the industries can make balanced regional development. By means of small industries, production of those goods are done which have limited local demand and this makes multiplicity in industrialization.
![]()
Question 5.
Give suggestion to promote the small industries?
Answer:
Followings are the suggestion to promote the small industries :
- For providing finance establishment of rural industries development bank.
- Giving loan by different public sector institutions to small industries on the basis of priority.
- Arrangement of training for small industries.
- Making arrangement of raw material and professional management.
Small Business Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the definition used by Government of India for small scale industries?
Answer:
The Government of India defines the small scale industries as per their investment in plant and machinery. In India the capital is scarce and labour is abundant this measure asks to keep in view the socio – economic environment.
Question 2.
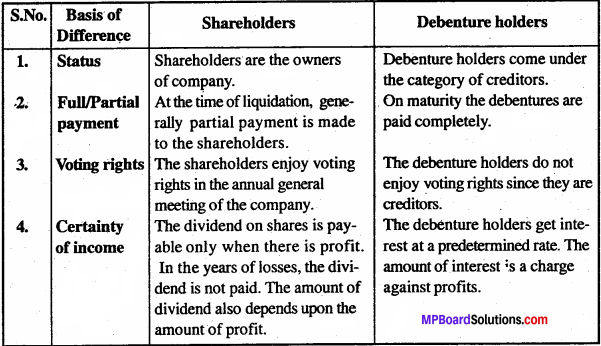
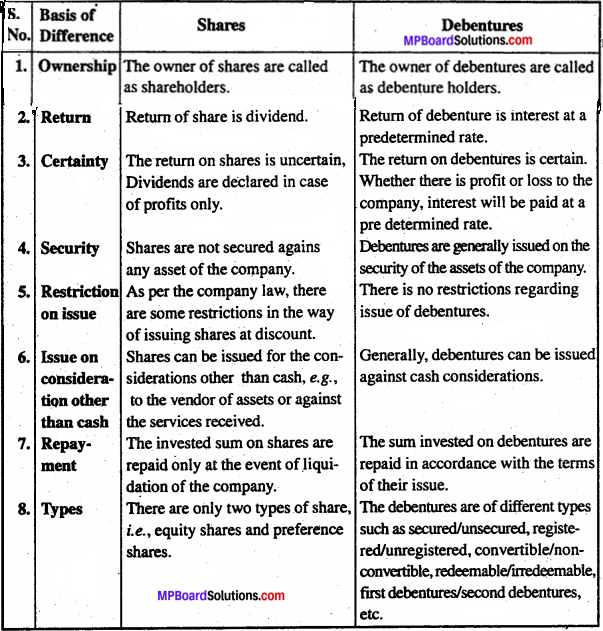
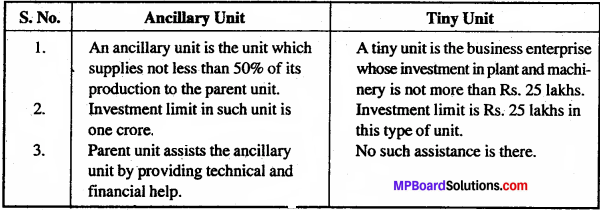
How would you differentiate between an ancillary unit and a tiny unit?
Answer:
Differences between an ancillary unit and a tiny unit:
Question 3.
What are the different parameters used to measure the size of business?
Answer:
Several parameters can be used to measure the size of business units. These include the number of persons employed in business, capital invested in business, volume of output or value of output of business and power consumed for business activities. Appropriate parameter may be used depending on the need and advantages or limitations of various measures.
Question 4.
State the features of cottage industries?
Answer:
Cottage industries are those where artistic goods are produced using manual techniques. For e.g. handloom, weaving etc. It is characterised by the following features:
- Cottage industries are organised by individuals, with private resources.
- Cottage industries normally use family labour and locally available talent.
- The equipment used in cottage industries is simple.
- Capital investment in cottage industries is small.
- Cottage industries produce simple products normally in their own premises.
![]()
Question 5.
How do small industries contribute to the development of Rural areas?
Answer:
India is a developing country and in developing countries the scope of small scale industries are very wide. It is contributing to the socio – economic development in the following ways:
1. Contribution in GDP, Small industries in India account for 95% of the industrial units in the country. They contribute almost 40% of the gross industrial value added in the economy.
2. Contribution in Exports 45% of the total exports from India come from small scale industries. Gems and jewellery, handicrafts, sports goods, etc. are some items of exports from small scale sector.
3. Employment generation small industries are the second largest employers of human resources. After agriculture and generate more number of employment opportunities per unit of capital invested compared to large industries.
4. Variety of production small industries produce a wide variety of products ranging from mass consumption goods, readymade garments, hosiery goods, stationery items, soaps and detergents, domestic utensils, leather, plastic and rubber goods, processed foods and vegetables, wood and steel furniture, paints, varnishes, safety matches, etc.
To the sophisticated items like electric and electronic goods, drugs and pharmaceuticals, agricultural tools and equipment and several other engineering products. Handlopms, handicrafts and other products from traditional village industries add to this diverse production from SSIs.
Question 6.
Write characteristics of small business.
Answer:
Followings are the characteristics of small scale industries:
- A small scale unit is generally owned by single entrepreneur or partnership.
- Small scale enterprises are generally managed by the owners only so there is die advantages of direct motivation, personal care, secrecy, flexibility etc.
- Small scale enterprises generally use labour intensive techniques.
- A small scale enterprise generally operates in a compact area however products are exported all over the world.
Small Business Long Answer Type Questions – I
Question 1.
How do small industries contribute to the socio – economic development of India?
Answer:
India is a developing country and in developing countries the scope of small scale industries are very wide. It is contributing to the socio – economic development in the following ways:
1. Contribution in GDP:
Small industries in India account for 95% of the industrial units in the country. They contribute almost 40% of the gross industrial value added in the economy.
2. Contribution in Exports:
45% of the total exports from India come from small scale industries. Gems and jewellery, handicrafts, sports goods, etc. are some items of exports from small scale sector.
3. Employment Generation:
Small industries are the second largest employers of human resources, after agriculture and generate more number of employment opportunities per unit of capital invested compared to large industries.
4. Variety of Production:
Small industries produce a wide variety of products rang-ing from mass Consumption goods, readymade garments, hosiery goods, stationery items, soaps and detergents, domestic utensils, leather, plastic and rubber goods, processed foods and vegetables, wood and steel furniture, paints, varnishes, safety matches, etc.
To the so – phisticated items like electric and electronic goods, drugs and pharmaceuticals, agricultural tools and equipment and several other engineering products. Handlooms, handicrafts and other products from traditional village industries add to this diverse production from SSIs.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the role of small business in rural India.
Answer:
Small Scale enterprises provide the numerous benefit in rural area.
The role of small business in rural India is explained in the following points:
1. Non – farm Employment Traditionally, rural households in India were exclusively engaged in agriculture. But now rural households have varied and multiple sources of income and participate in a wide range of non – agricultural activities such as wage employment and self – employment in commerce, manufacturing and services, along with the traditional rural activities of farming and agricultural labour. This can be largely attributed to the setting up of agro – based rural small industries.
2. Employment for Artisans Cottage arid rural industries play an important role in providing employment opportunities in the rural areas, especially for the traditional artisans and the weaker sections of society.
3. Prevention of Migration Development of rural and village industries can also prevent migration of rural population to urban areas in search of employment.
4. Poverty alleviation village and small industries are significant as producers of consumer goods and absorbers of surplus labour, thereby addressing the problems of poverty and unemployment. Promotion of small scale industries and rural industrialization has been considered by the Government of India as a powerful instrument for realizing the twin objectives of ‘accelerated industrial growth and creating additional productive employment potential in rural and backward areas.
5. Socio – economic aspects these industries contribute amply to other socio – economic aspects, such as reduction in income inequalities, dispersed development of industries and linkage with other sectors of the economy.
Question 3.
Explain the need and importance of small business.
Answer:
Followings are the need and importance of small business:
1. Employment:
Small scale industries are labour intensive so, they provide additional employment to men and women.
2. Use of local resources:
Small business uses the local resources which helps in development of those areas.
3. Balanced Development:
Small business units are established in the backward
areas and semi – urban areas which lead to the balanced development of the region.
4. Simplicity:
It is very simple to start and end the small business undertaking.
5. Motivation:
There is direct relation between the hard work and return, hence, it gives motivation for doing hard work.
Question 4.
Discuss the problems faced by small scale industries?
Answer:
Small business have been facing a large number of problems compared to large scale industries. The scale of operations, shortage of funds, procurement of raw materials are some of them. The detailed description of problems are as follows:
1. Finance the most serious problem faced by SSls is that non – availability of adequate finance to carry out their operations. Small scale sector lacks the creditworthiness and collateral required to raise capital from the capital markets or financial institutions and hence, they depend on local money lenders who charge high interest rates.
These units also suffer from lack of adequate working capital, either due to delayed payment of dues to them or locking up of their capital in unsold stocks.
2. Raw materials another major problem of small business is the procurement of raw materials. If the required materials are not available, they have to compromise on the quality or have to pay a high price to get good quality materials.
They purchase raw materials in small quantities due to lack of storage capacity and hence their bargaining power is low.
3. Managerial skills small business is generally promoted and operated by a single person, who may not possess all the managerial skills required to run the business. Many of the small business entrepreneurs possess sound technical knowledge but are less successful in marketing and may not find enough time to take care of all functional activities. At the same time they are not in a position to afford professional managers.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the incentives provided by the Government for industries in backward and hilly areas?
Answer:
Some of the common incentives provided by the Government for industries in backward and hilly areas are as follows:
1. Land every state offers developed plots for setting up of industries. The terms and conditions may vary. Some states don’t charge rent in the initial years, while some allow payment in installments.
2. Power is supplied at a concession rate of 50%, while some states exempt such units from payment in the initial years.
3. Water is supplied on no profit-no loss basis or with 50% concession or exemption from water charges for a period of 5 years.
4. Sales Tax in all union territories, industries are exempted from sales tax, while some states extend exemption on for 5 years period.
5. Octroi most states have abolished octroi.
6. Raw materials units located in backward areas get preferential treatment in the matter of allotment of scarce raw materials like cement, iron and steel etc.
Question 6.
What are the future expectations from the small level industries in India? Clarify.
Answer:
The present Era is the regime of WTO, in which the rules of trade are subject to frequent changes as per global expectations. As a founder member of WTO, India has too committed itself to the policy framework of WTO. As a result, small business is also moving away from the pre – liberalization era of protection.
Infact small business sector should view globalisation as an opportunity for its active participation as suppliers of specialized components and parts. If small businesses are to maintain their market share and healthy growth, they have to create a level playing field for themselves. In short the mantra of success for small businesses in this modem era has to be think global, act local.
![]()
Question 7.
Write a note on Small Industries Development Bank of India?
Answer:
This bank was established in the year 1989 as the public corporation. It started its working on 2 April, 1990. This bank is the main institution for the small industries. Followings are its functions:
- To provide loans and renewals of the banks of small industries and state finance corporations.
- To discount the bills of small industries get from sales.
- To develop the small industries in its distribution facilities.
- To help in development of industrial schemes.
- To provide technical services.
- To provide equity capital to the women and retired army personnels.
Question 8.
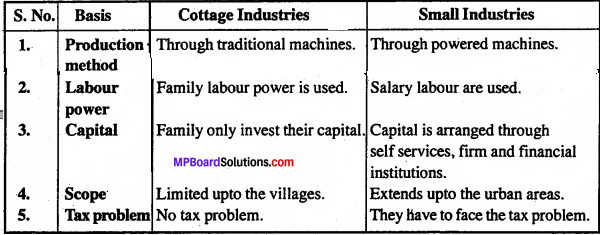
Differentiate between Cottage Industry and Small Industries?
Answer:
Differences between Cottage Industies and Small Industries:
Question 9.
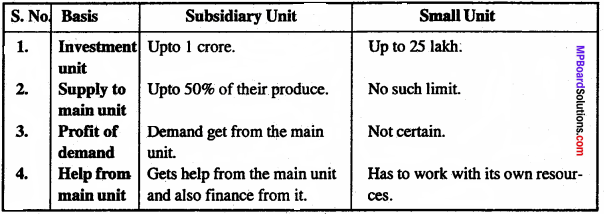
Differentiate between Subsidiary unit and Small unit?
Answer:
Differences between Subsidiary unit and Small unit:
Small Business Long Answer Type Questions – II
Question 1.
What measures has the government taken to solve the problem of finance and marketing in the small scale Sector ?
Answer:
The contribution of small scale industries are remarkable. Thus, Government has provided the following institutional support to solve the problem of finance and marketing in the small scale sector.
1. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD):
NAB ARD was setup in 1982, to promote integrated rural development Apart from agriculture, it supports small industries, cottage and village industries, and rural artisans.
It provides credit and offers counselling and consultancy services and organizes training and development programmes for rural entrepreneurs.
2. The Rural Small Business Development Centre (RSBDC):
It was set up by the – world association for small and medium enterprises and is sponsored by NAB ARD. It works for the benefit of socially and economically disadvantaged individuals and groups.
It aims at providing management and technical support to current and prospective micro and small entrepreneurs in rural areas.
3. Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI):
SIDBI was set up as an apex bank to provide direct/indirect financial assistance under different schemes, to meet credit needs of small business organizations and to co-ordinate the functions of other institutions in similar activities.
4. The National Commission for Enterprises in the Unorganized Sector (NCEUS):
The NCEUS was constituted in September, 2004, with the objectives of recommending measures considered necessary for improving the productivity of small enterprises in the informal sector and to enhance the competitiveness of the sector in the emerging global environment by developing linkages of the sector with other institutions in the areas of credit, raw materials, infrastructure, technology upgradation, marketing, etc.
5. Rural and Women Entrepreneurship Development (RWED):
The Rual and Women Entrepreneurship Development programme aims at promoting a conducive busi-ness environment and at building institutional and human capacities that will encourage and support the entrepreneurial initiatives of rural people and women by providing training and advisory services.
6. Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI):
The Central Government set up this fund to make the traditional industries more productive and competitive and to facilitate their sustainable development.
The main objectives of SFURTI are to develop clusters of traditional industries in various parts of the country build innovative and traditional skills, improve technologies and encourage public – private partnerships, develop market intelligence etc.