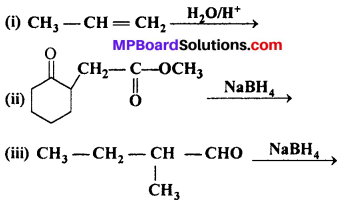
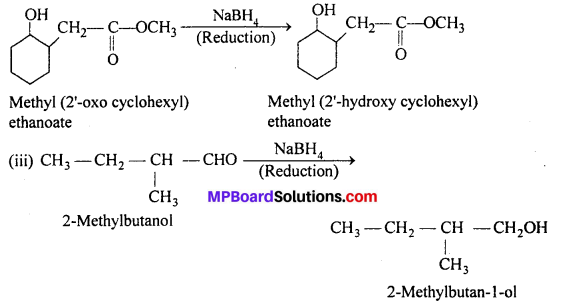
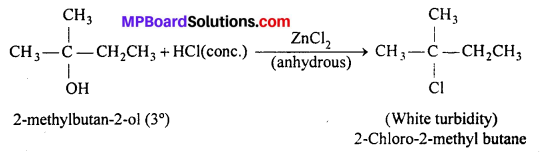
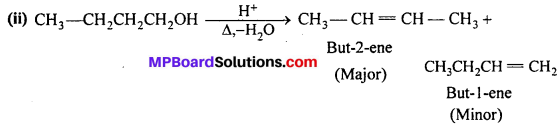
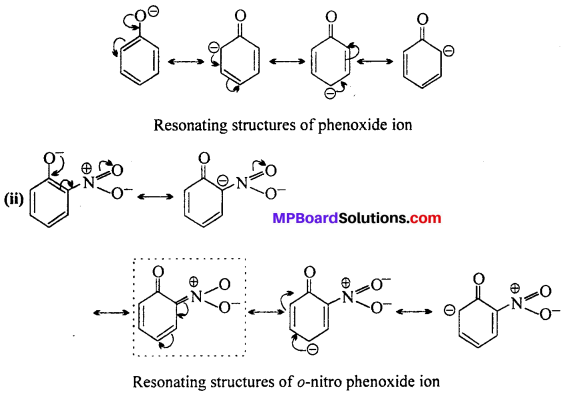
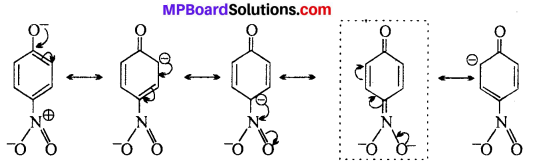
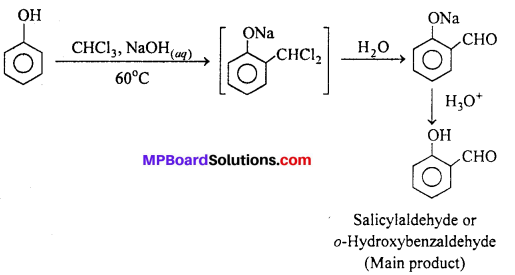
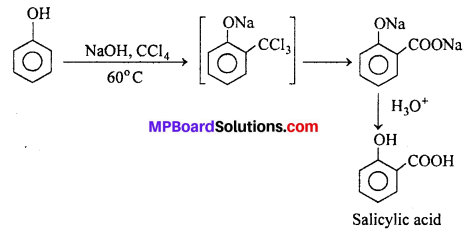
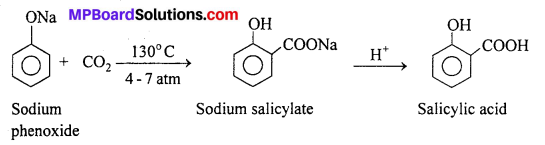
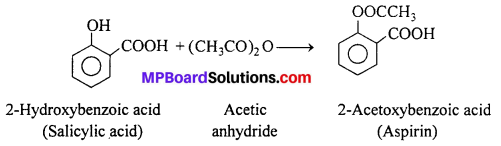
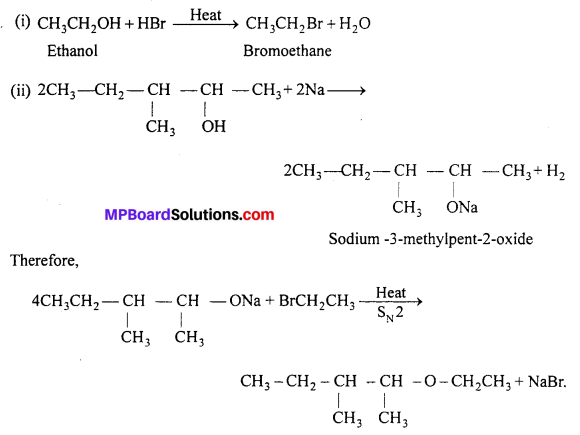
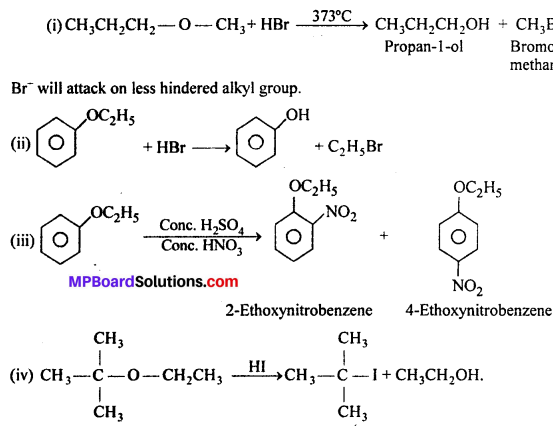
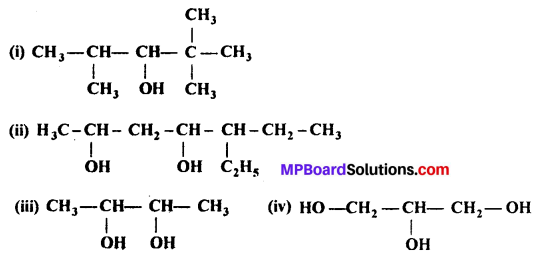
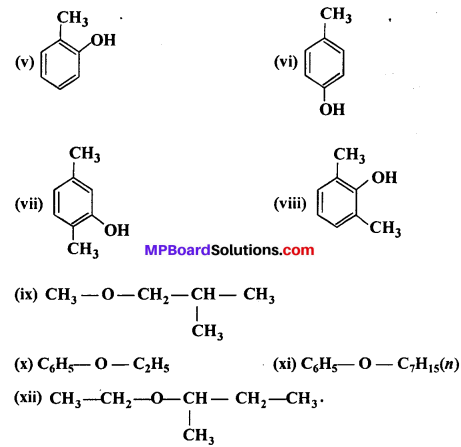
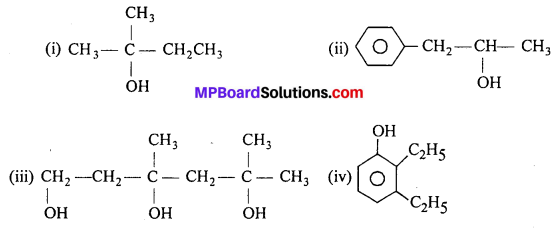
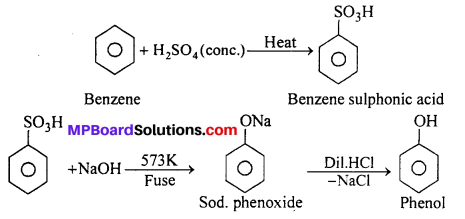
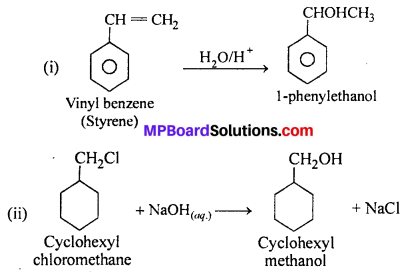
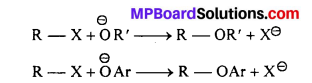
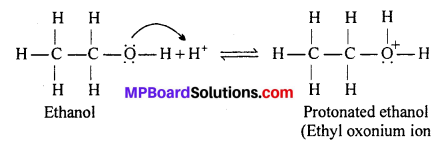
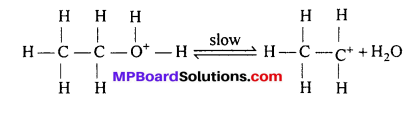
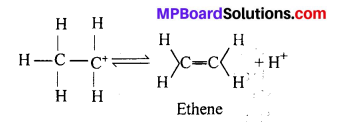
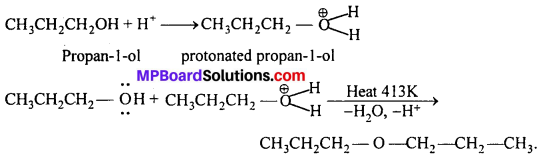
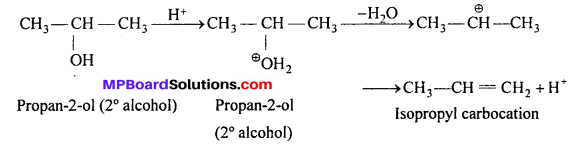
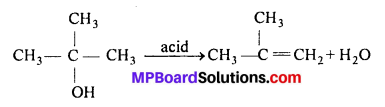
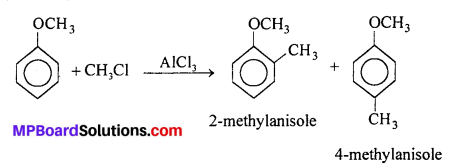
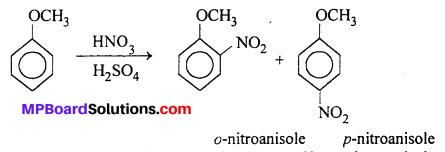
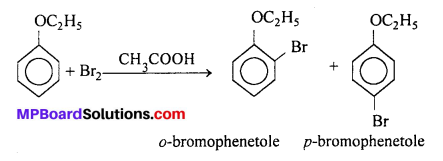
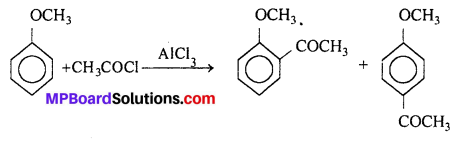
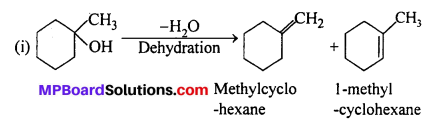
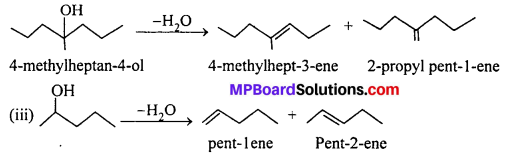
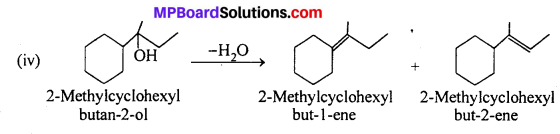
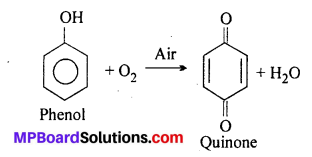
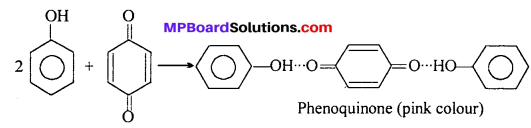
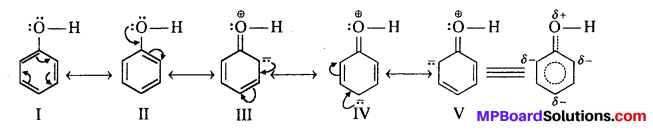
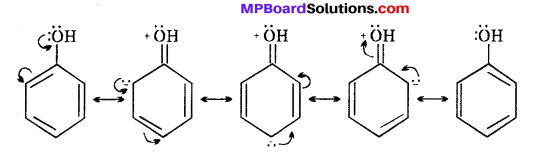
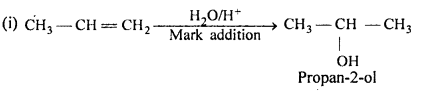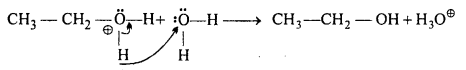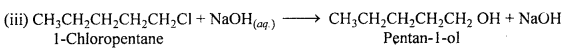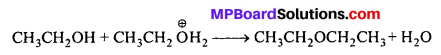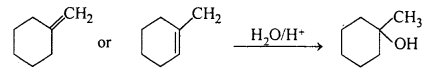MP Board Class 11th Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 16 Preparation of Final Accounts of Sole Trade
Preparation of Final Accounts of Sole Trade Important Questions
Preparation of Final Accounts of Sole Trade Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
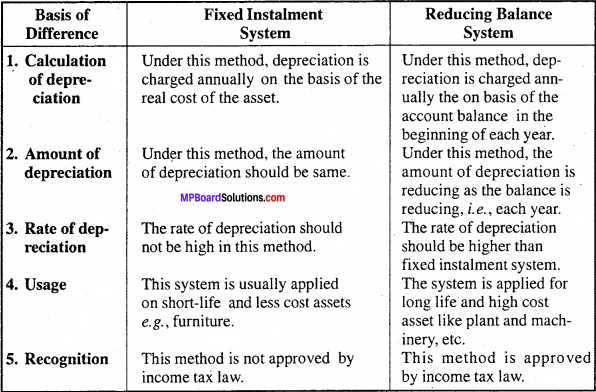
What adjustment are done in trading A/c? Prepare a format of trading A/c and show.
Answer:
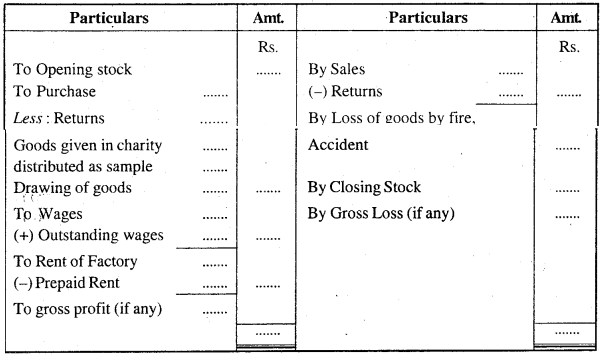
Question 2.
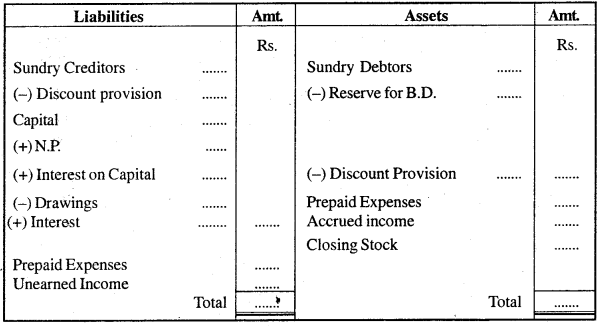
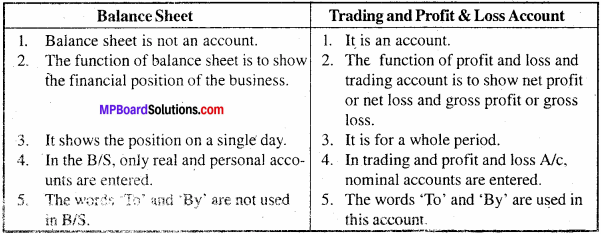
Show the format of a Balance Sheet with adjustments.
Answer:
Pro forma of Balance Sheet as on ……………………