MP Board Class 9th Social Science Solutions Chapter 4 India: Drainage System
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 Text Book Questions
Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
River in its last stage form –
(a) Waterfall
(b) Flood plains
(c) Delta or Estuary
(d) Ox-Bow lake
Answer:
(d) Ox-Bow lake
Question 2.
Which of the following is not the characteristics of the rivers of Northern India?
(a) Less number of Waterfalls
(b) Used for transportation
(c) Meanders are not formed
(d) Receives water from snow and rainfall.
Answer:
(c) Meanders are not formed
Question 3.
Which of the following separates India and Sri Lanka?
(a) Gulf of Cambay
(b) Rann of Kutch
(c) Bay of Bengal
(d) Gulf of Mannar
Answer:
(a) Gulf of Cambay
Question 4.
Which of the following river is known as Dakshin Ganga?
(a) The Narmada
(b) The Krishna
(c) The Kaveri
(d) The Godavari
Answer:
(d) The Godavari
Question 5.
Which states are drained by river Krishna?
(a) Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh
(c) Maharashtra, Kerala, Tamil Nadu
(d) Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisagarh, Orissa
Answer:
(a) Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh
Fill in the blank:
- The state of five rives is known as ……………..
- The river Ganga rises from ………………. glacier.
- The Narmada rises from the …………….. pleatue in Madhya Pradesh.
- Hirakund Dam is built on the river ………………
- Nagarjun Sagar Dam is built on the river ……………….
Answer:
- Punjab
- Gangotri
- Amarkantak
- The Mahanadi
- The Krishna
![]()
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by Drainage System?
Answer:
Drainage System means the river system of a particular area.
Question 2.
What do you mean by river capturing?
Answer:
When one river captures the water of the other river it is called river capturing.
Question 3.
Name four tributaries of river Ganga.
Answer:
Yamuna, Ghaghra, Gandak and Kosi.
Question 4.
Name five tributaries of river Indus.
Answer:
Jhelum, Chinab, Ravi, Beas and Satluj.
Question 5.
What are the different names of river Brahmaputra in Bangladesh?
Answer:
Padma and Meghana are the different names of river Brahmaputra in Bangladesh.
Question 6.
Name five major lakes of India.
Answer:
Wular lake, Chilka lake, Koleru lake, Pullicat lake, Lonar lake.
![]()
Question 7.
Name two rivers which drain in Arabian sea.
Answer:
The Narmada and the Tapi.
Question 8.
Which place is known as the region of five rivers?
Answer:
Punjab is known as the region of five rivers.
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the Indus river system.
Answer:
Indus river system comprises the Indus and its tributaries. The length of the Indus river is about 2900 km. It rises in Tibet near Mansarovar and flows towards west forming a beautiful 500 meters deep gorge in the Laddakh district of Jammu and Kashmir. From here it flows towards Southwest, enters Pakistan and finally joins the Arabian Sea. The five tributaries of Indus are Jhelum, Chmab, Ravi, Beas and Satluj. This region of five rivers is known as Punjab.
Question 2.
Describe the characteristics of the rivers of Northern India.
Answer:
The characteristics of the rivers of Northern India are:
- The rivers of Northern India have their origin in Himalayas and the Northern slopes of Peninsular India.
- Waterfalls are less.
- They are navigable.
- These rivers form deep, valleys.
- These rivers form meanders River courses often shift.
- Receive water from ice and snow.
Question 3.
How do rivers affect the economy? Explain.
Answer:
Rivers play an important role in the economy of our country. Alluvial plains formed by rivers are used for agriculture. Rivers provide fresh drinking water. In the ancient times villages and cities were located on the bank of the rivers. Religious and cultural Centers are located on the banks. Dams are built for hydro – electricity and irrigation.
Question 4.
Explain the location of adjoining seas of India?
Answer:
Indian Peninsula is surrounded by seas from three sides. In its south lies the Indian Ocean, Arabian sea in the west and Bay of Bengal in the east. Andaman Sea is in the east of Andaman Nicobar Islands. Gulf of Mannar separates India and Sri Lanka. Gulf of Cam-bay and Rann of Kutch are located in the coastal part of Gujarat.
![]()
Question 5.
What is river pollution? How could river pollution be prevented?
Answer:
Effluents from industries and sewage from houses are discharged in the rivers. Dead animals are thrown in the rivers. All this pollute the rivers. Spread of Water Hyacinth also pollute the rivers. To overcome the river pollution, it is essential to stop discharging industrial effluents in the rivers. Water of sewage line should be purified. Rivers should be cleaned time – to – time. Public awareness regarding this problem is much more important.
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the drainage system of Northern India.
Answer:
The rivers of Northern India receive water from rainfall as well as melting of snow from ice-capped mountains. As these rivers flow through high mountains they form deep valleys, gorges and waterfalls. In their nature stage deposition in the plains take place. They form meanders, ox-bow lake and flood plains in their middle and lower course. Three large rivers originate from Himalayas:
1. The Indus River System:
This system comprises the Indus and its tributaires. The length of the Indus river is about 2900 km. It rises in Tribet near Mansarovar and flows towards west forming a beautiful 500 meters deep gorge in the Laddakh district of Jammu and Kashmir. From here it flows towards southwest, enters Pakistan and finally joins the Arabian sea. The five tributaries of Indus are Jhelum, Chin’ab, Ravi, Beas and Satluj. This region of five rivers is known as Punjab.
2. The Gangas River System:
The length of river Ganga is more than 2500 km. Its source is near Gangotri. The Ganga enters the plains near Haridwar. Its main tributaries are Yamuna, Ghaghra, Gandak and Kosi. These rivers form a fertile flood plain. They form meanders and ox-bow lakes. Near Ambala a water divide separates the Ganga and the Indus drainage system.
The Ganga receives some of its tributaries like Chambal, Ken, Betwa, Son and Damodar from the peninsular pleteau. Big dams have been built on these rivers which are used for hydro – electricity and irrigation. Flowing southward it forms a delta and finally joins Bay of Bengal. The main stream of the Ganges enters Bangladesh and when it joins Brahmaputra river it is called Meghana.
3. The Brahmaputra River System:
It rises near the Mansarovar iake and the Kailash mountains. It flows parallel to Himalayas and enters Arunachal Pradesh. In India it flows for 1400 km. Its tributaries include Dibang, Luhit, Dhansiri, Kalang etc. River courses often shift during floods. River islands are also formed. It is known as Tsangpo in Tibet, Brahmaputra in India and Padma and Meghana in Bangladesh. It forms a large delta and finally drains into Bay of Bengal.
Question 2.
Compare the rivers of Northern and Southern India.
Answer:
Rivers of Northern India:
- The rivers of Northern India have their origin in Himalayas and the Northern slopes of Peninsular India.
- Waterfalls are less.
- They are navigable.
- These rivers form deep valleys.
- These rivers form meanders.
- Receive water from melting ice and snow.
Rivers of Southern India:
- The rivers of Southern India have their origin in Western Ghats, Satpura and Peninsular Plateau.
- Waterfalls are more.
- They are not navigable.
- They flow in broad valleys.
- These rivers do not form meanders.
- Flow of water depends only on monsoon rainfall.
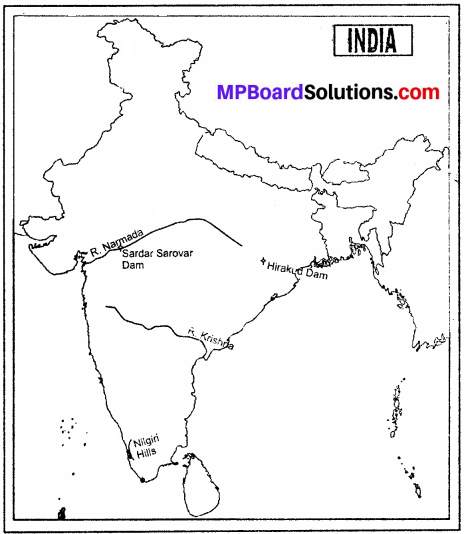
Question 3.
What is the importance of rivers in the economy? Explain.
Answer:
Rivers play an important role in the economy of our country. They are the lifeline of a country’s existence. Right from the beginning of the human civilization we have seen that people began to live on the bank of rivers. All the civilizations flourished there. The primary cause for this was that it had been the most convenient and cheapest means of transport. So, the trade and commerce flourished on the bailk of rivers. Most of the industrial towns have been settled along the river banks.
Dams and canals built on the rivers help us in our agriculture, which is the backbone of a country. We produce hydro -electricity from river water. Thus we see that rivers play a significant role in the economy of a country. Hence they must be protected from being polluted at all cost.
![]()
Questions related to Skill Development
Show the following in the outline map of India
- Nilgiri Mountains
- Narmada River
- Sardar Sarovar Dam
- Krishna River
- Hirakud Dam
Or
- Himalayan Mountain
- Satpura Ranges
- The Ganga Drainage System
- Chambal River
- Gandhi Sagar Dam
Project Work:
1. Students will prepare a model of river originating from Himalayas.
2. Prepare a model or chart of dams / canals or different projects made by man on the rivers and give a classroom presentation.
Answer:
Attempt yourself.
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 other important questions
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The Ganga enters the plains near –
(a) Prayag
(b) Haridwar
(c) Rameshwaram
(d) Kurushetra
Answer:
(b) Haridwar
Question 2.
The two large westward flowing rivers are –
(a) Narmada and Ganga
(b) Tapi and Brahmaputra
(c) Narmada and Tapi
(d) Krishna and Indu.
Answer:
(c) Narmada and Tapi
Question 3.
Hirakund dam has been built on the river –
(a) Mahanadi
(b) Ganga
(c) Brahamputra
(d) Narmada.
Answer:
(a) Mahanadi
Question 4.
Sambhar Lake is in –
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Gujarat
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Utter Pradesh.
Answer:
(a) Rajasthan
Question 5.
Indian Peninsula is surrounded by seas from –
(a) Four sides
(b) Three sides
(c) Two sides
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Three sides
![]()
Fill in the blank:
- ……………… Lake is situated in Orissa a state.
- Four tributaries of river Ganga are Yamuna, Ghagra …………… and ……………..
- Narmada river originates from ………………… state.
- River of Northern India are less …………………….
- Sambhar Lake is in ………………..
Answer:
- Chilka
- Gandak, Kosi
- Madhya Pradesh
- Waterfalls
- Rajasthan.
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which two factors form the drainage system?
Answer:
Amount of rainfall and topography form the drainage system.
Question 2.
What do you know about water divide?
Answer:
When we observe the river map of India we find that any highland like mountains separates two neighboring drainage basins. This highland is known as water divide.
Question 3.
In which two categories are the Indian rivers divided?
Answer:
The Indian rivers are divided in the following two categories:
- Rivers of Himalayas
- Rivers of Peninsula India
Question 4.
What is the main feature of the Himalayan rivers.
Answer:
The Himalayan rivers receive water throughout the year.
Question 5.
What is the length of the Indus river?
Answer:
The length of the Indus river is about 2900 km.
![]()
Question 6.
Where does the Brahmaputra river system rise?
Answer:
The Brahmaputra river system rises near the Mansarovar Lake and the Kailash mountains.
Question 7.
Name the rivers of Peninsular India?
Answer:
Mahanadi, Godawari, Krishna and Kaveri.
Question 8.
Where does the Narmada river drain?
Answer:
The Narmada river drains in Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat.
Question 9.
Which is the largest river systems of the Peninsular India?
Answer:
The Godavari is the largest river system of the Peninsular India.
Question 10.
Name four tributaries of the Godavari?
Answer:
Wardha, Manjra, Venganga and Penganga.
![]()
Question 11.
Why are lakes important?
Answer:
Lakes are important for tourism, fish farming / formation of salt etc.
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the Ganga Drainage System.
Answer:
The length of river Ganga in more than 2500 km. Its source is near Gangotri. The Ganga enters the plains near Haridwar. Its main tributaries are Yamuna, Ghaghara, Gandak and Kosi. These rivers form a fertile flood plain. They form meanders and ox-bow lakes. A water divide separates the Ganga and the Indus drainage system near Ambala.
The Ganga receives some of its tributatries like Chambal, Ken, Betwa, Son and Damodar from the Peninsular Plateau. Big dams have been built on these rivers which are used for hydro – electricity and irrigation. Flowing southward it forms a delta and finally join Bay of Bengal.
Question 2.
What are the main features of the rivers of Peninsular India?
Answer:
The main features of the rivers of Peninsular India are:
- They are seasonal.
- They flow frown a dry area.
- They do not form the plains.
- Rivers of Peninsular India like Mahanadi, Godawari, Krishna and Kavari flow eastward and drain into Bay of Bengal. They form Delta.
- The rivers flowing into the west of Western Ghats are small.
- Narmada and Tapi, the two large westward flowing rivers, flow in a rift valley and forming a tidal mouth it joins Arabian Sea.
Question 3.
What are the main features of the rivers of Southern India?
Answer:
The main features of the rivers of Southern India are:
- The rivers of Southern India have their origin in Western Ghats, Satpura and Peninsular Plateau.
- Waterfalls are, more.
- Not navigable.
- They flow in broad valleys
- Meanders are not formed.
- Flow of water depends only on Monsoon rainfall.
Question 4.
Describe the important lakes of India.
Answer:
Wular lake is the glacial lake of Kashmir. There are few lakes in South India. They are the Lonar in Buldhana district of Maharashtra, the Ghilka in Orissa, the Koleru in Andhra Pradesh ahd the Pullicat in Tamil Nadu. Lakes formed due to glacial erosion in Uttrakhand are Nainital, Bhimtal and Rakshastal etc. Sambhar lake of Rajasthan is famous as salt-water lake.
![]()
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Chapter 4 Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
Describe the rivers of Peninsular India.
Answer:
The rivers of Peninsular India are:
- The Narmada,
- The Tapi
- The Godavari,
- The Mahanadi
- The Krishna
- The Kaveri.
1. The Narmada:
It rises from Amarkantak Plateau in Madhya Pradesh flowing 1312 km. through a rift valley and finally drains in the Arabian Sea. It drains Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat. It forms Dhuandhar fall in the marble rocks of Bheraghat near Jabalpur. Its tributaries are very small.
2. The Tapi:
It rises near Multai in Betul district in Satpura range of Madhya Pradesh. It is 724 km. long. It flows in Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Gujarat and finally reaches Gulf of Cambay.
3. The Godavari:
It rises from Western Ghat near Nasik and flows for 1500 km in Orissa and Andhra Pradesh and drains in Bay of Bengal. Wardha, Manjra, Venganga and Penganga are its tributaries. It is the largest river system in the Peninusular India.
4. The Mahanadi:
It rises in Sihawa, a highland of Chhattisgarh. It is 858 km. long. Its drainage basin lies in Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Orissa, Hirakud Dam is build on this river.
5. The Krishna:
It rises in Maharashtra near Mahabaleshwar. It is 1400 km. long. It flows in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. Its Major tributaries are Koyna, Panchganga, Malprabha, Ghatphrabha, Bhima, Musi and Tungbhadra. Almati and Nagarjun Sagar Dam are built on this river.
6. The Kaveri:
It rises in the Brahmagiri hills in Co-org district. It is 60 km. long. Its tributaries are Hemavati, Amaravati and Bhavani.