These MP Board Class 11th Chemistry Notes for CChapter 2 Structure of Atom help students to get a brief overview of all the concepts.
MP Board Class 11th Chemistry Notes Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
→ Atom: Smallest particle which has all properties of the element is called atom.
→ Atomic structure : Distribution of fundamental constituent particles of atom is called atomic structure.
→ Cathode rays : Negatively charged rays which move from cathode to anode in discharge tube. Anode rays: Rays of positively charged particles which move opposite the cathode in discharge tube are called anode rays.
→ Electron (01e): Particle with unit negative charge 1.60 × 10-19 coulomb and mass 91 × 10-31 kg.
→ Proton (11e) : Fundamental particle of atom with unit positive charge 1.60 × 10-19 coulomb and mass 1.67 × 10-27 kg. Its mass is nearly equal to mass of hydrogen atom.
→ Neutron (11n) : Fundamental particle of atom which has no charge. Mass of neutron is 1.6747 × 10-27 kg. It is heavier than proton.
→ Nucleus: Central part of atom is called nucleus. Radius of nucleus is 10“23 cm. Total mass of atom and positive charge is in the nucleus.
![]()
→ Atomic number: Number of proton in the riucleus of atom or number of electrons in atom is . called atomic number.
→ Mass number : Sum of neutron and proton present in nucleus is called mass number.
→ Isotopes : Different atoms of elements which have same atomic number but different atomic mass are called isotopes.
→ Shell or Orbit : Electrons rotate in stable and definite circular orbits around the nucleus. These are called energy levels or shell or orbits.
→ Relation between frequency (υ) and wavelength (λ) υ = \(\frac{c}{\lambda}\) (Where c is velocity of light = 3 x 108ms-1)
→ Einstein equation E = mc2
Planck equation E = hυ = \(\frac{h c}{\lambda}\) (Where h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 x 10-34 Js)
![]()
→ Photoelectric Effect hυ = hυ0 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)mv2
Where hυ = Energy of Striking photon
hυ0 = w0 = Work function
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)mv2 = Kinetic energy of Ejected electron
(Where R = Rydberg constant = 1.09678 × 107 m-1)
→ Rydberg formula \(\bar{v}=\frac{1}{\lambda}=\mathrm{RZ}^{2}\left[\frac{1}{n_{1}^{2}}-\frac{1}{n_{2}^{2}}\right]\), n2 > n1
(Where R = Ryberg constant = 1.09678 × 107 m-1)
n1 =1, n2 = 2,3,4………………………….. UV region
n1 = 2, n2 = 3,4,5………………….. Visible region
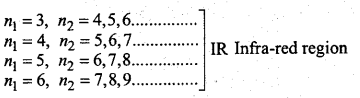
→ Frequency of the absorbed or emitted radiation at two unstable states of transmission v = \(=\frac{\Delta E}{h}=\frac{E_{2}-E_{1}}{h}\) (Where E1 and E2 are the energies of lower and higher states)
![]()
→ Energy of stable state En = -RH \(\left(\frac{1}{n^{2}}\right)\) where n = 1,2,3…………………..
→ Stable energy of H and species similar to H (Like : He+,Li2+,Be3+) i.e., one electron species ) En = -2.18 x 10-18\(\left(\frac{z^{2}}{n^{2}}\right)\) J
→ Radius of nth orbit rn = \(\frac{n^{2} a_{0}}{Z}\) [where a0 (Bohr’s radius of H) = \(\frac{h^{2}}{4 \mathrm{~A}^{2} m e^{2} k}\) = 0.529Å
→ de-Broglie equation \(\lambda=\frac{h}{m v}=\frac{h}{\sqrt{2 m(\mathrm{KE})}}\)
→ Angular momentum mvr = \(\frac{n h}{2 \pi}\)
→ Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle Δx . Δp ≥ \(\frac{h}{4 \pi}\) or Δx . Δp ≥ \(\frac{h}{4 \pi}m\)
[Where Δx and Δv are uncertainty in position and principle]
→ Velocity in n shell vn = 2.182 × 106 × \(\frac{z}{n}\).
→ Ionisation Energy (IE)H = ∆E ∝\(z^{2}\left[\frac{1}{n_{1}^{2}}-\frac{1}{n_{2}^{2}}\right]\)
→ Position of an electron in an atom is determined by four quantum numbers (n, l, in. s
(i) n (Principal Quantum number) = 1, 2, 3, 4 ………………n
(ii) l (Azimuthal Quantum number) = 0, 1, 2 ………….. (n – 1)
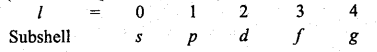
(iii) m (Magnetic Quantum number) = – l to + l
(iv) s (Spin Quantum number) = \(+\frac{1}{2}\) or \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
![]()
→ Determination of subshell = nl
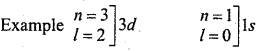
→ l also expresses the shape of orbital surrounded by electron : s – Spherical, p – dumbell, d – Double dumbell, f- Complex.
→ Total value of m – (2l + 1) = Number of orbitals in subshell = Number of spectrum lines in Magnetic or Electric field.
→ In an atom, l angular node, (n – l – 1) radial node i.e., Total nodes are (n – 1).
→ Electrons are filled in the various orbitals on the basis of the following rules :
(i) Aufbau’s Principle, (ii) Hund’s Rule, (iii) Pauli’s Exclusion Principle.
→ Electronic configuration of 24Cr = [Ar]3r54s1
→ Electronic configuration of 29CU = [Ar]3d104s1
→ Completely filled and half filled orbitals are more stable due to same symmetry and maxi¬mum energy exchange.
![]()
→ Energy of electron due to which it is bound to the nucleus = Work function (w0) of metal.
→ Subshell: In a shell all electrons do not have same energy so shells are divided in different subshells. These subshells are s, p, d and f
→ Orbital: Space around the nucleus where probability to find a electron is maximum is called orbital. ‘
→ Spectrum: On jumping of electrons from higher energy level to lower energy level, obtained lines on photographic plate from the produced light is called spectrum.
→ Visible spectrum : It is a part of electromagnetic radiation which can be seen by our eyes. Wavelength range is 4000 Å to 7500 Å.
→ Invisible spectrum : The wavelength range of 7500 Å to 3 x 1.06Å and before violet up to 4000A, which we cannot see is called invisible spectrum.
→ Hund’s rule : Pairing of electrons in orbitals of equivalent energy occurs when there is no vacant orbital.
→ Aufbau’s principle: Electrons are filled in subshells in increasing order of energy. Electrons are filled first in the shell whose (n + l) value is less. If (n + l) value is same, then electron will go to that shell whose in n value is lower.
![]()
→ Pauli’s exclusion principle: No two electrons in an atom have similar four quantum numbers