Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
Redox Reactions Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is meant by Oxidation process? Explain redox reaction with example.
Answer:
Addition of oxygen or electronegative element or removal of hydrogen or electropositive element is called oxidation.
2Mg + O2 → 2 MgO [Addition of oxygen]
2 FeCl2 + Cl2 → 2 FeCl3 [Addition of electronegative element]
H2S + Cl2 → S + 2 HCI [Removal of hydrogen] .
2K1 + H2O2 → 2KOH + I2 [Removal of electropositive element].
Question 2.
What is Reduction process? Explain with example.
Answer:
The tendency of a substance to accept hydrogen or electropositive element or to liberate oxygen or electronegative element is called reduction.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O [Liberation of oxygen]
2 FeCl3 + H2S → 2 FeCl2 + 2 HCl + S [Liberation of electronegative element]
Cl2 + H2S → 2HCl +S [Addition of hydrogen]
S + Fe → FeS [Addition of eletropositive element].
Question 3.
AgF2 is an unstable compound. If it is formed then this compound acts as a very powerful oxidizing agent. Why?
Answer:
In AgF2, Ag is in +2 oxidation state. It is extremely unstable. If readily accepts electron and attain +1 oxidation state, because Ag+ has a fully filled configuration which is more stable.
Ag2+ + e– → Ag+
That is why AgF2 acts as a powerful oxidizing agent.
Question 4.
In the following reactions, why does the same reducing agent thiosulphate reacts differently with iodine and bromine :
2S2O3(aq)2- + I2(s) → S4 O6(aq)2-+ 2I(aq)–
S2O3(aq)2- + 2Br2(l) + 5H2O → 2SO4(aq)2- + 4Br(aq)– + 10H(aq)+.
Answer:
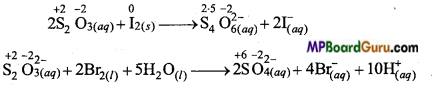
Bromine is stronger oxidizing agent than iodine. It oxidizes S (+2) of S2O3(aq)2- to SO42- (+6) whereas iodine can oxidize S (+2) in S2O3(aq)2- to S42- (2.5) We observe that oxidation number of S in S4O62- is less than in SO42-. That is why a single oxidizing agent thiosulphate behaves differently with iodine and bromine.
![]()
Question 5.
Justify the structure of S4O62-. Oxidation state of sulphur is + 5.
Answer:
Oxidation state of two central sulphur atoms is zero, because electron pair forming S-S bond will remain in the centre. Thus, remaining sulphur atoms which are in the structure at ends has an oxidation state of +5.
6(-2) + 2x =-2
or -12 + 2x = -2
or 2x = – 2 + 12 = 10
or x = \(\frac{10}{2}\) = 5.

Question 6.
What is electrochemical series?
Answer:
Electrochemical series: When different elements and ions are arranged in increasing order of their standard electrode potentials, a series is obtained which is called electrochemical series or activity series.
Question 7.
What is salt bridge? Write its two functions.
Answer:
A U-shaped tube filled with an electrolyte like KCl or KNO3 and jelly of agar-agar solution is called salt bridge.
Functions of salt bridge :
- It allows the flow of current by completing the circuit.
- It maintains electrical neutrality of the solutions in both the containers.
Question 8.
Justify oxidation and reduction on the basis of electron transfer.
Answer:
According to electronic theory, in oxidation process any atom, ion or radical loses one or more electrons i.e. its positive oxidation number increases or negative oxidation number decreases.
In reduction process, any atom, radical or ion gains one or more electrons due to which its positive oxidation number decreases or negative oxidation number increases.
K- e–→K+ Oxidation
Cu+2 + 2e– → Cu° Reduction
Question 9.
What is Electrochemical equivalent?
Answer:
The amount of substance deposited on passing 1-ampere current for 1 second through an electrolyte is called electrochemical equivalent. Its unit is gram/coulomb.
Question 10.
What happens when Zn metal is placed in CuSO4 solution? Explain with example.
Answer:
On placing Zn metal in CuSO4 solution, zinc displaces Cu because zinc is more reactive than Cu.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Question 11.
What is meants by standard electrode potential?
Answer:
The potential difference developed when a metal electrode is placed in a solution of 1 molar concentration at 298K temperature between the metal and solution is known as standard electrode potential. It is denoted by E°. If electrode is gaseous, then pressure of gas should be one atmospheric pressure.
Question 12.
Arrange the following metals on the tendency of their displacement from their salt solutions: Al, Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn.
Answer:
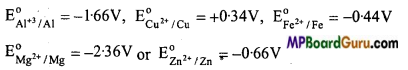
Metal with more negative E0(red) value is stronger reducing agent than the metal with
less negative or positive E0(red) value. Thus, Mg can displace all the other metals from aqueous solution of their salts. Al can displace all other metals except Mg from their aqueous solutions Zn can displace Fe and Cu from their aqueous salt solutions. Fe can displace only Cu from its aqueous salt solution.
Thus order of tendency of displacement of metals from their salt solution is Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Cu.
Question 13.
The following reaction represents the process of bleaching. Identify that species and write its name which bleach substances due to its oxidizing nature :
Cl2(g) + 2OH(aq)– → ClO(aq)– + Cl(aq)– + H2O(l)
Answer:
Write the oxidation state of each element above its symbol.
![]()
In this process oxidation number (0) of Cl (in Cl2) increases to 1 (in ClO–) whereas 0 (in Cl2) decreases to -1(in Cl–). Thus, chlorine behaves both as reducing and oxidizing agent. This is an example of a disproportionation reaction. In this reaction CIO– (hypochlorous ion) bleaches substances due to its oxidizing property. In ClO–,Cl can decrease its oxidation number from +1 to 0 or -1.
![]()
Question 14.
Define oxidizing and reducing agent.
Answer:
Oxidizing Agent : Reactant which accept electron from other reactants and oxidizes it and itself gets reduced is known as oxidizing agent.
Reducing Agent: Reactant which loses electron to reduce other reactant and itself gets oxidized is called reducing agent.
Question 15.
If an iron rod is placed in CuSO4 solution, then copper gets displaced. But on dipping a copper rod in FeSO4 solution, iron does not get displaced. Why?
Answer:
Iron is extremely reactive in comparison to copper, therefore on placing an Fe rod in CuSO4 solution, Fe displaces Cu from the solution.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
But Cu being less reactive, cannot displace Fe from FeSO4 solution.
Cu + FeSO4 → No reaction.
Question 16.
Can we store CuSO4 solution in a silver container and why?
Answer:
In Electrochemical series, silver comes below Cu, thus reactivity of Ag is less than Cu. Therefore, Ag will not displace Cu from CuSO4. Therefore CuSO4 can be stored in silver container.
Question 17.
What is oxidation number?
Answer:
Oxidation number of an element is the number which represents the charge present on the ion of an element. It can be positive, negative or neutral.
Example: Oxidation number of Mn in KMnO4 is +7.
Question 18.
Fluorine reacts with ice and undergo the following change :
H2O(s) + F2(g) → HF(g) + HOF(g)
Establish this reaction as redox reaction.
Answer:
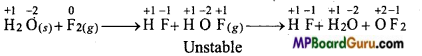
Oxidation number of F decreases from 0 (in F2) to -1 (in HF) and oxidation number of O increases from -2 (in H2O) to +2 (OF2). Thus, F2 is reduced and H2O is being oxidized. Thus, this reaction is redox reaction.
Question 19.
MnO42- represents disproportionation reaction in acidic medium but MnO–4 does not. Give reason.
Answer:
In MnO42- oxidation number of Mn is +6. It can increase (+7) or decrease (+4, +3, +2, 0) its oxidation number. Thus, it represents disproportionation reaction in acidic medium.
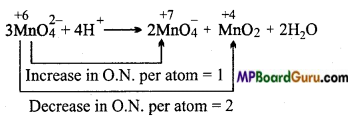
In MnO–4 , Mn is in its maximum oxidation state (+7). It can only decrease its oxida¬tion state, due to which it cannot represent disproportionation reaction.
Question 20.
In the following reaction which is oxidized and which is reduced :
PbS+ 4H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O
Answer:
In this reaction PbS is getting oxidized to PbSO4 and H2O2 is reduced to H2O.
Question 21.
What is the difference between Oxidation number and Valency.
Answer:
Differences between Oxidation number and Valency
| Oxidation Number | Valency |
| 1. It is the number which represents the charge on the ion. | 1. It is the number of electrons which is donated or gained by an atom. |
| 2. Oxidation number may be positive, negative and its value can be zero also. | 2. Valency is neither positive nor negative. |
| 3. Its value can be a whole number or in fractions also. | 3. Its value is always a whole number. |
Question 22.
In electrochemical series; in which order does the reactivity of metals decreases and increases?
Answer:
More negative the value of standard reduction potential of a metal, higher is its tendency to lose electron and more is the activity of the metal. This way reactivity decreases from top to bottom in the electrochemical series.
![]()
Question 23.
What does positive E°cell for a Galvanic cell represent?
Answer:
Positive E°cell of galvanic cell represent that:
1. Electrode which undergo oxidation acts as anode.
2. Electrode which undergo reduction acts as cathode.
Question 24.
What is electrode potential? On which factors does it depend?
Answer:
The potential difference developed between metal and its solution on keeping the metal electrode in the ions of its salt solution. Electrode potential depends on the ten¬dency of an electrode to lose or gain electrons in a half cell.
The electrode potential of any metal depends on the concentration of its ions and temperature.
Question 25.
Fluorine does not represent disproportionation reaction. Why?
Answer:
In disproportionation reaction, a single species undergo both oxidation and re¬duction. Thus, for such redox reactions, one such element should be in the. reactant species which represent at least three oxidation states. In reactant species, element should be in medium oxidation state whereas lower and higher oxidation states should be available for oxidation and reduction. Fluorine is the strongest oxidizing substance. It does not represeht positive oxidation state. That is why. it does not represent disproportionation reaction.
Question 26.
Consider a Galvanic cell in which the following reactions take place :
Zn(s) + 2 Ag+(aq) → Zn2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
Now, state that:
(a) Which electrode is negatively charged.
(b) Which is the motive of electric current in the cell.
(c) What reactions occur at each electrode.
Answer:
![]()
(a) Zn electrode is negatively charged. Zn is oxidized to Zn2+ ions.
(b) Current will flow from silver to zinc and electrons will flow from zinc to silver.
(c) Reactions occurring on electrodes are :
Anode : Zn → Zn2++2e–
Cathode : 2Ag+ + 2e– → 2Ag .
Question 27.
On the basis of standard electrode potentials given below, write the metals in the increasing order of their reducing tendency: K+ / K = -2.93 V, Ag+ / Ag = 0.80 V, Hg2+ / Hg = 0.79V, Mg2+ / Mg = -2.37V, Cr3+ / Cr = -0.74V .
Answer:
Lower the value of standard electrode potential (E0red) stronger is the reducing tendency of the substance. Thus, order of increasing reducing tendency of metals is as follows:
Ag < Hg < Cr < Mg < K
Question 28.
Why does the following reaction occur :
Xe06(aq) + 2F(aq) + 6H(aq) → Xe03(s) + F2(g) + 3H2O(l)
What conclusion about the compound Na4Xe06 (Of which XeOjJ- is a part) can be drawn from this equation ?
Answer:
![]()
In the above reaction, oxidation number of Xe from +8 (in XeO6-4) decreases to +6 (in XeO3) and oxidation number of F increases from -1 (in F–) to 0 (in F2). Thus XeO6-4 or Na4XeO6 reduces and F–oxidizes. This reaction is possible because Na4XeO6 or XeO6-4 is a stronger oxidizing agent than fluorine.
Question 29.
Among MgO, ZnO, CuO and CaO which oxide will be reduced by hydrogen and why ?
Answer:
In the electrochemical series, elements placed above hydrogen possess higher tendency to loose electrons than hydrogen. Thus, MgO, ZnO and CaO are very stable oxides because in these the electrons released by metals are absorbed by oxygen. Thus, they are not reduced by hydrogen. Since Cu lies below hydrogen in the electrochemical series thus hydrogen has more tendency to release electrons than Cu. Thus, CuO will be reduced by hydrogen and hydrogen will loose electron and form H2O.
![]()
Question 30.
E° values of Ag, Ba, Mg and Au are + 0.80, -2.90, -2.37 and +1.42 volt. Which of these metals will displace hydrogen from the acids and which will not?
Answer:
Metals with negative E° value are more reactive than hydrogen and can easily displace hydrogen from dilute acids. Therefore, Ba and Mg can displace H2 in dilute acids. E° values of Ag and Au are positive, these are less reactive than hydrogen, therefore they can not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question 31.
Write the definition of electrochemical cell. Express the chemical reaction of Daniel cell.
Answer:
System in which electric current is produced as a result of chemical reaction is called electrochemical cell.
In this, redox reaction takes place indirectly i.e. oxidation and reduction reaction occur in separate containers.
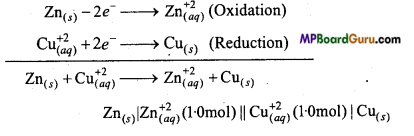
Redox Reactions Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Write the factors which affect electrode potential.
Answer:
The factors which affect electrode potential are as follows :
1. Tendency of metal to lose electron: Higher is the tendency of a metal to lose electron, higher is its electrode potential.
2. Temperature: On increasing the temperature of the solution, value of electrode potential increases.
3. Concentration of solution: Higher the concentration of metal ions in solution, higher is the electrode potential.
Question 2.
Determine the oxidation number of the following :
(1) Of Cr in K2Cr2O7 ,
(2) Of Mn in KMnO4,
(3) Of S in Na2S4O6,
(4) Of P in H3PO4,
(5) Of Mn in K2Mn04,
(6) Of Mn in Mn02.
Answer:
1. Of Cr in K2Cr2O7 :
2(+1) + 2x+7(-2) = 0
or 2 + 2x- 14 = 0
or 2x=12
or x = +6.
2. Of Mn in KMnO4:
1(+1) +1x + 4(-2) = 0
or 1 + x-8 = 0
or x = +7.
3. Of S in Na2S4O6 :
2(+1) + 4x +6(-2) = 0 .
or 2 + 4x-12 = 0
or 4x = 10
or x = \(\frac{10}{4}\) = 2.5
4. Of P in H3PO4 :
3(+1)+1 x + 4( – 2) = 0
or 3 + x-8 = 0
or x = +5.
5. Of Mn in K2MnO4 :
(+1 ×-2) +x + (-2 × 4) = 0
or 2 + x- 8 = 0
or x = 8 – 2
or x = 6.
6. Of Mn in MnO2:
x + (-2) × 2 = 0
or x – 4 = 0
or x = 4.
Question 3.
What is Redox reaction? Explain with example.
Answer:
Oxidation is a process in which an element loses one or more electrons, it is also known as de-electronation.
Reduction is a process in which an element gains one or more electron, it is also known as electronation. In this way, during the reaction an element donates electron and other element gains electron, thus both oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously in a reaction. Therefore it is also known as oxidation-reduction process or redox process. Thus, redox reactions are the reactions in which electrons are transferred from one reactant to the other.
![]()
Question 4.
Write the difference between Electrochemical and Electrolytic cell.
Answer:
Differences between Electrochemical cell and Electrolytic cell
| Electrochemical cell | Electrolytic cell |
| 1. In galvanic cell, chemical energy is changed into electrical energy. | In electrolytic cell, electrical energy is changed into chemical energy. |
| 2. Reaction in Electrochemical cell is spontaneous. | Reaction in electrolytic cell is non-spontaneous. |
| 3. Anode is negative while cathode is positive terminal. | Anode is positive while cathode is negative terminal. |
| 4. The electrons move from anode to cathode in the external circuit. | The electrons are supplied by the extemal circuit which enter through the cathode and come out through anode. |
| 5. Salt bridge is required. | No salt bridge is required. |
Question 5.
Write main characteristics of Electrochemical series.
Answer:
Characteristics of electrochemical series are as follows :
- In electrochemical series, chemical reactivity of metals decreases from top to bot¬tom.
- In electrochemical series chemical reactivity of non-metals increases from top to bottom.
- In the series, higher the negative standard reduction potential, the element will be more highly reducing.
- In the series, higher the positive standard reduction potential, the element will be a stronger oxidizing agent.
- Elements placed above hydrogen in the series can easily displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
- Elements placed below hydrogen in the series cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
- Elements placed above in the series can easily displace elements placed below from their salt solutions.
Question 6.
What is Nernst equation? Justify the relation between E and E°.
Answer:
Nemst developed a relation between the electrode potential determined under normal conditions and standard electrode potential as an equation known as Nemst equation.
E = E° – \(\frac{\mathrm{RT}}{n \mathrm{~F}}\)\(\ln _{e}\left[\frac{\mathrm{M}_{(s)}}{\mathrm{M}_{(a q)}^{n+}}\right]\)
or E = E° + \(\frac{\mathrm{RT}}{n \mathrm{~F}} \ln _{e}\left[\frac{\mathrm{M}_{(a q)}^{n+}}{\mathrm{M}_{(s)}}\right] \)
Converting Ine to log10
E = E° + \(\frac{2 \cdot 303 \mathrm{RT}}{n \mathrm{~F}}\)\(\log _{10}\left[\frac{\mathrm{M}_{(a q)}^{n+}}{\mathrm{M}_{(s)}}\right] \),
or E = E° + \(\frac{2 \cdot 303 \mathrm{RT}}{n \mathrm{~F}} \log _{10}\left[\mathrm{M}_{(a q)}^{n+}\right]\) [∵ M(s) = 1]
or E = E° + \(\frac{0.0591}{n} \log _{10}\left[\mathrm{M}_{(a q)}^{n+}\right]\), [∵ \(\frac{2 \cdot 303 \mathrm{RT}}{\mathrm{F}} \) = 0.0591 ]
![]()
Question 7.
Answer the following questions by the help of periodic table :
(a) Tell the name of possible non-metals, which can represent disproportionation reaction.
(b) Tell the name of three metals which can represent disproportionation reaction.
Answer:
(a) Phosphorus, chlorine and sulphur represent disproportionation reaction.
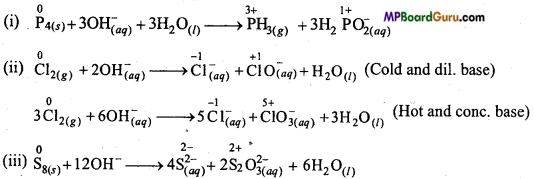
(b) Manganese, Copper, Gallium and Indium represent disproportionation reaction,
(i) img
(ii) 2Cu(aq) → Cu(aq)2+ + Cu(s)
(iii) 3Ga(aq) → Ga(aq)3+ + 2Ga(s)+
(iv) 3In(aq)+ → In(aq)3+ + 2In(s).
Question 8.
Write the main uses of electrochemical series.
Answer:
The uses of electrochemical series are :
1. Electropositive character of metal: Metal which looses electron easily from its outermost shell shows high electropositive character while the atom which looses electron with difficulty shows least electron positive character. In electrochemical series. Li shows maximum electropositive character while fluorine shows least electropositive character.
2. Comparison of reactivity of metals : Metal having negative value of E° looses electron easily. Hence, greater the negative value of E° more is the reactivity and reducing character of a metal.
3. Knowledge of oxidizing agent and reducing agent: Substance which gains electron and shows maximum value of standard electrode potential E°is strongest oxidizing agent. On the basis of this F is strongest oxidizing agent while Li is weakest oxidizing agent.
4. Displacement of elements : Metal having greater tendency to form ion displaces others. Therefore, elements getting priority in the series displace ions of the elements following them. For example: When Cu turnings is added to AgNO3 solution, Ag gets precipitated.
2AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) → CU(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
5. Electroplating: Process of depositing layer of gold or silver on copper, brass, iron etc. is called electroplating. It makes articles lustrous and attractive.
Question 9.
Chlorine is used to purity drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
Answer:
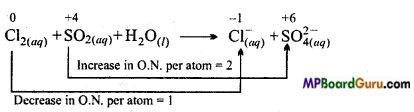
On multiplying Cl– by 2(because in Cl2 there are two Cl atoms)
Cl2(aq) + SO2(aq) + H2O(l) → 2 Cl–(aq)+ SO4(aq)2-
Firstly on adding 4H+ on right side to balance the charge and multiplying H2O by 2
Cl2(aq) + SO2(aq)+ 2H2 +2H2O(l) → 2 Cl–(aq)+ SO4(aq)2-+4H+
This is the balanced redox reaction.
Equilibrium Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
In Ostwald’s process for the manufacture of nitric acid, the first step involves the oxidation of ammonia gas by oxygen gas to give nitric oxide gas and steam. What is the maximum weight of nitric oxide that can be obtained starting only with 10.00 gm of ammonia and 20.00 gm of oxygen?
Answer:
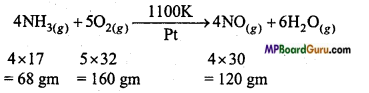
∵ 68 gm NH3 reacts with = 160 gm O2
∴ 1 gm NH3 will react with = \(\frac{160 \times 1}{68}\) gm O2
10 gm NH3 will react with = \(\frac{160 \times 10}{68}\) = 23.5 gm O2
But, available amount of O2 is 20.0 gm which is less than required amount (23.5 gm) for complete reaction with 10 gm NH3. Thus, O is the limiting reagent and it limits the amount of NO produced. By the above balanced equation :
∵ 160 gm O2 is produced by = 120 gm NO
1 gm O2 will be produced by = \(\frac{120 \times 1}{160}\) gm NO
∴ 20 gm O2 will be produced by =\(\frac{120 \times 1 \times 20}{160}\) = 15 gm NO.
Question 2.
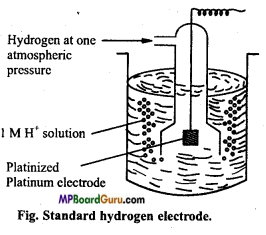
What is standard hydrogen electrode? How is it prepared?
Answer:
Standard hydrogen electrode : This consists of gas at 1 atmospheric pressure bubbling over a platinum electrode immersed in 1 M HCl at 25°C (298 K) as shown in figure. The platinum electrode is coated with platinum black to increase its surface. The hydrogen electrode thus constructed forms a half cell which on coupling with any other half cell begins to work on the principle of oxidation or reduction.
Electrode depending upon the circumstances works both as anode or cathode.
Cell reaction of standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) when it acts as anode is
H2(g) → 2H++2e–
It is as represented as
![]()
When it acts as cathode, the cell reaction is
2H+ +2e– → H2(aq)
and it is represented as
![]()
Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is arbitrarily assigned a potential of zero.
Question 3.
What is oxidation number? Write the rules for its determination.
Answer:
Oxidation number of an element is defined as, “the residual charge left on its atom when all the other atoms are removed from the molecule as ions.”
Atoms can have positive, negative or zero oxidation state depending upon their state of combination. In fact, oxidation number is the charge assigned to the atom in a species according to some rules. It is also known as oxidation state.
Rules for assigning oxidation number : The assignment of oxidation numbers is arbitrary and is usually
governed by the following conclusions:
- The oxidation number of an element in free state i.e., elementary state is regarded as zero.
- In a compound, the more electronegative elements are assigned negative (-) oxidation state and less electronegative elements are assigned positive (+) values. For example, in HC1 as chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen its oxidation state will have negative value while that of hydrogen will be positive.
- In the formula of a compound, the sum of the negative oxidation states is equal to the sum of the positive oxidation states.
- The sum of oxidation number of all the atoms in a neutral molecule is taken as zero.
- Hydrogen has an oxidation state +1 in compounds like H2S, H2O, HCl, etc. Exceptionally it has the oxidation number -1 in metallic hydrides, such as NaH, CaH2, etc.
- Oxygen is usually assigned oxidation number -2, except in H2O2 and in oxide of fluorine [F2O], in which the oxidation number – 1 and + 2 respectively. In all, oxidation number of oxygen is – 1.
- Fluorine being the most electronegative element is assigned oxidation number – 1 in all its compounds. Other halogens also show – 1 oxidation number.
- The number of monoatomic ion in an ionic compound is equal to its electric charge. Thus, the elements of group I A of the periodic table (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) all have oxidation number + 1, while the alkaline earth metals of group IIA (Ca, Sr, Ba) have oxidation number + 2.
Question 4.
How is redox reaction equation balanced by ion-electron method? Explain.
Answer:
- Represent the oxidation number of each element in the given chemical equa¬tion.
- On the basis of oxidation number, identify the oxidation and reduction process.
- Redox reaction is divided into two steps on the basis of oxidation and reduction.
- Except H2 and O2, balance the other elements in each half reaction.
- On the basis of change in oxidation number, charge is balanced by the gain or loss of electron.
- Oxygen is balanced by adding H2O to the side oxygen is deficient.
7.To balance H2 the following two steps are used :
- In Acidic Medium: If the reaction takes place in acidic medium,H+ ion is added to the side deficient in H2.
- In Basic Medium: If the reaction takes place in basic medium, H2O is added to the side deficient in H2 and same numbers of OH– is added to the other side.
8. For balancing the electrons in both the half reactions, is multiplied by a suitable number.
9. Both the half reactions are added to obtain a complete equation.
![]()
Question 5.
What information can you obtain from the following reactions :
(CN)2(g)+2OH(aq)– → CN(aq)– + CNO(aq)– + H2 O(l)
Answer:
(CN)2(g) + 2OH(aq)– → CN(aq)– + CNO(aq)– + H2 O(l)
(i) Let oxidation number of C in (CN)2 = x
2x + 2(-3) = 0
or x = +3
(ii) Let oxidation number of C in CN– = x
x + (-3) = -1
or ,x = +2
(iii) Let oxidation number of C in CNO– = x
x + (-3) + (-2) = -1
or . x = + 4
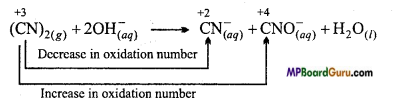
The following informations are obtained by the above equation :
- By hydrolysis in basic medium cyanogen forms cyanide ion (CN–) and cyanate ion (CNO–)
- Cyanogen behaves both as oxidizing and reducing agent.
- This reaction is an example of disproportionation reaction (specific type of redox reaction)
- Cyanogen is known as pseudo halogen whereas CN–, CNO– ions are known as halide ion.
Question 6.
Balance the following redox reaction by ion-electron method :
Cr2O7-2 + Fe+2 + H+ → Cr+3 + Fe+3
Answer:
1. Oxidation number of each element is represented :
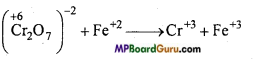
2. Identification of oxodation and reduction reaction:

Question 7.
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2 and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction .
Answer:
Skeleton of the reaction is as follows :
Mn(aq)3+ → Mn(aq)2++ MnO2(s)+H(aq)+
Reduction half reaction ‘ .
Mn(aq)3++ e– → Mn2+ ………….. (i)
Oxidation half reaction ,
Mn(aq)3+ → Mn+4O(s)+ e– ………………. (ii)
To balance oxygen, add H2O on the left side and to balance hydrogen add H+ the other side.
Mn(aq)3+ + 2H2O(l) → O2+ e– + 4H(aq)+
On adding eqn. (i) and (iii),
2Mn(aq)3+ + 2H2O(l) → Mn2++ MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq)
This is the last balanced ionic redox reaction (disproportionation reaction).
Question 8.
By the help of standard electrode potentials, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible:
(a) Fe(aq)3+ and I(aq)–
(b) Ag+(aq) and Cu(s),
(c) Fe(aq)3+ and Br–(aq),
(d) Ag(s) and Fe(aq)3+.
Given:
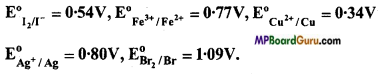
Answer:
For the feasibility of a reaction, E°cell should be positive.
E°cell = E°(reduction) – E°(oxidantion)
E°cell =E°(cathode) – E°(anode)
(a) Fe(aq)3+ and I–(aq) → 2Fe(aq)3+ and I–(aq)
Fe(aq)3+ + 2I–(aq) → 2Fe(aq)2++ I2(s)
Oxidation half reaction:
2I–(aq) → I2(s) + 2e– E° = -0.54 V
Reduction half reaction :
2Fe3+(aq) +2e– → 2Fe2+(aq) E° = +0.77 V
Complete reaction:
2Fe3+(aq) +2I–(aq) → 2Fe2+(aq) +I2(s)
Positive EME indicates that reaction is feasible.
(b) The possible reaction between Ag+(aq) and Cu(s) is as follows:
2Ag+(aq) +Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) +2Ag(aq)
Oxidation half reaction:
Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq)+ 2e– E° = -0.34 V
Reduction half reaction:
2Ag+(aq) + 2e– → 2Ag(s) E° = +0.80 V
Complete reaction:
Cu(s) +2Ag+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) +2Ag(s) E°cell = +0.46 V
E° value is positive which indicates that the reaction is feasible.
(c) Reaction between Fe3+(aq) and Cu(s) is as follows:
Fe3+(aq) + Cu(s) → Fe2+ + Cu2+
Oxidation half reaction:
Cu(s) → Cu2+ +2e– E° =-0.34 V
Reduction half reaction: .
[Fe3+(aq) +e– → Fe2+(aq)] × 2 E° =+0.77 V
Complete reaction:
Cu(s) + 2Fe3+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq)) E°cell = +0.43 V
Positive EMF indicates that the reaction is possible.
Note: It should be noted that, on multiplying an equation by a whole number, its E° is not multiplied by that whole number.
(d) The possible reaction between Fe3+(aq) and Ag(s) is as follows:
Ag(s) +Fe3+(aq) → Ag+(aq) +Fe2+(aq))
Oxidation half reaction:
Ag(s) → Ag+(aq)+ e– E°= -0.80 V
Reduction half reaction:
Fe3+(aq) + e– → Fe2+(aq) E° = +0.77 V
Complete reaction:
Ag(s) + Fe3+(aq) → Ag+(aq) + Fe2+(aq) E°cell = -0.33 V
Negative EMF indicates that the reaction is not feasible.
Question 9.
Identify such elements among Cs, Ne, I and F which :
(a) Exihibits only negative oxidation state.
(b) Exihibits only positive oxidation state.
(c) Exihibits both negative and positive oxidation states.
(d) Exihibits neither positive nor negative oxidation states.
Answer:
(a) F exihibits only negative oxidation state, since it is most electronegative element.
(b) Cs exihibits only positive oxidation state, since it is most electropositive element.
(c) Iodine exihibits both positive and negative oxidation states. Iodine exihibits -1,0,
+1, +3, +5 and +7 oxidation states (+3, +5 and +7 oxidation states are exihibited due to vacant J-orbital.
(d) Ne is an inert gas. Therefore it neither exihibit positive nor negative oxidation states.
Question 10.
Balance the following equations in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent:
(a) F4(s) + OH–(aq) → PH3(g) + H2PO–2(aq)
(b) N2H4(l) + CIO–(aq) → NO(g) + Cl–(aq)
(c) Cl2O7(g) + H2O2(aq) → CIO–2(aq) +O2(g).
Answer:
(a) (a) F4(s) + OH–(aq) → PH3(g) + H2PO–2(aq)
(i) Ion-electron method :
Reduction half reaction:

On balancing P atoms:
P4(s) → 4PH3(g) ……………. (ii)
On adding electrons and balancing oxidantion number:
P4(s) +12 e– → 4PH3(g) …………….. (iii)
On adding OH– ions and balancing the charge :
P4(s) +12 e– → 4PH3(g) + 12OH–(aq) …………… (iv)
Balancing oxygen atoms by adding water:
12H2O + P4(s) +12 e– → 4PH3(g) + 12OH–(aq) ………….. (v)
Oxidation half reaction:
(ii) Oxidation number method:
![]()
On balancing P atoms:
P4(s) → 4H2PO2(aq) ………………………. (vii)
On adding electrons and balancing oxidation number:
P4(s) → 4H2PO2(aq)– +4e– …………………. (viii)
On balancing charge by adding OH– ions:
P4(s) + 8OH–(aq) → 4H2PO2(aq)– + 4e– …………………………… (ix)
Oxygen and hydrogen are balanced itself. First of all eqn. (ix) is multiplied by 3 and on equalizing the number of electrons lost and number of electrons obtained in eqn. (v).
4P4(s) + 12OH–(aq) + 12H2 O(l) → 4PH3(g) + 12H2 PO–2(aq)
or P4(s) + 3OH–(aq) + 3H2 O(l) → PH3(g) + 3H2 PO–2(aq)
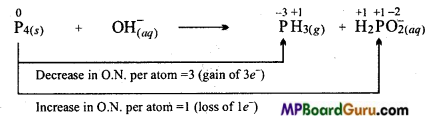
Decrease in electrons in balanced chemical equation = Gain of electrons.
Thus, on multiplying H2PO–2 by 3
P4(s)+ OH(aq)– → PH3(g)+ 3H2 PO–2(aq)
To balance the charge OH– is multiplied by 3
P4(s) +3OH–(aq) → PH3(g) + 3H2 PO–2(aq)
For balancing H on left side, on adding 3H2O
P4(s) + 3H2O(l) + 3OH–(aq) → PH3(g) + 3H2 PO–2(aq)
In this equation P4 acts both as oxidizing and reducing agent. This is an example of disproportionation reaction.
(b)N2H4(l) +ClO–3(aq) → NO(g)+Cl–(aq)
(i) ion – electron method:
Oxdation half reaction:
![]()
On balancing N atoms:
N2H4(l) → 2NO(g)
On adding 8e– for balancing oxidation number:
N2H4(l) → 2NO(g) + 8e–
On adding OH–
for balancing the charge:
N2H4(l) + 8OH–(aq) → 2NO(g) + 8e–
On adding H2O for balancing O-atoms:
N2H4(l) +8OH–(aq) → 2NO(g) +6H2O(l) +8e– ………………. (i)
Reduction half reaction:
![]()
On balancing oxidation number:
ClO–3(aq) +6e– → –(aq)
On adding OH– for balancing the charge:
ClO–3(aq) +6e– → Cl–(aq) +6OH–(aq)
On adding H2O for balancing 0-atoms:
ClO–3(aq)+3H2O(l)+6e– → Cl–(aq) +6OH–(aq) ………………. (ii)
To make the number of electrons lost and gained equation (i) is multiplied by 3 and (ii) by 4.
3N2H4(l) + 4CIO–3(aq) → 6NO(g) + 4Cl–(aq) + 6H2O(l)
This is the last redox reaction.
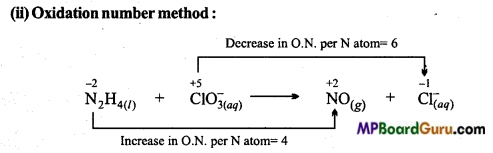
On multiplying NO by 2 (Since N2H4 contains 2 atoms)
N2H4(l) + CIO–3(aq) → 2NO(g) + Cl–(aq)
Total increase in oxidation number of N = 2 × 4 = 8 (Decrease in 8 electrons)
Total decrease in oxidation number of Cl– =1 × 6= 6 (Gain of 6e–)
Thus, for balancing increase or decrease in oxidation number, N2H4 is multiplied by 3, 2NO by 3 and Cl–by 4.
3N2H4(l)+ 4ClO –3(aq) + 4O2(g)
On adding 6H20 on right side for balancing number of O and H atoms:
3N2H4(l) +4ClO –3(aq) → 6NO(g) +4Cl–(aq) +6H2O(l)
In this reaction, N2H4 acts as a reducing agent and ClO–3 as an oxidizing agent.
(c) Cl2O7(g)+H2O2(aq) → ClO–2(aq) +O2(g)
(i) Ion – electron method:
Reduction half reaction:
![]()
On multiplying ClO–2 by 2(because Cl2O7(g) contains 2Cl atoms)
![]()
On balancing oxidation number by adding electron:
Cl2O7(g) + 8e– → 2ClO–2(aq)
On balancing charge on adding electron :
Cl2O7(g) + 8e– → 2ClO–2(aq)+6OH–(aq)
On balancing O by adding H2O left side:
Cl2O7(g) +3H2O(l)+8e– → 2ClO–2(aq)+6OH–(aq)
Oxidation half reaction:
![]()
On balancing oxidation number by adding electron:
H2O2(aq) + 2OH–(aq) → O2(g) +2e–
On balancing charge on adding OH– ion :
H2O2(aq)+2OH–(aq) → O2(g) +2e–
On balancing O by adding H2O left side:
H2O2(aq) +8OH–(aq) → 4O2(g) + 8H2O(l) + 8e–
On multiplying by 4:
4H2O2(aq) + 8OH–(aq) → 4O2(g) + 8H2O(l) +8e– …………………………… (ii)
On adding eqn. (i) and (ii)
Cl2O7(g) +4H2O2(aq) + OH–(aq) → 2ClO–2(aq) +5H2O(l)+4O2(g).
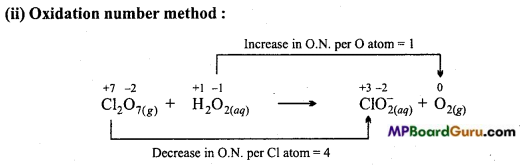
On multiplying ClO–2 by 2 (because Cl2O7 contains 2Cl atoms):
Cl2O7(g) +H2O(l) → 2ClO–2(aq) +O2(g)
Total decrease in oxidation number of Cl 2 × 4 = 8 (Gain of 8e–)
Total increasein oxidation number of 0 1 × 2 = 2 (Decrease in 2e–)
Thus, to balance increase and decrease in oxidation number, on multiplying H2O2 and O2 by 4,
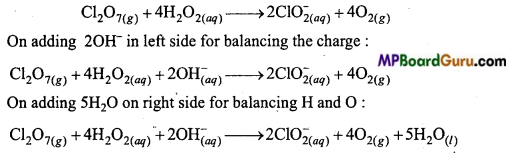
In this reaction, Cl2O7 acts as oxidizing agent and H2O2 as a reducing agent.
![]()
Question 11.
Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method :
(a) MnO4(aq)– + I–(aq) → MnO2(s) + I2(s) (Basic medium)
(b) MnO–4(aq) + SO2(g) → Mn+2(aq) + HSO–4(aq) (Acidic medium)
(c) H2O2(aq) + Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+(aq)+H2O(l) (Acidic medium)
(d) Cr2O7(aq)2- + SO2(g) → Cr(aq)3++ SO4(aq)2- (Acidic medium)
Answer:
![]()
On separating oxidation half and reduction half from the above equation.
(i) Oxidation half reaction :
I(aq)– → I2(s)
On balancing iodine atom :
2(aq)– → I2(s)
On adding 2e~ on right side for balancing oxidation number :
2(aq)– →I2 + 2e– ……………….. (i)
Since charge is same on both the sides, thus it is not required to balance the charge.
(ii) Reduction half reaction:
![]()
Balancing of oxidation number by adding 3e– on left side:
MnO–4(aq) + 3e– → MnO2(s)
For balancing charge, OH – is added on right side because reaction is in basic medium:
MnO–4(aq) + 3e– → MnO2 + 4OH –
On balancing O atom by adding H2O:
MnO–4(aq) + 3e– + 2H2O(l)→ MnO2(s) + 4OH –(aq) …………………… (ii)
By doing this H atoms are automatically balanced. For balancing the number of electrons, multiply eqn. (i) by 3 and eqn. (ii) by 2,
6I–(aq)→ >3I2(s) + 6e– ………………… (iii)
2MnO–4(aq) + 6e– + 4H2O(l) → 2MnO2(s) +8OH –(aq) …………………. (iv)
On adding eqn. (iii) and eqn. (iv), number of eLectrons are neglected from both the sides,
2MnO–4(aq) + 6I–(aq) + 4H2O(l) → 2MnO2(s) + 3I2(s) + 8OH–(aq)
This is the final balanced redox reaction.
(b) 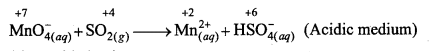
On writing oxidation half and reduction half separately.
(i) Oxidation half reaction :
![]()
For balancing oxidation number 2e– are added on right side:
SO2 → HSO–4+2e–
For balancing charge H is added on right side because the medium of the reaction is acidic:
SO2 → HSO–4 +3H++2e–
To balance H and O atoms, H2O is added on left side:
SO2 + 2H2O → HSO–4 +3H+ +2e– …………… (i)
(ii) Reduction half-reaction:
![]()
For balancing oxidation number 5e– are added on left side:
MnO–4 + 5e– → M2+
For balancing the charge H is added on left side (Acidic medium):
MnO–4 + 8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+
To balance O and H atom 4H20 is added on right side:
MnO–4 +8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+ +4H2O ……………. (ii)
On multiplying eqn. (i) by 5 and eqn. (ii) by 2, electrons of both the sides are neglected, 2MnO–4 + 4H++ 5SO2 + 2H2O → 2Mn+2 + 5HSO–4
This is the final balanced redox reaction.
(c) 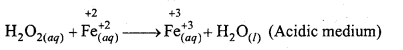
According to [Section (b)] the following balanced oxidation half reaction and reduction half reactions are obtained:
Reduction half reaction :
H2O2 +2H+ + 2e– → 2H2O
Oxidation half reaction:
[Fe2+ → Fe3+ e–] × 2 ………………… (ii)
On adding eqn. (i) and (ii) the following balanced equation is obtained:
H2O2(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H+(aq) → 2H2O(l) + 2Fe3+(aq).
(d) 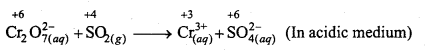
According to [Section (b)] the following balanced oxidation half reaction and reduction half reactions are obtained:
Reduction half reaction
Cr2O2-7 + 14H++ 6–→ 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Oxidation half reaction
SO2 +2H2O → SO2-4+4H++2e– ………….. (ii)
Multiplying eqn. (ii) by 3 and on adding,
Cr2O2-7(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 3SO2(g) → 2Cr 3+(aq) + 3SO2-4(aq) + H2O(l).
This is the final balanced redox reaction.
![]()
Question 12.
Which method is used to determine the tendency of oxidizing/ reducing agent in solution ? Explain with example.
Answer:
First of all, the given species is paired with standard hydrogen electrode to form redox pair and its electrode potential is measured. If it is positive then the given electrode of the species acts as a reducing agent and if it is negative then the given electrode of the species behaves as an oxidizing agent. By this method electrode potential of other given species is determined. These values are compared and their relative capability as a reducing or oxidizing agent is determined.
Example : Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is used as a reference electrode and standard electrode potential of Zn2+/Zn electrode is calculated as follows :
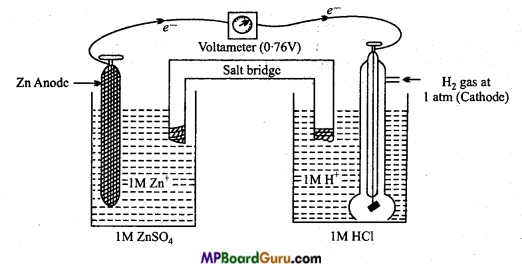
Electromotive force (EMF) of cell obtained is 0.76V (Reading of voltameter 0.76V). Zn2+/Zn pair acts as anode and standard hydrogen electrode acts as cathode.
E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
0.76 = 0 – E°anode
∴ E°anode = -0.76 V
E° Zn2+/Zn = -0.76 V.
Question 13.
Whenever a reaction between an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent is carried out, a compound of lower oxidation state is formed if the reducing agent is in excess and a compound of higher oxidation state is formed if the oxidizing agent is in excess. Justify this statement giving three illustrations.
Answer:
(a) P4 is a reducing agent and Cl2 an oxidizing agent.
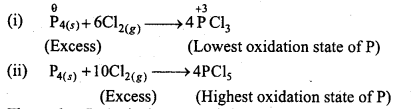
Thus, when P4 (reducing agent) is in excess PCl3 is formed in which oxidation state of P is +3 and if Cl2 (oxidizing agent) is in excess the PCl5 will be formed in which oxidation state of P is +5.
(b) C is a reducing agent whereas O2 is an oxidizing agent.
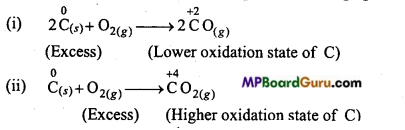
When reducing agent C is in excess, compound CO of lower oxidation state is formed. If oxidizing agent O2 is in excess then compound CO2 of higher oxidation state is formed.
(c) Na is a reducing agent whereas O2 is an oxidizing agent.
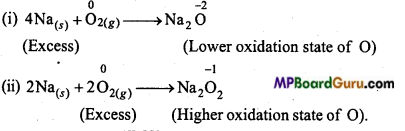
Question 14.
How do you count for the following observations :
Though alkaline potassium permanganate and acidic potassium permanganate both are used as oxidants, yet in the manufacture of benzoic acid from toluene we use alcoholic potassium permanganate as an oxidant, why ? Write a balanced redox equa-tion for the reaction.
Answer:
In acidic medium, oxidation of Toluene to Benzoic acid :
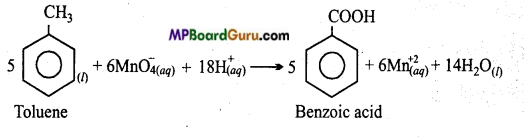
Oxidation of Toluene to Benzoic acid in alkaline and neutral medium:
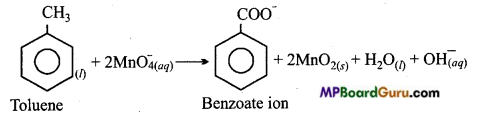
At commercial level, instead of acidic and alkaline KMnO4 , alcoholic KMnO4 is more useful. Like dissolves like, therefore benzoic acid and toluene being of covalent nature easily dissolve in alcohol to form a homogeneous solution. In presence of alcohol both reactants KMnO4 and C6H5CH3 (toluene) mutually form a homogeneous solution. Reaction in homogeneous medium is faster than in heterogeneous medium. Apart from this in neutral medium OH– ion are automatically formed in the reaction.
Question 15.
While sulphur dioxide and hydrogen peroxide can act as oxidizing as well as reducing agents in their reactions, ozone and nitric acid act only as oxidants. Why?
Answer:
1. In SO2, oxidation number of S is +4, Its minimum oxidation number is -2 and maximum oxidation number is +6. Thus, in SO2, S can decrease as well as increase its oxidation number. That is why, SO2 can behave both as an oxidant as well as reductant.
2. In H2O2, oxidation number of O is -1. its minimum oxidation number is -2 and maximum oxidation number of oxygen in O2F2 and OF2 +1 and +2 respectively are also possible. In H2O2, oxygen can reduce as well as increase its oxidation number. Thus, H2O2 can behave both as an oxidant as well as reductant.
3. In O3, oxidation number of O3 is zero. It cannot increase its oxidation number. It can only decrease its oxidation number from zero to -1 and -2. Thus, O3 can behave only as an oxidant.
4. In HNO3, oxidation number of N is +5 which is maximum. Thus, in HNO3, oxidation number of N can only decrease. Thus, it can only behave as an oxidant.
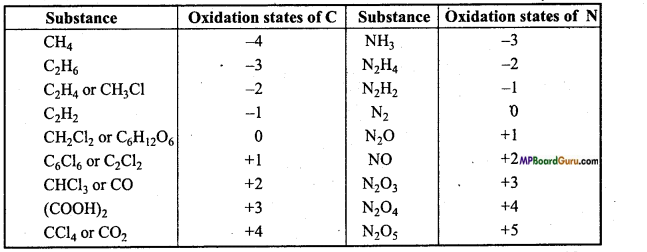
Question 16.
Suggest a list of the substances where carbon can exhibit oxidation states from -4 to +4 and nitrogen from -3 to +5.
Answer:
Q. 17. Justify giving reactions that among halogens, fluorine is the best oxidant among hydrohalic compounds, hydroiodic acid is the the best reductant.
Answer:
![]()
Standard reduction potential of halogens is positive and decreases from fluorine to iodine. Thus, halogens behave as strong oxidizing reagents and their oxidizing power de¬creases from fluorine to iodine. Fluorine is the strongest oxidizing reagent. It oxidizes other halide ions in solution or Ary state into corresponding halogens.
F2 + 2x– → 2F – + X2, (X– =Cr–, Br–,I–)
Normally halogen of lower atomic number oxidizes the halide ion of halogen of higher atomic number.
When halide ion X– or HX molecule reacts with an oxidant then it reduces the oxidizing substance and itself reduces to X2 molecule. Tendency of forming X2 molecule by losing electron from X– ion increases from F– to F ion. This reducing tendency of X–ions or HX molecules increases gradually from F– to I– ions or from HF to HI molecule.
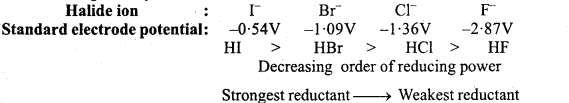
2HF + H2SO4 → No reaction
HC1 also does not react with H2SO4
But 2HI + H2SO4 → SO2 + 2H2O + I2
HBr also reacts like this.
HF or F– ion is a weak reductant. It is so weak reductant that it cannot reduce extremely strong oxidizing substance like H2SO4 also whereas HI or I– ion reduce strong oxidizing substances and itself get oxidize to I2. This is the reason that HI is the best reductant.
![]()
Question 18.
Identify the substance oxidized, reduced, oxidizing agent, reducing agent for each of the following reactions :
(i) 2AgBr(s) + C6H6O2(aq) → 2Ag(s)+ 2HBr(aq)+ C6H4O2(aq).
(ii) HCHO(l) + 2[Ag(NH3)2]) + 3OH–(aq) → 2Ag(s) + HCOO–(aq)+ 4NH3(aq) + 2H2O(l)
(iii) HCHO(l) + 2Cu(aq)2+ + 5OH–(aq) → Cu2O(s) + HCOO –(aq)+ 3H2O(l)
(iv) N2H4(l)+ 2H2O2(l) → N2(g) + 4H2O(l)
(v) Pb(s) +PbO2(s) +2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l).
Answer:
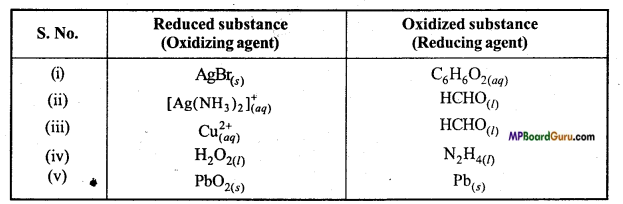
Question 19.
On the basis of standard electrode potential values, state which of the following reactions are feasible :
E°Cu2+/Cu = 0.34 V, E°Zn2+
E°Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V, E°Fe2+/Fe = -0.74 V
E°Br2/Br = +1.08 V, E°Cl2/Cl– = +1.36V, E°Cd2+/Cd = -0.44 V
(i) Cu +Zn2+ → Cu2++Zn
(ii) Mg + Fe2+ → Mg2+ + Fe
(iii) Br2+2Cl– → Cl2+2Br–
(iv) Fe + Cd2+ → Cd + Fe2+
Answer:
(i) Cu +Zn2+ → Cu2++Zn
E°Cu2/Cu = +0.34 V and E°Zn2+ = -0.74 V
In the given cell reaction Cu oxidizes to Cu2+. Thus Cu2+/Cu pair acts as anode and
Zn2+ reduces to Zn, therefore Zn2+/Zn pair will act as cathode.
E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
E°cell = -0.76 -(+0.74) = -1.10 V
Negative value of E°cell indicates that this reaction is not feasible.
(ii) Mg + Fe2+ → Mg2+ + Fe
E0Mg2+/Mg =- 2.37 V and E0 Fe2+ = – 0.74 V
Mg will oxidize to Mg2+ thus Mg2+//Mg will act as anode. Fe2+ will reduce to Fe,
thus Fe2+ /Fe pair will act as cathode.
E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
E°cell = -0.74 – (-2.37) = +1.63 V
Positive value of E indicates that this reaction is feasible.
(iii) Br2 + 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2Br–
E°Br2/Br– =+1.08 V and E°Cl2/Cl= +1.36 V
In the cell reaction Cl– oxidizes to Cl2, thus Cl2/Cl pair will act as anode and Br2
reduces to Br–, thus Br2/Br– pair will act as cathode.
E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
E°cell = +1.08 – (+1.36) = -0.28 V
Negative value of E°cell indicates that this reaction is not feasible.
(iv) Fe+Cd2+ → Cd+ Fe2+
In this reaction Fe oxidizes to Fe2+
Thus Fe2+/Fe will act as anode and Cd2+ reduces to Cd, thus Cd2+/Cd pair will act as cathode.
E°Fe2+/Fe = -0.74 V and E°Cd2+/Cd = -0.44 V
E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
E°cell = -0.44 – ( -0.74) = +0.34 V
Positive value of E indicates that this reaction is feasible.
Equilibrium Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Metals used in Daniell cell are :
(a) N and Cu
(b) Zn and Ag
(c) Ag and Cu
(d) Zn and Cu.
Answer:
(d) Zn and Cu.
Question 2.
Which of the following is strongly reducing :
(a) F–
(b) Cr–
(c) Br–
(d) I–.
Answer:
(d) I–.
Question 3.
Oxidation in electrolyte occurs :
(a) At anode
(b) At cathode
(c) At both the electrodes.
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) At anode
Question 4.
Which of the following statement is correct ? Galvanic cell converts:
(a) Chemical energy to electrical energy
(b) Electrical energy to chemical energy
(c) Elemental state of metal to combined state
(d) Electrolytes to ions.
Answer:
(a) Chemical energy to electrical energy
![]()
Question 5.
Oxidation number of Chlorine in HOCl is :
(a) -1
(b) 0
(c) +1
(d) +2.
Answer:
(c) +1
Question 6.
Oxidation number of Mn in K2MnO4 is :
(a) +2
(b) +6
(c) +7
(d) 0.
Answer:
(b) +6
Question 7.
Oxidation number of Cr in K2Cr2O7 is :
(a) -6
(b) +6
(c) +2
(d) -2.
Answer:
(b) +6
Question 8.
Oxidation number of Ni in Ni(CO)4 is :
(a) 0
(b) +2
(c) +1
(d) -1.
Answer:
(a) 0
Question 9.
Unit of cell constant is :
(a) ohm-1 cm-1
(b) ohm cm
(c) cm
(d) cm-1.
Answer:
(d) cm-1.
Question 10.
Oxidation state of nitrogen is maximum in :
(a) N3H
(b) NH2OH
(c) N2H4
(d) NH3.
Answer:
(a) N3H
Question 11.
Oxidation state of oxygen is zero in :
(a) CO
(b) O3
(c) SO2
(d) H2O2.
Answer:
(b) O3
Question 12.
Oxidation state of Fe in K4[Fe (CN)6] is :
(a)+ 2
(b) + 6
(c) + 3
(d) + 4.
Answer:
(a)+ 2
Question 13.
Oxidation state of S in H2S2O8 is :
(a)+ 2
(b) + 4
(c) + 6
(d) + 7.
Answer:
(c) + 6
Question 14.
Oxidation state of Mn in KMnO4 is :
(a) + 4
(b) + 6
(c) + 7
(d) + 5.
Answer:
(c) + 7
Question 15.
In which compound oxidation state of Cl is +1 :
(a) Cl2O
(b) HCl
(c) ICl
(d) HClO4.
Answer:
(a) Cl2O
Question 16.
Oxidation state of chlorine in ClO3– ion is :
(a)+ 4
(b) + 5
(c) + 3
(d) +2.
Answer:
(b) + 5
Question 17.
Halogen which reduces most easily:
(a) F2
(b) Cl2
(c) Br2
(d) I2.
Answer:
(a) F2
Question 18.
Oxidation number of C in CCl4 is:
(a) +4
(b) -4
(c) +6
(d) -6.
Answer:
(a) +4
Question 19.
Oxidation number of S in ISO4 is:
(a) +6
(b) -6
(c) +5
(d) -5.
Answer:
(a) +6
Question 20.
Oxidizing substance is:
(a) Electron acceptor
(b) Electron donor
(c) Proton acceptor
(d) Neutron acceptor.
Answer:
(a) Electron acceptor
Question 21.
Reaction 3ClO–(aq) → ClO–3(aq) + 2Cl–(aq) Is example of:
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
(c) Disproportionation
(d) Decomposition.
Answer:
(c) Disproportionation
![]()
Question 22.
OxidatIon number of S in S8, S2F2, H2S is:
(a) 0, +1, -2
(b) +2, +1, -2
(c) 0, +1, +2
(d) -2, + 1, -2.
Answer:
(a) 0, +1, -2
Question 23.
In the reaction : Mx+ +MnO4–+ MO3– +Mn2++\(\frac{1}{2}\)O2 if one mole MnO gets oxidized 1.67 mole Mx+ oxidizes to form MO–3 value of x will be:
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1.
Answer:
(c) 2
Question 24.
Oxidation number of Fe in Fe3O4 is:
(a) +2
(b) +3
(c) 8/3
(d) 2/3.
Answer:
(c) 8/3
Question 25.
A compound is formed by elements A, B and C. If their oxidation number A = +2,8 = +5 and C = -2, the formula of the compound will be:
(a) A3(BC4)2
(b) A3(B4C)2
(c) ABC2
(d) A3(BC3)2.
Answer:
(a) A3(BC4)2
Question 26.
In the reaction : xMnO4– + yH2O2 → 2Mn2+ + 5H2 + 9O2 + ze– value of x,y,z is:
(a) 2,5,6
(b) 5,2,9
(c) 3,5,5
(d) 2,6,6.
Answer:
(a) 2,5,6
Question 27.
In the redox reaction MnO4– + C2O4-2 + H+ → Mn2+ + CO2 +H2O molecular coefficients of MnO4–,C2O-2, H+ are:
(a) 2,5, 16
(b) 16,5,2
(c) 5, 11,2
(d) 2, 16,5.
Answer:
(a) 2,5, 16
![]()
Question 28.
Oxidation number of Cr in [Cr(PPh3)3CO3] is:
(a) +3
(b) +8
(c) Zero
(d) +5.
Answer:
(c) Zero
Question 29.
Which of the following is not a reducing agent:
(a) SO2
(b) H2O2
(c) CO2
(d) NO2.
Answer:
(c) CO2
Question 30.
Order of oxidation number of suipbur in SO3-2, S2O4-2 and S2O62- is:
(a) S2 O4-2 <SO32- <S2O6-2
(b) SO32- <S2 O4-2 <S2O6-2
(c) S2 O4-2 <S2O6-2 <SO32-
(d) S2O6-2 <S2 O4-2 <SO32-.
Answer:
(a) S2 O4-2 <SO32- <S2O6-2
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. Process of loss of electrons is called ………………. .
Answer:
Oxidation
2. Process of gain of electrons is called ………………. .
Answer:
Reduction
3. The deterioration of metals in presence of atmospheric gases and moisture is called ………………. .
Answer:
Corrosion
4. A device in which electric energy gets converted to chemical energy is called cell………………. .
Answer:
Electrolytic
5. In electrochemical series the ability to reduce ……………… on moving down.
Answer:
Decreases
6. Most strong reducing element is ………………. .
Answer:
Lithium
7. Most strong oxidizing element is ………………. .
Answer:
Fluorine
8. At equilibrium, value of Ecell is ………………. .
Answer:
Zero
9. In sodium amalgam, oxidation number of sodium is ……………….. .
Answer:
Zero
10. Oxidation number of Cr in Cr(CO)6 is ………………. .
Answer:
Zero
11. In Zn, Cu, Ag, Na, Sn weak reducing agent is ………………. .
Answer:
Ag
12. Oxidation number of Si in SiH4 is ………………. .
Answer:
-4
13. In OF2 and O2F2, oxidation number of O is ………………. .
Answer:
+ 2, +1
14. Oxidation number of Cl in Ca(OCl) Cl is ………………. .
Answer:
+1, -1.
3. Match the following:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. Maintains neutrality among two half cells | (a) Nernst equation |
| 2. Compound of Ni in +2 oxidation state | (b) Silver |
| 3. In Daniel cell Zn/Zn2+ is | (c) 0.00V |
| 4. Equation represents dependence of electrode potential on concentration | (d) Salt bridge |
| 5. Standard potential of SHE | (e) Anode |
| 6. Best electrical conducting metal | (f) [Ni(CN)4]2- |
Answer:
1. (d) Salt bridge
2. (f) [Ni(CN)4]2-
3. (e) Anode
4. (a) Nernst equation
5. (c) 0.00V
6. (b) Silver
![]()
4. Answer in one word/sentence:
1. What is balanced redox equation?
Answer:
Redox reactions in which amount of oxidation and reduction is to the same extent
2. Why does iron displace copper from its salt solution?
Answer:
Because standard electrode potential value of iron is less than the standard electrode potential value of copper
3. What is the oxidation state of chlorine in Cl2O?
Answer:
+1
4. Why does an electrolyte dissociate into ions when dissolved in water?
Answer:
4. Because the electrostatic attractive force
5. A saturated solution of KNO3 is used for the formation of salt bridge. Why?
Answer:
Because the speed of K+ and NO3– ions is almost same
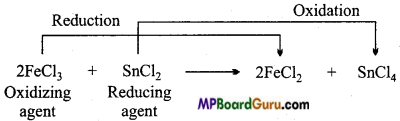
6. In SnCl2 + 2FeCl3 → SnCl4 + 2FeCl2 which compound is oxidized ?
Answer:
FeCl3
7. What is the oxidation number of Xe in XeO3?
Answer:
+6.