Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Biomolecules which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Biomolecules
Biomolecules Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is keratin?
Answer:
Keratin is a simple albuminoid protein and is the main constituent of hair, skin, nails, horns, feathers and wool. It is also known as scleroprotein. It is insoluble in neutral solvents but soluble in strong acids and bases.
Question 2.
What is chitin?
Answer:
Chitin is an important polysaccharide of invertebrates. It is found in the exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans and in the cell wall of fungi.
Question 3.
What do you understand by denaturation of proteins?
Answer:
The bonds of proteins are broken at higher temperature and thus structure and specific characters of proteins are changed. This phenomenon is called denaturation of protein.
![]()
Question 4.
What is nucleic acid?
Answer:
Nucleic acids are the polymer of nucleotides made up of C, H, O, N and P which controls the basic functions of the cell.
Question 5.
What are catalysts?
Answer:
Substance which can accelerate the rate of a chemical reaction are called as
catalysts.
Question 6.
What is enzyme? Explain.
Answer:
Enzymes are proteinic substances also called as biocatalysts, synthesized in living cells and initiate or accelerate metabolic reactions.
Question 7.
Define isoenzymes.
Answer:
Enzymes having different molecular configuration but having similar functions are known as isoenzymes, e.g., Lactic acid dehydrogenase (L.D.H.) which may occur in 5 possible forms in the blood sera and tissues of most vertebrates.
Question 8.
What is activation energy?
Answer:
The amount of energy required for the activation of a substance is called as activation energy. Enzymes lowering the energy of activation of the substrate so that biochemical reaction can take place at normal body temperature (at 37°C).
![]()
Question 9.
What is enzyme inhibition?
Answer:
The substance which reduces or inhibits the activity of enzyme are called enzyme inhibitor and the whole phenomenon is called as enzyme inhibition.
Question 10.
Give any two biological significance of enzymes.
Answer:
- Enzymes play an active role in all rnetabolic and catabolic reactions and it is required for all the types of activities of the body.
- Enzymes play an important role in biosynthesis, growth and repair of the body.
Question 11.
What are cofactors?
Answer:
A non-protein moiety attached to the protein part of enzyme is called as cofactor. If the cofactor is of inorganic nature like potassium, calcium, magnesium, manganese it is called prosthetic group. If cofactor attached to an enzyme protein is organic moiety like NAD, NADP or FAD it is known as coenzyme.
Question 12.
Define prosthetic group.
Answer:
The non-protein part of enzyme is called as cofactor. When the cofactor is of inorganic nature like K, Ca, Mg, Mn it is known as prosthetic group. Prosthetic group is generally tightly bounded to the protein part of enzyme.
Question 13.
Write differences between Apoenzyme and Hoioenzyme.
Answer:
All enzymes are proteins. However, there are some enzymes conjugated with a non-protein moiety (cofactor). Protein part of these conjugated enzymes are called as apoenzymes.
Enzymes with prosthetic group and apoenzyme are called as holoenzymes.
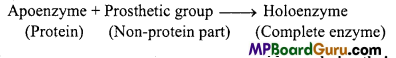
Question 14.
Write the names of any two polysaccharides and give their functions.
Answer:
- Cellulose : It forms cell wall of plant cell. ,
- Chitin : It forms exoskeleton of insects.
![]()
Question 15.
Write one difference in the following pair of words :
- Purineland pyrimidine,
- Starch and glycogen,
- Nucleoside and nucleotide,
- Fibrous and globular proteins.
Answer:
- Difference between purine and pyrimidine : Purine is two ringed heterocyclic nitrogenous base whereas pyrimidine is single ringed nitrogenous base.
- Difference between starch and glycogen : Starch is the storage food product of plants and glycogen of animals.
- Difference between nucleoside and nucleotide : Nucleotides are made up of nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate group whereas nucleosides are made up of only nitrogenous base and sugar.
- Difference between fibrous and globular proteins : Fibrous proteins are elongated molecules that may be constituted of several coiled peptide chains which are lightly linked whereas globular proteins are spherical or ovoid in shape due to folded peptide chains.
Question 16.
What do you understand by derived proteins?
Answer:
Derived proteins : Proteins which are derived from simple and conjugated proteins are called derived protein. They are not found in nature as such. They are obtained by the partial hydrolysis of natural proteins. These are formed by either change in the structure or breaking of their bonds, e.g., Peptones, protease, dipeptides, tri and tetrapeptides etc.
On complete hydrolysis of any protein the intermediate products are derived proteins whereas end-products are amino acids.

Question 17.
What is Dextrin? Give its importance.
Answer:
Dextrin is obtained by partial hydrolysis of starch, i.e., it is an intermediary substance of starch synthesis. It is used as sticking material in the cell.
Question 18.
What is agar-agar? Explain.
Answer:
Agar-agar is a polysaccharide, obtained from algae Gelidium, Gracilaria, which is mainly used in production of medium for culturing bacteria. It is neutral in nature. Iris- agar obtained from algae Chondrus crispes is used in preparation of chocolate, paint, toothpaste, ice-cream etc.
Question 19.
Write names of macromolecules of cell.
Answer:
Macromolecules of cell are:
- Polysaccharide,
- Protein,
- Nucleic acid etc.
![]()
Question 20.
Why are enzymes called biocatalysts?
Answer:
Enzymes are called as biocatalysts because they are the proteinous chemical substances which catalyse or accelerate rate of biochemical reactions occurs in the living body.
Question 21.
Give two important special characteristics of enzymes.
Answer:
- Catalytic properties : Enzymes are biological catalysts. The small quantity of enzyme may catalyse metabolism of larger quantity of substances.
- Specificity of enzymes : Enzymes are highly specific in nature, i.e., a particular enzyme can catalyse a particular reaction, e.g., Enzyme sucrase can catalyse only hydrolysis of sucrose.
Question 22.
What is Active site? Explain it.
Answer:
Part of the enzyme to which substrate molecule fit for biochemical reaction in the body of a living organism is called as active site. It is a three-dimensional structure to which substance fit. If geometry of active site changes then substrate fails to fit into the active site of enzyme. Actually active site is the binding site of the enzyme.
Biomolecules Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Explain any four factors affecting enzyme activity.
Answer:
The following four factors affect the activity of enzyme:
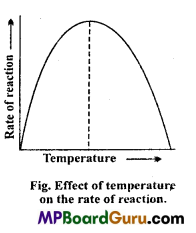
1. Temperature :
Metabolic reaction catalysed by enzymes increases the rate of activity at higher temperature because as temperature increases the kinetic energy of molecules also increases. But as the kinetic energy of molecules increases weak hydrogen bonds are more rapidly ruptured. The loss of hydrogen bonds modify the tertiary structure of enzymes and its catalytic activity, such alteration is called denaturation of enzyme.
2. Enzyme concentration:
As concentration of enzyme increases, the rate of enzyme activity also increases.
3. Substrate concentration:
In general, an increase in substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction but high concentration of the substrate, inhibits the activity of enzyme.
4. Hydrogen ion concentration (pH) :
An enzyme have an optimum pH, but the changes in hydrogen ion concentration causes change in enzyme activity. Every enzyme requires a specific pH for the maximum activity, e.g., Trypsin in duodenum acts in alkaline medium (pH = 8.5).
![]()
Question 2.
Explain exoenzymes and endoenzymes with suitable examples.
Answer:
Exoenzymes :
Enzymes which act outside the cells of their origin are called as exoenzymes. Enzymes secreted by the alimentary canal and used for digestion such as pepsin, trypsin, etc. are exoenzymes.
Endoenzymes :
Those enzymes which are produced inside the cell and participate in various reactions inside the cell are called intercellular or endoenzymes. They are active only inside the cells. Enzymes form mitochondria which takes part in cellular respiration.
Question 3.
What is the importance of enzymes?
Answer:
Importance of enzymes :
- Enzymes play an active role in all metabolic and catabolic reactions and it is required for every type of activities of the body,
- Enzymes catalyse and regulate the process of digestion, assimilation and absorption like chemical reactions,
- Enzymes play an important role in biosynthesis, growth and repair of the body,
- Enzymes regulate the energy release in respiration which is used in respiration, muscular, physical and mental activities.
Question 4.
Write down the similarities between enzymes and inorganic catalysts.
Answer:
Similarities between enzymes and inorganic catalysts :
- Enzymes and inorganic catalysts both of them remain unchanged at the end of the reaction chemically and quantitatively and can be used again to catalyse another reaction.
- Both are required in small quantity.
- They do not alter the equilibrium of the reversible reaction.
- Both of them increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy but they do not initiate the reaction.
- The complexes formed with the reactants by both of them are short lived.
Question 5.
What is peptide bond?
Answer:
The bond formed between the carboxylic group (- COOH) of one amino acid and amino group (- NH2) of another amino acid is called as peptide bond. A molecule of water is released during the formation of peptide bond.
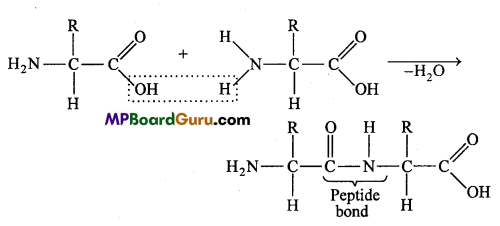
Each peptide chain of considerable length may possess 50 to millions of amino acid units. A peptide may be dipeptide (with 2 amino acid units), a tripeptide (with 3 units) and so on. Beyond 10 amino acid units, a peptide is called polypeptide.
Question 6.
What is deoxyribonucleoside? How it is converted into nucleotides?
Answer:
The substances which are formed from deoxyribose sugar and nitrogenous bases are called deoxyribonucleosides on the basis of nitrogenous bases they are of four types.
Nucleosides can be converted into nucleotides after their reaction with phosphoric acid. After condensation they form nucleic acids.
![]()
Question 7.
Name the constituents of the nucleotides found in DNA.
Answer:
The following four types of nucleotides are found in DNA :
| Nucleotide | Constituents |
| 1. Deoxyadenylic acid. | Deoxyribose sugar, adenine and phosphoric acid. |
| 2. Deoxyguanylic acid. | Deoxyribose sugar, guanine and phosphoric acid. |
| 3. Deoxycytidylic acid. | Deoxyribose sugar, cytosine and phosphoric acid. |
| 4. Deoxythymidylic acid. | Deoxyribose sugar, thymine and phosphoric acid. |
Question 8.
Write down the function of proteins.
Answer:
Function of proteins :
- Proteins form various structures of our body such as biomembranes, organelles (ribosome), hair and nails.
Skin, horns, wool (all contain keratin), cartilage (contains collagen) and bones (contain ossein protein). - Proteins function as biocatalyst (enzyme) in our body, e.g., Amylase and pepsin.
- The important cellular structures like cell membranes, connective tissue have proteins in their structure in which proteins functioning as a carrier molecule of different elements and compounds.
- Contractile proteins (e.g., Actin and myosin) participate in cellular movements and locomotion.
Question 9.
Write any four differences between DNA and RNA.
Or,
Write five differences between DNA and RNA on the basis of molecular composition and function.
Answer:
Differences between DNA and RNA
| DNA | RNA |
| 1. It contains deoxyribose sugar. | It contains ribose sugar. |
| 2. It has adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine as nitrogenous bases. | It has adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine as nitrogenous bases. |
| It has adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine as nitrogenous bases. | It consists of single polynucleotide chains, which may get folded on itself to form double helix. |
| 3. It consists of two polynucleotide chains, coiled into a double helix. | It is main constituent of ribosome and generally found in cytoplasm. |
| 4 It is main constituent of chromosome which is found in nucleus. | Generally RNA participates in the synthesis of protein. |
![]()
Question 10.
Define proteins and write their uses.
Answer:
Proteins :
Proteins are the polymer of amino acids. It is complex nitrogenous compound of the protoplasm. About 20 amino acids are joined together by means of peptide bonds form a protein molecule. About 20% part, the body of organisms is made up of proteins.
Uses of proteins :
Tertiary structure: Linear arrangement of amino acids through peptide linkage to form a polypeptide chain is called as Primary structure of protein. Folding of a linear polypeptide chain into specific coiled structure is referred as Secondary structure of protein.
1. Insulin : It is used for treatment of Diabetes mellitus.
2. Immunoglobulin : Immunoglobulin of the blood plasma in mammals and other animals act as antibodies which neutralize the harmful effect of foreign agents like viruses, bacterias etc.
3. Albumin : Albumin protein of egg (egg – white) is used for hair care.
4. Structural components of cells : Some proteins are essential structural compo-nents of cell membranes, organelles, cytoplasm, extracellular material and fibres. Keratin is the main constituent of hair, skin, nails, horns, feathers and wool. Cartilage is made of collagen. In plants protein is found in the walls of pollen grains.
5. Enzymes (Biocatalysts): The most important feature of proteins is their ability to function within the living cell as reaction catalysing enzymes. Enzymes usually increase the reaction rate by manifold. Enzymes play a key role in the metabolism.
6. Hormones : Proteins serve as hormones also. Hormones from pancreatic islets of Langerhans, pituitary, parathyroid and gastrointestinal mucosa are of peptide nature. Hormones of thyroid and adrenal medulla are derivatives of amino acid tyrosine.
7. As carriers : Haemoglobin, the respiratory pigment of many animals is a conju-gated protein composed of colourless basic proteins, the globin and haem. It has unique ability to bind oxygen in a loose and easily reversible combination. Myoglobin transports oxygen in muscles. In plants p-protein is involved in the transport of organic compounds through phloem.
8. Growth and repair : Proteins play a key role in general body growth and in the repair of wear and tear of the cells and body as a whole.
9. Formation of rhodopsin : The visual purple rhodopsin is made up of retinene an aldehyde derivative of vitamin-A and a protein opsin.
10. Melanin synthesis : Melanin, the skin pigment is derived from the tyrosine.
11. Formation of urea : In ureotelic animals, ornithine, citrulline and arginine (all amino acids) take part in the formation of urea by a cyclic process.
12. In some organisms protein is stored food, such as Albumin of egg, yolk of egg, in wheat as Glutein etc.
13. Fibroin protein secreted by silkworm produces silk on drying.
14. It may release energy by decomposing when required.
Question 11.
Draw a well labelled diagram of Watson and Crick model of DNA.
Answer:
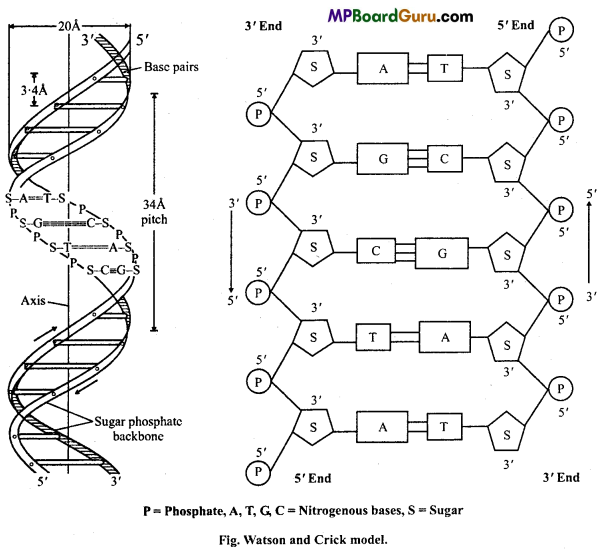
![]()
Question 12.
Write short note on structural polysaccharides.
Answer:
Structural Polysaccharides : These polysaccharides take part in forming the structural framework of the cell wall in plants and skeleton of animals. They are of two main types:
1. Cellulose :
Cellulose is an important constituent of cell walls of plant, which provides mechanical support to plant cell. It is polymer of glucose and made up of unbranched chain of approximately 6,000 β-D-glucose units linked by 1,4-glycosidic linkage. It consti¬tutes 20-40% of cell wall.
2. Chitin :
Chitin is an important heteropolysaccharide of invertebrates. It is found in the hard exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans and in the cell wall of fungi. It is polyglycol consisting of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units connected throughβ-1, 4-glycosidic linkage. Although chitin is soft and leathery it becomes hard when calcium carbonate or certain proteins are deposited in it. The insolubility of structural polysaccharides in water helps to retain the form and to strengthen the structure of the organism. In fungal cell wall chitin is often called as fungus cellulose.
Question 13.
Explain DNA replication.
Or,
Explain DNA duplication in short.
Answer:
Watson and Crick after giving the double helix model of DNA, also postulated the mechanism of DNA duplication, also known as replication. According to them, during duplication, the weak hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base of the nucleotides get separated, so that two polynucleotide chains of DNA also separate and uncoil. The chains thus, separated are complementary to one another.
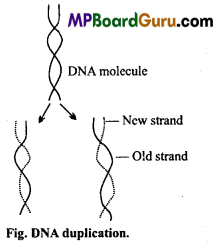
These strands act as template and because of the specificity of base pairing each nucleotide of separated chain attracts its complementary nucleotide from the cell cytoplasm. Once the nucleotides are attached by their hydrogen bonds their sugar radicals write through their phosphate components completing the formation of a new polynucleotide chain. This results in the formation of two double helixes of DNA where in each molecule has one old strand contributed by parent DNA and one synthesized new. This method of DNA duplication is known as semi-conservative method.
Question 14.
Describe the functions of nucleic acids.
Or,
Explain the utility of nucleic acids.
Answer:
Utility of nucleic acids:
- Nucleic acids are the hereditary materials of organisms which involve in the transfer of hereditary characters from one generation to the next.
- DNA controls the synthesis of enzymes which control the various activities of the body.
- Nucleic acids also control protein synthesis,
- Nucleic acids form maximum portion of chromatin network,
- It causes mutation in living beings,
- They form enzymes.
Question 15.
Elaborate the term RNA. Also describe the types and functions of RNA.
Or,
Write location and kinds of RNA in the cell.
Answer:
RNA : Ribonucleic acid (RNA) located in the nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes and in some other cell organelles.
Types of RNA and their functions : RNA are of three types :
1. Messenger RNA (mRNA):
It makes a small fraction 5-10%. This RNA directs the sequence of amino acids in protein synthesis after joining with ribosomes. It carries the genetic information contained in DNA. It is short lived and has rapid turn over. It is formed of 700-1500 nucleotides and has a molecular weight from 5,00,000 to 20,00,000. The sequence of three nitrogenous bases of tnRNA forms a codon which is responsible for coding of one amino acid.
2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) :
It makes 80% of total cell RNA. It is the most stable type of RNA and is associated with ribosomes.
3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) :
It makes a small fraction (10-15%) of RNA. These are smallest molecules formed of 73-93 nucleotides with molecular weight ranging between 25,000 to 30,000. tRNA works as adaptor molecules for carrying amino acids to the TMRNA template during protein synthesis.
![]()
Question 16.
Write names of the nucleosides which help in energy transfer.
Answer:
- ATP: Adenosine triphosphate,
- ADP: Adenosine diphosphate,
- GTP : Guanosine triphosphate,
- GDP : Guanosine diphosphate,
Question 17.
Describe structure of RNA.
Answer:
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) :
These are second type of nucleic acids which are found in the nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes and in some other cell organelles.
RNA occurs normally as long unbranched polymeric molecule in the form of a single chain. Generally non-genetic RNA of eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells have single strand except fRNA which has double strand but without helical structure. But the wound tumour virus (a plant virus) and Rheo virus (animal virus) have double strand in their RNA molecule.
Chemical composition of RNA :
RNA molecules are polymers of ribonucleotides. Each ribonucleotide is made up of three different molecules namely a ribose pentose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar as in DNA, a phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base.
Two types of nitrogenous bases are found in RNA :
- Purines : Adenine (A) and guanine (G).
- Pyrimidines : Uracil (U) and cytosine (C). Thus, uracil substitutes thymine of DNA. In RNA above four nitrogenous bases join with the ribose sugar to form ribonucleoside.
Nucleosides of RNA : There are four types of ribonucleosides are present in RNA :
- A + Ribose sugar = Riboadenosine
- G + Ribose sugar = Riboguanosine
- C + Ribose sugar = Ribocytidine ‘
- U + Ribose sugar = Ribouridine.
Nucleotides of RNA : Phosphoric acid joins with each ribonucleoside to form ribonucleotide.
- A + Ribose sugar + Phosphoric acid = Riboadenylic acid
- G + Ribose sugar + Phosphoric acid = Riboguanylic acid
- C + Ribose sugar + Phosphoric acid = Ribocytidylic acid
- U + Ribose sugar + Phosphoric acid = Ribouridylic acid.
These four ribonucleotides are linked together to form a long strand of ribopolynucleotide.
Question 18.
What is enzyme? Explain the characteristic features of enzymes.
Answer:
Enzymes are proteinic substances also called as biocatalysts synthesized in living cells and initiate or accelerate metabolic reactions by lowering activation energy.
Characteristic features of enzymes :
1. Physical properties :
Physically enzymes behave as colloids or as substance of high molecular mass. They are destroyed or inactivated at temperature below the boiling point of water. At 50°C most enzymes in a liquid medium are inactivated. Dried enzyme extract can endure temperature of 100°C to 120°C or even higher. Thus, enzymes are thermolabile.
2. Chemical properties:
(i) Catalytic properties :
Enzymes are biological catalyst. Catalysts are substances which accelerate the speed of chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent changes. The small quantity of enzyme catalyses the larger quantities of substrates.
(ii) Specificity of enzymes :
Enzymes are highly specific in nature, i.e., a particular enzyme can catalyse only a particular reaction at a particular temperature, e.g., Enzyme sucrase, can catalyse only hydrolysis of sucrose.
3. General properties:
- They initiate and accelerate the rate of biochemical reaction.
- The activity of enzymes depends upon the acidity of the medium (pH specific). Each enzyme is most active at a particular acidity (pH).
- Enzyme can accelerate the reaction in either directions :
![]()
- All enzymes possess active sites which participate in the biochemical reactions.
- They are very unstable compounds mostly soluble in water, dilute glycerol, NaCl and dilute alcohol.
- They act actively at optimum temperature.
- All enzymes are proteins but all proteins are not enzymes.
![]()
Question 19.
Give the composition of Triglyceride.
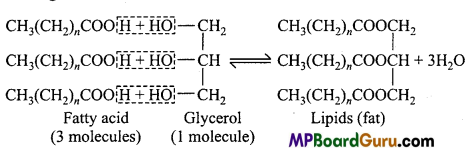
Answer:
Triglycerides are a group of stored lipid which include oil and fats. Chemically, lipids are the esters or glycerides of fatty acid and glycerol. It is made up of three molecules of fatty acid and one molecule of glycerol. Their general formula is CH3(CH2)n„COOH. The carboxylic group (- COOH) of each fatty acid react with alcoholic group (-OH) of glycerol and form ester linkage.
Question 20.
Write short note on Globular protein.
Answer:
Globular protein:
These are spherical or oval in shape because of the presence of peptide folded or coiled chain which forms compact structure, it is called as globular protein. It forms a three-dimensional structure, which is formed by relatively weak non-covalent bond. It is a secondary structure of protein, soluble in water. These include enzymes, protein, hormones like ACTH, oxytocin, glucagon and insulin etc.
Question 21.
Of which substance gum is made up? Is fevicol different than this?
Answer:
Gum is a carbohydrate, such as D-Galactose, D-Galactonic acid, which are natural substances, whereas fevicol is an artificial product which is used as gum.
Question 22.
Can you explain process of conversion of milk into curd or yogurt on the basis of concept of protein?
Answer:
Protein present in the milk is casein, which is a white coloured substance and has nutritional value. It consists of essential amino-acids required for the growth of human body. Conversion of milk into curd is a chemical process. Lactobacillus bacteria ferment lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid and help to settle casein. Settled casein is called as curd or yogurt.
Question 23.
Can you prepare biomolecule model using commercial model of atom (Ball and stick model)?
Answer:
Yes, we can prepare biomolecule model using commercial model of atom.
Question 24.
Which functional groups are released on titration of amino acid with weak base?
Answer:
On titration of amino acid with weak base two functional groups are released :
- – COOH group (Carboxylic group)
- – NH2 group (Amino group)
![]()
Question 25.
Give structural formula of amino acid Alanine.
Answer:
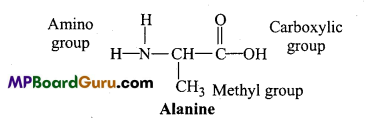
Question 26.
Write short note on conjugated protein and give two examples of it.
Answer:
Conjugated Proteins : These are complex protein molecules, which is formed by combination of simple protein molecule with characteristics non-protein substance called as prosthetic group, i. e., on hydrolysis conjugated protein yield a protein and a non-protein substance.
Protein + Prosthetic group → Conjugated protein
Conjugated proteins are of following types :
- Nucleoprotein,
- Mucoprotein,
- Glycoprotein,
- Chromoprotein,
- Lipoprotein,
- Metalloprotein and,
- Phosphoprotein.
e.g., Haemoglobin, Lipoprotein
Globin + Haem → Haemoglobin
Protein + lipid → Lipoprotein.
Biomolecules Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
If a given protein has primary structure, in which amino acids are present at both the ends, then can you connect this information with purity or homogeneity of protein?
Answer:
The primary structure of protein refers to the linear sequence of number of amino acids belonging to the polypeptide chain. The amino acids link together by peptide bond only. It is formed by binding of amino group (-NH2) of one amino acid with carboxylic group (-COOH) of another amino acid. Therefore, a single polypeptide chain has first amino acid at one end and the last amino acid at the other end. Amino group of first amino acid is called as ‘N’ terminal and carboxylic group of last amino acid is called as ‘C’ terminal.
By above information purity or homogeneity of a protein cannot be determined because many other amino acids (50 to millions) are found in between them.
Question 2.
Find out the proteins used as therapeutic agents and make a list. Give other uses of protein (as cosmetics) etc.
Answer:
1. Insulin : It is used for treatment of Diabetes mellitus.
2. Immunoglobulin : Immunoglobulin of the blood plasma in mammals and other animals act as antibodies which neutralize the harmful effect of foreign agents like viruses, bacterias etc.
3. Albumin : Albumin protein of egg (egg – white) is used for hair care.
4. Structural components of cells : Some proteins are essential structural compo-nents of cell membranes, organelles, cytoplasm, extracellular material and fibres. Keratin is the main constituent of hair, skin, nails, horns, feathers and wool. Cartilage is made of collagen. In plants protein is found in the walls of pollen grains.
5. Enzymes (Biocatalysts): The most important feature of proteins is their ability to function within the living cell as reaction catalysing enzymes. Enzymes usually increase the reaction rate by manifold. Enzymes play a key role in the metabolism.
6. Hormones : Proteins serve as hormones also. Hormones from pancreatic islets of Langerhans, pituitary, parathyroid and gastrointestinal mucosa are of peptide nature. Hormones of thyroid and adrenal medulla are derivatives of amino acid tyrosine.
7. As carriers : Haemoglobin, the respiratory pigment of many animals is a conju-gated protein composed of colourless basic proteins, the globin and haem. It has unique ability to bind oxygen in a loose and easily reversible combination. Myoglobin transports oxygen in muscles. In plants p-protein is involved in the transport of organic compounds through phloem.
8. Growth and repair : Proteins play a key role in general body growth and in the repair of wear and tear of the cells and body as a whole.
9. Formation of rhodopsin : The visual purple rhodopsin is made up of retinene an aldehyde derivative of vitamin-A and a protein opsin.
10. Melanin synthesis : Melanin, the skin pigment is derived from the tyrosine.
11. Formation of urea : In ureotelic animals, ornithine, citrulline and arginine (all amino acids) take part in the formation of urea by a cyclic process.
12. In some organisms protein is stored food, such as Albumin of egg, yolk of egg, in wheat as Glutein etc.
13. Fibroin protein secreted by silkworm produces silk on drying.
14. It may release energy by decomposing when required.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe Glycosidic, Peptide and Phosphodiester bonds.
Answer:
1. Glycosidic bond :
During the union of monosaccharide units water molecule is eliminated and the units are linked through an oxygen bridge known as glycoside linkage. Depending upon the steric configuration at carbon-1 of monosaccharide unit the bond is called α and β-bond.
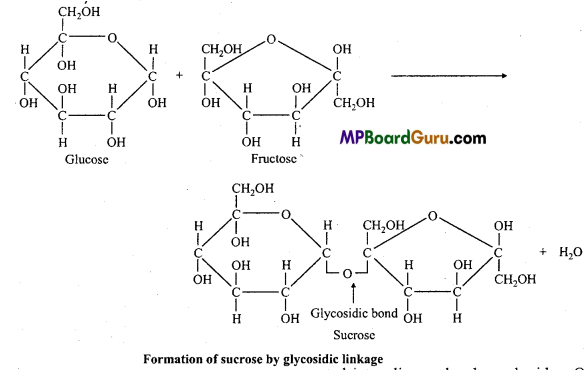
By this bond monosaccharides are converted into oligo and polysaccharides. On hydrolysis they yield monosaccharides.
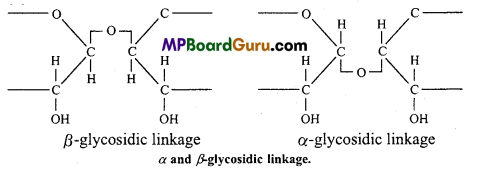
2. Peptide bond :
The bond formed between the carboxylic group (- COOH) of one amino acid and amino group (- NH2) of another amino acid is called as peptide bond. A molecule of water is released during the formation of peptide bond.
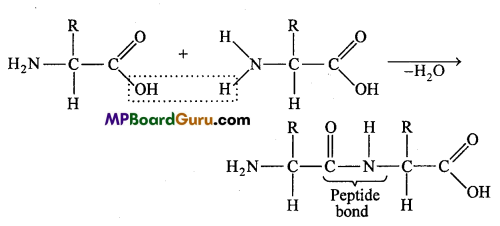
Each peptide chain of considerable length may possess 50 to millions of amino acid units. A peptide may be dipeptide (with 2 amino acid units), a tripeptide (with 3 units) and so on. Beyond 10 amino acid units, a peptide is called polypeptide.
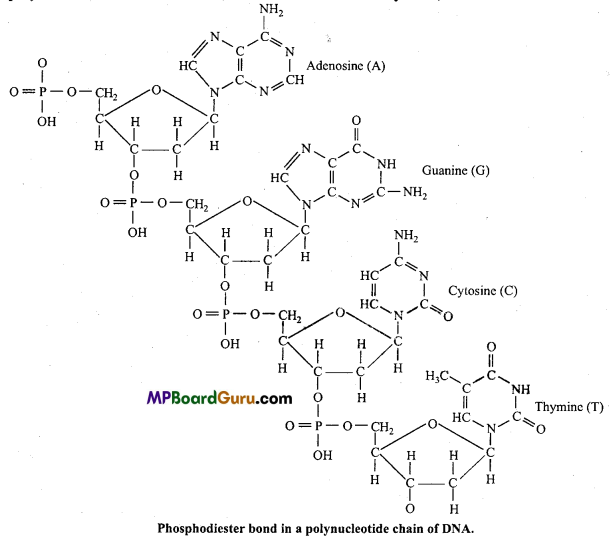
3. Phosphodiester bond :
Nucleic acid, like DNA molecules are polymers of deoxyribonucleotides. Each deoxyribonucleotides is made up of three different molecules :
(i) a decxyribose sugar (Pentose sugar),
(ii) a phosphoric acid and
(iii) a nitrogenous base. Nitrogenous base may be of two types :
1. Purines : Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
2. Pyrimidines : Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T).
3′ carbon of one nucleotide combine with 5′ carbon of next (adjacent) nucleotide by phosphate group. Ester bond is formed between phosphate of sugar and hydroxyl group. Ester bond is formed on both the sides of phosphate group, thus it is called as Phosphodiester bond.
Nucleotides unite with each other by phosphodiester bond to form long chain of polynucleotide of DNA or RNA, but in RNA instead of thymine, uracil is found.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Tertiary structure of protein?
Answer:
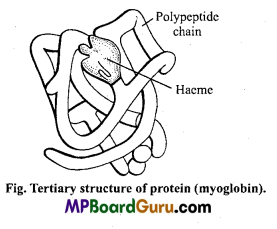
Tertiary structure: Linear arrangement of amino acids through peptide linkage to form a polypeptide chain is called as Primary structure of protein. Folding of a linear polypeptide chain into specific coiled structure is referred as Secondary structure of protein.
The arrangement and interrelationship of twisted chains of proteins into specific loops and bends are called the tertiary structure of protein.
Tertiary structure of protein is maintained by four kinds of bonds :
- Hydrogen bonds,
- Hydrophobic bonds,
- Ionic or electrostatic bonds and
- Disulphide bonds.
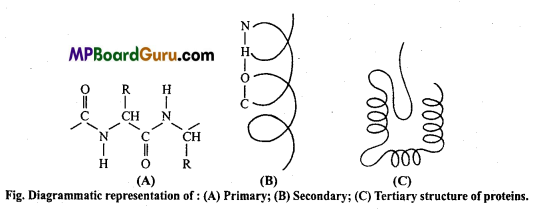
![]()
Question 5.
Write structural formula of 10 micro biomolecules of low molecular weight. Find out the industries involved in their production. Who are the customer of them? Find out.
Answer:
Structural formula of low molecular weight micro-biomolecules are as follows: (1) Monosaccharides :
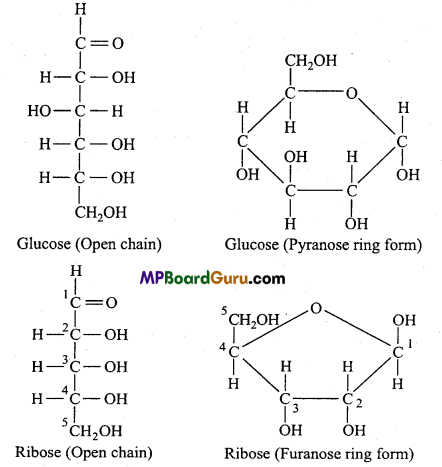
(2) Amino acids:

(3) Oil and fat:
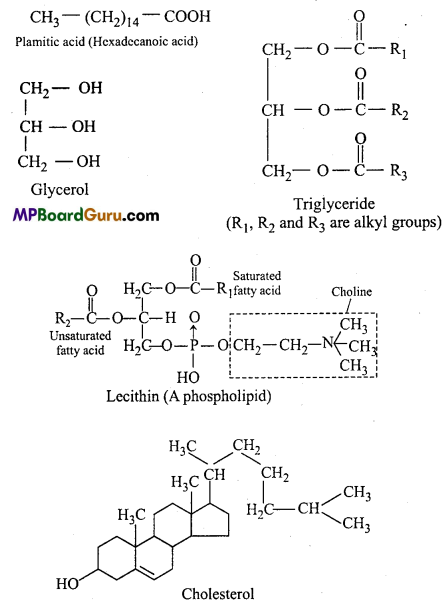
(4) Nitrogenous bases:
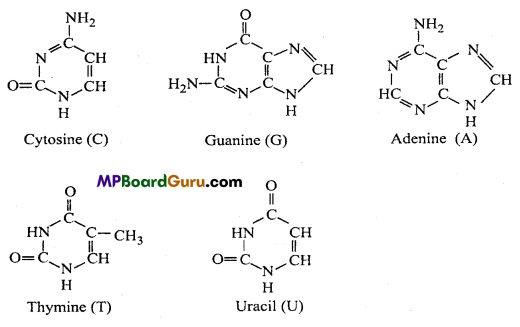
(5) Nucleoside and Nucleotide
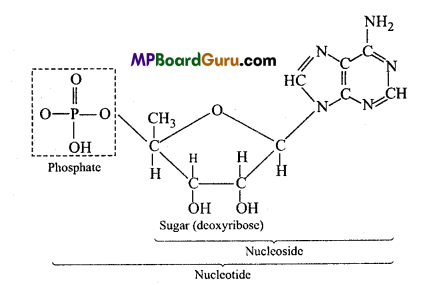
![]()
Question 6.
Give analytical test of protein, fat, oil and sugar and test presence of them
in any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine sample. (NCERT)
Answer:
(1) Test for Protein in sample of urine
| Experiment | Observation | Inference |
| 1. Take 5ml of Conc. HNO3 in a test tube Now slowly drop the urine sample to it with the help of a dropper by bending the test tube, so that slowly urine comes in contact of acid. | At the region of contact of urine white precipitate is formed. | Protein present. |
| 2. The solution containing white ppt. isheated. | Colour of the ppt. becomes yellow. | Protein confirmed. |
(2) Test for presence of Oil and Fat in food sample
| Experiment | Observation | Inference |
| 1. Put a drop of fat or oil at the centre of a paper. Spread it slowly with the help of finger. | Paper appears translucent. | Presence of oil or fat in food item confirmed. |
(3) Test for presence of Starch in food sample
| Experiment | Observation | Inference |
| 1. Take sample of food, grind it and dissolve in water to prepare a solution. Take 5ml of sample solution in a test tube, add freshly prepared iodine solution to it. | Solution turn into blue black colour.
|
Presence of starch in food sample is confirmed.
|
(4) Presence of Sugar in sample of fruit juice .
| Experiment | Observation | Inference |
| 1.Take 5ml of Benedict’s solution in a test tube. Add 8 drops of fruit juice sample in it. Heat the mixture for 2 minutes and cool it. | Green or yellow or orange or red coloured precipi tate is obtained. | Red colour indicates presence of more quantity of sugar and orange colour shows comparatively less sugar whereas yellow or green colour shows presence of less quantity of sugar. |
Question 7.
What do you mean by cellular macromolecules? Write the name of different macromolecules and describe any one in detail.
Answer:
Cellular macromolecules : The molecules formed by the process of polymerization are called as macromolecules. Macromolecules of the cell possess the following characteristic features:
- Chemically they are larger in size,
- Their molecular weight is very high,
- Their solubility is very low.
- Their molecular structure may be simple branched or unbranched and coiled,
- They are the polymers of micromolecules, e.g., (I) Polysaccharides, (II) Proteins and (III) Nucleic acids.
Polysaccharides :
They are polymers of monosaccharides and is made up of 10 to several thousand units of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkage. After hydrolysis they produce monosaccharides. Their empirical formula is (C6H10O5)n where n ranges from 10 to 10,000. Their molecular weight is very high.
Polysaccharides are of following two types :
1. Homopolysaccharides : These polysaccharides are made up of one kind of monosaccharides as in starch, cellulose, glycogen and insulin.
2. Heteropolysaccharides : These polysaccharides are made up of two or more kinds of monosaccharides as in agar, pectin and chitin.
On the basis of their functions polysaccharides are classified into following two groups:
(a) Storage polysaccharides and
(b) Structural polysaccharides.
(a) Storage polysaccharides : Polysaccharides which are synthesized by the process of photosynthesis and are stored in the form of food materials in plants and animals are called as storage polysaccharides, e.g., Starch, glycogen, gum, insulin, dextrin.
(i) Starch :
It is the storage carbohydrate of plants. It is formed during the process of photosynthesis and serves as an energy storing material. Starch is a polymer of glucose unit linked together in an α-1,4-glycosidic linkage. It yields only glucose on hydrolysis. In fact it is formed by condensation of amylase and amylopectin. Starch grains may be oval, spherical, lens shaped or irregular.
(ii) Glycogen :
Glycogen is the storage polysaccharide of animals and is called as animal starch. It is a branched polymer of glucose. It is stored mostly in muscles and liver of animals. The glycogen of liver supplies glucose to all tissue through blood. It is also found as storage product in blue-green algae, slime, moulds, fungi and bacteria. Their general formula is (C6H10O5)n)„. It consists of α-D glucose units mostly linked by 1, 4 but highly branched via 1,6-linkage each of which starts other α-1,4 chain of some 8-T 2 glucose units.
(b) Structural polysaccharides :
Polysaccharides which take part in the structural organization and protection mechanism of the body are called structural polysaccharides, e.g., Cellulose, chitin, etc.
Utility of polysaccharides :
- Polysaccharides serves as an important structural component in some animals and in all plants where they constitute cellulose framework.
- They are stored as storage food material and whenever required these can be hydrolyzed to yield energy.
- Cellulose forms protective covering as cell wall in plant cells. In some animals chitin forms protective exoskeleton.
- Mucilage acts as binding substance of cell walls and connective tissue.
Polysaccharides are also used in textile, furniture, printing, varnish, alcohol and film
industries.
![]()
Question 8.
How many kinds of nucleic acids are found in the cell? Give a detailed account of DNA.
Or,
Explain the structure of DNA.
Answer:
Every type of plant and animal cell (except virus) generally possess following two kinds of nucleic acids :
(i) DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid),
(ii) RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
Where viruses possess only one type of nucleic acid from the above.
Structure of DNA : Structurally DNA is the chain of polydeoxyribonucleotides. It means that DNA is formed by the polymerization of deoxyribonucleotides. Every DNA molecule possesses the following four kinds of nucleotides :
- Deoxyadenylic acid,
- Deoxyguanylic acid,
- Deoxycytidylic acid,
- Deoxythymidyhc acid.
Watson and Crick (1953) suggested a ‘double helix’ model of DNA. According to them, the DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide helically twisted strands which are complementary running in opposite direction (3′ – 5′, 5′ – 3 ‘) and connected together by steps.
The vertical bars are formed by alternate phosphate and sugar groups joined by phosphodiester bonds. These strands are formed together by hydrogen bonds which are established between specific nitrogen base in the sequence A = T, T = A, C ≡ G and G ≡ C. The length of one complete turn is 34Å. There are 10 nitrogenous base pairs in each turn. The distance between two nucleotides is 34 Å. The width of DNA is 20Å. Each successive nucleotide turns 36 degree in the horizontal plane. The twisting of strands results in the formation of deep and shallow spiral groove.
Significance of DNA:
- DNA is the genetic material which transmits parental characters from generation to generation,
- DNA together with protein form chromosomes,
- It is the constituent of ribosomes, mitochondria and plastids.
- It is responsible for mutation and organic evolution,
- It synthesizes enzymes required for various biological activities.
Question 9.
Describe important properties of enzyme.
Answer:
Important properties of enzymes are as follows :
(i) Catalytic properties :
Enzymes are biological catalyst. Catalysts are substances which accelerate the speed of chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent changes. The small quantity of enzyme catalyses the larger quantities of substrates,
(ii) Specificity of enzymes :
Enzymes are highly specific in nature, i.e., a particular enzyme can catalyse only a particular reaction at a particular temperature, e.g., Enzyme sucrase, can catalyse only hydrolysis of sucrose.
(iii) Colloidal state :
Physically enzymes behave as colloids or as substances of high molecular mass. They are hydrophilic in nature. They are amphoteric in nature. Thus, behave as alkali with acid and as acid with alkali.
(iv) Reversible in action : Enzymes can accelerate the reaction in either directions.
e.g., Sucrase enzyme hydrolyse sucrose into glucose and fructose. It also catalyse backward reaction.
![]()
(v) Sensitivity :
Each enzyme is catalytically active within a limited range of pH. Most enzymes operate effectively in a range of about 5 to 9 pH. For example, the optimal range for the activity of malt amylase is 5-2 pH, for salivary amylase between 6-7 to 6-8 pH, for trypsin 8 to 11 pH. In all these cases the activity gradually declines on either side of the optimum pH. Most intracellular enzymes function best at neutral pH 7.
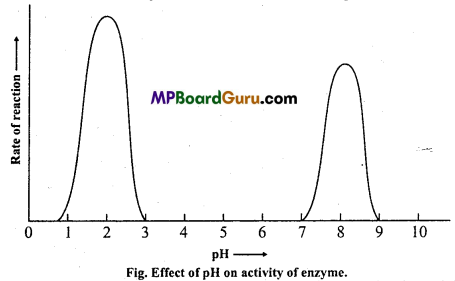
(vi) High molecular weight:
Enzymes are the proteins of high molecular weight, e.g., molecular weight of feredoxin of bacteria is 6000 and pyruvate dehydrogenase is 46,00,000.
(vii) High reactivity :
Small quantity of enzyme may catalyse reaction at fast rate. Total number of substrate molecule which may convert into product in one minute by one enzyme is called as Turnover number. Turnover number of different enzymes are as follows:
- Carbonic anhydrase : 36 million,
- Catalase : 5 million,
- Sucrase or Invertase : 10,000,
- Flavo protein : 90.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain biological significance of enzymes.
Answer:
Following are the biological importance of enzymes :
1. Healing of wound :
A protein digesting enzyme obtained from pancreas of the pig is very useful for skin diseases and healing of wound. These enzymes destroys protein digesting enzymes of human body thus help for healing of wound.
2. Dehairing of hides :
Enzymes obtained from pancreas destroys hair follicles of hair, thus help for removal of hair from hide.
3. Dissolving the blood clot:
An enzyme called as urokinase obtained from urea helps to dissolve blood clot which are formed in the brain or arteries, thus saves our life.
4. Changing blood group :
Prof. Ken Furunkawa in 1981 explained the blood group is determined by the presence of sugar found in R.B.Cs. for which specific enzymes are found. If these enzymes are destroyed, then blood group ‘A’ and ‘B’ can change into blood group‘O’.
5. Analysis of biochemicals :
Some enzymes are used for quantitative analysis of some specific substances found in blood. For example, uricase, urease and sucrase enzymes are used to determine quantity of uric acid, urea and sucrose present in the blood respectively.
6. Cheese making :
Animal renin (milk protein digesting enzyme) is used in cheese making.
7. Manufacture of fruit juice : Some enzymes are used for processing of some fruit juices. Pectic enzymes are added to these fruit juices to make it clean and clear.
Biomolecules Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Lipids contain carbohydrates and N2 are called :
(a) Phospholipids
(b) Chromolipids
(c) Aminolipids
(d) Glycolipids.
Answer:
(d) Glycolipids.
Question 2.
Lecithin is :
(a) Phospholipids
(b) Chromolipids
(c) Aminolipids
(d) Glycolipids.
Answer:
(a) Phospholipids
Question 3.
Fats and oils are decomposed by bases and produce :
(a) Soap
(b) Vegetable ghee
(c) Saturated fat
(d) Unsaturated fat.
Answer:
(a) Soap
Question 4.
Compounds with free amino and carboxylic group are called :
(a) Glucose
(b) Nucleotide
(c) Amino acid
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Amino acid
![]()
Question 5.
Nucleotide responsible for energy transfer is :
(a) NAD
(b) FAD
(c) FMN
(d) ATP.
Answer:
(d) ATP.
Question 6.
Unit of protein is :
(a) Fatty acids
(b) Monosaccharides
(c) Amino acids
(d) Glycerol.
Answer:
(c) Amino acids
Question 7.
Nucleic acids are the polymers of:
(a) Amino acids
(b) Nucleosides
(c) Nucleotides
(d) Globulin.
Answer:
(c) Nucleotides
Question 8.
Peptide bonds are found in:
(a) Proteins
(b) Fats
(c) Nucleic acids
(d) Carbohydrates.
Answer:
(a) Proteins
Question 9.
Glycosidic bonds are found in:
(a) Nucleic acids
(b) Proteins
(c) Polysaccharides
(d) Monosaccharides.
Answer:
(c) Polysaccharides
Question 10.
A nucleoside differs from nucleotide ¡s not having:
(a) Sugar
(b) Nitrogen base
(c) Phosphate
(d) Both (a) and (e).
Answer:
(c) Phosphate
Question 11.
A unit composed of sugar and nitrogen base linked by glycosidic bond is:
(a) Purine
(b) Glycoside
(c) Nucleoside
(d) Nucleotide.
Answer:
(c) Nucleoside
![]()
Question 12.
Building block of nucleic acid is:
(a) Amino acid
(b) Nucleoprotein
(c) Nucleotide
(d) Nucleoside.
Answer:
(c) Nucleotide
Question 13.
Lactose molecule ¡s composed of:
(a) Glucose + Fructose
(b) Glucose + Glucose
(c) Glucose + Galactose
(d) Fructose + Fructose.
Answer:
(c) Glucose + Galactose
Question 14.
Heredity is controlled by:
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) Generally DNA and sometimes RNA in few organisms
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Generally DNA and sometimes RNA in few organisms
Question 15.
DNA is made up of:
(a) Deoxyribonucleotide
(b) Ribonucleotide
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Polysaccharides.
Answer:
(a) Deoxyribonucleotide
Question 16.
Which base is absent in RNA:
(a) Adenine
(b) Guanine
(c) Thymine
(d) Uracil.
Answer:
(c) Thymine
Question 17.
Protein controlling the chemical reactions of the body is:
(a) Enzyme
(b) Vitamin
(e) Hormone
(d) Globulin.
Answer:
(a) Enzyme
Question 18.
Snake poison is a type of protein:
(a) Fibrous protein
(b) Globular protein
(c) Lipoprotein
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Globular protein
![]()
Question 19.
Nucleic acids were discovered by:
(a) Watson
(b) Crick
(c) Miescher
(d) Beadle.
Answer:
(c) Miescher
Question 20.
Wood and cotton having higher amount of:
(a) Cellulose
(b) Cutin
(c) Chitin
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Cellulose
Question 21.
Insulin is a type of:
(a) Pigment
(b) Food
(c) Protein
(d) Gas.
Answer:
(c) Protein
Question 22.
Unit of polysaccharide is:
(a) Monosaccharides
(b) Oligosaccharides
(o) Peptides
(d) Fatty acids.
Answer:
(a) Monosaccharides
Question 23.
Doctor generally prescribing to take oil in place of fats because:
(a) Oil contains unsaturated fatty acids
(b) It reduces the amount of cholesterol in blood
(c) They are quickly digested
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 24.
Double stranded model of DNA was proposed by:
(a) Watson and Crick
(b) Miescher
(c) Muller
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Watson and Crick
![]()
Question 25.
How RNA is synthesized:
(a) By DNA
(b) By RNA
(c) By ribosomes
(d) By lysosomes.
Answer:
(a) By DNA
Question 26.
Energy providing substance in our body is:
(a) Carbohydrate
(b) Protein
(c) Fat
(d) Vitamin.
Answer:
(a) Carbohydrate
Question 27.
Heparin of the blood is a:
(a) Glycoprotein
(b) Nucleoprotein
(c) Chromoprotein
(d) Glycolipid.
Answer:
(a) Glycoprotein
Question 28.
Term protein was coined by:
(a) Camilo Golgi
(b) Bergellius
(c) Bloor
(d) Funk.
Answer:
(b) Bergellius
Question 29
Mucin of saliva is:
(a) Nucleoprotein
(b) Glycoprotein
(c) Lipoprotein
(d) Chromoprotein.
Answer:
(b) Glycoprotein
![]()
Question 30.
The unit formed by β-glycosidic linkage between sugar and base is called as:
(a) Nucleotide
(b) Nucleoside
(c) Glycoside
(d) Punne.
Answer:
(b) Nucleoside
Question 31.
mRNAispolymerof:
(a) Deoxyribonucleoside
(b) Ribonucleoside
(c) Deoxyribonuc1eotk
(d) Ribonucleotide.
Answer:
(d) Ribonucleotide.
Question 32.
Purine of RNA are:
(a) Guanine and adenine
(b) Uracil and thymine
(c) Adenine and cytosine
(d) Uracil and guanine.
Answer:
(a) Guanine and adenine
Question 33.
Enzyme which convert the starch into sugar is:
(a) Hydrolases
(b) Lipases
(c) Amylases
(d) Nucleases.
Answer:
(c) Amylases
Question 34.
Protein part 01 enzyme is called:
(a) Apoenzyme
(b) Coenzyme
(c) Holoenzyme
(d) Cofactor.
Answer:
(a) Apoenzyme
Question 35.
Peptide bonds are formed between:
(a) Amino acids
(b) Glucose molecule
(c) Sucrose molecule
(d) Glycerol molecule.
Answer:
(a) Amino acids
![]()
Question 36.
How enzymes differ from organic catalysts :
(a) Their higher rate of diffusion
(b) Active under high temperature
(c) Active under low temperature
(d) Protein nature.
Answer:
(d) Protein nature.
Question 37.
Which ¡s not a character of enzyme:
(a) They are protein
(b) They increase the rate of biochemical processes
(c) They are specific for a reaction
(d) They are used and consumed in reaction
Answer:
(d) They are used and consumed in reaction
Question 38.
Protein synthesis occurs in:
(a) Ribosomes
(b) Mitochondria
(c) Chromosomes
(d) Centrosomes.
Answer:
(a) Ribosomes
Question 39.
Digestive enzymes in cells are found in:
(a) Ribosomes
(b) Lysosomes
(c) Golgi body
(d) Cell wall.
Answer:
(b) Lysosomes
Question 40.
Who said that enzymes are protein:
(a) Pasteur
(b) Leeuwenhoek
(c) Miller
(d) Sumner.
Answer:
(d) Sumner.
Question 41.
Non-protein part of enzyme ¡s called:
(a) Apoenzyme
(b) Holoenzyme
(c) Prosthetic group
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(c) Prosthetic group
Question 42.
Inorganic prosthetic group of enzyme is called:
(a) Coenzyme
(b) Activator
(c) Hormone
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(b) Activator
![]()
Question 43.
Substrate of the amylase enzyme is:
(a) Fat
(b) Protein
(c) Starch
(d) Sucrose.
Answer:
(c) Starch
Question 44.
Diastase enzyme digest:
(a) Starch
(b) Protein
(c) Fat
(d) Amino acid.
Answer:
(a) Starch
Question 45.
The percentage of enzyme in mitochondria is:
(a) 19%
(b) 70%
(c) 14%
(d) 10%.
Answer:
(b) 70%
Question 46.
Esterase enzyme belong to group known as:
(a) Oxidation-reduction
(b) Carhoxylating
(c) Hydrolyzing
(d) Transferase.
Answer:
(c) Hydrolyzing
Question 47.
NADPisa:
(a) Enzyme
(b) Part of sRNA
(c) Coenzyme
(d) Part of tRNA.
Answer:
(c) Coenzyme
Question 48.
Coenzyme is often a :
(a) Carbohydrate
(b) Protein
(c) Vitamin
(d) Fatty acid.
Answer:
(c) Vitamin
Question 49.
Temperature is increased from 3°C to 40°C. The rate of enzyme controlled
biochemical reaction will:
(a) Not change
(b) Increase
(c) Increase initially and then decrease
(d) Decrease.
Answer:
(c) Increase initially and then decrease
![]()
Question 50.
Enzymes, vitamins and hormones are common in :
(a) Being proteinaceous
(b) Being synthesized in the body of organisms
(c) Enhancing oxidative metabolism
(d) Regulating metabolism.
Answer:
(d) Regulating metabolism.
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. The molecule on which an enzyme acts is known as ……………….
Answer:
Substrate
2. The inactive form of an enzyme is known as ……………….
Answer:
Proenzyme
3. ……………… is the respiratory pigment of higher animals.
Answer:
Haemoglobin
4. Uracil nitrogenous bases is only found in ……………….
Answer:
RNA
5. A.T.P. is a ……………… nucleotide.
Answer:
Higher
6. Proteins are molecules of C, H, O and ………………….
Answer:
N(Nitrogen)
7. A vitamin is often associated as a ……………….. with an enzyme.
Answer:
Coenzyme
![]()
8. Biochemical reactions are regulated by catalysts called ……………….
Answer:
Enzymes
9. Enzymes which breakdown compounds without the involvement of water are
called ………………..
Answer:
Lyases
10. A compound with almost similar structure to the substrate can act as a ………………
Answer:
Competitive inhibitor
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. DNA | (a) Mucin |
| 2. Cellulose | (b) Lipid |
| 3. Glycoprotein | (c) Genes |
| 4. Phosphoprotein | (d) Roughage |
| 5. Oily substance | (e) Milk. |
Answer:
1. (c) Genes
2. (d) Roughage,
3. (a) Mucin
4. (e) Milk.
5. (b) Lipid
![]()
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Chromosome | (a) Protein synthesis |
| 2. Vitamin-A | (b) Nucleus |
| 3. Spirogyra | (c) Schleiden-Schwann |
| 4. mRNA | (d) Retinol |
| 5. Cell theory | (e) Algae. |
Answer:
1. (b) Nucleus,
2. (d) Retinol
3. (e) Algae
4. (a) Protein synthesis
5. (c) Schleiden-Schwann
(C)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Coenzyme | (a) Cofactor |
| 2. Amylase | (b) Carbonic anhydrase |
| 3. Cu, Fe | (c) Non-competitive inhibitor |
| 4. Fastest enzyme | (d) NADP |
| 5. Cyanide | (e) Starch. |
Answer:
1. (d) NADP
2. (e) Starch
3. (a) Cofactor
4. (b) Carbonic anhydrase
5. (c) Non-competitive inhibitor
4. Write true or false:
1. The wood contains sufficient amount of cellulose.
Answer:
True
2. An element, not present in a nitrogen base is carbon.
Answer:
False
![]()
3. Glucose is stored as glycogen in liver.
Answer:
True
4. The steroid, which has antifertility properties is protein.
Answer:
False
5. Most water present in mature plant cell is found in nucleus.
Answer:
False
6. The catalytic activity of inorganic catalyst cannot be changed by any regulating molecule.
Answer:
True
7. Salivary amylase act best at 6.6 pH.
Answer:
False
8. Phosphohexose isomerase enzyme is classified under transferases.
Answer:
False
9. The enzyme pyruvic decarboxylase catalyses, the removal of C02 from the substrate pyruvic acid.
Answer:
True
![]()
10. Enzymes retain their activity even when extracted from cells.
Answer:
True
5. Answer in one word:
1. Process by which edible oils are converted into hard fats is ……………..
Answer:
Hydrogenation
2. Glycogen is stored in animal body in ………………
Answer:
Liver
3. Molecule in the cell, which undergo self replication is ………………..
Answer:
DNA
4. Glycosidic bond is found in ……………….
Answer:
Disaccharide
5. The genetic material in Tobacco Mosaic Virus is …………….
Answer:
RNA
![]()
6. Protein part of enzymes is ……………………….
Answer:
Apoenzyme
7. Chemically enzymes are ………………..
Answer:
Proteins
8. Inorganic prosthetic group of enzyme is ………………..
Answer:
Activator
9. Protein synthesis occurs in ………………
Answer:
Ribosome
10. Substrate of amylase enzyme is ………………..
Answer:
Starch