Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
Animal Kingdom Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Write down three main characters due to which birds are able to fly.
Answer:
Three main characters due to which birds can fly are :
- Body is streamlined and is covered with feathers.
- Forelimbs are modified as wings for flying.
- Bones are pneumatic (Porous), this reduces the weight of the body.
![]()
Question 2.
Differentiate radial and bilateral symmetry. (Any two)
Answer:
Differences between Radial and Bilateral Symmetry
| Radial Symmetry | Bilateral Symmetry |
| 1. In this type of body organization organs of the body are arranged around an axis. | The body of these organisms is flat and body is dorsiventral. |
| 2. Body can be divided into two equal halves by cutting in any of radial plane. e.g., Hydra, Obelia, Starfish. | The body of these organisms can be divided into two equivalent halves through only one plane, e.g., Man, Earthworm. |
Question 3.
Write three characteristics of protochordata.
Answer:
- They possesses notochord either throughout the whole life or in some phase of life.
- Vertebral column does not develop.
- They do not have a cranium and the jaws.
Question 4.
Give examples of three stationary organisms.
Answer:
- Leucosolenia,
- Sycon,
- Grantia.
All these organisms belong to phylum Porifera and are found attached to the stone or substratum.
Question 5.
Write two characters of sub-phylum :
(a) Urochordata,
(b) Cephalochordata,
(c) Hemichordata.
Answer:
(a) Urochordata :
- They are marine.
- They are sessile forms and possess the notochord in the tail region in the larval stage which is degenerated completely in the adult stage.
- Adults are always enclosed in a tunic composed of animal cellulose, e.g., Herdmania known as sea squirt, etc.
(b) Cephalochordata :
- Animals of this sub-phylum are exclusively marine and solitary animal.
- They are small, fishlike animals.
- Notochord is present from head to tail.
- Many gonads are present, e.g., Amphioxsus, Asymmetron, etc.
(c) Hemichordata :
- Its body is divided into Probosis, Colar and Neck.
- In Probosis, notochord like structure is formed.
- They are marine animals, e.g., Balanoglossus.
Question 6.
What are glass sponges?
Answer:
Skeleton of some sponges are transparent and their spicules or spines are silicious thus they are called as glass sponges.
![]()
Animal Kingdom Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Differentiate between Intracellular digestion and Extracellular digestion. (NCERT)
Answer:
Intracellular digestion :
The process of digestion which occurs inside the cell is called as intracellular digestion. Unicellular organisms like Amoeba, Paramoecium engulf food by endocytosis process then hydrolytic enzymes present in the lysosomes help for digestion. After absorption of digested food, undigested food is released out of the body by exocytosis process. Whereas Extracellular digestion is the process of digestion which occurs outside the cell. In multicellular organisms extracellular digestion occurs in the digestive system.
Question 2.
Write differences between Direct and Indirect development.
Answer:
- Direct development: In this type of development larva stage is not found. Zygote directly develops to form individual, e.g., Human, Rat, Elephant, Monkey etc.
- Indirect development: In this type of development zygote first develops into larva, then larva develops to form young individual, e.g., Cockroach, frog etc.
Question 3.
What is the importance of presence of air bladder in fishes?
Answer:
Air bladder present in the fishes help for buoyancy, due to which they may swim easily, even if it reaches to the bottom it can come up easily, e.g., Exocoetus, Rohu fishes.
Question 4.
Write differences between Chordates and Non-chordates.
Answer:
Differences between Chordates and Non-chordates
| Chordates (Vertebrate) | Non-chordates (Invertebrate) |
| 1. Vertebral column present. | Vertebral column absent. |
| 2. Central nervous system is hollow and dorsal in position. | Central nervous system is solid and ventral in position. |
| 3. Heart is ventral in position. | Heart is dorsal in position. |
| 4. Gill slits are present. | Gill slits are absent. |
| 5. Haemoglobin present in red blood corpuscles. | Haemoglobin if present is dissolved in plasma. |
| 6. A post anal tail is found. | The anus is posterior in position, so no post anal tail. |
![]()
Question 5.
Explain adaptations in birds for aerial habitat.
Answer:
Basic features of birds with reference to habitat:
Birds are terrestrial organ-isms which can fly in the air. Following adaptations are found in them for aerial habitat:
- Body is covered with feathers which hold air and decreases body weight.
- Forelimbs are modified into wings.
- Digits of hind limbs are adapted for sitting on the branches of the tree.
- Bones are hollow and aerated thus decreases body weight for flying.
- Urinary bladder is not found and they do not store waste product in the body (As it is produced is released out from the body).
- Foot webs are found in aquatic birds for swimming.
- Air sacs are found on the lungs.
- Beak is adapted according to its food habit. It is toothless.
Question 6.
Write down the name of the animals which are related with the given organs :
1. Compound eye,
2. Carapace,
3. Medusa,
4. Flame cells,
5. Placoid scales,
6. Blabber,
7. Parapodia.
Answer:
Organs – Animals related to it
- Compound eye – Periplanata
- Carapace – Crab
- Medusa – Aurelia
- Flame cells – Plan aria
- Placoid cells – Scoliodon
- Blabber – Whale fish
- Parapodia – Nereis
- Tube feet – Starfish
Question 7.
Write down the difference between :
1. Coelomate and Pseudocoelomate,
2. Urochordata and Cephalochordata,
3. Flat worm and Round worm,
4. Bony fishes and Cartilage fishes, 5. Oviparous and Viviparous, 6. Diploblastic and Triploblastic.
Answer:
1. Coelomate and Pseudocoelomate:
Presence of true coelom with mesoderm surrounding the body cavity entirely is called Coelomate, whereas Pseudocoelomate are partially open fluid filled body cavity which develops in the blastocoel, so mesoderm does not entirely surround the body cavity.
2. Urochordata and Cephalochordata :
Urochordata are marine sessile animals possessing notochord in tail region in larval stage and degenerates in adult stage whereas Cephalochordata are marine and solitary animal possessing notochord from head to tail.
3. Flat Worm and Round Worm:
The animal body of Platyhelminthes are flat and tapering only at the anterior end are called Flat worm. Whereas the animal body of Nemathelminthes are round in shape, tapering at both ends.
4. Bony fishes and Cartilage fishes :
Fishes having bones are called Bony fishes and they are fresh water as well as marine whereas Cartilaginous fishes are having cartilage they are all marine.
5. Oviparous and Viviparous :
Oviparous animals lay eggs outside the body and fertilization may be internal or external, whereas Viviparous animals hatch eggs within the female body and fertilization is internal.
6. Diploblastic and Triploblastic :
Diploblastic animals are those where their embryo are made up of two germ layers : Ectoderm and endoderm, whereas Triploblastic animals are those where their embryo are made up of three germ layers : Ectoderm, meso-derm and endoderm.
![]()
Question 8.
What is False fish? Explain it with examples.
Answer:
Those animals which live in water and have the capacity to swim in water like fishes. But they do not come under class Pisces. So they are called false fish.
Example :
- Jelly fish : It is Aurelia genus and is in phylum Coelenterats.
- Silverfish : It is in phylum Arthropoda and is genus of Lepisma.
- Devilfish : It is in phylum Mollusca of genus Octopus.
- Starfish : It is in phylum Echinodermata of genus Asterias.
Question 9.
Describe the characteristic features of the class mammalia.
Or
In which class of Animalia human is included and why? Explain with five features of this class.
Answer:
Characteristics of class mammalia : It is the highly developed group of king-dom animalia.
Human is placed under the class mammalia, because of the following reason :
- They are isothermal. Body is covered by hairs. Skin contains sweat and oil glands.
- Females possess mammary glands, which secrete milk after the birth of young ones and thus, infant is given nutrition in the initial stage of growth.
- The heart is four chambered with two auricles and two ventricles. Only the left aortic arch is present.
- Ear with fleshy external ear or pinna.
- A muscular diaphragm is present, which separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
- They have well developed brain, this enables them to learn.
- Number of neck vertebrae is always seven.
- They are warm blooded animals.
Question 10.
What do you mean by Amphibian? Give eight characteristics of class Amphibia.
Answer:
Those animals of phylum Chordata which live both on land and in water are called Amphibian animals e.g., Frog (Rana tigrind), Bufo etc.
Characteristics of class Amphibia :
- Their body is fit for survival in water and on land.
- They are cold blooded animals.
- Their skin is moist, slippery and glandular, due to which they can respire both on land and in water.
- They possess ears which consists of tympanum.
- R.B.Cs. are nucleated.
- Heart is three chambered.
- Webs are present between the digits of hind limb.
- External fertilization occurs in water.
![]()
Question 11.
What do you understand by symmetry of animals? How many kinds of symmetry is found in animals ? Write at least any one character and give one example from each type of symmetry.
Answer:
Symmetry :
The arrangement of various parts of the body of organisms is called as symmetry .There are three types of symmetry found in animals :
- Asymmetry :
In asymmetrical arrangement body of animals cannot be divided into two equal parts in any plane, e.g., Gastropods, Sponges. - Radial symmetry :
In this type, body of animals can be divided into two equal halves by cutting in any of the radial planes, e.g., Hydra and Starfish. - Bilateral symmetry :
In this type, body of animals can be divided into two equal halves through only one plane i.e., main axis of the body passing through the center, e.g., All vertebrate animals.
Question 12.
Write the characters of the phylum Annelida.
Answer:
Characteristic features of the phylum Annelida :
- They are mostly aquatic, marine or fresh water, burrowing or living in tubes.
- The body is thin, elongated, cylindrical and is metamerically segmented, externally by transverse groove and internally by septa into a number of divisions, each division is called segment or metamere.
- Body is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomatic, which is covered by a contractile and muscular body wall. Epidermis is cuticulized.
- A straight, tube like alimentary canal is found in the center of body cavity which is extending from mouth to anus.
- Locomotion takes place by setae or chaetae.
- Blood vascular system is closed type. Blood is red due to presence of haemoglobin. R.B.Cs. are not found in the blood.
Question 13.
Describe the characteristic features of the kingdom Animalia.
Answer:
Characteristic features of the kingdom Animalia :
- The organisms of this kingdom are eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic and holozoic in nutrition.
- Cell wall and plastids are absent.
- Locomotion and movement occur.
- All of them are consumers.
- They reproduce sexually, except some lower animals.
- They possess muscles, which possess the capacity of expansion and contraction.
- Body is triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical and possesses the capacity of sensation.
- They possess nervous and hormonal systems for coordination.
![]()
Question 14.
Describe the important adaptations of the Arthropods.
Answer:
Phylum Arthropoda is the largest phylum of the animal kingdom. The following adaptive characters are found in the arthropods :
- Body is covered with a chitinous cuticle forming exoskeleton.
- The salts of CaC03 and calcium phosphates are also present in the exoskeleton, which increase the hardness of the body.
- Respiration through general body surface by gills in aquatic forms, trachea or booklungs in terrestrial forms.
- Moulting is present in the exoskeleton.
- The body is bilaterally symmetrical and metamerically segmented.
- Exoskeleton is solid, hence it provides the space for joining the muscles.
- The animals are suited for aquatic as well as terrestrial environment.
Ex. Butterfly, Scorpion, Cockroach, Housefly, Mosquito.
Question 15.
Describe the characteristic features of the phylum Chordata.
Or
(A) Write three important characters of phylum Chordata.
(B) Write the name of phylum of the following animal:
(i) Star fish,
(ii) Jelly fish,
(iii) Octopus,
(iv) Earthworm,
(v) Tape worm,
(vi) Paiaemon.
Answer:
Characteristic features of the phylum Chordata :
- Notochord is present in any stage of life.
- Nervechord is present.
- Gills are present in any stage of life.
- A heart made up of muscles is present.
- Presence of closed circulatory system and blood cells contain R.B.Cs.
- Endoskeleton is present, which is made up of bones and cartilages.
- Presence of two pairs of appendages and well developed system. e.g., Man, Frog, Lizards, etc.
(B)
Name of related animal and their phylum :
Animal – Phylum
- Starfish- Echinodermata
- Jellyfish – Coelenterata
- Octopus – Mollusca
- Earthworm – Annelida
- Tapeworm – Platyhelminthes
- Paiaemon – Arthropoda.
Question 16.
Give characteristic features of phylum Moliusca.
Answer:
Characteristic features of Moliusca :
- They are essentially aquatic, mostly marine, few fresh water and some terrestrial forms.
- The body is soft, bilaterally symmetrical and consists of head, foot, circular mantle and visceral mass.
- Body is protected by an exoskeletal of calcareous shell, secreted by mantle.
- They possess a mantle cavity between body wall and mantle, in which digestive system, reproductive system and kidneys are opened.
- Head is distinct, bearing the mouth and provided with eyes, tentacles and other sense o-gans.
- Ventral body is modified into muscular flat or foot, which is variously modified for creeping, burrowing and swimming.
- Pharynx contains a rasping organ the radula except in bivalvia (pelecypoda).
![]()
Question 17.
Name the class which is represented by bats. Give three reasons.
Answer:
Bats are placed under the class Mammalia due to the following features :
- It has mammary glands with teats,
- Body is covered by hairs and skin possessing sweat and oil glands,
- Females give birth to young ones,
- It has four chambered heart.
Question 18.
Why whale fish is placed under the class mammalia? Give four reasons.
Or
Why is whale included in Mammalia? Explain with five reasons.
Answer:
Whale is placed under the class Mammalia, because of the following reasons :
- Females give birth to young ones.
- It contains mammary glands with teats.
- Their heart is four chambered.
- Fertilization is internal.
- Young ones develop within uterus.
Question 19.
Why frogs are placed under the class Amphibia? Give four reasons.
Answer:
Frogs are placed under the class Amphibia, because of the following reasons :
- Their body is fit for survival in water and on land,
- They are cold blooded animals,
- Their skin is moist, slippery and glandular, due to which they can respire both on land and in water,
- They possess ears.
Question 20.
Give at least one example of the following animals :
1. Egg laying mammal,
2. Flying mammal,
3. Flying reptile,
4. Flying fish.
Answer:
Animal – Example
- Egg laying mammal – Echidna
- Flying mammal – Bat
- Flying reptile – Draco
- Flyingfish – Exocetus.
![]()
Question 21.
What do you understand by Bilateral Symmetry? Explain it with example.
Answer:
Bilateral symmetry : If the body can be divided into two equal halves by one plane only it is called bilateral symmetry. Here the body organs are paired and occur on the two sides of a central axis, e.g., all vertebrates like fishes, human beings, birds, etc.
Such animals possess a front or anterior end and a rear or posterior end. They also possess an upper back or dorsal side and a lower belly or ventral side. On the basis of dorsal and ventral sides the right and left side® ‘if the body are called lateral sides. Man, Snake, Earthworm are the examples of Bilateral symmetry.
Question 22.
Differentiate between Starfish and Flyingfish on the basis of their body
symmetry and exoskeleton.
Answer:
Differences between Starfish and Flyingfish
| Characters | Starfish | Flyingfish |
| 1. Body symmetry | Body is radially symmetrical. | Body is bilaterally symmetrical. |
| 2. Exoskeleton spines. | Body is covered by calciated spines. | Body is covered by |
Question 23.
Write down the name of phylum and class of the following animals :
1. Roundworm,
2. Leech,
3. Scorpion,
4. Bat.
Answer:
- Roundworm:Phylum – Aschelminthes
Class – Nematoda - Leech :Phylum – Annelida
Class – Hirudinia - Scorpion:Phylum – Arthropoda
Class – Arachnida - Bat:Phylum – Chordata
Class – Mammalia.
Question 24.
Write down the name of phylum and class of the following animals :
1. Tapeworm,
2. Nereis,
3. Cockroach,
4. Starfish.
Answer:
- Tapeworm:Phylum – Platyhelminthes
Class – Cestoda - Nereis:Phylum – Annelida
Class – Polychaeta - Cockroach :Phylum – Arthropoda
Class – Insecta - Starfish: Phylum – Echinodermata
Class – Asteroidia.
![]()
Question 25.
Write down the name of phylum and class of the following animals :
1. Hydra,
2. Earthworm,
3. Unio,
4. Horsefish,
5. Turtle.
Answer:
- Hydra :Phylum – Coelenterata
Class – Hydrozoa - Earthworm:Phylum – Annelida
Class – Oligochaeta - Unio: Phylum – Mollusca
Class – Gastropoda - Horse fish :Phylum – Chordata
Class – Osteichthyes - Turtle:Phylum – Chordata
Class – Amphibia.
Question 26.
Draw a well labelled diagram of Earthworm.
Answer:
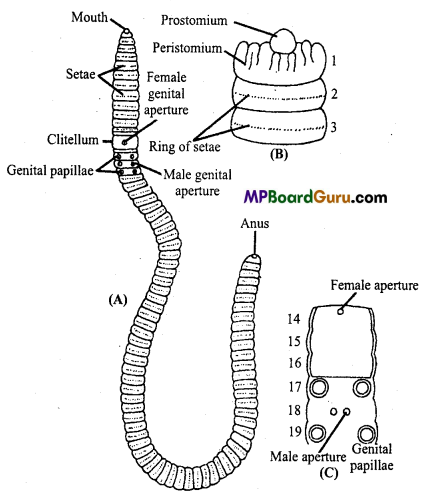
Fig. Earthworm (Pheretima) : (A) Ventral view; (B) Segment 1, 2 and 3; (C) Reproductive organs
Question 27.
Write down the zoological name of the following animals :
1. Housefly,
2. Elephant,
3. Ostrich,
4. Roundworm,
5. Kangaroo.
Answer:
Common Name – Zoological Name
- Housefly – Musca domestica
- Elephant – Elephas maximus
- Ostrich – Struthio
- Roundworm – Ascaris lumbricoidis
- Kangaroo – Macropus.
Question 28.
Pila and Octopus are kept in same phylum why?
Answer:
Pila and Octopus are kept in same phylum because :
- Their body is soft covered by shell.
- Body consists of head, visceral mass and foot.
- Whole body is covered by muscular mantle.
![]()
Question 29.
Write the name of locomotory organs of the following animals :
1. Amoeba,
2. Earthworm,
3. Paramoecium,
4. Snake,
5. Starfish,
6. Hydra,
7. Euglena.
Answer:
Animal – Name of the locomotory organs
- Amoeba – Pseudopodia.
- Earthworm – Setae.
- Paramoecium – Cilia.
- Snake – Ribs and scales.
- Starfish – Arms.
- Hydra – Tentacles.
- Eugiena – Flagella.
Question 30.
Write the phylum of following animals :
1. Starfish,
2. Jellyfish,
3. Dogfish,
4. Horsefish,
5. Devilfish,
6. Whalefish,
7. Silverfish.
Answer:
Animal – Phylum
- Starfish – Echinodermata
- Jellyfish – Coelenterata
- Dogfish – Chordata
- Horsefish – Chordata
- Devilfish – Mollusca
- Whalefish – Chordata –
- Silverfish – Arthropoda.
Question 31.
Give one example of each of the following :
1. Animal with largest life span,
2. Largest lizard,
3. Largest snake,
4. Largest animal of the world.
Answer:
Animal – Examples
- Animal with largest life span – Turtles
- Largest lizard – Kamado dragon
- Largest snake – Python
- Largest animal of the world – Blue whale.
Question 32.
All vertebrates are chordates, but all chordates are not vertebrates. Explain.
Answer:
All vertebrates have three important characteristics :
- Presence of Notochord,
- Presence of nerve chord and
- Presence of gill slits.
All vertebrates are bilaterally symmetrical, Notochord is replaced by vertebral column, Heart is ventrally situated, Level of organisation is observed, closed circulatory system is found in them, tail is found in them. On the basis of all above characteristics it is clear that all vertebrates are chordates, whereas all chordates are not vertebrates because in vertebrates notochord is found in embryonic stage whereas in adult stage it is replaced by vertebral column and chordate may or may not has cranium jaws, vertebral column and brain.
Thus, it is clear that all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
![]()
Question 33.
Write the scientific name of the following animal:
1. Frog,
2. Man,
3. Cat,
4. Ox.
Answer:
Common Name – Zoological name
- Frog – Ran a tigrina
- Man – Homo sapiens
- Cat – Felis domestica
- Ox – Bos indicus.
Question 34.
Classify the classes of Phylum chordata.
Answer:
Phylum chordata is classified into seven classes :
Class – Example
- Cyclostomata – Petromycin
- Chondricthyes – Scoliodon
- Osteichthyes – Labeo
- Amphibia – Rana
- Reptilia – Snakes
- Aves – Columbia
- Mammals – Macropus (Kangaroo)
Question 35.
Write five phylum giving examples.
Answer:
Five Phylum are :
Phylum – Example
- Porifera – Sycon
- Coelenterata – Hydra
- Platyhelminthes – Planaria
- Nemathelminthes – Ascaris
- Annelida – Pheritima.
![]()
Question 36.
Write short notes on :
1. Haemocoel,
2. Porifera,
3. Insecta,
4. Cyclostomata,
5. Protochordata,
6. Nematoda,
7. Metamerism.
Answer:
1. Haemocoel: Coelom is a cavity which lies between body wall and digestive tract. It is filled with a fluid called coelomic fluid, but in phylum Arthropoda, in place of coelomic fluid, blood is filled, therefore it is called Haemocoel. It works as transporter.
2. Porifera :
General characteristics of phylum Porifera :
- They are radially symmetrical, multicellular and diploblastic animals.
- They are mainly marine except few sedentary and colonial or solitary.
- The skeleton is formed of calcareous or siliceous spicules present in between gelatinous substance.
- Body is perforated by numerous pores called Ostia.
- Nervous system is absent. Digestion is intracellular. No respiratory and excretory organs are present, e.g., Sycon, Spongilla.
3. Insecta :
It is the class of Phylum Arthropoda, which has following points :
- Body is divisible into head, thorax and abdomen.
- Thorax is three segmented and carries three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings.
- Mostly terrestrial but some are aquatic.
4. Cyclostomata :
It is a part of Phylum chordata, which have following characters :
- It consists of Cranium box, Jaws are absent, but mouth is suctorial.
- Body is long, narrow, cylindrical with laterally compressed tail. ‘
- It appears like fish, but skin is naked glandular.
- Single nostril is found on the dorsal surface of the head, e.g., Petromyzon.
5. Protochordata :
It is a part of chordata, having following characters :
- Notochord is not properly developed.
- Cranium and Jaws are absent.
- Body is laterally compressed and leaf like.
6. Nematoda:
- Nematodes have tube within a tube body plan with mouth, pharynx, intestine and anus. Body is covered with thick cuticle.
- They have unsegmented triploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical cylindrical body.
- Posterior end of body is frequently curved in males while pointed in females. Males are always smaller than females.
- Body is not distinguished into different regions. Head is not distinct.
- They are pseudocoelomic.
7. Metamerism :
The body of many animals is formed of numerous segments which show serial repetition of parts. This kind of segmentation is called metameric segmentation and the phenomenon is known as metamerism.
Question 37.
Give eight characteristics of super class Pisces.
Answer:
Characteristics of super class Pisces :
- They are aquatic vertebrates,
- Body is covered by scales,
- They are cold-blooded organisms (Poikilothermal),
- Heart is two chambered,
- Respiration by gills,
- Tympanic membrane absent,
- Lateral line is found on the body,
- Fins present for swimming.
![]()
Question 38.
Compare the oviparous, viviparous and ovo-viviparous among animals.
Answer:
Comparison of Oviparous, Viviparous and Ovo-viviparous Animals
| Oviparous | Viviparous | Ovo-viviparous |
| 1. Female lays eggs. | Give birth to young ones. | Give birth to young ones. |
| 2. Fertilization may be external or internal. | Always internal. | Always internal. |
| 3. Egg is generally large in size. | Egg is small in size. | Egg is large in size. |
| 4. Development occurs outside the body of female. | Development occurs inside the body of female. | Development occurs inside the body of female. |
| 5. Placenta in not formed. eg., All birds, Amphibians and Most fishes. | Placenta is formed. eg., Most of mammals. | Placenta not formed. eg.,Rattle snake.
|
Question 39.
“Number of offsprings produced by oviparous and viviparous organisms is equal”. Yes or No? Give reason.(NCERT)
Answer:
Oviparous organisms lay eggs whereas Viviparous organisms gives birth to young one.
Number of offsprings produced by them are not equal because in oviparous organisms internal or external fertilization occurs. They lays large number of eggs which undergoes various stages of development. During this long period of development some eggs get spoiled and remaining hatches to produce offsprings, whereas viviparous organisms give birth to young individual which are very less in number. Development of embryo occurs directly in the uterus of mother and no larva stage appears.
Question 40.
If a specimen is provided to you, what step will you take to classify the organisms? (NCERT)
Answer:
Inspite of different external features and shapes, some basic similarities are found in cellular organization, body symmetry, type of coelome, digestive system, circulatory system and reproductive system of the organisms.
To classify, all these features can be considered.
Question 41.
How structure of coelome and coelomate is helpful in the classification of living organisms? (NCERT)
Answer:
Coelome is defined as a cavity lined by mesoderm, it lies between the body wall and the digestive tract in which various internal organs are found suspended. Presence or absence and nature of coelome is the main basis of classification. Organism with coelome is called as Coelomate. e.g., Annelids, Echinodermates and Chordates etc.
The animals without coelome are called as Acoelomate. eg., Sponges, coelentrates and flatworms. In some other organisms mesoderm is found in the form of small packs scattered in between outer ectoderm and inner endoderm. Such organisms are called are Pseudocoelomate. eg., Roundworms such as Ascaris.
![]()
Animal Kingdom Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Give the general characteristic of phylum Porifera.
Answer:
General characteristics of phylum Porifera :
- They are radially symmetrical, multicellular and diploblastic animals.
- They are mainly marine except few sedentary and colonial or solitary.
- The skeleton is formed of calcareous or siliceous spicules present in between gelatinous substance.
- Body is perforated by numerous pores called Ostia.
- Nervous system is absent. Digestion is intracellular. No respiratory and excretory organs are present, e.g., Sycon, Spongilla.
Question 2.
Give eight characteristics of phylum Coelenterata.
Answer:
Characteristics of phylum Coelenterata :
- They are multicellular animals showing cell-tissue level of body organisation with most of the cells specialised for different functions and some forming a tissue. They exhibit physiological division of labour.
- Cnidarians are diploblastic metazoans, the body wall is made up of two layers the outer ectoderm and inner endoderm (gastroderm) with middle non-living gelatinous layer mesoglea.
- Coelenterates exhibit a blind sac plan and are radially symmetrical.
- Cnidarians are acoelomate.
- Head and segmentation absent.
- These are short or slender, extensile projections called tentacles, encircle the mouth in one or more whorls and are used for food-capture, intake and defence.
- Coelome is not found in them. Only one cavity found in the body called coelenteron, which is enclosed by endoderm. e.g., Hydra, Aurelia.
Question 3.
“Arthropoda is regarded as largest group of animals.” Give reason.
Answer:
Arthropoda is regarded as a most successful and largest group of animals. It has about 9,00,000 species out of which 7,50,000 species are the members of class Insecta. Due to following adaptations they forms approximately two third (2/3) part of the total number of animals present in the world :
- Legs are divided into small segments.
- They are found in different habitats likes air, water, soil as parasites etc.
- Body is triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical.
- The true coelome is greatly reduced.
- Open circulatory system is found in them.
- Excretory organs are malpighian tubules.
- Compound eyes are found in them.
- Respiration occurs through tracheal system.
- The segments of the body bears paired, jointed and lateral appendages which are modified as jaws, gills and legs.
- Body is covered by thick exoskeleton containing Chitin. e.g., Palaemon, cockroach, Julus, Crab etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Write down the characteristics of phylum Platyhelminthes.
Answer:
General characters of Platyhelminthes :
- Flatworms are triploblastic (i.e., consists of three germinal layers ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm). Acoelomate, bilaterally symmetrical, dorsoventrally flattened organisms with anteriorly differentiated into a definite head.
- They have flattened body because of their primitive system of circulation and excretion. Each cell of the body must be near to the body surface to get nutrients and oxygen and for the removal of waste products and carbon dioxide.
- Platyhelminthes have unsegmented body except in tapeworms (Class-Cestoda). In Cestodes body is strobilated, i.e., it consists of large number of proglottids.
- Flatworms are with blind sac body plan.
- The alimentary canal is either absent or highly branched and only mouth is present and anus is absent.
- They do not have any body cavity or coelom, various organs are embedded in a sort of solid packing tissue known as mesenchyme or parenchyma.
Question 5.
Explain modern classification of Animal Kingdom giving two-two examples.
Answer:
Modem classification of Animal Kingdom, showing important phylum is as follows, Animal Kingdom is divided into three branches. They are :
(A) Mesozoa Branch :
They are tissueless group of cells. It consists of only one
phylum.
1. Phylum Mesozoa :
- Body is made up of group of cells.
- Found in water, e.g., Diacima.
(B) Parazoa Branch :
It has cellular organization, clear mouth, anus absent. It has only one phylum.
2. Phylum Parazoa :
- Body consists of numerous pores.
- It is found in stagnant and flowing water, e.g., Sycon, Euspongia.
(C) Eumetazoa Branch :
It consists of tissue, organ, mouth alimentary canal. It consists of following
phylum :
3. Phylum Coelenterata:
- Coelenteron present, radial symmetry and tissue present,
- It is a multicellular organism, e.g., Hydra, Aurelia.
4. Phylum Platyhelminthes :
- Body ribbon shaped,
- Body cavity absent, e.g., Taenia solium, Planaria.
5. Phylum Nematoda :
- Body is long and round,
- Female is longer than male. e.g., Ascaris.
6. Phylum Annelida :
- Body is segmented,
- Locomotion by setae. e.g., Leech, Earthworm.
7. Phylum Mollusca :
- Body is soft,
- Shell is present all round the body, e.g., Unio, Pila.
8. Phylum Arthropoda :
- Jointed legs,
- Exoskeleton made of Chitin,
- Eyes simple or compound, e.g., Cockroach, Scorpion.
9. Phylum Echinodermata :
- Body radially symmetrical,
- Skin covered with spines, e.g., Starfish.
10. Phylum Chordata:
- Animal having notochord, nervecord and gills are present.
- All organs are well developed, e.g., Frog, Man, Fish.
![]()
Question 6.
Write down the characteristics of Chordata; classify it giving two-two characters with examples.
Answer:
Characteristics of Chordata :
Characteristic features of the phylum Chordata :
- Notochord is present in any stage of life.
- Nervechord is present.
- Gills are present in any stage of life.
- A heart made up of muscles is present.
- Presence of closed circulatory system and blood cells contain R.B.Cs.
- Endoskeleton is present, which is made up of bones and cartilages.
- Presence of two pairs of appendages and well developed system. e.g., Man, Frog, Lizards, etc.
Phylum Chordata is further classified into 7 classes; they are :
1. Class Cyclostomata :
- Cranium box is present,
- Lower jaw absent,
- Suctorial mouth, e.g., Petromyzon, Myxine.
2. Class Chondrichthyes :
- Endoskeleton is cartilagenous,
- Operculum and air bladder are absent, e.g., Scoliodon, Torpedo.
3. Class Osteichthyes :
- Endoskeleton formed of bones,
- Gills are covered by operculum, e.g., Labeo, Hippocampus.
4. Class Amphibia :
- They are amphibian animals, living both on land and in water but its larva grows in water only,
- It consists of four limbs, e.g., Rana tigrina, Bufo.
5. Class Reptiles :
- They creep on land,
- Skin is dry. e.g., Calotis, Naja.
6. Class Aves :
- Forelimbs modified into wings, and whole body is covered by feathers,
- Air is filled in bones, e.g., Columba, Passer.
7. Class Mammals :
- Presence of hair on the body,
- Mammary glands with teats, e g., Macropus, Homo sapiens.
![]()
Question 7.
If there is lack of knowledge of basic features then will you face problem to classify animals? (NCERT)
Answer:
Following problems may be faced while classifying the animals :
- Different levels of organisations are found in different organisms, such as cellular level, tissue level, organ level etc.
- Some animals are radially symmetrical and some are bilaterally symmetrical.
- Some animals has closed circulatory system and some has open circulatory system.
- Some shows extracellular and some shows intracellular digestion.
- Some are acoelomate, some are coelomate and some are pseudocoelomate.
Thus, lack of all above basic knowledge causes problems to classify animals.
Question 8.
Classify Mammalia into subclasses with characters and examples.
Answer:
There are three subclasses : Prototheria, Metatheria and Eutheria.
(A) Prototheria :
- Nippleless mammary glands.
- External ear absent.
- Egg laying mammals.
Examples : Platypus, Ornithorincus.
(B) Metatheria :
- Mammary glands with nipples.
- External ear present.
Examples: Kangaroo.
(C) Eutheria :
- These are true mammals with allantoic placenta.
- They give birth to fully developed young ones.
- Mammary glands and their teats are well-developed.
- Embryo develops inside the uterus and is nourished by a true allantoic placenta.
Examples: Talpa, monkey, man, whale, dog, goat, rat, bat, elephant (Elephas), tigers, cows, horse, squirrel, etc.
![]()
Question 9.
Write short note on following :
(1) Class-Aves,
(2) Class-Reptilia,
(3) Class-Pisces.
Answer:
(1) Class-Aves:
It is an important class of phylum-Chordata. It includes organisms which can fly and has notochord, nerve cord and gill slits in some stages of its life cycle.
Characteristic features :
- They are warm blooded organisms,
- Body is covered with feathers,
- Body is divided into head, neck, trunk and tail,
- Air sacs are found on the lungs,
- Bones are hollow,
- Heart is four chambered,
- Forelimbs are modified into wings.
Examples : Columba, Peacock, Ostrich etc.
(2) Class-Reptilia :
Class-Reptilia belongs to phylum-Chordata.
Characteristic features :
- They are cold blooded animals,
- Skin is dry and consists of scales,
- RBCs are nucleated,
- Mostly terrestrial but some are aquatic,
- Heart consists of three chambers,
- They show internal fertilization,
- Body is divided into head, trunk and tail,
- They are oviparous, a few snakes are viviparous.
Examples : Lizard, Snake, Crocodile etc.
(3) Class-Pisces :
Class-Pisces is an important class of phylum-Chordata. It includes aquatic organisms.
Characteristic features :
- Body is streamlined,
- Body is covered by scales,
- They are cold blooded organisms,
- Heart is two chambered,
- Respiration by gills,
- Lateral line is found on the body,
- Fins help in swimming,
- Tympanic membrane is absent.
Example : Scoliodon, Rohu fish, Torpedo etc.
![]()
Animal Kingdom Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Water vascular system is the characteristics feature of:
(a) Porifera
(b) Cnideria
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Chordata.
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata
Question 2.
All members of ………………. are marine :
(a) Porifera
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Anthozoa.
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata
Question 3.
Following is the important feature of arthropoda :
(a) Jointed legs
(b) Three pairs of legs
(c) Sheath on body
(d) Two pairs of wings.
Answer:
(a) Jointed legs
Question 4.
Which of the following is a true fish :
(a) Cuttlefish
(b) Silverfish
(c) Whale
(d) Flyingfish.
Answer:
(d) Flyingfish.
Question 5.
Amnion is found in the embryo of:
(a) Cockroach
(b) Tadpole
(c) Fish
(d) Lizard.
Answer:
(d) Lizard.
Question 6.
Animals found in the bottom of sea are called as :
(a) Lentic
(b) Lotic
(c) Benthic
(d) Pelagic.
Answer:
(c) Benthic
![]()
Question 7.
Pearl formed from Pearl oyster is :
(a) First drop of rain
(b) Drop of dew
(c) Egg which cannot come outside the body
(d) A round external cup buried in the skin.
Answer:
(d) A round external cup buried in the skin.
Question 8.
Phylum which contains largest number of species :
(a) Chordata
(b) Arthropoda
(c) Insecta
(d) Mollusca.
Answer:
(b) Arthropoda
Question 9.
Which of the following animal possessing exo and endoskeleton :
(a) Frog
(b) Earthworm
(c) Snake
(d) Leech.
Answer:
(c) Snake
Question 10.
Which of the following is not a fish :
(a) Liingfish
(b) Dogfish
(c) Catfish
(d) Silverfish.
Answer:
(d) Silverfish.
Question 11.
Locomotory organ of Amoeba is:
(a) Tentacle
(b) Pseudopodia
(c) Flagella
(d) Cilia.
Answer:
(b) Pseudopodia
Question 12.
Kangaroo is :
(a) Prototheria
(b) Metatheria
(c) Eutheria
(d) Reptiles.
Answer:
(b) Metatheria
![]()
Question 13.
Animals of …………… class has three pairs of legs :
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Gastropoda
(c) Insecta
(d) Crustacea.
Answer:
(c) Insecta
Question 14.
Mesoglea is the characteristic feature of the phylum :
(a) Porifera
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Annelida
(d) Hydrozoa.
Answer:
(b) Coelenterata
Question 15.
Leech is:
(a) Parasitic
(b) Autotrophic
(c) Roundworm
(d) Flatworm.
Answer:
(a) Parasitic
Question 16.
Which of the following is an oviparous mammal:
(a) Whale
(b) Platypus
(e) Rabbit
(d) Snake.
Answer:
(b) Platypus
Question 17.
Best definition of birds:
(a) They are flying
(b) Isothermic
(e) Winged bipedal
(d) Above tetrapod.
Answer:
(d) Above tetrapod.
Question 18.
Which of the following is a flying fox:
(a) Fox
(b) Bat
(e) Reptile
(d) Mollusca.
Answer:
(b) Bat
Question 19.
Causal organism of filaria disease is:
(a) Fasciola
(b) Taenia
(c) Wuchereria
(d) Mosquìto.
Answer:
(c) Wuchereria
![]()
Question 20.
Light blue colour of the blood of arthropods is due to:
(a) Haemoglobin
(b) Haemocyanin
(c) Hirudin
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Haemocyanin
Question 21.
Blind chamber body arrangement is found in:
(a) Sponges
(b) Annelids
(c) Coelenterates
(d) Mammals.
Answer:
(c) Coelenterates
Question 22.
Cephalopoda is a class of animals having:
(a) Notochord is elongated up to head
(b) Feet are found on the head
(c) Head is found on legs
(d) Head is jointed with cephalothorax.
Answer:
(c) Head is found on legs
Question 23.
Pearl oyster is associated with the class:
(a) Gastropoda
(b) Pelecypoda
(e) Schiphozoa
(d) Amphineura.
Answer:
(b) Pelecypoda
Question 24.
Eutherian mammals are:
(a) Oviparous
(b) Viviparous
(c) Ovi-viviparous
(d) Both (a) and (c).
Answer:
(b) Viviparous
Question 25.
Mesoglea is made up of:
(a) Amoeboid cell
(b) Nerve cell
(e) Nematocyst
(d) A cellular jelly
Answer:
(d) A cellular jelly
![]()
2. Fill in the blanks:
(A)
1. The skeleton of Porifera is chiefly formed of ………………
Answer:
Spicules
2. Shell of Mollusca is secreted by …………………
Answer:
Mantle
3. Physalia is popularly known as ………………….
Answer:
Portuguese man of war
4. ………………… fishes are exclusively marine.
Answer:
Cartilaginous
5. Pneumatic bones are found in …………………..
Answer:
Birds
6. Jointed appendages is the important characteristic of ……………… phylum.
Answer:
Arthropoda
![]()
(B)
1. Arthropoda is classified on the basis of wings and ………………..
Answer:
Appendages
2. Silverfish belongs to …………………
Answer:
Arthropoda
3. Heart of amphibians consists of …………………. chambers.
Answer:
Three
4. Bones of birds are …………………..
Answer:
Hollow
5. Most of the flat worms are anaerobes, this is ………………… adaptation.
Answer:
Parasitic
6. Starfish is ………………… symmetrical.
Answer:
Radially
7. Jointed legs are found in …………………… phylum
Answer:
Arthropoda
8. Excretory organs of earthworm are …………….
Answer:
Nephridia
9. Malpighian tubules are the ……………….. organs of insect.
Answer:
Excretory
10. Presence of hairs on the body surface is the characteristic features of class …………………..
Answer:
Mammalia
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Reptalia | (a) Echinodermata |
| 2. Starfish | (b) Mollusca |
| 3. Devilfish | (c) Pisces |
| 4. Cartilage fish | (d) Tetrapoda. |
Answer:
1. (d) Tetrapoda.
2. (a) Echinodermata
3. (b) Mollusca
4. (c) Pisces
![]()
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Ostrich | (a) Platyhelminthes |
| 2. Whale | (b) Aves |
| 3. Round worm | (c) Mammalia |
| 4. Tapeworm | (d) Nematoda. |
Answer:
1. (b) Aves
2. (c) Mammalia
3. (d) Nematoda
4. (a) Platyhelminthes
(C)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Nematocyst | (a) Aurelia |
| 2. Tube feet | (b) Planaria |
| 3. Medusa | (c) Starfish |
| 4. Parapodia | (d) Hydra |
| 5. Flame cell | (e) Nereis. |
Answer:
1. (d) Hydra
2. (c) Starfish
3. (a) Aurelia
4. (e) Nereis
5. (b) Planaria
(D)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Operculum | (a) Ctinophora |
| 2. Setae | (b) Mollusca |
| 3. Scale | (c) Porifera |
| 4. Comb plate | (d) Reptilia |
| 5. Radula | (e) Annelida |
| 6. Hair | (f) Cyclostomata or Chonichthyes |
| 7. Choenocyte | (g) Mammalia |
| 8. Gill slits | (h) Osteichthyes. |
Answer:
1. (h) Osteichthyes.
2. (e) Annelida
3. (d) Reptilia
4. (a) Ctinophora
5. (b) Mollusca
6. (g) Mammalia
7. (c) Porifera
8. (f) Cyclostomata or Chonichthyes
![]()
4. Write true or false:
1. All major groups of animals have evolved in the sea.
Answer:
True
2. Exoskeleton is absent in Vertebrates.
Answer:
False
3. Snakes and Lizards shed their scales as skin cast.
Answer:
True
4. Toad skin is dry and warty and cannot absorb water.
Answer:
False
5. Flatworms are acoelomate organisms.
Answer:
True
5. Answer in one word:
1. The excretory organs in earthworm are.
Answer:
Nephridia
2. The process of transformation of a larva into an adult is called.
Answer:
Metamorphosis
3. The body fat of whale is called.
Answer:
Blubber
![]()
4. Malpighian tubules are the organs in insects.
Answer:
Excretory
5. The largest class of molluscs are.
Answer:
Gastropods
6. Write name of one bisexual animal of the phylum annelida.
Answer:
Hirudinaria (the cattle Leech)