Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration
Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Which hormone is known as emergency hormone? It is secreted by which gland?
Answer:
Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline epinephrine which is known as emergency hormone, as it has the capacity to stand in acute emergencies.
Question 2.
Name the diseases caused by hyposecretion of thyroxin.
Answer:
Cretinism, Goitre, Hashimoto’s disease, Myxedema.
![]()
Question 3.
Give chemical nature of hormones.
Answer:
Hormones can be divided into three categories :
- Steroid hormones : Aldosterone, Cortisone, Progesterone, Testosterone.
- Amino acid: Thyroxine and Epinephrin.
- Peptide and Protein hormone: Calcitonin, Parathormone, Insulin, Glucagon.
Question 4.
Name the two hormones secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Answer:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormones (T.S.H.)
- Growth stimulating hormone (G.S.H.)
Question 5.
Name the endocrine part of pancreas and also name the hormone secreted by them.
Answer:
The endocrine part of the pancreas is islets of Langerhans, this part secretes a hormone known as insulin.
Question 6.
Which hormone is known as delivery hormone and why?
Answer:
The hormone oxytocin is known as delivery hormone it helps in the delivery by contracting unstriated muscles of the uterus and bring it in normal position after delivery.
Question 7.
Name the endocrine glands found in mammal.
Answer:
Following endocrine glands are found in human :
- Pituitary,
- Thyroid,
- Parathyroid,
- Adrenalin,
- Thymus,
- Pancreas,
- Gonads.
Question 8.
Where are the progesterone and relaxin hormones formed? Give their function.
Answer:
Progesterone hormone is produced by the corpus luteum. It helps in development of mammary gland and attachment of embryo to the wall of uterus.Placenta of the embryo secretes relaxin during pregnancy. At the time of childbirth, it relaxes the muscles of pelvis so that the vaginal passage may widen and the child may come out easily.
![]()
Question 9.
Name the hormone responsible for growth in human.
Answer:
Somatotrophic hormone (STH) secreted by the anterior lobe of pituitary gland is responsible for growth in human. It is also called as growth hormone.
Question 10.
Explain function of FSH in brief. (NCERT)
Answer:
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the growth of the graffian follicle and secretion of estrogen hormone by the follicle cells in female, where as in male it stimulates the process of spermatogenesis. Due to its action on both the male and female gametes formation, F.S.H. is also referred as gametokinetic factor.
Question 11.
What is osteitis fibrosa cystic?
Answer:
Hypersecretion of parathormone causes Osteitis fibrosa cystica disease. Quantity of Ca++ increases in the blood and urine. More calcium collection occurs in the bones.
Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Name the glands secreting the following hormones :
(i) Thyroxine,
(ii) Insulin,
(iii) Adrenalin and
(iv) Oestrogen,
(v) Oxytocin.
Or,
Give the source and functions of the following hormones :
(i) Thyroxine,
(ii) Insulin,
(iii) Adrenalin,
(iv) Oestrogen,
(v) Oxytocin.
Answer:
| Hormone | Name of gland | Functions |
| (i) Thyroxine | Thyroid Somatotrophic | Controling metabolic activities. |
| (ii) Insulin | islets of langerhans (Pancreas) | Control the metabolism of glucose. |
| (iii) Adrenalin | Adrenal gland | Improve immune power. |
| (iv) Oestrogen | Ovary | Improve the development of secondarysexual characteristics in female. |
| (v) Oxytocin | Pituitary gland | Contraction of uterine muscle at the time of child birth. It also induces mammary gland to secrete milk. |
Question 2.
Show the effect of hyperactivity of thyroid hormone on human beings.
Answer:
Following are the symptoms of hyperactivity :
(i) Increased metabolic rate, i.e., higher body temperature and high heart rate and restlessness.
(ii) Excessive loss of Ca++ and phosphorus from bones or osteoporosis.
(iii) Protruding eyeballs.
(iv) Excessive perspiration.
(v) Excessive hunger but loss of weight.
(vi) Man becomes irritative in nature.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the mechanism of hormone action.
Answer:
Action of hormones takes place by the following two methods :
1. At plasma membrane level: Most of the hormones (proteins) are binded with cell membrane and induce the activity of adenyl cyclase enzyme. This enzyme hydrolyses ATP molecules of the cytoplasm. Hydrolysis of ATP affects cellular metabolism in many ways.
2. At gene level after synthesizing protein: Few hormone (steroids) after reaching the nucleus of the target cell activate the inactive genes or inactivate the active genes. This activity of hormones also affects mRNA synthesis. This mRNA is responsible for the synthesis of proteins and enzyme and thus affects the metabolic activities and growth, structure and development of cell.
Question 4.
Describe the name and significance of hormones secreted by parathyroid gland.
Answer:
Parathyroid gland secretes a hormone known as parathormone.
Significance :
(i) This hormone increases the absorption of Ca++ in the walls of intestine and renal tubules.
(ii) It helps in muscle contraction, heart beating and formation of bones.
The deficient secretion of parathormone will cause parathyroid tetany. The deficiency of parathormone during childhood causes stunted growth of teeth, bones and brain. The hypersecretion of this hormone causes osteoporosis, hypercalcaemia and kidney stone like diseases.
Question 5.
Write the name of cells that secrete insulin. Also write the functions of insulin hormone.
Answer:
Insulin is proteinaceous hormone which is secreted by β- cells of islet of langerhans in response to higher levels of glucose and amino acids in the blood.
The chief functions of this hormone are as follows :
- It controls the amount of sugar in blood and converts glucose into glycogen in liver cells.
- Conversion of glucose to fatty acids and formation of adipose tissue.
- Reduction, in the breakdown and oxidation of fat.
- Absorption of amino acids by the cells and synthesis of proteins from them.
Question 6.
Define following : (NCERT)
(a) Exocrine gland,
(b) Endocrine gland,
(c) Hormone.
Answer:
(a) Exocrine glands: The glands which are duct containing and secrete their secretion into the duct, which cany them to the body surface or on the cavities of the body part are called as exocrine glands, e.g., salivary glands, sweat glands etc.
(b) Endocrine glands: Ductless glands are called as endocrine glands. They secrete their secretion directly into the blood, e.g., Thyroid, Pituitary gland.
(c) Hormones: Hormones are chemically proteins or steroids secreted by the endocrine glands in limited quantity directly into the blood and transferred to some other parts where their physiological effect is observed.
![]()
Question 7.
What is pheromones?
Answer:
The term pheromones is used for the first time by Karlson and Butenandt in 1959. It is a chemical secreted by exocrine gland similar to that of hormones. It is also known as ectohormone e.g., female silk insect secretes a pheromone known as bombykol or gyplure which is meant for attraction of male silk insects. Social insects like ant, termite and honeybees are collected on a place due to these pheromones. Pheromones can transmit informations very fastly and distantly.
Question 8.
What are sex hormones? Describe about any two sex hormones.
Answer:
Sex hormones: Hormones which are responsible for sexual activities and regu¬lates the development of secondary sex characters are called as sex hormones. Androgen is the male and oestrogen, progesterone and relaxin are the female hormones.
1. Oestrogen hormone: It is secreted by ovary. Small quantities of this hormone is also secreted by adrenal glands and placenta. This hormone is responsible for development of secondary sexual characters. It stimulates the development of secondary sex organs like uterus, fallopian tubes, ducts of mammary glands and external sex characters like high pitch voice, pattern of distribution of body hairs in the female during puberty.
2. Testosterone: It is a steroid hormone secreted by interstitial cells of Leydig’s cell and also from Sertoli cells. Interstitial cells are not present in the testes of a child but they are present in the testes of newborn infants and also in the testes of adults after puberty. Its production dwindles rapidly beyond the age of 40 and almost zero by the age of 80.
Question 9.
Give examples of following : (NCERT)
(a) Hyperglycemic and Hypoglycemic hormone.
(b) Hypercalcemic hormone.
(c) Gonadotrophic hormone.
(d) Progestational hormone.
(e) Blood pressure lowering hormone.
(f) Androgen and Estrogen.
Answer:
(a) Glucagon and insulin.
(b) Parathormone.
(c) Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone.
(d) Progesteron.
(e) Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF).
(f) Testosterone and androsterone are collectively called as androgen. Estrogen is secreted by the ovary.
Question 10.
What do you understand by suiciding of thyroid gland (Hashimoto’s disease)?
Answer:
Hashimoto’s disease : When medicines are provided for removing the effects produced due to the deficiency of thyroxine hormone, functioning like a foreign substance, then antibodies are synthesized in the body. These antibodies destroys the thyroid gland. The disease produced due to this condition is called as Hashimoto’s disease. It is also called as the suicide of thyroid gland as it is destroyed.
![]()
Question 11.
Write differences between following :
(a) Hormone and Enzyme.
(b) Nervous and Endocrinal.
Answer:
(a) Differences between Hormone and Enzyme
| Hormones | Enzymes |
| 1. These maybe steroids, catecholamines, proteins and amino acid derivatives. | These are proteins. |
| 2. These have low molecular weights and often diffuse through cells membranes (exception protein hormones). | These have high molecular weights and are not diffusible. |
| 3. They generally act slowly. | They act very fast. |
| 4. Life span is short and destroyed. | They have long life span. |
| 5. Hormones controlled actions are irreversible. | Enzymes controlled reactions are reversible. |
| 6. These are secreted by ductless glands. | These are secreted by gland that have ducts. |
| 7. These are poured directly into the blood and are carried to target organ. | These generally pass viaducts to act in some part of the body. |
| 8. They act in low concentrations and their excess or deficiency causes physiological disorders. | Enzymes act in low concentration but their excess does not cause disease. |
(b) Differences between Nervous and Endocrinal co-ordination
| Nervous | Endocrine |
| 1. In this, conduction of message through axon occurs in the form of electrical impulse and in synapse in the form of chemicals. | In this, conduction of message occurs in the form of chemical. |
| 2. Message is conducted very fast in them. | Conduction of message occurs slowly. |
| 3. Effect is seen for short period of time. | Effect remain for long period of time. |
| 4. It effects a specific place. | It effects large area. |
Question 12.
Describe various abnormalities of adrenal cortex in brief.
Answer:
Following are the abnormalities of adrenal cortex :
1. Addison’s disease: Insufficiency of glucocorticoid leads to Addison’s Disease characterised by shock, reduced blood pressure, muscular weakness, digestive disturbances, high level of urea in the blood and elevated body temperature. This disease may be also caused due to the deficiency of mineralocorticoids. Symptoms also include low blood sugar, low plasma sodium ions, high plasma potassium ions and increased urinary sodium ions.
2. Hypoglycemia: It is caused due to insufficiency of glucocorticoid. In this disease activities of brain, liver, and heart muscle decreases. Temperature of the body decreases.
3. Conn’s disease: It is caused due to insufficiency of mineralocorticoid. In this disease muscles fails to function due to defect in nerves, and patient dies.
4. Cushing syndrome: Hypersecretion of cortisol from the adrenal cortex due to a tumor of the gland leads to Cushing’s disease or Cushing’s syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia i.e. high blood sugar, increased deposition of glycogen in the liver, increased protein catabolism, appearance of sugar in the urine,’obesity, wasting of limb muscles, disorder of skin and bones, hypertension, rise in plasma Na+, fall in plasma K+ and retention of water and sodium chloride in the body.
5. Adrenal virilism: Sex steroids influence the functioning of sex organs and development of accessory sex characters. The over production of sex corticoids produces male-type secondary sexual characters such as growing of beards, moustaches and developing male voice in women. This disease is called adrenal virilism.
Question 13.
(1) Which cells of testis secrete male sex hormone?
(2) Why L.H. is called as interstitial stimulating hormone?
Answer:
1. Male sex hormone are produced by the Ley dig’s cells of the testis which are found surrounding the seminiferous tubules.
2. L.H. is called as I.C.S.H. because it induces Leydig’s cells or interstitial cells to secrete testosterone hormone.
Question 14.
Give important functions of testosterone hormone.
Answer:
- It induces development of secondary sexual character in male.
- It induces development of external sexual characters, such as growth of beard, moustaches and development of hairs in hand and legs. It also helps in development of heavy and low voice in man.
- It induces production of sperms in the testis.
- It effects development of tissues in the body.
Question 15.
Name the endocrine glands which secretes protein containing hormone.
Answer:
Following endocrine glands secrete protein containing hormones :
| Endocrine gland | Hormone |
| 1. Thyroid 2. Parathyroid 3. Pancreas 4. Anterior lobe of pituitary gland 5. Middle lobe of pituitary gland 6. Posterior lobe of pituitary gland |
Thyroxine Parathormone Insulin, glucagon TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, GH and prolactin M.S.H. Oxytocin. |
Question 16.
Write the names of hormones related with the different functions like :
(i) Softening of pelvic ligaments at the time of child-birth.
(ii) Expulsion of milk from mammary glands, just after the child-birth.
(iii) Stimulates gametogenesis in male and female.
Answer:
(i) Relaxin.
(ii) Prolactin or Lactogenic or Luteio Tropic Hormone (LTH) and Oxytocin.
(iii) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
![]()
Question 17.
Draw labelled diagram showing location of various endocrine glands in human body. (NCERT)
Answer:
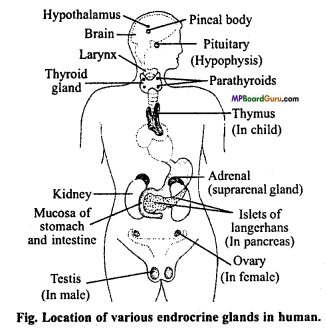
Question 18.
What is emergency hormone ? How does it help us to protect ourself from emergency condition ?
Answer:
Adrenalin or Epinephrine hormone is secreted by the medulla part of the adrenal gland. Adrenalin hormone is a derivative of tyrosine. Chromaffin cells secrete about 80% adrenalin hormone. This hormone effects all the organs effected by autonomous nervous system.
It is also known as emergency hormone as it is used as heart stimulant in acute emergencies. It is secreted in proportional to the stimulus through the central nervous system. Under the conditions of stimulus such as cold, heat, drugs and emotional excitement, the secretion of adrenalin is greatly increased. In circumstances of great stress, strain and emotional upheaval, the body requires additional energy in hurry. Adrenalin accordingly increases the conversion of glycogen to glucose and thus provides quickly available energy.
As it also increases blood flow, the available glucose may quickly go where it is needed. It dilates the blood vessels in the heart and skeletal muscles, thus decreasing the peripheral resistance and permitting a copious flow of blood to meet the needs of fight and flight.
Question 19.
Name the Endocrine glands from which following hormones are secreted. Give functions of them :
1. Parathormone,
2. Cortisone,
3. Somatotropic hormone,
4. Melatonin.
Answer:
| Hormone | Endocrine gland | Function |
| 1. Parathormone | Parathyroid | It regulates muscular contraction, heart beat, bone formation. |
| 2. Cortisone | Adrenal cortex | It regulates protein metabolism. |
| 3. Somatotrophic hormone | Anterior lobe of pituitary | Regulates general body growth. |
| 4. Melatonin | Pineal body | It delays sexual development. |
Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 Important Questions LongAnswer Type
Question 1.
Name the hormones secreted by following : (NCERT)
(a) Hypothalamus,
(b) Pituitary gland,
(c) Thyroid,
(d) Parathyroid,
(e) Adrenal gland,
(f) Pancreas,
(g) Testis,
(h) Ovary,
(i) Thymus,
(j) Atrium,
(k) Kidney,
(l) Gastrointestinal track.
Answer:
(a) Hypothalamus: Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH), Adrenocorticotro- phin Releasing Hormone (ARH), Gonadotrophin Releasing Hormone (GRH), Prolactin Re¬leasing Hormone (PRH), Somatotropin Releasing Hormone (SRH), Melanocyte Releasing Hormone (MRH).
(b) Pituitary gland: Somatotrophic hormone (STH), Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), Lactogenic hormone (LTH), Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), Gonadotrophic hormone (FSH, LH Or ICSH), Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH), Vasopressin, Oxytocin.
(c) Thyroid: Thyroxine, Thyrocalcitonin ‘
(d) Parathyroid: Parathormone
(e) Adrenal gland : Mineralocorticoid (aldosterone), Glucocorticoid, Sex hormones (Androgen, Estrogen), Adrenalin, Nor adrenalin.
(f) Pancreas : (islets of Langerhans): Insulin, Glucagon.
(g) Testis : Testosterone, Andosterone.
(h) Ovary : Estrogen, Progesterone.
(i) Thymus: Thymosin.
(j) Atrium : Atrial Netriuretic factor (ANF).
(k) Kidney: Renin, Erythrogenin.
(l) Gastrointestinal track : (Mucosa gland of alimentary canal): Gastrin, secretin, pancreozymins, cholecystokinin, enterocrinin, enterogastrone.
![]()
Question 2.
Write short note on functions of following hormones :
(a) Parathormone,
(b) Thyroxin hormone,
(c) Thymosin,
(d) Androgen,
(e) Estrogen,
(f) Insulin and glucagon.
Answer:
(a) Parathormone: Parathyroid gland secretes a hormone known as parathormone.
Significance :
(i) This hormone increases the absorption of Ca++ in the walls of intestine and renal tubules.
(ii) It helps in muscle contraction, heart beating and formation of bones.
The deficient secretion of parathormone will cause parathyroid tetany. The deficiency of parathormone during childhood causes stunted growth of teeth, bones and brain. The hypersecretion of this hormone causes osteoporosis, hypercalcaemia and kidney stone like diseases.
(b) Thyroxin hormone:
Thyroid Gland:
Origin: Thyroid gland develops from the endoderm of the embryo.
Location: Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland of the body which is located on the ventral side of the neck just below the larynx. It surrounds the front of the larynx and upper part of the trachea in the neck. It has two lobes on either side of trachea.
Structure: Thyroid gland is a pink coloured, H-shaped, bilobed gland, largest gland of the body. Their lobes are connected by an isthmus. In normal healthy person, its weight is about 25 gms, it is larger in female than in male. Thyroid is profusely supplied with blood vessels. The gland consists of large number of small closed follicles or acini of about 200 μ in diameter. Each follicle is lined by a secretory epithelium of cuboidal or low columnar type.
These follicles are held together by areolar tissue. Each follicle contains a clear viscid proteinaceous amber coloured colloid which normally comprises the greater part of the thyroid mass. The colloid consists mainly of iodinated thyroglobulin. In polybreeders like human beings the gland functions almost uniformly but in seasonal breeders the gland is active at one stage and inactive at the other.
Hormones of Thyroid Gland :
1. Thyroid gland secretes three hormones :
- Thyroxin or tetraidothyronine (T4),
- Triiodothyronine (T3) and
- Thyrocalcitonin (TCT).
1. Thyroxine: Thyroxine hormone contains about 60% of iodine.
Functions of thyroxine:
- Thyroxine hormone regulates approximately all types of metabolic reactions of the body.
- It effects all energy releasing oxidation processes.
- It controls the temperature of the body.
- It controls the amount of intracellular substances of the tissue.
- It maintains the normal stimulus of the cardiac muscles.
2. Tri-iodothyronine: It functions like thyroxine but more rapidly.
3. Thyrocalcitonin: It regulates the amount of Ca in urine and blood.
(c) Thymosin: It stimulates the proliferation of lymphocytes and also restores cell-mediated immunological functions such as the ability to reject first or second set skin grafts.
(d) Androgen: It includes Testosterone and Androsterone. Both Androsterone and Testosterone are secreted by the interstitial cells. It induces development of secondary sexual characters in male human.
(e) Estrogen:
Sex hormones: Hormones which are responsible for sexual activities and regu¬lates the development of secondary sex characters are called as sex hormones. Androgen is the male and oestrogen, progesterone and relaxin are the female hormones.
1. Oestrogen hormone: It is secreted by ovary. Small quantities of this hormone is also secreted by adrenal glands and placenta. This hormone is responsible for development of secondary sexual characters. It stimulates the development of secondary sex organs like uterus, fallopian tubes, ducts of mammary glands and external sex characters like high pitch voice, pattern of distribution of body hairs in the female during puberty.
2. Testosterone: It is a steroid hormone secreted by interstitial cells of Leydig’s cell and also from Sertoli cells. Interstitial cells are not present in the testes of a child but they are present in the testes of newborn infants and also in the testes of adults after puberty. Its production dwindles rapidly beyond the age of 40 and almost zero by the age of 80.
(f) Insulin and Glucagon: Insulin hormone is secreted by the /?-cells of islets of Langerhans. Its main function is to regulated amount of glucose in the blood by converting excess glucose into glycogen by glycogenesis process in the liver for storage. Glucagon hormone is secreted by the a-cells of islets of Langerhans. It stimulates glycogenolysis, thus glucose is releases into the blood from the liver when there is low concentration of glucose in the blood.
Question 3.
Describe the structure and position of pituitary gland and write the name and functions of hormones secreted by them.
Or,
Where is pituitary gland situated? Write the name of two hormones secreted by posterior lobe of pituitary gland.
Or,
Why pituitary gland is called master gland? Write its structure and hormones.
Answer:
Pituitary gland: It is a small and rounded gland which is found on the dorsal surface of brain just behind the optic chiasma and is closed within the cavity of celatersica.
It is known as hypo-physis. It is attached by a stalk with the infundibulum on the mid part of dorsal surface of the brain. It is the regulatory centre of other glands hence, it is also called as the master gland of the body. It is made up of following three parts :
- Fore lobe,
- Mid lobe and
- Hind lobe.
Hormones of fore lobe and their functions :
1. Somatotrophic hormones (STH): It controls the growth of the body. It is respon¬sible for the development of bones.
2. Thyrotrophic hormones (TSH): This hormone is responsible for the secre tion of thyroid gland.
3. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH): It is secreted by the anterior lobe of pituitary gland to control the synthesis and secretion of hormones from adrenal cortex.
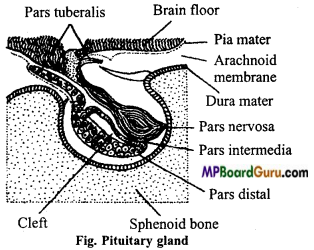
4. Follicle stimulating hormones (FSH): In male, FSH stimulates growth of the sperms in the testis and egg in the ovary of female.
5. Luteinizing hormones (LH): This hormone brings about ovulation, secretion of oestrogens and progesterone formation of corpus luteum in female and stimulates the interstitial cells of the testis to secrete testoster¬one in the male.
6. Prolactin or lactogenic or luteotrophic hormone (LTH): This hormone promotes mammary growth and lactation and maintains the corpus luteum and causes it to become actively secretory.
Neurotrophic hormone or hormones of posterior lobe :
- Vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone: It causes increased reabsorption of water in the kidney tubule also helps to maintain the arterial blood pressure within the normal range.
- Oxytocin hormone: It stimulates uterine contraction during childbirth and cause milk ejection from the mammary glands during sucking.
Question 4.
Describe the functions of hormones secreted by thyroid glands.
Or,
Write the position of thyroid gland. Write its function.
Answer: Thyroid Gland:
Origin: Thyroid gland develops from the endoderm of the embryo.
Location: Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland of the body which is located on the ventral side of the neck just below the larynx. It surrounds the front of the larynx and upper part of the trachea in the neck. It has two lobes on either side of trachea.
Structure: Thyroid gland is a pink coloured, H-shaped, bilobed gland, largest gland of the body. Their lobes are connected by an isthmus. In normal healthy person, its weight is about 25 gms, it is larger in female than in male. Thyroid is profusely supplied with blood vessels. The gland consists of large number of small closed follicles or acini of about 200 μ in diameter. Each follicle is lined by a secretory epithelium of cuboidal or low columnar type.
These follicles are held together by areolar tissue. Each follicle contains a clear viscid proteinaceous amber coloured colloid which normally comprises the greater part of the thyroid mass. The colloid consists mainly of iodinated thyroglobulin. In polybreeders like human beings the gland functions almost uniformly but in seasonal breeders the gland is active at one stage and inactive at the other.
Hormones of Thyroid Gland :
1. Thyroid gland secretes three hormones :
- Thyroxin or tetraiodothyronine (T4),
- Triiodothyronine (T3) and
- Thyrocalcitonin (TCT).
1. Thyroxine: Thyroxine hormone contains about 60% of iodine.
Functions of thyroxine:
- Thyroxine hormone regulates approximately all types of metabolic reactions of the body.
- It effects all energy releasing oxidation processes.
- It controls the temperature of the body.
- It controls the amount of intracellular substances of the tissue.
- It maintains the normal stimulus of the cardiac muscles.
2. Tri-iodothyronine: It functions like thyroxine but more rapidly.
3. Thyrocalcitonin: It regulates the amount of Ca in urine and blood.
![]()
Question 5.
Write down the names and significance of parathyroid gland hormones.
Answer:
The hormones released by parathyroid are called parathormone.
Functions: It controls Ca2+ and PO4-3 ” in blood along with muscle contraction, heartbeat, bone formation, etc.
Hyposecretion: Due to its deficiency bones, teeth do not develop properly.
Hypersecretion: Due to its overproduction osteoporosis, hypercalcimia, stone in kidney, calcitonin diseases occur.
Question 6.
What are ductless glands? Describe Thyroid, Adrenal, Ovary and Pancreas.
Answer:
Ductless gland: The glands which secrete, their secretion directly into the blood circulatory system as they do not have duct are called as ductless endocrine glands. The substance secreted by them are called as hormones which are transported to required part of the body through blood.
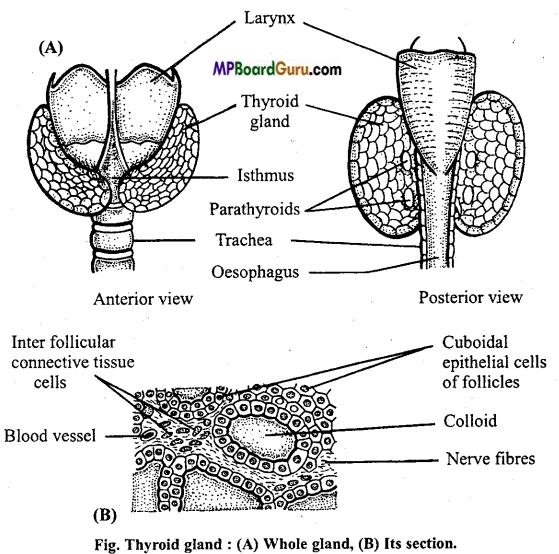
1.Thyroid: This gland is a soft bibbed structure formed of glandular tissue. It is situated in front of trachea immediately below the larynx. The two lobes of the gland are connected with each other by a narrow connective tissue structure called isthmus. The hormone secreted by it is Thyroxine. It is a colloidal substance containing much iodine. The whole hormone is C15H10O4N14.
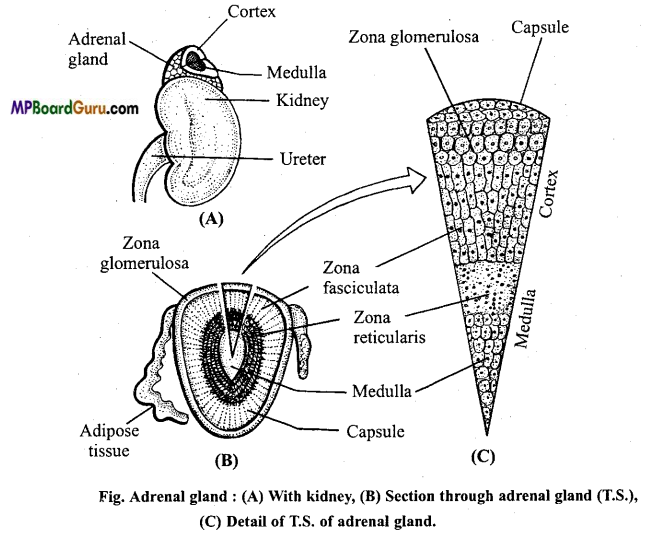
2. Adrenal: These glands are situated very close to the kidneys; therefore, they are called adrenal or suprarenal glands. The outer part of the glands is called cortex and inner medulla. The origin and function of both these parts are different.
(i) Cortex: It originates from mesodermal cells and is enclosed in a capsule. The secretion of cortex are very important for life. These substances control carbohydrate me¬tabolism, amount of salts in blood, regulate the volume of blood, control the sexual maturity and create the resistance from the diseases in the body of the animal.
It produces about 20 steroid compounds which are called cortisones, the important among which are following :
(a) Corticosterone or Glucocorticoid,
(b) Cortisone,
(c) Mineralocorticoid,
(d) Sex-hormone.
(ii) Medulla: It is present on the inner side of adrenal and surrounded by the cortex. It produces two hormones
(a) Adrenalin,
(b) Noradrenalin. Adrenalin is also called as emergency gland.
3. Ovary: In female one pair of ovaries are found. Three types of hormones are secreted by them :
- Estrogen,
- Progesterone,
- Relaxin.
4. Pancreas: Pancreas functions both as exocrine and endocrine. The organ has certain specialized cells which are histologically different from the rest of the pancreatic tissue. These cells are endocrine in function and was discovered by Langerhans, therefore, they are known as islets of Langerhans. The islets of Langerhans in the pancreas secrete the polypeptide hormone, glucagon and the protein hormone, insulin.
They are concerned with the regulation of intermediary metabolism. Glucagon elevates the blood glucose by stimu-lating hepatic glycogenolysis. They maintain the blood glucose level during starvation.
![]()
Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Which one of the following pairs is the matching pair of the part and the hormone it secretes :
(a) Thyroid-Epinephrin
(b) Alpha cells of pancreas-Glucagon
(c) Anterior pituitary-Adrenalin
(d) Stomach epithelium-Secretin.
Answer:
(b) Alpha cells of pancreas-Glucagon
Question 2.
Failure of insulin production results in :
(a) Addison’s disease
(b) Cushing’s disease
(c) Diabetes insipidus
(d) Diabetes mellitus.
Answer:
(d) Diabetes mellitus.
Question 3.
Oestrogens are the hormones produced by :
(a) Testes
(b) Ovary
(c) Pituitary
(d) Adrenal cortex.
Answer:
(b) Ovary
Question 4.
Development of secondary sexual characters in females are controlled by:
(a) Oestrogen
(b) Oxytocin
(c) Progesterone
(d) Androgen.
Answer:
(a) Oestrogen
![]()
Question 5.
Which hormone is secreted more in dark condition:
(a) Insulin
(b) Adrenalin
(c) Thyroxine
(d) Melatonin.
Answer:
(d) Melatonin.
Question 6.
Continued secretion of milk is maintained by :
(a) Pituitary
(b) Thyroid
(c) Pancreas
(d) Adrenal.
Answer:
(a) Pituitary
Question 7.
Progesterone hormone is secreted by :
(a) Corpus luteum
(b) Corpus callosum
(c) Corpus uteri
(d) Corpus albicans.
Answer:
(a) Corpus luteum
Question 8.
If adrenal cortex function is impaired, it results in decreased concentration of one of the following in the blood: (MP PMT 1988)
(a) Ammonium salts
(b) Sodium salts
(c) Glucose
(d) Calcium salts.
Answer:
(b) Sodium salts
![]()
Question 9.
Diabetes insipidus is caused due to the deficiency of :
(a) Oxytocin
(b) Insulin
(c) Vasopressin
(d) Glucagon.
Answer:
(c) Vasopressin
Question 10.
Adrenal glands are found located in abdominal cavity in close association with:
(a) Testes
(b) Spleen
(c) Liver
(d) Kidneys.
Answer:
(d) Kidneys.
Question 11.
The male hormone, testosterone is secreted by:
(a) Sperms
(b) Seminiferous tubules
(c) Prostrate glands
(d) Interstitial cells of testes.
Answer:
(d) Interstitial cells of testes.
Question 12.
The name of hormone secreted by the ovary which facilitates growth of ovarian follicle is :
(a) Progesterone
(b) LH
(c) FSH
(d) Estradiol.
Answer:
(d) Estradiol.
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the endocrine gland is mainly concerned with immunity in human :
(a) Parathyroid gland
(b) Adrenal gland
(c) Thymus gland
(d) Posterior pituitary gland.
Answer:
(c) Thymus gland
Question 14.
Emergency hormone ¡s:
(a) Aldostrerone
(b) Pentathromone
(c) Adrenaline
(d) Thyroxin.
Answer:
(c) Adrenaline
2. Fill in the blanks:
(A)
1. Islets of langerhans are formed in ………….. It secrets ………….. hormone.
Answer:
Pancrease, insulin,
2. ………….. is an antidiuretic hormone.
Answer:
Vasopressin,
3. Hyposecretion of somatotropin results in ………….. whereas its hypersecretion results …………..
Answer:
Dwarfism, Gigantism,
4. Deficiency of insulin hormone causes ………….. disease.
Answer:
Diabetes,
5. Goitre disease is caused due to deficiency of ………….. .
Answer:
Iodine,
6. Progesterone hormone is secreted by ………….. .
Answer:
Corpus luteum,
7. Adrenalin hormone increases ………….. and ………….. .
Answer:
Heart beat, blood pressure
8. Melatonin hormone is secreted by ………….. .
Answer:
Pituitary gland,
9. Human became dwarf due to deficiency of ………….. hormone.
Answer:
Thyroxin.
![]()
(B)
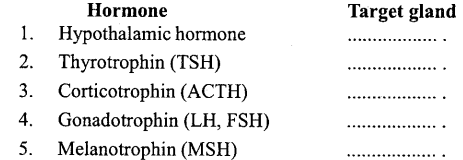
Answer:
1. Pituitary gland,
2. Thyroid gland,
3. Adrenal gland,
4. Gonads (Testis or ovary),
5. Hypothalamus.
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. T4 | (a) Hypothalamus |
| 2. PTH | (b)Thyroid |
| 3. Gonadotrophic releasing hormone | (c) Pituitary gland |
| 4. Luteinizing hormone | (d) Parathyroid. |
Answer:
1. (b)Thyroid
2. (d) Parathyroid.
3. (a) Hypothalamus
4. (c) Pituitary gland.
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Hypothalamus | (a) Testosterone |
| 2. Prolactin | (b) Somatotropin |
| 3. Corpus luteum | (c) Thyroxin |
| 4. Leydigs cells | (d) Milk secretion |
| 5 . Anterior lobe of pituitary | (e) Progesterone. |
Answer:
1. (c) Thyroxin
2. (d) Milk secretion
3. (e) Progesterone.
4. (a) Testosterone
5. (b) Somatotropin
(C)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Oxytocin | (a) Delivery hormone |
| 2. Relaxin | (b) Pituitary gland |
| 3. Ca++ level | (c) LH. |
| 4. Somatostatin | (d) Hypothalamus |
| 5. Estrogen | (e) Thyroid. |
Answer:
1. (b) Pituitary gland
2. (a) Delivery hormone
3. (e) Thyroid.
4. (d) Hypothalamus
5. (c) LH.
4. Answer in one word:
1. Name the part of brain in which pituitary gland is found.
Answer:
Thalamus,
2. Name the hormone which control the amount of Ca in blood.
Answer:
Parathyroid hormone,
3. Name the largest gland of our body.
Answer:
Pituitary gland,
4. Name the cell that secrets testosterone hormone.
Answer:
Interstitial cells,
5. Name the gland of man from which vasopressin hormone is secreted.
Answer:
Hypothalamus,
6. Name the hormone which stimulates the secretion of milk.
Answer:
Prolactin hormone,
7. Which hormone is known as delivery hormone.
Answer:
Relaxin,
8. Write the name of any two hormones secreted by the anterior part of pituitary gland.
Answer:
T.S.H. and S.T.H,
9. What we called the ratio of volume of air inspired and expired during respiration.
Answer:
Vital capacity.