Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement
Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is arthritis?
Answer:
Arthritis is a disease characterized by the inflammation of the joints. In this disease, the synovial membrane secretes extra fluid which causes swelling and pain in the joints. A hard tissue deposits over the articular cartilages. As a result the joints become stiff.
Question 2.
What is muscle twitch?
Answer:
When a muscle fibre receives only one stimulus, then it contracts only one time. This one time contraction of muscle fibre is called as muscle twitch.
![]()
Question 3.
How many vertebrates and ribs are found in human?
Answer:
In human 26 vertebrates, and 12 pairs of ribs are found.
Question 4.
Name the longest bone of human body.
Answer:
Longest bone of human body is femur.
Question 5.
Write name of the locomotory organs of the following organisms :
(i) Paramoecium,
(ii) Hydra,
(iii) Earthworm,
(iv) Octopus,
(v) Starfish.
Answer:
(i) Cilia,
(ii) Tentacle,
(iii) Setae,
(iv) Muscular arm,
(v) Tube feet.
Question 6.
What is Sliding filament theory? (NCERT)
Answer:
Sliding filament theory was proposed by Lein. Muscle fibres contract and relax on being excited by the nerve fibres. According to this theory, during the contraction of muscle, actin filaments slide over the myosin filaments.
Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is joint? Name the joints related to the following organs :
(i) Joint of knee,
(ii) Joint between glenoid cavity of pectoral girdle and acetabulum cavity of pelvic girdle with the humerus and femur,
(iii) Elbow joint,
(iv) Joint between skull bones,
(v) Joint between carpals and metacarpals of thumb,
(vi) Ankle joint.
Answer:
Joint: The region at which two or more bones of skeleton come in contact and move freely is called as Joint.
(i) Hinge joint,
(ii) Ball and Socket joint,
(iii) Hinge joint,
(iv) Immovable joint,
(v) Saddle joint,
(vi) Hinge joint.
![]()
Question 2.
How movement takes place in skeleton by muscles?
Answer:
The skeleton of our body is connected with each other by voluntary muscles. The fibres that connect the bones with any muscle are known as tendon, whereas the fibres that connect bones to bones are known as ligaments. Muscle cells are made up of muscle fibres having the property of contraction and expansion hence muscle cells also possessing these characteristics. The contraction and expansion of these muscles resulting in the movement of skeleton.
Question 3.
Describe any four functions of the skeletal system.
Answer:
The skeletal system of vertebrates performing the following functions:
- It protects the heart, brain and other soft organs.
- It provides base to the body and gives a definite shape to it.
- Skeletal system functioning like a pendulum and thus performing the process of movement and locomotion.
- The thick bones of skeleton system synthesise R.B.Cs. and W.B.Cs. within their bone marrow.
Question 4.
From where energy is obtained for contraction of muscles?
Answer:
The energy for the contraction of muscle fibres is obtained from a chemical substance known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is found in mitochondria. This sub¬stance is the source of energy required for the metabolic activities of cells. The energy obtained by the oxidation of glucose which is stored in ATP. Little glucose is present in muscle fibres but myosin is rich in ATP. When the muscle is excited, ATP itself changes into adenosine diphosphate (ADP), thereby releasing energy.
ATP → ADP + P04 + Energy
ADP is again converted into ATP by the energy obtained from the creatine phosphate. CP + ADP → ATP + C. Creatine is resynthesized into creatine phosphate by the energy ob¬tained from glucose of muscle glycogen.

Question 5.
Name various parts of human skeletal system and write number of bones found in them.
Answer:
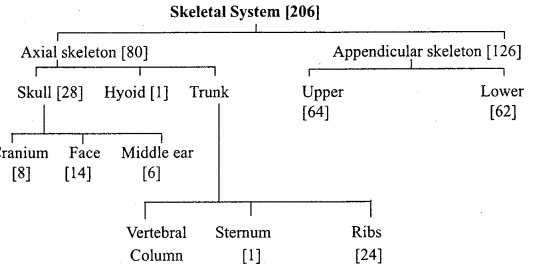
Question 6.
Red muscle fibres functioning up to a longer period of time than white muscle fibres, why?
Answer:
Red muscle fibres contain a large amount of myoglobin and mitochondria. Myo¬globin combine with oxygen to form oxymyoglobin. For muscular contraction oxygen is derived from oxymyoglobin. These muscles do not respire anaerobically due to presence of oxygen and thus lactic acid is not formed. Thus, red muscle fibres functioning up to a longer period of time without fatigue. White muscle fibres do not contain myoglobin.
The number of mitochondria is also few. Hence oxygen supply becomes irregular and lactic acid is formed in these muscle fibres due to anaerobic respiration. Thus, these muscles become fatigue and they do not functioning up to a longer period of time.
![]()
Question 7.
What is meant by twitch muscle and tetanus?
Answer:
Twitch muscle: When a muscle receive only one stimulus then it contracts only one time. This one time contraction of muscle fibre is called as muscle twitch.
Tetanus : It is the permanent contraction condition of the muscle which occurs due to continuous conduction of impulse. This may lead to death of the person.
Question 8.
What is oxygen debt?
Answer:
Oxygen debt: After heavy work or exercise muscle do not get oxygen to fulfil their energy requirement. Thus, they produces ATP by anaerobic process, and lactic acid is formed. In this stage more oxygen is required than normal stage. This requirement of extra quantity of oxygen is called as oxygen debt.
This extra oxygen is used up by the lactic acid for its aerobic oxidation. By this process creatine phosphate is produced. Some quantity of required oxygen is supplied by myoglobin which has capacity to store oxygen for future. During training of athletes rate of oxy- contraction of muscle is increased. Thus, athletes required less oxygen debt.
Question 9.
Write differences between Fixed joint and Synovial joint.
Answer:
Differences between Fixed joint and Synovial joint
| Fixed joint | Synovial joint |
| 1. In this type of joint bones are connected by connective tissue called as suture. |
A synovial cavity is found in between two bones which contains synovial fluid and two bones are jointed by ligaments. |
| 2. Movement do not occur. | Movement occurs. |
| 3. This type of joint is found in the bone of skull. | Found in all movable bones. |
Question 10.
Draw diagram showing one sarcomere of the striped muscle and label its various parts. (NCERT)
Answer:
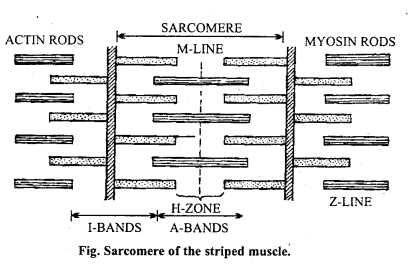
Question 11.
How will you differentiate skeletal muscle and Cardiac muscle? (NCERT)
Or,
Write differences between Striped, Unstriped and Cardiac muscles.
Answer:
Differences between Striped, Unstriped and Cardiac muscles
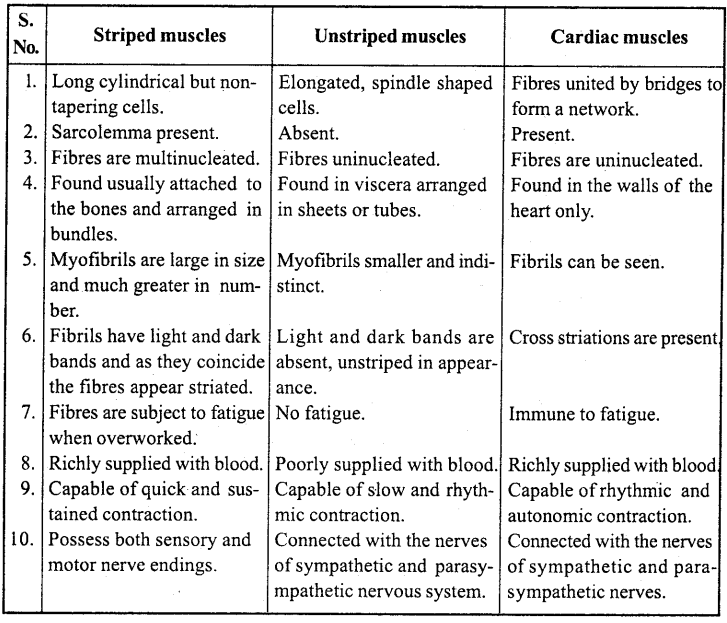
Question 12.
Draw a labelled diagram of pelvic girdle of human.
Answer:
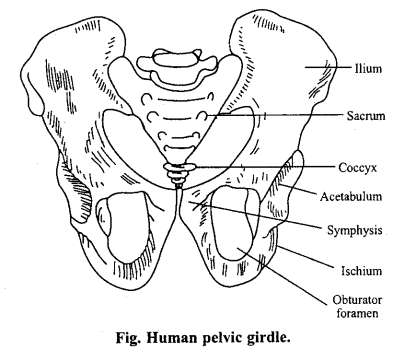
Question 13.
Name the type of joints found in the following : (NCERT)
(a) Atlas and axis,
(b) Carpal and metacarpal of thumb,
(c) Between phalanges,
(d) Femur and acetabulum,
(e) Between bones of skull,
(f) Between pubic bones of pelvic girdle.
Answer:
(a) Pivot joint,
(b) Saddle joint,
(c) Hinge joint,
(d) Ball and socket joint,
(e) Fibrous joint (sutures),
(f) Cartilaginous joint.
![]()
Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Write the differences between following : (NCERT)
(a) Actin and Myosin
(b) Red muscle fibre and White muscle fibre
(c) Pectoral and Pelvic girdle.
Answer:
(a) Differences between Actin and Myosin filament
| Actin filament | Myosin filament |
| 1. ‘I’ band of striped muscle is consists of actin protein. 2. A dark line is found at the centre of the ‘I’ band called as ‘Z’ line. 3. During contraction ‘I’ line disappear and ‘Z’ lines come nearer to each other. |
‘A’ band of striped muscle is consists of myosin protein. A light line is found at the centre of the ‘A’ band called as ‘H’ line. During contraction of muscle ‘A’ band do not show any change but ‘H’ line disappear. |
(b) Difference between Red and White muscle fibres
| Red muscle fibres | White muscle fibres |
| 1. Thin in size. | Thick in size. |
| 2. Dark red coloured due to the presence of haemoprotein known as myoglobin. It combines with oxygen to form oxymyoglobin and thus stores oxygen which can be released during muscle contraction. | Light red in colour as there is no myoglobin. |
| 3. Rate of contraction is slow. | Rate of contraction is fast. |
| 4. These muscle fibres contain large number of mitochondna. | These muscle fibres are poor in mitoch ondria.
|
| 5. These muscle fibres are able to carry out aerobic metabolism. So aerobic contraction of muscles takes place without accumulation of much lactic acid. | These fibres mainly depend upon anaerobic metabolism (glycolysis) and so anaerobic contraction of muscles takes place,accumulation of lot of lactic acid leading to muscle fatigue. |
| 6. These muscle fibres can do sustained but slower work for a long time. | These muscle fibres can do fast work, but for a short period only. |
| 7. Red muscle fibres are innervated by smaller nerve fibres.
Example: Extensor muscLes on the back of the human body, some flight muscles of birds. |
These are innervated by longer nerve fibres. Example: Extrinsic muscles of the eyeball, sparrow uses these muscles for short, fast flight. |
(c) Differences between Pectoral and Pelvic girdle
| Pectoral girdle | Pelvic girdle |
| 1. It is found in the shoulder region. | It is found in the hip region. |
| 2. It provides articulation with head of the humorous at glenoid cavity. | It provides articulation with head of the femur at acetabulum cavity. |
| 3. It has two halves, each half consists of two bones : Scapula and Clavicle. | It has two halves, each half consists of three bones – Ilium, Ischium and Pubis. |
| 4. It is also meant for attachment of the muscles of arm. | It provides surface for attachment of the muscles of the legs. |
| 5. It protects delicate organs of the thorax. | It protects the soft organs present inside the pelvic cavity. |
Question 2.
Describe main steps of muscular contraction. (NCERT)
Or,
Draw a labelled diagram of striped muscle and describe mechanism of muscular contraction in brief.
Answer:
Structure of striped or voluntary muscles: Since their movement is always at the will of the animal possessing them, they are known as voluntary muscles. They are always attached with the skeleton, hence called as skeletal muscles. Their cells are long and tubular and each is surrounded by thin membrane called sarcolemma. Many nuclei are found in the sarcoplasm surrounded by sarcolemma; therefore, muscular tissue is multinucleated or syncytial. A large number of parallel myofibrils are present in the sarcoplasm.
Transverse bands of light and dark shade are found in each muscle fibres. Dark bands are known as ‘A’ discs or Dobie’s dots while light bands are called ‘I’ discs. Each ‘I’ disc is divided into two another band known as ‘Z’ disc or Krause’s membrane. Similarly ‘A’ disc is also divided into two parts by Hensen’s disc or ‘H’ zone. The part between two ‘Z’ discs is known as sarcomere.
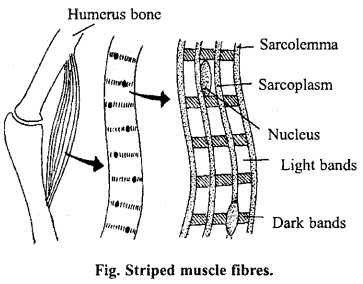
Electron microscopic studies have shown that these bands are formed of protein. ‘A’ bands are formed of parallel bars of a protein called myosin. ‘I’ bands are made up of similar bars of a protein known as actin. The muscles lengthen and shorten due to the contraction and expansion of these bars. These muscles take main part in the movement of organs as limbs, neck, eye etc.
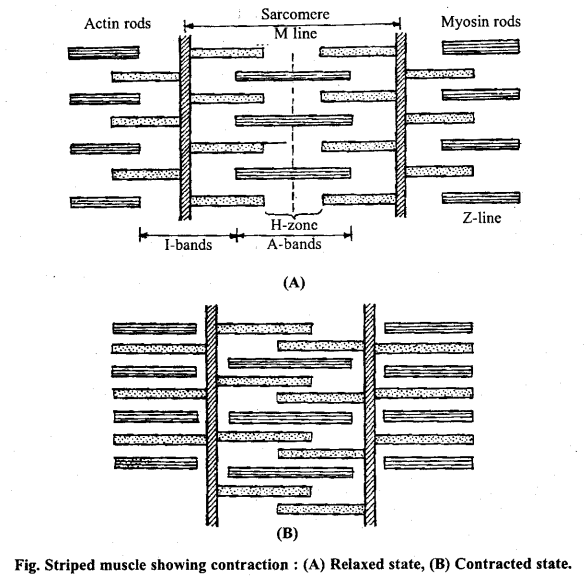
Working of striped muscle fibre: The muscle fibres contract and relax on being excited by the nerve fibres. H.E. Huxley and A.F. Huxley explained the working of muscle fibres with the help of electron microscopic studies. The theory proposed by Lein is known as sliding filament theory. It says that during contraction the actin filaments slide over the myosin filaments. There is no change in the length of ‘A’ bands at the time of contraction.
The actin bars of T bands slide on the myosin bars of ‘A’ bands and come so close that they overlap each other in the region of Hensen’s discs. Thus the muscle fibres contract due to the shortening of sarcomeres. The muscle fibres remain in their normal state when the effect of excitation is over, i.e. actin and myosin bars come back in their normal position. The sarcomeres are the functional units of striped muscle fibres.
![]()
Question 3.
What are joints? Describe the various types of joints found in human beings Or, What is joint ? Describe perfect joint and explain any three types of it.
Answer:
Joints: The region at which two or more bones of skeleton come in contact and move freely is called as joint.
Basically three types of joints are found in the body or vertebrates :
- Perfect joints,
- Imperfect joints,
- Immovable joints.
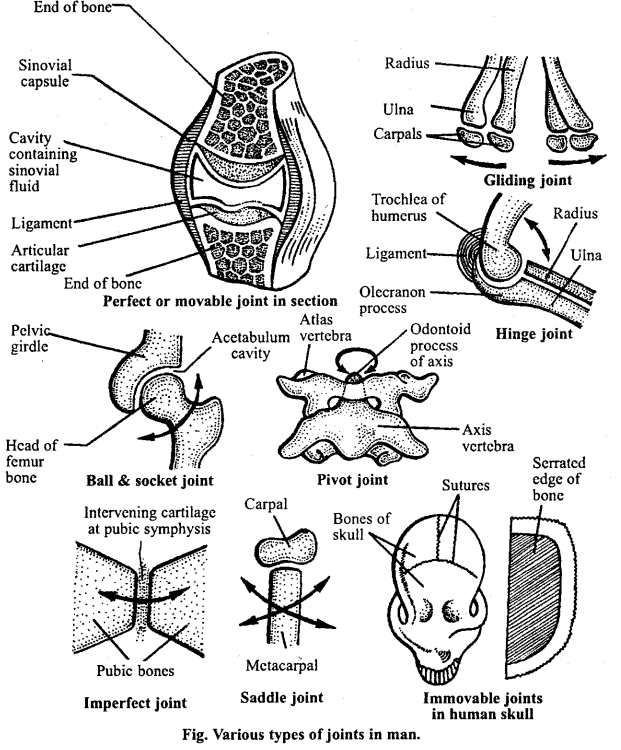
1.Perfect joints: These joints have synovial cavity which allow movement in more than one plane. The perfect joints may be of following types :
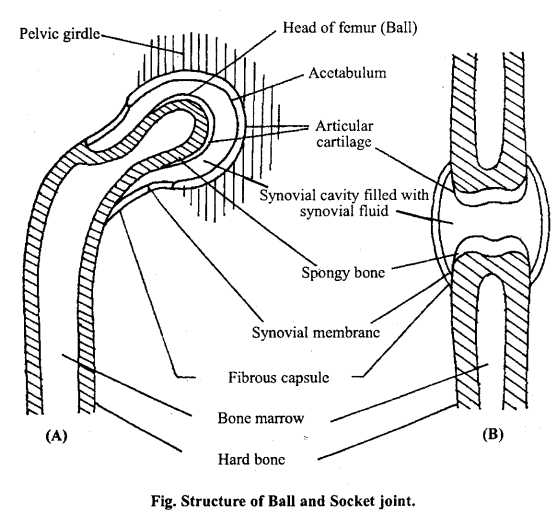
(a) Bail and Socket joint: Arthritis is a disease characterized by the inflammation of the joints. In this disease, the synovial membrane secretes extra fluid which causes swelling and pain in the joints. A hard tissue deposits over the articular cartilages. As a result the joints become stiff.
(b) Pivot joint: In this joint the articulating face of one bone is stationary like a pivot while the articulating face of the other can rotate over it. e.g. Joint between carotae and vertebral column.
(c) Hinge joint: It is just like a hinge of a door, allowing movement in one plane, e.g. Elbow joint, knee joint, ankle joint.
(d) Gliding joint : In such joint the articulating surface of the bone can glide one above the other, e.g. Joint between radio ulna and carpal.
(e) Saddle joint: It resembles the ball and socket joint except that in this case neither the ball nor the socket is fully developed, e.g. Metacarpal of the thumb joining the wrist bone in man.
2. Imperfect joint: These joints which do not possess synovial cavity or connecting ligaments are called imperfect joints, e.g. Joints between ileum of pelvic girdle and transverse process of sacral vertebrae.
3. Immovable joint: These joints which are permanently fixed and cannot perform any movement are termed as immovable joints, e.g. Bones of skull. These joints are called sutures. These joints lack synovial capsule.
Question 4.
What is Axial Skeleton? Describe various bones of Axial skeleton of human.
Answer:
Axial Skeleton: Skeleton which forms axis of the body is called as Axial skeleton. It consists of skull, Hyoid, vertebral column and ribs.
1. Skull: It is formed of 28 bones and is skeleton of the head region. Skull can be further divided into following regions :
(i) Cranium or brain box: It encloses the brain and is formed of eight bones namely frontal, parietal (two), temporal (two), occipital, sphenoid and ethmoid.
(ii) Facial bones : These form facial part of the skull and are fourteen in number. These include nasal 2, maxillary 2, squamosal 2, mandible 1, lachrymal 2, palatine 2, turbinals 2 and vomer 1.
(iii) Ear bones: These are three pairs of ear ossicles : malleus 2, incus 2 and stapes 2.
2. Hyoid: It supports tongue.
3. Vertebral column: It forms axis of the body and also known as backbone. Vertebral column supports the body like a beam. It is slightly curved vertical rod in the mid dorsal line of the body extended from the atlas vertebra to the caudal vertebra. Vertebral column protects the general viscera and houses the spinal cord also.
Vertebral column develops from the notochord part of the embryo. Total number of vertebrae in the vertebral column of human being is 26, however in primitive stage it is 33 in number. Vertebral column is differentiated into five regions, which are :
- Cervical vertebrae,
- Thoracic vertebrae,
- Lumbar vertebrae,
- Sacral vertebrae,
- Caudal vertebrae.
4. Sternum and ribs: It forms the floor of thoracic basket and supports anterior part of chest. Sternum has three parts manubrium, body and xiphoid process. 12 pairs of ribs are associated with the sternum.
Functions :
(i) Ribs form thoracic cavity along with sternum and vertebral column.
(ii) It protects lungs and heart.
(iii) These help in breathing.
![]()
Question 5.
What are Appendicular skeleton? Explain the bones of appendicular skeleton in man.
Answer:
Appendicular Skeleton: It is formed of bones appended to axial skeleton i.e., pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle and associated limbs.
Girdles: It consists of two types :
1. Pectoral girdle : It is found in the shoulder region where forelimbs join with it at the glenoid cavity. It is generally a duplex structure and functions as an intermediary structure through which the weight of the body is transferred to the forelimbs. Pectoral girdle is formed of two bones, scapula (2) and clavicle (2).
2. Pelvic girdle: It provides articulation with bones of hind limbs at acetabulum cavity. It has two halves, each half has three main bones ilium dorsal in position, ischium and pubis ventral in position. Each half of the girdle forms innominate bones or osinnominatum.
3. Limbs: These are meant for locomotion in tetrapod vertebrates. Limbs are differentiated into:
(i) A pair of forelimbs,
(ii) A pair of hind limbs.
(i) Forelimb : Forelimbs are attached to the pectoral girdle. Each forelimb has upper arm, forearm and hand. There are 30 bones in each forelimb namely, humerus in the upper arm, radius and ulna in forearm, eight carpals in the wrist, five metacarpals in the palm and 14 phalanges in the fingers of the hand.
(ii) Hind limbs : Hind limbs are attached to the pelvic girdle. Each hind limb has thigh, shank and foot. There are thirty bones in each hind limb namely, femur in the thigh, patella in the knee, tibia and fibula in the shank, 7 tarsals in the ankle, 5 metatarsals insole and 14 phalanges in the toes of the foot.
Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Synovial joints are found between :
(a) Two vertebrae
(b) Two skull bones
(c) Humerus and ulna
(d) Caudal vertebrae.
Answer:
(c) Humerus and ulna
Question 2.
The fluid present in ball and socket joints and which reduces the friction is:
(a) Pericardial fluid
(b) Mucin
(c) Synovial fluid
(d) Coelomic fluid.
Answer:
(c) Synovial fluid
Question 3.
The number of vertebrae in human is :
(a) 30
(b) 31
(c) 32
(d) 33.
Answer:
(d) 33.
Question 4.
Hinge joint is found between :
(a) Radius ulna and humerus
(b) Femur and acetabulum
(c) Humerus and acetabulum
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Radius ulna and humerus
Question 5.
The muscle fatigue is due to accumulation of:
(a) Lactic acid
(b) CO2
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Sulphuric acid.
Answer:
(b) CO2
![]()
Question 6.
The articulation of femur and pelvic girdle is an example of:
(a) Ball and socket joint
(b) Pivot joint
(c) Hinge joint
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Ball and socket joint
Question 7.
Which one is the contractile protein of a muscle :
(a) Actin
(b) Myosin
(c) Tropomyosin
(d) Globulin.
Answer:
(a) Actin
Question 8.
Our wrist joint is a :
(a) Sliding
(b) Hinge joint
(c) Pivot
(d) Fixed joint.
Answer:
(a) Sliding
![]()
Question 9.
The joint between the lower jaw and skull is :
(a) Perfect joint
(b) Hinge joint
(c) Gomphoses
(d) Gliding joint.
Answer:
(c) Gomphoses
Question 10.
Ends of long bones are covered with.
(a) Cartilage
(b) Muscles
(c) Ligaments
(d) Blood cells.
Answer:
(a) Cartilage
2. Fill in the blanks:
(A)
1. ……………… joint is found in the bones of skull.
Answer:
Immovable joint,
2. Skeletal movement takes place due to ……………… muscles.
Answer:
voluntary muscles,
3. ……………… is the smallest bone of the human body.
Answer:
Stapes,
4. Myoglobin stores ……………… .
Answer:
Oxygen,
5. Haversian system is found in ……………… .
Answer:
Bones,
6. Bone is made of ……………… protein and cartilage is made up of ……………… protein.
Answer:
Ossein, Chondrin,
7. ……………………… element is essential for the constriction of muscles.
Answer:
Ca++
8. Total ……………………… bones are found in the body of an adult human being.
Answer:
206.
![]()
(B)
1. In all vertebrates except few ……………… cervical vertebrates are found.
Answer:
7
2. In the fine fibre of myofibril 2 ‘F’ actin and two other proteins ……………… and ……………… are found.
Answer:
Tropomyosin, Troponin
3. In each human limb number of phalanges is ……………… .
Answer:
14,
4. In muscle fibre calcium is stored in the ……………… .
Answer:
Sarcoplasmic reticulum,
5. Cranium of human consists of ……………… bones.
Answer:
8.
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Hydra | (a) Cilia |
| 2. Starfish | (b) Setae |
| 3. Amoeba | (c) Tentacles |
| 4. Euglena | (d) Tube feet |
| 5. Earthworm | (e) Pseudopodia. |
Answer:
1. (c) Tentacles,
2. (d) Tube feet
3. (e) Pseudopodia.,
4. (a) Cilia
5. (b) Setae
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Pelvic girdle | (a) Ear |
| 2. Knee | (b) Ball and Socket joint |
| 3. Ligaments | (c) Hinge joint |
| 4. Tendon | (d) Bone-bone |
| 5. Malleus | (e) Bone-muscle. |
Answer:
1. (b) Ball and Socket joint
2. (c) Hinge joint
3. (d) Bone-bone
4. (e) Bone-muscle.
5. (a) Ear
(C)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Smooth muscle | (a) Myoglobin |
| 2. Tropomyosin | (b) Fine fibre |
| 3. Red muscle | (c) Suture |
| 4. Cranium | (d) Involuntary. |
Answer:
1. (d) Involuntary.,
2. (b) Fine fibre
3. Myoglobin
4. (a) Myoglobin.
4. Write true or false:
1. Actin is located in the fine fibre.
Answer:
True,
2. H-zone of striped muscle represents both thin and thick fibre.
Answer:
True,
3. Human skeleton consists of 206 bones.
Answer:
True,
4. Inhuman 11 pairs of ribs are found.
Answer:
False,
5. Sternum lies in the ventral surface of the body.
Answer:
True.
![]()
5. Answer in one word :
1. Name the joint found between humerus and radius ulna.
Answer:
Hinge joint,
2. What is the number of vertebrae and ribs in human being?
Answer:
33, 24,
3. Where is glenoid cavity found?
Answer:
In shoulder region,
4. Where is acetabulum found?
Answer:
In articulation of hind limbs,
5. Give one-one example of the following :
(a) Ball and socket joint,
(b) Immovable joint.
Answer:
(a) shoulder and hip joint
(b) Bones of the skull.
6. How many bones are there in human body?
Answer:
206
7. Name the smallest bone in human body. ‘
Answer:
Stapes
8. Name the longest bone in human body.
Answer:
Femur
9. Name the locomotory organ of Amoeba & starfish.
Answer:
Pseudopodia, Tube fee