Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 2 Biological Classification which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 2 Biological Classification
Biological Classification Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Name one bacterial disease of human and give name of the causal organism.
Answer:
A bacterial disease of human is Typhoid. It is caused by Salmonella typhi.
Question 2.
Name any two Nitrogen fixing bacterias.
Answer:
Two Nitrogen fixing bacterias are :
- Azobactor,
- Rhizobium.
![]()
Question 3.
Give one example of each :
- Gram positive bacteria,
- Gram negative bacteria,
- Sulphur bacteria,
- Iron bacteria,
- Nitrifying bacteria,
- One mycoplasm,
- One Cyanobacteria,
- Bacteria used for making curd from milk,
- One antibiotic bacteria.
Answer:
-
- Gram positive bacteria : e.g., Diplococcuspneumonae,
- Gram negative bacteria : e.g., E. coli,
- Sulphur bacteria : e.g., Thiobacillus,
- Iron bacteria : e.g., Ferrobacillus,
- Nitrifying bacteria : e.g., Nitrosomonas,
- One Mycoplasm : e.g., E. coli plasma,
- One Cyanobacteria : e.g., Nostoc,
- Bacteria used for making curd from milk: e.g., Lactobacillus,
- One antibiotic bacteria : e.g., Streptomyces.
Question 4.
What are archaebacteria?
Answer:
Archaebacteria:
Archaebacteria is a group of primitive bacteria, the cell wall of which is made up of polysaccharide and proteins and its cell membrane contains branched chains. This type of cell membrane protects bacteria from abnormal temperature and pH and thus it can survive in abnormal environmental conditions, hence it is called the organism of abnormal conditions. They can live in those places and under conditions where other organisms are unable to survive. These bacteria are a type of primitive organism that are also found today in its old or primitive atmospheric conditions only hence they are called as ‘living fossils’.
Question 5.
What are cyanobacteria?
Answer:
Cyanobacteria are the filamentous gram-negative blue-green bacteria which contains chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-c, c-phycocyanin, c-phycoerythrin and carotenoids. Their cells exhibit prokaryotic cell structure, e.g., Nostoc, Anabaena, Rivularia, etc.
Question 6.
What do you mean by sulphur bacteria?
Answer:
Those bacteria which depend upon inorganic substance or H2S to obtain energy is known as sulphur bacteria. Thiobacillus thioxidans, oxidises Sulphur to Sulphate state in order to obtain energy. These bacteria can bear strong acidic medium.

![]()
Question 7.
What are plasmid and episomes?
Answer:
The cytoplasm of the bacterial cells also contains some extranuclear hereditary units (DNA) other than nuclear DNA. These extranuclear or extrachromosomal units are called as plasmids. When these plasmids get associated with bacterial genome, it is called episome. These hereditary units participate in genetic transmission and genetic recombination.
Question 8.
Write any three important features of mycoplasma.
Answer:
- They are ultramicroscopic, parasitic and pleuromorphic organisms.
- It is a cell wall less prokaryotic organism.
- Movement and locomotion is absent and they may be globular to branched.
Question 9.
Which characteristics of fungi are similar to man?
Answer:
Fungi are heterotrophs like human and stored food in them is glycogen like human.
Question 10.
What do you understand by symbiotic plants?
Answer:
Symbiotic plants: Plants of two different species which lives together throughout the whole life to benifit each other are called as Symbiotic plants.
e.g., Lichen, which is an association of algae and fungi. Algae provide prepared food to fungi and fungi provide absorbed minerals and water to the algae.
Question 11.
Give full form of LSD. Name the fungi from which it is obtained.
Answer:
Full form of LSD is Lysergic acid Dimethyl Amide. It is obtained from a fungi called as Claviceps. It is a harmful drug.
![]()
Question 12.
Name the genera of fungi from which Penicillin antibiotic is obtained.
Answer:
From Genera Penicillum of fungi Penicilium notatum, antibiotic penicilin is obtained.
Question 13.
What are the components of Lichen?
Answer:
Lichen is an association of algae and fungi. Algae partner is called as Phycobiont which belongs to Chlorophyta and fungi partner is called as Mycobiont which belongs to Ascomycetes or Basidiomycetes.
Question 14.
Give characteristics of cell wall of fungi.
Answer:
Cell wall of fungi is made up of a nitrogen containing polysaccharide called as Chitin.
Question 15.
How Lichen is useful in formation of soil?
Answer:
Lichen is able to invade the bare rocks and help to break it and help for formation of soil. It makes the environment suitable for other forms of life also. They play important role in xerophytic plant succession.
![]()
Question 16.
Fungi of which class are called as Algal fungi?
Answer:
Fungi of Phycomycetes class are called as Algal fungi.
Question 17.
Which fungi are called as Moulds?
Answer:
Fungi belongs to Phycomycetes and Ascomycetes are called as Moulds.
e.g., Mucor, Aspergillus, Penicillium.
The Biological Classification Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Draw a well labelled diagram of a bacterial cell.
Answer:
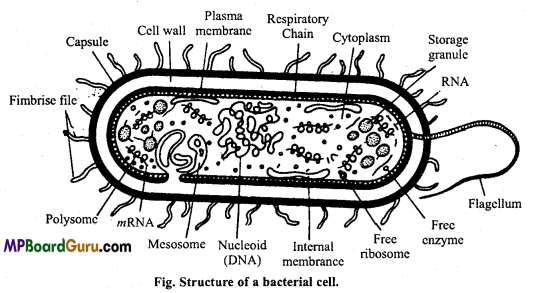
Question 2.
Describe two living and non-living characters of viruses.
Answer:
Living characters of viruses :
- Viruses possess the capacity of growth, reproduction and adaptation.
- Found in living host as parasites and multiply within living host only and contain nucleic acids.
Non-living characters of viruses :
- They do not have protoplasm and enzyme system, hence metabolic activities absent. “
- They can be crystallized.
![]()
Question 3.
Draw a well labelled diagram of Cyanobacteria.
Answer:
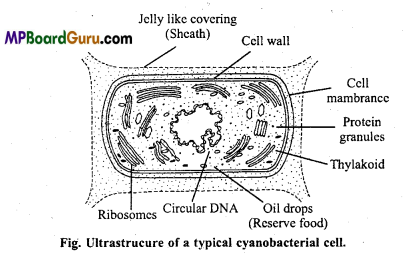
Question 4.
Write down any five characteristic features of kingdom monera.
Answer:
Characteristic features of kingdom monera :
- The cells of organism of this kingdom are prokaryotic.
- Bilayered membranous organelles are absent.
- They reproduce asexually but protosexual process is formed in the form of gene recombination.
- A hard cell wall is present around cells.
- They can easily survive in unfavourable conditions.
Question 5.
Describe the types of archaebacteria on the basis of their survival in unfavourable conditions.
Answer:
Archaebacteria are of following three types on the basis of their survival in unfavourable conditions :
- Methanogens :
Anaerobic bacteria that produce methane from C02 and Formic acid are called as methanogenic bacteria. - Halophytes:
These bacterias are found in concentrated salt solution. Methanogens and halopuyles are obligate anaerobes and form together anaerobic group of archaebacteria. - Thermoacidophyles :
These are a type of aerobic or anaerobic archaebacteria that are found in sulphur containing hot water falls. They convert Sulphur into Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) in aerobic co ditions while into H2S in anaerobic conditions.
Question 6.
Give the difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Answer:
Differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria
| Gram-positive Bacteria | Gram-negative Bacteria |
| 1. Higher amount of peptidoglycan is present in the cell wall. | Relatively less amount of peptidoglycan is present in the cell wall. |
| 2. Cell wall contains about 8 amino acids only. | Cell wall contains about 20 amino acids. |
| 3. Less amount (2-4%) of lipid is present in the cell wall but the amount of mucocomplexes is present. | Higher amount (20%) of lipids is present in the cell wall. |
| 4. Tichoic acid is present in the cell wall. | Tichoic acid is absent. |
| 5. Thickness of cell wall is about 100-200 Å | Thickness of cell wall is about 70-120 Å. |
Question 7.
Explain the Role of Monera in Cycling of Matters.
Answer:
Role of Monera in Cycling of Matters : Cycling of matter through living organisms and environment is a continuous process. Elements or matters are renewed in the nature due to cycling of matter.
All the living organisms use different elements such as : C, H2, N2, S, 02, etc. from nature to perform its life activities. Carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, nitrogen cycle, sulphur cycle are natural processes involving producers, consumers and decomposers. Decomposers of kingdom Monera and Fungi play an important role in cyclic transformation of matters. Majority of the decomposers are bacteria which are Monerans. They decompose the organic matter of dead bodies by enzymatic action and release the constituent inorganic elements, which are again used up by plants thus cycling of matter continues.
![]()
Question 8.
Write the names of any five pathogenic bacteria form and diseases caused by them.
Answer:
Bacterial diseases of Man
| Name of disease | Name of bacteria |
| 1. Tuberculosis (T.B.) | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| 2. Typhoid | Salmonella typhi |
| 3. Diphtheria | Corynebacterium dephtheri |
| 4. Tetanus | Clostridium tetani |
| 5. Leprosy | Mycobacterium leprae. |
Question 9.
List the names of any five pathogenic bacteria for plants and diseases caused by them.
Answer:
Bacterial diseases of Plants
| Name of disease | Name of bacteria |
| 1. Citrus canker | Xanthomonas citri |
| 2. Angular leaf of cotton | Xanthomonas malvaceamm |
| 3. Potato scab | Streptomyces scabes |
| 4. Bean blight | Xanthomonas phaseoli |
| 5. Blast of rice | Xanthomonas oryzae. |
Question 10.
Classify bacteria on the basis of nutrition. Write only names.
Answer:
Bacteria are classified into following three groups on the basis of nutrition :
1. Autotrophic bacteria:
(a) Photoautotrophic bacteria.
(b) Chemoautotrophic bacteria:
- Sulphur bacteria,
- Iron bacteria,
- Nitrifying bacteria,
- Hydrogen bacteria.
2. Heterotrophic bacteria :
(a) Obligate parasite.
(b) Facultative parasites.
(c) Saprophytic bacteria.
(d) Facultative saprophytic bacteria.
3. Symbiotic bacteria.
![]()
Question 11.
Draw well-labelled diagram of bacteriophage.
Answer:
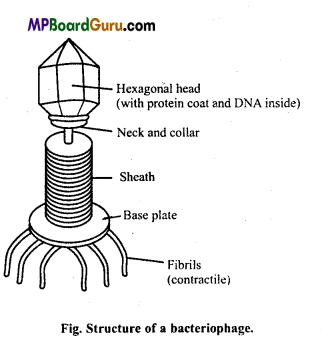
Question 12.
According to shape; how many types of bacteria are there, name them ?
Answer:
According to shape, bacteria are of following types :
(A) Cocci (Sperical or Oval shape): It is of following types :
- Diplococcus,
- Tetracoccus,
- Staphylococcus,
- Streptococcus, (5) Sarcina.
(B) Bacilli or Bacillus (Rod shaped) :
- Diplobacillus,
- Streptobacillus,
- Bacillus,
- Palisade bacillus.
(C) Spirillum :
- (1) Vibrio,
- Hellical,
- Comma.
Question 13.
Write down the difference between Plant virus and Animal virus.
Answer:
Differences between Plant and Animal Virus
| Plant Virus | Animal Virus |
| 1. Plant viruses do not have envelope. | Animal viruses are usually provided with an envelope |
| 2. Plant viruses usually contain RNA as genetic material. | Animal viruses usually contain DNA as genetic material, Some animal viruses also contain RNA. |
Question 14.
Name some antibiotics produced by bacteria.
Answer:
Antibiotics produced by bacteria
| Name of antibiotic | Name of bacteria from which it is obtained |
| 1. Streptomycin | Streptomyces gresius |
| 2 Chloromycetin | Streptomyces venzuelae |
| 3. Terramycin | Streptomyces remosus |
| 4. Auriomycin | Streptomyces auriofaciens. |
![]()
Question 15.
What are viruses? Explain their significance in brief.
Answer:
Viruses :
Viruses are the ultramicroscopic prokaryotic organisms, made up of nucleoproteins and are visible only under electron microscope. They are living and non-living both. When they come into contact of living host they behave as a living matter.
Economic importance of viruses:
Viruses are very harmful organisms as these cause various diseases in plants and animals.
(a) Plant diseases :
- Tobacco mosaic disease,
- Greening of banana,
- Leaf curl disease of papaya,
(b) Human diseases :
- Polio,
- Measles,
- AIDS,
- Influenza.
(c) It is used to prove the organic evolution as it is the connecting link of living and non-living things.
(d) Cyanophases are responsible for the sanitation of blue-green algae.
(e) Harmful bacteria can be killed by bacteriophages.
Question 16.
What is Herbarium ? Write its importance.
Answer:
Herbarium is the group of plants in which flowers, leaves are spread and kept inside the paper, as paper absorbs the water molecules and make it dry, so that it can be arranged serially and studied with reference.
Importances : Importance of herbarium are :
- Due to herbarium, it become easy to identify the plants.
- Due to herbarium, we are able to get seasonal plants to study.
- Due to herbarium, by monographics phytogeographic, we are able to study the plant.
- Due to herbarium we get the preserved plants to study.
Question 17.
Give some harmful activities of bacteria.
Answer:
Some harmful activities of bacteria are as follow :
- Disease :
Bacteria cause many dangerous diseases in human beings, animals and plants. - Denitrification :
Denitrification is a process in which nitrogenous compounds are converted into free nitrogen by the activity of Pseudomonas bacteria. - Food poisoning:
Some bacteria cause food poisoining. e.g., Clostridium botulinum.
![]()
Question 18.
Write differences between Virus and Viroids.
Answer:
Differences between Virus and Viroids
| Virus | Viroids |
| 1. They are smaller then bacteria. | They are smaller than viruses. |
| 2. They contain either DNA or RNA. | They contain only RNA. |
| 3. Protein coat is found. | Protien coat is absent. |
| 4. They may cause diseases in plants and animals. | They cause diseases in plants. |
Question 19.
Give characteristics of cell wail of Diatoms.
Answer:
Diatoms have a cellulose cell wall impregnated with glass like silica. The cell wall consists of two overlapping halves that fit together like a soap box.
When diatoms die their siliceous cell walls accumulate at the bottom of the ocean forming diposists of fossil diatoms known as diatomaceous earth. The powdered diatomaceous earth is used as materials for polishing silver and filtration to clarify oils, syrups etc.
Question 20.
What are Algal Bloom and Red tides.
Answer:
Algal Bloom :
Sometime algae like Caulepra, Spirogyra etc. grows in large number in water and makes it green coloured. In such condition it is called as Algal Bloom.
Red tides :
Red coloured dianoflagellates like desmids are found in fresh and salty water. Sometime they grows in large number in the sea water due to which the sea appears red coloured. Thus tides appears red and it is called as Red tides.
Question 21.
Give Two economic importance of:
(a) Eubacteria and
(b) Archaebacteria.
Answer:
(a) Eubacteria :
- Nitrogen fixation : Some free living bacteria like Clostridium, Azobactor and Symbiotic bacteria like Rhizobium help for Nitrogen fixation.
- Nitrifying bacteria : Some bacteria like Nitrosomonas convert ammonia into nitrite and Nitrobactor converts nitrite into nitrate.
- Decomposition of Dead organism : Some bacteria increase soil fertility by the decomposition of dead organic matter.
- In dairy industry : Bacteria also converts the lactose sugar of milk into curd or lactic acid.
- Medicine industry : Various types of antibiotics and enzymes are obtained from bacteria, e.g., Streptomycin.
(b) Archaeobacteria:
- Methanogenes : These are anaerobic bacteria. They form methane (CH4) from CO2 or formic acid.
- Halophiles : These are anaerobic bacteria, found in brine called as halophiles.
- Themoacidophiles: They are aerobic bacteria, can leave at very high temperature (80°C). They oxidise Sulphur to Sulphuric acid and make the environment highly acidic (pH-2). Under anaerobic conditions some forms can reduce Sulphur to Hydrogen Sulphide.
![]()
Question 22.
What do you mean by Phycobiont and Mycobiont?
Answer:
In Lichen, Algae partner is called as Phycobiont which are autotrophs and provides food to fungi partner. Fungi partner is called as Mycobiont which are heterotrophs. They provide absorbed minerals and water to the phycobiont.
An association of algae and fungi is called as Lichen.
Question 23.
Give comparative description of divisions of Kingdom fungi under following
points
(a) Method of Nutrition,
(b) Method of reproduction.
Answer:
| Division of Fungi | Method of Nutrition | Method of Reproduction |
| 1. Myxomycetes | Mainly saprophytic | Asexual and sexual reproduction. |
| 2. Phycomycetes | Mainly parasitic | Asexual and sexual reproduction. |
| 3. Zygomycetes | Mainly saprophytic | Asexual and sexual reproduction. |
| 4. Ascomycetes | Saprophytic or Parasitic | Asexual and sexual reproduction. |
| 5. Basidiomycetes | Saprophytic or Parasitic | Asexual and sexual reproduction. |
| 6. Deuteromycetes | Saprophytic or Parasitic | Only asexual reproduction. |
Question 24.
Give characteristic features of Euglenoids.
Answer:
Characteristics of Euglenoids :
- They are fresh water organisms.
- Cell wall is not found in them.
- Outer membrane is called as Pellicle.
- They have a whip like flagellum.
- They contain chlorophyll, thus can prepare food by photosynthesis process but in absence of light they shows holozoic nutrition. e.g., Euglena.
![]()
Biological Classification Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
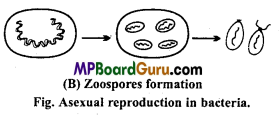
Explain the process of asexual reproduction in bacteria with suitable diagrams.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction in bacteria : In bacteria asexual reproduction is accompanied by the following methods :
(i) By endospores :
Endospores are formed during unfavourable conditions. At the time of endospore formation the cytoplasm of bacteria cell contracts to become rounded and a thick protective layer is formed around it. This structure is called endospore. On return of favourable conditions they germinate to produce a new bacterial cell.
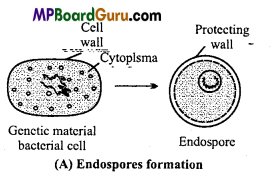
(ii) By zoospores:
This type of asexual spore is formed by the division of cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm of bacterial cell divides to form many zoospores. On rupturing cell wall these zoospores are liberated and germinate to form Zoospores formation
a new bacterial cell.
(iii) By conidia:
Few filamentous bacteria produce conidia. On germination they form a new bacterial cell.
Question 2.
Describe any seven useful activities of bacteria along with examples.
Or
Write five useful activities of bacteria.
Answer:
Useful activities of bacteria :
- N2 fixation : Some bacteria play an important role in nitrogen fixation. e.g.,Azoto- bactor, Clostridium, Rhizobium. These bacteria increase the fertility of soil by the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen.
- Lactic acid synthesis : Lactobacillus lacti converts the milk sugar into lactic acid.
- Acetic acid synthesis : Acetobactor acetii takes part in synthesis of acetic acid or vinegar.
- Rating of fibres : Isolation of wood fibres from the stem of plants is called rating. Clostridium butyricum is used in rating of fibres.
- Tobacco and tea industry : Some bacterias like Micococcus candisens is used to increase the flavour of the leaves of tobacco and tea. This process is called as seasoning.
- Medicine production : Bacteria are the chief source of antibiotics, hence they are used to extract antibiotics, e.g., Streptomyces gresius (Streptomycin).
- As symbionts: Bacteria present in our body help in the various metabolic reactions. e.g., E. coli.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the economic importance of bacteria.
Or
Write an essay on economic importance of bacteria.
Or
Justify the statement that “bacteria are our friend as well as enemy”.
Answer:
Bacteria are of great economic value in our daily life. They are useful as well as harmful. A large number of bacteria are employed in the manufacture of various industrial products. Many bacteria are harmful to human affairs in many ways because they produce many dangerous diseases in human beings and animals. Thus bacteria are our friend as well as enemy.
Useful activities :
- They increase the fertility of soil by N2 fixation.
- They help in the formation of curd from milk.
- They play an important role in vinegar industry, tobacco industry, leather and medicine industry.
- They help in the obtaining of stem fibres and are found as symbionts in our body.
Harmful activities :
- They produce various types of diseases in men, animals and plants.
- They reduce the fertility of soil by denitrification.
- They destroy the food and make them toxic.
Question 4.
Describe viruses on the basis of their structure and the genetic material found in them. Give names of four diseases caused by viruses.
Answer:
Structure of viruses :
Virus, a Latin word which means poison was discovered by Iwanowsky (1892). Viruses are intercellular parasites with protein and nucleic acid in their structure. They are ultramicroscopic structure ranging from 10µ to 300µ in size.
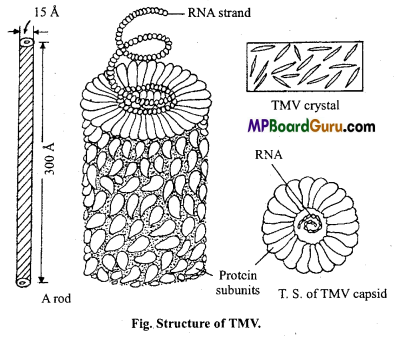
Structurally viruses are made up of the following two parts :
- Proteinaceous capsids and
- Nucleic acid.
The size of TMV is about 15× 300µ( 150 x 3000Å) which is made up of protein and RNA. The outer covering of TMV is made up of proteins which is known as capsid. Each capsid is made up of many smaller proteins.
Types of viruses: Viruses are classified on the basis of:
- Type of host,
- Type of disease,
- Type of nucleic acids.
Viruses are of following 4 types on the basis of their host or parasitism :
1. Animal viruses (Zoophagineae) : They infect animals and humans. They have mostly DNA as genetic material.
2. Plant viruses (Phytophagineae): They infect plants only. They have mostly RNA as genetic material which is single or double-stranded.
Diseases caused by viruses :
1. Plant diseases :
- Tobacco Mosaic disease,
- Green disease in banana.
2. Diseases in human :
- Polio,
- Measles,
- Influenza.
![]()
Question 5.
Write down the symbiotic forms of Monera.
Answer:
Symbiotic Forms:
Organisms living together with mutual beneficial association are called Symbionts and this phenomenon is known a Symbiosis. There are following forms of Symbionts:
1. Mutualism :
When two or more organism living together with beneficial associa-tion it is called mutualism, e.g., Lichens. The body of lichens is made up of a fungus and a cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria manufacture food for fungi and fungi absorb water and min¬erals for cyanobacteria.
2. Symbiotic:
When two organism living together in such way that only one organism take benefits from other, e.g., Symbiotic association of yeast and bacteria during the fermentation of vinegar or acetic acid. Here yeast cells ferment sugar into alcohol and bacteria ferment alcohol into acetic acid. Thus, bacteria take benefits from yeast cells.
3. Symbiosis :
When two organisms living together with beneficial association but both survive separately also, e.g., symbiosis between Rhizobium leguminosarum and roots of leguminous plants.
The members of Monera exhibit symbiosis with both the plants and animals. Few examples are given below :
- All insects sucking juice of plants and blood contain symbiotic bacteria.
- Micrococcus cerolyticcus and Candida albicans bacteria are found in the alimentary canal of birds eating wax of honey-bee comb. These bacteria decompose wax into simple organic compounds.
- E. coli is found in the intestine of human beings, it helps in digestion.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the autotrophic bacteria.
Answer:
Some bacteria are able to synthesize their food so they are autotrophic in their mode of nutrition. On the basis of sources of energy these are of two types :
1. Photoautotrophic bacteria:
These anaerobic photosynthetic bacteria may be rods, cocci or spirilla depending upon their colouration. They are known as green or purple bacteria. They use sunlight as source of energy for photosynthesis but like other eukaryotic cells they do not split water to transfer the energy or to obtain reducing power.
Thus, no oxygen is evolved by them. This process is, therefore, called anoxygenic (without producing oxygen) photosynthesis. In place of water these bacteria obtain reducing power from hydrogen sulphide, thiosulphate, hydrogen or even some organic compound. The photoautotrophic bacteria are further classified into two categories on the basis of hydrogen donor.
(a) Photolithotrops :
Here hydrogen donor is an inorganic substance.
Examples :
(i) Green sulphur bacteria :
These bacteria utilize H2S as hydrogen donor. They possess a chlorophyll called chlorobium chlorophyll. They synthesise their food in presence of light, e.g., Chlorobium.

(ii) Purple sulphur bacteria :
These bacteria utilize sulphur compounds as hydrogen donor. They contain a chlorophyll called bacteriochlorophyll. They synthesise their food in presence of light.

(b) Photo-organolithotrophs :
These bacteria use non-sulphur compounds as organic acids and alcohol as hydrogen donor, e.g., purple non-sulphur bacteria like Rhodospirillum.
![]()
2. Chemoautotrophic bacteria :
Chemoautotrophs are the organisms which oxidize inorganic substances with molecular oxygen to obtain the energy in the form of ATP. As they do not have pigment they cannot make use of light energy. The energy of ATP is utilized to reduce carbon dioxide to organic matter, so the source of carbon for these organisms is carbon dioxide, hence they do not need any organic compound as their food material.
They are also of two types :
(a) Chemolithotrophs :
These bacteria utilize the energy released by oxidation of inorganic substances. They are of following kinds :
(i) Sulphur bacteria : Thiobacillus thioxidans oxidises sulphur to sulphate state in order to obtain energy.

(ii) Nitrifying bacteria:
They oxidize ammonia to nitrites and then into nitrates, e.g., Nitrosomonas, Nitrobactor, etc.
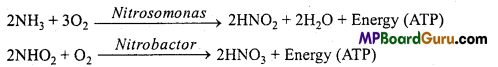
(iii) Iron bacteria:
They oxidize ferrous compound to ferric forms, e.g., Ferrobacillus, Ferroxidans.
![]()
(iv) Hydrogen bacteria :
They oxidize hydrogen to water. e.g., Bacillus pentotrophous.
![]()
(b) Chemo-organotrophs : These bacteria oxidize organic substance and utilize energy released during reaction. e.g., Methane bacteria like Methanococcus. This bacteria oxidize methane into CO2 and H2O.
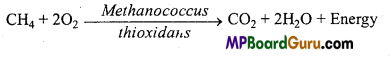
![]()
Question 7.
Write short note on :
(a) Transformation,
(b) Transduction.
Answer:
(a) Transformation :
Diplococcus pneumoniae could transfer their characteristics of its strain to non-virulent strain of living bacterial. It was observed that it is due to transfer of genetic material (DNA) from dead bacteria to living bacteria. And thereby a virulent type acquires the virulent nature. When donor cells break apart then explosive release and fragmentation of DNA takes place. Some of these DNA enters the recipient cells and become a part of recipient DNA. Such type of migration of genetic material is called transformation.
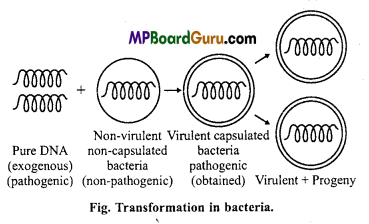
(b) Transduction :
It is discovered by Zinder and Lederberg in 1952 in Salmonella typhimurium. Bacteriophages transfer genetic material from one bacterium to another. This type of genetic migration from one bacterium to another takes place through the agency of bacteriophage is called transduction.
Transduction like transformation involves the transfer of only small segment of bacterial DNA from donor to recipient. In transformation DNA transferred is naked but in transduction it is passed to recipient cell as a packet surrounded by the coat of bacteriophage. When a bacteriophage particle is formed inside a bacterium, it may have a piece of bacterial DNA into its head in place of its own DNA. The bacteriophage particle is released when the parent bacterial cell undergoes lysogeny. These released bacteriophages may infect new bacteria cell carrying into it, some of the genes of bacteria, thus unknowingly transfer the gene.
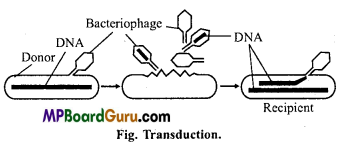
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the process of respiration in bacteria.
Answer:
Respiration in Bacteria : Bacteria are known to occur in every type of environment. Like all other organisms they also respire to obtain energy. Depending upon the requirement of oxygen for respiration, there are two types of bacteria :
1. Aerobic bacteria :
Some bacteria can respire only in the presence of oxygen and are called as aerobic bacteria. They cannot live without oxygen. Thus, they are also called as obligate aerobes, e.g., Bacillus subtilis.
2. Anaerobic bacteria:
Some bacteria respire in absence of oxygen and are called as anaerobic bacteria. They can live in absence of oxygen but cannot live in the presence of oxygen and thus they are called as obligate anaerobes, e.g., Clostridium botulinum.
Some bacteria can live in both, i.e., in presence or absence of oxygen and so are called as facultative bacteria.
Question 9.
Write down the difference between Bacteria and Cyanobacteria.
Answer:
Differences between Bacteria and Cyanobacteria
| Bacteria | Cyanobacteria |
| 1. They are comparatively smaller in size. | They are comparatively larger in size. |
| 2. They may bear tiagella. | They do not bear flagella. |
| 3. They may be autotrophic or heterotrophic. | Cyanobactena are always autotrophic. |
| 4. Photosynthetic pigments are bacteriochlo rophyll and chiorobium chlorophyll. | Photosynthetic pigment is chlorophyll-a. |
| 5. Accessory pigments are absent. | They contain accessory pigments like C-phycocyanin and C-phycocerythrin. |
| 6. During photosynthesis hydrogen donor is H2 | During photosynthesis hydrogen donor is water. |
| 7. Sulphur is evolved during photosynthesis. | Oxygen is evolved during photosynthesis. |
| 8. Reserve food is glycogen. | Reserve food is cyanophycean starch. |
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the uses and types of virus.
Answer:
Uses of Viruses :
- As it forms a link between non-living and living thus it help us to understand organic evolution,
- Cyanophage (Blue-green algae viruses) are used to destroy blue-green algae grown in different areas.
- Bacteriophages are used as biocides to destroy many harmful bacterias present in polluted area.
For example :
Water of the river Ganga always remain pure and clean in bottles year after year due to presence of bacteriophage in it.
Nucleic acids of viruses : Viruses generally contain only one type of nucleic acid DNA or RNA. DNA is found in animal viruses, whereas RNA is found in plant viruses.
Human Immuno Virus (HIV):
It causes AIDS disease in human. Full form of AIDS is Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome. This virus destroys immune system of the body, thus the patient of AIDS suffers from number of diseases at a time and at last he dies.
This virus is found surrounded by protein and a ring of RNA is found at the centre. Whole body of virus is surrounded by a covering of glycoprotein.
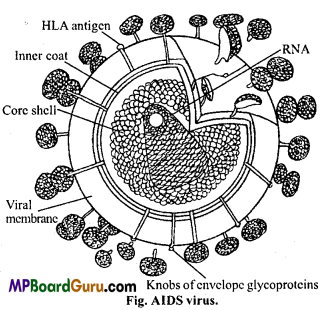
Type of Viruses : On the basis of host infected, viruses are grouped into following four groups :
- Animal viruses : Viruses which infect animals are called animal viruses. These viruses contain DNA as genetic material.
- Plant viruses : Viruses which infect plants are called plant viruses. These viruses contain RNA as genetic material.
- Cyanophages : Viruses that infect blue-green algae are called cyanophages. These viruses contain RNA as genetic material.
- Bacterial viruses or Bacteriophages : Viruses that infect bacteria are called as bacteriophages. They contain DNA as genetic materials.
![]()
Question 11.
Describe the process of reproduction in bacteriophages along with labelled diagrams.
Or
Explain the process of reproduction in viruses with the help of diagrams.
Answer:
Bacteriophages can reproduce only inside the host cells. During multiplication they infect bacterial cells (host). Their DNA enters the cell and then gets replicated. Multiplication involves the following steps :
- Infection : First of all bacteriophage infects bacterial cells and attaches on the surface of bacterial cell wall with the help of their tail fibres.
- Penetration : The bacterial cell wall present at the attachment site is dissolved to fonn a hole, through which genetic material (DNA) of the bacteriophage enters the bacterial cell.
- Biochemical multiplication : After reaching the nucleoid, the DNA of phage synthesizing mRNA. In turn this mRN A synthesizes viral protein in the cytoplasm of bacterial cell.
- Organization of virus : Proteins formed from /wRNA form the viral sheath and thus many bacteriophages are formed.
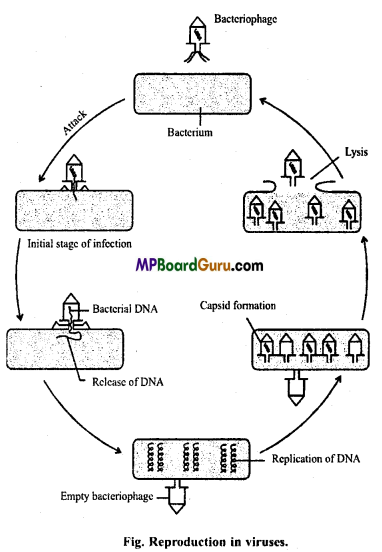
- Release : New bacteriophages formed inside the cell are then liberated due to the lysis of bacterial cell wall.
Question 12.
Explain changes in the system of classification with time.
Answer:
In different time different naturalists and philosophers provided different system of classification of organisms, which are as follows :
1. Linnaeus classification :
A Swedish biologist Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) classified all the living organisms into main kingdoms (Two kingdom classification) :
- Kingdom Plantae and
- Kingdom Animalia.
He also proposed Binomial nomenclature for giving scientific names to the organisms. In his book ‘Systema Naturae’ scientific names of 4378 organisms are given.
2. Artificial System of Classification :
Pliny adopted artificial system of classification for the first time in the first century AD. According to this system organisms are recognised on the basis of one or few superficial characters only. The characters were arbitraruy selected.
Pliny classified animals into two major groups :
- Animals which are abie to fly and
- Animals which can not fly.
On the basis of which butterfly, bats and birds came under same group. In the same way he classified Plants into four groups :
- Herbs,
- Under shrubs,
- Shrubs and
- Trees.
3. Natural System of classification :
This system was proposed by George Benthom (1800-1844) and Joseph Dalton Hooker (1817-1911). Natural system was based on many features of the organisms, so that its exact position and relationship with the c.’her organisms is properly established. Therefore a modem taxonomist uses many criteria to determine the position of organism in the plan of classification.
The main object of this classification is to establish homology, i.e., relationship of comparable structure in different organisms.
4. Phylogenic system of classification :
It was proposed by A. Engier Karl, A. F. Prantle and John Hutchinson. This system is mainly based on the evolutionary and genetic relationships of the plants. It helps to find out the ancestors ‘r derivatives of any taxon.
![]()
Question 13.
Describe four classes of Phylum Protozoa.
Answer:
On the basis of locomotary organs Phylum protozoa is classified mto four classes, which are as follows:
- Zooflagellates,
- Sarcodina,
- Sporozoa,
- Ciliata.
1. Zooflagellata :
- Body is covered by pellicle,
- Body has definite shape,
- Locomotary organ is flagella,
- Generally uninucleate but soir, _ time multinucleate, e.g., Giardia, Trypanosoma.
2. Sarcodina or Rhizopoda:
- They are irreguk in shape,
- Locomotion by means of pseudopodia,
- They show holozoic nutrition,
- Uninucleate organism, e.g.,Ar. oebas.
3. Sporozoa :
- They are endoparasites,
- Pellicle is found surrounding the body,
- Locomotary organs are not found in them,
- motion of generation is found in them,
- They causes diseases.
e.g., Plasmodium, Monocystis.
4. Ciliata :
- Body is covered by pellicle,
- Cilia are found 11 over the surface of tin ody and help for locomotion,
- Two nuclei are found in them. A large macronuclei and a small micronuclei,
- They show holozoic nutrition,
- Can reproduce asexually as sexually.
e.g., Paramoecium.
Question 14.
Discuss about the topics in your class “Viruses are Living or non-living”.
Answer:
Viruses are the first organisms of the earth forming a connecting link between living and non-living as they posses characteristics of both living and non-living.
Living characters of Viruses :
- Growth and reproduction occurs in them,
- It contains nucleic acid (RNA or DNA),
- They show mutation,
- They cause diseases in plants and animals,
- They exhibit adaptation,
- They are parasitic in nature,
- They possess sensitivity.
Non-living characters of Viruses :
- Cells are absent,
- Cytoplasm is absent,
- They can be crystallized,
- Nutrition and metabolism is not found in them,
- They can not grow and reproduce out of the host cell,
- They lack enzymes.
![]()
Biological Classification Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Term ‘Species’ is coined by :
(a) John Ray
(b) Linnaeus
(c) Aristotle
(d) Charak
Answer:
(a) John Ray
Question 2.
Author of ‘Systema Naturae’ is :
(a) Bentham
(b) Hooker
(c) Linnaeus
(d) Engler.
Answer:
(c) Linnaeus
Question 3.
Author of ‘Species Plantarum’ is :
(a) Lamarck
(b) Linnaeus
(c) Theophrastus
(d) Yen.
Answer:
(b) Linnaeus
Question 4.
Five kingdom classification was proposed by :
(a) Aristotle
(b) Tippoa
(c) Birbal Sahni
(d) Whittakar.
Answer:
(d) Whittakar.
Question 5.
Who crystallized viruses for the first time :
(a) Stanley
(b) Guirer
(c) Whittakar
(d) Vigemic.
Answer:
(a) Stanley
Question 6.
Hereditary material of viruses is :
(a) DNA and RNA
(b) DNA or RNA
(c) Chromosome
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) DNA or RNA
Question 7.
Basic unit of classification is ;
(a) Class
(b) Species
(c) Genus
(d) Kingdom.
Answer:
(b) Species
![]()
Question 8.
Highest taxon of the classification is :
(a) Class
(b) Phylum
(c) Genus
(d) Species.
Answer:
(b) Phylum
Question 9.
Homo sapiens is the classification of:
(a) Man
(b) Bull
(c) Leech
(d) Frog.
Answer:
(a) Man
Question 10.
Hybrid organism produced from the cross between female horse and male donkey is :
(a) Monkey
(b) Rat
(c) Mule
(d) Horse.
Answer:
(c) Mule
Question 11.
Unit of classification is :
(a) Species
(b) Genus
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Species
Question 12.
Binomial nomenclature system was proposed by :
(a) Darwin
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
(c) Hugo deVries
(d) Mendel.
Answer:
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
Question 13.
Author of ‘Genera Plantarum’ is :
(a) Bentham and Hooker
(b) Linnaeus
(c) Engler
(d) Prantle.
Answer:
(a) Bentham and Hooker
Question 14.
Naked seeds are formed in :
(a) Algae
(b) Pteridophytes
(c) Gymnosperm
(d) Angiosperm
Answer:
(c) Gymnosperm
Question 15.
Which of the following is most primitive vascular plant:
(a) Red algae
(b) Fem
(c) Brown algae
(d) Lichens
Answer:
(b) Fem
![]()
Question 16.
Basic unit of modern classification is :
(a) Species
(b) Genus
(c) Both
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Species
Question 17.
Classification given by Linnaeus was artificial because :
(a) It is based on evolutionary tradition
(b) Similarity and dissimilarity in floral and other morphological characters are taken
(c) It is based on functional characters
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Similarity and dissimilarity in floral and other morphological characters are taken
Question 18.
Phylogenetic classification is given on the basis of:
(a) Developmental history
(b) Floral similarities
(c) All morphological characters
(d) Increasing complexity.
Answer:
(a) Developmental history
Question 19.
First botanist of taxonomy is ;
(a) J. D. Hooker
(b) Engler
(c) Linnaeus
(d) Aristotle.
Answer:
(c) Linnaeus
Question 20.
Genus is the group of interrelated
(a) Families
(b) Species
(e) Order
(d) Genera.
Answer:
(b) Species
Question 21.
Basis of artificial classification is :
(a) One or two or more characters
(b) All possible characters
(c) Phylogenetic characteristics .
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) One or two or more characters
Question 22.
Objective of classification is :
(a) Collection of organisms
(b) Identification of organisms
(c) Discovery of animal
(d) Discovery, identification, nomenclature of organism and divide them into groups.
Answer:
(d) Discovery, identification, nomenclature of organism and divide them into groups.
![]()
Question 23.
Binomial nomenclature means writing name of organism in two words. These are :
(a) Type and species
(b) Order and species
(c) Type and variation
(d) Order and family.
Answer:
(a) Type and species
Question 24.
Who is known as father of classification :
(a) C. Darwin
(b) Lamarck
(c) Carolus Linnaeus
(d) Bentham and Hooker.
Answer:
(c) Carolus Linnaeus
Question 25.
A species can be defined as population of interbreeding individuals which are reproductively isolated from other species. Above statement was given by :
(a) Carolus Linnaeus
(b) Mayer
(c) J. B. Lamarck
(d) Charles Darwin.
Answer:
(b) Mayer
Question 26.
According to binomial system of nomenclature name of any plant consists of
how many words
(a) Three
(b) Two
(c) Five
(d) One
Answer:
(b) Two
Question 27.
Plant viruses have:
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) DNA and RNA
(d) Coiled nuclear
Answer:
(b) RNA
Question 28.
Viruses contain:
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) DNA or RNA
(d) Both DNA and RNA.
Answer:
(c) DNA or RNA
Question 29.
The viral capsid is made up of:
(a) Nucleic acids
(b) Proteins
(c) Lipids
(d) Carbohydrates.
Answer:
(a) Nucleic acids
![]()
Question 30.
In which plastids are not found :
(a) Blue-green algae
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 31.
Sexual reproduction is absent in :
(a) Cyanobacteria
(b) Bacteria
(c) Eukaryote
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Cyanobacteria
Question 32.
The viral capsid is made up of:
(a) Nucleic acid
(b) Proteins
(c) Lipids
(d) Carbohydrates.
Answer:
(b) Proteins
Question 33.
Which of the following disease is caused by bacteria
(a) T.B.
(b) Measles
(c) Small pox
(d) Polio
Answer:
(a) T.B.
Question 34.
Bacteria cell wall is made up of:
(a) Protein and cellulose
(b) Cellulose and fat
(c) Fat and protein
(d) Chitin and cellulose.
Answer:
(b) Cellulose and fat
Question 35.
Nostoc is a :
(a) Green algae
(b) Yellow-green algae
(c) Blue green algae
(d) Red algae.
Answer:
(c) Blue green algae
Question 36.
Transfer of DNA molecule by bacteriophage from one cell to another cell is called :
(a) Transformation
(b) Conjugation
(c) Mutation
(d) Transduction.
Answer:
(d) Transduction.
Question 37.
The amount of mucopeptides in the cell wall is highest in :
(a) Gram-positive bacteria
(b) Gram-negative bacteria
(c) Cyanobacteria
(d) Bacteriophages.
Answer:
(a) Gram-positive bacteria
![]()
Question 38.
Example of iron bacteria is :
(a) Beggiatoa
(b) Geobacillus
(c) Thiobacillus
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(d) None of these.
Question 39.
The causal organism of diphtheria is :
(a) Virus
(b) Eukaryotes
(c) Mycoplasma
(d) Bacteria.
Answer:
(d) Bacteria.
Question 40.
Which of the following statement is true for Mycoplasma :
(a) Absence of cell wall
(b) Presence of nucleus
(c) Presence of cell wall
(d) Definite shape.
Answer:
(a) Absence of cell wall
Question 41.
Nostoc is a:
(a) Cyanobacteria
(b) Beaded bacteria
(c) Bacteriophage
(d) Parasite.
Answer:
(a) Cyanobacteria
Question 42.
Leaf curl disease of potato is caused by :
(a) Mycoplasma
(b) Virus
(c) Microspore
(d) Bacteria.
Answer:
(a) Mycoplasma
Question 43.
Round bacteria is :
(a) Bacillus
(b) Cocci
(c) Spirillum
(d) Comma.
Answer:
(b) Cocci
![]()
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. …………………… is called as Father of Taxonomy.
Answer:
Carolus Linnaeus
2. The basic unit of classification is ………………..
Answer:
Species
3. Viruses are made up of protein and nucleic acid …………….. or ……………..
Answer:
DNA, RNA
4. The evolutionary history of any organism is called as …………………
Answer:
Phytogeny
5. Binomial nomenclature was proposed by ………………..
Answer:
Carolus Linnaeus
6. An association of algae and fungi is called as …………………..
Answer:
Lichen
7. …………………. proposed Five Kingdom classification.
Answer:
R.H. Whittakar
8. Connecting link organism between reptiles and birds is called as ………………..
Answer:
Archaeopteryx
9. Scientific name of man is ………………
Answer:
Homo sapiens
![]()
10. ……………. and ………………. tried for the first time to classify the organisms systematically.
Answer:
Hippocrates, Aristotle
11. …………………… described for the first time the Natural System of classification.
Answer:
John Ray
12. ……………… are the connecting link of living and non-living things.
Answer:
Viruses
13. Cell wall of fungi is made up of ……………..
Answer:
Chitin
14. ……………….. are called as living fossils.
Answer:
Archaebacteria
15. Stored food in fungi is ……………..
Answer:
Glycogen
16. Genetic material of Monerans is ………………..
Answer:
DNA
17. Minute prokaryotic structure is found in …………………
Answer:
Mycoplasma
18. Nitrifying bacteria are ……………….
Answer:
Saprophytic
![]()
19. Bacteria is discovered by ………………………
Answer:
Antony Van Leeuwenhoek
20. Bacteria, which are founds in human intestine is ………………..
Answer:
E. coli
21. The disease pneumonia is caused by ………………….
Answer:
Diplococcuspneumonae (Bacteria)
22. AIDS is caused by ………………. virus.
Answer:
Human immunodeficiency vims or HIV
23. ……………… are the extranuclear, circular DNA found in the bacterical cell.
Answer:
Plasmids
24. ………………. type of ribosomes are found in bacterial cells.
Answer:
70S
25. …………………………. bacteria are found in the root nodules of lenguminous plants, which help for N2 fixation.
Answer:
Rhizobium
![]()
3. Match the following:
Match the following : (A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Father of Ayurveda | (a) Copland |
| 2. Three kingdom classification | (b) John Ray |
| 3. Five kingdom classification | (c) Heckle |
| 4. Natural classification | (d) Charak |
| 5. Four kingdom classification | (e) R.H. Whittakar |
| 6. Binomial nomenclature | (f) Carolus Linnaeus. |
Answer:
1. (d) Charak
2. (c) Heckle
3. (e) R.H. Whittakar
4. (b) John Ray
5. (a) Copland
6. (f) Carolus Linnaeus.
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Bacillus | (a) A chain of cells like strand of beads |
| 2. Spirillum | (b) Spherical or oval shape |
| 3. Coccus | (c) Twisted like a screw |
| 4.Streptococcus | (d) Prokaryotic multicellular |
| 5. Monera | (e) Occurs singly. |
Answer:
1. (e) Occurs singly.
2. (c) Twisted like a screw
3. (b) Spherical or oval shape
4. (a) A chain of cells like strand of beads
5. (d) Prokaryotic multicellular
![]()
4. Write true or false:
1. Most of bacteria are heterotrophic due to absence of chlorophyll but some are photoautotrophic.
Answer:
True
2. Excess amount of sugar and salt destroys the substances present in Pickles and jelly.
Answer:
False
3. Bacteria found in human intestine is E. coli.
Answer:
True
4. Vims that infect blue-green algae are called animal vims.
Answer:
False
5. Vims is a link between living and non-living.
Answer:
True
6. Collection of plants specimens arranged in the sequence of an accepted classification is called as Herbarium.
Answer:
True
![]()
7. Addition of salt and sugar decay pickles.
Answer:
False
8. Multicellular organisms grows by mitosis cell division whereas Unicellular organisms multiply by this.
Answer:
True
9. Vimses can reproduce both in living and non-living.
Answer:
False
10. Tme nucleus is not found in Moneran.
Answer:
True
5. Answer in one word:
1. Name the organism possesses characteristics of living as well as non-living.
Answer:
Virus
2. Who proposed Five Kingdom classification?
Answer:
R.H.Whittakar
3. Branch of biology which help to know about correct position of living organism.
Answer:
Taxonomy
4. What helps to understand life of the living organisms lived in past.
Answer:
Fossils
![]()
5. Name the missing connecting link between Reptiles and Birds.
Answer:
Archaeopteryx
6. Bacteria helps for nitrogen fixation.
Answer:
Rhizobium
7. Name the causal organism of Diphtheria.
Answer:
Coryne bacterium diphtheria
8. Name the causal organism of disease Pneumonia.
Answer:
Diplococcus pneumoniae
9. Living fossil is?
Answer:
Archaebacteria
10. Bacteria which obtain energy from H2S or S is called as.
Answer:
Sulphur bacteria